SST
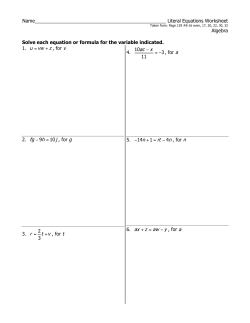
CLASS: - IX MATH Revision of chapter 1 Real numbers, chapter 2 polynomials and chapter 5 Introduction to Euclids geometry. SCIENCE MOTION 1. Define the following Rest, Motion, Distance, Displacement, frame of reference 2. Differentiate the following a. Distance and Displacement b. Speed and Velocity c. Acceleration and retardation 5. Define the following Uniform speed, Non-uniform speed, Average speed, Instantaneous speed Uniform Velocity, Non-uniform Velocity, Average Velocity, Instantaneous Velocity 6. Derive the following equations of motion a. v = u + at b. S = ut + at2 c. v2 = u2 + 2as d. average velocity = (Initial velocity + Final velocity)/2 7. Answer the following a. Name the device that measures the total distance travelled. b. Name the device that measures instantaneous speed. c. Name the device that increases the speed of a vehicle. d. Name the device that decreases the speed of a vehicle. 8. Define the motion from the following graphs 9. Define the motion from the following graphs 10. Which one will have greater velocity? 11. a. Find the acceleration of a body in each case. b. c. DISTANCE AND DISPLACEMENT 1. An object has moved through a distance. Can it have zero displacement? If yes, support your answer with an example. 2.Which of the following is true for displacement? (a) It cannot be zero. (b) Its magnitude is greater than the distance travelled by the object. 3. A farmer moves along the boundary of a square field of side 10 m in 40 s. What will be the magnitude of displacement of the farmer at the end of 2 minutes 20 seconds? 4. An athlete completes one round of a circular track of diameter 200 m in 40 s. What will be the distance covered and the displacement at the end of 2 minutes 20 s? AVERAGE SPEED AND VELOCITY 1. Under what condition(s) is the magnitude of average velocity of an object equal to its average speed? 2. Joseph jogs from one end A to the other end B of a straight 300 m road in 2 minutes 50 seconds and then turns around and jogs 100 m back to point C in another 1 minute. What are Joseph‟s average speeds and velocities in jogging (a) from A to B and (b) from A to C? 3. Abdul, while driving to school, computes the average speed for his trip to be 20 km h– 1. On his return trip along the same route, there is less traffic and the average speed is 40 km /h.. What is the average speed for Abdul‟s trip? 4. The odometer of a car reads 2000 km at the start of a trip and 2400 km at the end of the trip. If the trip took 8 h, calculate the average speed of the car in km/ h and m/s. 5. Usha swims in a 90 m long pool. She covers 180 m in one minute by swimming from one end to the other and back along the same straight path. Find the average speed and average velocity of Usha. ACCELERATION AND RETARDATION 1. When will you say a body is in (i) uniform acceleration? (ii) non-uniform acceleration? 2. A bus decreases its speed from 80 km h–1 to 60 km/h in 5 s. Find the acceleration of the bus. 3. A train starting from a railway station and moving with uniform acceleration attains a speed 40 km/h in 10 minutes. Find its acceleration. 4. Starting from a stationary position, Rahul paddles his bicycle to attain a velocity of 6 m/s in 30 s. Then he applies brakes such that the velocity of the bicycle comes down to 4 m/s in the next 5 s. Calculate the acceleration of the bicycle in both the cases. EQUATIONS OF MOTION 1. A ball is gently dropped from a height of 20 m. If its velocity increases uniformly at the rate of 10 m s-2, with what velocity will it strike the ground? After what time will it strike the ground? 2. A motorboat starting from rest on a lake accelerates in a straight line at a constant rate of 3.0 m s–2 for 8.0 s. How far does the boat travel during this time? 3. A train is travelling at a speed of 90 km/h. Brakes are applied so as to produce a uniform acceleration of – 0.5 m s-2. Find how far the train will go before it is brought to rest. 4. A trolley, while going down an inclined plane, has an acceleration of 2 cm s-2. What will be its velocity 3 s after the start? 