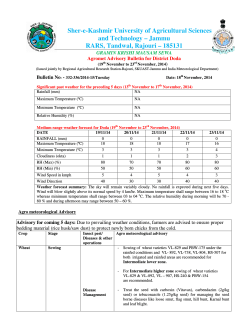
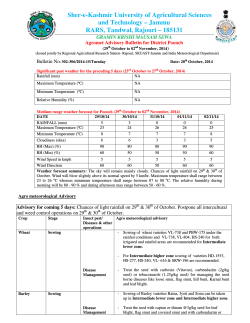
Crop Breeding with modern resources
Crop Breeding with modern resources Joint Director IARI, New Delhi Crop Varieties Released Crop Number of varieties released Wheat 15 Rice 02 Pearl Millet 01 Brassica 07 Chickpea 06 Soybean 03 Wheat Varieties Released (15) Variety Zone Production Condition Year Average Yield (t/ha) HD2967 NWPZ Irrigated timely sown 2011 5.50 HD 3059 (Pusa Pachheti) NWPZ Irrigated, Late Sown 2013 4.30 HD 3043 (Pusa Chaitnya) NWPZ Restricted irrigation timely sown 2013 4.28 HD 3086 (Pusa Gautami) NWPZ Irrigated timely sown 2014 5.46 HD 2985 (Pusa Basant) NEPZ Irrigated late sown 2011 3.78 HI1563 (Pusa Prachi) NEPZ Irrigated late sown 2010 4.20 HD 3090 (Pusa Amulya) PZ Irrigated, Late Sown 2014 4.21 HD 2987 (Pusa Bahar) PZ Rainfed timely sown and restricted irrigated timely sown 2011 1.75 (RF) 3.15 (RI) HW 1095 SZ - 2013 4.40 HW 1098 (Nilgiri Khapli) SZ - 2013 4.60 HW 5207 SZ - 2013 5.21 HW 5216 (Pusa Thennamalai) CZ - 2013 4.56 HI 8713 (Pusa Mangal) CZ Irrigated timely sown 2013 5.23 HS507 (Pusa Suketi) NHZ Timely sown-IR/RF HS 542 (PUSA KIRAN) NHZ Early sown-Rainfed condition 4.68(IR), 2.66 (RF) 3.29 HD 2967: A Miracle Wheat Wider adaptation: Suitable for both NEPZ and NWPZ A non-carrier of 1B-1R translocation Excellent Chapatti making quality Minor gene based yellow rust resistance Replaced PBW 343 in 80% of the area in Punjab within 4 years of its release Superfast Spread of HD 2967 HD2967 Area covered during: 2013-14 : 6.0 m ha, 2014-15: 8 m.ha Expected production at 5.5 t/ha: 33 million tons Approximate value @ Rs. 13000/t: 42,900 crores PBW343 HD2967 HD 2985(PUSA BASANT) Wheat Variety HD 2985 was released for commercial cultivation in the states of Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Jharkhand, West Bengal and Assam under late sown conditions in rice wheat cropping system. HD 2987(PUSA BAHAR) Wheat Variety HD 2987 was released for commercial cultivation in the states of Maharashtra and Karnataka under rainfed and restricted irrigated conditions. HD 3043: Restricted irrigation timely sown HD 3086 (PUSA GAUTAMI) NWPZ: Irrigated timely sown 9 HD3059 (Pusa Pachheti) An early maturing (121 days), semi-dwarf (93 cm) wheat variety with average yield of 4.3 t/ha and genetic potential of 5.9 t/ha under late sown, irrigated conditions of NWPZ HD3090 (Pusa Amulya) An early maturing (101 days), semi-dwarf (80 cm) wheat variety with average yield of 4.21 t/ha for irrigated late sown Varieties proposed for Conservation Agriculture Three varieties have been proposed for identification in Bihar and NCR region HDCSW18: For early seeding (mid of Oct) under CA HDCSW16: For normal time sowing i.e. first week of Nov to Mid of Dec HD 3117 : For late time seeding i.e. 1st of week of Dec to end of Dec. HD CSW 18 Breeding to exploit genotype x cropping system interaction to enhance resource use efficiency in wheat based cropping system in India HW 1095 dicoccum released as COW2 for the state of TN during 2013-14 • Developed through irradiation