Associate degree
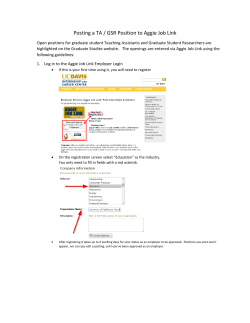
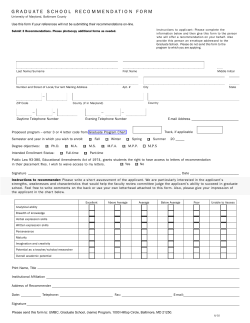
Measuring the Education Level of California Community College Students’ Parents: Current Status and Preliminary Findings Tom Leigh, Ph.D. Atsuko Nonoyama, Ph.D Research, Analysis, and Accountability Technology, Research & Information Systems California Community Colleges Chancellor’s Office TOPICS • Parent Education Data Element • Data Completeness • First-Generation • Definition • Characteristics • Educational Outcomes Parent Education Data Element Data Entered by Students at CCCApply Student Profile Section Parental Education Defined in CCCApply Instruction: “Regardless of your age, please indicate the education levels of the parents and/or guardians who raised you.” Data Entered by Students at CCCApply Student Profile Section Parental Education Defined in CCCApply Supplementary Instruction: “For the two parents, other family members, and/or guardians who in your belief played the largest roles in raising you, please indicate the highest level of education that you believe each attained.” Values Available for Parental Education Field (SG09) Coding 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Y X Meaning Grade 9 or less Grade 10, 11, or 12 but did not graduate High school graduate Some college but no degree AA/AS degree BA/BS degree Graduate or professional degree beyond a BA/BS Not applicable, no first (or second) parent/guardian Unknown / Unreported Position 1 – Parent/Guardian 1 Position 2 – Parent/Guardian 2 * Handout 81 Possible Combinations Parent/Guardian #2 Parent/ Guardian #1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 X Y 1 11 21 31 41 51 61 71 X1 Y1 2 12 22 32 42 52 62 72 X2 Y2 3 13 23 33 43 53 63 73 X3 Y3 4 14 24 34 44 54 64 74 X4 Y4 5 15 25 35 45 55 65 75 X5 Y5 6 16 26 36 46 56 66 76 X6 Y6 7 17 27 37 47 57 67 77 X7 Y7 X 1X 2X 3X 4X 5X 6X 7X XX YX Y 1Y 2Y 3Y 4Y 5Y 6Y 7Y XY YY Simplify! Highest Educational Level of the Parents: • • • • • • • • Grade 9 or less Grades 10, 11, or 12 but did not graduate High school graduate Some college but no degree Associate degree Baccalaureate degree Graduate or professional degree beyond a BA/BS Unknown/Unreported/Not Applicable * Handout w/ SAS coding Data Completeness Where are we now? Data Examined for Completeness 1) Students enrolled first time in higher education between Summer 2012 & Spring 2013 (n=251,828), in all CCCs 2) Both credit and non-credit students 3) Counting ‘Y’ (not applicable) as valid while ‘X’ (Unknown/Unreported) as missing 4) Including only students who attended at least one course Results Not Ready For Prime Time! College-level - The college with most complete data reported 94% with valid data - 52 colleges (=about half) reported no valid data - The median was 0.4%, mean was 19% Distribution of Colleges Based on Percent of Students w/ Valid Parental Ed Data Number of Colleges 80 74 College N=118 60 * Handout 40 20 7 6 6 6 3 7 5 2 2 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 % of Students with Parental Ed Data 100 Trend: Students Enrolled in Fall 2012 vs Spring 2013 Fall 2012 Spring 2013 Number of Colleges 82 80 76 60 40 20 3 8 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 % of Students with Parental Ed Data 100 More on Completeness of Data Student-level - 22.4% (=56,530/251,828) had valid parental education data reported - 10 colleges with largest # of valid data accounted for 64% of the reported data - Non-credit students are much less likely to have parental education data reported Credit vs. Non-credit Students Student N= 251,828 Percent of Students 100 80 6.5 25.3 60 40 93.5 74.7 20 0 Credit Non-credit W/ data Missing Data for Continuing Students? Fall 2012 first-time students are followed for 1 year… Percent of Students 100% 80% 23.6 25.7 76.4 74.3 After the first term After 1 year 2% 60% 40% 20% 0% W/ Data Missing Of the students whose parental education data are available, what do data look like? Distribution of Parental Education (*Highest) Parent Education