Mrs. Julee Rodgers Spain Park High School Hoover, Alabama
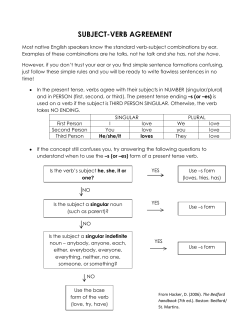
Mrs. Julee Rodgers Spain Park High School Hoover, Alabama Cross out prepositional phrases first! Subject VERB ACTION Transitive LINKING Intransitive Direct Object Indirect Object Subject Complement Predicate Nominative Object Complement Predicate Adjective The bears from Stygia ate my watermelon pickles after the tea party on the hill. The bears from Stygia ate my watermelon pickles after the tea party, on the hill. Then, you will be left with the basic parts of the sentence. The action or being word in the sentence is the easiest to find. For example: Sentence: My koala jumped over the sewing machine. Step 1: My koala jumped over the sewing machine. Step 2: My koala jumped over the sewing machine. Subject does the verb’s action. S V The mongoose hollered at me. S V Gypsies danced in the moonlight. S V The old woman sold crumbs for the birds. The verb will decide the rest of the sentence parts. ASK: Is it ACTION or LINKING? Easy: Just find out if it is linking. (To see how, go to next slide.) 2 ways to know: 1. know the list of linking verbs, then 2. substitute an equal sign (=) for the verb (alphabetical order, easy to memorize!) Forms of “to be” (am, is, are, was…) appear seem become smell feel sound grow stay look taste remain turn A linking verb MUST have a subject complement after it: Subject – linking verb – subject complement. My emu – smelled – flowery. The duck – appeared – tipsy. The bouncer – sounded – tough. So, if you have a linking verb in the sentence and there is a word after it, you can substitute an equal sign for the verb to check that you have a linking verb. Substitute an equal sign for the verb to check for a linking verb Subject – linking verb – subject complement. Subject = subject complement. My emu smelled flowery. My emu = flowery. The duck appeared tipsy. The duck = tipsy. The bouncer sounded tough. The bouncer = tough. Sentence must have pattern of Subject – Linking Verb – Subject Complement Subject Complement will be either Predicate Nominative (a noun) or Predicate Adjective (an adjective) Always comes after a linking verb. Subject – Linking Verb – Subject Complement Can be a noun (predicate nominative) OR Can be an adjective (predicate adjective) Subject – linking verb – subject complement (predicate nominative) Your car was a waste of money. The bartender became king of the planet. The Zulu warrior remained a leader of his men. Subject – linking verb – subject complement (predicate adjective) The clock became depressed about Daylight Savings Time. Sleeping Beauty remained dreamy for years. Her flowers grew taller in the sunshine. 1. a. b. Charlie only seems quiet and withdrawn. Predicate Nominative Predicate Adjective 2. This desk is my podium during lectures. a. Predicate Nominative b. Predicate Adjective 3. That train robbery remains an unsolved mystery. a. Predicate Nominative b. Predicate Adjective 4. The soaked and exhausted scouts looked miserable. a. Predicate Nominative b. Predicate Adjective Action Verb First, you have to find out: TRANSITIVE or INTRANSITIVE? TRANSITIVE has a DIRECT OBJECT INTRANSITIVE has NO OBJECT So, skip down to finding out if you have a direct object or not. ASK: verb who? verb what? For example: The aardvark wrestled the armadillo. wrestled who? wrestled what? wrestled the armadillo armadillo = direct object The cat ate my flowers. ate who? ate what? ate flowers. flowers = Direct Object The chimp aced the test. aced who? aced what? aced test. test = DO The turtle bit me. bit who? bit what? bit me. me = DO The monk rang the bells at sunset. rang who? rang what? rang bells. bells = DO …the Action Verb is Transitive. (That’s all that transitive means.) Subject – Action Verb Transitive – Direct Object If there is no answer to verb who? verb what?, you have an Intransitive Verb. For example: The bear slept in his cave. slept who? slept what? No Answer = no DO = verb is intransitive. Early astronomers observed the heavens constantly. 1. a. b. c. d. astronomers constantly observed heavens 2. When she visited our class, Ms. Bailey brought us weather maps and other data. a. class b. us c. Ms. Bailey d. maps, data 3. She teaches college students weather forecasting. a. she b. students c. teaches d. forecasting 4. The spacecraft photographed the surface of Venus. a. surface b. photographed c. spacecraft d. Venus Then check for Indirect Object ASK: verb to whom? verb to what? verb for whom? verb for what? ASK: verb to whom? verb to what? verb for whom? verb for what? For example: The cheetah sent me an invitation. (DO = invitation) sent to whom? sent to me. me = Indirect Object Beverly made Wog a cake. (DO = cake) made for whom? made for Wog. Wog = IO Always between Action Verb and Direct Object. Subject – Action Verb Trans – INDIRECT OBJECT – Direct Object 1. Ms. Bailey gave our class a lecture on weather. a. lecture b. class c. weather d. Ms. Bailey 2. By