at 200gray from NP 200 historic check • Having yield potential of 44q/ha with >15 protein • Semi dwarf and resistant to rust diseases HW 1098 released as ‘Nilgiri Khapli’ for all dicoccum growing areas in India during 2013 Semi-dwarf, high yielding rust resistant variety Developed from traditional variety NP 202 through irradiation (200gray) Having comparable grain quality as that of NP200/NP202 HW 5207 accepted for TN state release as COW3 which was developed through marker assisted breeding HW 5207 (Lr24+Sr24, Yr15, Sr2) A multiple disease resistant high yielding semi-dwarf variety carrying Lr24+Sr24, Yr15 and Sr2 Having yield potential of 59.6 q/ha with a mean yield of 52.1 q/ha Developed through Marker assisted breeding Produced luxurious and bold grain with high protein (> 11% )and micro nutrient- high level of iron (53.1ppm), Zinc (46.3ppm), Copper (5.33ppm) and manganese (47.5ppm) HW 5216 (Pusa Thenmalai) popularized in non-traditional areas A high yielding bread wheat released for Southern hill zone during 2013 and notified during 2014 by CVRC Having yield potential over 62q/ha and mean grain yield of 45.6q/ha Resistant to all the three rusts carrying Lr24+Sr24, Sr31 gene complex Marker Assisted Breeding and Hybrid Wheat Introgression of rust resistance genes Novel rust resistance genes transferred from Ae.markgrafii (2n=2x=14,genome CC) and T.militinae (2n=4x=28,genome AAGG) •Er9- seedling gene for leaf rust resistance from Ae.markgrafii •Er1-APR gene for stripe and leaf rust resistance from Ae.markgrafii •TM derivatives- Both leaf and stripe rust resistance genes from T.militinae Molecular mapping: Rust resistance genes •Leaf rust resistance gene Lr45 –Chromosome 2A •Stem rust resistance genes in WR95- chromosome 5DL and 2BL •Leaf rust resistance gene in T.durum genotype Trinakria- chromosome 5BS Fertility restoration genes •Rf8- a new gene on chromosome 2D Marker assisted backcross breeding: •Effective multiple rust resistance genes(Lr19,Lr24,Lr34,Sr26,Yr10 &Yr15) transferred in wheat varieties HD2932, HD2733 and HD2967 •Varieties nominated in trials in 2013: HD2932+Lr19/Sr25, HD2932+Sr26 Diversification of CMS and restorer lines: •Total number of CMS and restorer lines increased to more than hundred each •On the basis of last five years experience, promising CMS and restorer lines identified Introgression of Rust Resistance GenesThe stocks(RIL’S) for Leaf rust resistance maintained and utilized at IARI, RS, Wellington *Markers available – up to serial no.9 already completed Sl.No Leaf rust genes( Out of 68 cataloged genes) Source 1 Lr9* (Not effective) Aegilops umbellulata 2 Lr19*+Sr25 Thinopyrum ponticum= Agropyron elongatum 3 Lr24+Sr24* Thinopyrum ponticum= Agropyron elongatum 4 Lr26+Sr31+Yr9+Pm8* Secale cereale(Petkus Rye) 5 Lr28* Aegilops speltoides 6 Lr32 Aegilops squarossa=Triticum tauschii 7 Lr34*+Yr18+Bdv1+Ltn (individually not effective) Triticum aestivum 8 Lr35(APR Race specific)+Sr39* Ae.speltoides 9 Lr37+Sr38+Yr17* Ae.ventricosum Up to Lr37+ already introgressed into 30 commercial cultivars 10 Lr39* (Down this all are