Tech Talent Study - Austin Technology Council
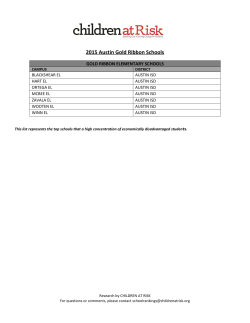
Tech Talent Study Preliminary Findings Brian Kelsey Civic Analytics LLC May 2015 Purpose • Quantify perceptions of tech “skills gap” and create a baseline for future assessment. • Identify critical skill (core) occupations in tech workforce necessary for growth. • Provide input on employer needs to education and training providers. • Inform ATC’s tech talent work plan focused on strengthening public-private partnerships. 2 Austin is among fastest growing tech markets in U.S. Tech Jobs % Tech 2013-14 Projected Job Growth, ‘14-’20 Raleigh 57,838 9.5% 9.4% Seattle Durham-Chapel Hill 32,920 10.4% 7.2% Salt Lake City San Jose 294,848 27.0% 6.4% San Francisco San Francisco 236,525 9.7% 5.7% Raleigh 11.4% Austin 108,310 11.1% 5.3% Austin 11.0% Boston 266,409 9.6% 4.0% Seattle 175,670 8.6% 3.8% 43,686 6.1% 2.6% Dallas 207,012 5.8% 2.2% Washington DC 295,106 8.8% -2.4% Durham-Chapel Hill 6,736,083 4.4% 2.6% Dallas Salt Lake City Nation Source: EMSI. Includes self-employment. Comparison regions selected based on anecdotal information of markets Austin likely competes with for tech talent. No statistical procedure was used to select comparisons. 16.0% 15.5% 14.8% Washington DC 9.9% San Jose 8.9% Boston 8.5% 6.0% 5.0% 3 Secondary Data Summary: Overview of Austin’s Tech Talent Landscape How are we defining “tech”? ATC generally follows the methodology used by TECNA/CompTIA/TechAmerica for their annual Cyberstates report.* It currently includes 49 industries. Austin’s largest tech sectors ranked by minimum of $1 billion contribution to regional gross domestic product: #1 #2 #3 #4 #5 Computer & Peripheral Equipment IT Services & Applications Internet & Telecommunications Semiconductors Software • $22.3 billion in value-added (GDP) • 4,182 establishments • 108,310 jobs (120,257 by 2020) • 67,546 “core” jobs in total tech talent labor pool in Austin (66% in tech) • ~6,000 avg monthly job postings for core occupations – ~2,500 to 3,500 avg core job openings expected per year in Austin, 2014-2024* • 1,539 core degrees awarded (2013) Source: EMSI, 2014. GDP is an estimate for 2013. Jobs include self-employment. *Job postings are unique, de-duplicated average monthly openings advertised online during March 2014-March 2015 and include job openings at tech and non-tech businesses (i.e. total demand for core technical workers). See full Tech Talent Report for details and explanation of methodology used for estimates. 4 Employer Survey • Web-based survey conducted in April 2015. • Sent via email to ATC contact database. • Included tech and life sciences firms. • 52 responses (8% response rate). • 87% respondents HQ in Austin. 5 Employer Survey Overall Perceptions Tech companies in Austin account for 108,310 jobs. Is Austin meeting current and future workforce needs? Source: EMSI, 2014. Includes self-employment. Survey Respondents (52 ATC Members) Employees Number % Total 21 * Software 1 to 10 19 37% IT Services/Apps 11 to 50 16 31% Semiconductors 51 to 125 8 15% E-Commerce 8 4 3 126 to 500 6 12% Life Sciences 3 501+ 3 6% Internet/Telecom 3 Total 52 100% Other Source: ATC Tech Talent Employer Survey. *Software is overrepresented in sample compared to its share of tech sector as measured by number of companies or jobs. Findings may change w/ higher response rate or more representative sample. 10 7 70% reported moderate-significant difficulty in hiring but majority confident in ability to grow in Austin Overall, how difficult is it to find qualified people to fill job openings at your company in Austin? How confident are you that Austin will be able to meet your future workforce demand? Extremely difficult Extremely confident 8 Very difficult 5 Very confident 9 8 Confident Difficult 16 19 Somewhat confident Somewhat difficult Not difficult 12 3 ≥ Difficult: 70% Source: ATC Tech Talent Employer Survey. 