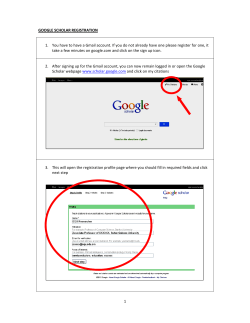
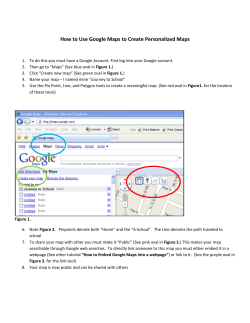
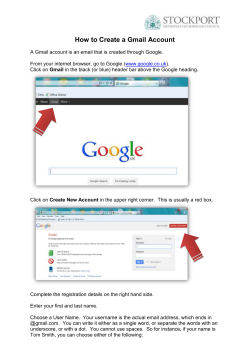
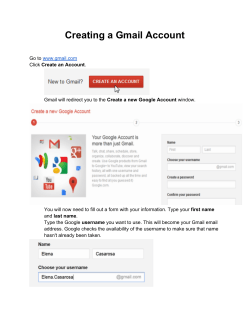
First Guide How to create a new e-enterprise
How to Create a new e-enterprise
First Guide
How to create a new e-enterprise
1
How to Create a new e-enterprise
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 ........................................................................................................................................................ 4
Defining e-enterprise ....................................................................................................................................... 4
1.0 Definition of an e-enterprise. ..................................................................................................................... 5
1.1 Definition of e-enterprise 2.0 ..................................................................................................................... 5
1.2.1 What instruments does an enterprise 2.0 have? .................................................................................... 5
1.2.2 What technology does it use? ................................................................................................................ 6
Chapter 2 ........................................................................................................................................................ 8
Advantages of an e-enterprise. Differences from a conventional enterprise .................................................. 8
2.0 The advantages of an e-enterprise. Differences from a conventional enterprise ..................................... 9
Chapter 3 .......................................................................................................................................................11
The procedures of developing an enterprise in Germany, Greece, Spain and the United Kingdom ..............11
3.1 The procedures of developing an enterprise in Germany ........................................................................11
3.1.1 Introduction ...........................................................................................................................................12
3.1.2 STEP 1. Financial plan.........................................................................................................................12
3.1.4 STEP 3. Chose the legal structure that is best for you .........................................................................14
3.1.6 Where to get advice and information in Germany ........................................................................18
3.2 The procedures of developing an enterprise in Greece ...........................................................................18
3.2.1 Introduction ...........................................................................................................................................18
3.2.2 STEP 1: The location of the business ...................................................................................................18
3.2.3 STEP 2: Legal Form..............................................................................................................................19
3.2.5 STEP 4: Work insurance .......................................................................................................................19
3.3.0 The procedures of developing an enterprise in Spain ...........................................................................23
3.3.1 Legal business structures in Spain .......................................................................................................23
3.3.2 Registration of the Name ......................................................................................................................23
3.3.3 Choose a legal business structure ........................................................................................................24
3.3.3.1 Sole Trader or Sole Proprietor (Empresario Individual or Autónomo) ................................................24
3.3.3.2 Community Property ( Comunidad de Bienes (C.B.) ..........................................................................24
3.3.3.3 Partnership (Sociedad Civil) ...............................................................................................................25
3.3.3.4 Public Limited Company or Corporation (Sociedad Anónima or S.A.) ...............................................26
3.3.3.5 Limited Liability Company (Sociedad de Responsabilidad Limitada, S.R.L., or S.L.) .........................26
3.3.4.1 Cooperative (Sociedad Cooperativa) Business Types .......................................................................28
3.3.4.2 General Partnerships (Sociedad Colectiva) .......................................................................................29
2
How to Create a new e-enterprise
3.3.4.3 Limited Partnership (Sociedad Comanditaria) ....................................................................................29
3.3.4 Secure licenses and permits .................................................................................................................30
3.4 The procedures of developing an enterprise in the UK ............................................................................31
3.4.1 Starting a new enterprise in the UK ......................................................................................................31
3.4.2 Tax payment processes ........................................................................................................................32
3.4.3 Going to work in the UK ...............................................................................................................33
Chapter 4 .......................................................................................................................................................35
Types of Websites for e-enterprises ..............................................................................................................35
4.1. Introduction .............................................................................................................................................36
4.2 Simple web sites ......................................................................................................................................36
4.3. Electronic Commerce web sites ..............................................................................................................37
4.3.1 Accepting payment on your website .....................................................................................................39
4.4 Online auctions web sites ........................................................................................................................39
4.5. Informational Websites............................................................................................................................40
4.6. Blogs / Forum Websites ..........................................................................................................................40
4.7. Social websites .......................................................................................................................................41
4.8. Photo Sharing Websites..........................................................................................................................41
Chapter 5 .......................................................................................................................................................41
What do I need to create my web site? .........................................................................................................42
5.1 Introduction ..............................................................................................................................................42
5.2. What do I need to create a web site ........................................................................................................43
Chapter 6 .......................................................................................................................................................45
Things you need to consider when building a website for your e-enterprise ................................................45
6.1 Introduction ..............................................................................................................................................46
6.2 Audience and design ...............................................................................................................................46
6.3 Technical design ......................................................................................................................................47
6.4 Dimensions – Resolution .........................................................................................................................47
6.5 Mobile web ...............................................................................................................................................47
6.6 Web Accessibility .....................................................................................................................................48
Introduction to electronic security for your e-enterprise and legislation .........................................................49
7.1 Introduction ..............................................................................................................................................50
7.2 Security issues regarding the Internet and e-mail ....................................................................................50
7.3 E-Commerce and the Law .......................................................................................................................51
Introduction ....................................................................................................................................................51
7.3.1 E-commerce Regulations ......................................................................................................................52
3
How to Create a new e-enterprise
Chapter 1
Defining e-enterprise
4
How to Create a new e-enterprise
1.0 Definition of an e-enterprise.
A short definition: A company that is engaged in e-commerce or a company that
conducts the majority of its business on the Internet.
Definition of e-commerce: “The use of inter-networked computers to create and
transform business relationships. It is most commonly associated with buying and
selling information, products, and services via the Internet, but it is also used to
transfer and share information within organizations through intranets to improve
decision-making and eliminate duplication of effort. The new paradigm of ecommerce is built not just on transactions but on building, sustaining and
improving relationships, both existing and potential”.
CommerceNet
White
Paper,
1
July
1999,
http://commerce.net/resources/pw/chap1-9/pg2.html
1.1 Definition of e-enterprise 2.0
The application of Web 2.0 to the enterprise
The use of emergent social software platforms within companies, or
between companies and their partners or customers
● The next generation of enterprise content management (ECM)
●
●
“A system of web-based technologies that provide rapid and agile
collaboration, information sharing, emergence and integration capabilities in
the extended enterprise.
1.2.1 What instruments does an enterprise 2.0 have?
SLATES
●
Search – search engine systems
●
Links – contents can be interconnected
5
How to Create a new e-enterprise
●
Authorship – users can become authors
●
Tagging – allowing different organization of data
●
Extension – extend knowledge by mining patterns and user activities
●
Signal – making information consumption efficient by pushing out
changes
FLATNESSES
●
Freedom – no barriers to authorship
●
Link – contents can be interconnected
●
Authorship – users can become authors
●
Tagging – allowing different organization of data
●
Network oriented – the net is the centre
●
Extension – exploitation of the value of information
●
Search – search engine systems
●
Social – emphasis on the relationship between users
●
Emergence – bottom up strategies are enhanced
●
Signals – making information consumption efficient by pushing out
changes
1.2.2 What technology does it use?
●
Wikis
●
Blogs
●
Podcasting
●
Social voting
●
Social ranking
●
Social Bookmarking
●
Social Networking
6
How to Create a new e-enterprise
Keywords/ characteristic
An Enterprise 2.0 is Transparent, Participative, always on, agile and dynamic.
7
How to Create a new e-enterprise
Chapter 2
Advantages of an e-enterprise.
Differences from a conventional enterprise
8
How to Create a new e-enterprise
2.0 The advantages of an e-enterprise.
Differences from a conventional enterprise
CONVENTIONAL ENTERPRISE
E-ENTERPRISE /ENTERPRISE 2.0
Hierarchical Organisation
Horizontal organisation
Frictions
Simplicity on the organizational flows
Bureaucracy
Operational agility
Rigidity
Flexibility
Innovation guided by technology
Innovation guided by the user
Centralised teams
Distributed teams
Barriers
Open spaces
Knowledge management
Open knowledge
Structured Information systems
Emerging information systems
Standards of ownership
Open standards
Scheduling of the activities
On demand
Long time to Market
Short Time to Market
Prof. Stefano Epifani, Sapienza University
Table 1: comparison of e-enterprise and conventional enterprise
The competitive advantage of each e-enterprise is embedded in the speed and
agility gained by establishing Net business models that leverage its existing asset
base. Compared to conventional enterprises, the e-enterprise is agile, smart, and
deadly.
E-enterprises allow a company to establish new markets on the net through
segmenting the needs of customers: marketing the products one to one,
9
How to Create a new e-enterprise
empowering customers with customer self-service, and building communities of
interest to promote goods and services.
E-enterprises: if a company has a strong business model and strategy, It could
quickly become a leading company.
Some examples of such companies are: Amazon.com; they rose to fame by
becoming the world’s biggest bookstore,
eBay which boasts millions of auctions every day.
Expedia.com which manages booking requests from all over the world.
10
How to Create a new e-enterprise
Chapter 3
The procedures of developing an enterprise in
Germany, Greece, Spain and the United Kingdom
_______________________________________________________
3.1 The procedures of developing an enterprise in Germany
11
How to Create a new e-enterprise
3.1.1 Introduction
In this section of the guide you will find all the necessary steps to follow in order
to start a business in Germany. It is a relatively straightforward process that can
be divided into 4 main steps: a) define an effective financial plan b) check the
formalities that need to be accomplished c) choose the best legal structure for
your company d) obtain the necessary information in regards to taxes that have
to be paid.
You will also find some useful templates that will assist you in writing your
business or capital requirement plan, as well as some useful tables and checklists.
3.1.2 STEP 1. Financial plan
How much money do you need for your start-up?
The first thing to do when planning to set up a company is to understand how
much money you need to invest in the project.
It is therefore very important to define an effective business plan and to check
whether it is has been well thought out .
In order to calculate the exact costs of your business project you should very
carefully analyze your expenses and develop an effective capital requirement
plan, paying special attention to the costs and the capital requirements for the
initial operational phase of your project. As at the beginning of your enterprise
you will probably be making very little money, it is crucial to provide enough
resources to cover the initial expenses and to fund the initial phase in advance.
You can easily start calculating your initial capital requirements with the help of
this simulator.
12
How to Create a new e-enterprise
Financing the capital requirement
You will also need to establish how much money your company will earn,
allowing you to cover your costs and how much additional capital you will have
to invest in your enterprise.
You will therefore have to monitor the liquidity of your company and define a
liquidity plan; be careful because if your costs are higher than your revenues, you
will have to look for extra capital and inject them into your company.
For this reason it is important to think about the profitability outlook of your
enterprise.
You could of course look for financial assistance
The Federal Republic of Germany, Germany’s individual Länder and the European
Union all have programmes to support people setting up in business.
For more information link
3.1.3 STEP 2. Check the formalities you should accomplish
What formalities should be completed?
To launch a new company you should first of all address several formalities as
your company must be registered with the following authorities:
Health insurance [Krankenversicherung]
You need to inform the statutory health-insurance if you move to selfemployment.
Tax office [Finanzamt]
A tax number is needed if you are offering a professional service.
Trade office [Gewerbeamt]
It is also necessary to register your business in the trade office of the municipality
in which the company is opened.
Once you have registered your company, the trade office will automatically
inform the relevant authorities with whom you also have to be registered: the tax
13
How to Create a new e-enterprise
office; accident insurance fund; the chamber of industry and commerce or
chamber of crafts; the local court (trade register); the trade supervisory office.
Occupational accident insurance fund (Berufsgenossenschaft)
The Berufsgenossenschaft (BG) is the statutory accident insurance fund for staff
members and also – depending on the sector – for the self-employed. For further
information you can enquire at the Association of Occupational Accident
Insurance Funds (Deutsche Gesetzliche Unfallversicherung – DGUV).
Commercial register (Handelsregister)
As in most other EU countries, all companies must be entered in the electronic
commercial register at the local court (Amtsgericht), except very small businesses
and companies organized as a GbR (Gesellschaft bürgerlichen Rechts),
3.1.4 STEP 3. Chose the legal structure that is best for you
Choosing the legal structure for your company is an important step that has to
be done very carefully.
In Germany there are various options from which to chose, but before deciding
on a legal structure, you should to clarify the following issues:
1.
Are you setting up your business alone?
If so, you should consider a sole proprietorship or a one-man GmbH or an
Unternehmergesellschaft (haftungsbeschränkt).
2.
Are you setting up a joint enterprise with one or more partners?
If so, you should consider a non-incorporated or incorporated firm.
If you are setting your business alone the following options are available to
you:
●
sole proprietorship
14
How to Create a new e-enterprise
●
one-man GmbH or a variation of the GmbH
●
Unternehmergesellschaft (haftungsbeschränkt) - UG
a) Sole proprietorship
If you manage the company alone, you could set up a Sole proprietorship, the
type of business entity that is owned and run by one individual and in which
there is no legal distinction between the owner and the business.
If you intend to conduct small trades with very transparent business relationship
you can but do not have to register in the commercial register,
if instead you need to establish your business as a commercial operation that
you need to register your company in the commercial register, and to observe
some rules:
- The company’s name, legal structure, principal place of business, court of
register and commercial register number must be stated on all business letters,
- Your accounts must be kept according to the rules of the German Commercial
Code (HGB).
b) One-man GmbH
The GmbH must be authenticated and entered in the commercial register by a
notary public and can be founded by persons involved in trade activities rather
than freelancers.
A one-man GmbH has the following characteristics:
As an employed manager you conduct the transactions in your company.
The liability for the company’s debts vis-à-vis business partners is equivalent
to the amount of the capital deposits (25,000 Euros). You are, however, liable
with your personal assets in the event of criminal infringements and
infringements of the German Product Liability Law and in the case of liability
to banks.
15
How to Create a new e-enterprise
The GmbH is subject to the provisions of commercial law.
c) Unternehmergesellschaft (haftungsbeschränkt)
The UG (limited liability) is ideal for people setting up small firms, and service
providers in particular, who wish to limit their liability and whose company can
survive with little equity, in fact the nominal capital amounts is of at least one
euro, even if 25 percent of the profits must go into a statutory reserve until the
minimum nominal capital of € 25,000 has been generated.
If you are setting your company with partners you would have two options:
non-incorporated firms or
incorporated firms
Non-incorporated firms
For this type of firms the partners bear liability for the debts of the firm with their
personal assets, they are owners and that the same time directors of their firm.
Types of non-incorporated firm are:
Gesellschaft des bürgerlichen Rechts (GbR)
Kommanditgesellschaft (KG)
Offene Handelsgesellschaft (OHG)
Partnerschaftsgesellschaft (PartG)
GmbH & Co. KG.
Incorporated firms
For this kind of firms instead the partners or shareholders are liable for
commercial activities – with exceptions – only to the amount they have invested.
In opposition to the non Incorporated firms, here partners or shareholders
provide capital but are not necessarily actively involved in the management of
the company. Types of incorporated firms are:
16
How to Create a new e-enterprise
Gesellschaft mit beschränkter Haftung (GmbH)
GmbH variant: Unternehmergesellschaft (haftungsbeschränkt)
Aktiengesellschaft (AG)
private company limited by shares (Ltd.)
You could also have a look at the most important criteria for the selection of the
right legal structure.
3.1.5 STEP 4. Get information on the taxes you will have to pay
Which Taxes will you pay?
Understanding what kind of taxes you have to pay is very important; therefore it
is better to look for the assistance of a tax consultant [Steuerberater].
Before even starting you business, you should be aware of these types of
tax:
Turnover or input tax [Umsatz- bzw. Vorsteuer]
Income tax [Einkommensteuer]
Trade tax [Gewerbesteuer]
Corporation tax [Körperschaftsteuer]
The actual taxes you will have to pay depend also on:
the size of your company,
the legal form for which you have opted, and
whether you are conducting a trade
or your activity is one of the liberal professions.
17
How to Create a new e-enterprise
Small entrepreneur regulation
A small enterprise does not have to pay any turnover tax to the tax office if:
●
its turnover in the previous calendar year did not exceed 17,500 euro
●
The turnover in the current year is not expected to exceed 50,000 euro.
You can also have a look at this short summary on who pays when ?
3.1.6 Where to get advice and information in Germany
You can find addresses and contacts of counseling organizations for business
start-ups here.
Consider the advice you may need before contacting them.
3.2 The procedures of developing an enterprise in Greece
3.2.1 Introduction
In the following chapter, you will find an easy to follow, step-by-step guide to
developing an e-enterprise in Greece. This guide includes how to create a
business and the necessary legal procedures that need to be followed. We have
also included links that provide additional information in case the reader wishes
to learn more details.
3.2.2 STEP 1: The location of the business
It is necessary procedure to have secured the location for your business before
any other action is undertaken.
18
How to Create a new e-enterprise
3.2.3 STEP 2: Legal Form
Legal entities (companies) are required to follow certain procedures and actions
such as obtaining legal advice and/or liaising with an economic-business
consultant.
Companies are required to disclose their statutes to the Government’s
Newspaper or local press. The SA requires submission for its status to the local
Chamber of Commerce or to the Department of Trade and Public Limited
Companies Prefectures. After the publication in the Government’s Newspaper the
SA is registered.
3.2.4 STEP 3: Chamber of Commerce
In most cases, it is mandatory for a new business to be included in a Chamber of
Commerce according to the law (N.2081/92).
Depending on the type of activity and the size, the business could be included in
the local handicraft chambers or the Industrial and Commercial Chambers.
The Chamber publishes an announcement with a pre-registration and certificate
of entitlement issued under the user name and title of the business.
