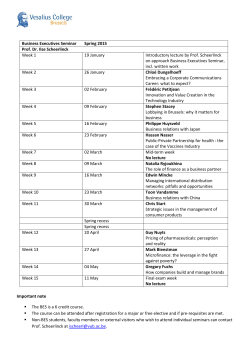
CONFERENCE SCHEDULE
2015 International Conference on Control, Automation and Robotics (ICCAR 2015) 2015 The 7th International Conference on Future Computer and Communication (ICFCC 2015) 2015 The 2nd International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Applications (ICIEA 2015) *ICCAR 2015 conference papers will be published in conference proceeding, which will not be available on conference site, and will be delivered to authors’ address after conference. *ICIEA 2015 conference papers are selected to be published in several journals, due to the publication schedule, only a few papers will be published before the conference, most paper are scheduled to be published after the conference, we wil post your journal to your address when it published. *ICFCC 2015 conference papers are selected to be published in several journals, according to the publication schedule, which will not be available on conference site, and will be delivered to authors’ address after conference. -2- We are pleased to welcome you to the 2015 SCIEI Singapore conferecnes, which will takes place at Nanyang Technological University from May 20-22, 2015. After several rounds review procedure, the program committee accepted those papers to be published in Journals and conference proceedings. We wish to express our sincere appreciation to all the individulas who have contribute to ICCAR 2015, ICIEA 2015 and ICFCC 2015 conference in various ways. Special thanks are extended to our colleagues in program committee for their thorough review of all the submissions, which is vital to the success of the conference, and also to the members in the organizing committee and the volunteers who had delicated their time and efforts in planning, promoting, organizing and helping the conference. Last but not least, our speacial thanks goes to invited keynote speakers as well as all the authors for contributing their latest research to the conference. This conference program is highlighed by three keynote speakers: Prof. Maode Ma, from Nanyang Technological University, Singapore; Prof. Yang Xiao, from The University of Alabama, Tuscaloosa, USA and Dr. Girija Chetty, from University of Canberra, Canberra, Australia. One best presentation will be selected from each session, evaluated from: Originality; Applicability; Technical Merit; PPT; English. The best one will be announced at the end of each Session, and awarded the certificate after each session. The winners’ photos will be updated on SCIEI official website: www.sciei.org. Singapore, officially the Republic of Singapore, is an island country with beautiful landscape and multi-cutural lifes. We hope that your stay in Singapore will be enriching and memorable! The technical program will send you back home motivated, enthusiastic, and full of innovative ideas. We wish you a success conference and enjoyable visit in Singapore. Alice Wu Science and Engineering Institute -3- International Advisory Committee Prof. Alexander Rotshtein, Dept. of Industrial Engineering & Management, Jerusalem College of Technology, Jerusalem, Israel Conference Chair Prof. Yang Xiao, The University of Alabama, Tuscaloosa, USA Prof. Girija.Chetty, University of Canberra, Australia Prof. Maode Ma, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore Program Chair Prof.Soumaya Yacout, Department of Mathematics and Industrial Engineering, École Polytechnique de Montréal, Canada. (Workshop Chair of ICIEA) Prof. Thumrongrat Amornraksa, King Mongkut’s University of Technology Thonburi, Thailand Assoc. Prof.S. H. Choi, University of Hong Kong Associate Professor Fernando Moreira da Silva/Faculty o fArchitecture of the Technical University of Lisbon/Portugal Prof. Pyung Hoi Koo/Pukyong National University, Korea Prof.An-Chen Lee, National Chiao Tung University, Taiwan Technical Committee Assoc.Prof. Muhammad Abaidullah Anwar/Al Ghurair University Dubai, UAE Prof. S. Mohammad Bagher Malaek/ Sharif University of Technology in Tehran – Iran Prof.King-Chu Hung, National Kaohsiung First University of Science and Technology, Taiwan Prof.Mozammel Huq Azad Khan, East West University, Bangladesh Dr.Amirhossein Sajadi, Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Department of Case Western Reserve University, OH, USA Dr. Sutep Tongngam, National Institute of Development Administration (NIDA), Thailand Dr. P.SIVAPRAKASH, Department of Mechanical Engineering, A.S.L.Pauls College of Engineering& Technology, Coimbatore, India. Assistant Prof.Pankaj Bhambri, Guru Nanak Dev Engineering College, India, Assistant. Prof., Sureshkumar M.S, Sri Ramakrishna Engineering College, India. Prof. Dr Bora I Kumova, İzmir Institute of Technology, Turkey Prof. Amala V. Rajan, Higher Colleges of Technology – Dubai Women’s College, UAE Prof. Javad Dodangeh, University of Technology Sydney, Australia Prof. Heonchang Yu, Department of Computer Science Education, Korea University Yong Mao, MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, USA Shudong Fang, University of Auckland, New Zealand Prof. Bandit Suksawat, King Mongkut's University of Technology North Bangkok. Thailand prof. Hiroshi Takami, Shibaura Institute of Technology, Department of Electrical Engineering, Japan. -4- Nanyang Executive Centre 50 Nanyang Avenue, Singapore, 639798 Tel. +65 6794 7860 or email to [email protected] http://www.ntu.edu.sg/NEC/Pages/default.aspx GMT/UTC +8 Get on at Changi Airport (CG2)transfer at Tanah Merah (EW4) take the train all the way to Boon Lay (EW27) or Pioneer station(EW28) NTU (journey time 1h30m) Notice: NTU shuttle bus service: Campus Rider is a free shuttle bus service to and from Pioneer MRT station. From Boon Lay station, Services 179 & 199 will take you in to NTU. From Pioneer station, hop on the Campus Rider which stops in front of Blk 649A. For more, please click: http://www.streetdirectory.com/travel/ http://www.ntu.edu.sg/has/Transportation/Pages/GettingToNTU.aspx By Taxi: Total Time: 32 min, Approx Fare $35.40. There are various taxi companies operating in Singapore. Comprehensive information on Singapore taxis is available at www.taxisingapore.com. Singapore is hot and humid all year-round, with temperatures usually reaching over 30°C. You should be prepared for rain at any time, which can be torrential but usually brief. The currency for the Singapore dollar (SGD), 1 Yuan is equal to 100 points. The paper money face value has 2 Yuan, 5 Yuan, 10 Yuan, 50 Yuan, 100 Yuan, 500 Yuan, 1000 Yuan, 10000 Yuan; The coin has 5 point, 10 point, 20 point, 50 point, 1 Yuan. -5- You are not allowed to smoke in all air-conditioned places, such as malls and eateries. There are designated smoking areas in some entertainment outlets and open-air eateries. You can drink water straight from the tap as the water in Singapore passes World Health Organization standards. You can also buy bottled water easily. Know more, please click: http://www.yoursingapore.com/en.html. Emergency (police, fire, ambulance) : 999/995/995 Weather report: 0065-65427788 Tourist Complaint Hotline: 18007363366 Voltage : 220-240 volts AC (50 cycles) -6- Oral Presentations Timing: a maximum of 15 minutes total, including speaking time and discussion. Please make sure your presentation is well timed. Please keep in mind that the program is full and that the speaker after you would like their allocated time available to them. You can use CD or USB flash drive (memory stick), and make sure you scanned viruses in your own computer. Each speaker is required to meet her/his session chair in the corresponding session rooms 10 minutes before the session starts and copy the slide file(PPT or PDF) to the computer, It is suggested that you email a copy of your presentation to your personal inbox as a backup. If for some reason the files can’t be accessed from your flash drive, you will be able to download them to the computer from your email. Please note that each session room will be equipped with a LCD projector, screen, point device, microphone, and a laptop with general presentation software such as Microsoft PowerPoint and Adobe Reader. Please make sure that your files are compatible and readable with our operation system by using commonly used fronts and symbols. If you plan to use your own computer, please try the connection and make sure it works before your presentation. Movies: If your PowerPoint files contain movies please make sure that they are well formatted and connected to the main files. Poster Presentations Maximum poster size is 36 inches wide by 48 inches high (3 ft. x 4 ft.) Posters are required to be condensed and attractive. The characters should be large enough so that they are visible from 1 meter apart. Please note that during your poster session, the author should stay by your poster paper to explain and discuss your paper with visiting delegates. Dress code Please wearing formal clothes or national characteristics of clothing -7- “Security Enhancements for Communication Networks in Smart Grid” Abstract: The ever growing demand of energy all over the world has compelled a shift from the traditional power distribution system to a more sustainable and efficient system incorporating the advances of Information technology and communication and networking technologies. This new energy infrastructure is envisioned not only to provide more optimal energy consumption and better real-time power requirement assessment but also to incorporate renewable energy generation sources at both consumer and provider sides for environment friendly power generation. In this talk, we investigate the security aspects of the home area networks (HANs) and neighborhood area networks (NANs) to support the operation of the smart grid in detail. We explore the vulnerabilities of the HANs and NANs under various malicious attacks and review current major solutions to protect the networks from those attacks. We further present an example to show the possible security enhancement over the NANs. About Prof. Maode Ma: Dr. Maode Ma received his Ph.D. degree in computer science from Hong Kong University of Science and Technology in 1999. Now, Dr. Ma is an Associate Professor in the School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering at Nanyang Technological University in Singapore. He has extensive research interests including wireless networking and network security. He has led and/or participated in 18 research projects funded by government, industry, military and universities in various countries. He has been a general chair, technical symposium chair, tutorial chair, publication chair, publicity chair and session chair for more than 70 international conferences. He has been a member of the technical program committees for more than 180 international conferences. Dr. Ma has more than 260 international academic publications including more than 110 journal papers and 150 conference papers. He currently serves as the Editor-in-Chief of International Journal of Computer and Communication Engineering and International Journal of Electronic Transport. He also serves as a Senior Editor for IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, and an Associate Editor for International Journal of Network and Computer Applications, International Journal of Security and Communication Networks, International Journal of Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing and International Journal of Communication Systems. He had been an Associate Editor for IEEE Communications Letters from 2003 to 2011. Dr. Ma is the Fellow of IET and a senior member of IEEE Communication Society and IEEE Education Society. He is the Chair of the IEEE Education Society, Singapore Chapter. He is serving as an IEEE Communication Society Distinguished Lecturer. -8- “Flow-Net Accountable Logging and Applications” Abstract: Accountability implies that any entity should be held responsible for its own specific action or behavior so that the entity is part of larger chains of accountability. One of the goals of accountability is that once an event has transpired, the events that took place are traceable so that the causes can be determined afterward. The poor accountability provided by today’s computers and networks wastes a great deal of money and effort. This is due to the simple fact that today’s computing and network infrastructure was not built with accountability in mind. In this talk we introduce our previous work: accountable logging methodology called flow-net. We apply this methodology to many applications ranging from operating system design to computer networks. About Prof. Yang Xiao: Dr. Yang Xiao is a full Professor of Department of Computer Science at the University of Alabama, Tuscaloosa, AL, USA. His current research interests include communications/networks and computer/network security. He has published over 200 SCI-indexed journal papers and over 200 EI indexed refereed conference papers and book chapters related to these research areas. Dr. Xiao’s papers have more than 12000 citations and his h-index is 56, based on Google scholar on Aug. 1 2014. Dr. Xiao was listed among 800 computer science researchers with h-index larger than or equal to 40. His research has been supported by the U.S. NSF, U.S. Army Research, GENI, Fleet Industrial Supply Center-San Diego, FIATECH, and The University of Alabama’s Research Grants Committee. Dr. Xiao was a Voting Member of IEEE 802.11 Working Group from 2001 to 2004, involving IEEE 802.11 (WIFI) standardization work. He is a Fellow of IET (FIET). He served/serves as a Panelist for the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF), The Global Environment for Network Innovations (GENI), Canada Foundation for Innovation’s Telecommunications expert committee, and the American Institute of Biological Sciences, as well as a Referee/Reviewer for many national and international funding agencies. He currently serves as Editor-in-Chief for International Journal of Security and Networks and International Journal of Sensor Networks. He had (s) been an Editorial Board or Associate Editor for 15 international journals, including IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, during 2014 to 2015, IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, during 2007 to 2009, and IEEE Communications Survey and Tutorials, during 2007 to 2014. He served (s) as a Guest Editor for over 20 times for different international journals, including IEEE Network , IEEE Wireless Communications , and ACM/Springer Mobile Networks and Applications (MONET). Dr. Xiao has delivered over 20 keynote speeches at international conferences around the world and gave more than 60 invited talks at different international institutes. -9- “” Abstract: About Dr. Girija Chetty: Dr. Girija Chetty has a Bachelors and Masters degree in Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, and PhD in Information Sciences and Engineering from Australia. She has more than 25 years of experience in Industry, Research and Teaching from Universities and Research and Development Companies from India and Australia, and has held several leadership