Influence of Animated Reality Mixing Techniques on User Experience
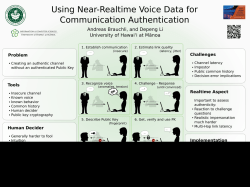
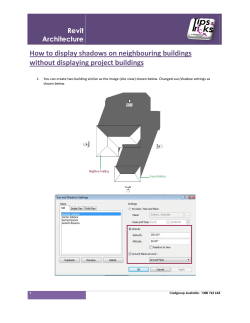
Influence of Animated Reality Mixing Techniques on User Experience Fabio Zünd1, Marcel Lancelle1, Mattia Ryffel2, Robert W. Sumner1,2, Kenny Mitchell2, Markus Gross1,2 1ETH Zurich, 2Disney Research Zurich Switzerland Motivation • Augmented Reality relies on mixing techniques Camera image (BG) 2 Virtual content (FG) Related Work • Camera artifacts rendering [Klein and Murray 2010] 3 Related Work • Perception study: Motion blur was noticeable but had no effect on performance in a racing game [Sharan et al. 2013] 4 Overview • Three experiments testing different aspects of mixing techniques – Motion blur – Latency – Visual realism • Record user’s experience and performance 5 ARTravelers 6 7 Experiment 1: Motion Blur • Depends on velocity of objects and camera exposure time • Three different motion blur configurations – A: no blur (bright scene) – B: only BG blur (dark scene, not matching FG and BG) – C: FG and BG blur (dark scene, matching FG and BG) • Hypothesis: In B player performance and experience is worse than in A an C. 8 9 Experiment 1: Motion Blur • 12 players, each 5 runs (1st run is training), 60 sec • Capture – User’s total score – Questions (1 to 5): • Enjoyment • Score satisfaction • Matching of FG and BG 10 Results Experiment 1: Motion Blur • Multivariate analysis shows no significant effect Player Experience Player Performance Enjoyment 11 Satisfaction Matching Results Experiment 1: Motion Blur • Correlation matrix confirms results 12 Experiment 2: Latency • Latency caused by hardware and software • Add artificial video latency – Between 0 ms and 1200 ms • Hypothesis: Latency decreases performance and experience 13 Experiment 2: Latency 14 Experiment 2: Latency • 9 players, each 7 runs (1st, 2nd run is training), 40 sec • Capture – User’s total score – Questions (1 to 5): • Enjoyment • Score satisfaction • Responsiveness 15 Results Experiment 2: Latency • Linear regression model • Latency has significant negative effect on score, satisfaction, and responsiveness Score (p=0.009) 16 Enjoyment (p=0.064) Score satisfaction (p=0.002) Responsiveness (p=0.001) Results Experiment 2: Latency • Correlation matrix confirms results 17 ARPix • Take a picture with the virtual character Eva 18 19 Experiment 3: Lighting/Camera Artifacts • Participant is presented with 4 versions • Chooses preferred one 20 Experiment 3: Lighting/Camera Artifacts • Correct lighting • Camera artifacts on 21 Experiment 3: Lighting/Camera Artifacts • Correct lighting • Camera artifacts off 22 Experiment 3: Lighting/Camera Artifacts • Incorrect lighting • Camera artifacts on 23 Experiment 3: Lighting/Camera Artifacts • Incorrect lighting • Camera artifacts off 24 Results Experiment 3: Lighting/Camera Artifacts • • 25 Chi-square goodness-of-fit test confirms significant differences in groups A, B, C, D Majority choose version A (correct lighting, artifacts on) Location 1 (32 users) Location 2 (40 users) Chi-square(3)=17.545 p=0.001 Chi-square(3)=17.157 p=0.001 Conclusion • In our Augmented Reality games – Even strong motion blur has only little effect – Latency strongly correlates with player performance and experience – Subtle visual realism is noticed and preferred 26 Thank you! 27
© Copyright 2026