Recitation 4.6 Review Problems
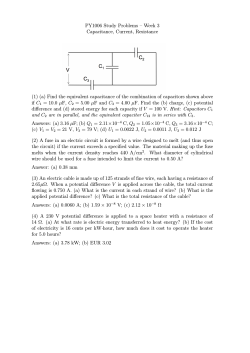
EF152 – Physics for Engineers Spring, 2015 Recitation 4.6 Review Problems 1. Three point charges are arranged along the x axis. Charge q1=+3.00μC is at the origin, and charge q2= (‐5.00) μC is at x=0.20m. Charge q3= (‐8.00) μC. Where is charge q3 located if the net force on q1 is 7.00N in the (‐x) direction? 2. A proton is placed in a uniform electric field of 2.75x103 N/C. Calculate: a. The magnitude of the electric force felt by the proton. b. The proton’s acceleration c. The proton’s position after 1.00 μs in the field, assuming it starts form rest. 3. A small particle has a charge of (‐5.00) μC and a mass of 2.00x10‐4 kg. It moves from point A, where the electric potential is VA=+200V, to point B where the electric potential is VB=+800V. The electric force is the only force acting on the particle. The particle has a speed of 5.00m/s at point A. What is its speed at point B? 4. In the figure to the right, C1=6.00μF, C2=3.00μF, C3=5.00μF. After the charges on the capacitors have reached their final values, the charge on C2 is 40.00μC. a. What is the charge on capacitor C3? b. What is the applied voltage Vab? 5. In household wiring, 12 gauge copper wire (2.05 mm diameter) is often used. Find the resistance of a 24.0 m (78.7 ft) length of this wire. 6. Each resistor in the circuit has a resistance of 4.5. The voltage source is 9.0V. What is the power dissipated by resistor 1? Now resistor R4 is removed from the circuit. Now what is the power dissipated by resistor 1? 7. Two hikers are reading a compass under an overhead transmission line that is 5.50 m above the ground and carries a current of 800 A in a horizontal direction from north to south. Find the magnetic field at a point on the ground directly underneath the conductor? 1 of 2 EF152 – Physics for Engineers Spring, 2015 Equation Sheet Constants me = 9.109x10-31 kg mp = 1.673x10-27 kg mn = 1.675x10-27kg Resistors R L / A V IR P IV Req R1 R2 R3 ... Series k = 9x109 -12 ε0 = 8.854 ·10 e = -1.6022 ·10-19 C (electron charge) eV = 1.6022·10-19 J (electron volt) 1 1 1 ... Parallel Req R1 R2 F 1 q1q 2 Kirchoff’s Rules Σ 0 for a closed loop Σ 0 for a junction k 2 4 0 r 2 r F 1 q E rˆ q 4 0 r 2 R-C circuit time constant Potential Energy; Potential Capacitors U 1 Vs N 1 10000 gauss 2 m Am Tm 0 4 107 A 1T 1 F q (v B ) 0 qv rˆ B 4 r 2 B Coulomb’s Law; Electric Field q1q 2 Magnetism qi q j 4 0 i j rij U V q0 qi 1 point charges V 4 0 i ri Va Vb Ed parallel plates RC C Q / Vab A C 0 d U 1 F 1 C/1V parallel plates 1 Q2 1 1 CV 2 QV 2 C 2 2 1 1 1 ... series C eq C1 C 2 C eq C1 C 2 C 3 ... parallel 2 of 2 0 I 2 r straight wire
© Copyright 2026