RAJESH UPRETY-case studies
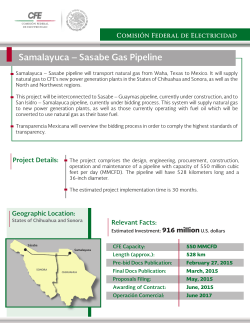
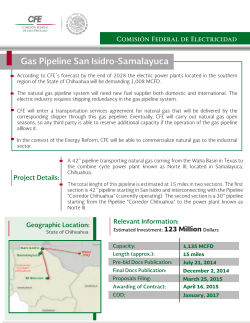
Presentation on CASE STUDIES – SAFETY IN PIPELINE OPERATION By RAJESH UPRETY, ADDITIONAL DIRECTOR (PIPELINES) Oil Industry Safety Directorate Date: 18.04.2015 NARMADA RIVER – SNAPPING OF PIPELINES LOCATION MAP SCHEMATIC VIEW OF THE NARMADA RIVER SITE TOTAL NO. OF PIPELINES PASSING THROUGH NARMADA RIVER S.No. Pipeline Operator Pipe Size Remarks (1) Reliance (RGTIL) Natural Gas 48” OD x 1.000” WT (25.4 mm), API 5L X70 Gr. Line is intact (2) GAIL India Natural Gas 30” OD x 19.1/11.9 mm WT, API 5L X 70 Gr. Snapped & burst (3) Reliance Industries 26” OD x 0.500” WT, API Snapped & burst. Pipe Limited (RIL) 5L X 60 Gr. has got stuck in the Ch. 29.150 KM (NG) nearby electrical tower Natural Gas (4) Reliance Industries 24” OD x 0.500” WT API Snapped & burst. Limited (RIL)(NG) 5L X 60 Gr. Ch. 29.150 KM TOTAL NO. OF PIPELINES PASSING THROUGH NARMADA RIVER S.No. Pipeline Operator Pipe Size Remarks (5) Gujarat State Petronet 24” OD x 0.688” (17.5 About 100 m pipeline is exposed. Ltd., (GSPL – NG) mm) WT, API 5L X 60 Gr. Ch. 17.000 KM (6) ONGC (Ch. 14.200 KM) 8.625” OD x 0.375” (9.53 Leakage in line CRUDE OIL mm) WT, API 5L X 46 Gr. (7) IOCL (Amod Pipeline) (8) ONGC (OPAL) Naptha Hazira 12.75” OD x 0.219” WT, Line is intact API 5L X 60 Gr. 12.75” OD x 0.25” WT, API Under construction 5L X 46 Gr. ROOT CAUSE OF THE INCIDENT S.No CAUSE OF THE INCIDENT (1) It was a natural calamity. Unprecedented sudden floods due to heavy rains and large quantity of discharge of water from Sardar Sarovar Dam. (2) The river bank (south side) was not reinforced, which resulted in heavy soil erosion. (3) Removal of plants and vegetation during the construction of Electrical Transmission Tower of Torrent Power close to the river bank, which has resulted in loosening of the parent soil. (4) Irrigation Dept. did not provide any prior warning before release of abrupt water discharge in such a large quantity. (5) Soil erosion is a gradual process, which takes number of years. Pipeline Operators should closely monitor such behavior of the river course and the adjoining banks on a regular basis. ROOT CAUSE OF THE INCIDENT S.No CAUSE OF THE INCIDENT (6) It was a natural calamity. Unprecedented sudden floods due to heavy rains and large quantity of discharge of water from Sardar Sarovar Dam. (7) Because of the erosion of the soil from the river bank, pipe line, which was buried in the ground became exposed and pipe line in the eroded portion became unsupported. Due to the force of water on this exposed portion of pipe line, it started oscillating and finally one of the pipelines got snapped due to heavy oscillation effect in hanging pipe line section. The velocity of water and turbulence in the river was extremely high at the time of incident. REVIEW OF CHANGE IN DESIGN & ENGG., IF ANY S.No DESCRIPTION (1) No changes are required w.r.t. design and engineering of pipeline, however, the extent of HDD shall be increased based on the present situation of this particular river crossing, to avoid the future flood scenario. (2) Provision already exists in the codes as per clause no. 11.7.3 of OISD standard 141 for oil pipelines and 10.6.4.1 of OISD 226 for Gas pipelines that ‘Special considerations shall be required for river crossings which are characterized by their perennial nature, meandering course, steep and potentially erodible banks, potentially scouring bed, large erodible flood plain and wide water course (high flood level) both during the design and installation of such crossings’. IMPORTANT POINTS PERTAINING TO IRRIGATION DEPARTMENT S.No DESCRIPTION (1) Regarding future trend and width of the Narmada River, It was informed that it is not possible to predict the future scenario. However they confirmed that only the Highest Flood Data can be made available by Irrigation Deptt., which shall be useful for deciding the length of the HDD. (2) Presently there is no controlling device (Gate/ Sluice Valve) provided at Sardar Sarovar Dam, as a result of which there was no control to the flow of water. Now it has been told that there is a proposal to provide a