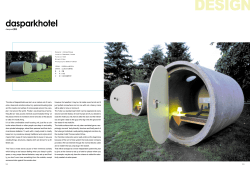
B.Sc. â Applied Science Hotel Management Course
B.Sc. – Applied Science Hotel Management Course Structure & Course syllabus 1 COURSE OBJECTIVES To provide an educational foundation for a range of administrative and management careers in the hospitality industry. To develop in the student, the ability to think logically, communicate clearly develop an eye for detail, cost consciousness and optimum utilization of time energy and materials To equip the student with a thorough understanding of the administrative production skills required. Maintenance of discipline, neat & pleasant appearance, and high level of personal and job hygiene. To provide skills to manage in a computerized environment and a rapidly changing IT Environment and its effect in the hospitality environment. Also to provide work ethics and adequate work habits essential for working in a team. To develop in the students skills and personal qualities of general importance and applicability in all aspects of working life. To acquire skill for future management roles of various types of hospitality units and being aware & conscious of social responsibilities that an organization owes to its employees & clients. ELIGIBILITY FOR ADMISSION TO THE COURSE : A pass in Higher Secondary/Technical Higher Secondary/Vocational Higher Secondary Examination of the central government or State Government With any subject combination or any other examination declared by any University as equivalent thereto with a minimum of 40% marks in aggregate DURATION OF THE COURSE : The course shall extend over a period of three years comprising of Semester pattern. It year shall consist of training in any of the hotel classified under three or above category for a period of 10 weeks at the end of which they will submit a training /project report. Examinations shall be conducted at the end of every year for the respective subjects. The medium of instruction in all the theory and practical subjects shall be in English No candidate shall be eligible for the Graduation unless he/she has undergone the prescribed course of study for a period of 3 academic years 2 B.Sc. - Hotel Management Course Duration: Three years, six semesters Eligibility for Admission: Hsc (+2) pass in any group or its equivalent First Year, First Semester Course Course Title Code 1 French-I 2 English communication 3 Core – I: Food production-I 4 Core – II: Food and beverage service - I 5 Core – III: Front office operation - I 6 Allied –I: Hotel Law 3A Practical-I: Food production 4A Practical-II Food & beverage service-I 5A Practical-III-Front office – I Total First Year, Second Semester Course Course Title Code 7 French-II 8 English communication 9 Core – IV: Food production-II 10 Core – V: Food and beverage service - II 11 Core – VI: Accommodation operation - I 12 Allied-II : Hotel accounts 9A Practical-IV: Food production – II 10A Practical-V: Food & beverage service –II 11A Practical-VI:Accommodation operation–I Total 3 L T P C Marks 2 2 3 3 3 2 0 0 0 15 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 3 2 2 7 2 3 3 3 3 2 3 2 2 23 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 900 L T P C Marks 2 2 3 3 3 2 0 0 0 15 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 3 2 2 7 2 3 3 3 3 2 3 2 2 23 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 900 Second Year, Third Semester Course Course Title L Code 12 Core – VII: Food production-III 2 13 Core–VIII:Food and beverage service-III 4 14 Core – IX: Front office operation – II 4 15 Core – X: Hotel engineering 3 16 Allied – III: Computer applications 2 12A Practical-VII :Food production – III 0 13A Practical-VIII: Food & beverage service-III 0 14A Practical-IX: Front office Operation –III 0 Total 15 Second Year, Fourth Semester Course Course Title Code 17 Core –XI :Advance food production- IV Core – XII: Advance food and beverage 18 service–IV 19 20 21 17A 18A 19A Core – XIII: Accommodation operation–II Allied – IV: Nutrition and food science Elective –I: Personality development Practical –X: Food production – IV Practical- XI :Food & beverage service–IV Practical-XII: Accommodation operation–II Total 4 T P C Marks 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 3 3 2 8 3 4 4 3 2 3 3 2 24 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 800 L T P C Marks 3 3 0 0 0 0 3 3 100 100 4 3 3 0 0 0 16 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 4 0 3 0 3 3 3 3 3 2 2 7 24 100 100 100 100 100 100 900 Third Year, Fifth Semester Course Course Title Code 22 Core - XIV : Food and beverage management 23 Core -XV: Project work and Report 24 Allied- V: Travel and Tourism 25 Optional –II: Food Production Food and Beverage Service Front Office Operation Accommodation Operation 26 Elective-II: Human resource management 25A Optional practical: Food Production Food &Beverage Service Front Office Operation Accommodation Operation Total Third Year, Sixth Semester Course Course Title Code 27 Core – XVI: Industrial training & Industrial Report (10 weeks) 28 Allied –VI : Sales and marketing 29 Allied – VII :Event management Total 5 L T P C Marks 3 0 3 3 1 3 0 0 0 3 0 0 4 6 3 3 100 100 100 100 3 0 0 0 0 5 3 5 100 100 9 4 8 24 500 L T P C Marks 0 8 8 16 100 3 0 3 1 6 9 0 0 8 3 4 23 100 100 300 1. HOTEL FRENCH-I L 2 T 0 P 0 C 2 Marks Hrs 100 30 OBJECTIVE To create awareness about the importance of French in the hotel operations and to acquire the correct pronunciation of French terminology. To use standard phrases in French in hotel operations. To integrate the French curriculum with the core syllabus of the course. UNIT – 1 : INTRODUCTION TO FRENCH GRAMMAR The alphabets - Use of Capital letter - The accents in French – Liason - The Vowels & consonant - Elision UNIT – 2 : THE ARTICLES Le, La, Les; un, une, des and their usage with common nouns e.g. the table, the chair, a wall, a window etc. - Counting Numbers Ordinal & Cardinal: 1-100; 1st100th. - Common adjectives – e.g. Grand/Petit/Haut/Bas etc. - Conjugation (Affirmative and Negative)–er ending regular verbs + the verbs être and avoir (present indicative tense). The verb ‘aller’; boire; server, faire, prendre, finir, voir, lire, dire - The days of the seasons, weeks & months of the year in French. - Les professions (le médecin etc.); les noms de pays ( Angletterre, Allemande, Espagne, Inde, etc.) UNIT – 3 : VOCBULARY & COMPREHENSION Dialogue: Ordering breakfast; translation of French menu terms - Common greetings and frequently used phrases (Short phrases) - Learning complaint handling in French - Writing short phrases - Comprehensive & translation Between 2 persons - Meals (Le repas) UNIT – 4 : AU RECEPTION Translation & comprehension - Front Office , reception – conversation, practicing various French terms. UNIT – 5 : AU RESTAURANT Basic Conversation, practicing basic French terms OUTCOME: The student will have full knowledge of the basic grammatical structures of the French language. They should be able to read and translate information regarding time, weather, directions, shopping, food etc. 6 Reference books: 1. A.Talukdar- Parlez a l hotel 2. Bhattacharya - French for Hotel Management 3. G. Mauger- Cours de langue et de civilization francaise 7 2. ENGLISH COMMUNICATION SKILLS - I L 2 T 1 P 0 C 3 Marks Hrs 100 45 OBJECTIVE To introduce students to the process of communication & presentation skills needed by the hospitality professional. The tutorials are to be used to improve oral communication skills. UNIT - I – GRAMMER Subjects and Predicates –Nouns - Pronouns –Verbs- Verbal - Adverbs - Adjectives Prepositions – Gerunds - Modal Verbs - Clauses and Phrases – Voice - Sentence patterns - Tenses– Principle – Punctuation - Infinitives UNIT - II – VOCABULARY Synonyms – Antonyms - super ordinates – hyponyms -compound nouns - prepositional Phrases - Prefixes and suffixes - use of reference words - sequential expressions Discourse Makers - Idioms and Phrases - – Transformation of sentences - Word formation - prefixes and suffixes. UNIT - III – WRITING Paragraph writing, Coherence and Cohesion, Use of Headings, Letter Writing (Personal