positions including Head of Software Engineering and Computer Science, and Course Director for Master of Computing Course. Currently, she is the Head of Multimodal Systems and Information Fusion Group in University of Canberra, Australia, and leads a research group with several PhD students, Post Docs, research assistants and regular International and National visiting researchers. She is a Senior Member of IEEE, USA, and senior member of Australian Computer Society, and her research interests are in the area of multimodal systems, computer vision, pattern recognition and image processing. She has published extensively with more than 120 fully refereed publications in several invited book chapters, edited books, high quality conference and journals, and she is in the editorial boards, technical review committees and regular reviewer for several IEEE, Elsevier and IET journals in Computer Vision, Pattern Recognition and Image Processing. - 10 - May 20th| Wednesday| Morning Registration (Lobby) & PPT copy Add&Tel: Nanyang Executive Centre, 50 Nanyang Avenue, Singapore, 639798, Tel. +65 6794 7860 Notes: 10:00am-17:00pm *Collecting conference materials *Delegates will get the certificate at the registration desk. *The organizer won't provide accommodation, and we suggest you make an early reservation. May 20th| Wednesday| Afternoon Room A Opening Remarks: Prof. Maode Ma, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore Keynote Speech 1: Prof. Yang Xiao, The University of Alabama, Tuscaloosa, USA Keynote Speech 2: Dr. Girija Chetty, University of Canberra, Canberra, Australia COFFEE BREAK & GROUP PHOTO Prof. Maode Ma, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore 14:30pm-14:35pm 14:35pm-15:15pm 15:15pm-15:55pm 15:55pm-16:35pm 16:35pm-17:15pm May 21st| Thursday| Morning Room B Session 1A: Electronics and Information Technology-6 COFFEE BREAK Session 1B: Electronics and Information Technology-6 9:00am-10:30am 10:30am-10:45am 10:45am-12:15am Room C Session 2A: Machinery Manufacturing and Industrial Engineering 9:00am-10:30am COFFEE BREAK 10:30am-10:45am Session 2B: Machinery Manufacturing and Industrial Engineering 10:45am-12:15am Lunch at Fusion Spoon 12:15am-13:00pm May 21st| Thursday| Afternoon Room B Session 3: Communication and Information System-10 COFFEE BREAK 15:30pm-15:45pm Session 4: Robot and Control System-16 15:45pm-19:30pm Room C Session 5: Image and Video Processing Technology-10 COFFEE BREAK Session 6: Computer and Information Technology-16 Dinner at Fusion Spoon May 22nd 13:00pm-15:30pm Half-day Visit to NTU 13:00pm-15:30pm 15:30pm-15:45pm 15:45pm-19:30pm 19:30pm-20:30pm 9:30am-12:00am - 11 - Venue: Room A Chair: Prof. Maode Ma, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore Time: 14:30pm-17:15pm 14:30pm-14:35pm 14:35pm-15:15pm 15:15pm-15:55pm Opening Remarks Prof. Maode Ma, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore Keynote Speech I Prof. Yang Xiao, The University of Alabama, Tuscaloosa, USA “Flow-Net Accountable Logging and Applications” Keynote Speech II Dr. Girija Chetty, University of Canberra, Canberra, Australia “” 15:55pm-16:35pm Coffee Break & Group Photo 16:35pm-17:15pm Keynote Speech III Prof. Maode Ma, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore “Security Enhancements for Communication Networks in Smart Grid” *The Group Photo will be updated on the conference webpage and SCIEI official website: www.sciei.org **One best presentation will be selected from each session, the best one will be announced and awarded the certificate after each session, and the winners’ photos will be updated on SCIEI official website: www.sciei.org. ***Best Presentation will be evaluated from: Originality; Applicability; Technical Merit; PPT; English. **** Please arrive at the conference room 10 minutes earlier before the session starts, copy your PPT to the laptop. - 12 - Venue: Room B Chair: Prof. Yang Xiao, The University of Alabama, Tuscaloosa, USA Time: 9:00am-10:30am One-Class Classification by Local Target Selection Mr. Younghoon Kim, Seoung Bum Kim Korea University, Republic of Korea One-class classification plays an important role in outlier and novelty detection. Traditional one-class classification algorithms determine a decision boundary that identifies the property of the target data. In this work, we propose a novel algorithm for one-class classification based on the mixed integer quadratic programming method. The proposed method minimizes the radius of a spherically shaped boundary subject to the number of target data being equal to a constant value specified by users. By modifying this constant value, users can exactly control the proportion of target data described by the spherically shaped boundary. Moreover, analogous to Support Vector Classifier, the boundary can be made flexible by using some kernel functions. The usefulness of the proposed method was demonstrated through experiments with simulated data. A Research Paper Recommendation based on Citation Networks Ms. Jieun Son, SeoungBum Kim Korea University, Republic of Korea Recommendations have attracted growing attentions from both academia and industry. Compared to other applications such as books, movies, and music, relatively few studies have been conducted on the recommendation for research papers. Typically, researchers filter the huge mass of existing research papers to find out relevant publications associated with their research. However, this filtering process is generally time consuming because the number of research paper published is exponentially growing. To address these problems, past studies have focused on finding better recommendations for searching research papers. Citation analysis, content analysis, and social networks have been utilized for better paper recommendations. Of these, algorithms based on citation analysis have been widely used. However, citation analysis-based techniques have some drawbacks. Their analysis depends solely on co-citation and bibliographic coupling. These techniques count the number of links that directly cite or are cited at single-level networks. Therefore, recently published papers do not tend to be recommended because of their fewer citations. In this paper, we propose a recommendation algorithm for research papers by combining citation and networks analyses. The proposed algorithm uses the distance and weight of links in a multiple-level simultaneous citation networks to measure the relationship among the papers. The multiple-level citation network can simultaneously consider mutual relationships among the papers which are connected indirectly. Further, the proposed algorithm takes into account various measures that characterize the network (e.g., degree centrality, closeness centrality, betweenness centrality) to determine the core papers. The comparison results based on real data showed that proposed algorithm outperformed the existing ones from ‘Google Scholar’ - 14 - and ‘SCOPUS’. Group-wise Variable Selection for Virtual Metrology Modeling of Process Signals Mr. Chanhee Park, Seoung Bum Kim Korea University,Republic of Korea Lot to lot process control is widely implemented in semiconductor manufacturing processes and it is being replaced with wafer to wafer control to achieve tighter process control. Virtual methodology (VM) has been developed to perform wafer to wafer control economically. VM model can be constructed based upon not only traditional process variables, but also advanced spectroscopic signal data. Analysis of spectroscopic signals involves combinations of multiple samples collected over time, each with a large number of features (wavelengths). This leads to a huge number of data points and a situation that challenges analytical and computational capabilities. Furthermore, the spectroscopic signals include several groups of features which are highly correlated with each other. To simplify such a complexity in spectroscopic signals while taking into account their correlation structure, appropriate data reduction techniques are required. In this study, we propose to use regularized regression methods including group lasso and sparse group lasso that have desired effect of group-wise variable selection for virtual modeling of spectroscopic signals. Experiments on data from real semiconductor manufacturing processes demonstrated the usefulness and applicability of the group lasso and sparse group lasso models. A Hybrid Monitoring Method for Robust Multivariate Process Control Mr. Sung Ho Park and Seoung Bum Kim Korea University, Republic of Korea Control chart, the most representative statistical process control technique, can be considered to share a common goal with classification algorithms in that both of them aim at estimating the decision boundaries that classify the observations into either in-control or the out-of-control classes. The main limitation that conventional control chart cannot take advantage of using out-of-control information can be eased by integrating classification algorithms with existing monitoring techniques. In the present study, we proposed a hybrid scheme that combines T2 control chart and binary class classification algorithms by eliciting the nature of class distributions. Simulation and real case studies demonstrated that the proposed method can be effectively used for monitoring multivariate processes when their distributions are nonnormally distributed or unknown. Ethics Responsibilities of Undergraduate students at INU Dr. Khader Musbah Titi Irbid National University, Jordan The world is changing in all our life aspects, new information technologies are effective software tools in helping individuals and organization. However, the power of these technologies such as the Internet can be used for bad as well as for good. Software engineers make decisions about when a product is free of errors and safe and thus ready to be released and used by individuals or companies. People make decisions about access to and use of private information. People make - 15 - decision either to buy an original copy or just a copied version of a book or a CD. These decisions have to be fair and honest. The main aim of this research is to conduct a survey to study some ethical issues related to actions and decisions of students at Irbid National University in Jordan. Modified Delphi-AHP Method Based on Minimum-Cost Consensus Model and Vague Set Theory for Road Junction Control Method Evaluation Criteria Selection Mr. P. K. Kwok and Henry Y.K. Lau The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong Group decision making is an important symbol of a democratic society. It helps to explore problems from wider angles and the results generated will usually be widely accepted by the public. Yet, there are drawbacks of group decision making. It usually takes more time and resources than individual decision making and also sometimes the one with a louder voice will dominate the discussion. In this paper, a group decision making framework derived that are based on the modified Delphi-AHP method based on minimum-cost consensus model (MCCM) and vague set theory is proposed to gather different experts’ opinions on the evaluation criteria and their relative importance for choosing a suitable road junction control method in a multi-objectives environment. It is believed that the proposed framework can help to strengthen the advantages and to solve the above drawbacks of group decision making. A numerical case study is proposed to demonstrate the use of this framework. Study of a Three-Phase Bridgeless Flyback PFC Mr. Boyang Chen, Lei Li, and Xinran Zhang Nanjing University of Science and Technology, China Traditional power factor correction (PFC) circuit, which limits the power density is often passive components. With the development of power electronics technology, high-frequency, modular, miniaturization is the inevitable trend of development. In pursuit of efficiency and the use of bridgeless topology brought about more complex control method compared with the conventional topology. In this paper a three-phase bridgeless Flyback PFC topology is studied, the use of three-phase input, which greatly reduce the storage capacity of the capacitor, working in discontinuous current mode (DCM), using fixed duty cycle control to achieve unity power factor, with a simple and efficient, simple control advantages .The simulation results from a 250W universal input prototype are given to verify the effectiveness of the analysis. A Novel Half-Bridge Converter for Battery Charging-Discharging Mr.Yifan Zhou, Zhixiang Liu, Lei Li, Peiyao Wu Nanjing University of Science and Technology, China Charging-discharging converter for battery cells is widely used in modern industry to measure the performance of the battery. With the rapid development of the technology of switching power supply today, converters with high efficiency and small size are becoming more and more important. This paper proposes a novel half-bridge converter for battery charging-discharging based on Thevenin equivalent model with high efficiency and simplified structure. The control - 16 - circuit and detecting circuit are also analyzed in the main system. The simulation results from two series of 28V, 800Ah lead-acid battery cells are given to verify the stability and reliability of the converter. - 17 - Venue: Room B Chair: Prof. Yang Xiao, The University of Alabama, Tuscaloosa, USA Time: 10:45am-12:15am Online Identification and Internal Model Control for Regulating Hemodynamic Variables in Congestive Heart Failure Patient Ms. Arpita Bhattacharjee, Ashoke Sutradhar Indian Institute of Engineering Science and Technology, Shibpur, India This paper deals with one of the most challenging task of simultaneous control of two hemodynamic variables by the infusion of sensitive cardiac drugs in congestive heart failure (CHF) patients. A nonparametric internal model control (IMC) algorithm along with an integral control action has been proposed in this work for regulating two hemodynamic variables, the mean arterial pressure (MAP) and the cardiac output (CO) by simultaneous administration of two drugs – sodium nitroprusside (SNP) and dopamine (DPM). The two-input two-output physiological model of CHF patient is identified online by solving Volterra kernels from the input-output data of the physiological process. FFTs are taken on respective time domain kernels to obtain the Volterra transfer function (VTF) of the multivariable system. The internal model control algorithm is developed using this VTF. The integral control action has been combined with IMC for set-point tracking. Using this closed loop control algorithm MAP and CO reaches the steady state value within a very short time with the minimum infusion of highly sensitive cardiac drugs in presence of actuator and sensor noises. Recommendation of Personalized Surveillance Interval of Colonoscopy via Survival Analysis Ms. Jayeon Gu, Eun Sun Kim, Seoung Bum Kim Korea University,Republic of Korea A colonoscopy is important because it detects the presence of polyps in the colon that can