under current programe) T.tauschii 11 Lr41 T.tauschii 12 Lr42 T.tauschii 13 Lr44 Triticum spelta 14 Lr45 Secale cereale(Imperial Rye) 15 Lr46(APR-Race non-specific)+Yr29* T.aestivum 16 Lr47* Ae.speltoides 17 Lr48 T.aestivum 18 Lr49 T.aestivum 19 Lr53+Yr35* T. dicoccoides 20 Lr57 Aegilops geniculata 21 Lr67+Yr46(APR gene) T.aestivum 22 Lr68+(APR) T.aestivum ICAR-Indian Agricultural Research Institute, New Delhi ACCUMULATING FAVOURABLE REGIONS ind. 1 x ind. 2 1st Recombination ind. 3 ind. 4 x 2nd Recombination x 19 DBW 43(P2) ICAR-Indian Agricultural Research Institute, New Delhi HI 1500 (P1) F1 Phenotyping in E1, E2, E3 and E4 in Rainfed and irrigated F2 Genotyping and QTL validation F 4 And F5 generation Delhi 2011-12 Selection of lines for intercrossing based on multilocation AMMI Analyses of phenotype (RF + RI) and QTLs genotyping Fam.1 2 3 F5:F1 4 5 F5:F1 Delhi 2012-13 Lahoul 2012-13 F5:F1 F5:F1 Delhi Power kheda 2013-14 F5:F2 F5:F2 F5:F2 7… .25 6 F5:F2 DC Lahoul 2013-14 F5:F3 DC F5:F4 DC F5:F4 Delhi 2014-15 ICAR-Indian Agricultural Research Institute, New Delhi Traits targeted and phenotyped Morphological traits 1. Days to flag leaf emergence 2. Days to 50% heading 3. Plant height (cm) 3. Ground cover (E1) 4. Grain yield (g/plot) 5. Harvest index 6. Above ground biomass (g/plot) 7. Test weight (g) 8. Grain filling duration 9. Days to maturity 10. Gn wt/10 spike (E1) 11. Spike length (E1) Physiological traits 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. NDVI (E1 & E4) Canopy temperature (CT) (E1& E4) Photosynthetic rate(IRGA) (E1) Chlorophyll content (SPAD) (E1, E3 & E4) Chlorophyll florescence (E1) LAI(leaf area index) (E1) Leaf area (E1) Phenomics (E1) ICAR-Indian Agricultural Research Institute, New Delhi Intercrossed Progenie with high Yield Potential P159-2 /P 157-8 ICAR-Indian Agricultural Research Institute, New Delhi During Kisan Mela……………………. 900 800 700 600 YLD (g) ICAR-Indian Agricultural Research Institute, New Delhi 1000 500 400 300 200 100 0 153-9 63-14 63-2M 68-15 8-21M 8-22F HD 3043 HD3043 HI 1500 DBW 43 Advanced lines in F8 Generation proposed for station trail ICAR-Indian Agricultural Research Institute, New Delhi Elite Lines promoted to CVT 2014-15 Location CVT ENTRY PEDEGREE Central Zone TS C0F8 MARS cross 1 P63-1 DBW 43 × HI 1500 NWPZ VLS C0F8 MARS cross 1 P102-9 DBW 43 × HI 1500 NWPZ VLS C0F8 MARS cross 3 P5 (VL755/UP2338//BAU/KAUZ)х( K.S…1 × PBW 562) NWPZ VLS C0F8 MARS cross 4 P11 PBW 442 × INQ*3/TUKURU//DBW 18 co MARS cross 1 P102-9 ICAR-Indian Agricultural Research Institute, New Delhi C0 MARS cross-1 P102-9 Markers Traits Allele BARC 68(3B) Fv/Fm, chl Homo for DBW 43 positive allele WMC 487 (6B) 1000 Gn wt Homo for DBW 43 positive allele GWM 337 CT Homo for DBW 43 positive allele Cfd 79 Yld (drought) Homo for DBW 43 allele positive allele Barc 147 yld Homo for HI1500 positive allele BARC 170 (4A) CT , Fv/Fm Homo for HI1500 positive allele Co MARS cross 1 P102-9 YLD(g) 900 800 700 600 BARC 186BARC 151(5A) CT Homo for HI 1500 positive allele 500 400 300 200 100 0 P102-9 HI1500 DBW43 HD 3043 Wheat