PRESCHOOL EVALUATION SCALE SCHOOL VERSION RATING FORM PROFILE SHEET
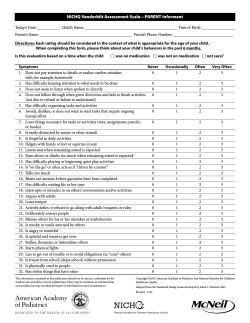
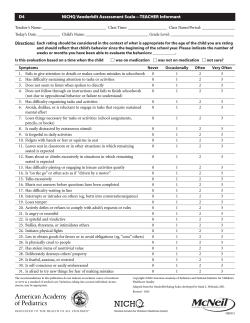
PRESCHOOL EVALUATION SCALE SCHOOL VERSION RATING FORM Stephen B. McCarney, Ed.D. PROFILE SHEET Name of student: Austin Williams Gender: Male Class: Tues/Thur a.m. State: PA Midvale 2002 Date of rating: Date of birth: 6 28 (year) (month) (day) 1999 7 1 (year) (month) (day) Large Muscle Skills 33 9 0.98 Small Muscle Skills 21 6 1.25 Cognitive Thinking 29 8 1.02 Expressive Language Skills 25 8 1.12 Social/Emotional 23 9 1.55 Self-Help Skills 21 8 1.07 E R CO N S K IO C I U VER LE Q -2 OL AMP S PE HO E S SC FIL O R P 35 (months) Age at rating in months: Total Scale Sum of Subscale SS %ile Rated by (observer's name): M Jackson Dates during which observation of child occurred: From: 09/01/2001 To: 06/28/2002 Standard Scores 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 Large Muscle Skills Small Muscle Skills X PES-2 SV 0-35 Raw Standard SS Score Score Score SEM Subscales School: Midvale Preschool City: SUMMARY OF SCORES Copyright © 1992, 2010 Hawthorne Educational Services, Inc. 19 87 Quotient Confidence SEM Interval 3.07 68% SUBSCALES Cognitive Thinking X X 48 Quotient Expressive Language Skills X Social/ Emotional X Self-Help Skills X Percentiles >99 95 90 85 80 75 70 65 60 55 50 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 <1 Percentile Rank X The Large Muscle Skills subscale assesses gross motor skills, which require movement of large muscles (e.g., walking, throwing, crawling, climbing, etc.). Austin scored within one standard deviation below the mean on the Large Muscle Skills subscale. The following are primary behaviors of concern: 14. Kicks a large ball while standing in place 15. Independently jumps in place on toes with both feet off the ground 18. Walks up stairs alternating feet The Small Muscle Skills subscale assesses fine motor skills, which require use of small muscles (e.g., grasping, writing, cutting, stacking, etc.). BE P SC H ES H AV -2 O I Q O O U L R IC V S ER O K S SI F C CO O O R N N E SA CE M RN PL E Austin scored more than one standard deviation below the mean on the Small Muscle Skills subscale. The following are primary behaviors of concern: 28. Can correctly complete a three-piece form board consisting of a circle, square, and triangle 29. Imitates drawing a circular and vertical stroke after seeing a demonstration 30. Can unscrew bottle lids approximately two inches in diameter 31. Builds a tower of eight blocks 32. Uses a thumb and forefinger grasp in holding a pencil, instead of using a fist 33. Builds a tower of ten blocks 34. Can cut a piece of paper from one side to the other with scissors The Cognitive Thinking subscale assesses mental development including basic sensorimotor skills and concept development. Austin scored within one standard deviation below the mean on the Cognitive Thinking subscale. The following are primary behaviors of concern: 46. Points to pictures in a book when asked 48. Points to four body parts when named 49. Points to three pictures of common actions such as running, eating, sleeping, crying, etc. 50. Can point to an object by its usage, such as what we eat with, sit on, ride in, etc. 51. Points to ten pictures of common objects when asked The Expressive Language Skills subscale assesses receptive and expressive communication skills. Austin scored within one standard deviation below the mean on the Expressive Language Skills subscale. The following are primary behaviors of concern: 62. Has fifty words or more in spoken vocabulary 63. Uses three-word sentences when communicating 64. Can name five pictures when asked, "What is this?" 65. Names a preferred object when asked, "Do you want the ball or the car?" 66. Speaks intelligibly, can be understood by someone who is not familiar with him/her The Social/Emotional subscale assesses skills related to social interactions. Austin scored within one standard deviation below the mean on the Social/Emotional subscale. The following are primary behaviors of concern: 77. Is beginning associative play (e.g., actively plays with another child) 78. Verbalizes displeasure rather than physically hurting peers 79. Can share toys in a reciprocal fashion The Self-Help Skills subscale assesses skills related to independent daily functioning. Austin scored within one standard deviation below the mean on the Self-Help Skills subscale. The following are primary behaviors of concern: 86. Uses a spoon with minimal