Homework 8
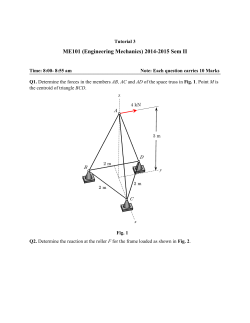
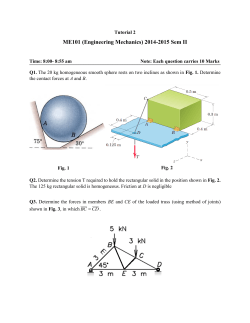
Homework 8 ME 121: Engineering Mechanics II D. H. Kelley 55 points 1. The concrete shape shown in Fig. 1 is formed by rotating the shaded area about the y axis. Determine the moment of inertia Iy . The specific weight of concrete is γ = 150 lb/ft3 . (6 points) Figure 1: Problem 1. Figure 2: Problem 2. 2. The mountain bike shown in Fig. 2 has a mass of 40 kg with center of mass at point G1 , whereas the rider has a mass of 60 kg with center of mass at point G2 . Determine the maximum deceleration when the brake is applied to the front wheel, without causing the rear wheel B to leave the ground. Assume the front wheel does not slip. Neglect the mass of all the wheels. (6 points) 3. The pipe shown in Fig. 3 has a mass of 800 kg and is being towed behind a truck. If the angle θ = 30◦ , determine the acceleration of the truck and the tension in the cable. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the pipe and the ground is µk = 0.1. (7 points) Figure 3: Problem 3. Figure 4: Problem 4. 4. If shaft BC, shown in Fig. 4, is subjected to a torque M = (0.45t1/2 ) N · m, where t is in seconds, determine the angular velocity of the 3-kg rod AB when t = 4 s, starting from rest. Neglect the mass of shaft BC. (8 points) 5. The 15-kg block A and 20-kg cylinder B, shown in Fig. 5, are connected by a light cord that passes over a 5-kg pulley (disk). If the system is released from rest, determine the cylinder’s velocity after its has traveled downwards 2 m. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the horizontal plane is µk = 0.3.Assume the cord does not slip over the pulley. (10 points) 6. The uniform rod having a weight 10 lb is pin supported at A from a roller which rides on a horizontal track, as shown in Fig. 6. If the rod is originally at rest, and a horizontal force F = 15 lb is applied to the roller, determine the acceleration of the roller. Neglect the mass of the roller and its size d in the computations. (9 points) Figure 6: Problem 6. Figure 5: Problem 5. 7. The uniform beam shown in Fig. 7 has a weight W . If it is originally at rest while being supported at A and B by cables, determine the tension in cable A if cable B suddenly fails. Assume the beam is a slender rod. (9 points) Figure 7: Problem 7. 2
© Copyright 2026