15 Not confident I don’t know 5 2 ≥ Confident: 57% 8 Smaller companies may be feeling disproportionate impact of perceived shortage – “2nd Stage” effect? Overall, how difficult is it to find qualified people to fill job openings at your company in Austin? 1 = Not difficult 2 = Somewhat difficult 3 = Difficult 4 = Very difficult 5 = Extremely difficult How confident are you that Austin will be able to meet your future workforce demand? 1 = Not confident 2 = Somewhat confident 3 = Confident 4 = Very confident 5 = Extremely confident 0 = I don’t know 31% respondents reported that unfilled jobs having harmful to extremely harmful effect. Not harmful/didn’t know: 33% Employees Respondents Difficulty Confidence Number* Average Average 1 to 10 19 3.1 2.8 11 to 50 15 3.5 2.5 51 to 125 7 3.6 2.4 126 to 500 6 2.5 2.8 501+ 3 2.3 3.7 50 3.1 2.7 Total (Ans) Source: ATC Tech Talent Employer Survey. Second-stage firms have reached a growth stage of $1M to $50M in receipts and 10 to 100 employees. For more on second-stage company research see Edward Lowe Foundation at http://edwardlowe.org/who-we-serve/secondstage. *Complete responses only (n = 50). Differences not statistically significant. 9 Employer Survey Core Occupations There are more than 250 different types of occupations reflected in Austin’s tech workforce, including 19 core occupations foundational to Austin’s tech talent pipeline based on required technical skills, high volume of job postings, and projected employment growth. Developers likely driving perceptions of shortages but could be “spiky” by industry & growth stage How difficult is it to find qualified people to fill job openings in Austin? Occupation 1 = Not difficult 3 = Difficult 5 = Extremely difficult 2 = Somewhat difficult 4 = Very difficult N/A = Not applicable Average N/A Occupation Average N/A Comp & Info Research Scientists 3.2 65% Electronics Engineers 2.7 76% Information Security Analysts 3.2 65% Network & Comp Systems Admins 2.7 52% Software Developers, Apps 3.2 18% Computer Hardware Engineers 2.5 78% Software Developers, Systems 3.2 29% Computer & Info Systems Managers 2.4 51% Computer Network Architects 3.1 55% Computer Miscellaneous (QA, testers) 2.3 51% Electrical Engineers 3.1 71% Industrial Engineers 2.3 82% Computer Programmers 2.9 40% Comp Network Support Specialists 2.0 61% Database Administrators 2.8 51% Electrical/Electronics Engin Techs 2.0 76% Web Developers 2.8 41% Computer User Support Specialists 1.8 53% Computer Systems Analysts 2.7 69% Developers accounted for 43% of reported job openings. Source: ATC Tech Talent Employer Survey. Scores were averaged from number of respondents providing a rating or answering N/A (i.e. blank responses were excluded). 11 Employer Survey Supply-Side Issues Are secondary & postsecondary programs aligned to needs of employers in Austin? Are postsecondary institutions graduating enough students to meet labor demand? Tech skills should be CTE priority in K-12 but current offerings in Austin not aligned w/ employer needs Career & tech education (CTE) Employer Needs Avg 1.9 44% JavaScript 3.8 Cisco Net Associate (CCNA) 1.8 47% Linux 3.5 A+ 1.8 50% Java 3.4 Cisco Entry Net Tech (CCENT) 1.7 47% C++ 3.1 60% of respondents reported that all certifications currently offered in Austin area school districts were not applicable or not important. Internet & Comp Core Cert (IC3) 1.7 48% PHP 3.1 Sun Cert Java Associate (SCJA) 1.6 47% Python 3.1 Adobe Dreamweaver 1.5 48% Ruby 3.0 Internet Webmaster (CIW) 1.5 48% C# 2.9 Others: Lisp 1.7/40% Go 1.5/45% Strata IT Fundamentals 1.3 55% Perl 2.6 TestOut PC Pro 1.3 54% Haskell 2.0 1 = Not important 2 = Somewhat important 3 = Important 4 = Very important 5 = Extremely important N/A = Not applicable Write-ins: Objective-C Swift ISD Certifications Offered Avg Network+ Source: ATC Tech Talent Employer Survey. List of certifications offered in Austin area school districts was provided by E3 Alliance (October 2014). Scores were averaged from number of respondents providing a rating or answering N/A (i.e. blank responses were excluded). N/A 13 Hiring every local graduate of core related programs would still fall short of meeting core labor demand Postsecondary institutions in Austin awarded 1,539 degrees (2013) in programs preparing students for critical skill (core) occupations. Core Related Programs Degrees Awarded The University of Texas at Austin 836 Texas State University 269 ~450 bachelor’s degrees awarded in comp & information science & related fields. 