lead to colon cancer. How often one needs to repeat a colonoscopy may depend on various factors. The main purpose of this study is to determine personalized surveillance interval of colonoscopy based on characteristics of patients including their clinical information. The clustering analysis using a partitioning around medoids algorithm was conducted on 626 patients who had a medical examination at Korea University Anam Hospital and found several subgroups of patients. For each cluster, we then performed survival analysis that provides the probability of having polyps according to the number of days until next visit. The results of survival analysis indicated that different survival distributions exist among different patients’ groups. We believe that the procedure proposed in this study can provide the patients with personalized medical information about how often they need to repeat a colonoscopy. A Disease Diagnostic Assistant System using DTI and Extreme Learning Machine Dr. Wang shuqiang, Shen Yanyan, Hu Jinxing, Zeng Dewei Institute of Advanced Computing and Digital Engineering, Shenzhen Institute of Advanced - 18 - Technology, Chinese Academy of Science, China There is a growing interest in applying diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) to the evaluation of brain and spinal cord related disease. In the present study, the DTI data and extreme learning machine were employed to identify the levels with cervical spondylotic myelopathy (CSM) in spinal cord. In this work, there are 40 volunteers including 20 healthy people and 20 patients with CSM ranging from 24 to 81 years old. Experiment results show that the extreme learning machine based classifier performs well in detecting the patients with CSM (accuracy 93.6%, sensitivity: 91.2%, specificity 94.7%). The current work reveals the potential of using diffusion tensor imaging in conjunction with extreme learning machine to automate the classification of healthy subjects and subjects with brain and spinal cord related disease. Regularized Classification for Discrimination of Mass Spectra from Bacterial Strains Mr. Jaehong Yu, Seoung Bum Kim Korea University,Republic of Korea Mass spectrometry is widely used in biomedical fields for diagnosing diseases or monitoring pathogenic activities. Analyzing mass spectra usually involves combinations of multiple samples, each with a large number of features. Dimensionality reduction is important in coping with this complexity. Dimensionality reduction can generally be achieved by feature extraction or feature selection techniques. Feature extraction methods transform the original features to extract new features. In general, the first few features from feature extraction methods are sufficient to account for the original data. However, these transformed features do not provide any clear interpretations with respect to the original features because they are linear combinations of a large number of original features. Feature selection methods directly identify a subset of features that are most predictive of a given response feature. However, most of traditional feature selection methods do not take into account the correlation structure of the features. Some feature selection methods consider the relationships among the features but they tend to only eliminate the redundant features not irrelevant ones. In this study, we propose to use a logistic lasso algorithm as an effective feature selection algorithm in high-dimensional mass spectra. A logistic lasso algorithm automatically selects significant features while taking into account the correlation structure of the features and uses them to construct classification models. The usefulness and accuracy of the logistic lasso model were demonstrated by the mass spectra from bacteria in which the purpose of this analysis is to identify the important features that differentiate between different strains of bacteria. Implementation of Wireless Electrocardiogram Monitoring System Thanapong Chaichana, Yutthana Pititeeraphab, Manas Sangworasil, Takenobu Masuura, Ms.Nutchanat Kitsongsang Rangsit University, Thailand We describe the design and development of wireless electrocardiogram monitoring system to meet the biomedical needs. Our system is able to acquire, display and record the patient’s real time electrocardiogram (ECG) data. Patient data received from this system can be further used for analysis of abnormal heart rate and new clinical applications. System hardware comprises of an electrode as part of signal input, signal conditioning components for manipulating signal, the 8051 microcontroller unit to perform signal processing and wireless communication module. Software was developed in Visual Basic 6 to record and visualise ECG signal in real time. Therefore, we implemented ECG report system, and this can be used to advanced ECG study. - 19 - These instructions give you basic guidelines for preparing camera-ready papers. Implementation of Electric Wheelchair with Microcontroller Yutthana Pititeeraphab, Thanapong Chaichana, Nuntachai Thongpance, Ms. Pimchanok Rungrueng Rangsit University, Thailand This paper presents the design of electric wheelchair. We build machine that is capable to attach with any traditional wheelchair, and to control its movement semi-automatically. This helps handicapped person who has difficult body-movement to be able to travel simply. The machine comprises of power-driven system including a metal tube frame, wheels, motor, brake and accelerator, and electronic control department based H-bridge circuit and programmable microcontroller with the ATmega168. Software was developed in C++ for programming microcontroller. Running test was on flat straight and slope courses. Results showed that it achieved a maximum load is 100 kilograms with a top speed of 8.42 kilometres per hour, and the average of battery lifetime is up to 1 hour and 30 minutes. Thus, we build a cost effective machine to provide an opportunity to translate conventional wheelchair to be an electric wheelchair. A Novel Control Sheme To Reduce Storage Capacitor Of Flyback PFC Converter Mr. Boyang Chen, Lei Li, Xinran Zhang Nanjing University of Science and Technology, China DCM Flyback PFC converter is mainly used in medium and low power applications, having such advantages as zero-current turning on of switch, no reverse recovery of diode and high PF. At the time power electronics widely used today, passive components volume limits the improvement of power density. This paper derives the expressions of the switching turn-on time and the input current of DCM Flyback PFC converter, and based on which, a variable duty control is proposed so as to make the energy storage capacitor reduce to the original 65.6% at the same voltage ripple level while PF is not less than 0.9.The simulation results from a 200W universal input prototype are given to verify the effectiveness of the analysis. Equalization Chargers Using Parallel- or Series-Parallel-Resonant Inverter for Series-Connected Supercapacitors Mr. Yifan Zhou and Lei Li Nanjing University of Science and Technology, China A equalization charger using parallel-or series-parallel-resonant inverter for series-connected supercapacitors is proposed in this paper, according to low voltage characteristic of supercapacitor. This topology reduces a large number switches and only has resonant structure including some diodes and a single transformer. In addition, because of the characteristic of parallel resonant inverter, the equalization charging current can be limited in the numerical value. So the topology can work steadily without feedback control. The control circuit is greatly simplified. The simulation results from a 200W universal input prototype are given to verify the effectiveness of the analysis and the merits and demerits of this topology also are introduced. - 20 - Venue: Room C Chair: Time: 9:00am-10:30am Dynamic Buffer Management for Raw Material Supply in the Footwear Industry Prof. John Reyes, Kevin Alvarez, Rosa Vazquez Universidad Técnica de Ambato, Ecuador In this paper, the application of inventory buffers is proposed as a management tool for the supply of raw material in the footwear industry. This allows to increase competitiveness and a significant decrease in investment in materials stored in the warehouses. This technique based on the holistic view will achieve the global optimum of the system giving importance to factors that prevent success of companies. In this sense, it is identified that the market demand is the system´s constraint for the development of the master production schedule. Considering this, it is necessary to concentrate all the materials in the central warehouse to establish an optimum inventory levels or buffers. Using a technique of colors materials ordering program is regularly reviewed through dynamic buffer management. As a result, the model improves the way how inventory of materials in the footwear industries is managed for resupply. Giving a priority to the materials low in stock. This generates 18,7 % of annual saving in inventory costs. Application of AHP in the Analysis of Flexible Manufacturing System Assoc. Prof. Sandeep Singhal, Rajveer Singh, and Parveen Sharma National Institute of Technology, India In recent years, the area of manufacturing has become more intensive and competitive. Now-a-days all the service fields are attempting to find ways to improve their flexibility by changing their manufacturing strategy. The main aim of Flexible Manufacturing is to adopt effective and efficient strategies to fulfill the demands of consumers. In this highly competitive global market the industries are forced to focus more on increasing productivity and quality coupled with decreasing cost by right selection of efficient manufacturing system. Present study highlights a logical procedure to select the effective flexible manufacturing process in terms of various aspects as quality improvement, faster delivery, profitability, etc. by using Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP) method. The AHP is used in flexible manufacturing as a potential decision making tool. The primary requirement of AHP is to make a matrix of the variables for their paired comparison. There are a lot of AHP processes, but here only the two of them i.e. Additive Normalization Method and Geometric Mean Method are being used by analyzing the flexible manufacturing with respect to micro and macro variables. A Novel Multifunctional Energy Storage System in Industrial Distribution Network Mr. Tong Wu, George You Zhou, Jianna Niu National Institute of Clean and Low Carbon Energy, Beijing, China In order to meet the increasing safety demands from coal industry and mining company, a lead - 21 - acid and lithium iron phosphate(LFP) battery energy storage based megawatt level multifunctional emergency power station is designed and developed for a famous coal mine in Inner Mongolia, China. The major function of system is: when the local power grid works normally, the developed system will play the reactive power compensation function instead of traditional static capacitor; when the local grid occurs failure, the energy storage based emergency power station will provides stable power to the extremely critical loads of coal mine for at least 30min. Besides, the proposed energy storage system also can play the ‘peak shaving’ and distributed new energy generation smoothing according to the customer requirement. The This paper firstly describes the system integration design and major functions; secondly introduce the power conversion system design and NI software/hardware based central control unit; thirdly analyzes the solutions for increasing system lifetime including novel harmonics control for charging & discharging and battery regular online maintenance strategy; finally provides the simulation and test results which demonstrate the correctness of system design, software/hardware development and integration. The business value evaluation shows the high market potential of the proposed system in China and worldwide. Adjustable Robust Planning for Multi-Period Production and Distribution Systems Assit. Prof. Byung Do Chung, Jae Sang Lee Sungkyunkwan Univsersity, Republic of Korea For many companies, the uncertainty is one of the challenging issues and the consideration of uncertain demand is critically important, especially when demand history is not available. This paper aims to develop a robust planning model to solve a multi-period production and distribution problem under demand uncertainty. In this paper, no probability distribution is presumed and a box-type uncertainty set is assumed. In other words, we only need a range of uncertain demand at each time period, which is different from the traditional stochastic programming approach. First, we develop a deterministic linear programming model and introduce a set of uncertain parameters. The problem is reformulated as a tractable robust counterpart (RC). Next, the robust counterpart is extended to the affinly adjustable robust counterpart (AARC) by assuming a specific form of linear decision rules. The AARC is also a linear programming model and easily solved with a commercial solver. Finally, a simulation experiments are conducted in order to compare the performance of the deterministic model, RC and AARC. The results show that the AARC solution outperforms the others in terms of mean, standard deviation and worst-case cost. A Novel Embedded Energy Storage System for Diesel Engine Test Platform Ms. Jianna Niu, George You Zhou, Tong Wu National Institute of Clean and Low Carbon Energy, Beijing, China As is known to all, components of locomotive will be abraded, deformed or damaged after a period of running. In order to ensure the locomotive running stably and extend its lifetime, periodic maintenance and testing must be performed. At present, as a means of load test, water resistance test has been widely used in locomotive diesel engine test field. According to conservative estimates, the static continuous test will accounts 15 ~ 30% of the energy production through the whole engine life. It will not only cause great waste of energy, but also cause severe corrosion of metal plate. This paper proposes a novel embedded energy storage system used in an energy harvesting demonstration project which is implemented to storage the energy produced during diesel engine test process. This paper also describes the project overall design and the function of key equipment. System simulation and experiment results show that - 22 - this system is stable and reliable during energy harvesting. Importance of Product Life Cycle Management in Design and Development of a Product Dr. R. Henry Xavier, H.Donna Xavier Vel Tech High Tech Dr. Rangarajan Dr. Sakunthala Engineering College, India. Product life cycle management (PLM) is a process of managing the entire life cycle of a product from its conception through design and manufacture to service and disposal. PLM integrates people, data, processes and business systems. In this paper, a full