• The Chamber shall also be required to establish operations.
• It is essential for individual businesses that they are included within the correct
chamber within two months of starting work, (statement of work in TAX Service
office), and within 2 months of the formation of the company, (publication of the
Statute).
3.2.5 STEP 4: Work insurance
According to law (N2084/92), individuals or partners in the business, over the
legal age of eighteen years old, are required to have work insurance for a
business activity that is pursued in a city of over 2,000 people (in some cases
possibly less). Operators-owners of SMEs are usually written in the local Fund
19
How to Create a new e-enterprise
Professional Craftsmen (TEVE), the Fund Dealers (TAE) and in special cases in
some other funds.
It is necessary to provide all the relevant documents to the Insurance officers.
3.2.6 STEP 5: Permission on opening business and professional license
of practice
• Some categories of professionals are required to have a License to practice in
order to operate professionally.
• Some companies practicing certain professions are required to issue a Special
Operation Authorization (regardless of the Technical Operating License in the
previous paragraph).
The majority of professional licenses and Special Operation Licenses are issued
for the appropriate activity by the D / Directorates of local prefectures, such as D
/ Directorates for Industry, Health, Transport etc. and other authorities such as
police (weapons), EOT (tourism), D / Department of Trade Ministry of
Development. You will be informed by the relevant chambers if any additional
documentation is required.
3.2.7 STEP 6: Opening statement number, tax (vat) number and
endorsement/keeping books necessary for the business
• Each applicant shall submit form M5 “statement of establishing an enterprise”
to the competent trader Internal Revenue Service (IRS-TAX SERVICE). At the same
time the form M2 "Statement on / change individual work" has to be completed
and submitted by individuals or Form M3 "Statement on / Do not change the
work of an individual" by legal persons. A number of other statements and
documents verifying a ‘Statement of work’ have to be submitted to the tax office.
The company is also responsible for informing the tax office on the location of
20
How to Create a new e-enterprise
the premises. The amount of tax paid, capital concentration (1% of the share
capital) and stamp duty, varies depending on the legal form of business and the
amount of employees present in the workplace.
• Upon registering at your local tax office, your company will be issued with a
unique tax number. The business applies the VAT after the statement of work and
does not change regardless of changes in legal form, its founder, the name etc.
The only exception is the conversion from corporate to personal business and
vice versa, whereupon the business will be issued with a new VAT. The relevant
Tax Office needs to be informed of the details through required documentation.
• Businesses and professionals are required to keep certain annotated books and
records, as defined by the Code of Tax Books and Records, according to their
legal form, the type of activity, class bookkeeping etc.
More information:
http://www.acci.gr/acci/business_information/newCompanies/Proceduresforsettin
gupbusinesses/tabid/487/language/el-GR/Default.aspx
3.2.8 STEP 7: PERSONNEL
• The employer is required to file a Statement of Employment card for each
worker hired, to Manpower Employment Organization (OAED).
• Then the employer submits personal status and working hours of the employee,
at the local offices of the Labour Inspectorate of the Ministry of Labour and Social
Insurance. If the worker is from a country that is a member of the European
Union (EU), they should attach the form "Declaration of Employer for recruiting a
Community worker." If the worker is a non-EU citizen then it may be necessary for
the employer to provide other documents. The information in this case is the
responsibility of the Public Employment and Directorate of Labour local
prefectures.
21
How to Create a new e-enterprise
• Finally, the employer is obliged to present (as employer) and state employees in
their insurance officer, which is normally the local Social Insurance Foundation
(IKA).
3.2.9 STEP 8: Other needs/activities
Depending on the nature of your business, you may be required to complete
other necessary steps to finalize the process of establishing a business. For
example:
• A company may seek trademark registration. (Law, 2239/94). The Ministry
responsible for this is Assoc D / Department of Commerce.
• For the production.
• For Sales of certain products it is essential that the CE mark be displayed clearly
on these products. A Competent body includes the Quality Policy Directorate
General Secretariat of the Ministry of Industry Development.
• The patent or industrial design or intellectual property may also be necessary.
• There are various other obligations in regards to installation and operating
permits. It may be necessary to apply for further licenses such as; Building
(Planning), Environmental Impact Assessment (Prefecture), Mechanical Engineer,
etc.
•There may be significant variations and requirements to establishing a business
depending on the type of the business.. Differences also exist between nationals
of member states of EU and non-EU countries. In any case, the company or
individual should seek additional information from the relevant bodies. (The
Ministry of Finance: N / Directorates Register, Code-Element Books, Inc., etc.).
3.2.10 Useful links Chamber of Commerce & Industry
Information and legal statue of a new business
http://www.acci.gr/acci/business_information/newCompanies/tabid/1491/langua
ge/el-GR/Default.aspx
22
How to Create a new e-enterprise
Tax office Service on Line http://www.gsis.gr/on_line_ypiresies/epixiriseis/eepixiriseis.html
Ministry of Finance http://www.minfin.gr/portal/
Social Security office http://www.ika.gr/gr/infopages/yphr/home.cfm
Chamber of Commerce: http://www.eea.gr/
3.3.0 The procedures of developing an enterprise in Spain
3.3.1 Legal business structures in Spain
We assume that before you begin to start your Spanish business and undertake
the parade of legal requirements, that you already have a solid business idea
(business plan)., you have done sufficient market research to confirm the
economic viability of your proposed business ( and the financing needed), you
ideally have previous experience in your intended industry;
It also important to know that in Spain there are 3 different administrations that
can be responsible for certain activities related with industry, taxes, and economic
activities.
3.3.2 Registration of the Name
A good business name is your business’s first asset. You can choose to register
your business name with Spain’s Business Name Registry (Registro del Nombre
Comercial), which in theory gives the name holder the exclusive right to use that
name for commercial purposes. Business name registration is optional and is
handled by the Industrial Property Registry (Registro de la Propiedad Industrial).
23
How to Create a new e-enterprise
When you register a business name, you will need to provide proof of
registration for IAE tax (Impuesto de Actividades Económicas).
3.3.3 Choose a legal business structure
Spain offers several legal business structures, also known as business entities, to
suit a variety of needs, each one with a different set of legal and fiscal
responsibilities. Choosing the right one is important to accommodate your
business-to-be’s present and future goals.
The legal business structures in Spain are the following (formas jurídicas):
3.3.3.1 Sole Trader or Sole Proprietor (Empresario Individual or
Autónomo)
The easiest and most common business entity to set up and get your Spanish
company up and running is the Sole Trader (Empresario Individual) business. This
business is legally considered one and the same with the person running it. For
that reason, the business owner does not have to file any special tax forms come
tax time (just the normal Impuesto sobre la Renta de las Personas Físicas or IRPF,
which you should be filing anyway) and is responsible for all debts incurred by
the company. There is no minimum financial investment to start a Sole Trader
(Empresario Individual) business in Spain.
To become an Empresario Individual, you will need to: 1) register to pay IAE tax
(Impuesto de Actividades Económicas), although as a small business in Spain you
probably won’t be required to actually pay any, 2) file a declaration that you’re
opening your business (Declaración Censal de Inicio de Actividad) and 3) register
with Social Security (Seguridad Social).
3.3.3.2 Community Property (Comunidad de Bienes (C.B.)
24
How to Create a new e-enterprise
The Comunidad de Bienes is almost identical to the Spanish Sole Trader
(Empresario Individual) business, except that the business is composed of more
than one individual and these members share ownership of a common
property or right to something. The members or owners of the Comunidad de
Bienes are personally liable for debts, but there is no minimum financial
investment and tax is reported on each individual’s IRPF tax form.
To start a Comunidad de Bienes in Spain, you will need to: 1) create a partnership
agreement for the business (contrato de constitución), 2) request a CIF (Código
de Identificación Fiscal, Tax Identification Code), 3) register to pay IAE tax
(Impuesto de Actividades Económicas) and 3) register with Social Security
(Seguridad Social).
3.3.3.3 Partnership (Sociedad Civil)
The Partnership, or Sociedad Civil, in Spain is a business relationship formed by
two or more people who contribute money, equipment and/or labour and
divide the profits amongst themselves as they have agreed. Accordingly, any
debts or financial obligations will also be divided amongst the parties. It’s good
to keep in mind that anything not expressly agreed upon, either publicly or
privately, will be governed by Spain’s Civil Code.
The Sociedad Civil doesn’t actually need to become an “official” business except
in certain cases, if one of the parties should contribute real estate, for example.
For that reason, no minimum financial investment is required. However, if you do
make the business “official”, the business name should include the words
Sociedad Civil.
An “official” Sociedad Civil in Spain must create a partnership agreement for the
business (contrato de constitución) that is then signed before a notary, and
register to pay IAE tax (Impuesto de Actividades Económicas), though in some
cases the Sociedad Civil may not be required to pay it.
25
How to Create a new e-enterprise
3.3.3.4 Public Limited Company or Corporation (Sociedad Anónima or
S.A.)
As a stock company, the Public Limited Company, or Sociedad Anónima, in Spain
is highly structured and regulated, decisions are decided by the majority and
annual audits are required. This type of Spanish company is an autonomous legal
entity and shareholders are not responsible for debts incurred by the company.
All sociedades, not just the Sociedad Anónima, must pay some form of Company
Tax (Impuesto sobre Sociedades), currently at 30 to 35% for Sociedades
Anónimas.
To start a Sociedad Anónima in Spain, you will need to draft and notarize the
articles of incorporation and have a minimum available investment of
€60,101.21. You will also need to register with the Commercial Registry in Spain
(Registro Mercantil), request a CIF (Código de Identificación Fiscal, Tax
Identification Code), register to pay IAE tax (Impuesto de Actividades
Económicas), register with Social Security (Seguridad Social) for you and workers
if you plan to hire some and fulfill other obligations, like obtaining a CNN
(Certificación Negativa de Denominación), which proves that another sociedad is
not already using the name you propose to use. Consult with your regional
Spanish government (comunidad autonóma) and a legal advisor for further
details on the obligations of starting a Sociedad Anónima.
3.3.3.5 Limited Liability Company (Sociedad de Responsabilidad
Limitada, S.R.L., or S.L.)
The Limited Liability Company, or Sociedad de Responsabilidad Limitada, in Spain
is another type of Spanish stock company. Like the Sociedad Anónima, the
Sociedad de Responsabilidad Limitada is an autonomous legal entity and
shareholders are not responsible for debts incurred by the company. All
26
How to Create a new e-enterprise
sociedades must pay Company Tax (Impuesto sobre Sociedades). Yet the
Sociedad de Responsabilidad Limitada’s minimum required investment is
considerably less than for a Sociedad Anónima. (There are also different reporting
requirements for each type of sociedad.) In addition, a Sociedad de
Responsabilidad Limitada’s shares cannot be traded on the stock exchange.
To start a Sociedad de Responsabilidad Limitada in Spain, you will need to draft
and notarize articles of incorporation and have a minimum available
investment of €3,005.06. You will also need to register with the Commercial
Registry in Spain (Registro Mercantil), request a CIF (Código de Identificación
Fiscal, Tax Identification Code), register to pay IAE tax (Impuesto de Actividades
Económicas), register with Social Security (Seguridad Social) for you and workers
if you plan to hire some and fulfil other obligations.
3.3.4 Social economy Cooperatives: The Worker-Owned Company
(Sociedad Laboral)
The Worker-Owned Company, or Sociedad Laboral, in Spain is a special type of
Public Limited Company (Sociedad Anónima) OR Limited Liability Company
(Sociedad de Responsabilidad Limitada). The shares are held by A) workers, in this
case the clase laboral, and B) those who do not work for the business, the clase
general. Workers who directly contribute their labour to the business must own
at least 51% of the shares. Workers who do NOT own shares must not work more
than 15% of the total hours worked each year, or not more than 25% if the
company has less than 25 workers with shares.
The Worker-Owned Company (Sociedad Laboral) is created and governed as
either a Public Limited Company (Sociedad Anónima) or Limited Liability
27
How to Create a new e-enterprise
Company (Sociedad de Responsabilidad Limitada), but with a few exceptions.
Before registering with the Commercial Registry in Spain (Registro Mercantil), the
company must be registered at the Registro de Sociedades Laborales del
Ministerio de Trabajo y Asuntos Sociales. According to its base entity type, the
company’s name must also include Sociedad Anónima Laboral (or S.A.L.) or
Sociedad de Responsabilidad Limitada Laboral (or S.L.L.).
3.3.4.1 Cooperative (Sociedad Cooperativa) Business Types
The Cooperative, or Sociedad Cooperativa, is designed for groups of people or
companies in Spain to work together as a democratic block for common
economic and/or social reasons, while operating with a profit motive. Some
examples
include
producer
cooperatives,
trade
cooperatives,
consumer
cooperatives and financial cooperatives. Unless stipulated otherwise, all
cooperative members have the same rights.
There are two kinds of cooperatives: grade one and grade two cooperatives.
Grade one cooperatives consist of at least three people and/or companies. Grade
two cooperatives consist of two or more cooperatives.
The minimum required investment is €1,804 euros, with the exception of student
cooperatives. As a sociedad, the Sociedad Cooperativa must pay Company Tax
(Impuesto sobre Sociedades), yet it has certain tax advantages other sociedades
don’t have.
To create a Sociedad Cooperativa you will need to: 1) Request a Certificado de
Denominación de la Sección Central del Registro de Cooperativas from the
Cooperatives Registry (Registro de Cooperativas). Like the CNN for Public Limited
Companies (Sociedades Anónimas), this is designed to prove that another
sociedad is not already using the name you propose to use. 2) Draft and notarize
the articles of incorporation. 3) Create a public deed for the Cooperative’s
incorporation (Escritura Pública de Constitución). 4) Register with the
28
How to Create a new e-enterprise
Cooperatives Registry (Registro de Cooperativas). 5) Request a CIF (Código de
Identificación Fiscal, Tax Identification Code).
The Cooperative will also be required to keep at least three types of official
“accounting books”: the Libro Registro de Socios (a record of the Cooperative’s
members), the Libro Registro de Aportaciones al Capital Social (a record of the
financial contributions of each member) and the Libro de Actas de la Asamblea
General (a record of the General Assembly’s minutes).
3.3.4.2 General Partnerships (Sociedad Colectiva)
The General Partnership, or Sociedad Colectiva, is a type of Spanish company that
is personally managed and owned by the partners. This type of sociedad is
singular though in that it is a separate legal entity or “person”, yet it is the
partners who are personally liable for the company’s debts. The partners must
abide by certain requirements, which include personal management of the
company unless agreed to be delegated to someone else, and not competing
with company.
To start a Sociedad Colectiva in Spain, you will need to draft and notarize the
articles of incorporation and register with the Commercial Registry in Spain
(Registro Mercantil). The company’s name must include the name of at least one
of the partners. In the case that not all of the partners’ names are used in the
company name, the phrase “and Company” (y Compañía) must be used.
3.3.4.3 Limited Partnership (Sociedad Comanditaria)
The Limited Partnership, or Sociedad Comanditaria, in Spain consists of two types
of partners: general partners and limited liability partners. The general partners
(socios colectivos) are, as in the case of the General Partnership (Sociedad
Colectiva), personally liable for the company’s debts, but the limited liability
partners (socios comanditarios), are not. The participation of limited liability
29
How to Create a new e-enterprise
partners may or may not be represented by shares. However, if there are no
general partners, then at least one of the limited liability partners will be held
personally responsible for the company’s debts. The obligations of the general
partners are the same as for the General Partnership (Sociedad Colectiva), which
includes personal management of the company unless it is agreed to be
delegated to someone else, and not competing with the company.
The creation of a Limited Partnership (Sociedad Comanditaria) is similar to that of
a Public Limited Company (Sociedad Anónima), but the Sociedad Comanditaria
also has specific naming conventions regarding the use of y Compañía and
Sociedad en comandita por acciones (or S. Com por A.), futher stipulating that
limited liability partners’ names may not appear in the company name. Consult
with your comunidad autonóma and a legal advisor for further details on the
obligations of starting a Sociedad Comanditaria.
3.3.4 Secure licenses and permits
You’ll need licenses and permits from your respective municipal and regional
governments. Check with your local Ayuntamiento (city council) and comunidad
autónoma (Regional Government) for the latest requirements.
To get an idea of what may be required, in the city of Valencia for example, a
license (licencia urbanística) must be obtained if you intend to build, change,
renovate or demolish anything (interior or exterior) where you will conduct your
business. License fees vary depending on what exactly you’re doing and how
many square meters you’re doing it in.
Then there’s the opening license (licencia de apertura), which may include the
submission of floor plans indicating all installations OR an official Proyecto
Técnico that details such things as what the market rate for the equipment you’re
going to use is, and other such documents.
If you’ve bought the location where you’re going to set up your business, then
Valencia also requires you to register at the Registro de la Propiedad Inmobiliaria.
30
How to Create a new e-enterprise
On a regional level, certain business activities are required to obtain activityspecific licenses, such as travel agencies, tattoo parlors, auto body repair shops,
etc. Some licenses you will have to pay a fee for.
Depending on what your proposed business is, other types of licenses may be
required as well.
Not a license per se, you should also be prepared to charge Value Added Tax on
goods and services (Impuesto sobre el Valor Añadido, IVA), which ranges from 416%. The tax rules are governed by different plans (regímenes) depending on
what your business is. Check with the national Tax Agency and your tax or
financial advisor regarding your tax and reporting obligations.
Your business will also need a “Visitors Book” (Libro de Visita). You must acquire
it from your province’s Dirección Provincial del Ministerio de Trabajo y Asuntos
Sociales and have it available at all times for labor and Social Security inspectors.
3.4 The procedures of developing an enterprise in the UK
3.4.1 Starting a new enterprise in the UK
If you wish to start a new company in the UK, you are required to register your
business at the Companies House. (http://www.companieshouse.gov.uk/index.shtml).
Once you have a Company Name and Address, a Director, a Secretary, Share
Capital and Shareholders Details, you can choose the easiest way for you to
register your company
(http://www.companieshouse.gov.uk/infoAndGuide/companyRegistration.shtml).