5. A racing car has a uniform acceleration of 4 m s-2. What distance will it cover in 10 s after start? 6. A stone is thrown in a vertically upward direction with a velocity of 5 m s-1. If the acceleration of the stone during its motion is 10 m s–2 in the downward direction, what will be the height attained by the stone and how much time will it take to reach there? 7. A bus starting from rest moves with a uniform acceleration of 0.1 m s-2 for 2 minutes. Find (a) the speed acquired, (b) the distance travelled. 8. The brakes applied to a car produce an acceleration of 6 m s-2 in the opposite direction to the motion. If the car takes 2 s to stop after the application of brakes, calculate the distance it travels during this time. 9. A car accelerates uniformly from 18 km/h to 36 km/h in 5 s. Calculate (i) the acceleration and (ii) the distance covered by the car in that time. 10. A train starting from rest attains a velocity of 72 km/h in 5 minutes. Assuming that the acceleration is uniform, find (i) the acceleration and (ii) the distance travelled by the train for attaining this velocity. LAWS OF MOTION 1. State Newton‟s first law of motion? 2. What does the first part of the Newton‟s first law of motion define? 3. Define inertia. 4. Name the physical quantity that measures inertia? 5. Define “Inertia of Rest” and “Inertia of Motion”. 6. Explain why? a. When a bus at rest suddenly stops we fall backward. b. When a bus in motion suddenly stops we fall forward. c. When we beat a blanket, dust particles fly away. d. When a galloping horse suddenly stops the rider fall forward. e. When a tree is given a sudden jerk, dry leaves fall down. f. Before taking a long jump or a high jump an athlete runs some distance. 7. What does the second part of the Newton‟s first law of motion define? 8. Define “Force”. 9. Which of the following has more inertia: (a) a rubber ball and a stone of the same size? (b) a bicycle and a train? (c) a five rupees coin and a one-rupee coin? 10. Why is it advised to tie any luggage kept on the roof of a bus with a rope? 11. In the following example, try to identify the number of times the velocity of the ball changes:“A football player kicks a football to another player of his team who kicks the football towards the goal. The goalkeeper of the opposite team collects the football and kicks it towards a player of his own team”. Also identify the agent supplying the force in each case. MOMENTUM 1. Define Momentum. 2. Write down the formulae for momentum. 3. Write down the unit of momentum. 4. There are two bullets each of mass 50gm.One is fired by a gun and the other is thrown by hand. The bullet fired by the gun can kill a tiger but the bullet thrown by hand can‟t even hurt a cat. Explain why? 5. There are two bullets each of mass 50gm.One is fired by a gun and the other is thrown by hand. The bullet fired by the gun can pierce into the glass window of a car but the bullet thrown by hand makes a crack. Explain why? 6. There is a car of mass 100kg and a bicycle of mass 40kg. Both are moving with the same velocity 15km/hr. You can stop the bicycle not the car. Explain why? 7. A body of mass 500gm is moving with a velocity of 20m/s. What is the momentum of the body? 8. A body of mass 2kg posses a momentum of 24kg-m/s. Find the velocity of the body. 9. A body of unknown mass is moving with a velocity of 4m/s. It possesses a momentum of 24kg-m/s. Find the mass of the body? 10. There are two bodies of equal mass. One is moving with a velocity of 10m/s and the other is moving with a velocity of 30m/s. Which one is having more momentum? 11. There are two bodies one is heavier and the other one is lighter. Both are moving with same velocity of 10m/s. Which one is having more momentum? 12. A body of mass “m” was moving with a velocity “u”. After sometime its velocity is found to be “v”. Find out the change in momentum. 13. How much momentums will a dumb-bell of mass 10 kg transfer to the floor if it falls from a height of 80 cm? Take its downward acceleration to be 10 m s–2. NEWTON‟S SECOND LAW OF MOTION 1. State Newton‟s Second Law of Motion. Prove that „F=ma”. 