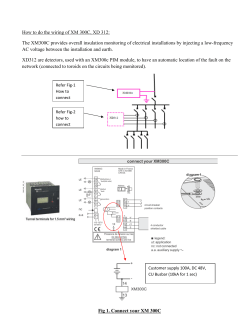
BFD Features
BFD Features
Session Objectives
At the end of the session, the participants should:
Understand advantages of BFD implementation on S9700
Understand when to use BFD on S9700
1
Contents
BFD introduction and protocol features
BFD on S9700 – snapshot
BFD on S9700 – software implementation details
BFD on S9700 – configuration
Summary
2
Why BFD
Lightweight hello protocol over different protocols IPv4, MPLS…
Used for fast (often sub-second) communication failure detection
Single, common & standardized mechanism
Independent of specific routing, VRRP and other client protocols
dst UDP port 3784 & 4784 (4784 is used for multi-hop BFD)
RFC 5880
So lots protocols could leverage this lightweight BFD to achieve fast
hello without more CPU burden.
SRU (Supervisor)
OSPF
VRRP
PIM
BGP
BFD
3
IS-IS
Etc.
BFD Advantages
Many protocols use same hellos-reduce control plane load
No impact due to sup switchover, unless the route down
ms-level fault detection performance
Proprietary one-arm-echo BFD function can be used with device which does
not support BFD
Proprietary multicast BFD can be used to detect the L2 link and the specific
member in a trunk, and bind the interface state.
Associating with oam protocol , notifies the link faults
Associating with the protocols running on the ring network
4
Contents
BFD introduction and protocol features
BFD on S9700 – snapshot
BFD on S9700 – software implementation details
BFD on S9700 – configuration
Summary
5
BFD on S9700: Snapshot
Software support start: V200R001
Hardware support:
All current and future I/O modules
Centralized packet processing
Master CPU transmit/receive BFD packets
with OAM Chip, we could do hardware offload
SRU-D has already integrated OAM FPGA, so no extra cost.
MCU(S9703) is done by a process in CPU.
BFD packets sent with TOS-EXP
6
S97’s BFD Modes brief
Asynchronous mode – Supported from S9700
Systems establish BFD session and periodically exchange control packets
If some number of control packets missed (default is 3 ) session declared down
One ARM Echo mode – Huawei proprietary mode
Worked with other devices does not support BFD
Multicast BFD – Huawei proprietary mode
Could run at L2 links, no IP interface needs.
7
Async timer negotiate
R1
My desc = foo
Your desc = xxx
Required Rx = 50ms
Desired Tx = 100ms
My desc = bar
Your desc = foo
Required Rx = 60ms
Desired Tx = 40ms
Compare minRX from peer vs
self Desire TX,
the slower win
So send @
100ms
R1
My desc = foo
Your desc = bar
Required Rx = 50ms
Desired Tx = 100ms
R1
R2
Compare min-RX from
peer vs self Desire TX,
the slower win.
So send @ 50ms
Handshake Complete
Session is UP
R2
8
BFD one-arm-mode – Huawei
proprietary
Application scenario
Connect with a 3rd party device, which doesn’t support BFDv1
3rd Device
Only BFD echo frames
No control frames exchange
sth. Fails
Trigger hooked clients
9
Multicast BFD –
Huawei proprietary
Application scenario
Test a link if no IP address could be specified.
Capture this mc-addr.
Need avoid conflict.
Capture this mc-addr.
Need avoid conflict.
L2 Link or unnumbered interface
BFD control frames
with multicast
address
Specify a dedicated 224.x.x.x mc-IP-address
The MC address must be same in 2 devices.
10
S97 BFD software features (1)
Static BFD
Dynamic BFD
Triggered by protocol, like: OSPF, BGP, IS-IS, MPLS LDP, RSVP-
TE, PWE3、PIM.
BFD for single hop & multi-hop
BFD for supervisor’s switch-over
S97’s BFD session won’t teardown when supervisor do a switchover.
BFD for static route / OSPF / BGP / IS-IS
BFD for PIM
BFD for VRRP
BFD for FRR (LDP FRR/ TE FRR /VPN FRR /VLL FRR)
11
S97 BFD software features (2)
BFD over Ports
L3 GE & 10GE ports
VLAN-IF interface
L3 dot1Q interface
L3 Eth-trunk Logical
Single BFD session for whole trunk
When BFD run over trunk, BFD packets are sent over some link
members using hashing.