spilling 87. Unzips zippers 88. Indicates toileting needs by squatting, holding self, or verbalizing 90. Puts on coat independently 92. Unties and removes shoes 93. Can independently put on shoes although they are often on incorrect feet 94.0-35 SV Snaps front snaps PES Copyright (c) 1992 Hawthorne Educational Services, Inc. Page 2 of 4 PRESCHOOL EVALUATION SCALE HOME VERSION RATING FORM Stephen B. McCarney, Ed.D. PROFILE SHEET Name of student: Thomas Andrews Gender: Male Class: State: PA Midvale Date of rating: Date of birth: 1998 9 (year) (month) (day) 1996 2 13 (year) (month) (day) 15 Standard Scores 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 PES-2 HV 0-35 0.75 Small Muscle Skills 21 8 0.94 Cognitive Thinking 34 12 0.92 Expressive Language Skills 28 0.98 Social/Emotional 25 11 12 Self-Help Skills 24 10 1.06 1.26 64 102 55 2.42 68% SUBSCALES Cognitive Thinking X X 11 Sum of Quotient Confidence Subscale SS Percentile Quotient SEM Interval Dates during which observation of child occurred: From: 02/13/1996 To: 09/15/1998 Small Muscle Skills 33 Total Scale Rated by (observer's name): M. Jackson Large Muscle Skills Standard Standard Score Score SEM Large Muscle Skills E R CO S K ON C I U ERI LE Q P V -2 M S E PE OM E SA H FIL O R P 31 (months) Age at rating in months: Raw Score Subscales School: City: SUMMARY OF SCORES X Copyright © 2004, 2010 Hawthorne Educational Services, Inc. Expressive Language Social/ Skills Emotional X Self-Help Skills X X Quotients 150 145 140 135 130 125 120 115 110 105 100 95 90 85 80 75 70 65 60 55 50 Quotient X Percentiles >99 95 90 85 80 75 70 65 60 55 50 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 <1 Percentile Rank X The Large Muscle Skills subscale assesses gross motor skills, which require movement of large muscles (e.g., walking, throwing, crawling, climbing, etc.). Thomas scored within one standard deviation above the mean on the Large Muscle Skills subscale. The following are primary behaviors of concern: 11. Seldom falls when walking alone 15. Independently jumps in place on toes with both feet off the ground 18. Walks up stairs alternating feet The Small Muscle Skills subscale assesses fine motor skills, which require use of small muscles (e.g., grasping, writing, cutting, stacking, etc.). BE P H H ESO AV 2 M I Q E OR UI V ER S O CK SI F SC O CO O N R N SA C E M ER PL N E Thomas scored within one standard deviation below the mean on the Small Muscle Skills subscale. The following are primary behaviors of concern: 20. Enjoys watching his/her hands move and putting them in mouth 24. Lines up a small object in one hand with an object in the other hand 26. Can insert a circular block in a form board 28. Can correctly complete a three-piece form board consisting of a circle, square, and triangle 29. Imitates drawing a circular and vertical stroke after seeing a demonstration 30. Can unscrew bottle lids approximately two inches in diameter 31. Builds a tower of eight blocks 33. Builds a tower of ten blocks 34. Can cut a piece of paper from one side to the other with scissors The Cognitive Thinking subscale assesses mental development including basic sensorimotor skills and concept development. Thomas scored within one standard deviation above the mean on the Cognitive Thinking subscale. The following are primary behaviors of concern: The Expressive Language Skills subscale assesses receptive and expressive communication skills. Thomas scored within one standard deviation above the mean on the Expressive Language Skills subscale. The following are primary behaviors of concern: 62. Has fifty words or more in spoken vocabulary 63. Uses three-word sentences when communicating The Social/Emotional subscale assesses skills related to social interactions. Thomas scored within one standard deviation above the mean on the Social/Emotional subscale. The following are primary behaviors of concern: 74. Predominately plays side-by-side with peers with very little interaction with them The Self-Help Skills subscale assesses skills related to independent daily functioning. Thomas scored at the mean on the Self-Help Skills subscale. The following are primary behaviors of concern: 84. Independently pulls off socks 88. Indicates toileting needs by squatting, holding self, or verbalizing 90. Puts on coat independently 92. Unties and removes shoes 93. Can independently put on shoes although they are often on incorrect feet 94. Snaps front snaps PES 0-35 HV Copyright (c) 2004 Hawthorne Educational Services, Inc. Page 2 of 4
© Copyright 2026