31
How to Create a new e-enterprise
On the Companies House website you can register your company in three
different ways:
1. Online: You will need your email address and password and you will be
charged £18 for this service.
2. Formation Agent: you can use a Formation agent who can provide
specialist advice.
3. On paper: You can fill the forms in and send them to Companies House.
3.4.2 Tax payment processes
When you start up a business as a self-employed person, a partnership or
a limited company, you need to register as self-employed or the partnership for
business taxes with HM Revenue & Customs (HMRC), or register a limited
company at Companies House and they will inform HMRC.
●
If you are self-employed, you are responsible for paying your own
tax
and
National
Insurance
contributions
(http://www.hmrc.gov.uk/working/intro/selfemployed.htm)
●
In a partnership, each business partner must also register
themselves
for
Self
Assessment
and
National
Insurance
(http://www.hmrc.gov.uk/sa/parts-partners.htm).
●
Once a limited company is registered at the Company House and
HMRC has been informed, you will receive a reference number known
as
a
Unique
Taxpayer
Reference
(UTR)
(http://www.hmrc.gov.uk/ct/getting-started/new-company/startup.htm)[1] .
1
For further information on what you need to do for tax and National Insurance purposes when
you start up a business, you can visit the HM Revenue & Customs website
(http://www.hmrc.gov.uk/startingup/index.htm).
32
How to Create a new e-enterprise
To learn more about Self Assessment and self-employed tax and processes you
can watch the video “An introduction to registering for Self Assessment”
http://bcove.me/3qfhsurd [2]
Taxes to pay and processes to use will depend on your business' legal status,
annual turnover and taxable profits. The main business taxes are Income Tax,
Corporation Tax and VAT and National Insurance.
It's important that you keep records of your income and expenses from
the start.
The principal business tax payment processes are:
●
Self Assessment for the self-employed, business partners and business
partnerships
●
Corporation Tax - for limited companies and some organizations (clubs,
friendly societies, etc)
●
the Construction Industry Scheme (CIS) - but only if you operate in the
construction industry
●
PAYE (Pay As You Earn) - but only if you are an employer[3]
3.4.3 Going to work in the UK
2
http://online.businesslink.gov.uk/bdotg/action/hubChassis?itemId=1097101977&r.l1=107385880
5&r.s=e&type=HUBCHASSIS
3
You can learn more about tax, payroll and company information through the link below:
http://www.businesslink.gov.uk/bdotg/action/layer?r.i=1097101977&r.l1=1073858805&r.s=m&r.t
=HUBCHASSIS&topicId=1073858808
33
How to Create a new e-enterprise
If you wish to go to the UK and you are not a British or a European
Economic Area (EEA) citizen, or a Swiss national, you may need a visa [4] before
you can visit the UK and a work permit [5] if you want to work in the UK[6].
If you work in the UK, you have to pay Income Tax and National Insurance
on your wages on the base of how much you earn, and whether you work for
someone (employed), or for yourself (self-employed). National Insurance pays for
some benefits and the State Pension.[7]
If you work for yourself you need to pay tax by filling in a form for a Self
Assessment tax return once a year. In this way you inform HMRC about what you
have earned.[8]
4
To find out how to apply for a UK visa visit the British Government website
www.ukba.homeoffice.gov.uk
5
To find out how to apply for a work permit visit the Home Office UKBA website
http://www.ukba.homeoffice.gov.uk/visas-immigration/working/tier2/work-permit-holders/
6
You can find the information about the documents required in order to work in the Uk on the
HMRC website http://www.hmrc.gov.uk/migrantworkers/documents.htm
7
To find out how to get a National Insurance number you can follow the link below:
http://www.direct.gov.uk/en/MoneyTaxAndBenefits/Taxes/BeginnersGuideToTax/NationalInsuran
ce/IntroductiontoNationalInsurance/DG_190057
8
To learn more about Tax returns if you're self-employed or in a partnership follow the link
below:
http://www.hmrc.gov.uk/sa/self-emp-part.htm
34
How to Create a new e-enterprise
Chapter 4
Types of Websites for e-enterprises
_______________________________________________________
35
How to Create a new e-enterprise
4.1. Introduction
In this chapter we describe the different types of enterprises that partially or fully
have a presence in the internet.
4.2 Simple web sites
Simple web sites are often selected as a mean of providing information about an
idea, an activity, an interest. Usually are used from individuals, groups and small
businesses.
In most cases they are easy to create, require little to no
maintenance and contain static information. The simple websites are considered
36
How to Create a new e-enterprise
as the first step for small businesses to announce` their presence over the
internet and with a quite low cost too.
The standard cost for a website is its name (domain name) and the space that it is
needed for the website files over a web server (hosting). The price for a domain is
around 12 Euros per year depending the type of domain e.g. .eu , .com , .net , .tv ,
.org. In some cases the domain is free of charge but the customer is enchained
on a specific type of domain which in many cases is hard to memorize and also
unfriendly to search engines. Therefore unless you promote your website though
conventional means such as business cards the potential visitors would not be
able to find your website.
The hosting of the website again varies depending the needs of the customer.
Examples of factors that affect the price of hosting is the available space that are
reserved for the website, the bandwidth (the amount of data that can be
transferred from the web site to the world) , the company and server location,
security features etc. Hosting can be free with some limitations but in most cases
costs from around 40 Euros to over the price of 150 Euros per year in proportion
to the needs of the customer.
Usually simple web sites are used by small companies as the first important step,
for helping them expand by approaching more potential customers and improve
their image.
4.3. Electronic Commerce web sites
Electronic commerce websites in general refers to conducting business by buying
and selling products and services in the online environment. Electronic commerce
uses technologies of electronic funds transfer, supply chain management,
internet marketing, online transaction processing, electronic data interchange,
inventory management systems, and automated data collection systems.
37
How to Create a new e-enterprise
Analyzing the e-commerce dealing we identify
additional types of business
involving gathering and use of demographic data through web contacts, business
to business exchange of data, use of marketing processes targeted to customers
that have used some of the company’s services before, business to business
buying and selling and security of business transactions.
There are two types of companies that use e-commerce web sites. Those that
developed a website without any previous existence as a firm and companies that
operated for some time and decided to expand their activities over the internet.
In both cases customer service is very important and already established
companies have the advantage of experience through the time of their operation
and also they already have customers that trust them.
Key elements of an e-commerce web site are the effective presentation of
products that instantly attracts the attention of the customer and product check
out process-shopping cart.
Persons that are looking to buy a product or a service through the internet
usually spend 15 to 20 seconds over an e-commerce web site trying to find what
they want. If they don’t they move to another e-commerce web site. For that
reason first page should be designed in a way that informs the customers about
how useful the product or service is for them, why is better to buy it in the
specific website and not to other competitive ones. The rest website should
support the first page with more information, images and facts about the product
in order keep the customer interested.
The checkout process of the website should be easy for the customers. Otherwise
it is quite possible to abandon the process and move to another website.
Simplicity should always be in balance with security and security should be stated
in order to make customers feel comfortable about purchasing over the internet.
If their first shopping experience with a specific e-commerce website is
satisfactory then is quite possible they will be back to purchase more. Shopping
38
How to Create a new e-enterprise
cart should be available at all times on an ecommerce website allowing the
customers to have the control of the number of items they intend to purchase
along with their prices and total charges.
4.3.1 Accepting payment on your website
in 4.3, systems such as online funds transfer and transaction processing are very
important if you want your website to generate income. This can be done in a
variety of ways. You could decide to take payments over the phone by providing
a phone number for your customers to call, alternatively, you could integrate a
payment gateway into your website. There are different options available for this,
one is PayPal, this allows you to accept payments and manage your money
online. A PayPal account can easily be created on www.paypal.com and is free to
use for new businesses; more complex accounts include additional features and
usually carry a small monthly fee.
Another option is integrating a ‘payment
gateway’ into your website, these systems come with many more options and
often charge a small fee per transaction processed on your website. You may
need to provide certain information (such as bank details and proof that you own
your business) in order to setup a payment gateway, you will also need the terms
and conditions of your website accessible online to your customers, good
examples of websites offering these systems include www.cardsave.net and
www.worldpay.com.
4.4 Online auctions web sites
Online auctions work with the same concept of traditional auctions but with
greater advantages. Electronic auctions allow everyone interested to bid against
each other in a faster and cost effective way and also allows the sellers to get
better prices since the possibility of founding someone to bid higher is increased
because the number of participants can be larger than the traditional auctions.
39
How to Create a new e-enterprise
There are forward auctions where sales are done to the highest bidder and can
be used also for acquiring new customers and product testing. Reverse auctions
involves suppliers that compete on prices. The lowest bid wins a supplying
contract. The advantages of that are less time and administrative costs from a
larger group of suppliers.
4.5. Informational Websites
Informational web sites are easy to maintain and can benefit businesses and
organizations. Information needs to be up to date and refreshed accordingly. A
successful informational site is Wikipedia. Types of informational websites are
also catalogues and directories. They are used in many e-marketplaces providing
searchable databases of information about suppliers, products and services.
Company’s owners should make sure that their company is listed in the right
industry sector and in as many relevant listing possible. This will help customers
find the company easier over the internet and improve its search engine rankings.
4.6. Blogs / Forum Websites
Blogs is the short version of the words Web Logs and can be categorized as
online diaries, journals, or editorials that give the opportunity to people to
express their opinion, knowledge, experience about everything – whether it is
their view of a political issue or just what they think about a restaurant they
recently visited. Successful and popular blogs have on a daily basis hundreds
even thousands of viewers. This provides them financial benefits in the form of
online advertisements and reproduction of contents of the blog from other
informational/news websites. Businesses are also using it as a medium of
updating on certain information their employees and also inform their customers
for events, special offers or new products. Blogs is a cheap way of reaching a
40
How to Create a new e-enterprise
wide customer basis and can be used for marketing. Maintenance should be high
in order to keep the viewers updated and even more if the blog uses a comment
system for readers.
4.7. Social websites
Social websites build online communities where their members can meet, interact
and create information with other members that share common interests.
Examples of such websites are Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, and Google+.
4.8. Photo Sharing Websites
Photo sharing websites help users to transfer pictures online and also provide
them the tools to manage the pictures and share them with other users. The first
photo sharing sites started at late 1990s and now there are many sites that apart
from pictures share videos as well. Popular photo sharing websites are Flickr,
Zooomr, and Picasa.
Chapter 5
41
How to Create a new e-enterprise
What do I need
to create my web site?
_______________________________________________________
5.1 Introduction
42
How to Create a new e-enterprise
In this chapter we provide information to the user on the requirements of
developing a website whether it is a simple one or a complex like an ecommerce.
5.2. What do I need to create a web site?
There are cheap solutions, even free solutions; however there are always
limitations on such a website creation. Business demands professionalism and
this should be visible in the electronic presence of the company. For that reason
you need to allocate some money and resources to the elements that combine
your web site.
1.
Domain name: You need to select an appropriate domain name for
your website. We recommend you to select a name that is easy for the
customers to remember and write it. However finding an appropriate
domain name is not always easy. Competitors in many cases are in
front of you and have already bought the name that fitted your
business idea greatly. So you need to make a research, compromise in
some cases and select an appropriate domain that fits your business
profile. Examples of companies that rents domain names and have
online tools for availability search are many and can be found easily
with a simple search. A couple of these are http://www.godaddy.com/
and http://www.register.eu
You can always purchase a domain that has been already taken from its
current owner if you like. In order to do that you need to find the
owner and negotiate the price. There are services over the internet that
could help you on that for example http://www.whois.net/ . You can
also ask the domain name provider for more information and guidance
to this matter.
2.
Hosting: There are many companies that provide web site hosting.
Choosing a web host affects a lot the overall user experience on your
website. For that reason you need to choose carefully. Quality usually
goes together with the price and you need to avoid cheap solutions
that do not guarantee service quality. When choosing a web host you
need to look for a company that offers reasonable specifications. The
location of the server is another issue. Usually servers that are located
in distant locations e.g. U.S.A perform better in their areas and poorer
in other continents e.g. Europe. For that reason you need to consider
43
How to Create a new e-enterprise
the location of the company that hosts your site too, especially if your
website has heavy content such as video streaming.
3.
Appropriate design and content: Website design and content is the
most important of all the marketing media for the business. The
website needs to be attractive and accurate in order to draw potential
customers and hold their attention until they find what they are
searching for. Designing web pages is easy. Especially with all new
applications that allow a person to create a website without knowing
any coding languages is considered a job that anyone could do.
However developing a good website is something difficult. There are
many elements that someone has to combine in order to develop a
good website. HTML, JavaScript, XML and other coding languages,
graphic design to design and manipulate images, knowledge on how
to design your web site for better search engine rankings etc.
Concluding, a professionally designed website needs to be developed
by someone or a team of people that have deeper knowledge of its
elements and their use. Fortunately the last few years many companies
have developed quite nice and effective website templates that can be
edited and transformed in a way that serves the goals of the individual
/ company, are technically correct and can be purchased in very good
prices. Most of them vary from 50 Euros to 250 Euros. However there
are much higher prices as well depending on the type of the website
and the technologies it uses. Again these website templates need to be
edited and worked by an expert person. Therefore the total cost of
such a work for many companies is low since the developer does not
need to develop all the coding from the beginning.
4.
Business Banking: If you have set up your business as a ‘Ltd’
organisation you will need to set up a business bank account to be able
to trade, although, it is often a good idea to have a business account so
you can keep the company’s finances separate from your own. You will
be able to set up an account with any high-street bank, however, all will
have slightly different requirements and you should look around for the
best deal for new businesses. You will need to provide the bank with
the certificate of incorporation and shareholder certificates (for Ltd
companies), proof of your address and a copy of your passport as proof
of identity. It is always advisable that you keep a file with all documents
about your e-enterprise at all times as banks may ask to see this. An
example of a good comparison website for business banking accounts
is
http://www.money.co.uk/current-accounts/business-bankaccounts.htm.
44
How to Create a new e-enterprise
Chapter 6
Things you need to consider
when building a website for your
e-enterprise
_______________________________________________________
45
How to Create a new e-enterprise
6.1 Introduction
In this chapter we provide information on the key elements of a successful web
site. Since an e-enterprise uses its website as a fundamental tool, the right design
and development is fundamental to the enterprise’s success.
6.2 Audience and design
The first thing that you need to consider when building a website is its purpose
and how it will benefit the enterprise. Usually companies build websites to
promote brand awareness, selling products, reduce overheads and provide better
customer support.
Secondly you need to develop a content that supports the purposes of the
website and consider the way it will be displayed. A good idea is to visit
competitors’ websites to research other business opportunities that your eenterprise could include.
One very important factor for the website’s success is to understand the targeted
audience. Once you understand the target audience you can then use this
knowledge to create a website that they will want to keep returning to. The web
site needs to be user-friendly ensuring that visitors find it effective and efficient.
Website optimization doesn’t stop when it becomes available to the public, but
you should continue optimizing it by using a combination of benchmarking,
performance measuring and user testing.
46
How to Create a new e-enterprise
The website also needs to stand apart from your competitors’ websites. This
presupposes extra work such as case studies, unique product descriptions, and
supportive information. The results will reward the effort.
6.3 Technical design
Developing a website using the latest technology and graphic effects does not
necessarily ensure that the result will be a success. There are several technical
issues that need to be considered when designing the enterprise’s website.
Firstly, the website has to be compatible with all the popular browsing software
available especially with Microsoft Internet Explorer, Google Chrome, Mozilla
Firefox, and Apple Safari. For that reason extensive testing should be performed
not only in different operating systems but on older versions of browsers as well.
In this way we ensure that the enterprise’s website will be visible by most users
accessing it from different types of computers.
6.4 Dimensions – Resolution
The most common resolution for web sites nowadays is 1024 x 768 pixels.
However, higher resolutions are also used. If the website of the e-enterprise is
built in a higher resolution than 1024 x 768 pixels, then the content will possibly
not display well on the screen that are only able to support lower resolution. And
this will discourage some people from visiting the website again.
6.5 Mobile web
Lately the industry of net books, smart phones and tablet computers has
increased and since most of the users are accessing the internet through these
47
How to Create a new e-enterprise
devices, web site owners are adjusting their websites to meet the needs of the
small mobile screens. The e-enterprise’s web site has to be tested on mobile
devices and be adjusted in order to provide a more efficient and effective
experience. In many cases this changes the style of the website and for that
reason companies develop a separate mobile version of the website.
6.6 Web Accessibility
By making your e-enterprise website more widely accessible using the latest
technology and adjusting your site according to each group’s specific needs, you
automatically make it available to a much more diverse group of users. In some
countries having an accessible website is obligatory by law.
Examples of such adjustments include font size, changing buttons for persons
with visual impairments including elderly people, and using navigation systems
that can be read by screen reader software for blind persons etc. Details on how
to adjust your website in order to be accessible can be found here.
48
How to Create a new e-enterprise
Chapter 7
Introduction to electronic security
for your e-enterprise and legislation
49
How to Create a new e-enterprise
7.1 Introduction
In this chapter we will introduce you to the risks that your e-enterprise could face
from the internet and the measures that you can take in order to minimize those
threats.
7.2 Security issues regarding the Internet and e-mail
The Internet and e-mail provides your business with great benefits such as
flexibility and efficiency. However, there are risks for e-enterprises largely due to
the fact that the internet is unregulated.
Some of the risks include the possibility of malicious software (viruses, Trojans)
infecting your computers and website, hacker attacks to your website and
attempts at stealing valuable data from you, including your clients’ credit card
information. There is also the risk of DoS (Denial of Service) attacks where a
website is heavily bombarded with traffic from other infected computers and as a
result stops functioning.
In order to minimize the risks from these types of attacks there is a number of
approaches that we can follow. These include:
Backup systems – To ensure you can recover quickly from any type of electronic
attack you need regularly backup your website.
50
How to Create a new e-enterprise
Authentication - techniques should be used to identify the persons that interact
with your website / e-commerce system. There are also different types of access
control for users in order to monitor the actions that are performed by each
authorized person.