fledge knowledge about product life cycle management is given. The history of PLM, Benefits of PLM, Phases of PLM, Importance of PLM, in design and development of a product, Various modern software and tools used in design and development of a product however complex has been discussed. Also various applications with a special reference to aircraft industry have been discussed. AHP Based Methodology for Selecting Section of Subway Construction in Thailand Mr. Phikid Vayophad and Warapoj Meethom Department of Industrial Engineering, King Mongkut's University of Technology North Bangkok, Thailand Safe workplace in the subway construction make a major contribution to personnel safety. Safety of the section in the subway construction is often guaranteed or enhanced by work complexity, machine and equipment, accident statistic, accident severity, work environment, and number of workers for these projects. The choice of a sector safety risk in the subway construction involves multiple criteria decision making and ranking of alternatives according to often contrasting performance measures. In this paper, a systematic methodology for selecting a type of sector of subway construction at risk possible to accidents aimed at reducing physical environmental hazards of type of sector in subway construction is presented. The method at first includes a classification of type of sector in the subway construction, then introduces an exhaustive list of 6 factors useful to judge the suitability of selecting a type of sector in the subway construction for comparison purposes. A comparison of relative importance between the rating criteria is then carried out in the framework of the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) decision making approach, based on expert opinion, allowing unambiguous prioritization of the above decision making factors. Limitation and future work of this study are also discussed. The Deteriorations of Productivity Output During Unforeseen Disruption Mr. John M. Ikome, MG. Kanakana, S.P Ayodeji and M.E Ikome Tshwane University of Technology/Department of Industrial Engineering, Pretoria, South Africa. In most real-world environments, production scheduling is an ongoing process where the presence of a variety of unforeseen disruptions is usually inevitable, and continually forces reconsideration and revision of pre-established schedules. Many of the approaches developed to solve the problem of production scheduling are often unfeasible in real-world environments, and the near-optimal schedules with respect to the estimated data may become obsolete when they are released to the production lines or shop floor. This paper outlines the impact of unforeseen - 23 - disruptions that affect manufacturing systems during production and being able to cope or react to this determines a company’s out-put and profitability. The theory of multifactor productivity and line balancing are employed to determine how disruption affect productivity out-put. The result reveals that, when disruption occurs continuously with time, the total productivity out-put decreases and on the other hand, requiring more resources to meet up with the planned capacity demand. Two stage supply chain enterprises’ production and reduction decision-making mechanism research considering emission trading Mr. Jianan Sun, Zhongdong Xiao, Guanghui Zhou Xi’an Jiaotong University, China Economic activities should reflect scarce and efficient allocation of environmental resources after carbon emission quota has become a kind of resource. These low-carbon economy characteristics profoundly change the cost structure, profit model and market risk compared with the traditional supply chain. This paper puts forward the topic ‘the research of two stage supply chain enterprises’ production and reduction decision-making mechanism considering emission trading’. The paper compares performance of the different decision modes in supply chain on carbon emission. Analyze the members profit and the whole supply chain profit by different two modes. Through investigating how upstream and downstream enterprises in the supply chain choose cooperation reduction strategy while they are facing environmental regulation, we can get their profits and reduction efficiencies in two different decision-making models. It can be obtained that in the centralized decision-making case, both their profit and reduction efficiency are optimal. The result shows that in the process of low carbonization of manufacturing enterprises, government should aim at the enterprises which emit larger carbon emission and grab from the source of supply chain firstly. And also enterprises must reduce their optimal output in order to reduce their total carbon emissions. - 24 - Venue: Room C Chair: Time: 10:45am-12:15am Defective Reduction from Solder-Paste Strains on a Flexible Printed Circuit Mr. Chantach Luxnanan, Oran Kittithreerapronchai Department of Industrial Engineering, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, Thailand During the last decades, consumer electronic devices have been integrated with our everyday activities. One component that helps these devices to achieve with their small sizes and versatile functions is a flexible printed circuit (FPC). Each FPC consists of various electronic components on a flexible conducted surface using a special assembling process, called surface mount technology (SMT). Within the SMT process, the most significant defective is the solder-paste strain on pads of a FPC, which accounts for 0.28% of total products manufactured. Such defective products cannot be reworked. Small group techniques revealed that the cleaning routine of a solder printing machine is one of the root causes. Followed the six-sigma approach, the defective rate is selected as the main response for hypothesis tests and design of experiment. Determining of the optimal parameters in the cleaning routine using two-level full factorial design with two replications suggest same direction and 80 cm per second cleaning speed without vacuum as optimal setting. The result after one month of implementation showed that the defective rate was reduced to 0.04%. A Responsive Framework for Optimal Advertising Policy in the Digital Music Market Ms. Tobey H. Ko and Henry Y.K. Lau The University of Hong Kong,Hong Kong This paper proposes a novel responsive framework to help the record label in making profit maximizing advertising decisions in the product pre-release phase. We describe a market of potential consumers where the consumer behaviors are backed by an interactive Markov Chain, in which the periodic advertising activities carried out by the record label varies the population frequencies of the potential consumer market. We demonstrate the working of the proposed framework through an illustrative numerical example, results of the study show the proposed framework's superiority both in terms of reach to potential consumers and the net profit it brings. Thermal and Fluid Characteristics of an Oval Finned-Tube Heat Exchanger for Large Diameters Mr. Kyungjin Bae, Dongan Cha, Ohkyung Kwon Korea Institute of Industrial Technology, Korea The objectives of this paper are to investigate heat transfer and pressure drop for oval finned-tube heat exchanger with large diameters used in a textile machine dryer. Numerical tests using ANSYS CFX are performed for four different parameters; tube size, fin pitch, transverse - 25 - tube pitch and longitudinal tube pitch. It was found that the Nusselt number linearly increased with increasing Reynolds number, but friction factor slightly decreased with increasing Reynolds number. It was also found that the variation of longitudinal tube pitch made a little effect on the Nusselt number and friction factor than other parameters below 2.0 and 2.5%, respectively. Nonparametric Multivariate Control Chart Based on Statistical Learning Algorithms Ms. Seulki Lee, Seoung Bum Kim Korea University,Republic of Korea Statistical process control techniques have been widely used in many industries to improve process capabilities by reducing variations and diagnosing processes. In modern manufacturing systems containing the complexity and variability of processes, appropriate control chart techniques that can efficiently handle the nonnormal processes are required. Furthermore, in real manufacturing fields, process changes occur frequently because of various factors such as product and set-point changes, seasonal variations and sensor drifting. However, traditional control chart schemes cannot accommodate all possible future condition of the process because they are formulated based on the information of the early process stage. In recent years, several attempts have been made to convert a support vector data description (SVDD) algorithm into control charts for monitoring a nonnormally-distributed processes. . In the present paper, we propose a novel control chart based on an incremental SVDD and a bootstrap method that can handle not only nonnormal in-control observations, but also time-varying processes. Incremental SVDD is used to update the SVDD boundary and a bootstrap technique is used to establish the control limits. Time-varying process monitoring charts should accommodate the normal gradual changes but detect real process faults. The proposed control chart allows efficient model updates and the detection of out-of-control signals simultaneously. The effectiveness and applicability of the proposed chart was demonstrated through experiments with simulated data and real data from a TFT-LCD manufacturing process. Forecasting Construction Equipment Demand using Regularized Regression Mr. Hyung Rok Do, Jae Hong Yu, Jieun Son, Kye Hyun Choi, Jong Hyung Lim, Seoung Bum Kim Korea University,Republic of Korea Successful implementation of demand forecasting in construction equipment market enables corporations to cope with uncertainty in the business environments. The information from forecasting can be used in various fields including production planning, research and development, inventory control, and sales management. In this study, we propose to use regularized regression models to predict the demand for construction machinery based upon its sales and operational information. Lasso and L1-norm support vector regression were used as predictive models to forecast the demand and to identify the significant variables for prediction. The usefulness and applicability of two regularized regression models were demonstrated by real operational data and sales data from one of the leading construction equipment companies in South Korea. - 26 - Work Wearing Protective Clothing in Hot Environments: Lessons Learned from the Development of Firefighter Personal Protective Clothing Standard Test Assoc. Prof. Ilham Bakri and Yutaka Tochihara Hasanuddin University, Indonesia Some inconsistencies within the existing test standards for firefighter’s personal protective clothing (PPE) are still remain. For that reason, and to response the need for an easier and reliable PPE standard, a new firefighter PPE standard test was developed in our laboratory. The aim of this paper is to describe some valuable lessons found in related to the men working using PPE in hot environment. Firstly, there is still more space to reduce the burden on firefighters by improving the SCBA and its harness design. Secondly, a PPE should be tested in hot environment to have a better understanding about the physiological impact of the PPE in a similar condition that it will be used. And lastly, although the tympanic temperature was more reactive, the tympanic temperature profiles were in a similar tendency to the rectal temperature profile so that the tympanic temperature measurement is acceptable in a PPE standard test. Differential Evolutionary Algorithms with Novel Mutation Operator for Solving the Permutation Flowshop Scheduling Problem Ms. Chi-Hua Tien, Meng-Hui Chen, Chia-Yu Hsu, Pei-Chann Chang Department of Information Management, Yuan Ze University, R.O.C Taiwan Differential evolutionary (DE) algorithm is an effective algorithm to solve combinational optimization problems, such as scheduling problems. This paper aims to propose an improved differential evolutionary algorithm for the permutation flow-shop scheduling problem (PFSP) by considering the minimum makespan, where the new mutation mechanism is used to enable an appropriate sequencing for each job. For the reason, the main idea in this paper is to find out the key scheme from the better solution and making the assimilation operator in mutation procedure adopts the strategy based on the sequence. To evaluate the performance of the proposed approach, eight benchmark tests by Taillard’s instance is used. The results demonstrate that the proposed improved differential evolutionary algorithm outperform than the conventional differential evolution algorithm. Job Shop Scheduling with Flexible Routings based on Analytical Target Cascading Yanguang Li, Prof. Guanghui Zhou, Zhongdong Xiao Xi’an Jiaotong University, China For solving the large-scale job shop scheduling problems considering flexible routings with the characteristics of process planning and scheduling optimization, a hierarchical coordination optimization model based on analytical target cascading is proposed in this paper, which is divided into three sub-layers. The process planning layer is for optimal processing routes of all jobs, and multiple manufacturing units is formed by clustering all machines based on factor analysis method in the unit planning layer, and then the optimal scheduling solutions of jobs in each unit is obtained by adopting the improved genetic algorithm respectively in the job scheduling layer, which then gives feedback to the upper layer and repeatedly coordinates to obtain the global optimal solution. Finally, a typical computational experiment comparatively demonstrates the validity of the proposed model and algorithm, showing its efficient advantage in solving the large-scale job shop scheduling problems with flexible routings. - 27 - Technology Development for Fully-controlled Artificial Light-type Plant Factory Prof. Masashi Sugano Osaka Prefecture University, Japan Plant factories are cultivation facilities that, through advanced and precise control of the environment by monitoring the cultivation conditions and growth of plants, enable year-round production of vegetables and other produce. In Osaka Prefecture University, the R&D Center for the plant factory has been established as a cutting-edge R&D base specializing in a fully artificial light-type facility. This plant factory is the maximum scale among the Japanese universities and has the ability to produce 5000 lettuce in every day. In this talk, I will explain some technologies such as energy conservation and automation applied to this plant factory. - 28 - Venue: Room B Chair: Prof. Maode Ma, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore Time: 13:00pm-15:30pm Mutual Authentication Protocol for RFID Security Using NFSR Mr. T. Suresh and M.Ramakrishnan Tagore Engineering College, Chennai, India. Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) is an automated identification procedure, relying on storing and remotely recovering information using devices called RFID tag. RFID tags contain an electronic product code (EPC) that may uniquely determine every tagged item. The RFID tag stores its distinctive EPC with related product information within the tag’s memory and sends this information whenever the reader requests them. Researchers have proven that the Electronic Product Code (EPC) Class-1 Generation-2 (C1G2) specification has critical security problems. In this paper, we proposed a new ultra lightweight mutual authentication scheme to overcome weakness in an EPC C1G2 Protocol. We only use XOR operation and appropriate Non- Linear Feedback Shift Register (NFSR) to accomplish high security. Security analysis demonstrates that our protocol will offer numerous privacy properties and avoid suffering from different kinds of attacks, including tag anonymity, reader privacy, transfer secrecy, tag, location protection and mutual authentication, replay attack etc. The proposed scheme was simulated using the ISE simulator and synthesized using Xilinx synthesis technology. The proposed method was implemented on FPGA. Contribution-enabled Congestion-aware Scheme for P2P Real-time Multimedia Streaming Systems Mr. Cheng-Yun Ho, Ming-Hsiang Huang, and Chien-Chao Tseng Department of Computer Science, National Chiao Tung University, Taiwan In this article, a contribution-enabled congestion-aware (CECA) scheme is proposed to enhance the fairness and efficiency of content distribution, and improve the entire bandwidth utility for mesh peer-to-peer (P2P) real-time multimedia streaming systems. This is because the mesh P2P streaming system outperforms others in many aspects, but most content distribution mechanisms use only one of upload bandwidth and link latency as a factor that malfunctions the reward and punishment scheme. Besides, their congestion controls partially or mostly rely on the transport layer protocol such as transmission control protocol (TCP). Hence, the CECA dynamically adjusts a receiver peer’s content window size (CWS) based on the contribution and packet loss rate of the receiver peer. Furthermore, the CECA is implemented in NS2 and experimental results show that the CECA could at the most shorten the receiving time about 20.78%, 32.26%, 30.74%, and 26.18%, and improve the entire performance about 11.42%, 18.87%, 14.55%, and 14.19% at the most, when it compares with the BLACE, the Coolstreaming, the Coolstreaming with bandwidth preference, and the Coolstreaming with latency preference, respectively. - 29 - A Hybrid Two-Stage Sweep Algorithm for Capacitated Vehicle Routing Problem Meng-Hui Chen, Ching-Ying Chiu, Pei-Chann Chang, Sivachandra Prabhu Annadurai Yuan Ze University, Taiwan Capacitated Vehicle Routing Problem (CVRP) is a variant of Vehicle Routing Problem (VRP), where CVRP is only considered the capacity restrictions, and the object is to minimize the cost of the vehicles serve all customers. In this study, we proposed an approach which is hybrid two-phase sweep algorithm (SA) and greedy search for solving CVRP. At the first stage of SA, all customers are clustered by SA and define each cluster as a block. The second stage is to reconstruct each neighbour clusters based on the first stage. Then the greedy search is applied to minimize the cost of each vehicle. Finally, the computational result on standard instances show the proposed approach is effective. A Hybrid Edge Recombination Approach to solve Price Collecting Vehicle Routing Problem Anurag Tiwari, Dr. Gouthaman Elangovan, Sivachandra Prabhu Annadurai , Pei-Chann Chang Yuan Ze University, Taiwan In this paper, we consider a Prize Colleting Vehicle Routing Problem (PCVRP). Prize collecting Vehicle Routing Problem is a Variant of Vehicle routing Problem. One of the major concerns of the Prize collecting Vehicle routing problem is that all customers need not to be visited compulsory, but prize must be collected from each customer visited and a penalty has to be paid for every unvisited customer. To guarantee good customer satisfaction, the demand of all visited customers should reach a pre specified value. The objective of this paper is minimization of total distance and total cost of schedule by maximizing the total prize collected by each customer. We have proposed a Hybrid edge recombination approach to solve the PCVRP. To avoid the bias we compare the result with other well know evolutionary algorithm. Computational result shows that the proposed methodology has the promising result. Method and Simulation for Spacecraft Clock Correction Based on X-ray Pulsars Signal Mr. Sun Chen, Assoc. Prof. Gui Xianzhou,and Huang Senlin College of Aerospace Science and Engineering, National University of Defense Technology X-ray pulsar-based spacecraft navigation comes to be a new kind of autonomous navigation technology with high potential, for the advantages of high reliability, good autonomy, high precision and wide applicability. Timing, determination of position and attitude are main prospects of using X-ray pulsars [1, 2]. To realize the pulse signal timing, in this paper, a Phase-Locked Loop circuit for tracking pulsar signal frequency is designed; PLL is built in the Simulink environment and tested by using simple pulse signal to get circuit parameters with good track effect. The Crab Nebula pulse profile, which is used as the simulation signal source, is modelled by using the mathematical method [3]. The simulation results show that the PLL circuit designed in the paper can track the frequency of pulse signal precisely and can be used for spacecraft clock correction. - 30 - A Steady Tracking Technology Adopted to Fast FHBPSK Signal Under Satellite Channel Prof. Guo SuLi ,Wang XiDuo, Xia Shuangzhi The 54th Research Institute of China Electronics Technology Group Corporation, Shijiazhuang, HeBei, 050081, China In order to survive under the conditions with great jamming and interference, fast frequency hopped signal are employed in satellite communication system. This paper discusses the nonlinear phases induced by the equipment and atmosphere, and their influence on the FFH/BPSK tracking loop. Two methods are developed including compensating phase which is based on channel estimation and compensating Doppler frequency based on velocity normalization. Simulation results for a real circuit with proper parameters shows that the degradation due to the demodulation of frequency-hopped is only a fraction of one dB in an AWGN environment under satellite channel. A Community-based Data Dissemination Scheme in Opportunistic Networks Chun-Chih Lo, I-Hsun Chuang, Pey-Wen Lai, Mr. Bing-Jie Guo and Yau-Hwang Kuo Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering, National Cheng Kung University, Tainan, Taiwan In opportunistic networks, data are often delivered by dissemination-based routing approaches using the store-carry-and-forward concept. However, the heavy overheads incurred by these approaches lead to inefficient data delivery. Generally, users in an area usually demand similar data, called “locality of demand”, and this area is referred to as a community. Based on such property, this paper presents a community-based data dissemination (ComD) scheme to improve the data delivery efficiency in the opportunistic network. By delivering data to appropriate communities, users can obtain what they are actually interested in. Moreover, the ComD also uses the cooperative caching technique to reduce transmission redundancy. To optimize system utility, the proposed delivery model is formulated as a multiple knapsack problem to determine which data should be carried, and a greedy-based method is adopted to reduce the computational complexity. Simulation results show ComD can significantly improves the system utility and delivery rate under various situations. An Integrated Secure Inter-mobility IPv4/IPv6 Address Translation Architecture for Corporate Networks Ms. Amutha J and Albert Rabara S Joseph College, India Next Generation Networks (NGN), the heterogeneous all-IP model with inherent capacity of providing next generation services as Always Best Connected (ABC), Anytime Anywhere with seamless mobility meriting the motto ‘All over IP and IP over All’ is effectively realized in IPv6 to supersede the current IPv4 protocol. Several initiatives have been made by researchers to integrate secure, inter-mobility and translation architecture together. But, not much progress has been reported in recent past. Hence, in this research, an Integrated Secure Inter-Mobility IPv4/IPv6 Address Translation Architecture for Corporate Networks has been proposed to achieve secure communication, inter-mobility between IPv4 and IPv6 networks and IP address - 31 - translation with an IPv4/IPv6 Enabled Gateway Translator (IP46EGT). Network performance is evaluated and the generated results are tabulated and graphically presented. AS-aware Relay Selection Mechanism for Multiparty Streaming Service in Overlay Network Mr. Cheng-Yun Ho, Jyun-Chen Huang, Li-Hsing Yen, and Chien-Chao Tseng Department of Computer Science, National Chiao Tung University, Taiwan It has been shown that relay nodes can improve the quality of streaming data delivery in an overlay network. Therefore, many researchers have proposed methods for relay node selection. However, existing methods have some issues, such as scalability, long service start-up time, and not on multiparty service. In this paper, we propose an AS-aware relay selection (ASRS) mechanism to enhance the efficiency of multiparty streaming service in overlay networks. We verified and evaluated ASRS using ns2 network simulator. The experimental results show that ASRS has a short relay selection time. It can also reduce the bandwidth need of multipoint control unit (MCU) effectively so as to supports more users. Role of Body Area Sensor Networks in Smart Health Care Debasis Das and Ms. Neelanjana Basu Roy NIIT University, India The term “computer” or “PC” has never yielded another term “personal”. It is just regarded as a machine with inputs from human beings giving required outputs. However the term or the budding field of Body Area Networks gives new meaning or leverage now to the term “personal” in PCs. In short, this wireless technology leverages wireless communications protocols allowing low-powered sensors to communicate with one another and transmit data to a local base station and to remote places like hospitals. This paper on Wireless Body Area Networks will present a detailed discussion on the various applications of WBANs in smart healthcare systems, its history of development, advantages, disadvantages and the future prospect and scenario of this system. We will also highlight project performed earlier that helped WBANs to provide long-term healthcare monitoring. Our main aim in this paper, is to understand one of the major applications of Body Area Sensor Networks, termed as “Amplifier Ear” which helps people suffering from auditory problems to function properly. - 32 - Venue: Room B Chair: Time: 15:45pm-19:30pm Optimal Tuning of Scaling Factors and Membership functions for Mamdani Type PID Fuzzy Controllers Ana Sebastião, Catarina Lucena, Luí s Palma, Alberto Cardoso and Senior Prof. Paulo Gil Coimbra University, Portugal This study addresses the problem of tuning Mamdani-type fuzzy Proportional-Integral-Derivative controllers by solving a constrained nonlinear optimisation problem. Two different schemes are discussed. One considers merely the scaling factors optimisation, while assuming the membership functions width unchanged. In second methodology both scaling factors and membership functions width adjusted. The cost function under minimisation is chosen as the closed loop performance index, with the system dynamics described by a nonlinear model. In addition, a set of constraints to the optimisation problem are taken into account, namely bounds on scaling factors, control actions and also on the system outputs. For the second approach, extra constraints on membership functions width are also included in problem formulation. Experimental results carried out on a Multi-Input Multi-Output benchmark system shows the out-performance of considering the optimising of both scaling factors and membership function widths. Flexible Development Environment for Educational Robotics Mr. Christoph Krofitsch, Wilfried Lepuschitz, Markus Klein, Gottfried Koppensteiner Practical Robotics Institute Austria Robotics is considered to be a powerful tool for teaching STEM especially when employing white-box platforms to build and program robots. In this context, programming environments should be simple and understandable for increasing the learning success and for easing the entry for teachers with non-informatics background. Furthermore, many robotics applications can also benefit from flexibility in the program deployment in contrast to the usual code-compile-download paradigm. To address these issues, this paper presents a flexible programming environment based on a layered robot control architecture, which involves the usage of mobile devices. Source code created on a smartphone or tablet can be downloaded to the robot controller, which organizes the programs having on-board compilation and execution environments. Besides, a versioning system adds to the comfort. The presented approach enables students to intuitively handle their robots, but can also be applied in more sophisticated scenarios where module-based flexible programming is required. Touching an Android Robot: Would You Do It and How? Dr. Kerstin Sophie Haring, Katsumi Watanabe, David Silvera-Tawil, Mari Velonaki and Yoshio Matsumoto The University of Tokyo, Japan - 33 - As the presence of robots in everyday life becomes more common, it is expected that interactions between humans and robots will include the modality of touch. To date, however, little research has been conducted on tactile interactions between humans and anthropomorphic robots. This study investigates human induced tactile interaction with an android robot. To facilitate data analysis, existing touch dictionaries were revised and adapted for the specifics of human-android interaction. By measuring the participants' personality traits and their perception of the robot, it was found that some tactile gestures are related to participants’ personality traits, such as neuroticism and extroversion, and others to robot attributes such as anthropomorphism and animacy. To the best of our knowledge this is the first study to report on how people touch an android robot, and the correlation that exists between the tactile gestures used and the participants' personality traits. Possible implications are discussed. A Decentralized Interactive Architecture for Aerial and Ground Mobile Robots Cooperation Dr. El Houssein Chouaib Harik, François Guerin, Frederic Guinand, Jean-François Brethe, Herve Pelvillain University of Le Havre, France This paper presents a novel