PAs in Health Care Systems - Michigan Academy of Physician
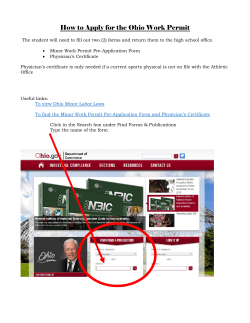
Hospitals and HealthCare Systems What you were “Not” taught in PA School Folusho Ogunfiditimi, DM, MPH, PA-C Director, Mid-Level Provider Harper University Hospital/ Hutzel Women’s Hospital Detroit Medical Center Tenet Health System [email protected] Objectives • Understand the roles of PA’s – Recruitment and Retention – Onboarding and Orientation – Compensation and Provider enrollment – Clinical Practice Models – Regulatory Standards and Compliance – Productivity, Value and Reimbursement – Team membership/Physician Collaboration – Quality, Safety and Patient Satisfaction Recruitment and Retention History of Non – Traditionally Trained Medical Practitioners. Modern Advanced Practice Providers 1965 1963 1869 1965 1989 From Graduation to Hire • • • • • • • • Average of 90 days Graduation-Board Certification – Licensure Interviews – Start early PA-Intern / Graduate PA Job Descriptions PA Recruiter PA Leader / Director Shadow opportunities • Graduate Physician Assistant is (GPA) is a recently graduated Physician Assistant who has met the academic and State of Michigan practice requirements for certification and Licensure as a Physician Assistant, but who has yet to obtain full organizational credentialing status with the DMC. In accordance with DMC bylaws all licensed physician assistants must undergo organizational credentialing and privileging prior to providing health care services to patients. To this effect the title Physician Assistant Certified (PA-C) cannot be used until fully credentialed at the DMC and newly graduated PAs, awaiting credentialing will use the title Graduate Physician Assistants. Credentialing • Credentialed through Medical Affairs – JC requirement • Supervising Physician (employed) • PA’s must have an NPI and DEA License. (NPs as well) • Scope of Practice and Core Competencies- Every specialty • OPPE and FPPE Disagree* Agree PATIENT CARE Provides care that is compassionate, appropriate, and effective for the promotion of health, prevention of illness, treatment of disease and support at the end of life. Agree Disagree* MEDICAL/CLINICAL KNOWLEDGE Demonstrates knowledge of established and evolving biomedical, clinical, procedural and social sciences, and applies this knowledge to patient care. Agree Disagree* PRACTICE BASED LEARNING AND IMPROVEMENT Uses scientific evidence and methods to investigate, evaluate and improve patient care processes. Agree Disagree* INTERPERSONAL & COMMUNICATION SKILLS Demonstrates interpersonal and communication skills that enable the provider to establish and maintain professional relationships with patients, families and other members of health care teams and administration Agree Disagree* PROFESSIONALISM Demonstrates behaviors that reflect a commitment to continuous professional development, ethical practice, understanding and sensitivity to diversity, and a responsible attitude towards patients, the hospital and the medical profession Agree Disagree* SYSTEM BASED PRACTICE Understands the contexts and systems in which health care is provided, and applies this knowledge to improve and optimize health care Req Approval Job request from Hospital/Office Temp Privileges Approval Approval Approval Start Date HR Process HR job posting /screening Medical Affairs PA/NP office Interviews Medical dept /mlp office Recruiting NP/PA’s Exec Dir.- DMC MG notification DMC MG Recruiter Job offer And acceptance Risk MGT NP / PA Training, EMR/CIS Third Party Enrollment and Billing Start NP/PA orientation Final Credentialing Approval from Medical Affairs Best Fit and Benefits • • • • • • • Salaried vs. Hourly Incentives, RVU based, Bonuses CME Sign-on Bonus vs. Retention Bonus Loan Repayment, Immigration Support STD, LTD, Vacation and Sick Leave More rigidity, Less flexibility On boarding and Orientation Department Dynamics • Medicine – Medicine Service – Medicine Subspecialties • Surgery – General Surgery – Surgery Subspecialties • Emergency Medicine • Ambulatory Care Centers Team Dynamics • • • • • PA only NP only PA/NP only PA/NP and Residents PA/NP, Residents, SW, CM, PT/OT, Pharmacy Horizontal continuum of care Staffing, Training, Governance GME, Research, Nursing Model Integrated Health Care Medical and Nursing teams, Advanced Practice Providers, Pharmacy, Administration etc.. Medical Model Productivity, Quality, and Compensation Human Resources Patient Hospital and Health Systems Orientation • None (rare, in very small hospitals) • Formal – 1 to 7days – System, Hospital, Department, EMR • Informal – 30 days to Lifetime • Checklist Req Approval Job request from Hospital/Office Temp Privileges Approval Approval Approval Start Date HR Process HR job posting /screening Medical Affairs Interviews Medical /dept /mlp office Recruiting NP/PA’s Exec Dir.