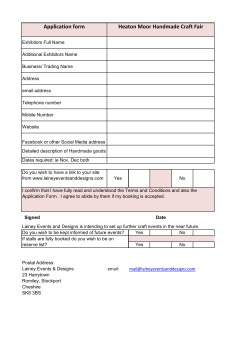
GCSE Textiles Technology Controlled Assessment Handout Summer 2011
GCSE Textiles Technology Controlled Assessment Handout Summer 2011 Tips and hints . . . . What to do What NOT so do • • • • • • • • • • • Be imaginative and innovative Show creativity, flair and originality Consider sustainability Demonstrate high levels of skills Use a range of tools and technologies skilfully Be rigorous and demanding Show high levels of accuracy and finish Be commercially viable Be suitable for the target market Involve a wide variety of techniques • • • • • • Pretend to design but actually copy existing designs Choose and copy a commercial and then pretend to have designed something original Produce development samples of techniques e.g. darts and hems, when the commercial pattern tells you the most appropriate technique As a class activity produce decorative technique samples that are not relevant to your design Make a toile that is actually a practice of the commercial pattern Don’t make it clear where a pattern has come from or how it has been developed Use a commercial pattern without modifications or showing little originality Contents to include . . . (page titles) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. Task Analysis Mood Board Shop Profile/Customer Profile Existing Products/Consumer Survey Review of Trip The Swinging Sixties/Punk Research Research Analysis/Design Specification Inspiration Sheet Initial Design Ideas Initial Design Ideas Development Planning Development: Shape/Size/Colour/Style Development: Techniques Development: Techniques 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 Development: Construction Development: Construction Development: Fabric Choice Further Development: Designing an ethnic and environmentally friendly product Manufacturing Specification Planning for Manufacture Planning for Manufacture Production Record Advertising Testing and Evaluating Testing and Evaluating Page 1: Task Analysis What should I include? Context Design Brief Time Plan (Gantt Chart) Task Analysis (see across) Keywords Imagery to help ‘set the scene’ Some ‘initial thoughts’ of what the task analysis page is about A conclusion – say how the thought shower has helped you. Spider Diagrams you could include: Theme - Sixties Theme – Punk Sixties Icons Sixties fashions Punk Fashion Punk Icons Garments High Street Stores Task Analysis Research – how/where could you carry out research that is relevant Target Market – age group and profile of the people your product must appeal to. Similar products – what existing products are available? Fabrics/Materials – what fabrics/materials could be used? Construction – how could the product be constructed? Techniques – what techniques could you use for decoration? Components – what components could be used? Processes – What processes might be involved in making it? Function – what will the product do? Environment – where will the product be used? Safety – How will you ensure the product is safe to use? Ergonomics – how will the product be designed to suit the user? Aesthetics –how will the product look/ be styled? Page 2: Mood Board What do I need to include? What is a Mood Board? • Wide selection of images based on your theme (swinging sixties or punk) Keywords based on your theme Experimentation with textures/fabrics (swatches, rubbings etc) Evaluation of mood board – What have you focused on in theme? – What have you found out/achieved from doing it – Which parts are you going to take further (what has inspired you the most?) • A mood board is a tool used by designers to help them get a good idea of what their clients are looking for. Mood boards are basically collages of items such as photographs, sketches, clippings, fabric swatches and colour samples. Page 3: Shop Profile Page 3: Customer Profile This should be a few short paragraphs describing a typical store where your product would be sold. ALWAYS USE FULL SENTANCES! What is the name of the store? Include the following statement Topshop/Primark/Sports Direct for example How many stores do they have in their chain? Use internet to find out Is it just based in the UK or is it a worldwide chain? What does it sell? Use internet to find out Fashion/sports/work wear Clothes, accessories/shoes/jewellery/bags/hats Does it use in-house designers? Check their website for this information What current trends do they stock? What is the store layout typically like? Are products on shelves/racks Are the shops spacious/too crowded Are all jeans together for example, or are products arranged by collections? What is the cost of the products they sell? Check their website for this information Are they at the low/middle/high end of price range Why is this? Who are their main target market? Male or female? Children/young adults for example Include an image of the shop logo Include a picture of an actual shop Include images of the products they sell Complete an evaluation of the page (both parts) Explain what you have found out and how you can use this information ‘’Below is the customer profile for the product I am designing. The profile will help me develop my designs and target my advertising and marketing’’. Describe your ‘typical’ client. Use the following questions to guide you Could be done as a list or in paragraphs Describe the type pf person who could be your typical customer What is the age range of potential customers? Are potential customers likely to be male or female or does gender not matter? What is the geographical location of potential customers? Where are they likely to live? What are the most likely occupations of potential customers? What