Neutralization Reactions
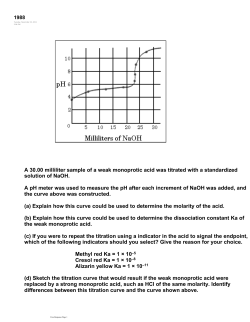
Neutralization Reactions Ex: HCl + NaOH NaCl + HOH These are double replacement reactions Ions switch partners. Water is formed. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8IRI5gPR5EY&safe=active Neutralization Forms Water H+ from acid + OH- from base H 2O neutral This “net” reaction for neutralization is found on Table I. It is an exothermic reaction. Forming a Salt (+) cation from the base (-) anion from the acid combine to form a salt. If equal concentrations of hydrogen ion H+ and hydroxide ions OH- are mixed, it results in a neutral solution. Ex: .1M LiOH + .1M HCl = Neutral Solution pH = 7 Completing and Balancing Neutralization Equations Write charges for ions in acid and base. Switch ion partners. (+ ions stay in front!!) Do not bring over subscripts except if part of a polyatomic ion! Criss-Cross charges to balance formulas. Balance entire equation. Name the acid, base and salt. You Try It Complete equation and balance formulas Balance equation. Name acid base and salt Ex: KOH + H2SO4 KOH + H2SO4 HOH + K2SO4 Ex: Mg(OH)2 + HNO3 Mg(OH)2 + HNO3 HOH + Mg(NO3)2 Hydrolysis Opposite reaction to neutralization Salt + Water Acid + Base Parent Acid/Base If you know the salt involved you should be able to determine which acid and base it would form if water is added. Salt + Water Acid + Base Ex: NaCl with water (HOH) would form HCl and NaOH You Try It Name the “parent” acid and base that would be produced from these salts. Ex: Potassium chloride Magnesium carbonate Let’s Practice Which substance is always a product when an Arrhenius acid in an aqueous solution reacts with an Arrhenius base in an aqueous solution? (1) HBr (2) KBr (3) H2O (4) KOH Which word equation represents a neutralization reaction? (1) base + acid → salt + water (2) base +salt → water + acid (3) salt + acid → base + water (4) salt + water → acid + base What are the products of a reaction between KOH(aq) and HCl(aq)? (1) H2 and KClO (2) KH and HClO (3) H2O and KCl (4) KOH and HCl Sulfuric acid, H2SO4(aq), can be used to neutralize barium hydroxide, Ba(OH)2(aq). What is the formula for the salt produced by this neutralization? (1) BaS (3) BaSO3 (2) BaSO2 (4) BaSO4 Which compound could serve as a reactant in a neutralization reaction? (1) NaCl (2) CH3OH (3) KOH (4) CH3CHO Answer: 3 Titrations Purpose: To determine the concentration of an acid or base through a neutralization reaction. Acid/Base Titration Buret is filled with a “standard solution” of known concentration (M). Erlenmeyer Flask contains solution of unknown conc.. Indicator (phenolphthalein) added to the flask. Acid/Base Titrations Slowly “titrate” or drip liquid into flask from buret until indicator changes color. This is the “endpoint” or “equivalence point”. (Moles H+ = Moles OH-) Record total volume (V) used from buret. Titration Formula MA x VA = MB x VB Molarity Acid x Volume Acid = Molarity Base x Volume Base Titration Applet http://group.chem.iastate.edu/Greenbowe/se ctions/projectfolder/flashfiles/stoichiometry /acid_base.html You Try It! A 50 ml sample of .2M HCl is neutralized by 75ml of NaOH. What is the conc. of the base? HCl NaOH .2M x 50ml = MB x 75ml MB = .13M Important Note Multiply acid/base side of equation by number of H+ or OH- ions it produces when dissociating!!! Ex: H2SO4 produces 2 H+ so you would multiply the acid side by “2” You Try It! How much of a .1M H2SO4 solution is needed to neutralize 50 ml of a .05 KOH solution? H2SO4 KOH 2 x .1M x VA = .05M x 50ml VA = 12.5 ml Titration Demonstration http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5BZ0MPI geEE&safe=active Let’s Practice During which process can 10.0 milliliters of a 0.05 M HCl(aq) solution be used to determine the unknown concentration of a given volume of NaOH(aq) solution? (1) evaporation (2) filtration (3) distillation (4) titration The data collected from a laboratory titration are used to calculate the (1) rate of a chemical reaction (2) heat of a chemical reaction (3) concentration of a solution (4) boiling point of a solution A student completes a titration by adding 12.0 ml of NaOH(aq) of unknown concentration to 16.0 ml of 0.15 M HCl(aq). What is the molar concentration of the NaOH(aq)? (1) 0.11 M (2) 1.1 M (3) 0.20 M (4) 5.0 M
© Copyright 2026