building a well, we gave the South American villagers a chance. a. well b. building c. villagers d. chance e. we 3. She offered the class her opinion. a. direct object b. indirect object 4. She offered the class her opinion. a. direct object b. indirect object 5. Mrs. Hines showed us pictures of the first thermometers from the seventeenth century. a. direct object b. indirect object 6. In turn, these records provide meteorologists statistics. a. direct object b. indirect object …check for Object Complement Object Complement Verbs • these verbs may indicate an object complement • verbs meaning “make” or “consider” appoint find call keep choose make color paint consider render elect Always AFTER the Direct Object Subj. – Action Verb Trans – Direct Object – Object Complement (See examples next slide.) S AV-T DO OC My giraffe painted my study purple. S AV-T DO OC The gerbils elected Marty president. S AV-T DO OC Maudie found his manners horrendous. S AV-T DO OC The rat called the cat a tramp. Direct Object = Object Complement From examples in previous slide: study = purple Marty = president manners = horrendous cat = tramp 1. The committee selected Spain Park the winner of the Blue Ribbon Award for Academic Excellence. a. committee b. Spain Park c. winner d. Award 2. Gail considers astronomy the most compelling science. a. science b. Gail c. astronomy d. compelling 3. I have always found botany fascinating. a. I b. always c. fascinating d. botany 4. We, on the other hand, consider her starstruck. a. We b. hand c. her d. starstruck 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) Cross out prepositional phrases. Find verb. Find subject (does verb’s action). Go back to verb: action or linking? Check for linking: list, = sign. If linking, name subject complement as noun or adjective (PN or PA). If action verb, find direct object to decide transitive or intransitive. 8) If no direct object, verb is intransitive and sentence analysis is complete. 9) If direct object, check for indirect object. 10) If no indirect object, check for object complement. 7) 1. Subject – action~intransitive verb 2. Subject – action~transitive verb – direct object 3. Subject – action~transitive verb – indirect object – direct object 4. Subject – action~transitive verb – direct object – object complement 5. Subject – linking verb – subject complement (predicate nominative) 6. Subject – linking verb – subject complement (predicate adjective) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. S AV-I The ostrich sang. S AV-T DO The ostrich sang an aria. S AV-T IO DO The ostrich sang me an aria. S AV-T DO OC The ostrich made the aria beautiful. S LV SC(PN) The ostrich was a singer. S LV SC(PA) The ostrich was fantastic. 1.Cross out prepositional phrases first! 3. Subject 2+4. VERB 5. ACTION 7. Transitive 5 .LINKING 7. Intransitive 6. Direct Object 8. Indirect Object 6. Subject Complement 7. Predicate Nominative 8. Object Complement 7. Predicate Adjective Divide the complete subject and complete predicate by choosing the two words where the division occurs. 1. My friend Helen wants to be a teacher. a. My | friend b. Helen | wants c. friend | Helen d. wants | to 2. Suddenly, several passengers spotted a giraffe and several lions. a. SS- passengers SP-spotted b. SS- several SP- spotted c. SS- giraffe SP- and d. SS- several passengers SP- spotted 3. Clouds of dust around the van obscured our vision. a. SS- dust SP-around b. SS- dust SP- obscured c. SS- clouds of dust SP- vision d. SS- clouds SP- obscured 4. The fans in the stadium cheered for the Spain Park Jags. a. stadium cheered b. fans in the stadium c. cheered for the Spain Park Jags d. cheered 5. Gabriella will take her science project to the state fair. a. will b. will take her project c. will take d. will take her project to the state fair 6. Neither the drama teacher nor the club president can decide. a. Neither, nor b. drama, president c. drama, club d. teacher, president 7. Directors can add elements, but cannot save a weak script. a. can add, can save b. add, save c. can, add d. save, weak 8. On its surface, tiny Mercury resembles our moon. a. surface b. Mercury c. moon d. resembles 9. The new CEO gave the old boss a smooth transition. a. new b. boss c. smooth d. CEO e. transition 10. Our science teacher, Mrs. Hines, sent Ms. Bailey an invitation. a. teacher b. Mrs. Hines c. Ms. Bailey d. invitation 11. She offered the class her opinion. a. direct object b. indirect object 12. Weather stations once gave others information on current conditions by telegraph. a. direct object b. indirect object 13. My name became official on June 9, 1990. a. Predicate Nominative b. Predicate Adjective 14. Mr. Kravitz may become our new history teacher. a. Predicate Nominative b. Predicate Adjective 15. Our science club chose Gail the chairperson. a. club b. Gail c. science d. chairperson 16. Our science club chose Gail the chairperson. a. club b. Gail c. science d. chairperson
© Copyright 2026