2. Define One Newton. 3. Newton First law defines Force. What does the Newton‟s Second Law do? 4. A constant force acts on an object of mass 2 kg for a duration of 4 s. It increases the object‟s velocity from 8 m/ s to 12 m/s. Find the magnitude of the applied force. Now, if the force was applied for duration of 3 s, what would be the final velocity of the object? 5. A motorcar is moving with a velocity of 90 km/h and it takes 4 s to stop after the brakes are applied. Calculate the force exerted by the brakes on the motorcar if its mass along with the passengers is 800 kg. 6. A force of 10 N acts on a body of mass 2Kg, and the same force acts on a body of mass 5kg.Find the acceleration in each case. What acceleration would it give if both the masses were tied together? 7. a. Find the force acts on a body of mass 5kg in each case. b. c. 8. A truck starts from rest and rolls down a hill with a constant acceleration. It travels a distance of 400 m in 20 s. Find its acceleration. Find the force acting on it if it‟s mass is 7 metric tonnes (Hint: 1 metric tonne = 1000 kg.) 9. A stone of 1 kg is thrown with a velocity of 20 m/s across the frozen surface of a lake and comes to rest after travelling a distance of 50 m. What is the force of friction between the stone and the ice? 10. A 8000 kg engine pulls a train of 5 wagons, each of 2000 kg, along a horizontal track. If the engine exerts a force of 40000 N and the track offers a friction force of 5000 N, then calculate: (a) the net accelerating force; (b) the acceleration of the train; and (c) the force of wagon 1 on wagon 2. An automobile vehicle has a mass of 1500 kg. What must be the force between the vehicle and road if the vehicle is to be stopped with a negative acceleration of 1.7 m s–2? 11. 12. Using a horizontal force of 200 N, we intend to move a wooden cabinet across a floor at a constant velocity. What is the friction force that will be exerted on the cabinet? 13. A hockey ball of mass 200 g travelling at 10 m/s is struck by a hockey stick so as to return it along its original path with a velocity at 5 m/s. Calculate the change of momentum occurred in the motion of the hockey ball by the force applied by the hockey stick. 14. A bullet of mass 10 g travelling horizontally with a velocity of 150 m/s strikes a stationary wooden block and comes to rest in 0.03 s. Calculate the distance of penetration of the bullet into the block. Also calculate the magnitude of the force exerted by the wooden block on the bullet. CONSERVATION OF LINEAR MOMENTUM 1. State and prove the law of conservation of momentum. 2. Why does a cricket player lower his hand while taking a catch? 3. Shock absorbers are provided in vehicles. Why? 4. A karate player breaks a slab of ice with a single blow. How? 5. In a high jump athletic event, the athletes are made to fall either on a cushioned bed or on a sand bed. Why? 6. A bullet of mass 20 g is horizontally fired with a velocity 150 m/s from a pistol of mass 2 kg. What is the recoil velocity of the pistol? 7. A girl of mass 40 kg jumps with a horizontal velocity of 5m/s onto a stationary cart with frictionless wheels. The mass of the cart is 3 kg. What is her velocity as the cart starts moving? Assume that there is no external unbalanced force working in the horizontal direction. 8. Two hockey players of opposite teams, while trying to hit a hockey ball on the ground collide and immediately become entangled. One has a mass of 60 kg and was moving with a velocity 5.0 m/ s while the other has a mass of 55 kg and was moving faster with a velocity 6.0 m s–1 towards the first player. In which direction and with what velocity will they move after they become entangled? Assume that the frictional force acting between the feet of the two players and ground is negligible. From a rifle of mass 4 kg, a bullet of mass 50 g is fired with an initial velocity of 35 m/s. Calculate the initial recoil velocity of the rifle. 9. 