decentralized interactive architecture for aerial and ground mobile robots cooperation. The aerial mobile robot is used to provide a global coverage during an area inspection, while the ground mobile robot is used to provide a local coverage of ground features. We include a human-in-the-loop to provide waypoints for the ground mobile robot to progress safely in the inspected area. The aerial mobile robot follows continuously the ground mobile robot in order to always keep it in its coverage view. Method for Vectorial Robot Movement Determination Enabling Accuracy Improvements Mr. Arnd Buschhaus, Nicky Apel and Joerg Franke Institute for Factory Automation and Production Systems, Germany Promising approaches for robot accuracy improvements belong to the visual servoing methods. These methods comprise closed-loop control systems, which utilize sensors to guide the robot relative to visible features of a work-piece. However, the known methods show limitations regarding their usability for highly accurate applications or tasks without a predetermined process pathway. To overcome this problem, at FAPS a system for high-speed monitoring of the work-piece’s movement is investigated. The system enables a closed-loop control of the robots motion, if a deviation between actual and planned movement is determined. For the actual movement determination, a highly efficient and accurate image data processing system, based on a vectorial movement determination of fiducial markers is developed. In this context, a highly efficient and geometrical accurate actual state determination constitutes a significant challenge. Experiments show, that the system allows a position determination in an area of ten microns at a frequency faster than 500 Hz, thus enabling a reactive robot control and accuracy improvement. A New Approach to Inverse Kinematic Solution for a Partially Decoupled Robot Assoc. Prof. Lei Zhang, JunQin Zuo, Xinguo Zhang, Xingtian Yao, Liguo Shuai Nantong University, China - 34 - Conventional D-H model based inverse kinematic solution algorithms have to hypothesize that d6 0 at the end of the robot hand, or the joint variables of D-H based kinematic equations can hardly be isolated to be solved. In practical application, d6 0 usually occurs, hence it is required for supplemental transformation between the last frame of the D-H models and real operation frame, which decreases the efficiency. In this paper, a new inverse kinematic solution without the hypothesis of d6 0 is proposed. We found that the joint variables of the partially decoupled robot can be separated without great difficulty even though d6 0 . The new approach uses a new multiplication sequence of the inverse matrix for solving the variables of the kinematic equation of the robot. The inverse solution process is straightforward and computationally cheap. Last, some exemplifications are given to valid the accuracy of the proposed approach. Sensors Fault Diagnosis in Autonomous Mobile Robots Using Observer - Based Technique Assit.Prof.Dr.George K. Fourlas, George C. Karras, Kostas J. Kyriakopoulos Department of Computer Engineering, Technological Educational Institute (T. E. I.) of Central Greece, Lamia, Greece This research investigates a sensors fault diagnosis in autonomous mobile robot. Through this study we use the observer – Kalman filter identification technique. According to this observer based method, the experimental input-output data are being exploited for system identification. The motive is to design observers exclusively for each sensor of the system that allows generating residuals. The research goal is to provide early sensors fault diagnosis. In order to prove the efficacy of the proposed method, we investigated different type of faults and an experimental procedure was carried out using a Pioneer 3AT mobile robot. Improving IMC Method for BLDC Speed Control by Using Steady-state DC Model Hoang-Hon Trinh and Mr. Duc-Thinh Le Ho Chi Minh city University of Technology, Vietnam This paper describes an improved method for controlling speed of brushless DC motor (BLDC). Internal model control (IMC) method is used to achieve the good characteristics such as robustness, easiness, flexibility and stability. Here, this novel idea uses the steady-state DC model instead of BLDC’s or general DC’s to reduce large amount of calculation but it still achieves positive features of IMC method. To challenge the robustness, the proposed method is performed with not only nominal parameters but also large change of plant’s parameters. On MatLAB Simulink, the obtained results show that the output signals well respond the referred signals. To be more objective, our results are compared with 2 previous approaches. Applicability of Stereo High Speed Camera Systems for Robot Dynamics Analysis Mr. Kai Wu, Jan Brueninghaus, Benjamin Johnen and Bernd Kuhlenkoetter Institute of Production system, TU-Dortmund, Germany Industrial robots are widely used in industrial area. Requirements for more accuracy and stable performance are raised in the applications. Especially when the robot executes machining task, the dynamic performance in the machining process has influence on the work piece quality. This - 35 - article utilizes a high speed camera measuring system to analyze the robot motion for the sake of process improvement. Linear paths with different accelerations are programmed. The position distributions in 3D space are presented and the path linearity is discussed. In addition, the path velocity and acceleration are obtained. The differences of the running velocity to programmed velocity are given. Changes of the accelerations are also described. According to this application, Characteristics of the measuring system are introduced. Evaluation is made based on the experiment results. Two Channels SEMG Controller Unit for Electric Hand Gripper: Amputee Hand Training Device Chanchai Supakitamonphan, Nutchanat Kitsongsang, Praetana Poohrungrueang, Thanapong Chaichana, Ms. Praetana Poohrungrueang Rangsit University, Thailand This research aims to the design and construct of two channels SEMG controller unit of an electric gripper hand for amputee hand training device to use before prosthetic hand. This project has adopted the principles of physiology, biomedical electronics and microcontroller. The designed and constructed the prototype consists of three main parts; 1) detector and signal conditioner part, 2) signal control and processing part using microcontroller ATMEL 328 on board (Adriano Pro Mini 328) and 3) electric gripper hand drives with DC servo motor. The results of functional testing by was done by picking up objects, which to performing success of correction and precision grasps of cuboidal and cylinder, rotate a wrist hand in 30 times found that the percentage accuracy was 90% and 83% respectively. The production cost of design and construct the prototype was 7,850 baht. Versatile Climbing Robot for Vessels Inspection Mr. Mohamed Gouda Ramadan Alkalla, Mohamed A. Fanni, Abdel-Fatah Mohamed Egypt-Japan University for Science and Technology, Egypt. This work focuses on proposing and designing a new climbing robot to explore the interiors of industrial vessels and enables a human outside the vessels to implement required regular inspection tasks efficiently. There are two main adhesion systems in the literature: magnetic and air suction systems. The magnetic system climbs surfaces made of ferromagnetic materials only, while air suction system cannot handle irregular surfaces due to possible seals damage. Opposite to previous climbing robots, the proposed robot here can climb and navigate vessels made from different materials besides handling possible irregular surfaces during inspection. Its main task is visual inspection of welds and any critical spots inside these vessels. The novelty of this robot comes from utilizing a hybrid actuation system. This hybrid actuation system consists of upturned propellers fixed on mobile robot and motorized wheels of the mobile robot. The pressure generated from the upturned propellers increase the friction force between the wheels of the mobile robot and the wall. The wheels’ motors generate the required torque either to fix the robot in any position or to move it to any place. Since the motion of the robot comes mainly from the motorized wheel, the stability of the system during navigation is guaranteed. Size and topology optimizations are carried out to achieve optimum design of the proposed robot. Simulation results of the designed robot using ADAMS software prove its feasibility. - 36 - Prototyping a Simple Small Smart Robotic Arm – Manipulator Dr. Meteb Altaf, Dr. Eball Ahmad, Abdulmohsin Jarwali, Faisal Al-Ateeq, Faisal Alturki King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology (KACST),UAE In many experiments, it is frequently necessary to be able to perform several types of applications using simple manipulators for pick and place as in the case of sample preparation for different types of experiments. This paper describes a simple small and smart manipulator prototype using 3D printer which overcomes the need for small manipulations and handling applications. This manipulator will use pizo electric materials to perform the required operation. This manipulator will have only two links with small gripper and limited motion. The design will describe the motion and the required parts to get this small simple smart manipulator working. Mobile Robot Path Planning for Circular Shaped Obstacles Using Simulated Annealing Mr. Sikandar Hayat, Zareena Kausar Air University, Islamabad, Pakistan Many heuristic methods are used for path planning by researchers in the past and contemporary work but due to easy implementation, convergence properties, capability of escaping local optima and the use of hill-climbing moves have made simulated annealing (SA) a good choice for path planning. In this research the simulated annealing algorithm is used to obtain a collision-free optimal path among fixed circular shaped obstacles for a mobile robot. A feasible path is computed by series of points in cells generated between start to goal point. The effectiveness of the proposed algorithm in different environments is shown through simulation results. Mobile Robot Path Planning in Environments Cluttered with Non-Convex Obstacles using Particle Swarm Optimization Mr. Muhammad Shahab Alam, Muhammad Usman Rafique Air University, Pakistan Generally workspaces of mobile robots are cluttered with obstacles of different sizes and shapes. Majority of the path planning algorithms get stuck in non-convex obstacles pertaining to local minima. Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) is by comparison simple and readily intelligible yet a very powerful optimization technique which makes it an apt choice for path finding problems in complex environments. This paper presents a particle swarm optimization based path planning algorithm developed for finding a shortest collision-free path for a mobile robot in an environment strewed with non-convex obstacles. The proposed method uses random sampling and finds the optimal path while avoiding non-convex obstacles without exhaustive search. Detailed simulation results show the functionality and effectiveness of the proposed algorithm in different scenarios. - 37 - An Investigation on the Application of Fuzzy and PID Algorithm in the Two Wheeled Robot with Self Balancing System Using Microcontroller Mr. Adik Susilo Wardoyo, Hendi S, Darwin Sebayang, Imam Hidayat, Andi Adriansyah Universitas Mercubuana, Indonesia The Fuzzy logic combined with PID control is designed to implement the effect of a disturbance force varying in magnitude, position, and duration to optimize the two wheeled and self-balancing robot. Matlab software was used to obtain Simulink-simulation of the experiment process. The simulation results shows that PID parameters that obtained from the use of auto-tuning is Kp = 16.60, Ki = 8.47, and Kd = 8.90. The simulation results of Fuzzy and PID combination shows that the error can be reduce approximately around 60 %. It is indicated that the Fuzzy logic with PID was better to reduce error in Two Wheeled and Self Balancing Robot than using Fuzzy logic. Kinematics of Parallel Mechanism Based Robot Manipulator with Passive Joints Variables Assoc. Prof. J.M.Prajapati The M S University of Baroda, India. Because of potential benefits like, structural rigidity, good dynamic performance and positioning accuracy, parallel mechanism based robot manipulators became more popular over the serial mechanism based robot manipulators. The forward kinematics of parallel mechanism is complex in comparison to the serial mechanism. This paper presents the forward instantaneous kinematics of a six degree of freedom parallel robot manipulator. Three non linear points are considered on the end effector. The presented method is based on the velocities of these points. A numerical example is solved to demonstrate the solution process. - 38 - Venue: Room C Chair: Time: 13:00pm-15:30pm Anthropometric Proportions Estimation Using recCAL in Multi-Camera Environment Mr. O. Kainz, D. Cymbalák, and F. Jakab Technical University of Košice, Slovakia In this paper, a new technique for anthropometric proportions estimation using multi-camera environment is presented. We refer to this system as a recCAL. System is represented in a form of a 3D model and as well real-world physical model, both used as a reference model/object in the size estimation process. Further anthropometric proportions of human body and face are utilized to provide an estimate of real size from series of images as captured by multi-camera system. recCAL has potential applications in variety of areas where anthropometric proportions or size of other objects may be useful. Real-Time Automatic Selection of the Best Shot on Object in 4K Video Stream Based on Tracking Methods in Virtual Cropped Views Mr. D. Cymbalák, O. Kainz, and F. Jakab Technical University of Košice, Slovakia In this paper, a novel approach for real-time automatic object tracking from multiple cropped views using 4K video capturing device is presented. System itself is based on TLD object tracking algorithm. As a first ultra-high definition video and selected object tracking method is analyzed. Subsections of 4K video output from capturing device are utilized to create new, so called “virtual copped views”. The developed model was rudimentary implemented and tested in the laboratory conditions and it is expected to be used in the real conditions. Video based in-space orientation model for artificial intelligence systems Dr. Jaroslav Lamer and Frantisek Jakab Technical University of Kosice, Slovakia Many of the currently solved problems aim to map the real world into the virtual space. In this article we discuss a new model, which may be used as basis for in space orientation in artificial intelligence systems, such as robots, control mechanisms, vehicles, autonomous devices etc. Experimental results of human orientation in workspace experiments are