Encryption – is a technique that scrambles data and is used to protect
information being held on a computer or transmitted over a network. It is quite
useful for an e-business, but it is essential for electronic commerce websites since
they manage sensitive data such as credit cards numbers.
Firewall – can be a hardware or software security device that filters information
and requests of access passing between internal and external networks. A firewall
controls access to the internet and prevents outside parties gaining access to
systems and information on the internal network.
Intrusion detection – is a system that allows us to monitor systems and network
activity and informs you if someone is trying to gain access to an area that they
are not authorized to be in.
Anti-virus software - can detect viruses, trojans and prevent access to infected
files. A common way to infect computers is through emails. For that reason every
email that we receive should be scanned before we open it and no links opened
that have not previously been verified.
Your business should organize and adopt a security policy in order to protect
your assets. For example, backups should be created on a regular basis and
security codes should be changed regularly.
7.3 E-Commerce and the Law
Introduction
51
How to Create a new e-enterprise
Electronic commerce, commonly known as e-commerce or e-comm, refers to the
buying and selling of products/ goods or services using electronic systems such
as the Internet and other computer networks.(Wikipedia) Electronic commerce is
generally considered as the sales aspect of e-business. It also consists of the
exchange of data to facilitate the financing and payment aspects of business
transactions (Wikipedia) .In this chapter we will refer to the legal aspects and
regulations of an e-business,
7.3.1 E-commerce Regulations
E-Commerce concerns businesses sell products or services to other businesses or
consumers through the internet, by email, SMS or via text messages as has
already been mentioned in previous chapters. The field of e-commerce has been
under European regulations in order to achieve a fair balance between consumer
and citizens’ rights. The rights of the consumer in Europe need to be upheld and
respected.
The EU regulations on e-commerce include issues such as privacy and data
protection, consumer rights & common sales law, Alternative & online dispute
resolution, digital internal market (and regulatory burdens for cross-border ecommerce) and Online Trustmark.
The Regulations include provision for:
the national law that will apply to online services
The information an online service provider is required to give a consumer
includes discounts and offers in online advertising and how to bring
contracts to fruition.
More information can be found in each language on the links below
52
How to Create a new e-enterprise
http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=CELEX:32000L0031:EN:NOT
( GR) http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2000:178:0001:0016:EL:PDF
(ES) http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2000:178:0001:0016:ES:PDF
(GER) http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2000:178:0001:0016:DE:PDF
(UK) For detailed information, download a guide to the Provision of Services Regulations
from the Department for Business, Innovation & Skills (BIS) website (PDF, 814K) - Opens in a new
window.
53
Second Guide
How to be a successful e-entrepreneur
How to be a successful e-entrepreneur
Table of Contents
Introduction ....................................................................................................................................4
1.0 I want to be an entrepreneur. Do I have everything that is needed to become one? ..6
1.1 Introduction ..........................................................................................................................6
1.2 A self assessment .................................................................................................................6
2.0 How can I develop my skills in order to become more successful as an entrepreneur?
....................................................................................................................................................... 11
2.1 Introduction ....................................................................................................................... 11
2.2 Interpersonal Skills ............................................................................................................ 11
2.2.1 Leadership and Motivation ....................................................................................... 12
2.2.2 Motivation................................................................................................................... 13
2.2.3 Communication Skills ................................................................................................ 15
2.2.4 Listening ...................................................................................................................... 16
2.2.5 Personal Relations...................................................................................................... 18
2.2.6 Negotiation ................................................................................................................. 21
2.2.7 Ethics in business ....................................................................................................... 23
2.3 Critical and Creative Thinking Skills ................................................................................ 23
2.3.1 Creative thinking ........................................................................................................ 24
2.3.2 Problem-solving and decision-making ................................................................... 25
2.3.3 Recognizing Opportunities ....................................................................................... 26
2.4 Practical Skills .................................................................................................................... 27
2.4.1 Introduction ................................................................................................................ 27
2.4.2 Goal Setting ................................................................................................................ 27
2.4.3 Planning and Organizing .......................................................................................... 28
2.4.4 Decision Making......................................................................................................... 29
2.4.5 Knowledge .................................................................................................................. 31
Appendix 1 ........................................................................................................................... 34
2
How to be a successful e-entrepreneur
List of Figures
Figure 1: The above figure describes the way that motivation affects people.............................. 14
Figure 2: In this figure can be observed the relation between oral communication, non verbal
and written communication as well .............................................................................................. 16
Figure 3: Goleman’s (2001) Emotional Intelligence model ........................................................... 19
Figure 4: Decision Tree.................................................................................................................. 29
3
How to be a successful e-entrepreneur
Introduction
Being an entrepreneur might be stressful. It’s a never ending job with a high risk
of failure if one lacks flexibility. However, it can be very rewarding in that it offers
a lot of opportunity to be creative. This is the reality that an entrepreneur has to
face in their daily working life.
People become entrepreneurs for many different reasons, some to fulfill their
dreams of being successful and earning a lot of money, others to help and
support people. Whatever drives us to start our own business, we need to
carefully think about the ways to develop the skills necessary to help us become
successful professionals.
4
How to be a successful e-entrepreneur
Chapter 1
Do I have what is needed to be an
entrepreneur?
5
How to be a successful e-entrepreneur
1.0 I want to be an entrepreneur. Do I have
everything that is needed to become one?
1.1 Introduction
Managing an entrepreneurship is a demanding job. Many people believe that
they are capable of running an entrepreneurship without any problems as they
see many others do. However, in many cases after launching their business they
demonstrate lack of skills and expertise, and face problems in an inefficient way.
In order to help people who would like to become entrepreneurs we developed
the following questionnaire. It gives a potential entrepreneur a general idea of
the requirements, skills and knowledge that are necessary to run a business.
The analysis of your score will help you gain a better understanding of the kind of
further guidance you might need to get in order to become a successful
entrepreneur.
1.2 A self assessment
For each question please tick the box that best describes you on the scale from 1
(strongly disagree) to 5 (strongly agree)
Question
1. Strongly
Disagree
1. I have the ability to
inspire people with a
vision.
2. When I am working in a
team I can offer
guidance. I make myself
available to all in order
to solve problems and
advise people. I have a
6
2.
3.
4.
5. Strongly
Agree
How to be a successful e-entrepreneur
positive effect on others.
3. When talking with
people I understand
their emotions and I
listen carefully to what
they say, which makes
me a good listener.
4. I make decisions quickly
without much hesitation.
People say I am decisive
5. I am tolerant of people
who disagree with me.
6. I recognize and welcome
the accomplishments of
others.
7. I admit my mistakes. I
encourage people to
admit their mistakes.
8. In disagreements and
conflicts I hold my
temper.
9. People often say that I
am honest when dealing
with others and that I
prefer being direct
when expressing
opinions.
10. Whenever I undertake a
project I am strongly
dedicated to it and see it
through to the end.
11. I don’t hesitate to
express my ideas when I
work in a group.
12. I have the ability to
persuade people when
7
How to be a successful e-entrepreneur
they are reluctant to
undertake or complete a
project.
13. I like to influence
people with my ideas
14. People often find my
ideas innovative
15. When negotiating I can
easily understand what
the other part wants to
achieve
16. I am willing to
compromise in order to
benefit the group.
17. When I am talking to
people from abroad I
take cultural differences
into consideration.
18. When I communicate
with people they can
easily understand what I
am talking about.
19. During a conversation I
don’t interrupt in order
to express my opinion.
20. During a conversation I
observe body language.
21. I know what makes me
happy and what is truly
important for me in my
life. I have clearly
defined values.
22. When dealing with huge
amounts of information I
use charts, diagrams and
notes in order to help
8
How to be a successful e-entrepreneur
people to understand
the underlying concepts.
23. If I don’t understand
something in a text, I try
to find out the meaning.
Score Interpretation
Score
Comment
23– 45
You have low entrepreneurial skills. You need to improve them.
Please study the suggestions of the guide.
46 - 91
You are good at some things but you still need to develop your
entrepreneurial skills.
92 - 115
You have high entrepreneurial skills.
9
How to be a successful e-entrepreneur
Chapter 2
How can I develop my skills in order to
become more successful as an
entrepreneur?
10
How to be a successful e-entrepreneur
2.0 How can I develop my skills in order to become
more successful as an entrepreneur?
2.1 Introduction
Being an expert in the area or having great knowledge about internet
technologies does not guarantee that you will succeed in e-entrepreneurship.
There are many elements that help you to manage your entrepreneurship, such
as creativity, good social skills for creating strong teams, and the ability to
continue despite the difficulties. In order to start your business it is essential that
you learn those skills. In this chapter we will provide a short analysis of the skills
that can be used to develop the elements of a successful entrepreneurship.
2.2 Interpersonal Skills
Interpersonal skills are very important in daily working life as they help you to
interact with people being the foundation of building relationships with others.
This paragraph attempts to give you a better understanding of the different
elements constituting what is commonly known as Interpersonal Skills. The
elements in question are: Leadership and Motivation, Communication, Listening ,
Personal Relations, Negotiation and Ethics.
11
How to be a successful e-entrepreneur
2.2.1 Leadership and Motivation
The term leadership is often used to refer to a person’s ability to lead a team in
an effective way. A leader can successfully engage a group of people in the
process of achieving a target or completing a project.
There are several types of Leadership mentioned in different books. For the
purpose of this guide we will only refer to the leadership types directly relevant to
someone who wants to gain better understanding of Interpersonal Skills required
to be a successful entrepreneur.
We will also refer to the theory of Bernard M Bass who developed a model for the
leadership types based on two simple objectives. The leadership styles
described below reflect different types of tasks. According to Bernard M. Bass
leadership can be Directive, Consultative, Participative, Negotiative and
Delegative type.
1) The Directive leadership style requires a leader who suggests to his followers
what to do, and how to do it exactly. The leader requires particular standards from
his followers and exerts authority over them.
2) Consultative leadership style is the leader who seeks the counsel of the
whole team before making a decision on what the team should do. This type of
leader is also task oriented, but he seeks the opinion of his followers as well.
3) Participative leadership style involves a leader who is a member of the team
and discusses possible decisions with the team. This kind of a leader seeks
agreement before coming to a decision and everyone is supposed to take
ownership in the final decision.
12
How to be a successful e-entrepreneur
4) Negotiative leadership style is the leader who employs a more political
approach to leadership. He has a personal interest in his decisions and he uses
incentives to tempt his followers to achieve certain tasks.
5) Delegative leadership style is represented by a leader who takes back seat
toward decision making and allows his team to obtain their own way of action.
He only sits down together with the team to discuss possible decisions that could
be adopted.
2.2.2 Motivation
Continuing our description of the Interpersonal Skills for successful eentrepreneurs we will refer to the term of motivation.
‘’A simple definition of motivation is the capacity to change behavior. It is a drive
that compels one to act because human behavior is directed toward some
goal.’’(Encyclopedia of Business and Finance).
Motivation starts internally and is based on the personal interests, desires, and
achievements. Though, external factors such as rewards, praise and promotions
also influence motivation.
Daft says that motivation refers to "the forces either within or external to a
person that arouse enthusiasm and persistence to pursue a certain course of
action" (p. 526, Daft, Richard L. (1997). Management, 4th ed. Orlando, Fl.:
Harcourt Brace).
There is an important part of management in Business which helps to organize
work in a more satisfying and rewarding way as well as keeping employees’
motivation consistent with organizational objectives. Many factors, including the
influences of different cultures, affect what people value and what is rewarding to
them.
13
How to be a successful e-entrepreneur
From a manager's point of view, it is important to understand what prompts
people, what influences them, and why they persist in particular actions. Quick
presents four underlying principles which help to understand motivation( Quick,
Thomas L. (1985). The Manager's Motivation Desk Book. New York: Wiley):
1.
People have reasons for everything they do.
2.
Whatever people choose as a goal it is something they believe is good for
them.
3.
The goal people choose must be seen as attainable.
4.
The conditions under which work is done can affect its value and the
employee’s perception of attainability or success
Motivation
Needs
Behavior
Satisfaction
Figure 1: The above figure describes the way that motivation affects people
14
How to be a successful e-entrepreneur
2.2.3 Communication Skills
Communicating with others is an essential skill in business dealings, in our
relationships, in family life, and in our daily activities.
‘Communication is the exchange of thoughts, feelings messages, or information,
as by speech, signals, writing, or behavior’. (Wikipedia)
“Communication requires a sender, a message, and a recipient, although the
receiver need not be present or aware of the sender's intent to communicate at
the time of communication; communication is only successful when both the
sender and the receiver understand the same information as a result of the
communication.
Communication can be oral, verbal or non-verbal and written. Oral
communication is the ability to explain and present your ideas in your language
(mother language or not).This ability also includes understanding of non-verbal
signals, such as body language and face expressions. Oral communication
requires the background skills of giving presentations, audience awareness and
critical listening .
Written communication is the ability to write efficiently in a variety of contexts
and for different audiences and purposes. Additionally, written or electronic
communication (emails, sms, chat etc) include the ability to write in an
understandable way for different kinds of audience.
15
How to be a successful e-entrepreneur
Non verbal
Oral
communication
on
Written
communication
on
Figure 2: In this figure can be observed the relation between oral communication, non
verbal and written communication as well
2.2.4 Listening
Listening is one of the most important skills that an entrepreneur must have. The
way people listen to each other affects their job and the quality of their
relationships. The main purpose of listening is to gather information, to
understand, to learn or to enjoy a conversation.
When we listen to a conversation, a talk or a lecture we remember 25% or 50% of
what we have heard. This means that the attention of the listener is not so good
16
How to be a successful e-entrepreneur
and a lot of information is lost. Listening is therefore a skill that we can all benefit
from improving.
A good listener can improve his productivity at work, as well as his ability to
influence and persuade others. By paying attention a good listener will avoid
conflict and misunderstandings.
To become a better listener you need to practise a technique known as "active
listening." Active listening will help the listeners to understand not only the words
another person is saying but, more importantly, the complete message being
sent, including face expression and body language.
In order to become an active listener you need to
Pay attention to the speaker
Give the speaker your whole attention and acknowledge the message. Remember
that non-verbal communication also "speaks" loudly.
Show That You're Listening
Use body language and gestures to show your attention. Help the
conversation to develop, listen actively, make comments and encourage
the speaker to continue.
Provide feedback
As a listener you need to answer questions when necessary. It is also good
to check your understanding of what the speaker is saying by asking
questions yourself, summarizing what has been said so far.
Defer Judgment
Try not to interrupt the speaker, allow him/her to finish .
Respond Appropriately
Dynamic listening is a model for respect and understanding. As a listener you
need to be open, and honest in your response. Also,
state your opinions respectfully and treat the other person with respect.
17
How to be a successful e-entrepreneur
A successful e-entrepreneur needs to have all the skills analyzed in this chapter .A
good way for the entrepreneur to evaluate his/hers skills is to check their answers
to the questionnaire and then study each section carefully.
2.2.5 Personal Relations
Introduction
Many people believe that in order to be successful in business you only have to
be smart, well trained and experienced in your field. However, lately it has been
suggested that managing others is an equally important skill in the success of
your business. Recent studies indicate that emotional intelligence provides more
opportunities and chances of success than intelligence alone. Many companies
are changing their training programs focusing more on the development of
emotional intelligence in order to implement their corporate development
strategy more effectively.
Defining Emotional Intelligence
We can say that emotional intelligence is the ability to understand and manage
your emotions. This involves asking yourself why you experience certain
emotions, and what these emotions are telling you. Another aspect of Emotional
Intelligence is the ability to understand how your emotions affect people around
you. Understanding how people feel helps you to avoid mistakes, take the
appropriate approach manage relationships more effectively.
Characteristics of Emotional Intelligence
According to an American psychologist Daniel Goleman emotional intelligence
consists of five elements.
1. Self awareness
Self awareness is characteristic of people with highly developed emotional
intelligence. They are able to control their emotions because they
understand them. They also recognize their strengths and weaknesses,
which enables them to work on their personal development.
2. Self Regulation
18
How to be a successful e-entrepreneur
Self Regulation is the way you control your emotions and impulses. People
who have developed self regulation are able to take decisions without the
influence of impulsive emotions. They will not act if they do not think it
through first.
3. Motivation
People who are motivated in life usually have their emotional intelligence
developed. They are willing to complete their tasks in order to reach their
long term aim.
Emotional Intelligence Model
Figure 3: Goleman’s (2001) Emotional Intelligence model 1
4. Empathy
Empathy is considered to be another very important element of Emotional
Intelligence. People with developed empathy are able to identify and
understand the views, needs and wants of others. They are also capable of
recognizing the feelings of those who are trying to hide them.
5. Social skills
1
Goleman, D. (2001). Emotional intelligence: Issues in paradigm building. In C.
Cherniss
19
How to be a successful e-entrepreneur
People with developed social skills are team players who are approachable
and know how to put others at ease. Their strength lies in the ability to
build and maintain very strong relationships. They have excellent
communication and negotiation skills.
Improving your Emotional Intelligence
It is possible to learn how to become an Emotionally Intelligent person. There is a
variety of books, seminars and workshops that can improve some, or all of the
elements that constitute Emotional Intelligence. However, apart from reading
about it you need to practise it in your daily life. You should start from identifying
the elements you need to develop more. Here are some tips that could help you
do that.
Reduce stress
In order to reduce stress you need to be able to recognize the signs telling you
that you are stressed, e.g., chest pain, clenched hands, shortness of breath. You
also need to think of how you react to stress-some people tend to become
aggressive, others depressed or withdrawn. Understanding all this is very
important to effectively cope with stress. The best way to reduce stress is by
engaging your senses. Each person responds to sensory input in a different way
and they should use this knowledge in order to handle stress. For example,
people who respond to sound can use music to reduce their stress level.
Emotional awareness
Understanding your emotions as well as those of others around you, is a very
important element of Emotional Intelligence. By doing that you will be able to
determine your needs and motivations, and communicate with others in a better
way.
Nonverbal communication
Successful communication requires good verbal skills and a good understanding
of body language. Acquiring the two skills will enable you to communicate your
messages better by holding the listener’s attention and building trust. You will be
in a position to read and accurately respond to the non verbal signals that other
people send you.