10. Two objects, each of mass 1.5 kg, are moving in the same straight line but in opposite directions. The velocity of each object is 2.5 m s-1 before the collision during which they stick together. What will be the velocity of the combined object after collision? 11. An object of mass 1 kg travelling in a straight line with a velocity of 10 m/s collides with, and sticks to, a stationary wooden block of mass 5 kg. Then they both move off together in the same straight line. Calculate the total momentum just before the impact and just after the impact. Also, calculate the velocity of the combined object. rd NEWTON‟S THIRD LAW 1. State Newton‟s 3 law. 2. Explain, why is it difficult for a fireman to hold a hose, which ejects large amounts of water at a high velocity. 3. If action is always equal to the reaction, explain how a horse can pull a cart. GRAVITATION 1. State the universal law of gravitation. Derive the relation 2. Write the formula to find the magnitude of the gravitational force between the earth and an object on the surface of the earth. 3. What do you mean by free fall? 4. What do you mean by acceleration due to gravity? 5. Write down the differences between mass and weight. 6. Why is the weight of an object on the moon 1/6 th of its weight on the earth? An object weighs 10 N when measured on the surface of the earth. What would be its weight when measured on the surface of the moon? 7. How does the force of gravitation between two objects change when the distance between them is reduced to half ? 8. Gravitational force acts on all objects in proportion to their masses. Why then, a heavy object does not fall faster than a light object? 9. What is the magnitude of the gravitational force between the earth and a 1 kg object on its surface? (Mass of the earth is 6X1024 kg and radius of the earth is 6.4X106 m.) 10. The earth and the moon are attracted to each other by gravitational force. Does the earth attract the moon with a force that is greater or smaller or the same as the force with which the moon attracts the earth? Why? 11. If the moon attracts the earth, why does the earth not move towards the moon? 12. What happens to the force between two objects, if (i) the mass of one object is doubled? (ii) the distance between the objects is doubled and tripled? (iii) the masses of both objects are doubled? 13. What is the importance of universal law of gravitation? 14. What is the acceleration of free fall? 15. What do we call the gravitational force between the earth and an object? 16. Amit buys few grams of gold at the poles as per the instruction of one of his friends. He hands over the same when he meets him at the equator. Will the friend agree with the weight of gold bought? If not, why? [Hint: The value of g is greater at the poles than at the equator.] 17. Why will a sheet of paper fall slower than one that is crumpled into a ball? 18. The mass of the earth is 6 x1024 kg and that of the moon is 7.4 × 1022 kg. If the distance between the earth and the moon is 3.84×105 km, calculate the force exerted by the earth on the moon. G = 6.7 × 10–11 N m2 kg-2. 19. A car falls off a ledge and drops to the ground in 0.5 s. Let g = 10 m s–2 (for simplifying the calculations). (i) What is its speed on striking the ground? (ii) What is its average speed during the 0.5 s? (iii) How high is the ledge from the ground? 20. An object is thrown vertically upwards and rises to a height of 10 m. Calculate (i) the velocity with which the object was thrown upwards and (ii) the time taken by the object to reach the highest point. 21. What is the magnitude of the gravitational force between the earth and a 1 kg object on its surface? (Mass of the earth is 6X 1024 kg and radius of the earth is 6.4X106 m.) 22. A ball is thrown vertically upwards with a velocity of 49 m/s. Calculate (i) the maximum height to which it rises, (ii) the total time it takes to return to the surface of the earth. 23. A stone is released from the top of a tower of height 19.6 m.Calculate its final velocity. 