PLTW Human Body Systems
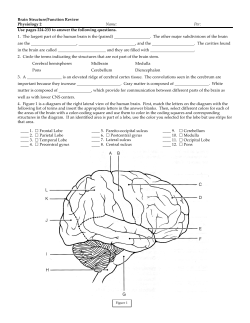
PLTW Human Body Systems COURSE 2 Highlights of the Course ▪ Using the Manikens ▪ Dissection Labs ▪ Learning About The Central Nervous System ▪ Sherlock Bones Lab ▪ How the course helps in other areas Manikens WHAT WE LEARNED AND HOW WE LEARNED IT Using the Manikens http://www.usd422.org/vnews/display.v/ART/544ff7af1784f http://www.localiiz.com/optimum-performance-studio-28#.VINHbzGzEr4 By Using the Manikens… Human Skeletal System Human Muscular System That isn’t it! http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/imagepages/19089.htm www.boundless.com/biology/textbooks/boundless-biology-textbook/the-musculoskeletal-system-38/joints-and-skeletal-movement217/types-of-synovial-joints-822-12066 Dissections (THE BEST PART) The Cow Elbow Learned about: http://atsbiomed.weebly.com/blog/category/hbs • Different joint types • Movement terminology • The purpose of synovial fluid The Kidney Capsule Renal Artery Inside the Kidney Cortex We learned about… • Nephrons and how they function • Structures of the kidney and their functions • Why we only need one kidney • Urine formation pathway Renal Vein Calyx Ureter Medullary Pyramid The Cow Eye Also in the lab… What we learned: ▪ Where visual signals are processed in the brain ▪ Differences between cow eyes and human eyes ▪ The structures of the eye and their functions ▪ The pathway of light through the eye http://brickellvision.com/eye-diagram-eye-diagrams/eye-diagram/ ▪ How light affects the pupils The Central Nervous System Central Nervous System Interneuron Neurons Voluntary Activities Peripheral Nervous System Sympathetic Division Involuntary Activities Efferent Autonomic NS Afferent Parasympathetic Division Region of the Brain Location Primary Function Specific Activities and Processes Occipital Lobe (Cerebrum) Back of the brain, slightly towards the bottom Processes visual input that is sent to the brain from the retinas Vision Frontal Lobe (Cerebrum) Front of the brain, at the top Executing behavior; controls individual muscles Happiness, movement, problem solving, reasoning, speech production Parietal Lobe (Cerebrum) Behind the frontal lobe, in front of occipital Contains neurons that receive sensory information Bodily sensations Temporal Lobe (Cerebrum) Above brain stem Combines auditory and visual information Hearing, language comprehension, smell Medulla In the brain stem, in front of cerebellum Helps transfer messages to spinal cord, controls breathing, heart/blood vessel function, digestion, sneezing, and swallowing Breathing, BP regulation Pons Above medulla Sensory analysis, motor skills, sleep and consciousness Sleeping and waking Hypothalamus Just above brain stem Hormone production, homeostasis Thirst, hunger, smell Amygdala Middle of temporal lobe Processing of emotions Happiness Hippocampus Next to amygdala Long term memory, spatial navigation Remembrance Cerebellum Bottom of the brain, in the back Fine motor skills, balance, posture, quick/repetitive movements Muscle coordination, balance, movement Sherlock Bones Lab Calipers They measure lengths. In this case, bones! What You Can Determine Using Bones • Gender • Race • Height • Age Height Estimation of YOU! Femur ▪ Male: (2.32 X MLF) + 65.53 +/- 3.94 ▪ Female: (2.47 X MLF) + 54.10 +/- 3.72 Humerus ▪ Male: (2.97 X MLH) + 73.5 +/- 3.94 ▪ Female: (3.14 X MLH) +65 +/- 3.72 (There’s more specifics involved too!) Other Areas the Course Has Helped In Other Courses… http://www.docstoc.com/docs/90470282/Giant-Hormone-Chart Body cells take up more glucose Beta cells of pancreas release insulin into the blood Liver takes up glucose and stores it as glycogen Negative Feedback Loops Alpha cells of pancreas release glucagon Liver breaks down glycogen and releases glucose http://www.proprofs.com/flashcards/story.php?title=bio-lecture-3-page-12111-lecture-pt-3 The Sliding Filament Theory How muscles move https://wikis.engrade.com/slidingfilamenttheory College Credits Missouri University of Science and Technology
© Copyright 2026