- DMC MG notification DMC MG Recruiter Job offer And acceptance PA/NP office Risk MGT NP / PA Training, EMR/CIS Third Party Enrollment and Billing Start NP/PA orientation Final Credentialing Approval from Medical Affairs Medicine Roles • Participate in all aspects and stages of care: – Front Line: ED, Admissions, Admit H/Ps, Outpt, Inpt and Intra - Op – Function in the Middle: keep the dialogue open and process running smoothly: • LOS and UR management – Inpt setting • Follow up visits in outpt settings • Patient and family education in person and by phone. – Function as “Closers”: to finish the “health care deal”; • Transition of care Surgical Role Pre Operative Role Clinical evaluation to include H/P’s, Diagnostic evaluation, ancillary study review and medical clearances Operative Role First and Second Assist Robotic assistance Facilitating training and education of residents/students Post Operative Role Discharge management Post operative clinical evaluation, participate in the overall care of patients from presentation onward. Develop and maintain social programs Compensation and Provider Enrollment Salary Models • • • • • • • • • Salaried – Exempt Employees No overtime “Moonlighting Opportunity” RVU Based compensation Incentive laden Salaries Productivity and Value provides leverage Market Analysis and Adjustments 92-96% of the 50-65 percentile Critical to Fill positions Provider Enrollenment • Medicare and Medicaid – Provider Enrollment Chain and Ownership system (PECOS) – internet based • CAQH – Council for Affordable Quality Healthcare – Non profit organization formed by various trade associations – Streamline provider credentials with third party billers Provider Enrollment • Third Party Billing • Everyone is different Regulatory Standards and Compliance Law vs. Regulation • Federal laws – Federal agencies and VA • Stark Laws – Limits on practice delivery models with physicians • State Laws vs. Organizational Bylaws • Be aware of laws affecting similar professions • Billing and Reimbursement regulations Physician Certification and 2 Midnight rule • ACA – Calls for all admissions to be certified by a Physician • Verbal toggle of war between Admitting Physician and Ordering Physician • CMS – 2 MN rule – Observation vs. Inpatient Admission Hospital and Professional Physician Billing (Part A and Part B) • • • • Cost Report Employment relationships No “Incident too” in hospital based clinics Billing opportunities – – – – – – H/P, daytime and after hours Subsequent hospital care Consults, Procedures Surgery Discharges Section 6407 of the ACA established a face-to-face encounter requirement for certain items of DME. The law requires that a physician must document that a physician, nurse practitioner, physician assistant, or clinical nurse specialist has had a face-to-face encounter with the patient. The encounter must occur within the 6 months before the order is written for the DME. Clinical Practice Models Horizontal Continuum of Care APRNs (NP, CNM CRNA) Education, research , training , care coordination, pt.assessment, evaluation, Dx Tx, Surgical Assist, Anesthesiology, Pre, Ante and Post care. Enhanced Patient Outcomes and Patient Satisfaction PAs Types of Clinical Practice • Ambulatory Practice – Scribes – Shared – Side by Side – Autonomous • Inpatient Practice • Interoperative Practice • Combined Practice Scribe Practice PATIENT (New and F/U) PA/NP Takes H/P Reports to MD (May or May not dictate) MD repeats all the work of PA/NP and dictates MD Bills at 100% Scribe Practice Pros • PA/NP learns clinical practice, dictate etc. • Acceptable teaching model for new graduates Cons • Physician still has to do full history and exam • Double work/single service/ • Mild incentive for the MD/poor incentive for the PA/NP • Expensive utilization of Providers. Shared Practice Patient (New and F/U) Additional Patients seen by MD PA/NP does complete E/M service, communicates to MD and dictates MD sees patient briefly, and discuses the MDM of the Service. MD bills at 100% Shared Practice Pros • Patient seen by two providers. • Physician does not have to do full exam, • Good incentive for the Physician • Billing is done by Physician • Meets CMS