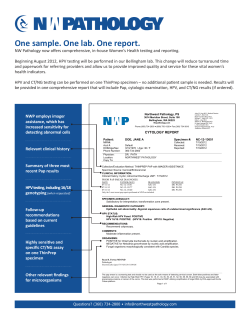
Retrospektiv populasjonsbasert HPV-studie basert på unike data fra Kreftregisteret i Norge:
Retrospektiv populasjonsbasert HPV-studie basert på unike data fra Kreftregisteret i Norge: HPV-data og celleforandringer hos kvinner som er konisert en gang og som må gjennomgå ny konisering Steinar Ø Thoresen Klinisk forskningssjef GSK Professor dr med UiB Oslo 25. mai 2010 Out-line of presentation Background: HPV and development of cervical neoplasi Rationale for study Why Norway and Why The Cancer Registry of Norway? Current study: objectives and study design Conclusion Out-line of presentation Background: HPV and development of cervical neoplasi Natural History From Infection to Cervical Cancer Time Normal epithelium Months HPV infection; koilocytosis CIN I Low grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (ASCUS/LSIL) Years CIN II High grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL) From incident to persistent HPV infection Spontaneous regression Screening Treatment CIN III Invasive Carcinoma Conization and later pregnancy out-come Distribution of HPV-types in CC 16 18 17,2 45 6,7 31 2,9 33 2,6 52 HPV genotype 53.5% 70.7% 77.4% 80.3% 82.9% 85.2% 87.4% 88.8% 53,5 2,3 58 2,2 35 1,4 59 1,3 56 1,2 51 1,0 39 0,7 68 0,6 73 0,5 82 0,3 Other 1,2 4,4 X 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 Cervical cancer cases attributed to the most frequent HPV genotypes (%) Munoz N et al. Int J Cancer 2004; 111: 278–85. 100 Oncogenic HPV distribution in CIN2/3 Norway HPV Type % AHUS (n=643) 16 51.2 18 10.8 31 16.3 33 15.2 35 3.4 39 9.3 52 11.2 AHUS: Sjøborg et al, Gyn Oncol 2010 HUMAN PAPILLOMAVIRUS TYPE DISTRIBUTION IN CERVICAL NEOPLASIA: RESULTS FROM TWO PARALLEL EPIDEMIOLOGICAL STUDIES IN WOMEN WITH HIGH-GRADE CERVICAL INTRAEPITHELIAL NEOPLASIA AND INVASIVE CERVICAL CANCER IN EUROPE W. Tjalma on behalf of the HERACLES/SCALE study group (Montreal IPV Congress July 2010) Cervarix® efficacy in TVC-naïve: final analysis of Phase III trial (39.4 months) Primary analysis (TVC-naïve) Vaccine Efficacy (96.1%CI) Endpoint CIN2+ HPV 16/18 Group N n HPV 5,449 1 Control 5,436 63 % LL UL p-value 98.4 90.4 100 < 0.0001 Vaccine Efficacy (96.1%CI) Endpoint CIN3+ HPV 16/18 Group N n HPV 5,449 0 Control 5,436 13 % LL UL p-value 100 64.7 100 < 0.0001 The TVC-naïve cohort approximates adolescent girls pre-exposure Paavonen J, et al. Lancet 2009; 374:301–314. Results CIN2+ (CERVARIX) Vaccine efficacy associated with the most frequent non-vaccine oncogenic HPV types and 14 oncogenic types (TVC naive) HPV type N n HPV 31/45 Vaccine 2 most frequent nonControl vaccine types 5449 0 5436 24 HPV 31/33/45/52/58 Vaccine 5 most frequent nonControl vaccine types 5449 15 HPV 31/33/35/ 39/45/51/52/56/58/ 59/66/68 any oncogenic types except 16/18 Group Vaccine Control HPV 16/18/31/33/35/ Vaccine 39/45/51/52/56/58/ 59/66/68 14 oncogenic types Control including 16/18 5436 47 5449 20 5436 63 5449 22 5436 Vaccine Efficacy % 96.1% CI p-value 100 (82.2; 100) < 0.0001 68,2 (40.5; 84.1) < 0.0001 68.4 (45.7; 82.4) < 0.0001 77.7 (63.5; 87.0) < 0.0001 98 N = number of evaluable women in each group; n = number of evaluable women reporting at least one event in each group Paavonen J, et al. Lancet 2009; 374:301–314; Adapted from Skinner SR et al. IPvC 2009:Abstract Out-line of presentation The scientific challenge and rationale for study Will Cervarix show efficacy in women treated for CIN2+ lesions? ( about 3 000 women/year) • Oncogenic HPV-infections High-grade lesions Surgery on cervical uterus (conization) HPV-persistent after surgery? New HPV-infections? High risk of recurrence of CIN and ICC • HPV-vaccination or not? • • • • • Cervarix-vaccination in women submitted to conization? As a first step to fill this gap of knowledge, GSK will implement a register-based retrospective study of natural history of HPV infections and cervical lesion (CIN2+) recurrences in women submitted to a conization, in Norway. Out-line of presentation Why Norway and why The Cancer Registry of Norway? The Cancer Registry of Norway, established 1951 Nationwide - population-based Compulsory reporting on all cancers Complete on all solid cancers Includes: ID of patients and all specimens Sites, histology (grading), staging ID of labs and all parafin blocks (stored) Copy and ID of reports Treatment Survival, time and cause of death The Cancer Registry of Norway, established 1951 Nationwide - population-based National cervical cancer screening program since 1995: One cytology form One national cytology database (1992) One national cervical biopsy database (2002) National CIN-treatment database (1997) CIN 2+ registration ICC registration The Cancer Registry of Norway, established 1951 Completeness of records and blocks (in the hospitals): Bilet et al: Acta Oncol 2009: Completeness estimate of CC in CRN was 98.8% in 1985 and 100% in 1999. Availability of blocks in hospitals: 97.9 % in both years. Out-line of presentation Current study: objectives and study design A retrospective, register-based, epidemiological study of natural history of HPV infections in women aged 18 years and above with recurrent conization following a primary conization for high grade lesion diagnosis/ microinvasive cervical carcinomas, in Norway. Utprøvere: Professor Ole Erik Iversen og professor Olav Vintermyr UiB, Haukeland Universitetsykehus Tor Molden GSK Bio Ann-Kirst Johansen GSK Norway Steinar Thoresen GSK Norway Primary objetives To assess the distribution of oncogenic HPVtypes in recurrent conization considered as: New infections or Probably recurrent infections Study design The Cancer Registry to identify 550 women with the first conization 19982003 and the second conization 2003-2008; including all biopsies between conizations. 100 % follow-up of all patients Retrieve all parafin blocks from Norwegian pat labs Review of all blocks/slides in one dedicated lab HPV-testing in one dedicated lab Approved by EC/SLV and based on informed consent Decision tree for sample selection and testing Conclusion The infrastructure of The Norwegian Cancer Registry is unique for retrospective population-based epidemiological research on HPV and cervival neoplasi, including the retrieval of parafin blocks and complete follow-up of all participants The current post-conization study could not be performed out-side Norway ( Scandinavia) We expect the current study to provide new knowledge about HPVinfections after primary conization and be an important step before a Cervarix vaccination phase lll study in women submitted for conization
© Copyright 2026