Presentation of the heat cost allocation`s principles - Eric
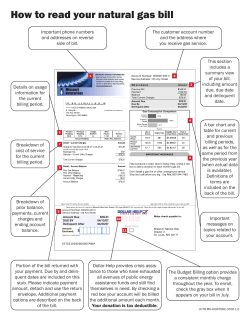
Presentation of the heat cost allocation’s principles Eric FARNIER Innovative Products Purchasing & Industrial Deputy Manager Heat Cost Allocation and Billing Workshop - Paris, 5-6 may 2015 Sub Billing of Heating and Hot water shall be measured as electricity, gas or water Heat Cost Allocation and Billing Workshop - Paris, 5-6 may 2015 5 Heat cost charges without individualisation Assumed average 120kWh/m² 725 € - 67 m2 725 € - 67 m2 725 € - 67 m2 Overall consumption : 24 120 kWh, 2170,00€ Collective source of energy for heating and hot water Without Heat cost allocation : • Every body pays according to apartments’ surface 3 Heat Cost Allocation and Billing Workshop - Paris, 5-6 may 2015 Heat cost allocation : increase consumer’s awareness, based on equity, and saving incentives 520 € - 80 KWh/m² 710 € - 125 KWh/m² 595 € - 98 KWh/m² Overall consumption : 20 300 kWh 1830,00€ Mr A, left home 2 months & reduced T° Mr B, keeps opening windows to cool down Mr C, smartly managed temperature Collective source of energy for heating and hot water With Heat cost allocation : Every body pays according to the individual heating energy measure of each dwelling People reduce their consumption by making them aware of their energy consumption Heat Cost Allocation and Billing Workshop - Paris, 5-6 may 2015 3 Heat cost allocation : transparency, equity, environment friendly Overall objective of heat cost allocation • • • • Building manager’s preoccupation Unpaid invoices Track energy waste The occupants wellbeing Tenants‘ complaints about exaggerated consumptions • Monitor et contain its budget, and environment impact • Be aware and pay for their consumption • Understand the energy charges Occupant’s preoccupation Heat Cost Allocation and Billing Workshop - Paris, 5-6 may 2015 4 Two different technologies are used depending on the fluid distribution column 2 topologies : Horizontal loops, one single entry point per flat Multiple distribution columns, several entry points in each flat Heat meter Heat Cost Allocation and Billing Workshop - Paris, 5-6 may 2015 Heat cost allocators 6 Heat meters No moving part, no maintenance, long lasting accuracy More expensive than mechanical meters, although difference is reducing static Mechanical Small dimensions, economical solution Sensitive to fluid quality, installation costs Heat Cost Allocation and Billing Workshop - Paris, 5-6 may 2015 7 How does a heat meter calculates the energy consumed? Energy is computed out of three measures: • Heating liquid flow • Inlet temperature • Return temperature Heat Cost Allocation and Billing Workshop - Paris, 5-6 may 2015 8 Two different technologies are used depending on the distribution column 2 topologies : Horizontal loops, one single entry point per flat Heat meter Multiple distribution columns, several entry points in each flat Heat cost allocators Heat Cost Allocation and Billing Workshop - Paris, 5-6 may 2015 9 HCA (Heat cost allocators) • • Electronic temperature measurements, accurate, reliable Remote transmission for web data availability Evaporator • • • Electronic The heat makes the liquid contained in the device evaporate The evaporation is measured on the graduated scale The evaporation is proportional to the heat Heat Cost Allocation and Billing Workshop - Paris, 5-6 may 2015 10 General principle of the heat cost allocators Position of the heat cost allocator : • Easy installation heat cost allocator probes: • measure very frequently (4 typical) Probe 1 Probe 2 How it works : Troom KC KQ Tsurface • • Energy delivered KC : coefficient of the association between the radiator and the heat cost allocator KQ : coefficient of the radiator’s power Heat Cost Allocation and Billing Workshop - Paris, 5-6 may 2015 11 The coefficient are scientifically identified Where do Kc and Kq come from? • Independant labs (with over 20 years experience) work on the calculation of the KC which links one HCA model with a radiator type: • The KQ is given by the manufacturer of the radiators, and standardized Tools and software used during installation allow a strict pairing of HCA and radiator, which is key for an efficient consumption calculation Heat Cost Allocation and Billing Workshop - Paris, 5-6 may 2015 12 Heat meters vs. Heat Cost Allocator Heat Cost Allocation and Billing Workshop - Paris, 5-6 may 2015 13 HCA and Heat Meters : two reliable, proven technologies European Standards : Heat meters Heat cost allocators MID and EN 1434 EN 834 130M° heat cost allocator operated today in Europe More than 30 years of experience in operation for most of them EN834 published in 1994 Heat Cost Allocation and Billing Workshop - Paris, 5-6 may 2015 14 The heat cost allocator is as efficient as the heat meter GDF Suez lab in 2004 compared the measures given by the heat meters and the heat cost allocators over different periods in three experimental apartments Here are the results (over one month and with the meters taken as references): Apartment 1 Apartment 2 Apartment 3 Meter (%) 13,99 36,01 50,00 Allocator (%) 14,34 32,84 52,82 Difference (%) 0,35 3,17 2,82 Conclusion of the experiments : The differences between the 2 types of equipment are negligible compared to the equipment Maximal Permitted Errors (flow sensor + temperature sensors + electronic calculator for a Heat meter) Heat Cost Allocation and Billing Workshop - Paris, 5-6 may 2015 15 HCA and heat meters are based on an innovative integrated intelligent infrastructure GSM GPRS Mobile Carrier Computer Center Heat Billing Services Water Smoke Alarm Services: Electricity Billing Web Portal … Energy Data Management and Billing Information Gas Supply Property Survey Hardwaremanagement Reading, Data Processing, Billing & other Services Heat Cost Allocation and Billing Workshop - Paris, 5-6 may 2015 Controlling and further Optimisations for additional Savings 16 CO2 emission saving due to consumption based billing Study Comparison of the CO2 emissions produced during the entire life cycle of Heat Cost Allocator (HCA) radio and the CO2 savings due to individual heating cost billing. Based on 18 million heat cost allocators in more than 400.000 properties in Germany. Result: Consumption-dependent heating cost billing based on the HCA radio saves 158 times as much CO2 as is produced over the entire life cycle. Cause Saving The HCA radio causes 0.53 kg of CO2 emissions each year. (= production cost of approx. 100 sheets of virgin fibre paper) The consumption-dependent billing saves 84 kg of CO2 emissions each year (= production cost of approx. 15,800 sheets of virgin fibre paper) Heat Cost Allocation and Billing Workshop - Paris, 5-6 may 2015 17 Thank you for you attention Questions & answers ????
© Copyright 2026