24. A stone is thrown vertically upward with an initial velocity of 40 m/s. Taking g = 10 m/s2, find the maximum height reached by the stone. What is the net displacement and the total distance covered by the stone? 25. Calculate the force of gravitation between the earth and the Sun, given that the mass of the earth = 6 X1024 kg and of the Sun = 2X1030 kg. The average distance between the two is 1.5X 1011 m. 26. A stone is allowed to fall from the top of a tower 100 m high and at the same time another stone is projected vertically upwards from the ground with a velocity of 25 m/s. Calculate when and where the two stones will meet. 27. A ball thrown up vertically returns to the thrower after 6 s. Find (a) the velocity with which it was thrown up, (b) the maximum height it reaches, and (c) its position after 4 s. SST 1. Briefly state what happened in France after the fall of Jacobin Government. 2. Define the term of triangular trade. 3. Write a brief account on third Estate 4. Name any 4 countries which enjoy veto power in the Secretary Council of UNO. 5. Make a note on UNO 6. Give your arguments for Universal Adult Franchise. 7. What do you mean by economic activities? 8. What are farm and non-farm products? 9. How the use of chemical fertilizers can be harmful? 10. What are the purposes of money in agriculture? 11. Why the farm laborers poor? 12. Distinguish between natural and man-made resources. 13. Describe the boundaries of India. 14. Name the Islands of our country. (India). 15. Make a note on location of India. PROJECT WORKS DEMOCRATIC COUNTRIES OF THE WORLD CLASS IX B A. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Out of 05 make any one project for Social science exhibition Plastics- A new and powerful enemy of the environment. Role of Human capital in the development of the Indian economy. Impact of tourism industry on the environment. Public awareness of human rights- global issue Role of women in freedom struggle These questions answer you have to write in copy. 1. Write the main features of the French Constitution of 1791. 2. What was the impact of the French revolution on France? 3. Briefly discuss the role of the philosophers in the French revolution. 4. Give reasons- Why India is often referred to as a sub-continent? 5. The tropic of cancer runs almost half way through the country. What does this imply? 6. Mention the role of Security of council of union nation. 7. Describe the development (expansion) of democracy after the end of Second World War in 1945? 8. Which freedoms are usually taken away when a democracy is overthrown by the military? 9. What is the working capital required by the farmer using modern farming methods. 10. Name the four requirements for the production of goods and services? HINDI Hindi-IX-A प्र :१ जफ झूयी ने फैरो को गमा के हवारे कय ददमा तफ मदद उन्हे ईश्वय ने वाणी दी होती तो फैरो की क्मा प्रततक्रिमा होती ? प्र:२ भोती ने दीवाय को कैसे गगयामा ?दीवाय गगयते ही कोन –कोन बागा ? प्र:३ ददिमर के हायकय चरे जाने के ऩश्चात हीया औय भोती भे क्मा सॊवाद हुमा होगा ? प्र;४ मात्रा वत ृ ाॊत के आधाय ऩय ततब्फत की बौगोलरक दृश का शब्द गचत्रण प्रस्तुत कये ,वहाॉ की दशा आऩके याज्म /शहय से क्रकस प्रकाय बीन है ? प्र:५ ततब्फत भे जभीन की क्मा स्स्थतत है ? प्र:६ कफीय ने दोहो भे क्रकस फात ऩय फर ददमा हैं ? प्र:७ ररघड़ के ऩदो को क्मा कहा जाता हैं ? प्र:८ फाखों का प्रततऩाद्ध क्मा है ? प्र:९ “इस जार प्ररम भे “ रूग कहा जा यहे थे औय रोगो की जुफान ऩय क्मा फात थी ? प्र:१० कोन सा सभाचाय इस जार प्ररम भे ददर दहराने वारा था उस सभाचाय का क्मा प्रबाव ददखाई ददमा ? प्र:११ १९४९ की भहानन्दा की फाि के सभम रेखक के साथ क्मा घटना घाटी ? प्र:१२ गोरॊफय के ऩास जनसॊऩकक की गाड़ी से क्मा ऐरान क्रकमा जा यहा था? प्र:१३ सवेये सािे ऩाॉच फजे ऩानी की खफय सुनकय रेखक ऩय क्मा प्रततक्रिमा हुईं ?उसने क्मा दृश दे खा ? प्र:१४ सवैमा छन्द क्मा होता है ? प्र:१५ प्रस्तुत सवैमा भे जीआईएस प्रकाय ब्रज बूलभ के प्रतत प्रेभ अलबव्मक्त हुआ है ,उसी तयह आऩ अऩनी भातब ृ ूलभ के प्रतत अऩने भनोबावों को अलबव्मक्त कीस्जमे | प्र:१६ ऩाठ्म ऩस् ु तक से १० भह ु ावये चन ु े औय उसके अथक लरखकय वाक्म भे प्रमोग कये | प्र:१७ “बायत भे फाि का दृश “इस कथन ऩय सबी फच्चे एक एक ऩरयमोजना कामक तैमाय कये | Hindi-IX-B 1.रडक्रकमों की सॊख्मा कभ होने ऩय सभाज का क्मा स्वरूऩ होगा ? ववचाय कय लरखें । 