Improvement for temperature and moisture suppressive environments Molecular Breeding for improving WUE, heat and drought tolerance in wheat 1A 1B 1D 2A 2B 2D Yield traits from Parent DBW43 3A 3B 3D 5A 6A 6B 7A 7B 7D Drought tolerance from Parent B HI 1500 Strategies: MABB/MARS/GS Quality Improvement in Wheat Industrial trait: flour values, flour strength and extensibility traits Varieties released after 1985 have not been screened for these traits 50 varieties have been fully characterized. Variation in bread and biscuit quality in Indian wheat varieties NI5439 PBW 343 HD 2687 (Soft endosperm is a primary factor improving the cookie quality (judged by tests such as Spread factor and Solvent retention capacity in addition to cookie making) but most Indian cultivars are medium hard to hard) Particle fraction of the flour is negatively correlated with biscuit making quality Cookies with relatively better spread factor can be produced from flours having weak and extensible dough even from medium soft and medium hard grain Basmati Revolution and Forex Earning Total Export: 4.0 million tons (2013-14) Total Earning (2009-14): 90,000 crores US $ 5.1 billion 33000 35000 (Rs. in crores) 30000 25000 19391 20000 15449 15000 10889 11354 10000 5000 2009-10 2010-11 2011-12 (Year) 2012-13 2013-14 Pusa Basmati 1509 Pusa Basmati 1121 Pusa Basmati 1121 Pusa Basmati 1509 Pusa 1612: A MAS derived blast resistant NIL of Pusa Sugandh 5 released (2013) Group Achievement First MAS derived variety in India to be released through NIL trial Identified for release in Region II (Punjab, Haryana, Delhi and Jammu & Kashmir) of the Basmati growing areas of northwestern India for which the recurrent parent Pusa Sugandh 5 has been released Pusa 1609: The first MAS derived neck blast resistant Basmati rice variety The first MAS derived neck blast resistant Basmati rice variety Identified for release in the Basmati growing regions of the Uttar Pradesh, National Capital Region of Delhi, Uttarakhand and Punjab Pusa 1592: A MAS derived BB resistant NIL of Pusa Sugandh 5 Pusa 1592-06-5-2 (IET 22289), is a MAS derived bacterial blight resistant NIL of Pusa Sugandh 5 developed by pyramiding of bacterial blight resistance genes, xa13 and Xa21 Identified for release in Region II (Punjab, Haryana, Delhi and Jammu & Kashmir) of the Basmati growing areas of north-western India for which the recurrent parent Pusa Sugandh 5 has been released Development of PB1-NILs with Blast Resistance D1 PB1 (Pi1+Pi54+Pita) F1 X D2 (Pi5) PB1 F1 PB1 X D3 (Pi9) PB1 PB1 F1 D4 (Pi2) PB1 F1 PB1 X X BC4F1 BC4F1 BC4F1 BC4F1 Pusa 1633 (Pi1+Pi54+Pita) Pusa 1636 (Pi5) Pusa 1637 (Pi9) Pusa 1634 (Pi2) Pusa 1878 (Pi5+Pi9) Pusa 1680 Pusa 1680 (Pita+Pi5+Pi9) (Pi1+Pi54+Pi5+Pi9) PB1 PB1 Pusa 1879 (Pi2+Pib) Pusa 1681 (Pi2+Pib+Pi5+Pi9) Pusa 1887 Pusa 1682 (Pi1+Pi54+Pita+Pi5+Pi9) (Pi1+Pi54+Pib+Pi5+Pi2+Pi9) D5 (Pib) F1 X BC4F1 Pusa 1635 (Pib) PB1 Grain and cooking quality of Blast resistant PB 1 NILs with two genes Pi9+Pi5 Pusa Basmati 1 IRBL9-W(Pi9) IRBL5-M (Pi5) Pusa 1878-1 Pusa 1878-2 Pi5+Pi9 Pusa 1401 NILs with bacterial