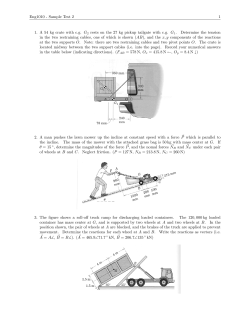
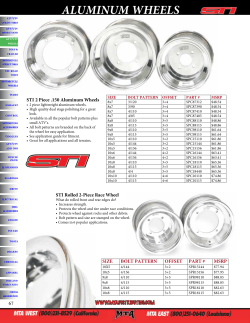
File - Girl Scouts Robotics Teams
VEX Drive Trains J.M. Gabrielse Drive Trains • • • • • • • • • Vocabulary Four Wheel / Six Wheel Skid Steering (Tank Drive) Swerve (Crab) Drive Holonomic (Omni) Drive X Drive H Drive & U Drive Mecanum Drive 2 Speed Transmission J.M. Gabrielse Drive Train A robot’s drive train consists of all of the components used to make the robot move. – Motors – Wheels – Transmissions (gears / sprocket & chain) J.M. Gabrielse Motor VEX 2-Wire Motor 393 • The 2-Wire Motor 393 is the primary actuator used in the VEX Robotics Design System. Build rotational mechanisms, drive bases, rotational joints, conveyor belts - anything that spins can be built using the 2-wire Motor 393. • Strong, steel internal gears. • Can be configured into a "high speed" version. • The 2-Wire Motor 393 does not have an internal motor controller. J.M. Gabrielse Wheels 5" Wheels 4" High Traction Tire VEX has the right tire for any terrain. Here are different size wheel diameters (2.75“, 4“, 5") are available each with a different tread type; choose the perfect wheel for your application. 4" Wheels 2.75" High Traction Wheels Intake Rollers J.M. Gabrielse Omni-Directional Wheels 2.75" Omni Directional Wheel 3.25" OmniDirectional Wheel Omni-Wheels roll forward like normal wheels, but slide sideways with almost no friction (no skidding during turns). Use these wheels to make your robot turn smoothly or build a holonomic drivetrain. 2.75" Omni Directional Wheel 4" OmniDirectional Wheel J.M. Gabrielse Special “Wheels” 6" Wheel Leg Intake Roller J.M. Gabrielse Gear Types standard gears high strength gears differential bevel gears rack & pinion worm gear J.M. Gabrielse Sprockets & Chains Standards Sprockets & Chains High Strength Sprockets & Chains J.M. Gabrielse Four Wheel / Six Wheel Squarebot (4-wheeldrive) 6-wheeldrive J.M. Gabrielse n-Wheel Drive n = how many wheels are connected to motors • Two wheel drive: two wheels are powered • Four wheel drive: four wheels are powered How many motors the robot has doesn’t matter: • The squarebot has only two motors, but it is an example of four wheel drive since all four wheels are connected to motors. J.M. Gabrielse Squarebot J.M. Gabrielse Skid Steering (Tank Drive) The left and right side of the robot are independently powered. To rotate, one side goes forward and the other goes backwards. J.M. Gabrielse Swerve/Crab Drive A swerve drive robot has the ability to rotate its wheels. J.M. Gabrielse Omni-Directional (Omni) Drive aka Holonomic Drive Omni wheels pointing in opposite directions allow the robot to move in any direction or spin. J.M. Gabrielse Omni-Directional (Omni) Drive aka Holonomic Drive formation A drivetrain that can move in any direction at a given moment, without waiting for wheels to steer is called an Omni-Directional Drivetrain. These drivetrains use special wheels, called “omni-wheels”. Omni-wheels are wheels with small rollers around the perimeter that freely spin perpendicular to the wheel’s rolling direction. This means that the wheels can slide sideways with very low friction. J.M. Gabrielse Omni-Directional (Omni) Drive aka Holonomic Drive J.M. Gabrielse Omni-Directional (Omni) Drive This is a true holonomic drive aka X Drive. J.M. Gabrielse H Drive & U Drive Other holonomic drives Four Wheel Drive Square Robot H formation U formation Two Wheel Drive Square Robot U formation J.M. Gabrielse Train Drives J.M. Gabrielse Mecanum Drive The Mecanum drive is also a holonomic drive. J.M. Gabrielse Mecanum Holonomic Drive in Action If video do not play, go to this link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pP8ajNMx84k A VEX robot with a holonomic drive. J.M. Gabrielse 2 Speed Transmission Drive J.M. Gabrielse 2 Speed Transmission Drive J.M. Gabrielse VEX Drive Trains Thanks! J.M. Gabrielse
© Copyright 2026