In a Smart Grid's vision what is the role of
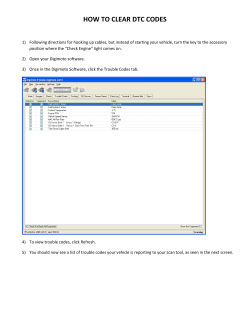
In a Smart Grid's vision what is the role of grid automation Carlos Mota Pinto Nuno Santos Associate Director Smart Systems Development Geospatial EAM & Intelligent Solutions Practice Leader EDP Distribuição Logica April 2011 Agenda • EDP Distribution in brief • Driving sustainability through technology • EDP smart grids strategy • Conclusions 1 ~20.6 GW of installed capacity ~ 3 GW of hydro projects under construction and development +67% since 2005 #1 in Europe More than 6.2 GW of wind capacity #3 in the world Market capitalisation of ~€11bn #1 in Portugal EDP Distribuição in Portugal and Hidrocantábrico Distribution in Spain provide electricity to almost 7 million customers Technical figures 400 Substations HV/MV 16.000 MVA 1.000 HV Lines 8.500 km 4.000 MV Lines 71.000 km 62.000 MV/LV Stations 18.000 MVA Consumer profile Résidentiel 28% * EDPD: Includes EDP D + EDP EC + EME2 + InovGrid – workers in EDP SA ** EDPD: Net assets in PT GAAP (POC) *** Spain includes all distribution activities, HCDE, and Fevasa, Solanar, IERI, Electra de Llobregat. Services 30% Agriculture 2% Industrie 39% Transport 1% 3 EDP Distribution Presentation Video 4 EDP Distribuição has been successful in improving its price/ quality relationship through a strong investment policy Network Capex(1) & Equivalent Interruption Time(2) Opex(3)/km of Network (€m; min.) (‘000€/km) Expansion Service Quality Other Average EIT (Internal) CAGR 2005-2009 -76% -2% 385 New regulatory targets on customer service quality 180 150 2,6 2,4 2,4 2,6 2,5 2006 2007 2008 2009 80 93 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2000-2009: Internal EIT improved 76% Strong investments for service quality improvement: ~€150 M 2005 Opex/km efficiency ratio improved by an average of 2% p.a. between 2005 and 2009 (1) EDP Distribuição’s Capex in accordance with PT GAAP; (2) Equivalent Interruption Time internal to EDP Distribuição (regarding interruptions originated at EDP Distribuição’s network); (3) Supplies and Services + Personnel Costs + Costs with Social Benefits (excluding HR Restructuring costs) 5 Substation automation plays a major role in reducing outage time Supply restoration time for Clients (HV/MV/LV) 300 3. Most Substations with Automation (8 of 11) 250 Fanhões Injector Carriche Injector Vermoim Injector 200 2. Some Substations with Automation Clients 150 (x1.000) 1. Restoration without Automation 100 and lengthy MV network 50 0 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500 Time (min) 6 And complemented with DA are cost effective strategies to reduce outage time 40 DA devices 900 km MV network 7 The EU has set ambitious goals to progressively decarbonise its economy Emissions targets in EU GtCO2e 5,6 -8% -20% -80%/-95% 1990 International agreement 2008-2012 Kyoto Protocol 2020 EU 2020 Climate & Energy Package 2050 G8 summit in Italy 8 This goal can only be achieved by increasing electrification of energy demand and decarbonising the power sector Emissions reduction as a function of the share of electricity in final energy demand Emissions factor % CO2 emissions reduction Zero Decarbonise power • Renewables • Nuclear • Carbon capture & storage Today´s Increase electrification • Transport (EV) • H&C • Energy efficiency % electricity in final energy demand 9 ICT role in leveraging industry and business strategy For the last 2 decades EDP developed a remote control and automation strategy aligned with business goals Main business drivers 1980’s •Historical OPEX reduction Challenges 1990’s Increase Service Quality • OPEX reduction • QoS improvement 2000 2007 • • • CAPEX reduction CAPEX and OPEX pressure Engineering cost reduction O&M cost reduction ICT Strategy • Substation telecontrol • Substation automation • Standard substation design • Distribution Automation project Challenges •New OPEX reduction • Further improvement MoreQoS renewables and 2008 2020 micro-generation in the grid • Additional QoS enhancement Efficiency • DER &Energy Micro generation • New customer services New business models and • Trans-european market technologies • Aging assets • Increased CAPEX Constraints Electric Vehicles • Cross functional, multilayered and integrated • InovGrid: EDP smartgrids project Smart Grids are key meet these new challenges in an integrated way Advanced Metering Infrastructure Improved energy efficiency capabilities with the ability to integrate new business models Capacity to integrate more distributed generation and the electric vehicle Improved network automation & sensoring Smart Grids 11 There is a considerable degree of visibility and control over the High and Medium Voltage networks but less over the Low Voltage network Distribution HV network MV network LV network 2 3 1 Production Transmission Station VHV/HV Substation HV/MV Retailer/ Consumer Secondary Substation MV/LV meter Main figures EDP Distribuição • 9.000 Km • 73.000 Km • 400 Substations • 62.000 SS MV/LV (~ 1:150 SS) (~ 1:100 customers) • 16.000 MVA installed • 136.000 Km • 6,1M customers Level of monitoring and automation, today Improvement Smart Automation •On-line sensing & monitoring •critical elements •failure modes •Advanced protection & automation Network efficiency •Risk management •Pre-fault detection •Fault location & Self-healing There is a lack of real-time knowledge about the network in this area Prosumer experience • Demand response • Energy efficiency • New energy services • Trade development • Better QoS-fault location 12 The goal is to extend the “intelligence” on the grid to the low voltage network using new equipments and technologies Distribution HV network Production Transmission Station VHV/HV MV network Substation HV/MV LV network Retailer/ Consumer Secondary Substation MV/LV EB WAN Central Systems (commercial & technical) • Management • Operation • Data management • Integration with current systems • ... HAN C B A LAN Distribution Transformer Controller (DTC) • Monitoring & Control • Metering • Concentrator • Microgeneration and load control (future) • ... Energy Box (EB) • Metering • Remote operation • Circuit breaker • Tariff flexibility • HAN interface • QoS information • ... 13 The architecture of InovGrid solution considers specific devices at the Customer Premises – the Energy Box (EB), and at the MV/LV station – the Distribution Transformer Controller (DTC) Central Information Systems SCADA/ DMS EMS /MMS Leased line to Telco Operators Information flows: Technical flow Commercial flow WAN (Telco Operator) GPRS DTC DTC DTC DTC DMS – Distribution Manag. System EMS – Energy Manag. System MMS – Meter Manag. System C- Plug Box C C Background: GIS – SCADA/DMS & OMS (PowerOn) integration enable a common view of the network model which enables business process integration spawning all three systems GIS Network model Network model Events PowerOn Outage Management System SCADA/DMS Inputs from the intelligent devices enable a view of LV network improving Outage Management PowerOn Outage Management System • • • SCADA/DMS AMI • • • • • WAN & LAN EB (Energy Box) DTC (Distribution Transformer Controller) Near real time information of LV network Accurate prediction of outage root cause Reduce outage duration improving QoS Crew allocation optimization Confirmation of client restoration Allows proactive client feedback during outages Improvement of data quality Availability of QoS data from EB’s Three Outage Management activities were optimized through the integration of PowerOn and AMI PowerOn Outage Management System A. Substation (MV/LV)outage creation SCADA/DMS AMI B. LV outage prediction C. Outage restoration WAN & LAN EB (Energy Box) DTC (Distribution Transformer Controller) A. MV & Substation (MV/LV)outage creation PowerOn uses LV network knowledge provided by AMI to accurately predict outage root cause PowerOn Outage Management System 1. DTC sends information of absence of Voltage 2. PowerOn creates a confirmed outage Station HV/HV MV network WAN DTC (Distribution Transformer Controller) B. Low Voltage outage prediction Process begins with call from customer 2 1 3 PowerOn Outage Management System 1. Customer reports outage to call center 2. Call center operator registers call 3. PowerOn creates a predicted outage that is displayed to the Dispatcher B. Low