blight resistance Pusa 1401 Pusa 1460 Pusa 1401+xa13+Xa21 Pusa 1401 (PB 6)NILs with Blast Resistance Pusa 1401 Pusa 1602 (Piz5) Pusa1603 (Pi54) Pusa 1401+Piz5+Pi54 QTL mapping for Grain Chalkiness Pusa1266 Jaya Indian J. Genet., 73(3): 244-251 (2013) Accelerated development of QPM S.No . Hybrids Parental Inbreds* Area of adaptation 1. HM-4 HKI-1105 × HKI-323 Delhi, Punjab, Haryana 2. HM-8 HKI-1105 × HKI-161 AP, TN, Maharashtra, Karnataka 3. HM-9 HKI-1105 × HKI-1128 Bihar, Jharkhand, Orissa 4. HM-10 HKI-193-2 × HKI-1128 Delhi, Punjab, Haryana, Western UP, Rajasthan, MP, Gujarat, AP, TN, Maharashtra, Karnataka 5. HM-11 HKI1128 × HKI163 Across country except Himalayan belt * Black coloured inbreds are QPM, red coloured inbreds are normal type HM-8 QPM version of HM-8 Beta-Carotene-enriched Hybrids Target hybrids: VQPM9 Vivek Hybrid 27 HM 4 HM 8 25 21.64 21.51 20 17.02 15 12.49 10 5 2.03 1.97 1.85 2.54 0 Vivek QPM-9 Vivek Hybrid-27 HM-4 HM-8 Combining sh2 and su1 genes Sucrose cytosol Class 1 mutant 20 DAP Maturity shrunken2 (sh2sh2) Plastid Class 2 mutant Sugary (su1su1) Sh2 based hybrids have better shelf life, more sugar (~20-25%) but kernels are dull (not preferred) Su1 based hybrids have low shelf life, less sugar (~12-15%), but kernels are creamy and glossy (due to high WSP. By combining the two, enhanced sugar , long shelf life and glossy kernels can be achieved. Development of su1su1sh2sh2 sh2sh2 x su1su1 Su1_/sh2sh2 (F1: Normal) Sh2sh2/Su1su1 su1su1/Sh2_ F2 9: Sh2_/Su1_ 3: sh2sh2/Su1_ 3: Sh2_/su1su1 1: sh2sh2/su1su1 Su1_/Sh2_ su1su1/sh2sh2 su1su1sh2sh2 F1 ear: F2 seeds Water-logging tolerant maize hybrids Pearl millet Varieties Released during 2009-2014 Pusa Composite 612 (MP 480) Released in 2010 for zone-B, an early maturing, fast growing pearl millet composite variety, highly resistant to downy mildew disease and suitable for rain-fed and irrigated conditions White grain pearl millet lines developed Suitable for food industry 655 white grain pearl millet lines developed 82 lines totally free from Downy Mildew Five breeding lines with high Fe and zinc lines were developed in Pearl millet Several mapping populations for downy mildew resistance, high iron, thick spike were developed Six QTL (s) were identified for downy mildew resistance in pearl millet Brassica: Achievements at a Glance Released and notified seven varieties at national level Pusa Mustard 24 (Quality) 2009 NWPZ Pusa Mustard 25 (Early) 2010 NWPZ Pusa Mustard 26 (Late) 2011 NWPZ Pusa Mustard 27 (Early) 2011 CZ Pusa Mustard 28 (Early) 2012 NWPZ Pusa Mustard 29 (Quality) 2013 NWPZ Pusa Mustard 30 (Quality) 2013 CZ Two new entries PDZ-1 & PDZ-2 of double zero B. juncea contributed to AICRP RM testing during 2013-14 for the first time in the country Use of molecular tools: MAS/MABB for quality, White rust, Identified new SNPs, tagged white rust resistance gene, heat tolerance contd… Protocols/Methodology: Three (Heat tolerance, Methyl ester, Maintenance breeding), Breeder and nucleus seed production: Share of IARI Indian mustard varieties in breeder seed indent ranged from 