Letters, Official Letters, Letters to the Editor), Essay Writing, Note-Making, Use of Symbols and Icons, Abbreviations, Non-Verbal Devices, (Flowcharts, Fishbone Diagrams, Tables), Units of Measurements. UNIT - IV – RHETORICAL FUNCTONS Definition, Description, Process Description, Comparison, Classification, Stating problems and proposing solutions, Making Lists, Narrating Events, Asking Questions and Answering. UNIT - V – COMMUNICATION AND ORAL PRESENTATION Introduction: Communication, Definition, process, elements of communication, types of communication, verbal, non-verbal, barriers to communication and correctness Vs communication. Oral Presentation: Preparing a Speech, delivery techniques, using the visual aids, handling a hostile audience, overcoming errors in public speaking and presenting the successful seminar. 8 OUTCOME: Students are expected to learn the basics of the language and refine their pronunciation and communication skills. Text Book: 1. V.Chellammal, , 2002- Learning to Communicate, Kamakhya Publications, Coimbatore. 2. Lakshminarayanan, 2002-K.R. English for Technical Communication, Vol. 1 & 2, Chennai: Scitech Publications (India) Pvt. Ltd. Reference Books: 1. Farhathullah, 2002 T.M. English Practice Book for Technical Communication, Chennai, RBA Publication. 2. Balasubramanian, M & G Anbalagan, 2001- English for Engineering Students, Kumbakonam R.M.S. Anuradha Agencies Reprint. 9 3. FOOD PRODUCTION – I (THEORY) L 3 T 0 P 0 C 3 Marks 100 Hrs 45 OBJECTIVE Food Production is an integral part of the Hospitality Industry. To prepare the students to cater to the need of the industry, it is important to inculcate in them sound knowledge of the principles of Food Production so that they can be put to use in an efficient & effective way. UNIT – I : INTRODUCTION TO PROFESSIONAL COOKERY, STANDARDS OF PROFESSIONALISM & KITHEN HYGIENE Culinary history - Origins of modern cookery - Modern developments in equipments and foodstuff. Levels of skill - Attitude towards work - Personal hygiene. Facility and equipment sanitation - Cleanliness of surface - Garbage disposal - Comfort facilities: ventilation and lighting - Dish washing procedure, Pot washing procedure. UNIT – II : KITCHEN ORGANIZATION & EQUIPMENT AND TOOLS: Classical kitchen Brigade - Apportioning of staff among sections - Duties and responsibilities of Executive Chef - Responsibilities of each section - Modern kitchen Brigades - Co-operation with other departments. Pre-preparation equipments Preparation equipments - storage equipments - Ancillary equipments - knives, Utensils, pots and pans - Bakery equipment UNIT – III : BASIC METHODS OF COOKERY & UNDERSTANDING RAW MATERIALS Modes of Heat Transfer - Various methods of Cooking: Definition, Rules, Associated Terms, Moist Methods: Boiling, Poaching, Steaming, Stewing, Braising. Dry Methods: Frying, Grilling, Roasting, Broiling, and Baking - Modern Methods. Understanding of common ingredients classification and available forms - Uses and storage - Salt, Liquids, sweetening, Fats, and Oils, Raising or Leavening agents - Thickening and binding agents, Flavourings and seasoning. UNIT – IV : COMMODITIES MILK AND MILK PRODUCTS: Composition of milk, storage, types of milk, cream, butter, curd - CHEESE Production of cheese, types of cheese – VEGETABLES - Classification, selection and cooking - FRUITS. 10 UNIT-V : FOUNDATION OF CONTINENTAL COOKERY: Stock: Definition, Classification and types, Rules for stocks, Recipe of while chicken stock, Brown stock, fish and vegetable stock. (2) - Soups: Definitions, Classification on soups; Examples - Sauces: Definition, Use and importance of sauces. Mother saucesRecipes, Derivative sauces - Dough and Pastes - Creams: Types and uses - Assembling into finished products - Garnishes and Accompaniments. Out Come: The student should be able to understand basic methods of cooking and ingredients used both in Indian and Continental Cookery Text Books: 1) Rocky Mohan, Roli -Art of Indian Cookery 2) Prasad,J. Inder Singh Kalra, - Cooking with Masters. Reference Book: 1. Philip E.Thangam, Orient Longman -Modern Cookery (Vol-l) For Teaching & Trad. 2. Paul Hamlyn -Larousse Gastronomique-Cookery Encyclopedia 3. Escoffier -The Complete Guide to the Art of Modern Cookery. 