standards • Good teaching and supervisory provisions Cons • +/- Access Improvement • Poor utilization of resources • Low volume days= low productivity from all providers • Mild incentive for the PA/NP Side by Side Practice PATIENT (New, +/- F/u) PATIENT (F/U, +/- New) MD may see New patient as a shared visit MD (in clinic @ the same time) PA/NP does entire E/M service Constant Comm PA/NP bills at 85% if not seen by MD MD bills for his own pt....... and may bill for PA/NP pt....... if seen, at 100% Side by Side Practice Pros • Improved Access • MD can see New, PA/NP can see F/U • Direct access to MD • Easy conversion to Shared Practice • CMS compliance with billing and supervisory regulations • Good incentive for all providers Cons • Not always suitable for New or Consults . • Subject to over booking • Billing and Reimbursement Limitations: Enrollment, 85% • Understanding Legal and Compliance rules. • Administrative ImpactResources and Space Autonomous Practice MD provides indirect supervision and available for consultation if needed. MD free to be in clinic/OR/Procedure. MD gets downstream opportunities from PA/NP Patients (New and F/U) PA /NP does complete E/M, dictates and bills at 85% Autonomous Practice Pros • Best model in ideal setting • Improves Access for all patients • Good incentive • Downstream Feeders • Provider is always busy. • Safety net for last minute add-Ons • Productivity justifies administrative Impact. Cons • Requires well experienced, confident PA/NP • MD may not be present for complex cases • Patients may not see MD on 1st visit • Requires trust and good communication between PA/NP and MD Inpatient Utilization Pros • Prompt/ Direct/Consistent Pt. access. • Autonomous practice • MDs gain confidence in PA/NP • Good learning opportunities Cons • Poor billing / reimbursement • Difficult Productivity measurements • PA/NP may be subjected to “scut” work • Requires well experienced, confident PA/NP • PA/NP has limited view of patients Inpatient Utilization PA/NP Rounds alone or with team, writes Progress notes Discharges Pt. MD Rounds In- Patient RVU Formulas Initial Hosp Visit = 5.82/pt. Sub Hosp Visit = 2.07/pt. Inpatient Consult = 3.26/pt. Ave. 6 pt...... daily = 22.3 RVU Approx. $550/day OR Utilization and ROI Patient (Operation) Surgeon (MD) First Assist (PA/NP) Surgeon Bills at 100% and PA/NP Bills at 85% of First Assist Fee = 16% of the Surgeons Fee If MD fee for VIP = $12,000 PA/NP fee = $1920 Operating Room Utilization Pros • Improved Revenue generation: Surgeon fee and First Assistant fee. • Develop expertise in OR • Comfort and Trust with MD. • Standardization of procedures • Good quality metrics Cons • • • • Can be monotonous Limited view of patient Need experienced provider Specific language is needed in GME programs • Competition with GME trainees. Combined Utilization Pros • Maximum Utilization • Jack of all Trades • Experienced flexible provider • Develop Trust and Confidence with MD . • Maximum Access • Maximum RVU generation. • • • • Cons Potential for PA/NP burn out Master of None Competency measurement is critical Commands higher salary Combined Practice Ambulatory Practice In-Patient Practice OR Practice Experienced PA/NP MD MD MD Recommended Practice Pattern • PA/NP New Grad (<1yr of clinical experience) – – – – Scribe Practice (not favored) Shared Practice (ideal for this group) Side by Side Practice (ideal for fast learner) Inpatient Utilization (ok for fast learner, but need good orientation), • PA/NP (1 – 3 yrs. of clinical experience) – – – – – Shared Practice Side by Side Practice Autonomous Practice Inpatient Utilization (Ongoing evaluation needed) OR Utilization (Direct supervision and training required) • PA/NP (3 - 5yrs of clinical experience) – All practice patterns, Limited direct supervision in OR • PA/NP (>5 yrs. of clinical experience) Productivity, Value, Billing and Reimbursement ROI- Scribe Practice 50% New (2.22 RVUs) 50% Returns (1.48 RVUs) APP @ 440/day 15 pts.. @ 1.85 rvu/pt. APP @ 1 FTE MD@ 1150/day MD @1 FTE RVU’s=27.75/day (approx. $685) Amount is based on Level 3 coding using 2011 Cf of $24.67 ROI- Shared Practice APP @ 1 FTE APP @ 440/day 25 pts. @ 1.85 rvu/pt. 50% New 50% Returns MD@ 1150/day RVUs=46.25/day Approx.. $1141/day MD @ 1 FTE 40% Increase in RVU with 10 additional patients ROI – Side by Side Practice • 15 pts. @ 1.97rvu/pt. • More New, less Return 15 Pts. @ 1.72 rvu/pt. • (More Returns, less new) • MD may see new pt...... as shared MD Available for Direct Consultation APP maintain