20
How to be a successful e-entrepreneur
Tips for improving non verbal communication.
1. Focus on the person you communicate with.
2. When you communicate with a person it is necessary to keep eye contact.
3. You need to pay attention to the non verbal communication signals such
as facial expression, tone of voice, gestures etc.
Humor laughter
Humor, laugher and play work as natural stress reducer and also elevate your
mood. Playful communication helps to broaden Emotional Intelligence and allows
you to:
1. see the disappointments you experience from a new angle and will make
you recover faster from setbacks and hard times.
2. present things with the use of gentle humor, that otherwise would be
difficult to express.
Resolving conflict positively
Conflicts and disagreements happen all the time as it is quite common to have
people with different needs, opinions and expectations. That is not necessarily a
bad thing. When conflicts and disagreements are resolved in a constructive way it
can strengthen the bonds in a relationship. The ability to successfully resolve
conflicts is connected with the skills of Emotional Intelligence. If you understand
and practise those skills, you will be capable to handle emotionally charged
situations in a better way.
Tips for resolving conflicts positively
1. Do not think about old hurts and unpleasant situations. Focus on the
current situation.
2. Think about the arguments you want to use. Consider the things you want
to argue about and those you don’t.
3. When you see that the conflict cannot be resolved, it is better to choose to
disengage from it, even if you still disagree.
2.2.6 Negotiation
21
How to be a successful e-entrepreneur
Effective negotiation will help you to provide a solution where there is a conflict
of interest because the involved parties want different things. Effective
negotiation should leave both parties feeling that they won something from the
conflict.
There are several types of negotiation in business depending on the
circumstances.
When there is no intention to continue doing business with the same person the
negotiations are hard as both parties seek to win as much as possible without
caring about the other person’s losses.
However, this approach is bad for resolving disputes with people you have an
ongoing relationship with. In a conflict if a person negotiates hard without letting
the other person win something, it will create the feeling of unfair treatment.
Also using underhand tricks and manipulation will result in undermining trust and
will damage teamwork. When people work together on a frequent basis the best
policy for negotiations is openness and honesty.
How to become better in negotiations
Negotiations on small issues don’t need much preparation, as opposed to
negotiations on major issues, which require careful preparation of arguments. It is
better not to waste time on small disagreements during the negotiation process
as it may be counter-productive and weaken your position. Some key points that
need to be considered are the following.
1. Setting goals. Define your negotiation goals. What is it that your
partner wants to get from the negotiations?
2. When negotiating you need to compromise. Think of what you can
compromise in the process
3. What would be the consequences of negotiations that fail? Are
there any other alternatives? Is the failed negotiation going to
affect your future opportunities? How will this failed negotiation
affect others?
4. Is the relationship with the other negotiating part strong or weak?
Are there any past events that could influence the negotiation?
22
How to be a successful e-entrepreneur
2.2.7 Ethics in business
Business ethics is an integral part of your business relationships with others. An
ethical company can only survive if it is managed by ethical people. In small
entrepreneurships ethical leaders who do the right thing at the right time for the
right reason inspire their team to do the same. As a result they build a strong
relationship with their team members, who are dedicated and willing to work very
hard for their leaders.
As a leader you need to know your values and the values of your new
organization. Some key questions that will help you define those are:
1.
What standards of behavior would I like to adopt for my company?
2.
What are the values I believe a good leader should have? Do I agree
with those values?
3.
What if those values put me in a disadvantaged position? Would I still
follow them?
After defining the core values of your entrepreneurship it would be appropriate
to create the right environment for your team and the organization.
Creating the environment is not something easy. It is essential to demonstrate
the values in action, only by doing this will you convince others that the values
are working. Leading the company by example is the best approach to achieve it.
2.3 Critical and Creative Thinking Skills
“Your business is your art…
And you are the artist, the creator.
Everything you do as an entrepreneur,
whether it’s writing, speaking, coming up with innovative ideas, etc…
is sourced from your creativity.”
Katie Freiling
As an entrepreneur, you will have to come up with fresh ideas, and make good
decisions about opportunities and potential projects.
23
How to be a successful e-entrepreneur
2.3.1 Creative thinking
Many people think that creativity is a matter of waiting for inspiration and for
inspiring ideas to come about. This is however regarded as a rather mysterious
process, depending on your level of creativity.
But it would be a mistake to think that creativity is a passive state of mind. While
it is true that there is no special algorithm for creativity, there are thinking skills
that you can be taught and things you can do to enhance your creativity.
You will find below some tips that you might find useful to improve your creative
abilities
Keep track of your ideas at all times. If an idea is not written down
within 24 hours it is usually forgotten.
Ask yourself new questions every day. An inquiring mind is a creatively
active one that enlarges its area of awareness.
Keep abreast of your field and try to be as updated as possible. Read
magazines, trade journals, and other literature in your field to make
sure you are not using yesterday's technology to solve today's
problems.
Invest your free time and engage in creative hobbies. Hobbies can also
help you relax. An active mind is necessary for creative growth.
Learn about things outside your specialty. Use cross-fertilization to
bring ideas and concepts from one field or specialty to another.
Avoid rigid, set patterns of doing things. Try to look at the problem
from a fresh and new point of view, always developing at least two or
more alternative solutions to your problem.
Be open and receptive to ideas (yours and others).
24
How to be a successful e-entrepreneur
Be alert in your observations. Look for similarities, differences, as well
as unique and distinguishing features in situations and problems.
Adopt a risk taking attitude. Outlining the ways you could fail and how
you would deal with these failures will reduce the obstacles to
creativity.
Keep your sense of humour. Humour helps in putting your problems
(and yourself) in perspective. Many times it relieves tension and makes
you more relaxed.
2.3.2 Problem-solving and decision-making
"In any moment of decision the best thing you can do
is the right thing, the next best thing is the wrong thing,
and the worst thing you can do is nothing."
(attributed to Theodore Roosevelt )
no problems, no business.
Problem-solving and decision-making are closely linked, and each requires
creativity in identifying and developing possible options.
Creating a startup, or managing any business, is all about problem solving. Every
business is in fact about solutions to customer problems. Problems are faced by
entrepreneurs on a daily basis. Developing problem solving skills is therefore
crucial in order to become a good entrepreneur.
Here you will find some useful methods for effective decision-making and
problem-solving: first a short and simple step-by-step process for effective
decision-making and problem-solving.
Decision-making process
1. Define the issue – does it require an action? If so, now? Is the matter
urgent, important or both.
2. Gather all the facts and understand their causes.
25
How to be a successful e-entrepreneur
3. Think about or brainstorm possible options and solutions.
4. Consider and compare the pros and cons of each option.
5. Select the best option - avoid vagueness and chose clearly only one of the
existing options.
6. Explain your decision to those involved and affected, and follow up to
ensure proper and effective implementation.
Complex problems and decisions
For more complex decisions and problems involving more than two possible
options you can use several pros and cons tables in conjunction, to compare the
overall weight of each option.
Also consider that some decisions and challenges might seem difficult to you
because you do not have the necessary knowledge or experience. Every time you
find a decision particularly difficult you should first establish if the decision or
challenge is actually appropriate and necessary for you at this stage.
Some decisions have to be made whether you are ready or not, others might not
be as urgent as you imagine.
Whatever you do – always try to be as objective as you can be.
Remember that well prepared decisions are easier to make and to implement,
and generally produce the best results.
2.3.3 Recognizing Opportunities
Do you recognize opportunities when they present themselves? And would you
be able to create a plan to take advantage of them?
There are business opportunities all around us, but many times we fail to
recognize them until it’s too late. Others capitalize on them before we realize the
opportunity even existed.
A very useful tool that could guide you in recognizing opportunities is the SWOT
Analysis, a useful technique for understanding your Strengths and Weaknesses,
26
How to be a successful e-entrepreneur
and for identifying both the Opportunities open to you and the Threats you face.
An interesting template and an explanation of how the SWOT analysis can be
applied in the decision making process can be found in Annex 1.
2.4 Practical Skills
2.4.1 Introduction
Young entrepreneurs are not just lucky and most of their success is due to the
time they spend working on their ideas.
Both general, theoretical knowledge of the area of business you want to launch
and practical skills are necessary for creating a successful business.
Becoming a successful entrepreneur is a long process and we can establish three
main categories of practical skills you need to consider for this purpose:
2.4.2 Goal Setting
The first step to be a successful entrepreneur is setting goals and creating a plan.
You have to set goals for yourself on a daily basis as well as keeping record of
your progress.
To be able to set goals and achieve them respecting your deadlines, you need to
be proactive, forward-looking and you need to have a positive attitude.
Setting goals is a way to organize your ideas. It is important because if we know
what we want to achieve, we can focus on the target without getting distracted.
Clearly defined goals can also be a highly motivating factor.
It is very important to set attainable goals. If your goals are unattainable you are
likely to fail. Should this happen you need to analyze the reason of your failure
and find the way to improve your skills.
27
How to be a successful e-entrepreneur
You need to make sure that the goals you are setting for yourself are realistic.
When you set a goal you should be confident you will be able to achieve it but
avoid the trap of setting your goals too low for the fear of failure. To acquire the
skill to set goals at the right level you need practice.
2.4.3 Planning and Organizing
After you have decided what to do and how to do it, you can now start the
process of setting up you business. Once you have all the necessary information,
you need to plan the implementation of your ideas. It's usually a long process
taking up a lot of your time, but it is necessary if you want to run a successful
business. Organizing your activities and developing your plan once you set your
goals is the key to achieving your targets in an effective and efficient manner.
Planning and organizing help you to identify both short and long term needs and
gives you a realistic vision of your entire work.
Planning is a way to save your time and improve your productivity. By spending
10 or 20 minutes per day looking at your goals and incomes, you make it is easier
for yourself to achieve your objectives.
Planning helps you to make decisions and proactive choices as well as preparing
you to deal with unexpected situations more effectively.
By planning what you are going to do you can also get over bad habits and the
fear of failure. Having a plan allows you to focus on what is important and to set
priorities right.
Below you can find some golden rules to follow when planning and organizing:
- Set up goals and plans which are designed to handle concrete, immediate
situational objectives;
- Be focused and pay attention to planning details and activities;
- See long range goals, and design plans and strategies for attaining these goals
through small steps.
28
How to be a successful e-entrepreneur
- Set the immediate and concrete needs through an action plan for meeting
these needs.
2.4.4 Decision Making
The way you make decisions is extremely important for the management process
of your business. Skilled decision making will take into consideration the
outcomes and consequences of alternative decisions.
In order to make a decision you need to choose from among different
alternatives. Choices, analysis, and doubt are the main elements of making a
decision. You should consider relevant information and foresee the potential
consequences.
A good way to make a clear and fair decision is to create a
Decision Tree.
Figure 4: Decision Tree
The Decision Tree is an excellent tool to help you to choose between different
actions. It also allows you to define options and investigate the possible
outcomes of your choices. It can be useful to consider the risks or rewards related
to each possible event.
Below you can find some tips given by Richard Branson, the founder of Virgin,
about the decision-making process:
29
How to be a successful e-entrepreneur
“a. Trust yourself and your instinct:
There have been many occasions when I have led our team into markets that
industry experts told us to avoid because the competition was too fierce or the
cost of entry too high.
b. Focus on your customers, not your critics.
It wasn't just our team that occasionally worried about our stepping into tough
markets. Over the years, our critics fretted about Virgin's expansion into airlines,
financial services and mobile phone services. What did our company know about
these industries and how would we manage the complex issues? (....)
c. Always support your team.
(....) Day-to-day management has never been my forte, and my early decision to
step back from operations gave me the freedom to focus on our main challenges
and opportunities. This meant that I had to learn to trust the management teams,
and to support them when they saw an opportunity. When Matthew Bucknall and
Frank Reed came to us in 1999 with the concept of a family friendly health club,
we decided to invest. Very quickly, they impressed all of us with their innovative
approach to customer service and team building. (....)
d. Know when to say goodbye.
It can be very difficult to know when to sell, since as a founder and entrepreneur
you become very attached to your business and your team. Look into whether
selling will be good for the overall health of your company, or if you need
objectivity, ask trusted advisers to do this. But brace yourself -- the answer might
be yes. We have sold a number of Virgin companies over the years. Probably the
most notable occasion was in 1992, when we sold Virgin Records to EMI and
used the cash to expand Virgin Atlantic and other companies in the group. It was
a very emotional day for me -- at one point, I broke down in tears. Looking back,
it's clear that we sold at the right time and the decision made sense for Virgin as
30
How to be a successful e-entrepreneur
a whole. That secured our group's future and gave us a war chest for investing in
new businesses. Selling is difficult, and you will be tempted to hold on too long.
This is one of the biggest mistakes an entrepreneur or chief executive can
make.”2
2.4.5 Knowledge
You need knowledge in several areas when starting or running a business. For
instance:
-
Business knowledge:
Business knowledge is the general knowledge of business areas such as
Operations, Marketing, Customer Service/Sales and Finance. Good knowledge of
the business you're running means knowing your staff- their background and
work experience, the company’s targets and objectives, the documents or files
related to your business and its processes.
Business knowledge will help to share company's competences among its levels
(team, organization, making it possible for your business to flourish, and for the
entrepreneur to foresee risks, and investigate all the opportunities in full.
To acquire Business Knowledge you need to do a Market Research. This should
help you identify more and less successful sectors in business enabling you to
share your workers competences and skills among the various levels of your
company.
- Entrepreneurial knowledge
Entrepreneurial Knowledge is the ability to recognize a new service/brand, a new
product, or to improve an existing one. This knowledge aims to improve the
existing knowledge through the creation of a new system/product, and does not
put the profit at the top of its targets.
2 Richard Branson, “Decision-Making For Entrepreneurs”, http://www.entrepreneur.com/article/222739
31
How to be a successful e-entrepreneur
Entrepreneurship Knowledge is the engine of your business, which will help you
to explore new chances and opportunities foreseeing all risks. This kind of
knowledge is now considered the engine of modern economy. Indeed innovation
can boost the job market and therefore your company.
The best thing to do in order to acquire this kind of knowledge is to understand
how successful entrepreneurs create their capitals. Secondly, an in depth analysis
of successful business models will definitely be helping a new entrepreneur in his
mission.
●
Opportunity-specific knowledge
Opportunity-specific knowledge is related to new and unexplored markets. It's
highly important to acquire this kind of knowledge if you want
to create a
successful business.
Opportunity- specific Knowledge allows a young entrepreneur to choose the
right field for his business, chasing a new idea/market, facing few competitors,
and establishing a successful leading company.
Opportunity-Specific Knowledge can be developed mainly through a direct
experience of the market. In other words, only those who actually know about the
possibility of a new market acquire it. This is definitely a tough knowledge to be
acquired as there's no class or University able to teach you about that. It can be
developed only through marketplace experience. Our suggestion is to study and
analyze the existing markets and needs.
●
Venture-specific knowledge
Venture-Specific knowledge is the series of skills/competences based on
experience that allows entrepreneurs to produce a particular service or product.
Venture-specific knowledge deals with the specifics of a market or sector. In
other words, if you want to run a business in food export, you need to know how
to obtain a trade license. That's the example of the venture-specific knowledge.
32
How to be a successful e-entrepreneur
It's undoubtedly the most difficult knowledge to acquire as the only relevant
environment where you can learn it is the market/field. We suggest 3 ways to
gain this kind of experience-based knowledge:
To create a business plan based on in depth market analysis and studies.
To start up a venture experience and learn by doing.
To have some experience within the desired market and learn from your
daily experience.
33
Appendix 1
SWOT Analysis Template
State what you are assessing here _____________________________________________________________________________________
(This particular example is for a new business opportunity. Many criteria can apply to more than one quadrant. Identify criteria appropriate to your own SWOT situation.)
criteria examples
Advantages of proposition?
Capabilities?
Competitive advantages?
USP's (unique selling points)?
Resources, Assets, People?
Experience, knowledge, data?
Financial reserves, likely returns?
Marketing - reach, distribution,
awareness?
Innovative aspects?
Location and geographical?
Price, value, quality?
Accreditations, qualifications,
certifications?
Processes, systems, IT,
communications?
Cultural, attitudinal, behavioural?
Management cover, succession?
Philosophy and values?
strengths
weaknesses
criteria examples
Disadvantages of proposition? Gaps
in capabilities?
Lack of competitive strength?
Reputation, presence and reach?
the internal environment - the situation
inside the company or organization
for example, factors relating to products, pricing,
costs, profitability, performance, quality, people,
skills, adaptability, brands, services, reputation,
processes, infrastructure, etc.
Financials?
Own known vulnerabilities?
Timescales, deadlines and
pressures?
Cashflow, start-up cash-drain?
Continuity, supply chain robustness?
Effects on core activities, distraction?
Reliability of data, plan
predictability?
Morale, commitment, leadership?
Accreditations, etc?
criteria examples
Market developments? Competitors'
vulnerabilities? Industry or lifestyle
trends? Technology development and
innovation?
Global influences?
New markets, vertical, horizontal?
Niche target markets? Geographical,
export, import?
New USP's?
Tactics: eg, surprise, major
contracts?
Business and product development?
Information and research?
Partnerships, agencies, distribution?
Volumes, production, economies?
Seasonal, weather, fashion
influences?
opportunities
threats
the external environment - the situation
inside the company or organization
for example, factors relating to markets, sectors,
audience, fashion, seasonality, trends, competition,
economics, politics, society, culture, technology,
environmental, media, law, etc.
Processesexamples
and systems, etc?
criteria
Management cover, succession?
Political effects?
Legislative effects?
Environmental effects?
IT developments?
Competitor intentions - various?
Market demand?
New technologies, services, ideas?
Vital contracts and partners?
Sustaining internal capabilities?
Obstacles faced?
Insurmountable weaknesses?
Loss of key staff?
Sustainable financial backing?
Economy - home, abroad?
Seasonality, weather effects?
