DAY FOUR FALLS AND OTHER HAZARDS OF HOSPITALIZATION
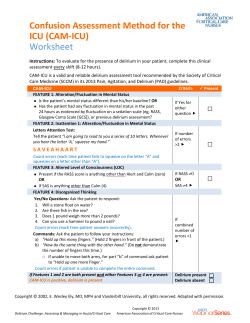
DAY FOUR FALLS AND OTHER HAZARDS OF HOSPITALIZATION Alicia A. Puppione MS, RN Sarah H. Kagan PhD, RN Outline Best rest and deconditioning Hyperactive delirium and physical restraints Geriatric Syndromes From Inouye and colleagues (2007) Geriatric Syndromes From Inouye and colleagues (2007) U.S. Patient Safety and Quality of Care National Patient Safety Goals for Hospitals Goal 1 – Improve the accuracy of patient identification. Goal 2 – Improve the effectiveness of communication among caregivers. Goal 3 – Improve the safety of using medications. Goal 7 – Reduce the risk of health care–associated infections. Goal 8 – Accurately and completely reconcile medications across the continuum of care. Goal 9 – Reduce the risk of patient harm resulting from falls. Goal 14 – Prevent health care–associated pressure ulcers (decubitus ulcers). Goal 15 – The organization identifies safety risks inherent in its patient population. Universal Protocol for Preventing Wrong Site, Wrong Procedure, and Wrong Person Surgery™ U.S. Patient Safety and Quality of Care U.S. Pay for Performance and Quality Healthcare revolution? Value Performance Quality Ownership What does it mean for nurses? TCAB EBP Lots of work… Patient Safety and Quality of Care Quality of care for older adults How do we define it? How can we measure it? What do nurses have to do with it? Parsing Out Overt Error in Falls and Falls Injury Using fundamentals of “good care” Rethinking old habits in practice Readdressing evidence for practice Best Rest and Deconditioning Creditor’s Associated Hazards Creditor’s Proposed Solutions Best Rest and Deconditioning Relevant Phenomena Geriatric syndromes Geriatric principles Frailty Sarcopenia Frequent falls Sensory-perceptual aging Biological age Functional reserve Care practices Safety assessments Tethering treatments Institutional environment Nursing Management Targeting referrals Sustaining self-care Early ambulation Functional exercise Educating for self-care Educating caregivers Reducing physical tethers Personalizing environment Initiating discharge plans Falls and Iatrogenic Injury People over aged 65 are at increased risk Falls 1/3 falls each year in community Falls with injury 20-30% of all elder fallers About 18,000 deaths Risk factors Intrinsic Extrinsic Reporting Falls/1000 hospital days Falls with injury/1000 hospital days Falls and Iatrogenic Injury Relevant Phenomena Geriatric syndromes Geriatric principles Frailty Sarcopenia Falls Fear of falling Functional reserve Failure to thrive Care practices Falls assessment Restrictive precautions Limited exercise Nursing Management Functional assessment Therapy referrals Ambulation Functional exercise Coaching for activity Cognitive assessment Family involvement Falls Risk Factor Examples Intrinsic Gait Strength Balance Coordination Posture Osteoporosis Visual acuity Cognitive impairment Medications Extrinsic Footwear Bathroom appliances Stairs and railings Floor coverings Lighting Maintenance Clutter Assistive devices Falls Assessment Scale Assessing Physical Risk of Falls Get Up and Go Test Initial Exam From a sitting position, stand without using their arms for support. Walk several paces, turn, and return to the chair. Sit back in the chair without using their arms for support. Individuals who have difficulty require further assessment. Follow Up Exam Sit in a chair. Stand without using their arms for support. Close their eyes for a few seconds, while standing in place. Stand with eyes closed, while you push gently on his or her sternum. Walk a short distance and come to a complete stop. Turn around and return to the chair. Sit in the chair without using their arms for support. Get Up and Go Follow Up Is the person steady and balanced when sitting upright? Is the person able to stand with the arms folded? When standing, is the person steady in narrow stance? With eyes closed, does the person remain steady? When nudged, does the person recover without difficulty? Does with person start walking without hesitancy? When walking, does each foot clear the floor well? Is there step symmetry, with the steps equal length and regular ? Does the person take continuous, regular steps? Does the person walk straight without a walking aid? Does the person stand with heels close together? Is the person able to sit safely and judge distance correctly? Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes No No No No No No No No No No No No Reducing Falls Risk Exercise and strength training Dietary supplementation Medication modification Environmental modification Successful Falls Prevention? What Works? Global programs Heightened awareness Family involvement Early intervention Strength building Balance work Self care initiatives What Does Not? Identification programs Risk stratification Patient reminders Reducing mobility Frequent Rounds Move Closer to the Nursing Station Delirium/Confusion Involve Family Pharmacy Review of Medications Call Light Reinforcement Diarrhea Frequent Toileting Rounds Bedside Commode PT evaluation for balance/transfer training Diuretics Toileting Rounds Especially Around Diuretic Times Bedside Commode/Multiple Urinals PT evaluation for balance/transfer training Call Light Reinforcement Doesn’t Get It Move Closer to the Nursing Station Frequent Rounds PT evaluation for gait/ balance training • Keep beds down and locked • Keep personal items within reach • Keep call light within reach • Provide patients with nonskid socks • Teach them to wear socks when OOB • Provide patients with commodes or urinals • Provide help with toileting • Make sure you round on patients every hour – – – – – Pain Position Personal items Potty “Is there anything I can do for you before I go” • Assess patients’ strength, gait and balance – Make referrals to PT/OT as appropriate • Teach patients to adhere to standard safety precautions Hyperactive Delirium & Physical Restraints Relevant Phenomena Geriatric syndromes Frailty Comorbidity Polypharmacy Geriatric principles Nursing Management Biological age Functional reserve Excess disability Care practices Pharmacologic focus Missed diagnosis Ageist assumptions Shift work CAM Medication review Communicated findings Targeted referrals Early mobilization Restraint reduction Individualized care Family coaching Symptom treatment Debriefing Hyperactive Delirium & Physical Restraints Hyperactive delirium Psychomotor agitation Illusions Delusions Hallucinations Physical restraints Attempted behavioral control Fail to prevent Rarely effective Falls Device disruption Increases Falls with injury Pressure ulcers UTIs Skin tears Death Physical Restraints Definition Devices to restrict free movement Examples Bedrails Sheets Vests Belts Mitts Beds Physical Restraint Reduction Treatment interference Pain relief Device camouflage Dummy dressings Distracting activities Treatment evaluation Physical Restraint Reduction Falls risk Physical therapy Functional exercise Physical training programs Low beds Fall mats Hip protectors Physical Restraint Reduction Wandering Needs assessment Reminiscence therapy Distracting activities Personal possessions Name sign Stop sign Functional exercise Delirium Treatment Etiology resolution Remove deliriogenic medication Substitute non-deliriogenic medication Remove sources of infection risk Treat infections and symptoms Correct electrolyte imbalance Correct hypoxia and hypoxemia Correct hypercarbia Delirium Treatment Symptom treatment Treat negative and frightening symptoms Antipsychotic medication Haloperidol 0.125 to 0.5 po/IV every 8 to 12 hours ATC Options include respiridone, olanzepine Treat pain and discomfort Treat diarrhea and constipation Delirium Treatment Manage personal and care environment Regulate stimulation Care interactions Family support TV and radio Ambient noise Control light and dark Remove safety hazards Promote mobility Debrief experience Closing for Today Questions and comments Workshop this afternoon Plan for tomorrow Thank you
© Copyright 2026