individual schedule MD • APP @ 440/day • MD @ 1150/day RVU = 55.4/day Approx.. $1366/day 50 ROI - Autonomous Practice 15 Pts. @ 1.82rvu/pt. (New and F/U) MD - Run separate clinic, OR, Research, etc. Revenue Generation dependent on daily activities. RVU = 27.38 + MD Approx.. $675 + MD @85%=$573 APP @ 440/day Inpatient Utilization PA/NP Rounds alone or with team, writes Progress notes Discharges Pt. MD Rounds In- Patient RVU Formulas Initial Hosp Visit = 5.82/pt. Sub Hosp Visit = 2.07/pt. Inpatient Consult = 3.26/pt. Ave. 6 pt...... daily = 22.3 RVU Approx. $550/day OR Utilization and ROI Patient (Operation) Surgeon (MD) First Assist (PA/NP) Surgeon Bills at 100% and PA/NP Bills at 85% of First Assist Fee = 16% of the Surgeons Fee If MD fee for VIP = $12,000 PA/NP fee = $1920 ROI - Combined Practice Ambulatory Practice $625/day In-Patient Practice $550/day OR Practice $1920/day Experienced PA/NP ($440/day) MD MD MD Results – Inpatient Study Business Meeting Collection of 1% Physiological Data 2% Special Reports Telephone 3% Consultation by NPP 3% Analysis of Clinical Data Service Value 8% Team 35.12% Conferences 16% Lunch meeting 0.27% Other 3.29% Cafeteria 3% Other Revenue Generating Activities 1% Other Service Value Activities 3% Subsequent Hospital Care 34% Discharge Management 16% Admission H/P Procedure 4% Documentation Procedures Post Op Care 3% 3% 1% Charts for each area can be seen in the Appendix Revenue Generating 61.59% Results – Inpatient Study IP Activities Revenue Service Occurrences Generating Value Subsequent Hospital Care Discharge Management Admission H/P Post Op Care 245 116 30 22 x x x x Procedures 21 x Procedure Documentation Other Revenue Generating Activities Team Conferences Analysis of Clinical Data Telephone Consultation by NPP Special Reports Collection of Physiological Data Business Meeting Council or Committee Other Service Value Activities 6 x 9 114 55 25 24 12 x 7 19 CPT 2010 Code 99231 - 99233 99238 - 99239 99221 - 99223 99024 Based on procedure code Based on procedure code x x x x x 99366 99090 98966 - 98968 99080 99091 x x N/A Results – Outpatient Study Service Value 38.23% Collection of Physiological Data 1% Telephone Consultation Patient Follow-Up 4% Collection of Student Precepting Physiological Data 2% 1% Research Visit Documentation 3% Team Conference 4% Other Service Value Activities 2% Revenue Generating 59.04% Analysis of Clinical Data 18% Outpatient Visit 32% Outpatient FollowUp 11% Other 1% Other 2.73% Personal Time 1% Cafeteria 1% Other Revenue Generating Activities 0.39% Procedure 2% Procedure Documentation 6% General Documentation 8% Statistical Analysis Outpatient Percent of Time Spent on RVU Activities Inpatient Percent of Time Spent on RVU Activities 80.0% 70.0% 60.0% 50.0% 40.0% 30.0% 20.0% 10.0% 0.0% 80.0% 70.0% 60.0% 50.0% 40.0% 30.0% 20.0% 10.0% 0.0% Medicine Department Surgical Department Compared surgical and medicine departments (inpatient and outpatient combined) No difference found between surgical department activities (p = 0.205) Medicine departments are different (p<0.05) Summary of Results Comparison of Activity Categories 70.00% 60.00% 50.00% 40.00% IP OP 30.00% ED 20.00% OB 10.00% 0.00% Revenue Generating Service Value Other Employee (PA) Engagement and Physician Collaboration Engagement Opportunties • Hospital committee participation – From P/T to Medical Executive committee • • • • • Utilization Resource committee Volunteer opportunities Physician Champion PA’s know about PA’s….. etc. Be Visible – Do not presume that others know Strategic Initiatives • • • • • • PCMH Ambulatory Care centers Centers of Excellence Service Line development Less Inpatient – More Outpatient Transition of Care Quality, Safety and Patient Satisfaction Quality and Safety • 2015 – Reimbursement tied to value not volume (1-2% penalty) • Quality Metrics – Discharge Management – Morbidity and Mortality – Core Measures – AMI, HF, Pneumonia, Stroke and SCIP Patient Satisfaction • HCAPS – Hospital Consumer Survey of Healthcare Providers and systems – 6 Domains –Pain, Communication, Nursing, Hospitals systems – 1 domain – dedicated to Physicians/Providers – NPI used to run reports Summary • PA’s are extremely well positioned – Organizational and Patient Throughput – Transition of Inpatient care to Acute care Management – Transition of Care – Productivity tools – Advocacy to Improve Laws – ACA, Medicaid Expansion – Ideas are needed to achieve maximum Patient Access, satisfaction and maintain quality measures Questions
© Copyright 2026