L2 port
Need Huawei proprietary multicast BFD.
Eth-trunk Per-link
Separate BFD sessions for each link in interface for resiliency
Need Huawei proprietary multicast BFD session.
12
S97 BFD software features (3)
BFD Interface support
Static LSP
LDP LSP
MPLS TE
VLL PW
No detective for backup PW
No support for PW over TE
VPLS PW
No support for PW over TE
13
BFD vs Per-Protocol Timers
Per-Protocol Timers:
Single interface may have 2-3+ protocols establishing adjacency
E.g., VRRP, PIM, OSPF on each vlanif/subinterfaceI
Tuning down timers for every protocol increases inband and CPU
utilization. This wastes CPU effort and link bandwidth
Configuration complexity
BFD:
One BFD session can track link-state for all client protocol sessions
between an IP node pair
14
Contents
BFD introduction and protocol features
BFD on S9700 – snapshot
BFD on S9700 – software implementation details
BFD on S9700 – configuration
Summary
15
BFD on S9700 Software
Architecture
Switching Route Unit
OSPF
RIP
PIM
BGP
IS-IS
Etc.
BFD
BFD Client
Hardware
Hardware
Hardware
I/O Module
I/O Module
I/O Module
16
Client Behavior – OSPF
OSPF 1
BFD 2
BFD 1
OSPF 2
Establish OSPF Adj
Establish OSPF Adj
OSPF FULL
OSPF FULL
Register OSPF neighbor IP
with BFD
Register OSPF neighbor IP
with BFD
OSPF Registered
BFD notifies OSPF
OSPF Registered
BFD packets
BFD packets
Send OSPF Hellos
Send OSPF Hellos
Device Fails
BFD notifies OSPF
OSPF de-Registered
17
OSPF Adj removed
De-register neighbor IP with
BFD
Client Behavior – PIM
PIM 1
BFD 2
BFD 1
PIM 2
Send PIM Hellos
Send PIM Hellos
PIM Adj
Register neighbor IP
with BFD
PIM Adj
Register neighbor IP
with BFD
PIM Registered
BFD notifies PIM
BFD packets
BFD packets
PIM Registered
Send PIM Hellos
Send PIM Hellos
Device Fails
BFD notifies PIM
PIM de-Registered
18
PIM Adj removed
De-register neighbor IP
with BFD
Client Behavior –static routes
static route 1
BFD 2
BFD 1
static route 2
Add a static BFD
configuration
Track static route with
BFD
Track static route with
BFD
BFD packets
BFD packets
Device Fails
BFD notifies static
route
19
static route turn to
inactive
Proprietary BFD: one-arm-echo (1)
static route 1
BFD 1
Third-part device without
BFD function
Add a static BFD
configuration oneside only
Track static route with
BFD
IP loop
BFD packets
static route turn to
inactive
BFD notifies static
route
sth. Fails
20
One-arm-echo vs Echo
Unlike standard echo mode.
one-arm-echo only send
echo BFD frames, no BFD
control frame exchange.
Be carefully, by default echo frames use self-interface-ip as src & dst ip, so you
should disable some security check function along with the path.
21
BFD Interoperability
Tested with:
NE40E
C7600
S9500
22
Contents
BFD introduction and protocol features
BFD on S9700 – snapshot
BFD on S9700 – software implementation details
BFD on S9700 – configuration
Summary
23
BFD Configuration (1)
Pre-configuration Tasks
Before configuring BFD, complete the following tasks:
1. Connecting each interface correctly
2. Configuring IP addresses for Layer 3 interfaces
Data Preparation
To configure BFD, you need the following data.
1. BFD configuration name
2. Peer IP address, local interface type and number for the directly-connected link
detected by BFD, and default multicast address used by BFD if it checks the
physical layer status of the link
3. BFD session parameters: local and remote discriminators
24
BFD Configuration (2)
BFD min-tx-interval <10-1000> min-rx-interval < 10-1000 > multiplier <3-50>
Global or per-interface control of BFD timers
Interval –frequency in msec at which to send BFD messages
Multiplier: BFD declared down if no packet received within (interval*multiplier)
msec
Default is interval = 10 msec and multiplier = 3
failover detection in 30 msec
25
BFD Configuration (3)
one arm echo config:
bfd cfg-name bind peer-ip peer-ip [ vpn-instance vpn-instancename ] interface interface-type interface-number [ source-ip sourceip ] one-arm-echo
Notice:
1) only in sing-hop BFD
2) Only need local discriminate. “discriminator local discr-value ”.