Level Count Percent Grade 9 or less 6,123 10.8 Grades 10,11,or 12 but did not graduate 4,814 8.5 12,505 22.1 Some college but no degree 9,844 17.4 Associate degree 5,172 9.1 10,015 17.7 7,267 12.9 790 1.4 56,530 100.0 High school graduate Baccalaureate degree Graduate or professional degree Not applicable, no parent/guardian All Grade 9 or less Grade 10, 11, or 12 but did not graduate High school graduate Some college but no degree AA/AS degree BA/BS degree Graduate or professional degree beyond a BA/BS Not applicable, no second parent/guardian ' 10.8 8.5 22.1 17.4 9.1 Less than AA/AS 0% 20% 40% 17.7 12.9 1.4 AA/AS or Higher 60% 80% 100% Using The Parent Education Data Element: First-Generation College Students “Uncertain Climbers” (Richard and Skinner, 1992) Selected First-Generation Characteristics: • Female (Nomi, 2005) • Older (Engle, et. al, 2006 ) • Rely on financial aid (Nunez & Cuccaro-Alamin, 1998) • Less academically prepared for college (U.S. Department of Education 2008). • Under-represented minority. Selected First-Generation Characteristics (cont’d): • Less likely to persist into the second year (Chen & Carroll, 2005) • Complete fewer academic credits (Pascarella, • et. al., 2003) • Less likely to successfully complete coursework (Davis, 2010) Variable Definitions of First-Generation • less than a bachelor degree • less than an associate degree • no postsecondary education Options Grades Some Grade Nine 10,11,or 12 High School College No Or Less But Did Not Graduate Degree Graduate Option 1 First Generation First Generation First First First Generation Generation Generation College College Option 2 First Generation First Generation First First Generation Generation College College College Option 3 First Generation First Generation First Generation College College College College Graduate or Associate Baccalaureate Professional Degree Degree Degree First-Generation Student Definition: • less than an associate degree Options Grades Some Grade Nine 10,11,or 12 High School College No Or Less But Did Not Graduate Degree Graduate Option 2 First Generation First Generation First First Generation Generation Graduate or Associate Baccalaureate Professional Degree Degree Degree College College College First-Generation Counts and Percentages* Status Count Percent First-Generation 19,256 60.7 Non-First-Generation 12,458 39.3 All 31,714 100.0 * Fall 2012 first-time student with valid parent education value. Caveat: Although these findings are helpful in assessing the construct validity of the Parent Education data element they are not generalizable to the CCC system due to missing data. First-Generation Status by Gender First-Time Students Fall 2012 100% 90% 80% 49.4 70% 51.3 46.3 60% 50% Female 40% Male 30% 50.6 48.7 53.7 All (N=31,474) First-Generation (N=19,118) Non-First-Generation (N=12,356) 20% 10% 0% First-Generation Status by Age Group First-time Students Fall 2012 100% 90% 80% 70% 60% 72.4 72.1 72.9 18-19 20-24 50% 25-29 40% 30-39 30% 40-49 20% 10% 0% 12.4 10.6 4.1 4.3 3.8 3.5 4.3 4.3 3.5 3.3 3.8 4.4 4.4 3.9 All (N=27,455) First-Generation (N=17,103) Non-First-Generation (N=10,352) 11.7 50-70 First-Generation Status by Race-Ethnicity First-Time Students Fall 2012 100% 90% 7.5 0.3 11.6 7.9 0.3 9.2 6.8 0.4 15.4 80% African American 70% 23.8 60% 44.2 57.3 50% 6.8 0.3 40% 30% 4.9 0.4 46.4 21.0 0% All (N=31,425) Hispanic First-Generation (N=19,099) Pacific Islander White 31.0 10% Asian Multi-Race 3.7 0.5 20% American Indian Non-First-Generation (N= 12,326) Parent Education Level by Race-Ethnicity N = 31,425 All 44.2 31.0 Grade Nine Or Less 87.4 Grades 10,11,or 12 But Did Not Graduate 74.2 3.5 8.8 African American American Indian High School Graduate 48.7 Some College No Degree 25.5 41.6 Associate Degree 31.9 35.4 37.0 Asian Hispanic Multi-Race Pacific Islander White Baccalaureate Degree Graduate or Professional Degree 19.6 20.5 47.2 53.5 0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60% 70% 80% 90% 100% First-Generation Status by Financial Aid Receipt