32.19% (2009-10) to 56% (2013-14) with an average of ~40% annually in comparison to national indents Short duration varieties as a replacement of toria Pusa Mustard 25 Pusa Mustard 27 Released in 2010 for CZ Average yield: 15.35 q/ ha Maturity: 118 days Oil content : 41.7% Tolerant to high temperature (seedling stage) and salinity to some extent Released in 2010 for NWPZ Average seed yield 1.5 t/ ha Maturity ̴100 days Productivity: >14 kg/ day/ha Variety for late sown condition Pusa Mustard 26 Released in 2011 for NWPZ for late sown conditions, Yield: 16.04 q/ ha, Maturity: 125 days, Tolerant to high temperatures at seedling and maturity Low Erucic Acid Mustard Varieties Pusa Mustard 24 Average seed yield - 20.25 q/ha, Oil content - 36.55% Maturity : 140 days, NWPZ Pusa Mustard 29 • Seed yield : 21.69 q/ha • 1000-seed weight : ~4.0 g • Oil content : 37.2% • Maturity : 143 days • Moderately tolerant to high temp at seedling & maturity Low erucic acid variety for Central India Pusa Mustard 30 (LES-43) Seed yield: 18.24 q/ha 1000-seed weight: 5.38g Oil content : 37.7% Maturity : 137 days Moderately tolerant to high temp at seedling & maturity Maintenance of quality materials Chickpea Varieties Released during 2009-2014 S. No 1 2 3 4 5 6. Variety Pusa 5023 (Pusa Shaktiman) Pusa 5028 (Pusa Bheema) Pusa 2085 Pusa Green 112 BGD 103 (desi) BG 1105 (Kabuli) Year of Release 2012 2012 2013 2013 2009 2009 Area of adaptation Delhi State Delhi State Delhi State Delhi State Karnataka Karnataka Varieties released during 2012 Varieties released during 2013 Share of IARI Chickpea Varieties in Total Breeder seed Indent 10000 9000 INDENT (QT) 8000 TOTAL INDENT 7000 6000 IARI VARIETIES INDENT 5000 4000 3000 2000 4.16% 1000 0 2009-10 2010-11 2011-12 YEAR 2012-13 Pigeonpea: Significant Achievement Extra early maturity (120 days), dwarf genotypes suitable for pigeonpea-wheat rotation, mechanical harvesting have been developed Pusa 2012-1 : Promoted into AVT1(Early) for NWPZ, Yield: 27.04 q/ha Inheritance of male fertility restoration 31 new A lines (16 A2 + 15 A4 Cytoplasm) and 50 new R lines have been developed from interspecific cross C. scarabaeoides x Pusa 33 QTLs for different yield related traits mapped from RILs of cross Dwarf X H 2001-4 Compact erect plant type with long pods, 4-5 seeds/pod, bold seeds and profuse bearing for pigeonpea-wheat CS Row to row distance can be further reduced from 60 to 45 cm to increase plant population/ unit area Soybean :Varieties released DS12-13 Released for North Plain Zone By CVRC, a bold seeded variety having high oil content (19.60%), resistant to yellow mosaic virus, Rhizoctonia Arial blight and Bacterial Pustule DS2614 (Pusa 14) Released for Delhi State, a medium bold seeded variety having good seed longevity and high oil content (20.26%), resistant to yellow mosaic virus, Rhizoctonia Arial blight and Bacterial Pustule DS12-5 Released for North Plain Zone, a bold seeded variety having high oil content (20.08%), resistant to yellow mosaic virus, Rhizoctonia Arial blight and Bacterial Pustule •Thanks NSAI
© Copyright 2026