3) “min-echo-rx-interval interval” could set the echo interval, default is 10ms.
26
BFD Configuration: other parameters
WTR configured (default 0) [WTR is a timer to hold when BFD
session state change from down to up.]
Run: wtr wtr-value
Set the priority of BFD packets (default 7, lowest priority 0)
Run: tos-exp tos
Configure the number of the default destination port for the multi-hop
BFD control packet
Run: multi-hop destination-port { 3784 | 4784 }
27
BFD Configuration Example 1
BFD for OSPF
1 Display the system view:
Run: system-view
2 Display the OSPF view:
Run: ospf process-id
3 Establish BFD sessions for OSPF:
Run: bfd all-interfaces enable
4 Specify the value for each parameter used to establish a BFD session(Optional):
Run: bfd all-interfaces { min-rx-interval receive-interval | min-tx-interval
transmit-interval | detect-multiplier multiplier-value } *
5 Check the information about the BFD session:
Run: display ospf [process-id ] bfd session interface-type interfacenumber [ router-id ] or
display ospf[process-id ] bfd session { router-id | all }
28
BFD Configuration Example 2
BFD for PIM
1 Display the system view:
Run: system-view
2 Display the interface view (Interface type must be VLANIF):
Run: interface interface-type interface-number
3 PIM BFD is enabled :
Run: pim bfd enable
4 PIM BFD parameters are adjusted.
Run: pim bfd { min-tx-interval tx-value | min-rx-interval rx-value | detect-multiplier
multiplier-value }*
5 check information about a PIM BFD session :
Run: display pim [ vpn-instance vpn-instance-name | all-instance ] bfd session
statistics
29
BFD Configuration example 3
one-arm-bfd example
src & dst ip is local interface IP address by default
Also could change it by CLI: src IP= Loopback IP, dst IP = local
interface IP
Src-MAC = local interface MAC, dst-MAC = peer’s MAC
30
BFD Configuration example 4
Multicast BFD example
bfd 1 bind peer-ip default-ip interface ?
Eth-Trunk
Ethernet
Ethernet-Trunk interface
Ethernet interface
GigabitEthernet GigabitEthernet interface
When use MC-BFD @ Eth-trunk
1)
Multi MC-BFD sessions for individual link
2)
(Optional) Associate BFD with port status
3)
(Optional) Set min-active link parameter in Eth-Trunk
For example:
A 4 links Eth-trunk. If 3 member links down, then
teardown the eth-trunks.
31
BFD Monitoring
CLI and XML available to obtain BFD information and status
Run: <SwitchA> display bfd session all verbose
BFD MIB
Clear BFD statistics in the user view
Run: reset bfd statistics { all | discriminator discr-value }
32
BFD troubleshooting
•
Make sure pre-configuration requirements are met.
•
Make sure neighbor supports BFD except one-arm-echo scenario.
•
Make sure neighbor supports running BFD over same type of interface (i.e trunk).
•
Debugs
Enable the debugging of the BFD module
Run: debugging bfd { all | defect-detect | error | event | fsm | ha | packet | process
| product-interface | session-management | timer }
33
Contents
BFD introduction and protocol features
BFD on S9700 – snapshot
BFD on S9700 – software implementation details
BFD on S9700 – configuration
Summary
34
Summary Top 5 things to remember
Dedicated HW offload the CPU’s BFD process burden
Support both single hop & multi-hop mode
Proprietary BFD one arm echo mode
Proprietary multicast BFD
Worked with other 3rd device, which don’t support BFDv1
Worked in L2 links
BFD trigger interface status & BFD action
35
HUAWEI ENTERPRISE ICT SOLUTIONS A BETTER WAY
Copyright©2012 Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
The information in this document may contain predictive statements including, without limitation, statements regarding the future financial and
operating results, future product portfolio, new technology, etc. There are a number of factors that could cause actual results and developments to
differ materially from those expressed or implied in the predictive statements. Therefore, such information is provided for reference purpose only and
constitutes neither an offer nor an acceptance. Huawei may change the information at any time without notice.
© Copyright 2026