gate before next monsoon. This will enable to control the flow, thereby minimizing the impact at site due to release of sudden discharge of water. (3) Any construction work near the river bank should be discouraged as this leads to loosening of the parent soil due to removal of plant and vegetation. In this case an Electrical Transmission Tower was constructed near the river . IMPORTANT POINTS PERTAINING TO IRRIGATION DEPARTMENT S.No DESCRIPTION (4) In case there is any planning to release sudden water from the dam, same should be shared with all the pipeline operators by Irrigation Department. (5) Close liaisoning and co-ordination to be maintained with all the pipeline operators. FINAL RECOMMENDATIONS S.No DESCRIPTION (1) Reinforcement of the river banks must be carried out in order to arrest the soil erosion. Pre-installation surveys shall be carried out to establish the prevailing river bank profiles including collection of data on fluvial geomorphology and channel processes for design purposes. (2) Execution methodology of bank protection works shall be designed/ implemented in such a manner that the normal operations of the pipelines are not hampered. (3) Fresh hydrological survey needs to be performed based on the recent flood discharge and hydraulics to arrive at new scour profile. Additionally, topographical and geotechnical investigations shall be performed to firm up the extent of HDD length. FINAL RECOMMENDATIONS S.No DESCRIPTION (4) New HDD shall be performed for the damaged pipelines. HDD length of all the damaged pipelines must be kept sufficiently large, which shall be based on the topographical survey of the site. (5) There should be a close co-ordination and liaisoning between all the Pipeline operators and irrigation department. (6) The distance between two sectionalizing valves across the Narmada river must be kept immediately (as close as possible) near the upstream and the downstream bank of the river and these valves must be remote operated so that in case of an emergency, valves can be closed immediately and the section can be isolated thus minimizing the quantum of product loss and minimizing the environmental impact. FINAL RECOMMENDATIONS S.No DESCRIPTION (7) Disaster Management Plan should be reviewed to take care of such an emergency. (8) Irrigation Deptt. should not allow construction of any structures near the river bank as these tend to make the parent soil loose due to uprooting of plant and vegetation. (9) All pipeline operators must be focused on such river crossings and closely monitor the soil erosion pattern regularly on both the banks and take immediate corrective measures by way of providing reinforcement to the bank or increasing the length of the HDD so that such accidents can be avoided. (10) Whenever, such incidents take place, it should be immediately brought to the notice of OISD in the prescribed format. In this case, none of the affected operators gave the information to OISD. FINAL RECOMMENDATIONS S.No DESCRIPTION (11) During the second floods which took place on 25-27th September 2013, it was observed that about 70 M of the 24” OD NG line of M/s GSPL was hanging (photo enclosed) and the line was swinging up and down, but the line was kept in operation. This is a very serious issue. (12) Proper health monitoring must be done for all those lines which are not damaged before putting them back into operation. GAIL – TATIPAKA CATASTROPHIC FAILURE DUE TO CORROSION (FIRE & EXPLOSION INCIDENT) NATURAL GAS PIPELINE Leak/Burst site Date/Time of incident 27th June 2014 at about 0545 hours No. of fatalities 22 Operating pressure 42 to 45 Kg/cm2 Design pressure 72 Kg/cm2 Pipeline size and grade 18” OD API 5L X60 Grade RIVER BRIDGE SV-1 SV-2 18" (API 5L X-60) ORIGINATING STATION SV-5 SV-4/ I P HIGHWAY X-ING SV-3 (PIGGING STATION) (CANAL) POWER PLANT RIVER X-ING SV-6 SV-7 SV-8 12 ANALYSIS / OBSERVATIONS OF THE FIRE INCIDENT • Cross country pipeline – supplying Natural Gas to power plant • The pipeline was being operated at a lower flow rate and lower pressure w.r.t. the design parameters. • Pipeline was transporting wet gas while it was originally designed for transporting dry natural gas. • The gas contained CO2 and some traces of Sulphur. • Leakage took place at the lowest point where the pipeline was crossing a canal at 6 o’clock position. 