introduced. Another part of article presents practical evaluation and precision tests of experimental prototype implementation. Comparison of real coordinates and model calculations are represented in graphical form. - 39 - Deep Learning for Reducing Dimensionality of Graph Data Mr. Young Joon Park, Seoung Bum Kim Korea University,Republic of Korea Analysis of graph data has become an important research topic recently because of its numerous applications in social networking, metabolic networks in biology, community detection, and computer networks. However, learning from graphs is very difficult because of their complex structure with high dimensionality, resulting in high-level abstractions in data. Therefore, dimensionality reduction is critical in graph data. In this study, we propose to use a deep learning algorithm that has the capability of dealing with high-level abstractions for dimensionality reduction of vertex-multi-labeled graph data. Experiments on simulated datasets were conducted to compare the performance of deep learning with that of principal component analysis and locally linear embedding, which are existing unsupervised feature extraction methods. The experimental results showed that the deep learning outperformed its competitors in terms of reduced dimensionality and robustness. Analysis Electromyography on Computer Interaction Devices to the Riska of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Dr. Hartomo Soewardi, Ms. Annisa Riska Anugraheni, Nella Shabrina Islamic University of Indonesia, Indonesia Use of interaction devices on human-computer system may cause muscolusceletal disorders on hands and wrists. The paper presents an Electromyography study to evaluate the hand muscle activities when it is interacted with the computer using mouse, keyboard and joystick. These muscles investigated are flexor pollicis brevis, flexor digitorium superficiallis and abductor pollicis brevis. Average of Root Mean Square (mRMS) signal was used as parameter measurement. Experimental study was conducted in ergonomic laboratory where 8 females and 7 males student university were participated in this study to complete virtual task for 15 minutes. Virtual manufacturing robots system was used as case study. Non parametric statistical method was conducted to test the hypothesis. The result of electromyography shows that the strongest muscle contraction of mRMS signal on m.flexor pollicis brevis is 275.4 mV that it was found in the joystick devices, while 72 mV mRMS was found in the keyboard and 53.4 mV in the mouse. In the second muscle, m.flexor digitorium superficiallis, the strongest muscle contraction of mRMS signal 53.13 mV was found in the keyboard, then 48.9 mV was found in the joystick and the weakest is 34.86 mV was found in the mouse. For the third muscle m.abductor pollicis brevis, the strongest muscle contraction of mRMS signal was found in the joystick it is 252.67 mV then in the keyboard is 130.47 mV and weakest is 60 mV in the mouse. Statistical test shows that there were significant differences in muscle contraction of flexor pollicis brevis muscle (p = 0.000) and abductor pollicis brevis muscle (p = 0.002). But in muscle contraction of flexor digitorium superficiallis does not indicate a significant difference (p = 0.184). It concluded that the highest risk of carpal tunnel syndrome was found in the joystick on flexor pollicis brevis muscle and abductor pollicis brevis muscle. Meanwhile on flexor digitorium superficiallis muscle contraction showed that the highest risk of carpal tunnel syndrome was found in the keyboard devices. - 40 - Performance Comparison of Feature Selection Methods Ms. Thu Zar Phyu and Nyein Nyein Oo Yangon Technological University (YTU),Republic of the Union of Myanmar Feature Subset Selection is an essential pre-processing task in Data Mining. Feature selection process refers to choosing subset of attributes from the set of original attributes. This technique attempts to identify and remove as much irrelevant and redundant information as possible. In this paper, a new feature subset selection algorithm based on conditional mutual information approach is proposed to select the effective feature subset. The effectiveness of the proposed algorithm is evaluated by comparing with the other well-known existing feature selection algorithms using standard datasets from UC Iravine and WEKA (Waikato Environment for Knowledge Analysis). The performance of the proposed algorithm is evaluated by multi-criteria that take into account not only the classification accuracy but also number of selected features. Mobile Based Palmprint Recognition System Prof. Li fang and Neera Nanyang Technological University, Singapore Personal identification and verification are playing more and more important role in the society. Traditional authentication method such as password and smart card, often cannot meet today’s security as they can be easily forgotten, lost or stolen. Biometric technology has appeared as a new solution to these problem. Among all the variable biometric technologies, automatic palmprint verification is an important complement to biometric authentication. This paper describes the adopted mobile based palmprint recognition system. Pineapple Quality Grading Using Image Processing and Fuzzy Logic Based on Thai Agriculture Standards Assit.Prof.Dr.Bandit Suksawat and Preecha Komkum King Mongkut’s University of Technology North Bangkok, Thailand This research aimed to create a tool for pineapples quality grading according to the standard weight and size of Thai Agricultural Commodity Food Standard. The standard weights of pineapple are divided into 10 levels (A-J) and the standard sizes of pineapple are categorized into two classes (class I and class II). The developed tool consists of hardware components and a grading software program. The control light source box was constructed for camera and load cell installation to capture pineapple image and measure pineapple weight, respectively. The obtained image was sent to software program to change colors of the image into gray scale and to reduce noises in the image. The clearly edges of the image were employed to compute size of a pineapple and the data were transferred to fuzzy system. The inputs of fuzzy system determined the size and weight of pineapple which used to establish twenty fuzzy rules. The experiments performed by random selection size and weight of three pineapple kinds including Nanglae, Sriracha, Phuket. The experimental results reveal that classification of pineapple by the created tool exhibited high accuracy of size and weight detection equaled 87.5%. The average relative error performed 2.30% and 5.24% of size and weight, respectively. - 41 - Ultrasonic Sensor based Approach for Identifying the Camera ROI Mr. Pradeep S., Shashi Kumar M.S., Avinash.N Wittybot Technologies/Jain University, India Image segmentation and classification is a tough when there are partial occlusion, reflection, and shadows in the image which increase false alarms. This paper describes the method for defining regions of interest in an image using ultrasonic sensors data which will be further used for image segmentation and classification. Sensors mounted in the view of the camera are calibrated for their position with respect to the camera to the relative distance between the human and robot. Depending on these calibration parameters, the image is divided into number of regions that is equivalent to number of sensors. An Implementation and Pragmatic Analysis of the Digital Image Forgery Detection Schemes Dr. Hansoo Kim and Joong Lee National Forensic Service, The Republic of Korea We select the most effective and remarkable schemes among the state-of-the-art digital forgery detection schemes and implement a system based on these schemes. With that, we compare the advantages and limitations of each scheme by experimental analysis. As a result, the detection rate of the schemes is dependent of the parameters of the schemes and the forgery method of the image, although the schemes succeed to detect most of the forged images. Also, a number of forged images are not detected which are off the detection points of the schemes. Building Detection in Terrestrial Images Mr. Teerapat Chaloeivoot and Suebskul Phiphobmongkol Department of Computer Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, Thailand This paper presents a method to detect buildings in terrestrial images. High resolution terrestrial images are normally taken from land survey vehicles. These images and other surveyed data along roads are needed by many agencies that require new data as time passes by. Land use in rural area is an example that needs information about buildings and can benefit from terrestrial images. The proposed method was aimed to detect buildings in terrestrial images to benefit the above needs. The method consists of two stages. The first stage removes unwanted objects, performs image segmentation, and finds regions of interest. Image processing techniques such as greenness extraction, sky detection, color segmentation, color detection, shape detection are used. The second stage performs building detection. It includes the possible building parts detection, projection profiles finding, and the building determination. The method can identify a partial building if the whole building is not shown in an image. The proposed method was tested on 936 images (332 images with buildings and 604 images without buildings). The images were from Google Street View. The accuracy was determined by human inspection. The method gave promising results with an average accuracy of 82.5%. Positive faults were 4.7% average. - 42 - Venue: Room C Chair: Dr. Girija Chetty University of Canberra, Canberra, Australia Time: 15:45pm-19:30pm Fast Range-based Localization of Targets using Particle Swarm Optimization Ms. Vidya Viswanathan, Soumya Jana, Shanti Swarup Indian Institute of Technology Hyderabad, India Target localization is an active area of research which has several applications in the fields of robotics, defense and geology. In this paper, our goal is to localize a target based on range measurements obtained using a network of sensors scattered in the 3D continuum. To this end, we make use of the biologically inspired particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm. In this context, we propose a novel modification of PSO algorithm that leads to faster convergence, and eliminates the flip ambiguity encountered by coplanar sensors. Our initial results over several simulation runs highlight the accuracy and speed of the proposed approach. This paper also proposes a statistical approach to optimally place a given set of sensors such that the localization error is minimized over certain trajectories of the target. The optimal locations of the sensors are estimated using the Cramer-Rao lower bound (CRLB) as the cost function. Memory Allocation Vulnerability Analysis and Analysis Optimization for C Programs based on Formal Methods Dr. Hui Deng, Hui Liu, Ying Guo and Baofeng Zhang China Information Technology Security Evaluation Center, China The information security problems caused by the software vulnerabilities have become more and more complex. Among these vulnerabilities, the ones existing in memory allocations appear to be difficult to diagnose due to the absence of an appropriate method. In order to solve this problem, we introduce a methodology including four novel frameworks in this paper. The formalization for a program called algebraic transition system is proposed first. It aims to transform the data exchange process and its security attribute of a program into algebraic systems which are able to be considered as objection functions and constraint conditions, respectively. Based on the systems, the behavior and structure of formalization are optimized with bisimulation to reduce the computing cost in the subsequent processes. The determination of bisimulation is implemented by numerical and symbolic computation. Finally, the specific detection of the memory allocation vulnerability in the C program can be changed into a constraints solving problem called Max function which is able to be resolved with the filled function method. The experiment results represent that our approach is feasible. High Dimensional Data Mining Systems by Kernel Orthonormalized Partial Least Square Analysis Prof. Shian-Chang Huang, Nan-Yu Wang, and Tung-Kuang Wu National Changhua University of Education, Taiwan - 43 - Mining high-dimensional business data is a popular and important problem. However, there are two challenges for mining such data, including (1) the curse of dimensionality and (2) the meaningfulness of the similarity measure in the high dimension space. This paper proposes a novel approach to overcome the problems, which builds a generalized multiple kernel machine (GMKM) on a special subspace created by the kernel orthonormalized partial least square (KOPLS). GMKM takes products of kernels-corresponding to a tensor product of feature spaces. This leads to a richer and much higher dimensional feature representation. Therefore, GMKM is powerful in identifying relevant features and their apposite kernel representation. KOPLS finds a low dimensional representation of data, which uncovers the hidden information and simultaneously respects the intrinsic geometry of data manifold. Our new system robustly overcomes the weakness of traditional multiple kernel machines, and outperforms traditional classification systems. Analysis of Two Different Sequences of Old Arena Viruses by Decision Tree, Apriori Algorithm, and Shannon Entropy Ms. Yuree Chung, Yujin Moon and Taeseon Yoon HAFS, The Republic of Korea LASV (Lassa virus) and LCMV (Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis virus), which show the different mortality in spite of same symptoms and origin, are introduced into the human population by rodents which shed the virus in urine and droppings. Direct contact with these materials, touching virus-infected objects, eating contaminated food, or exposure to open cuts or sores develop infection. In this paper, we analyzed 4 different proteins of LASV and LCMV: glycoprotein, Z protein, nucleoprotein, and L protein. Also, we investigated the similarities between them based on the frequency of amino acids by decision tree. Furthermore, we look for one amino acid’s frequency of relating rates to another amino acid to find the difference between two viruses by Apriori algorithm. A NoSQL Geo-data Solution for the Consumption of Services on the Web Mr. P. Cau, S. Manca, R. Demontis, D. Muroni, C. Soru, L. Muscas, E. Lorrai and P. A. Marras Center for Advanced Studies, Research and development in Sardinia (CRS4). Polaris, Pula Web applications and portals are strategic gateways to deliver tools, data, computational infrastructures and services over the Internet. Software and data interoperability is the key factor to enable the integration of knowledge and share common objectives. Web applications are using ever more big spatial data ecosystems