20% of total is associate’s degrees/certifications. ITT Technical Institute-Austin 126 Austin Community College District 123 The Art Institute of Austin 58 The number of students graduating with core credentials is growing slowly, ~70 per year. CyberTex Institute of Technology 56 Saint Edward's University 38 MakerSquare & other non-traditional educ & training programs not reflected in data. Huston-Tillotson University 10 Strayer University-Texas 10 6,075 avg monthly job postings online for core positions at Austin companies.* ~2,500-3,500 core openings expected per year, 2014-2024. Southwestern University 8 Various 5 Total 1,539 Source: EMSI, 2013 (latest available). Includes only data reported to the National Center for Education Statistics and therefore may not be comprehensive. *Job postings are unique, de-duplicated average monthly openings advertised online during March 2014-March 2015 and include job openings at tech and non-tech businesses (i.e. total demand for core technical workers). See full report for details & methodology. 14 Austin is trailing other leading regional tech markets in # of degrees awarded from core tech programs Study Follow-Up: No single, authoritative source for collecting, validating, and tracking postsecondary data for labor market research exists in Austin. This is one area of opportunity for ATC & its members. See Recommendations for more on this. Washington DC 8,811 Boston 4,705 Dallas 3,923 Seattle 3,600 Salt Lake City 2,209 San Jose 2,158 San Francisco 2,152 Raleigh 1,744 Austin Durham-Chapel Hill 1,539 635 Source: EMSI, 2013 (latest available). Includes only data reported to the National Center for Education Statistics and therefore may not be comprehensive. Nationally, there were 228,731 degrees awarded in core tech occupation programs in 2013. Figures include only accredited postsecondary institutions that report data to National Center for Education Statistics (i.e. no data for MakerSquare, etc.). 15 Job Postings for Core Occupations (March 2015) 37% respondents reported outsourcing work to firms outside Austin to mitigate impact of unfilled jobs. Study Follow-Up: What is impact on Austin’s economic development of outsourcing work outside Austin as a result of talent shortages at tech firms? 422 124 377 104 171 94 148 85 133 80 124 78 Source: ATC Tech Talent Employer Survey, EMSI. Job postings are unique, de-duplicated average monthly openings advertised online in March 2015 and include job openings at tech and non-tech businesses (i.e. total demand for core technical workers). Only top 12 companies listed here based on number of job postings. More than 50 companies in Austin had at least 25 job postings as of March 2015. 16 Employer Survey Demand-Side Issues What are the opportunities & challenges associated with strengthening Austin’s tech talent pipeline? Tech Talent Pipeline Opportunities • 67% respondents estimated at least 50% of new hires are already living in Austin – and nearly half respondents said at least 75%. • 33% of respondents reported employees w/ certificates and associate’s degrees – not all tech jobs require advanced degrees. • 71% respondents hire student interns and 48% respondents reported preference for hiring more local graduates. Source: ATC Tech Talent Employer Survey. 18 Tech Talent Pipeline Opportunities • 92% respondents support outside education & training for employees (38% respondents subsidize tuition and/or training costs). • Only 1 respondent could name a program in Austin that provides employers w/ publiclyfunded job training assistance – how can we increase awareness & participation? • 27% respondents are active in schools, job shadowing, and/or STEM non-profits. Source: ATC Tech Talent Employer Survey. 