Index
1. Enterprise 2.0 ...................................................................................................................................3
3. Strategy for the creation of an E-Enterprise .....................................................................................6
4. Digital Reputation for an enterprise. Investigation, monitor and management ...............................8
4.1. The importance of the on-line reputation management ............................................................9
4.2. Creation and management of the on-line digital reputation ....................................................11
4.3. Monitorization of the on-line reputation .................................................................................12
5. Tools for creating, controling and improving the e-enterprise reputation .....................................13
5.1. Create ......................................................................................................................................13
5.1.1. Your name ........................................................................................................................13
5.1.2. Social Networks ...............................................................................................................15
5.1.2.1. Facebook ...................................................................................................................15
5.1.2.2. Twitter .......................................................................................................................21
5.1.2.3. Google+ .....................................................................................................................26
5.1.2.4. LinkedIn ....................................................................................................................35
5.1.3. Others ...............................................................................................................................38
5.1.3.1. Youtube .....................................................................................................................38
5.1.3.2. Flickr .........................................................................................................................39
5.1.3.3. Foursquare .................................................................................................................42
5.1.3.4. Blogs..........................................................................................................................45
5.1.3.5. Wikis .........................................................................................................................46
5.1.3.6. Forums .......................................................................................................................46
5.1.3.7. Slideshare ..................................................................................................................47
5.1.3.8. RSS ............................................................................................................................47
5.2. Control .....................................................................................................................................48
5.2.1. Google Alerts ...................................................................................................................48
5.2.2. Google Analytics ..............................................................................................................48
5.2.3. Tweetreach .......................................................................................................................49
5.2.4. Facebook insight ..............................................................................................................49
5.2.5. Flickr Stats........................................................................................................................50
5.2.6. Youtube insight ................................................................................................................50
5.2.7. Howsociable .....................................................................................................................50
5.2.8. Google Blog Search .........................................................................................................51
5.2.9. Google Trends ..................................................................................................................51
5.3. Improve and maintain..............................................................................................................52
5.3.1. Tweetdeck ........................................................................................................................52
5.3.2. Hootsuite ..........................................................................................................................56
5.3.3. Google adwords................................................................................................................58
2
1. Enterprise 2.0
Enterprise 2.0 was created to help organizations to get into social networks and online
programmes (social software tools). This phenomenon does not only influence technology
and tool web, but, also brings about important changes in personal identities and in the
way people and organizations relate with each other.
The ability of individual companies to stay in touch with social software tools, imporves
customers’perception of the company. In addition, this ability helps companies to get the
hightest position in the competitive market.
In enterprises 2.0, the information that consumers have about the actions, values and
mission of the organization increases. It also improves the perceived quality, increases the
range of choices available and, in particular, the preferences and purchasing decisions
made by consumers.
In many cases, achieving and ensuring a competitive edge in the market is only obtained
by influencing the decision-making processes of consumers, especially at their level of
involvement, attitude and tendency to respond favorably or unfavorably to an object in a
consistent manner.
Many companies are adapting their philosophy and methodologies to the social web as an
operational framework. The concept was first analyzed by Andrew McAfee, a researcher at
Harvard University. He describes the enterprise 2.0 as the use of social software platforms
within companies or between companies, and their audiences (partners, suppliers,
customers and general public).
In addition, organizations can create content and communities as individuals already do.
To describe this phenomenon McAfee uses the acronym SLATES which synthesizes six
structural ideas about enterprise 2.0:
Search: looking for valuable information is a crucial activity for workers and
Enterprise 2.0 is committed to making relevant content easily available to
customers.
Links: Internet narration is not linear; the sequence from a resource to another
resource is of the hypertext.
Authority: Authority in a particular area is the key to achieving credibility and
attention. However through democratizing Web 2.0 everybody can produce and
create content, which implies that the company cannot keep full control of the
information posted on the Internet.
Tag: there is not a single way to label or tag contents. This ability to label contents
in a variety of ways is exclusively human, and cannot be developed by machines.
Each person or organization can create new richer and deeper information systems
through folksonomy: digital content is tagged and linked by each user.
Extensions: the Internet is configured by recommendation networks that extend the
search term. Enterprise 2.0 interacts in an ecosystem of recommendations, social
filtering and comments with which knowledge is organized.
Signals (señales): Signals: the network is millions of contents which are constantly
evolving. For tracking and monitoring the network it is essential to follow certain
signals through RSS technology, involving a system to access the knowledge
associated with Web 2.0.
3
These six ideas reflect the social, technological and economic development of web 2.0.
This new phenomenon requires revisiting the past and present of communication and
managing the brand by companies to adopt new more effective and strategic future
perspectives:
From an internal point of view, a 2.0 enterprise encourages knowledge
management, integrating, ordering and labeling communications within the
organization itself.
2. E-Costumers Analisys
Market segmentation is the process of identifying groups of consumers who share similar
needs under certain segmentation criteria. A segment has to be identifiable, reachable, and
measurable and must be big enough to be viable. Consumers can be segmented on
various criteria such as:
Geographic segmentation: the consumers are classified based on the region where
they are located: country, city, zip code etc. On the Internet, some geographic
information can be captured via IP address, on the particular search engine used in
individual countries.
Demographic Segmentation: the consumers are classified based on variables like
age, gender, family size, income, generational level, nationality, ethnicity, religion,
education and occupation. Demographic information and geographic information
can be combined to obtain powerful insights into your consumers.
Behavioural Segmentation: the consumers are classified based on actual user
behaviour. Such behaviours include: benefits the customer is seeking, how the
consumer intends to use the product, consumer’s brand loyalty, and even usage
occasion.
Psychographic Segmentation: also called life-style segmentation is used to create
extensive consumer profiles based on their lifestyles or their Activities, Interests,
Opinions (also called the AIO). VALS™ (value and lifestyle survey) conducted a
research on consumers’ behaviour. Consequently, 8 types of consumers have been
defined as follows. According to http://www.sric-bi.com/VALS/: the 8 segments are:
◦ Innovators: Innovators are successful, sophisticated, take-charge people with
high self-esteem.
◦ Thinkers: are motivated by ideals. They are mature, satisfied, comfortable,
and reflective people who value order, knowledge, and responsibility.
◦ Achievers: motivated by the desire for achievement, Achievers have goaloriented lifestyles and a deep commitment to career and family.
◦ Experiencers: are motivated by self-expression, they seek variety and
excitement, savoring the new, the offbeat, and the risky.
◦ Believers: are conservative, conventional people with concrete beliefs based
on traditional, established codes: family, religion, community, and the nation.
◦ Strivers: are trendy and fun loving. Strivers are concerned about the opinions
and approval of others.
4
◦ Makers: are motivated by self-expression. Makers are practical people who
have constructive skills and value self-sufficiency
◦ Survivors: live narrowly focused lives and are cautious consumers. They
represent a very modest market for most products and services. They are
loyal to favourite brands.
Importance of Segmentation
Thanks to the segmentation you will be able to focus your marketing efforts and better
target the customers you are trying to reach. It is in fact much easier to address the needs
of smaller groups of customers sharing similar needs.
By identifying customers based on segmentation criteria you can in fact adapt the content
of the site to their needs.
For example market segmentation can be used to create different web sections for large
business customers, public sector and retail customers (e.g. premier pages with customized
content for important customers). Web sites also use consumer behavioural and
demographic information to create unique offers and online experience. For example, past
purchase data, browsing data and even demographic data can be used to customize the
web page of a company.
Online User Segments
Companies can use several data sources to effectively segment their consumers in the
online context. But what kind of consumers are online consumers—are they different than
offline consumers? Are they well educated and well-off? Is there a digital divide?
A large scale study by McKinsey & Company found six behaviour based categories of
online users. Here are some insights from this report to give you a brief overview of these
segments:
1. Simplifiers: account for 29% of Internet users and seek convenience and ease of
use when browsing sites.
2. Surfers: 8 percent of the active users. They use the Web to find information, explore
and also shop.
3. Bargainers: 8% of active users. They use the web to find deals and browse the Web
for shopping and entertainment.
4. Connectors: 36% of active users. They tend to be new to the Web and use it
primarily to stay in touch with people.
5. Routiners: 15% of active users and use the Web generally to obtain information
and revisit their informational sites of interest.
6. Sportsters: 4% of active users. They are similar to routiners but they spend most of
their time on sports and entertainment sites.
In order to identify as efficiently as possible your target customers you should become
familiar with targeting activities, as well as personalization and customization of your offer:
5
1. Targeting requires the identification of customers, individually or by segments,
which have a high probability of responding to an offer that is made to meet their
known needs and desires. Profiles can be identified, based on registration or other
overt provision of data to the marketer, or anonymous, based on click-stream data
on the web.
2. Personalization requires profiling and provision of content based on the profile of
the costumer. At most basic level customer databases can be used to develop
marketing programs that recognize the customers by name, or target market, or
value proposition. It implies that the content already exists and that the marketer is
using profiles to determine which content to supply to which customers. Profiles can
be anonymous or identified. For example, when you sign into your Yahoo or Google
account the web page recognizes you and caters the content relevant to you.
3. Customization implies the creation of new content, services or products based on
customer needs. For this reason you may find offers for customized radio station for
you, or adverts for shops that correspond to your taste.
3. Strategy for the creation of an E-Enterprise
Public objective/aim
Competence
Analysis
Sector
Resources
Objectives (real, achievable, measurable
objectives/aims)
Blog
Plan of
action
Foros
Wikis
Reasons for being in social networks
Quantitative objectives
Qualitative objectives
Awareness, branding, marketing, recruiting,
loyalty
Content
Dynamization
Strategy
Web
http://www.forrester.com
Twitter search, Google,
Howsociable
Google Alerts / Google
Insight / Google Trends
Time and €/£
Content
Tags
Callme back
Chat
Content and
image
Cross-links
Mention sources
Blog roll
Participate
Content
Collaboration
Engadgement
6
Blogspot.com
Wordpress.com
Enfemenino
Forocoches
Foroimpagados
Wikipedia
Facebook
Company
Twitter
Foursquare
Youtube
Flickr
LinkedIn
Content and
design
Information
Apps
Plugins (‘I
like’button, login,
comments)
Advertising
Places
Content and
design
Information
Plugins (tweet
button, widget
timeline, etc…)
Advertisement
Visual
Information
Plugins
Information
Content
Tags
Category and
description
Advertisement
Information
Content
Tags
Descriptive title
Badge
Data and
information
Services and/or
products
Content
Plugins
www.business.twitter.com/about/resources
www.businnes.twitter.com/advertise/start
Crear y reclamar sitio
https://www.ads.youtube.com/campaign_set
up
www.flickr.com/badge.gne
www.linkedin.com/publishers
Advertisement
Participate
Monitorization
http://www.telemakingweb.com/ejemplosapp-paginas-fan
www.facebook.com/apps
www.involver.com
www.pagemodo.com
www.facebooktapsite.com
www.wildfireapp.com
www.facebook..com/plugins
www.facebook..com/advertising
www.facebook.com/places
www.linkedin.com/ads/home
Hootsuite
Participación
multiplataforma
Participación
multiplataforma
Tweetdeck
7
Tweetreach
Tweetsearch
Google Analytics
Facebook insight
Youtube insight
Flickr stats
LinkedIn
Adwords
Howsociable
Alexa
Seguimiento tweeter
Seguimiento tweeter
Web y blogs
Facebook
Youtube
Flickr
Solo tiene estadísticas para
grupos y el administrador
de los mismos
Publicidad de Google
Notoriedad marca online
SEO
4. Digital Reputation for an enterprise. Investigation, monitor and
management
A few years ago there were very limited means available to people to express a public
complaint. However, today the social web has brought about new scenery for customers
and users to express their opinions on brands and products.
This is totally new scenery for companies, and it is also an excellent opportunity for them
to become part of this conversation and be able to correct mistakes, improve products,
exercise influence and ultimately, improve their online corporate reputation as a whole.
Therefore, to build, monitor and improve online corporate reputation has become an
essential strategy in any company.
Corporate reputation is a broad and complex concept that not only affects communication,
public relations or marketing departments, but also includes all policies and actions carried
out by a company, and how it behaves in its whole as an organism. Therefore, corporate
reputation comes to include elements such as human resources policies and labour
relations, financial performance, R & D, corporate social responsibility and environmental
policies departments, the brand image perceived by both the internal and the external
public, business ethics, and so on. For these reasons, before talking about the
management of online corporate reputation, it is necessary to analyse its primal concept.
A successful definition of corporate reputation is that offered by the expert in
management Javier Fernández Aguado, for whom corportate reputation is “consolidated
and well-established prestige that a body achieves before all its stakeholders. This credit
must be grounded in the thorough and appropriate response, both technical and ethical,
of the commitments taken on by the entity and all its members, as far as the objectives of
the organisation are concerned. Meeting the legitimate expectations of all stakeholders of
an organization leads to this corporate reputation. That reputation then becomes a
competitive advantage to any entity, but it is an end in itself, it is not justified for the
improvement in the achievements obtained by the entity. "
This diversity of indicators and the heterogeneity of the concept make the measurement of
corporate reputation complex. There is a great number of meters to evaluate it: America's
Most Admired Companies (2008), Reputation Quotient, Good Reputation Index, Danish
Ranking, Britain's Most Admired Companies, Spanish Financial Intermediaries, MERCO
(Spanish Corporate Reputation Monitor), and so on.
The influence of the social web on corporate reputation is remarkable, both from a positive
8
and negative point of view. There are many examples of companies that have been
affected by information published on blogs or social networks; not only their image has
been affected, but some have experienced significant losses in sales (Kryptonite or Dell);
for some others, their corporate reputation has improved thanks to their management of
online reputation (ComCast or Caja Navarra).
The Corporate online reputation is the intensive knowledge and personal assessment
of an organization shared by its interlocutors on the Internet.
When addressing the online reputation, we must clearly differentiate three concepts:
Research on the online reputation. It is done back in time, between one and two
years depending on the brand/s climate of opinion. It is a methodology based on
the quantitative research and the analysis of social networks; they make it possible
to cover two aspects: first, the most quantitative aspects for the research on the
online reputation identifying categories of opinion makers and the media where
opinions are shared; second, the appraisal attitudes derived from each opinion
maker and media (blog, forums, social networks, opinion aggregators, traditional
media, etc.).
Monitoring the Online Reputation. It basically consists in following, from a specific
point in time, all the content generated on the social web around certain keywords
that are considered strategic for the company (company name, product, board of
directors, etc.).
Management of the online reputation. It is done through the generation of
relevant content, the creation and management of the digital identity, the online
monitoring and the communication activities 2.0, always according to a pre-planned
strategy to be implemented in the medium term.
4.1. The importance of the on-line reputation management
The influence of the social web, what it is said in it, the word of mouth that it generates
and the information shared and distributed by its users are too important to the corporate
reputation of the companies to ignore it. It is essential for any organisation to know what
customers, employees and the market are saying about it, its brands or products. It is
therefore crucially important to manage proactively the online corporate reputation.
The management of the online corporate reputation should be planned strategically and
consistently with the offline communication actions. A simple model of action is the
following:
To create and manage our digital identity, we need to approach our audience and do it
through the social networks and the media in which they participate. This step requires
taking the time to find out where my audience is, a preliminary analysis which is essential
when it comes to managing our digital identity based on our objectives.
Participate in social networks helps to generate quality content and useful applications for
users, put aside the intrusiveness and brand presence, comment on other blogs, respond to
questions or concerns of other users, etc. This section covers the various 2.0.
communication activities.
Stay in touch with the community through using other blogs as sources and building a
9
network of real contacts within the site. Deal with people in a personal basis, putting aside
traditional media relations applied to bloggers and participate in all networks you are part
in adding value to networks.
Relying on the responsibility of employees and the responsibility of all areas of the
company involved in corporate participation in the social web. We are part of the
community and we are useful to that community which is also useful to us.
Monitoring and analyzing consistently to check the strategy.
On the Internet, a priori, reputation depends more on others than on the company itself,
and on the usual mechanisms of communication. This forces you to plan your online
strategy and build strong digital identity in the medium and long term. This is not a threat
but an opportunity, because we can use the same users’ tools to communicate with them.
Therefore, to build, monitor and improve corporate reputation online, we must plan 2.0
communications strategically, in perfect harmony with all actions and strategies offline.
This is not a channel or another medium, but a new way of doing our work to reach our
audiences.
In the UK, the corporate reputation management online advances inexorably. It is known
under the acronym ORM (Online Reputation Management).
The Qudsi, Online Reputation Management goes through three phases:
It is important to know what is being said online about a company, product or
person giving more importance to the most relevant or influential comments and
sites. Symilarly to the offline world, negative comments about a company made in the
national television are not as damaging as critical commets made in a local television.
• Analyze the gathered information, prioritizing negative messages as the most
important ones to track.
• Work on the negative messages, learning to counter such criticism if it is
constructive.
"This is a multidisciplinary work; it is a mixture of marketing, public relations and
search engine optimization."
When a "relevant online reputation crisis" takes place, it is important to act quickly to avoid
what is known as domino effect: correct the faults that can be mended and avoid the
expansion of negative reviews through search engines.
You may have a 99% customer satisfaction but they may never visit your website to leave
good comments about you and. On the contrary, you may have only 1% of dissatisfied
customers, or even your own former employees, who may start
a discredit campaign against you on the Internet. It is only fair and logical to stay alert and
try to correct the consequences.
Finding a negative opinion about a company in one of the first three pages of Google can
inflict much damage to its online and offline reputation. Search engines have become not
only information searchers, but, increasingly, reputation searchers: brand, business or
person reputation.
10
Many brands which are just starting to use social applications are surprised at the number
of comments or news about them which they find when they use the tools for monitoring
online reputation.
Reading the comments about a brand, a company or a product is essential; but it is more
productive to join that discussion to learn how to act in the future.
4.2. Creation and management of the on-line digital reputation
Undoubtedly, nowadays Google has become a real reputation manager due to the fact
that the results it provides after searches are significantly influenced by social websites, i.e.
the digital identity built by the company on the various social networks in which it is
present, or the 2.0 tools that the company uses.
This, together with the fact that Google search engine (which in Europe has a market share
of over 90%) offers real-time searches with an increasing social component (results from
Wikipedia, blogs content, images, videos, etc.) forces us to manage proactively our digital
identity, which becomes the best way to manage our online corporate reputation.