that usually involve cross-border data flows and rely on open Internet. Demand of web GIS based applications, in particular, shows a steady growth over the last few years, indicative of a scenario where spatial-data infrastructures will be ever more consumed by mobile and web applications. Management and analysis of large and growing volumes of geo-data is challenging the scientific community without clear long term solutions. Empowering Enterprise Storage of Future Datacenter – Hybrid Disk Drive Storage System Development Dr. Yonghong Wilson Wang, Chun Teck Lim, Kyawt Kyawt Khaing and Khai Leong Yong Data Storage Institute, Singapore - 44 - A hybrid disk drive consists of a small amount of non-volatile NAND flash memory as fast storage media to complement the rotational magnetic recording disk, normally considered slow but with large storage capacity. In this paper, we present the design and development work of enterprise hybrid drive storage system for future datacentre. We also design a new type of dynamic cache algorithms that can simplify and enhance conventional cache management architecture. Evaluation with enterprise storage workloads shows that the average IOPS (I/O per second) can be increased up to 300% and can outperform the IOPS of high speed enterprise SAS (Serial Attached SCSI) drive for certain workloads. Another advantage of hybrid drive is power saving, for which the power consumption can be reduced by more than 50%, compared with the enterprise hard disk drive. We envision that hybrid disk drives can be a cost-effective replacement for conventional high speed disk drive in enterprise storage systems that empower datacenters with large storage capacities, higher performance and lower energy consumption. Investigation into Interoperability in Cloud Computing: An Architectural Model Ms. Susan Sutherland and Girija Chetty University of Canberra, ACT, 2616 This paper presents an architectural model that enables the convergence of the interoperability of Enterprise Architecture (EA), Service Oriented Architecture (SOA) and Cloud Services. As per the reviewed literature by the authors, there is a lack of research in this space of cloud computing. Hence the authors' research developed an innovative solution to provide a ‘plug and play’ architectural model to seamlessly connect the enterprise systems to cloud within the governance standards of enterprise architecture. The rest of the paper discusses the identified research problem and articulates the developed model while validating the model with a few use cases, and concluding that the research community could further validate the model with their respective application use cases. Adaptation of Distributed File System to VDI Storage by Client-Side Cache Mr. Cheiyol Kim, Sangmin Lee, Youngkyun Kim, Daewha Seo Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute, The Republic of Korea Distributed File system was widely used as a cloud computing backend storage with high scalability, low cost, and reasonable sequential I/O performance. VDI I/O workload is mostly composed of small random I/O and distributed file system does not have enough performance for this I/O pattern. Compensating for this gap, we applied a cache using memory and SSD (Solid State Drive) to distributed file system. This cache was implemented in the file system’s client side. It uses memory as write cache and SSD as read cache with write-back policy for minimizing the I/O response time. Based distributed file system was implemented on user-level using Fuse (File system in User space) framework. When the client-side cache was used, the file server which previously could not support even 1024 users was improved enough to support more than 3000 users. By applying the client-side cache, it is possible to solve the performance drawback of the distributed file system used for VDI storage. - 45 - Comparative Analysis of Technical Methods for Detecting Software Thefts Prof. Hyun-il Lim Kyungnam University, Republic of Korea Software plays an important role in current computing environments, and it is protected as intellectual property of its author. However, the cases of software thefts are increasing every year. To deal with the problem, there have been researches on detecting software thefts. In this paper, we introduce technical methods for detecting software thefts, and compare characteristics of the methods according to several performance evaluation criteria. NVMFS: NVM-accelerated File System for Future Data Centre Mr. Qingsong Wei, Cheng Chen, Jun Yang, Chundong Wang, Mingdi Xue Data Storage Institute, Singapore File system performance is dominated by metadata access. In this paper, an NVM-accelerated file system (referred to as NVMFS) is proposed to optimize metadata access by exploiting the persistency and byte-addressability of Non-volatile Memory (NVM). The NVMFS decouples data and metadata access path, putting data on disk and metadata in byte-addressable NVM at runtime. Thus, data is accessed in block from I/O bus and metadata is accessed in byte-addressable manner from memory bus. Metadata access is accelerated and metadata I/O is eliminated because metadata in NVM is not flushed back to disk anymore. A consistency mechanism combining copy-on-write and transaction is introduced in the NVMFS. The NVMFS is implemented in kernel on real NVDIMM platform. Evaluation results show that the NVMFS is up to 9X faster than existing file systems. Homomorphic Exclusive-Or Operation for Secure Deduplication Dr. Yibin Ng, Shu Qin Ren and Khin Mi Mi Aung Data Storage Institute, Singapore Deduplication has been widely recognized as an essential method to save storage costs for cloud-based storage providers such as Dropbox and Google Drive. To enable deduplication, deterministic encryption schemes are used where the same ciphertext is always generated for the same plaintext. This has the drawback of leaking information on equality of the underlying plaintexts. Also, an attacker is also able to gain knowledge of the access patterns of other users asking for the same file. As such, although data is stored securely in the cloud, information is still leaked during the data upload and retrieval process. In this work, we propose the homomorphic exclusive-or (XOR) encryption scheme to secure the data against plaintext equality and access pattern leakage. All encrypted data is randomized by a XOR operation with a random bit-string. This effectively protects data-in-transit against passive attack such as ciphertext analysis due to the randomization. - 46 - Large Scale Hybrid Storage System Dr. Haixiang Shi, Kyawt Kyawt Khaing, Donghong Wang Data Storage Institute, A*STAR, Singapore In order to tackle the big data storage problem, a petabyte storage system is proposed which consists of multiple storage tiers. The proposed large scale hybrid storage system uses hybrid storage including Non-volatile Memory (NVM), Solid State Device (SSD), Hybrid Drive disks and conventional hard disks. Data placement, dynamic caching and metadata management algorithms are proposed for this system. Furthermore, the proposed hybrid storage system is used as a test bed to integrate with other research works including NVM File System (NVMFS), Data Security and Encryption, and Hybrid File System (HybridFS), to show the performance of the fully integrated storages system. Distributed Metadata Search in the Cloud Yang Yu, Dr. Yongqing Zhu, and Juniarto Samsudin Data Storage Institute, A*STAR, Singapore The excessively large amounts of data stored in clouds lead to a big challenge for users to access and manage the data. And the corresponding metadata access likely becomes a severe performance bottleneck. In this paper, we propose a distributed metadata search system for the cloud. This system provides efficient index and search for multi-dimensional metadata. Our system achieves optimized performance by improving K-D-B tree based index/search and utilizing index partitioning techniques. Experiment results show that our system can perform well in terms of memory utilization, search speed and scalability. Secure Large Scale Shared Storage System Mr. Rodel Miguel, Sivaraman Sundaram, Khin Mi Mi Aung Data Storage Institute, Singapore The integration of next generation NVM into storage network architecture requires redesigning the current storage security infrastructure, to fully realize the performance potential of future storage systems. As a minimum, the following three layers of security control architecture need to be modified: credential management at application layer, access controls at system layer, and secured ultra-bandwidth peripheral communication at hardware layer. The main purpose of this paper is to redesign and develop storage security infrastructure to support the future storage network architecture that is based on NVM technologies. Regenerating-Local Reconstruction Codes for Distributed Storage Systems Mr. Quanqing Xu, Hong Wai Ng, Weiya Xi and Chao Jin Data Storage Institute, A*STAR, Singapore In this paper, we propose Regenerating-Local Reconstruction Codes (R-LRC) and describe their - 47 - encoding and decoding techniques. After that, their repair bandwidths are investigated for different failure patterns. We also explore an alternative of R-LRC, which gives R-LRC lower repair bandwidth. Since R-LRC are extended version of Pyramid codes, optimization of repair bandwidth of a single failure will also apply to R-LRC. Compared with Pyramid Codes, Regenerating-Local Reconstruction Codes have two benefits. Firstly, in average, they use around 2:8 blocks in repairing 2 failures, while the Pyramid codes use about 3:7 blocks. Therefore, they have lower IOs than Pyramid Codes. Secondly, when 2 failures occur at common block group and special block group, they re-quire only Mk _(k2 + 1), which is lower compared with Mk _(k2 + k2 )= M in Pyramid codes when k _ 2. SELDAC: Software-defined storage based efficient load distribution and auto scaling in Cloud Data Centers Dr. Renuga Kanagavelu and Khin Mi Mi Aung A*STAR, Data Storage Institute, Singapore Cloud computing allows the cloud users to access the shared pool of configurable resources such as compute, network and storage on-demand basis from the cloud Data Centers. Cloud storage provides the storage resources to the cloud users over the network. The massive growth of cloud data due to the applications such as video streaming, big data processing, social networking, banking and scientific applications fueled the storage demand. An increase in storage demand resulted in the expansion of the cloud storage with additional storage nodes. The expansion of the cloud storage necessitates the migration of data across the storage nodes to keep them balanced. Efficient management and migration of tera bytes or peta bytes of such cloud data depends not only on the storage availability but also on the networking cost which is proportional to the distance and the bandwidth requirement. In this scenario, software defined environment opens up the new opportunities to orchestrate the network and storage resources control strategies to provide an effective solution. In this paper, we present the software-defined orchestration framework for efficient load distribution and auto scaling mechanism and shows that it improves the overall efficiency in terms of latency and retrieval cost. We demonstrate the effectiveness and the efficiency of the proposed mechanism using simulations. - 48 - Mr. Wei Gong 4399 Network Co., Ltd, China Mr. Haigui Wu 4399 Network Co., Ltd, China Mr. Zhaolu Xiao 4399 Network Co., Ltd, China Mr. Bin Yang 4399 Network Co., Ltd, China Mr. Govinda Ram PANERU Ministry of Education, Kathmandu, NEPAL Mr. Subhash PRAJAPATI Ministry of Education, Kathmandu, NEPAL Mr. Debasis Das NIIT University, India Prof. SeoungBum Kim Korea University, Republic of Korea Mr. Ji Soo Kim Laboratory - Dependable Embedded Control Systems,Graduate School of Electronics Engineering,Kyungpook National University(KNU),Korea Mr. Lim Eng Chye Roy Panasonic Industrial Devices Singapore, Singapore - 49 - Name Adik Susilo Wardoyo Amutha J Annisa Riska Anugraheni Arnd Buschhaus Arpita Bhattacharjee Bandit Suksawat Bing-Jie Guo Boyang Chen Boyang Chen ID N3007 F076 Session S4 S3 Page 38 31 EA3020 S5 40 N0025 N2007 N0029 F077 EA3005 EA3004 S4 S1B S5 S3 S1B S1A 34 18 41 31 20 16 Byung Do Chung Chanhee Park Chantach Luxnanan Cheiyol Kim Cheng-Yun Ho Cheng-Yun Ho Chi-Hua Tien Christoph Krofitsch D. Cymbalak Duc-Thinh Le El Houssein Chouaib Harik George K. Fourlas Gouthaman Elangovan Guanghui Zhou Gui Xianzhou Guo SuLi Haixiang Shi Hansoo Kim Hartomo Soewardi Hui Deng Hyung Rok Do Hyun-il Lim Ilham Bakri J.M.Prajapati Jaehong Yu Jaroslav Lamer Jayeon Gu Jianan Sun Jianna Niu Jieun Son John M. Ikome John Reyes Kai Wu Kerstin Sophie Haring EA3008 EA3011 EA009 F088 F053 F054 N3010 N0005 F020 N0035 S2A S1A S2B S6 S3 S3 S2B S4 S5 S4 22 15 25 45 29 32 27 33 39 35 N0028 S4 34 N0034 S4 35 N3013 S3 30 N0015 F1012 F1011 F070 F068 EA3020 F006 EA3018 F091 EA011 N0021 EA3014 F050 EA3017 N2008 EA2004 EA3019 EA007 EA004 N0030 S2B S3 S3 S6 S5 S5 S6 S2B S6 S2B S4 S1B S5 S1B S2A S2A S1A S2A S2A S4 27 30 31 47 42 40 43 26 46 27 38 19 39 18 24 22 14 23 21 35 N0007 S4 33 - 50 - Khader Musbah Titi Kyungjin Bae Lei Zhang Li fang Masashi Sugano Meteb Altaf Mohamed Gouda Ramadan Alkalla Muhammad Shahab Alam Neelanjana Basu Roy Nutchanat Kitsongsang O. Kainz P. K. Kwok N2005 EA012 N2011 N3009 N3040 N3006 S1A S2B S4 S5 S2B S4 15 25 34 41 28 37 N0024 S4 36 N0026 S4 37 F093 S3 32 N0042 S1B 19 F019 EA3022 S5 S1A 39 16 Paulo Gil Phikid Vayophad Pimchanok Rungrueng Pradeep S. Praetana Poohrungrueang Qingsong Wei Quanqing Xu R. Henry Xavier Renuga Kanagavelu Rodel Miguel Sandeep Singhal Seulki Lee Shian-Chang Huang Sikandar Hayat Sivachandra Prabhu Annadurai Sun Chen Sung Ho Park Susan Sutherland T. Suresh Teerapat Chaloeivoot Thu Zar Phyu Tobey H. Ko Tong Wu Vidya Viswanathan Wang shuqiang Yibin Ng Yifan Zhou Yifan Zhou Yonghong Wilson Wang N0008 EA005 S4 S2A 33 23 N0044 S1B 20 N0033 S5 42 N0043 S4 36 F080 F072 EA3009 F081 F083 EA2005 EA3007 F067 N3008 S6 S6 S2A S6 S6 S2A S2B S6 S4 46 47 23 48 47 21 26 43 37 N3012 S3 30 F1012 EA3010 F3003 N0012 F3001 N2009 EA008 EA2003 N0014 F1009 F069 EA3016 EA3021 S3 S1A S6 S3 S5 S5 S2B S2A S6 S1B S6 S1A S1B 30 15 45 29 42 41 25 21 43 18 46 16 20 F078 S6 44 Yongqing Zhu Young Joon Park Younghoon Kim F085 EA3012 EA3006 S6 S5 S1A 47 40 14 Yuree Chung - 51 - F010 S6 44 Route: 1st Notice: 1. Please be noted that this is totally free of charge visit to one of the advanced labors in Nanyang Technological University. During this time period, please follow the guidance and behave properly. 2. On the way to labor, please carefully follow our staff, and feel free to call us if you have any question. 3. There may be some minor changes of the time due to the practical situation. 4. If you don’t want to join the half-day visit, you are free to arrange your own discovery tourism in Singapore. - 52 - Memo ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ - 53 -
© Copyright 2026