Permit to Work System
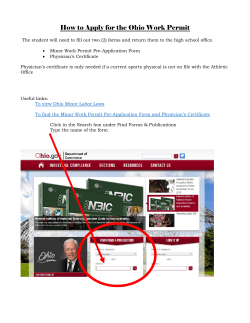
PTWS – Permit Orientation Training Permit to Work System Permit Orientation Training Typical work at our site Introducing: • Sue – who has come to repair the toilet at Z Mana • Fred – who has come to install new electrical socket • Jack – who has come to install a tank for a new site • Lisa – who has come to drop off tobacco at Z Skyway PTW System –PI Training PTWS Requirements At Z, we reckon everybody should work safe and go home safe. The PTWS is: • Risk focused • Specific to Z work activities • Specific to Z site environments • A system to ensure hazards are: - identified, - risk assessed, - controls established and - work undertaken by competent people PTW System –PI Training PTWS– Other HSSE Z policies/systems/rules for HSSE: These include: - HSSE Management System Manual - Life Saving Rules - Working at height policy - Contractor Prequalification - Site specific rules (e.g. ChCh airport depot, Retail sites, construction sites); Standard Operating Procedures - Permit to work system All workers are required to comply with all regulatory requirements and Z policies/systems/rules. PTW System – PI Training PTWS Requirements Authority: • All Z employees, site representatives, contractors and workers, are authorised to stop the work if there is a HSSE concern. • This new PTWS requirements - effective as of 1 May 2014. • Existing requirements remains in force until then. PTW System –PI Training Z’s Life Saving Rules PTW System – PI Training PTWS Applicability • Applies to all workers conducting work for and on behalf of Z on premises operated by Z. • The PTWS is mandatory and applies to non- routine work being completed at workplaces under Z operational control, Retail sites, Mini Tanker Zee sites, work conducted under a Z Construction Contract, or when working on Z owned equipment at sites owned or operated by others. • A permit is required for all permitable activities. PTW System – PI Training Non-routine Work Non-routine Work - Work that is NOT performed regularly in a controlled environment with an approved Standing Operating Procedure or equivalent document. For example non-routine work is a work activity that is, but not limited to, any of the below: • Performed infrequently • Outside of normal duties • Does not have an approved standing operating procedure • Performed in a different way from the standing operating procedure • Has never been performed before PTW System – PI Training Roles Z CEO – overall owner of PTWS HSSE Manager – PTWS custodian, responsible for the implementation of this PTWS. PTWS Orientation Trainer – provides PTWS training. PTWS Administrator –administering documents, records, PTWS website Senior Permit Issuer –monitors operational performance of the PTWS PTW System – PI Training Roles Permit Issuer - prepares, authorises and issues Permits to Work Permit Holder – ensures the permit requirements are put in practice; taking all necessary steps to perform the work in a safe and environmentally sound manner Authorised Gas Tester – tests and confirms the environmental working condition is safe to work in Site Representative - the site staff member who confirms the site environment is safe for the contractor to work; sign contractor on and off site via the Work Clearance Form (WCF) PTW System – PI Training Responsibilities Permit Issuer primary responsibility: By signing the permit the Permit Issuer agrees that they have reviewed and discussed the work scope and required documentation with the Permit Holder, and identified any hazards they are aware of in the permit Permit Holder primary responsibility: By signing the permit the Permit Holder agrees to comply by putting in place the permit and supporting documents requirements and continuously supervising the work PTW System – PI Training Roles Matrix Role Issue permits Self permits Appoints PI PTWS assurance activities system Stop work if necessary HSSE Manager X X X Administrator X X X Trainer X X Senior Permit Issuer X X Permit Issuer X X X Permit Holder X X X X Authorised Gas Tester X X X X Z Site Representative X X X X Workers X X X X Z Staff X X X X Key: X = is not responsible and cannot undertake the task/role = is responsible and can undertake the task/role PTW System – PI Training Activity Risk Levels Work activities are categorised based on risk: Permitable (High Risk) activities Non-permitable: • Medium Risk activities, • Low Risk activities, and • Deliveries Each risk category has different control measure requirements PTW System – PI Training Permitable Activities Permitable Activities - High Risk: • Hot work in hazardous area • Confined space entry • Excavations >/= 1.5 m • Live Electrical Work • Abnormal work or maintenance - overriding/disabling safety critical device • Hazardous substance exposure of high residual risk or greater • Energised high pressure system work to hydrant lines • Live Product Line Work • Work at height exceeding 1.8 metres (refer exclusions) PTW System – PI Training Permitable Activities Permitable Activities continued - High Risk: • Shop roof construction and/or installation • Canopy construction and /or installation • Working on single skin canopy roof • Working on a non-trafficable secondary surface • Tank Removal and/or installation • Demolition – excluding soft strip out • Crane work – excluding standard stock deliveries • Any other activity that has a high or extreme residual risk • Any other activity as determined by Z senior management/permit issuer PTW System – PI Training Non Permitable Medium Risk Activities: • Restricted Space • Excavations between 0.5 metres and 1.5 metres • High pressure system work to a compressed air system • Work at height 0.5 metres or greater (excluding permitable) • Non powered