Voltage outage prediction PowerOn uses LV network knowledge provided by AMI to accurately predict outage root cause PowerOn Outage Management System Secondary Substation MV/LV LV Link Box LB EB EB EB EB EB EB EB EB 4. PowerOn pings customer meter; outage prediction is at meter level 5. PowerOn pings other meters on same building; outage predicion is moved to the building 6. PowerOn pings other meters on same circuit; outage prediction is moved to Link Box LV network LAN WAN EB (Energy Box) DTC (Distribution Transformer Controller) C. Outage restoration After outage has been restored, PowerOn pings LV meters to confirm energy supply has in fact been resumed PowerOn Outage Management System Secondary Substation MV/LV 1. PowerOn customer meters to confirm outage was fully restored 2. After confirmation, the outage is safely closed LV Link Box LB EB EB EB EB EB EB EB EB LV network LAN WAN EB (Energy Box) DTC (Distribution Transformer Controller) A large number of Portuguese and international players has joined EDP in this project DSO’s Academia Industrial companies Technological companies 22 The first step is to install the platform in the distribution network of the City of Évora - Unesco World Heritage Monument 1. Évora municipality: • 54.000 inhabitants • 1.307 km2 of area • Urban and rural areas 2. The project includes: • • • • • 30k Energy Boxes 341 DTC in MV/LV transformers Integration of IT systems Communications infrastructures Set-up of new services and products 3. Involvement of the major players of the municipality 4. Coordination with the national electric vehicle charging network 23 EDP is also installing a technology that will offer new services and products to a selected group of consumers Improved operational efficiency In-home displays EV charging network Public lighting using LED technology Network monitoring and automation Connection to PC/PDA 24 EDP Distribuição is aligned with the most important standardisation projects in Europe and actively participates in several international forums OPEN METER Eurelectric EU Commission Task-Force for Smart Grids Initiative/ Organisation European Distribution System Operators Association for Smart Grids (EDSO SG) Smart Metering Mandate (M/441) Power Line Intelligent Metering Evolution (PRIME) European Regulators' Group for Electricity and Gas (ERGEG) Open Architecture for Secondary Nodes of the Electricity SmartGrid (OPEN NODE) 25 The consumer will benefit from the development of new and better energy services Today Tomorrow • Based on quarterly manual meter readings combined with energy estimation • Based on remote reading and real time consumption Acess to the information • Avaliable by internet only and based on the last meter reading • Increased flexibility through an access to the energy profile using internet, displays, PDA, etc. Services • Contract changes typically need to be scheduled and performed on location • All contract changes can be performed remotely Tariffs • Fewer price plans and tariffs • Increased flexibility in pricing and tariffs. • Limited value added services • Capacity to inform consumers by different channels including social networks • Energy management kits Billing Value added services 26 Conclusion • On top of improving the quality of service while maximizing operational efficiency, DSOs also need to integrate more renewables and to promote energy efficiency • Smart grids are the answer to these new challenges; smart metering is one first step towards that direction • Involvement of customers and other stakeholders is key for the success of the project, as well as a solid communications infrastructure • EDP Distribuição developed an innovative SmartGrid Project, tested in Évora during 2010 and 2011. It will allow to test smartgrids from a commercial perspective (cost-benefit analysis). • The project is aligned with the most innovative trends in the sector across the world. • Évora InovCity is a privileged location for testing the new solution being developed and to prepare a future nationwide rollout 27 InovCity Presentation Video 28 InovCity Évora, Portugal You are invited! Visit us at: www.inovcity.pt 29
© Copyright 2026