Therefore, the creation of a digital identity is very important for the organization and the
content generates within the social web. The preliminary process of research and analysis
should be comprehensive, with the aim of finding out which social media are best suited to
build online digital identity.
The process of managing the digital identity takes a lot of learning, and involves trying and
making mistakes, but all in all, common sense should prevail: the social web is formed by
people who want to talk, communicate, learn, and play, and so on.
There is no creation without research and analysis, nor management without continuous
learning.
However, in order to manage our digital identity in the best posible way, we must carry out
a preliminary research in order to identify the most appropriate tools to reach our
audiences where they are and share and create content.
Components of digital identity:
Profiles:
o Social networks.
o Personal information.
Comments:
o Forums.
o Blogs.
o Social networks.
Digital content:
o Photo sharing websites.
o Video sharing websites.
o Presentations.
o Personal blogs.
o Web page.
11
Contacts:
o Social networks.
o Twitter.
o Blogs.
4.3. Monitorization of the on-line reputation
Trendwatching website referred to the monitoring and alerts as one of the ten key trends
for 2010. However, monitoring is the most overlooked, but the most necessary action on
the social web. It is an essential task when it comes to draft reports on any action. This
evolution cannot be discovered by simply taking into account a specific number of
followers on Twitter.
Monitoring can sometimes be problematic for two different reasons. It is possible that the
company’s budget is too low to hire external monitorin tools. It is also possible, that the
company only uses free availabre tools when in the developing stage a specific action, or
just in certain situations. In both cases, the company forgets the importance of continuous
monitoring, which should take into account what people say about the company, where it
is said, who says it, etc. In case the company does not develop a continuous monitoring
system, it might be difficult to manage such a huge amount of data.
Here are some useful tips to organise the monitoring:
Monitor before starting.
Any kind of monitoring is better tan doing nothing.
Have clear objectives: you should always be focused before starting any action.
Choose four or five tools, those you feel most comfortable with.
Use the tools, but always use some creativity of the same line.
The key point is the keywords.
Once you have decided to start monitoring, you must take the following aspects into
account:
Choose the keywords below to direct you to different tools necessary to do research
and registration.
Examples of useful keywords:
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
Directors
Company, subsidiaries…
Brands, products names, services…
Slogan
Competition
Sector
Suppliers, customers, partners, etc.
Manage the results on RSS readers. As we have seen it is important to select tools
that allow us to receive the results of our searches via RSS. One of the most
recommended tools is:
o Google Reader: if we create a specific account related to what we want to
monitor, it can be an interesting tool, although it is visually much poorer than
12
others.
Manage the tools properly. When it comes to managing and controlling our tools, it
could be interesting to divide them as follows:
o
o
o
o
o
o
News Alerts
Blogs
Comments and conversations
Social media
Markers
Twitter
5. Tools for creating, controling and improving the e-enterprise reputation
5.1. Create
5.1.1. Your name
Go to http://google.com/gmail.
13
Figure 1 - How to create a gmail account- Step 1
Click on Create Account located in the upper right corner of the page.
Figure 2 - How to create a gmail account - Step 2
Fill in the fields about your personal information.
14
Figure 3 - How to create a gmail account – Step 3
Click on Continue to Gmail.
5.1.2. Social Networks
5.1.2.1. Facebook
Figure 4 – Facebook Logo
Facebook is a social networking service and website launched in February 2004. Users
must register before using the site, after which they may create a personal profile, add
other users as friends, and exchange messages, including automatic notifications when
they update their profile. Additionally, users may join common-interest user groups,
organized by workplace, school or college, or other organizations, and categorize their
friends into lists such as "People From Work" or "Close Friends". Facebook allows all users
who declare themselves to be at least 13 years old to become registered users of the site.
The website's membership was initially limited by the founders to Harvard students, but
was expanded to other colleges in the Boston area, the Ivy League, and Stanford
University. It gradually added support for students at various other universities before
opening to high school students, and eventually to anyone aged 13 and over.
These pages are created for businesses, organizations and brands interested in sharing
their information and in connecting with people.
You can create and manage a Facebook Page from your personal account.
15
Registration
Go to http:// http://www.facebook.com/ and click on Create a Page.
16
Figure 5 – How to crate your Company Facebook Page - Step 1
Here we have some options; we’ll click on Company, Organization or Institution.
17
Figure 6 – How to crate your Company Facebook Page – Step 2
Here, we have to select the category from the list, enter the company name, click on I
agree and then we can click on Get Started.
Figure 7 - How to crate your Company Facebook Page – Step 3
If you already have a Facebook account, simply begin using your account. If, however, you
do not have one, select the second option and proceed to create it.
18
Figure 8 – How to create your Facebook account
Once you start your session, there are two steps to complete for the creation of the
Facebook page. The first step is to select the photo that will serve as a profile picture.
Figure 9 – How to add a picture to your Facebook profile
Once selected, the assistant will guide you to the second step related to basic information
about your site.
19
Figure 10 – How to add a description and link about your company on your Facebook Page
On the site, two sections can be distinguished: the first one is the Admin Panel, where you
can configure your site.
Figure 11 – How to set the information you wish to provide on your Company Facebook Page
The second section, just below, shows the wall where you can insert statements, photos,
links, events, etc, like a normal Facebook profile.
20
Figure 12 – Example of a Company Facebook Wall
5.1.2.2. Twitter
Figure 13 – Twitter Logo
Twitter is an online social networking service and microblogging service that enables its
users to send and read text-based posts of up to 140 characters, known as "tweets". It was
created in March 2006 by Jack Dorsey and launched that July. The service rapidly gained
worldwide popularity, with over 140 million active users as of 2012, generating over 340
million tweets daily and handling over 1.6 billion search queries per day.
It has been described as "the SMS of theInternet". Unregistered users can read the tweets,
while registered users can post tweets through the website interface, SMS, or a range
of apps for mobile devices.
Registration
Go to http://www.twitter.com. In that page, you can find a register form. Fill it in and click
21
on Sign up for Twitter.
Figure 14 – How to create your Company Twitter account – Step 1
Now, you will be redirected to another page to check if the data are correct.
Figure 15 - How to create your Company Twitter account – Step 2
After verifying the data, click on Create my account. Once this is done, Twitter will help us
to set up our profile.
Figure 16 – How to create your Company Twitter account – Step 3
The first step shows a list of people you might be interested in following. Please note that
you can skip this step.
22
Figure 17 - How to create your Company Twitter account – Step 4
The second step shows well-known people divided into different categories.
23
Figure 18 - How to create your Company Twitter account – Step 5
The next step allows us to follow those contacts in our email address.
24
Figure 19 – How to find people you know on Twitter
Finally, you can upload a profile photo and a brief description.
Figure 20 - How to add a picture and a brief description about your company to your Twitter profile.
When you have completed all those steps, your Twitter profile configuration will be
finished.
25
Figure 21 – How to set your Company Twitter profile.
5.1.2.3. Google+
Figure 22 – Google + logo.
Google+ (pronounced and sometimes written as Google Plus, sometimes abbreviated
as G+) is a social networking and identity service owned and operated by Google Inc.
The service was launched as an invitation-only "field test" in June 2011. Early invites were
soon suspended due to an "insane demand" for new accounts. On September 20, 2011,
Google+ was opened to everyone 18 years of age or older without the need for an
invitation. It was opened for a younger age group (13+ years old in US and most countries,
14+ in South Korea and Spain, 16+ in Netherlands) on January 26, 2012.
Google+ integrates social services such as Google Profiles, and introduces new services
identified as Circles, Hangouts and Sparks. Google+ is available as a website and on mobile
devices.
In November 2011, Google+ was integrated into the account creation process for other
Google services, such as Google Mail.
Google+ Pages was launched on November 7, 2011 to all users. It allows entities which
are not individuals (such as organizations, companies, and publications) to set up profiles,
or pages, for the posting and syndication of posts.
26
Registration
Go to http://www.plus.google.com and click on Sign In if you already have a Google
account or click on Create an account if you do not.
Figure 23 – How to create your Comany Google+ account – Step 1
Enter your address and password on the new page.
Figure 24 - How to create your company Google+ account – Step 2
27
First you will be asked to set up your Google Profile +. Then, click on Add your photo and
a new page will appear where you can drag the file you want, or click on Select a photo
from your computer.
Figure 25 – How to add a picture to your company Google+ profile.
Once you have uploaded your photo and indicated your name and gender, click on
Upgrade.
28
Figure 26 – How to create your company public profile on Google+.
The second step allows you to add people to your circles from your accounts...
Figure 27 - How to find people you know on Google +.
29
… And at the same time, you can follow people or web pages you know. Once you have
selected them, click on Continue.
Figure 28 – How to follow people and page on Google+.
30
The third and final step consists in adding basic information about us.
Figure 29 – How to update your company public Google+ profile and picture.
When the previous step is completed, you are registered in Google +, but you have a user
profile, not a page. To create your page, select More and then Pages.
Figure 30 – How to create our company Google+ page – Step 1
31
You will be informed that you do not have a page yet. To create it, just click on Create new
page.
Figure 31- How to create our company Google+ page – Step 2.
A list of categories appears and a brief description when you place your cursor over them.
Figure 32 - How to create our company Google+ page – Step 3.
32
Select the category which fits your needs best and fill in the fields of basic data record. To
continue, click on Create.
Figure 33 - How to create your company Google+ page – Step 4.
Once this is done, upload a profile picture. Select it and click on Continue.
33
Figure 34 - How to create your company Google+ page – Step 5.
Finally, you can notify people that your page has been created.
Figure 35 - How to create your company Google+ page – Step 6.
A message will indicate that you are now using Google + as a page, not as a personal
profile, and it will inform you about what you can do on the page.
Figure 36 - How to create your company Google+ page – Step 7
34
5.1.2.4. LinkedIn
Figure 37 – LinkedIn logo
LinkedIn is a professional social networking website. Founded in December 2002 and
launched in May 2003, it is mainly used for professional networking. The site is available
in English, French, German, Italian, Portuguese, Spanish, Dutch, Swedish, Romanian,
Russian, Turkish, Japanese, Czech and Polish. LinkedIn filed for an initial public offering in
January 2011 and traded its first shares on May 19, 2011, under the NYSE symbol "LNKD".
Registration
Go to http://www.linkedin.com/, fill the registration form and click on Join now.
Figure 38 – How to create your company LinkedIn account – Step 1.
This step will lead you to another registration form. Now, you indicate the country you live
in, zip code, what your job is, in what sector and what company. After filling all fields in,
click on Create my profile.
35
Figure 39 - How to create your company LinkedIn account – Step 2.
In the following step, you have to enter your email address.
Figure 40 - How to create your company LinkedIn account – Step 3.
In the third step, you are informed about different people, some of them well-known
people.
Figure 41 - How to find people ou know on LinkedIn.
In the fourth step, you can inform people via Facebook or Twitter about the new creation
of your profile in LinkedIn.
36
Figure 42 - How to create your company LinkedIn account – Step 4.
In the fifth step, you can select a premium account or a regular account.
Figure 43 - How to create your company LinkedIn account – Step 5.
Once this is done, your profile on LinkedIn is created, in order to register a company, go to
Home y and click on Companies on the top bar.
Figure 44 - How to create your company LinkedIn account – Step 6
Now Click on Add a Company.
Figure 45 - How to create your company LinkedIn account – Step 7.
A registration form will appear. Fill it in and click on Continue.
Figure 46 - How to create your company LinkedIn account – Step 8.
37
Now, you just have to fill in the following form and your company will be registered on
LinkedIn.
5.1.3. Others
5.1.3.1. Youtube
Figure 47 – You Tube logo
YouTube is a video-sharing website, created by three former PayPal employees in
February 2005, on which users can upload, view and share videos. It uses Adobe Flash
Video and HTML5 technology to display a wide variety of user-generated video content,
including movie clips, TV clips, and music videos, as well as amateur content such as video
blogging and short original videos.
Unregistered users can watch videos, while registered users can upload an unlimited
number of videos. Videos considered to contain offensive content are available only to
registered users at least 18 years old. In November 2006, YouTube, LLC was bought
by Google for US$1.65 billion, and now operates as a subsidiary of Google.
Registration
Go to http://www.youtube.com and, in the top right, click on Sign In.
Figure 48 - How to create your Your Tube account – Step 1.
Enter your email in the new form.
Figure 49 - How to create your You Tube account – Step 2.
38
Click on Sign in and your YouTube account will be created and your session open.
Figure 50 - How to create your You Tube account – Step 3.
5.1.3.2. Flickr
Figure 51 – Flickr logo.
Flickr is an image hosting and video hosting website, web services suite, and online
community that was created by Ludicorp in 2004 and acquired by Yahoo! in 2005. In
addition to being a popular website for users to share and embed personal photographs,
the service is widely used by bloggers to host images that they embed in blogs and social
media.
Photos and videos can be accessed from Flickr without the need to register an account, but
an account must be made in order to upload content onto the website. Registering an
account also allows users to create a profile page containing photos and videos that the
user has uploaded and also grants the ability to add another Flickr user as a contact. It is
also available for mobile phones.
Registration
Go to http://www.flickr.com and, in the top right, click on Sign Up.
Figure 52 - How to create your Flickr account – Step 1.
39
Once this is done, a window will appear and you can register using a Yahoo, Facebook or
Google email account. Click on Google.
Figure 53 - How to create your Flickr account – Step 2.
You can confirm and click on Allow.
Figure 54 - How to create your Flickr account – Step 3.
40
Now you start the registration process. Fill in the registration form and click on Continue.
Figure 55 - How to create your Flickr account – Step 4.
The window will close. The registration will be completed clicking on Sign In.
Figure 56 – How to create your Flickr account – Step 5.
Now, you can get into your account.
Figure 57 – Example of a Flickr profile.
41
5.1.3.3. Foursquare
Figure 58 – Foursquare logo.
Foursquare is a location-based social networking website for mobile devices, such
as smartphones. Users "check in" at venues using a mobile website, text messaging or a
device-specific application by selecting from a list of venues the application locates
nearby.Location is based on GPS hardware in the mobile device or network location
provided by the application. Each check-in awards the user points and sometimes
"badges". The service was created in 2009 by Dennis Crowley and Naveen Selvadurai.
Support for French, Italian, German, Spanish, and Japanese was added in February 2011.
Support for Indonesian, Korean, Portuguese, Russian, and Thai was added in September
2011.
Register
Go to http://www.foursquare.com. At the bottom of the screen, click on Sign up with
Email. You can also register using your Facebook account.
Figure 59 - How to create your Foursquare account - Step 1.
42
You will be redirected to a registration form. Fill it in and click on Join.
Figure 60 - How to create your Foursquare account - Step 2.
Now, you can look for your contacts on Facebook, Gmail, Twitter and/or Yahoo!
Figure 61 - How to create your Foursquare account - Step 3.
You can skip this step at the bottom of the page.
43
Figure 62 – How to create your Foursquare account - Step 4.
The following step recommends you people to follow.
Figure 63 - How to create your Foursquare account - Step 5.
Finally, you can download the client for smartphones and it provides you with a link to go
to Home.
Figure 64 - How to create your Foursquare account – Step 6.
44
Clicking on the link, you will be redirected to the main screen in Foursquare. You just
started your session.
Figure 65 - How to create your Foursquare account – Step 7.
5.1.3.4. Blogs
Figure 66 – Blogs logo
A blog is a personal journal published on the World Wide Web consisting of discrete
entries ("posts") typically displayed in reverse chronological order so the most recent post
appears first. Blogs are usually the work of a single individual, occasionally of a small
group, and often are themed on a single subject. Blog can also be used as a verb,
meaning to maintain or add content to a blog.
The emergence and growth of blogs in the late 1990s coincided with the advent of web
publishing tools that facilitated the posting of content by non-technical users.
Although not a must, most good quality blogs are interactive, allowing visitors to leave
comments and even message each other and it is this interactivity that distinguishes them
from other static websites. In that sense, blogging can be seen as a form of social
45
networking. Indeed, bloggers do not only produce content to post on their blogs but also
build social relations with their readers and other bloggers.
Many blogs provide commentary on a particular subject; others function as more
personal online diaries; yet still others function more as online brand advertising of a
particular individual or company. A typical blog combines text, images, and links to other
blogs, Web pages, and other media related to its topic.
5.1.3.5. Wikis
Figure 67 – Wikis logo
A wiki is a website whose users can add, modify, or delete its content via a web
browser using a simplified markup language or a rich-text editor. Wikis are powered
by wiki software. Most are created collaboratively.
Wikis may serve many different purposes, such as knowledge
management and notetaking. Wikis can be community websites and intranets, for
example. Some permit control over different functions (levels of access). For example,
editing rights may permit changing, adding or removing material. Others may permit
access without enforcing access control. Other rules may also be imposed for organizing
content.
Ward Cunningham, the developer of the first wiki software, WikiWikiWeb, originally
described it as "the simplest online database that could possibly work.
5.1.3.6. Forums
An Internet forum, or message board, is an online discussion site where people can hold
conversations in the form of posted messages. They differ from chat rooms in that
messages are at least temporarily archived. Also, depending on the access level of a user or
the forum set-up, a posted message might need to be approved by a moderator before it
becomes visible.
Forums have a specific set of jargon associated with them; e.g. a single conversation is
called a thread.
A discussion forum is hierarchical or tree-like in structure: a forum can contain a number of
subforums, each of which may have several topics. Within a forum's topic, each new
discussion started is called a thread, and can be replied to by as many people as so wish.
Depending on the forum's settings, users can be anonymous or have to register with the
forum and then subsequently log in in order to post messages. On most forums, users do
not have to log in to read existing messages.
46
5.1.3.7. Slideshare
Figure 68 – Slideshare logo.
SlideShare is a Web 2.0 based slide hosting service. Users can upload files privately or
publicly in the following file
formats: PowerPoint, PDF, Keynote or OpenOffice presentations. Slide decks can then
be viewed on the site itself, on hand held devices or embedded on other sites.