hoist use involving a suspended load • Work off site in roadways • Work on electrical equipment and circuits • Erection structures PTW System – PI Training Non Permitable • Medium Risk Activities continued: • Pump out of product from tanks • Drilling of monitoring wells or soil borings • Hazardous substance exposure of medium residual risk • Hot work outside of the hazardous zone • Any other risk that has a medium residual risk • Any other activity as determined by Z senior management/permit issuer PTW System – PI Training Non Permitable Low Risk: • Any other activity deemed low risk using Z’s risk matrix • E.g. changing the washer on the tap Deliveries: • Delivery only services – drop off and pickup standard deliveries of stock • For example: - Coca cola delivery to retail store or - construction material to a stock pile on site PTW System – PI Training Documentation Documentation for the PTWS is available at www.z.co.nz/ptwinfo. • Work Clearance Form must be completed daily by all Contractors for all work prior to starting work • Safe Work Method Statement must be completed for Permitable activities – high risk prior to obtaining the permit • Job Safety Analysis or equivalent must be completed for Medium risk work prior to performing the work • Permit (permit to work) must be completed by the PermitIssuer for Permitable work. • Certificates where applicable must be used with a Permit PTW System – PI Training Permit Certificates Certificates: • A – Hot Work Certificate • B – Confined Space Certificate • C - Work at Height - roofs, canopies and temporary structures • D – Excavation Certificate • E – Isolation Certificate • F – Tank Removal / Installation Certificate • G - Demolition Certificate • H - Overhead Crane Certificate PTW System – PI Training Work Clearance Form Work Clearance Form: • a process of hazard identification • designed to stop work or trigger the need for a Permit etc • completed by the contractor/worker performing the work in conjunction with the Z Site Representative for manned sites/offices. PTW System – PI Training Z Risk Assessment Matrix CONSEQUENCES LIKELIHOOD 90-100% probability that the event will occur in the next 12 months Almost Certain 1 50-90% probability that the event will occur in the next 12 months Likely 2 25-50% probability that the event will occur in the next 12 months Possible 3 5-25% probability that the event will occur in the next 12 months Unlikely 4 0-5% probability that the event will occur in the next 12 months Rare 5 MEDIUM Risk is generally acceptable provided that the risk is managed. Report Medium residual risks up through the management chain to the appropriate Operational Manager. Risk mitigation actions are to be developed or introduce sufficient controls to lower risk level as soon as possible. Further treatment should be considered. High risks must be reported to the Executive as soon as possible after it has been identified. Requires Z Executive Team management attention and at least quarterly review. Monitoring of control effectiveness is important. Risk without control shall be treated immediately and controls put in place. LOW In general risks rated as Low residual risk should be able to be accepted. Acceptable risks do not require treatment; however the controls, procedures and practices will need periodic monitoring to ensure that the level of the risk has not changed. Environmental impact Further treatment should be considered immediately. Consider ceasing operations created by the risk or revise the strategy to increase the opportunity for treatment. Critical risks must be reported to the Executive and the CEO immediately upon its identification. Critical risks require Z Executive Team level management review and acceptance if the risk is to continue. Monitoring of control effectiveness is critical. Risks without control shall be treated immediately. HIGH Damage and loss CRITICAL Health and injury Reporting and Mitigation Actions Insignificant Minor Moderate Major Extreme A B C D E Injuries with severity up to first aid Medical treatment case , Lost work day cases resulting in cases. restricted work case, & lost work up to 21 days away from work. day cases resulting in up to 7 days away from work. Life-threatening consequences; Permanent total disability (PTD) or injury with irreversible health problems resulting from injury or occupational illness. Fatality or multiple or widespread long-term health impacts. Little damage or threat to health. Minor health effect, fully reversible in the short term Diagnosed occupational illness case, irreversible damage to health; long-term disabilites. Loss of containment (LOC) or loss of primary containment (LOPC) up to 5 litres (except marine oil spill which is of higher risk) Loss of containment (LOC) or loss of primary containment (LOPC) up to 70 litres (except marine oil spill which is of higher risk) Loss of containment (LOC) or loss of primary containment (LOPC) above 70 litres and up to 700 litres (except marine oil spill) Loss of containment (LOC) or loss of primary containment (LOPC) above 700 litres (except marine oil spill) Tier 1 marine oil spill Tier 2 marine oil spill Tier 3 marine oil spill Frequent (1 or 2 per year) exceedance of statutory environmental limits, requiring remediation work of a between 1 week and 1 month. Multiple environmental impacts (more than 2 within 12 months) resulting in remediation work for a period of greater than 1 month and less than 3 months. Medium/Long-term environmental impacts requiring remediation work for a period greater than 3 months. Single exceedance of statutory environmental limits requiring remediation work of no more than 7 days. Damage and remediation < $100K except when process safety related) Damage and remediation $100K