2.कफीय के जीवन दशकन ऩय प्रकाश डालरए ? 3.आत्भा एवॊ ऩयभात्भा के सॊदबक भें ररद्दद के ववचायों को स्ऩष्ट कयें । 4.इस जर प्ररम भें ऩाठ के आधाय ऩय फताएॊ क्रक जर क्रक अततशमता जन – जीवन को क्रकस प्रकाय प्रबाववत कयती है ? 5.पणीश्वयनाथ ये णु के जर प्ररम ऩय लरखखत रयऩोताकजों के नाभ लरखें । 6.इस जर प्ररम भें ऩाठ भें क्रकन – क्रकन नददमों के नाभ आए है जो फाि की ववबीवषका का कायण यही हैं ? 7.21 वीॊ सदी का बायत ववषम ऩय अऩने ववचाय प्रकट कयें । 8.अऩने ऩसन्द के क्रकसी एक कवव के जीवन एवॊ दशकन ऩय प्रकाश डारें। 9. सॊगचत ज्ञान एवॊ ‘ल्हासा की औय’ ऩाठ को आधाय फनाते हुए दहभारम के सौंदमक ऩय प्रकाश डारें साथ ही दहभारम ऩय कुछ स्वयगचत ऩॊस्क्तमाॉ कववता के रूऩ भें लरखने का प्रमास कयें । 10. अनुप्रास, मभक, उऩभा, रूऩक अरॊकायों के ऩाॉच - ऩाॉच उदाहयण लरखें । ENGLISH 1. Read chapters I to X in the novel THREE MEN IN A BOAT by Jerome K. Jerome and write a BOOK REVIEW of 10 pages in a Project File. 2. Write all the formats and an example of the topics under Writing Section – Notice, Message, Formal Letter, Informal Letter, Diary Entry and e-mail. (in Grammar part of the Copy) 3. Read the headlines of an English News Paper daily and follow English News on Television. Daniel Vijaya Prakash TGT-English CLASS: - X MATH Chapter: 1. Real Numbers 1. Define the following: (a) Euclid‟s division lemma. (b) Fundamental theorem of arithmetic (c) Terminating and non-terminating decimal expensions. 2. Prove that the square of any positive integer is of the form 5q, 5q + 1, 5q + 4 for some integer q. 3. Use Euclid‟s division Lemma to show that the cube of any positive integer is either of the form 9m, 9m + 1, or 9m + 8 for some integer m. 4. Use Euclid‟s division algorithm to find the HCF of-----(i) 135 and 225 (ii) 196 and 38220 5. Express each of the following as a product of its prime factors: (i)420 (ii)468 6. Prove that √ √ is irrational. 7. Prove that √ is irrational. 8. Write a paragraph of 80 words on real numbers. Chapter: 2.Polynomial 9. Define the following: (a) Polynomial (b) Degree of a polynomial (c) Constant polynomial (d) Linear polynomial (e) Quadratic polynomial (f) Value of a polynomial (g) Zero of a polynomial 10. Find the zeros of each of the following quadratic polynomials and verify the relationship between the zeros and their coefficients. (a) F(x)= (b) P(x)= - 7x -3 11. Find the other zeroes of the polynomial it is given that two its zeroes are -√ √ . Chapter:3 Pair of Linear Equations in two variables. 12. Write all the conditions of one unique solution, no solutions and infinite many solutions for a given pair of linear equations in two variables. 13. Choose any one pair of Linear equations in two variables and Find its solutions by various methods, i.e. -Graphical method -Elimination method -Substitution method -Cross multiplication method 14. Two straight path are represented by the equations Check whether the Paths cross each other or not. 15. Father‟s age is three times the sum of ages of his two children. After 5 years his age will be twice the sum of the ages of two children. Find the age of father. 16. A person can row downstream 20 km in 2 hours and upstream 4 km in 2 hours. Find man‟s speed of rowing in still water and the speed of the currents. 17. Write a short paragraph of 80 words on the topic „ Pair of Linear equations in two variables”. Write true or false 1. LCM HCF of two numbers is equal to the product of those two numbers. 2. The HCF of 30, 72 and 432 is 3. 3. an irrational number. 4. Product of two consecutive natural numbers is always a even number. 5. 6. . 7. . 8. . 9. √ 10. is rational having non-terminating repeating decimal expensions. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. √ . −axis. SCIENCE WRITTEN WORK:Q.1 Explain the human digestive system. Q.2 Draw the labeled diagram of nephron. Q. 3 Derive the mathematically formula of resistors in series and parallel combination. Q. 4 Explain various types of chemical reaction with example. Q.6 Compare the physical and chemical properties of acids and bases. PROJECT WORK:Visit your colony houses during summer days and make a list of children (10 children) suffering from malnutrition. Ask the family members about the problem face by them and how you will suggest them to providing balanced diet for their children. (it should done in stick file) ASSIGNMENT:Write short notes on production of electricity from various form of energy.