25 FURTHER OBSERVATIONS OF THE FIRE INCIDENT • It was raining on the day of the incident, so it is inferred that vapour cloud formed due to heavy weather. • A tea stall owner. who turned on the stove in the morning, possibly provided the source of ignition. • There has been a history of previous leaks near the place of accident. 26 ROOT CAUSE OF THE FIRE INCIDENT • Leak due to internal corrosion – presence of CO2 led to formation of H2CO3. • During earlier repairs external coating got damaged resulting in external corrosion. • Improper pigging – foam pig used instead of scrapper pigs. • Pig residue analysis not carried out. • IPS carried out in 2010 - Maximum metal loss reported in IPS is equivalent of 50% of wall thickness. • Use of wet natural gas instead of dry natural gas. • Not using corrosion inhibitor. 27 RECOMMENDATIONS • Proper cleaning pigging to be carried out regularly followed by pig residue analysis. • Instrumented pig survey to be carried out regularly and the anomaly rectification to be carried out as per the recommendations . • Proper procedure to be made for repair of pipeline. • Any change from the initial change should be routed through a management of change procedure after proper technical analysis. • Corrosion inhibitor to be used in the line as per requirement. • In addition to OFC communication there should also be another stand by mode of communication. • Proper maintenance and inspection practice to be followed. 28 RECOMMENDATIONS • Effective CP monitoring to be carried out. • Effective Line patrolling to be carried out using modern gadgets such as GPS, GIS based decision support system etc. • Leak detection system should be provided in the mainline. • Health monitoring of all non-piggable lines to be carried out using Direct Assessment • Wherever the pipe elevation is changing draining drastically from lower to higher elevation , an additional pigging station to be provided for removal of the condensate. 29 PHOTOGRAPHS • 30 PHOTOGRAPHS 31 PHOTOGRAPHS 32 GAIL – SURYAPET FATAL INCIDENT) STUCK PIG PIG RESIDUE VENT/ DRAIN VALVE MAINLINE 38 Kg/cm2 Pig came out from here • Pyrophoric iron in contact with air liberated heat which resulted in explosion of LPG-air mixture inside the barrel resulting in propulsion of pig at a very high force. The persons standing in front of the open door of the barrel were hit by the pig which resulted in fatality & injury. • Draining of entrapped LPG inside the barrel between barrel valve & pig could not be done due to absence of drain or vent. • A pig train was being used consisting of cups, brush and magnetic pig all coupled together - this is a unique case where pigs have been tied together & not the industry practice. • The length of the scrapper receiving barrel was more. • All the drain and the vent points were near the quick opening-quick closure door of the barrel. • Iron content (Fe2O3) was very high (>90%), which indicates that health of the pipeline is not good and there appears to be considerable metal loss due to internal corrosion. • The residue analysis report reveals that there is a presence of 90.99% by mass of iron as Fe2O3 and 5400 ppm of sulfur. The health assessment of the entire line is required to be carried out. • Health assessment of the LPG pipeline must be carried out since the pig residue indicate considerable high iron content (90.99%) indicating metal loss due to corrosion. • An additional vent & drain point with pressure gauge shall be provided in the neck portion of the barrel to drain the HC. • Pig train must not be used with all pigs in tied condition. This is not a usual practice. • Magnetic pigs should be used only when it is ascertained that the iron content is nominal. • While receiving the pigs, it shall be ensured that proper venting has been carried out between barrel body valve and the pig to ensure that the barrel is free from any hydrocarbons. • While receiving the pig it shall be ensured that no person is standing directly in front of the barrel.
© Copyright 2026