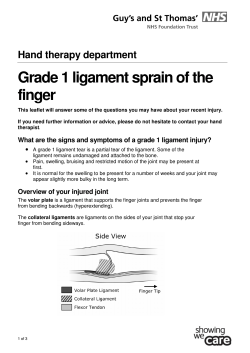
Posterior and Retinaculum Ligament Sprains
Unraveling the Mystery of Ankle Pain #3: Posterior and Retinaculum Ligament Sprains 1 Instructor: Ben Benjamin, Ph.D. 2 1 Instructor: Ben Benjamin, Ph.D. 3 Webinar Goals • Explore the Assessment and Treatment of Posterior and Retinaculum Ankle Ligament Sprains 4 2 Logistics • Time: 60 minutes • Schedule: • Presentation 30-40 minutes • Questions 15–20 minutes • Ongoing questions: Use Question box. If I don’t get to your question, ask me on my Dr Ben Benjamin Facebook page after the webinar. • Get a pen and paper please 5 Pretest 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Pain behind the ankle on the posterior lateral aspect indicates a: a.) calcaneofibular ligament injury, b.) fibularis tendon or tibialis posterior injury, c.) posterior talofibular ligament injury, or d.) tibialis posterior tendon injury The posterior talofibular ligament: a.) doesn’t have an effective assessment test, b.) never gets injured, c.) doesn’t connect any bones, or d.) is connected to the anterior talofibular ligament Posterior ligament sprains are: a.) the least common of the lateral ligament sprains, b.) the most common of the lateral ligament sprains, c.) more common than calcaneofibular ligament sprains, or d.) easy to detect The cruciate crural ligament or retinaculum holds: a.) the nerves of the foot in place, b.) the flexor hallucis in place, c.) many of the extensor tendons of the foot in place, or d.) the ankle joint in place How many cruciate crural ligaments are there? a.) Five, b.) Three, c.) Two, or d.) Six The retinaculum is often injured along with: a.) a deltoid ligament, b.) a cuboid ligament, c.) a medial ankle sprain or with falling, or d.) a lateral ankle sprain or with something heavy dropped on the foot 6 3 Anatomy 7 The Posterior Talofibular Ligaments 8 4 The Primary Ankle Ligaments 9 Assessment Posterior Talofibular Ligament 10 5 Assessment History and Tests for the Posterior Talofibular Ligament 1. Posterior Palpation in Dorsiflexion 2. Passive dorsiflexion 3. Passive plantarflexion 4. Heat test 5. Heel raises 11 Finding the Posterior Talofibular Ligament 12 6 Posterior Palpation in Dorsiflexion 13 Passive Dorsiflexion 14 7 Passive Plantar Flexion 15 Heat Test 16 8 Achilles Tendon Differentiation 17 Alignment Check 18 9 Assessment Tests Extensor Retinaculum/Cruciate Crural Ligament 19 Four Toe Resisted Extension 20 10 Four Toe Resisted Extension with Palpation 21 Theory 22 11 Posterior Talofibular Ligament Sprain Positive Tests MI: Posterior Palpation in Dorsiflexion AUX: Passive Dorsiflexion of the ankle is painful and often limited AUX: Passive Plantarflexion of the ankle is painful and often limited AUX: Heat Test is positive. The injured ankle is often hot or at least warmer then the other one 23 Posterior Talofibular Ligament 24 12 Posterior Ankle Sprains 25 Persistent Swelling 13 What to watch out for confusion Fibularis Tendon 27 Persistent Swelling 14 Treatment 30 15 Posterior Talofibular Ligament Friction Friction Therapy 31 Friction Therapy of Crucial Crural Ligament Extensor Retinaculum Ligament Friction 32 16 Myofascial Therapy 33 Massage Therapy 34 17 Exercise Therapy 35 Exercise Therapy 36 18 Exercise Therapy 37 Exercise Therapy 38 19 Exercise Therapy 39 Exercise Therapy 40 20 Exercise Therapy 41 Exercise Therapy Lateral Stretch Medial Stretch Anterior Stretch 42 21 Questions Facebook.com/DrBenBenjamin 43 Post-test 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Pain behind the ankle on the posterior lateral aspect indicates a: a.) calcaneofibular ligament injury, b.) fibularis tendon or tibialis posterior injury, c.) posterior talofibular ligament injury, or d.) tibialis posterior tendon injury The posterior talofibular ligament: a.) doesn’t have an effective assessment test, b.) never gets injured, c.) doesn’t connect any bones, or d.) is connected to the anterior talofibular ligament Posterior ligament sprains are: a.) the least common of the lateral ligament sprains, b.) the most common of the lateral ligament sprains, c.) more common than calcaneofibular ligament sprains, or d.) easy to detect The cruciate crural ligament or retinaculum holds: a.) the nerves of the foot in place, b.) the flexor hallucis in place, c.) many of the extensor tendons of the foot in place, or d.) the ankle joint in place How many cruciate crural ligaments are there? a.) Five, b.) Three, c.) Two, or d.) Six The retinaculum is often injured along with: a.) a deltoid ligament, b.) a cuboid ligament, c.) a medial ankle sprain or with falling, or d.) a lateral ankle sprain or with something heavy dropped on the foot 44 22
© Copyright 2026