(it should write in A-4 size paper and words limit 400-500 words) FOR LEARNING1 Chemical reactions and equations 2 Acids, bases and salts 3 Electricity 4 Life processes SST CLASS-X A 1- What are major characteristics of the black soil? 2- Name the soil forming factors. 3- Which soil develops due to intense leaching process? 4- Why do you think average income is an important criterion for development? 5- How body mass index calculated? Explain. 6- Explain the meaning of HDI. Mention three components of measuring HDI. 7- Which international agency is held responsible for the preparation for HDI? 8- What is IMR? 9- Write a note on Oriya Novel. 10- What are the prudential and moral reasons of power sharing? 11- Name the writers of the following novelsa- Anguriya Binimoy b- Pamela c- Gaban d- Durgesh nandini e- Kadambari f- Godan g- Muktalekha h- Jungle Book i- Chandrkanta j- The mayor of Caster Bridge k- Pickwick Papers l- Henrietta Temple m- Saudamani n- Rangbhumi o- Anadmath p- Jane Eyre q- Pride and Prejudice r- Treasure Island CLASS-X B A. Out of 05 make any one project for Social science exhibition 1. Plastics- A new and powerful enemy of the environment. 2. 3. 4. 5. Role of Human capital in the development of the Indian economy. Impact of tourism industry on the environment. Public awareness of human rights- global issue Role of women in freedom struggle OR B. Write a Project on the topic “Federalism in India” not more than 10 pages on same format which was given in the class room. These questions answer you have to write in copy. 1. What is the importance of soil? Explain types of soil? 2. Explain the factors responsible for resources development in India. 3. Explain with examples, how mining and over irrigation are responsible for land degradation? 4. Explain how did novels become a popular medium of entertainment among the middle class during the late 19th century in India? 5. “Novels were useful for both the colonial administrators and Indians in colonial India” Support the statement with examples? 6. Examine the role and involvement of women in the readership and authorship of novels in India? 7. How powers are shared in different social groups and why? 8. Why is sustainable development essential for economic growth? Give two reasons. 9. How does industrial pollution degrade the environment? Explain three measures to control environmental degradation. 10. Why do you think average income is an important criterion for development? HINDI 1. दे व अऩना सहामक क्रकसे फनाना चाहते हैं? 2. कृष्ण के नेत्रों की क्मा ववशेषता फताई गई है ? 3. नातमका साड़ी ओिकय क्रकसकी नज़य उताय यही है ? 4. दे व द्वाया यगचत ऩद कववता भें फसॊत का गचत्रण ऩयम्ऩयागत रूऩ से लबन्न हुआ है , कैसे ? 5. दे व के काव्म की ववशेषताएॉ फताइए? 5.सेनानी ना होते हुए बी चश्भे वारे को कैप्ट्न क्मों कहा जाता था ? 6.भतू तक ऩय सयकॊडे का चश्भा क्मा उम्भीद जगाता है ? 7 क्रकन आधायों ऩय फारगोबफन बगत को साधु कह सकते हैं ? 8 बगत क्रकन प्रचलरत भान्मताओॊ को नहीॊ भानते थे ? 9.कवव सयू का जीवन, ऩरयचम ,दे ते हुए उनकी,, यचनाएॉ, एवॊ सयू -काव्म की ववशेषताएॉ फताएॉ । 10.गोवऩमों द्वाया उद्धव को बाग्मवान कहने भें क्मा व्मॊग्म तनदहत है ? 11 marjaada na lahI ko maaQyama sao kaOna saI mayaa-da na rhnao kI baat kI jaa rhI hO 12 Pa`stut pdaoM ko AaQaar pr gaaoipyaaoM ka yaaoga saaQanaa ko p`it dRiYTkaoNa spYT kroM. 13. भाता का अॊचर ऩाठ का भूर बाव स्ऩष्ट कयें ? ENGLISH 1. Read chapters I to X in the novel THE DIARY OF A YOUNG GIRL by Anne Frank and write a BOOK REVIEW of 10 pages in a Project File. 2. Write all the formats and an example of the topics under Writing Section – Notice, Message, Formal Letter, Informal Letter, Diary Entry, e-mail, Speech, Article, Debate and Report writing. ( in Grammar copy) 3. Read the headlines of an English News Paper daily and follow English News on Television.
© Copyright 2026