Damage and remediation $1M - Damage and remediation $10M Damage and remediation > - $1M (except when process $10M (except when process - $50M (except when process $50M safety related) safety related) safety related) Incident results in temporary Temporary loss of local shutdown of infrastructure for less infrastructure (less than a week) than 4 hours. Tier 2 process safety incident Tier 1 process safety incident Loss of major infrastructure for period of 1 month. Loss of major infrastructure for a period of greater than 1 month and less than 3 months. Loss of major infrastructure for a period greater than 3 months SWMS/JSA Hierarchy of Controls Hierarchy of controls for determining control measures in order: 1. Eliminate the hazard e.g. by changing the work 2. Substitute e.g. change material/equipment to one with less hazards 3. Isolate the hazard e.g. by providing a form of barrier 4. Engineering Controls e.g. physical guards, structures, stop buttons 5. Administration Controls e.g. SWMS, Procedures, Training 6. PPE e.g. by providing protective equipment PTW System – PI Training Hierarchy of Fall Protection Controls Fall Protection hierarchy of controls for determining work at height control measures in order: 1. Eliminate the work at height e.g. by changing the work 2. Work from permanent guard rail 3. Work from temporary guard rail or elevating working platform (scissor lift/boom 4. Work with fall restraint means - PPE 5. Work with fall arrest means - PPE PTW System – PI Training Permit Validity Permit is valid for: • a specific activity, site, within a specific period of time. • only issued for a maximum of 5 consecutive calendar days. • applied for in advance of the work – ideally 10 working days • issued immediately prior to the start of the permitable work • renewed via the Work Clearance Form each day by Permit Holder • expires after 5 days regardless of the activity Self Permits • No one is allowed to issue a Permit to themselves PTW System – PI Training Permit Validity Remote Permits A remote Permit can ONLY be issued if ALL of the following criteria is satisfied: - The PI has knowledge of the site or has reliable drawings and site data - The PI has a detailed knowledge of the task and activities to be permitted - The PI has experience working with the Contractor and individual PH. - The Z senior permit issuer or delegate confirms remote permitting is appropriate and the above criteria have been met. PTW System – PI Training Permit Validity Contractor Permitting • A PI may issue a Permit to another person in the same Contractor organisation. Blanket Permits • Blanket Permits are not permitted. Derogations and standard operating procedure approval • SOP more appropriate for repetitive, routine activities. • Refer to PTWS Manual for procedure to obtain derogation approval Changes in Conditions • Stop work and notify Permit Issuer PTW System – PI Training Training and Competency Permit Issuer Training Roles Training Courses / Certification Completed Permit Issuer Z PTWS Orientation quiz 90% pass, (can retest up to 3 times) Permit Issuer 2 Supervised Permits and recommended as PI Permit Issuer 4 years work experience for relevant activities they want to issue Permits for Permit Issuer Permit Issuer - Hot Work Permit Issuer - Confined Space Permit Issuer - Excavation Permit Issuer - Isolation Permit Issuer - Work at Height Permit Holder (Recommend) Permit Holder (Recommend) Key Personnel Z Key Personnel Contractors (Recommended) Work Clearance Form - Z Site Rep/Site Manager US 17590 Hot Work Certificate Issuer Confined Space Certificate Issuer Excavation Certificate Issuer Isolation Certificate Electrical / Mechanical Issuer Working at Height Issuer Z PTWS Orientation US 17588 Z PTWS Orientation attendance (record by COD pass on to them) Z PTWS Orientation attendance Z PTWS site rep Litmos module (records in Litmos) PTW System – PI Training Training and Competency Permit Issuer Training – specific activity requirements Permit Type Confined Space Qualification US 3058 Gas testing in high risk industries US 25510 Atmospheric testing US 17599 Confined Space planning US 18426 Hazard Identification Hot Work US 3058 Gas testing in high risk industries US 25510 Atmospheric testing US 25043 Energy isolation Work at Height US 17600 Safe work practices for working at heights US 25045 Employ height safety equipment in the workplace Excavation US 14611 Excavation hazards and traffic control US 10543 Protect underground services during excavation and reinstatement Electrical / Mechanical Isolation US 25043 Energy isolation PTW System – PI Training PTWS Documentation Available • www.z.co.nz/ptwinfo Contacts • Andy Velasquez • [email protected] • Tracy – PTWS Orientation Trainer • [email protected] PTW System – PI Training Transition Timeline PTWS transitional requirements timeframe : • 1 May 14 - effective date for all criteria except: - 30 Jun 14 - 1 Jul 14 Updated Z PTWS Orientation training completed SWMS template compliance by Permit Holder - 1 May 15 Updated Safetrac training completed by Z employees - 1 May 15 Updated legal documents - 1 May 15 Full Permit Issuer competency requirements compliance (plan to meet requirements and progress evidence to be submitted to the PTWS Trainer by 30 Jun 14, 1 Dec 14, 1 Mar 15 - 1 May 15 PTW System – PI Training Full compliance to PTWS Manual Typical work at our site Introducing: • Sue – who has come to repair the toilet at Z Mana • Fred – who has come to install new electrical socket • Jack – who has come to install a tank for a new site • Lisa – who has come to drop off tobacco at Z Skyway PTW System –PI Training Tank installation Tank installation Tank installation Tank installation Tank installation Tank installation Tank installation
© Copyright 2026