are the general likes/dislikes of potential customers? What does a typical customer want from the product you will design and manufacture? What are the most common design requirements shared by your potential customers? What factors are your potential customers likely to consider before purchasing your product? How will potential customers find out about the product you are selling? Does the cost of your product influence a customer’s decision to buy from you? Page 4: Existing Products Page 4: Survey What do I need to include? • Copy and complete ‘When researching a project it is very important to look at existing designs. Often the best ideas are developed from existing designs because they can be improved and lessons learned from earlier mistakes or design faults’. Using the internet find 4 examples of products similar to what you intend to make. Copy and complete the table (shown) Use FULL SENTANCES Product Image Shop Descripti on Price Value for money Complete an evaluation of the page Explain what you have found out and how you can use this information Include the following statement ‘’ This questionnaire will help me design my product, because it will tell what my target market wants, and what people are prepared to buy’’ Identify who the target market is, and how many people you asked questions to Write a list of the questions you asked (approx 6 questions) Think about price, colour choice, pictures or patterns, fastenings, fabric choices, comfortable or practical and so on. What questions could you ask to help you design your product? Write as many possible choices for your questions Draw a bar chart, pictogram, table or graph of results for each question in excel. If you choose to draw a pictogram, use pictures that represent the theme. Write a summary of your findings at the bottom of the page. This should clearly say what you have learnt from the answers to the questionnaire. Page 5: Educational Visit • Introduction: – Where did you go? – Why did you go there? – Include dates, times etc • Main Content: – Summary of the visit in the form of a diary or a summary of what you did there • Conclusion: – How has the visit been beneficial? – How will it help you with your project? • What other things could you include? – – – – Ticket Pass Photos Any leaflets or advertising from venue – Programme of events – Notes of an interview with a person Page 6: Theme Research Page 6: Research into Theme: • • Use this page to research into your theme This could be . . . – Icons of the sixties – Sixties fashion – Swinging sixties – Events of the sixties – Icons of punk – Punk fashion – Punk timeline – Punk music Complete an evaluation of the page Explain what you have found out and how you can use this information • What other things could you include? – – – – Photos Imagery Keywords Timeline Page 7: Design Specification Page 7: Research Analysis • • Copy and complete the following table USE FULL SENTANCES!!! Research What did I do? What did I find out? Mood Board How did it help me? Visual aid Shop Profile Customer Profile Existing Products Say that it must be commercially viable Copy this statement out – ‘Having carried several types of research I am ready to start designing, before I do this I need to decide on criteria for my designs to meet. I am going to take these criteria firstly from brief as this was the task I was set, so these are things my designs must be. I will then look at what I found out from doing my research and the things my target market want in a product, as it is vital that my product appeals to its intended market so it sells. Finally I will look at things I could include in my designs either to make them more original or meet with my own views’. • A design specification is a list of criteria which my design ideas are to be based on. I have broken it down into 3 areas: Must Criteria (choose 4/5 things from your brief or initial research which must be included in your designs) Should Criteria (Choose 3/4 things from your research which you want to include in you designs i.e colours, style of product, easy care, cost etc) Could Criteria (Identify 2/3 things that you would like your designs to include i.e. use natural fabrics, be recyclable, use specific technique or element in design) Survey Educational Visit Theme Research Think about purpose, target market, theme, performance, environmental issues, safety, quality, techniques, time and life expectancy Page 8: Inspiration Sheet • • • • Use your mood board and your research to fill a page with sketches, doodles, drawings that are reflective of your them This will help you with your designs and developments An example is shown Tips – You could do it all in pencil and draw attention to certain parts using a little colour – You could just colour the main part, or the one which inspired you the most Page 9: Initial Design Ideas • Do 6 design ideas on this page that ALL meet the specification They should be coloured and labelled in detail with written explanation of what idea is i.e shirt made from 100% cotton, with cad print of graffiti appliquéd on front and beadwork detail to neck ad hem line. Think about the following . . . What do you think of the design? What do you think of the colour scheme? How much will it cost to produce? Is the design safe? Will you buy it? Will you find it useful? Does your idea answer the design problem? Is it designed ergonomically? Will it suit the target market that it is designed for? What materials will be used in it’s manufacture? Why? Use BLOWOUTS to show detail Page 10: Initial Design Ideas Complete 2 more design ideas on this page in the same way you did the last 6. Idea 1 Must 1 Must 