Launched on October 4, 2006, the website is considered to be similar to YouTube, but for
slideshows. The website was originally meant to be used for businesses to share slides
among employees more easily, but it has since expanded to also become a host of a large
number of slides which are uploaded merely to entertain.
Although the website is primarily a slide hosting service, it also supports documents, PDFs,
videos and webinars. SlideShare also provides users the ability to rate, comment on, and
share the uploaded content.
5.1.3.8. RSS
Figure 69 – Rss logo.
RSS is a family of web feed formats used to publish frequently updated works (such
as blog entries, news headlines, audio, and video) in a standardized format. An RSS
document (which is called a "feed", "web feed", or "channel") includes full or summarized
text, plus metadata such as publishing dates and authorship.
RSS feeds benefit publishers by letting them syndicate content automatically
They benefit readers who want to subscribe to timely updates from favorite websites or to
aggregate feeds from many sites into one place.
RSS feeds can be read using software called an RSS reader, feed reader, or aggregator,
which can be web-based, desktop-based, or mobile-device-based. The user subscribes to a
feed by entering into the reader the feed's URI or by clicking a feed icon in a web browser
that initiates the subscription process. The RSS reader checks the user's subscribed feeds
regularly for new work, downloads any updates that it finds, and provides a user
47
interface to monitor and read the feeds. RSS allows users to avoid manually inspecting all
of the websites they are interested in, and instead subscribe to websites such that all new
content is pushed onto their browsers when it becomes available.
5.2. Control
5.2.1. Google Alerts
Figure 70 – Google Alerts logo.
Founded in February 2003 Google Alerts' is a content change detection and
notification service, offered by the search engine company Google, that automatically
notifies users when new content from news, web, blogs, video and/or discussion groups
matches a set of search terms selected by the user and stored by the Google Alerts service.
Notifications can be sent by email, as a web feed, or displayed on the
users iGoogle page. The service is available to the general public as an open beta release.
Google Alerts only provides content from Google's own search engine.
Users determine the frequency of checks for new results. Three options are available: "once
a day", "once a week", or "as it happens". These options set the maximum frequency of
alerts and do not necessarily control how often they will receive alerts.
Alerts are sent only if new content matches the user-selected search terms.
5.2.2. Google Analytics
Figure 71 – Google Analitycts logo.
Google Analytics (GA) is a free service offered by Google that generates
detailed statistics about the visitors to a website. A premium version is also available for a
fee. The product is aimed at marketers as opposed to webmasters and technologists
from which the industry of web analytics originally grew.
GA can track visitors from all referrers, including search engines, display advertising, payper-click networks, e-mail marketing and digital collateral such as links
within PDF documents.
Integrated with AdWords, users can review online campaigns by tracking landing page
48
quality and conversions (goals). Goals might include sales, lead generation, viewing a
specific page, or downloading a particular file. These can also be monetized. By using GA,
marketers can determine which ads are performing, and which are not, providing the
information to optimise or cull campaigns.
GA's approach is to show high-level, dashboard-type data for the casual user, and more indepth data further into the report set. Through the use of GA analysis poor performing
pages can be identified using techniques such as funnel visualization, where visitors came
from (referrers), how long they stayed and their geographical position. It also provides
more advanced features, including custom visitor segmentation.
If your site sells products or services online, you can use Google Analytics ecommerce reporting to track sales activity and performance. The e-commerce reports
show you your site’s transactions, revenue, and many other commerce-related metrics.
Users can officially add up to 50 site profiles. Each profile generally corresponds to
one website. It is limited to sites which have a traffic of fewer than 5 million pageviews per
month (roughly 2 pageviews per second), unless the site is linked to
an AdWords campaign.
5.2.3. Tweetreach
Figure 72 – Tweetreach logo.
Tweet Reach is an application which offers a statistical service for twitter. You can follow
the tweets’ scope using Tweet Reach. To use this application, first, log in your user name
and the application will report you a series of data. In addition, note that this application
analyze accounts of other users or certain phrases or hashtags. A noteworthy service allows
us to analyze the last 50 tweets for free.
5.2.4. Facebook insight
Figure 73 – Facebook insight logo.
Facebook Insights provides Facebook Platform developers and Facebook Page owners with
metrics around their content. By understanding and analyzing trends within user growth
and demographics, consumption of content, and creation of content, Page owners and
Platform developers are better equipped to improve their business and create better
experiences on Facebook.
49
5.2.5. Flickr Stats
Figure 74 – Flickr Stats logo
Flickr’s stats now mean that photographers can keep track of which images are most
popular, what their viewers are looking for and where they’re coming from.
Most importantly, it also means that they can target keywords and sources to build up a
portfolio of images that can appeal to markets.
It shows the total number of views your images have received broken down into individual
photo pages, photostream, sets and collections.
This page also lists your most viewed photos, together with the number of times they’ve
been faved and commented on; information about how many of your photos have been
tagged, geotagged and grouped; and most interestingly, the referrers (or domain sources)
of the people who looked at your images yesterday and for “all time.”
5.2.6. Youtube insight
Figure 75 – You tube Insight logo.
YouTube Insight is a free tool that enables anyone with a YouTube account to view
detailed statistics about the videos that they upload to the site. For example, uploaders can
see how often their videos are viewed in different geographic regions, as well as how
popular they are relative to all videos in that market over a given period of time. You can
also delve deeper into the lifecycle of your videos, like how long it takes for a video to
become popular, and what happens to video views as popularity peaks.
With this information, you can concentrate on creating compelling new content that
appeals to your target audiences, and post these videos on days you know these viewers
are on the site
5.2.7. Howsociable
Figure 76 – Howsociable logo.
This tool can measure the visibility of your brand in networks such as Google + Yahoo,
50
Twitter, Facebook, Youtube, LinkedIn, among others.
HowSociable has been developed by Inuda Innovations engineers in order to measure
the influence a company has, giving important information about your brand. To use it,
you must enter the name of your brand or blog and the page will do the rest. It will
calculate the quantity of presence of your product in social networks and websites. When
the scanning is completed, you will be given a score to compare your visibility to other
sites, brands and blogs.
The platform experiment with results and test them in comparison to other brands. The
page is very effective when comparing different brands. Although it is free, you can choose
an option for $ 19 per month, which will give you full information about your product or
service.
5.2.8. Google Blog Search
Figure 77 – Google Blog Search logo
Google Blog Search is a specialized service of Google which is used to search blogs.
It was released in 2005. The Blog Search searches are done identically to the Google Search
by typing your search terms in the search field and seeing the most relevant results related
to the topic. The Blog Search looks out for various services in the world of blogs
like Blogger, Live Journal, Weblog, etc.
5.2.9. Google Trends
Figure 78 – Google Trends logo.
Google Trends is a public web facility of Google Inc., based on Google Search, that shows
how often a particular search-term is entered relative to the total search-volume across
various regions of the world, and in various languages.
It only displays the relative combined search volumes from all countries that share a
particular language. On August 5, 2008, Google launched Google Insights for Search, a
more sophisticated and advanced service displaying search trends data.
51
5.3. Improve and maintain
5.3.1. Tweetdeck
Figure 79 – TweetDeck logo.
TweetDeck is designed to let users create new things they cannot do in the Twitter
interface, such as sending the same message to multiple accounts, track your recent
hashtags, and manage multiple social networking accounts, including Facebook,
Foursquare, and Of course, Twitter).
TweetDeck is an excellent tool for companies. It is particularly useful for managing and
organizing Twitter accounts. The possibility of pre-posting is also useful because constant
updates are important to build a brand through social networks.
These are some TweetDeck features that improve Twitter as a more efficient business
tool:
1. Multiple messages to one message: It's perfect for small and medium enterprises
(SMEs) because it enables them to constantly update their account (without manual
updating).
2. Tweet-shrinking: It is useful for people who usually write long comments.
TweetDeck help people not to exceed the 140 character limit by substituting words
for numbers, shortening words, etc.
3. TweetDeck Translation: this is a useful tool especially if you do business
transactions with other countries.
4.
Keyword Filtering: The TweetDeck search options are better than Twitter
functions. You can filter tweets by keyword as well as by source, name and time.
5. Integrating Social Media: This is one TweetDeck feature that Twitter must keep.
This service lets users manage multiple social networking accounts - such as
Facebook and LinkedIn, o n the same site. If Twitter removes this option users will
complain.
52
6.
Desktop Client: The desktop client TweetDeck is attractive, organized and clean.
Register
Go to http://www.tweetdeck.com and click on the yellow buttom Sign In.
Figure 80 – How to create your TweetDeck account – Step 1
Now, a new page asks you to log in. As you have not created your own yet, click on Create
Account.
53
Figure 81 - How to create your TweetDeck account – Step 2.
Fill in the registration form and click on Sign Up.
Figure 82 - How to create your TweetDeck account – Step 3.
You have a Tweet Deck account now. In the next step, you can add a Twitter account
and/or a Facebook account.
54
Figure 83 - How to add a Twitter account to Tweet Deck – Step 1.
Click on Add Twitter Account and a new page will appear. Now, click on Authorize app.
55
Figure 84 - How to add a Twitter account to Tweet Deck – Step 2.
If you click on Add Facebook Account a new page will appear. Click on Go to App.
Figure 85 - How to add a Facebook account to Tweet Deck.
Closing the window which allow us to add accounts you will be redirected to TweetDeck
Home page.
Figure 86 – Example of Tweet Deck Home page.
5.3.2. Hootsuite
Figure 87 – Hootsuite logo.
HootSuite is a social media management system for brand management created by Ryan
Holmes in 2008. The system’s user interface takes the form of a dashboard, and supports
social network integrations
for Facebook, Twitter,LinkedIn, Google+, Foursquare, Mixi, MySpace, Ping.fm,
and WordPress.
Additional integrations are available via HootSuite’s App Directory which includes support
56
for Tumblr, Trendspottr, Constant Contact, Digg, Flickr, Get Satisfaction, InboxQ,
and YouTube.
Register
Go to http://www.hootsuite.com. A registration form will appear in the upper right corner.
Fill it in and click on Sign Up Now.
Figure 88 – How to create your Hootsuite account – Step 1.
Now, you will be redirected to Hootsuite Home page and you can add your own accounts.
Figure 89 - How to create your Hootsuite account – Step 2.
When an account is added, you can continue adding other accounts.
57
Figure 90 - How to create your Hootsuite account – Step 3.
5.3.3. Google adwords
Figure 91 – Google AdWords logo.
Google AdWords is Google's main advertising product and main source of revenue.
AdWords offers pay-per-click (PPC) advertising, cost-per-thousand (CPM) advertising, and
site-targeted advertising for text, banner, and rich-media ads. The AdWords program
includes local, national, and international distribution. Google's text advertisements are
short, consisting of one headline consisting of 25 characters and two additional text lines
consisting of 35 characters each. Image ads can be one of several different Interactive
Advertising Bureau (IAB) standard sizes
Register
Go to http://www.adwords.google.com and log in your Google account.
58
Figure 92 – How to create your Google AdWords account – Step 1.
You will be asked to set up your time zone and currency. Now, click on Continue.
Figure 93 - How to create your Google AdWords account – Step 2.
Third step: Checking/verifying the account. Click on Log In to your Adwords account.
59
Figure 94 - How to create your Google AdWords account – Step 3.
You will be redirected to Google Adwords Home Page.
Figure 95 – Example of Google AdWords Home page.
List of Figures
Figure 1 - How to create a gmail account- Step 1 ..............................................................................14
Figure 2 - How to create a gmail account - Step 2 .............................................................................14
Figure 3 - How to create a gmail account – Step 3 ............................................................................15
Figure 4 – Facebook Logo .................................................................................................................15
Figure 5 – How to crate your Company Facebook Page - Step 1 ......................................................17
Figure 6 – How to crate your Company Facebook Page – Step 2 .....................................................18
Figure 7 - How to crate your Company Facebook Page – Step 3 ......................................................18
Figure 8 – How to create your Facebook account ..............................................................................19
Figure 9 – How to add a picture to your Facebook profile ................................................................19
Figure 10 – How to add a description and link about your company on your Facebook Page ..........20
Figure 11 – How to set the information you wish to provide on your Company Facebook Page .....20
Figure 12 – Example of a Company Facebook Wall .........................................................................21
Figure 13 – Twitter Logo ...................................................................................................................21
Figure 14 – How to create your Company Twitter account – Step 1 .................................................22
Figure 15 - How to create your Company Twitter account – Step 2 .................................................22
60
Figure 16 – How to create your Company Twitter account – Step 3 .................................................22
Figure 17 - How to create your Company Twitter account – Step 4 .................................................23
Figure 18 - How to create your Company Twitter account – Step 5 .................................................24
Figure 19 – How to find people you know on Twitter .......................................................................25
Figure 20 - How to add a picture and a brief description about your company to your Twitter
profile. ................................................................................................................................................25
Figure 21 – How to set your Company Twitter profile. .....................................................................26
Figure 22 – Google + logo. ................................................................................................................26
Figure 23 – How to create your Comany Google+ account – Step 1.................................................27
Figure 24 - How to create your company Google+ account – Step 2 ................................................27
Figure 25 – How to add a picture to your company Google+ profile. ...............................................28
Figure 26 – How to create your company public profile on Google+. ..............................................29
Figure 27 - How to find people you know on Google +. ...................................................................29
Figure 28 – How to follow people and page on Google+. .................................................................30
Figure 29 – How to update your company public Google+ profile and picture. ...............................31
Figure 30 – How to create our company Google+ page – Step 1 ......................................................31
Figure 31- How to create our company Google+ page – Step 2. .......................................................32
Figure 32 - How to create our company Google+ page – Step 3. ......................................................32
Figure 33 - How to create your company Google+ page – Step 4. ....................................................33
Figure 34 - How to create your company Google+ page – Step 5. ....................................................34
Figure 35 - How to create your company Google+ page – Step 6. ....................................................34
Figure 36 - How to create your company Google+ page – Step 7 .....................................................34
Figure 37 – LinkedIn logo ..................................................................................................................35
Figure 38 – How to create your company LinkedIn account – Step 1. ..............................................35
Figure 39 - How to create your company LinkedIn account – Step 2. ..............................................36
Figure 40 - How to create your company LinkedIn account – Step 3. ..............................................36
Figure 41 - How to find people ou know on LinkedIn.......................................................................36
Figure 42 - How to create your company LinkedIn account – Step 4. ..............................................37
Figure 43 - How to create your company LinkedIn account – Step 5. ..............................................37
Figure 44 - How to create your company LinkedIn account – Step 6 ...............................................37
Figure 45 - How to create your company LinkedIn account – Step 7. ..............................................37
Figure 46 - How to create your company LinkedIn account – Step 8. ..............................................37
Figure 47 – You Tube logo ................................................................................................................38
Figure 48 - How to create your Your Tube account – Step 1. ...........................................................38
Figure 49 - How to create your You Tube account – Step 2. .............................................................38
Figure 50 - How to create your You Tube account – Step 3. ............................................................39
Figure 51 – Flickr logo. ......................................................................................................................39
Figure 52 - How to create your Flickr account – Step 1. ...................................................................39
Figure 53 - How to create your Flickr account – Step 2. ...................................................................40
Figure 54 - How to create your Flickr account – Step 3. ...................................................................40
Figure 55 - How to create your Flickr account – Step 4. ...................................................................41
Figure 56 – How to create your Flickr account – Step 5....................................................................41
Figure 57 – Example of a Flickr profile. ............................................................................................41
Figure 58 – Foursquare logo. .............................................................................................................42
Figure 59 - How to create your Foursquare account - Step 1. ...........................................................42
Figure 60 - How to create your Foursquare account - Step 2. ...........................................................43
Figure 61 - How to create your Foursquare account - Step 3. ...........................................................43
Figure 62 – How to create your Foursquare account - Step 4. ...........................................................44
Figure 63 - How to create your Foursquare account - Step 5. ...........................................................44
Figure 64 - How to create your Foursquare account – Step 6. ...........................................................44
Figure 65 - How to create your Foursquare account – Step 7. ...........................................................45
Figure 66 – Blogs logo .......................................................................................................................45
61
Figure 67 – Wikis logo .......................................................................................................................46
Figure 68 – Slideshare logo. ...............................................................................................................47
Figure 69 – Rss logo...........................................................................................................................47
Figure 70 – Google Alerts logo. .........................................................................................................48
Figure 71 – Google Analitycts logo. ..................................................................................................48
Figure 72 – Tweetreach logo. .............................................................................................................49
Figure 73 – Facebook insight logo. ....................................................................................................49
Figure 74 – Flickr Stats logo ..............................................................................................................50
Figure 75 – You tube Insight logo. ....................................................................................................50
Figure 76 – Howsociable logo. ..........................................................................................................50
Figure 77 – Google Blog Search logo ................................................................................................51
Figure 78 – Google Trends logo. .......................................................................................................51
Figure 79 – TweetDeck logo. .............................................................................................................52
Figure 80 – How to create your TweetDeck account – Step 1 ...........................................................53
Figure 81 - How to create your TweetDeck account – Step 2. ..........................................................54
Figure 82 - How to create your TweetDeck account – Step 3. ..........................................................54
Figure 83 - How to add a Twitter account to Tweet Deck – Step 1. ..................................................55
Figure 84 - How to add a Twitter account to Tweet Deck – Step 2. ..................................................56
Figure 85 - How to add a Facebook account to Tweet Deck. ............................................................56
Figure 86 – Example of Tweet Deck Home page. .............................................................................56
Figure 87 – Hootsuite logo. ................................................................................................................56
Figure 88 – How to create your Hootsuite account – Step 1..............................................................57
Figure 89 - How to create your Hootsuite account – Step 2. .............................................................57
Figure 90 - How to create your Hootsuite account – Step 3. .............................................................58
Figure 91 – Google AdWords logo. ...................................................................................................58
Figure 92 – How to create your Google AdWords account – Step 1. ................................................59
Figure 93 - How to create your Google AdWords account – Step 2. ................................................59
Figure 94 - How to create your Google AdWords account – Step 3. ................................................60
Figure 95 – Example of Google AdWords Home page. ....................................................................60
62
© Copyright 2026