19 Tech Talent Pipeline Challenges • 42% of respondents require at least 5 years of work experience for job applicants to be considered qualified for technical jobs. • 25% of respondents don’t hire recent college graduates and 24% don’t offer internships. • Only 12% of respondents reported that they consider recent college graduates qualified, or don’t ask for min years work experience. Source: ATC Tech Talent Employer Survey. 20 Austin’s challenges may be impacting tech recruitment Salary Traffic Housing Why do candidates living outside Austin typically turn down job offers? Source: ATC Tech Talent Employer Survey. Transit Of the respondents who ask candidates why they decline job offers in Austin, 47% said that low salary was a factor. Nearly 1 in 5 respondents do not ask candidates why they decline job offers in Austin. 21 Cost of living is (still) lower in Austin, but salary gaps are significant with other leading regional markets Table shows wage comparisons for core occupation (19) jobs in tech as of 2013 (latest available). Bottom 10% and Top 10% refer to the wage level signifying that 10% of all jobs pay below (or above). Wages do not include benefits. Study Follow-Up: We need better grasp on impact of lower salaries in Austin to understand how talent supply is affected – e.g., where are most job offer declines occurring, early-career, mid, senior? Median Wage Bottom 10% Top 10% San Jose $116,314 $74,110 $178,693 Seattle $102,066 $66,706 $148,824 Washington DC $101,712 $62,899 $154,565 San Francisco $100,547 $63,398 $155,480 Boston $96,616 $61,797 $148,387 Durham-Chapel Hill $88,691 $56,992 $135,886 Raleigh $83,054 $53,955 $123,386 Dallas $81,848 $50,710 $127,150 Austin $80,454 $49,150 $127,442 Salt Lake City $75,254 $47,424 $111,155 National $81,037 $49,275 $129,480 Source: EMSI, U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. Data is for 2013. Includes self-employment. Wages do not include benefits. 22 Summary Observations • Tech talent shortage not at critical level yet overall, but may be for second-stage firms – a serious concern for Austin growth model. • Graduates of core programs are increasing, but slowly – capacity for education/training may be adequate, but what about demand? • Significant mismatch in certifications offered in K-12 and skills demanded by tech firms in Austin – greater alignment only possible w/ stronger public-private partnerships. 23 Recommendations • We need more data to make more informed conclusions – repeat employer survey to get better response rate & more representative sample of all tech companies in Austin. • Collect and integrate completion data from MakerSquare & other non-traditional educ and training providers to improve estimate for locally-produced tech talent supply. 24 Recommendations • Explore feasibility of partnering with higher education institution (Ray Marshall Center) to create a Tech Talent Institute to improve access to data & sustain effort. • Convene K-12 & postsecondary education & workforce development partners to review and validate study findings & develop plan for achieving greater alignment w/ hiring needs of local tech companies. 25 Recommendations • Develop an employer-driven strategy & peerto-peer marketing campaign to increase the number of employers in Austin who are able to invest in work-study experience – it’s only way to increase # of work-ready graduates. • Work through ATC Foundation to identify & prioritize federal & state programs that can subsidize STEM education/training projects. 26 Recommendations • Engage in discussions about how proposed Innovation District anchored by UT Medical School could be leveraged as testing ground for pilot tech talent initiatives. • Develop and commit to regional tech talent strategy w/ SMART goals for improving the pipeline – we’ll be having this conversation again five years from now otherwise. 27 7600 Burnet Road, Suite 108 Austin, Texas 78757 @civicanalytics http://civicanalytics.com
© Copyright 2026