First-Time Students Fall 2012 100% 90% 37.4 80% 70% 56.1 68.2 60% 50% Yes 40% 65.6 30% 20% 43.9 31.8 10% 0% All (N=31,662) First-Generation (N=19,228) Non-First-Generation (N=12,434) No Educational Attainment: • • • • • Developmental Course Enrollment Persistence Fall-to-Fall Course Retention Course Success Units Earned First-Generation Status by Developmental Course Enrollment* First-Time Students Fall 2012 Terms Fall 2012 through Fall 2013 100% 90% 80% 70% 60% 67.2 54.4 75.1 50% Yes 40% No 30% 20% 10% 32.8 45.6 24.9 0% All (N=22,683) First-Generation (N=14,019) Non-First-Generation (N=8,664) *Developmental course defined with 2014 Scorecard cohort criteria. First-Generation Status by Fall-to-Fall Persistence First-Time Students Fall 2012 100% 90% 80% 70% 63.2 61.6 65.7 60% 50% Yes 40% No 30% 20% 36.8 38.5 34.3 All (N=30,542) First-Generation (N=18,823) Non-First-Generation (N=11,719) 10% 0% First-Generation Status by Course Retention First-Time Students Fall 2012 Terms Fall 2012 through Fall 2013 100% 90% 80% 70% 60% 50% 87.45 86.51 88.85 Yes 40% No 30% 20% 10% 0% 12.55 13.49 11.15 All (N=254,788) First Generation (N=152,258) Non-First Generation (N=102,530) First-Generation Status by Course Success First-Time Students Fall 2012 Terms Fall 2012 through Fall 2013 100% 90% 80% 70% 68.1 65.0 60% 72.8 50% Yes 40% No 30% 20% 31.9 35.0 All (N=254,788) First Generation (N=152,258) 10% 27.2 0% Non-First Generation (N=102,530) Average Units Earned Per Student Per Semester First-Time Students Fall 2012 Major Terms Fall 2012 through Fall 2013 9.0 8.0 7.9 7.5 7.2 All (N=78,952) First Generation (N=47,058) 7.0 6.0 5.0 4.0 3.0 2.0 1.0 0.0 Non-First Generation (N=31,894) Summary of Findings No Effect • Age • Course Retention Small-to-Moderate Confirming Effects • Gender • Persistence Fall-to-Fall • Course Success • Average Units Earned Per Semester Large Confirming Effects • Race-Ethnicity • Financial Aid Receipt • Developmental Course Enrollment Future Directions • Continue to improve the completeness and quality of the Parent Education Level data element. • Include the First-Generation subgroup in routine reporting of student demographics and educational outcomes. • Analyze subgroups within the Parent Education data elements. Thank You. Questions or Comments? References Chen, X. & Carroll, C. D. (2005). First-generation students in postsecondary education: A look at their college transcripts. Washington, DC: U. S. Department of Education, National Center for Education Statistics. Davis, J. (2010). The first-generation student experience: Implications for campus practice, and strategies for improving persistence and success. College Student Education International. Sterling, VA. Nomi, Takako. (2005). Faces of the future: A portrait of first-generation community college students. American Association of Community Colleges. Washington, DC Nunez, Anne-Marie, Stephanie Cuccaro-Alamin. ( 1998). First generation students: Undergraduates whose parents never enrolled in postsecondary education. Washington, DC: U.S. Department of Education, National Center for Education Statistics (NCES). References cont’d Pascarella, E., Wolniak, G.C., Pierson, C.T., & Terenzini, P.T. (2003). Experiences and outcomes of first-generation students in community colleges. Journal of College Student Development, 44, 420-429. Engle, J., Bermeo, A., & O'Brien, C. (2006). Straight from the Source: What works for first-generation college students. The Pell Institute For The Study of Opportunity In Higher Education . Washington, DC Richardson, R.C., & Skinner, E.F. (1992). Helping first-generation minority students achieve degrees. In L.S. Zwerling & H.B. London (Eds.), Firstgeneration students: Confronting the cultural issues (New Directions for Community Colleges Series, No. 80, pp. 29-43). San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass. U.S. Department of Education, National Center for Education Statistics. (2008). National Postsecondary Student Aid Study. NPSAS: 08. Data Analysis System.
© Copyright 2026