2 Idea 2 Idea 3 Idea 4 Idea 5 Idea 6 Idea 7 Idea 8 Compare each idea against the specification the table shown Give each idea a tick or a cross to show whether or not it meets each criteria Total up ticks for each idea This will indicate which ideas are the strongest ones Add keywords to your page, such as innovative, imaginative, colourful, bold, fashion – anything that springs to mind that reflects your ideas/the theme/is inspirational Evaluation of ideas – Say which design was your target markets favourite, which meets specification the best and which 1 you prefer and why. Then say that you are going to take design forward and develop it in 4/5 ways to improve design. Must 3 Must 4 Must 5 Sh 1 Sh 2 Sh 3 Sh 4 Cd 1 Cd 2 Cd 3 Total Page 11: Development Planning •Draw a spider diagram for each of the following areas and add as many ‘legs’ as you can What needs developing? Materials Why? What do I need to find out? What work do I need to do? •Materials •Shape •Size Shape •Fastenings Size •Techniques Fastenings •Colour •Texture Techniques and pattern Colour and texture •Components •Construction •Health and safety Components Construction Health and safety Environment •Environment •Copy and complete the table •USE FULL SENTANCES Complete an evaluation of the page Explain what you have found out and how you can use this information Page 12: Development of shape, size, colour and style Select your best idea carefully. You may decide that selecting aspects from many designs and putting them together as one idea is better than choosing one idea Draw your selected idea in the centre of the page – pencil drawing with accurate details sketched on Identify up to 6 or 7 improvements. Include headings such as Health and Safety, cost, shape / colour, Industrial manufacture, materials, and other improvements that only apply to your project For each heading, do a spider diagram or short paragraph exaplaining how you intend to make improvements Include sketches to help visualise what you are talking about. Developments can be done using CAD, or hand drawings They must be coloured and labelled in detail with written explanation of design idea next to each one. Evaluation of Developments Evaluate your developments stating what you have learnt, which designs you like best and why and which design you are going to develop into your final proposal. Page 13 and 14: Development: Techniques START WITH A THOUGHT SHOWER OF TECHNIQUES – include as many as possible – highlight ones you think will be appropriate/effective for your design You then need to experiment with surface decoration techniques DO NOT just do any techniques! Make sure they are relevant to your development drawings • Appliqué, sequins, beading, 3D pints, decorative stitching, reverse appliqué, quilting, CAD printing, transfer printing, screen printing, batik, embroidery by hand or machine etc Evaluation of Developments – Evaluate your EACH OF YOUR DEVELOPMENTS stating what you have learnt, which designs you like best and why and which design you are going to develop into your final proposal. Page 15: Development: Construction • • • Try to do an initial step by step plan of how you could construct your garment What do you still need to find out – make a list – For example ‘I still need to make a paper pattern’ or ‘I still need to find out about costing’ – For each – list what you need to do and explain how you will do this Sketch a front and back view of your garment (no colour) and label what construction could be developed • • Test out different seams, hems, shaping techniques and layering (e.g. use of interfacing) that could REALISTICALLY be used on your garment For each sample, explain how you have made each one, the benefits of the sample, where the sample is typically used, and how it could be used on your garment. Page 16: Development: Construction Firstly, you need to experiment with, adapt and modify a commercial textiles pattern for the product you have chosen • • • • • • To do this, you will be given a commercial paper pattern which you will assemble on the sewing machine using calico You will then model this, and with the help of your research, in order to adapt the pattern to suit your design developments Parts can be added, taken away, adapted, proportions can be changed and so on Sketch all your design details and notes onto the paper pattern ALL OF THIS WORK WILL BE PHOTOGRAPHED AS EVIDENCE This calico pattern will then be used to make the actual pattern for your final product, using the garments you have chosen to dis-assemble. DO NOT make a toile that is actually a practice of the commercial pattern Make it ABSOLUTELY clear where a pattern has come from or how it has been developed When using a commercial pattern always show your modifications and your originality Evaluation of Developments – Evaluate your developments stating what you have learnt, which designs you like best and why and which design you are going to develop into your final proposal. Page 17: Development: Fabric Choice • What to include: – – – General Introduction – describe why you are doing this Thought shower on fabrics and their properties to help you decide what to use Then, more detailed research into 3 or 4 of the most likely fabrics you will use for your garment • – – – Samples of each of these fabrics Table of the cost of fabrics you may use i.e. cost per metre Suggested fabric specification outlining exactly what the fabric MUST do in order to be used on your product i.e. be strong and durable, be sustainable, be affordable and within the price range of my target market Any fabric testing you have done i.e. with dyes. Evaluation of Developments – Evaluate your developments stating what you have learnt, which designs you like best and why and which design you are going to develop into your final proposal. Page 18: Further Development: Designing an ethnic and environmentally friendly product • What to include: – A general introduction – why are you doing this page? – Your responsibility as a designer – explain why you should take these issues into account. – Research into how your product could be made ethical end environmentally friendly • Sustainability • Product life cycle • Organic cotton • Fair-trade • Recycling • Re-use of components/fabrics • Environmental issues when using textiles • Use of dyes and their environmental impact • Social and moral issues • Labelling – giving the consumer advice on how to care for the product – eco label? – Conclusion: what have you learned from this page? How will it help you? Page 19: Manufacturing Specification – Working drawings are normally presented in a very formal manner. – This means that colour and shade are not used. Outline drawings are the usual mode of presentation. Colour can hide or mask detail. – A working drawing is a precise piece of work and colour or shade could make a drawing look more complicated than it actually is. What do I need to include? – You need to draw detailed drawing of front and back of design, complete with; Sizes Fabrics used Stitches used Seams used Hems used Components used Textile techniques used Costing Pattern pieces Care labelling information (appropriate to fabric etc you have used) Fabric ‘swatches’ Industrial production suggestions Page 20: Planning for Manufacture • • • • • • • • Make a list of materials Make a list of equipment Make a list of all the steps to make your project Include any decisions with the steps you will take in the making process Place the steps in order Decide what shapes each of your steps will be Draw out your plan of making Link all the steps with flow lines Start / stop Flow line Process Decision Page 21: Planning for Manufacture Gantt Chart A Time Chart is a way of planning your project. A simple grid and the stages of the production process should be listed down the left hand side. As part of your project you need to show how much time you intend to spend making each section of the project. You should include a key which shows the amount of time that each unit represents. • • Start your production record on this page also. See next page for details. Page 22: Production Record As you make your product keep a note of what you achieve each lesson, any alterations you’ve had to make and why, how you feel about product, and if your time planning was realistic. PHOTOGRAPH EACH STAGE OF THE MAKING PROCESS This page should be displayed as a series of photos/sketches/diagrams in a logical order with accompanying notes. Production records are essential when a product is being made as it records all the manufacturing problems and suggested solutions. This means that improvements can be made to the manufacturing process. Keep a note of any problems in the production record. Use it to suggest changing the way tools and equipment are used. A simple improvement to the way a product is manufactured may lift the overall quality of the finished product. A good production record will outline every stage of making the product. A GOOD production record incorporates quality control procedures which means that the product is constantly checked during its manufacture. This should ensure that the finished item is manufactured to a high standard. A production record plays a significant part in keeping a work efficient, productive and competitive. Page 23: Advertising my Product • • • • • Describe what advertising is – Types of advertising Describe what marketing is Describe the functions of packaging Describe what labelling is – Its purpose – types of labelling FROM ALL OF THIS RESEARCH, SUGGEST HOW YOU WILL ADVERTISE YOUR PRODUCT AND EXPLAIN WHY • THINK ABOUT . . . • Sales Team Website Point of Sale Surveys Communications Distribution Department Research & Development Marketing Literature - through the post. Direct Mail Exhibitions Advertising - TV, Radio, Internet, Magazines, Newspapers, Billboards etc.... Page 24 and 25: Testing and Evaluating • • Designers evaluate their finished products or prototypes in order to test whether they work well and if the design can be corrected or improved. Whatever you have designed it is important to evaluate your work constantly during the project. Evaluation can take a variety of forms: – General discussion with other pupils, staff and others. – Questionnaires / surveys carried out at any time during the project. – Your personal views, what you think of existing designs. – Most important of all - what do you think of your designs, prototypes and finished products ? – Can you think of any other ways of evaluating your work ? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. What do you think of the overall design ? What changes would you make ? Are you happy with the materials you chose ? Would you make adjustments next time? Is the colour scheme exactly what you expected ? What alterations would you make ? Did the project take too long to make ? Would this alter the cost of manufacture ? Would it be easy to set up a production line for the manufacture of your solution ? Is your solution safe ? Could it be made safer ? Are the techniques you used to make your solution adequate or would you use a different range of manufacturing techniques? Is the solution the right size/shape ? What are the views of other people regarding your design ? 10. Does it work ? What changes are required ?
© Copyright 2026