11 4. FOOD AND BEVERAGE SERVICE – I (THEORY) L 3 T 0 P 0 C 3 Marks 100 Hrs 45 OBJECTIVE The course will give the students a comprehensive knowledge and develop technical skills in the basic aspects of food & beverage service operations in the Hotel Industry. UNIT - I : INTRODUCTION TO THE CATERING INDUSTRY & DEPARTMENTAL ORGANIZATION Introduction and growth of catering-industry Classification of catering establishments: Commercial, Transport, Welfare, Industrial, Institutional - A brief description of each type showing the career opportunities in each. Organization of the hotel - Where F & B department stands; A Total meal experience, The hotel-gueststeward relationship - Relationship between F & B service department with other departments of the hotel - Types of F & B outlets - Organization of staff in various F & B Outlets - Duties and responsibilities of all F & B staff - Attributes of a waiter: Effective communication skills, Personal hygiene. UNIT –II : RESTURANT SERVICE & TYPE OF MEALS & MENU Forms and methods of services: English; French & Russian - Mis en place, Arranging side-board - Receiving the Guests & Social Skills - Service of a Table - Types of meal: Breakfast Lunch/Dinner/Supper/Brunch/High teal Afternoon Tea/Elevenses - Type of Menu: Table d'hote, A la carte, carte-du-jour - Courses of French classical menu (3) d. Menu terminology - Fundamental of menu planning Continental, Indian with accompaniments - Breakfast menu: English, American, Continental, Indian. High tea and Afternoon tea menu UNIT – III : RESTAURANT EQUIPMENTS & ANCILLARY DEPARTMENTS Crockery - Glassware - Cutlery, Flatware, Hollow ware -Silver and stainless steel Lilies, Furnishing, fittings, and disposable - Care and maintenance of restaurant equipment. Pantry, still room, plate room, hotplate, wash kitchen stewarding a brief description. UNIT – IV : ROOM SERVICE Type of Room Service / Centralized / Decentralized / Decentralized Mobile - List of Equipments - Trolley & Tray Setup - House Rules of Room Service Waiter - Room Service Menu 12 UINT-V : DIFFERENT TYPES OF OUTLET IN F&B DEPARTMENT Types of Restaurants- Multi-cuisine, specialty-cuisine, Oriental-cuisine, Grill room. Banquets- Board rooms, conference, Finger buffet, Fork Buffet. Fast-foods, Pub, Bar, Take Away, Franchised outlets, Boutiques. Out Come :The student should imbibe the knowledge of Kitchen & restaurant brigade. They should have vital knowledge of auxiliary departments. They should be able to plan different menus, lay tables for different services. Text Books: 1) Sudhir Andrews, Tata McGraw Hill- Food & Beverage Service Training Manual 2) Lillicrap& Cousins-Food & Beverage Service 3) John Fuller -Modern Restaurant Service 4) Brian Varghese -Food & Beverage Service Management 5) Brown, Heppner &Deegan -Introduction F& B Service Reference Books: 1) Brian Varghese -Professional Food & Beverage Service Management 2) Peter Jones & Cassel-Food Service Operations 3) Joyce Rubash -Master Dictionary of Food & Wine 4) JaksaKivela, Hospitality Press -Menu planning 5) Lipinski -The Restaurant (From Concept to Operation) 6) Sergio Andrioli& Peter Douglas, Heinemann Professional -Professional Food Service 7) John Drysale -Profitable Menu Planning 13 5. FRONT OFFICE OPERATION –I (THEORY) L 3 T 0 P 0 C 3 Marks 100 Hrs 45 OBJECTIVE This course aims to establish the importance of Front Office within the hospitality industry. It also prepares the student to acquire basic skills and knowledge necessary to identify the required standards. UNIT - I : INTRODUCTION TO FRONT OFFICE Introduction to hotel industry, Evolution, Definition of modern hotel, Classification and categorization - Position, Role and Importance of Front off-ice in the hotel. Types of Hotel- Budget Hotel, Business class Hotel, Motel, Flotel. UNIT - II : ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE OF FRONT OFFICE Structure and functions of each section - Duties and responsibilities of Front office staff. Layout of Front Office department. Explain the role & importance of concierge in hotels. Guest telephone service , voice mail , PBX, PABX , EPBAX& other systems. UNIT–III : ATTRIBUTES OF FRONT OFFICE STAFF AND FRONT OFFICE TERMINOLOGY Attributes of Front office staff - Front office terminology regarding guests, plans, rooms hotels tariff and other front office activities. UNIT - IV : RESERVATION OPERATIONS The importance of reservation section - The modes of reservation: R.S. and I.R.S. Various tools of reservation: Room status board - Reservation form, Advance-Letting chart, Density control chart, Hotel Diary, Whitney system of reservation - Cancellation and amendment procedure - Preparation of arrival list/movement list - Group reservation. UNIT-V : Front Office Operations: The Guest Cycle, Front Office System, Front Office Forms and Formats, The Front Desk, Telecommunication and its importance, Property Management System. 14 Out Come: Students should gain knowledge of various sections and functions of front office and their procedures. They should be able to Hand various tools and equipments of the front office. Text Books: 1) Colin Dix &Chirs Baird-Front office operations 2) James Bardi, VNR -Hotel Front office management 3) Kasavana& Brooks -Managing front office operations 4) Sudhir Andrews, Tata McGraw Hill-Front office training manual 5) Raymond S Schmidgall -Managerial accounting and hospitality accounting Reference Books: 1) Michael Kasavana and Cahell -Managing computers in hospitality industry 2) Michael Kasavana, CBI-VNR -Effective Front Office Operation 3) J.R.S.Beavis&S.Medlik, Heinemann Professional A Manual of Hotel Reception 4) Colin Dix, Pitman -Accommodation Operation - Front Office 5) Sue Baker& Jeremy Huyton, Continuum- Principles of Hotel Front Office Operations 15 6. HOTEL LAW L 2 T 0 P 0 C 2 Marks 100 Hrs 30 OBJECTIVES To provide the knowledge to the students about the different constitutional law and acts in the hospitality industry UNIT‐I : INTRODUCTION Law and society - Need for the knowledge of law - Sources of Indian law Classifications of law - List of licenses and permits required for operating a Hotel/Restaurant and other - catering Establishments under various local, state and union laws - Procedure for Procurement, Renewal, Suspension and Termination of licenses UNIT‐II : EVALUATION OF MERCANTILE LAW The Partnership ACT 1932- The Indian companies Act, 1956 - The Sale of goods Act 1930- The Negotiable instruments Act 1881 - The Insurance Act 1939 - The law of Agency UNIT –III : THE INDIAN CONTRACT ACT, 1872 Meaning and definition of Contract - Essential elements of contract - Classification of contract - Time and place of performance - Discharge of contract - Contract of Bailment and pledge UNIT‐IV : EVALUATION OF INDUSTRIAL LAW The Factories Act, 1948 - The Industrial Dispute ACT, 1947 - The Employment (standing order act) 1976 - The Employees State Insurance Act, 1953 - The provident fund Ac, 1952 - The Payment of Gratuity Act, 1972 - The Bonus Act, 1965 UNIT –V : MANAGER OF HOTEL AND OWNER OF LODGING HOUSE Paying guest‐Premises‐Tenant‐Tenement - Lien of Inn keeper - The Central committee for food standards - Central food laboratory - Food Inspector and their Powers and duties - Procedure followed by the food inspector 16 OUT COME: The student will Gain the essential knowledge on our Indian Law and Different types of contracts. Text Book: 1. N.D.Kapoor -Mercantile law Reference Book: 2. N.D.Kapoor -Industrial law 17 3A. FOOD PRODUCTION PRACTICALS –I L 0 T 0 P 3 C 3 Marks 100 Hrs 90 a) Four weeks of demonstration classes to make students familiar with: The pre-preparation, preparation and method of cookery. 1) Preparing and cooking vegetables. 2) Preparing and cooking Fish & Shellfish 3) Preparing and cooking Poultry 4) Preparing and cooking Eggs 5) Preparing and cooking Soups, Stocks & Sauces 6) Preparation of Basic Indian Gravies 7) Making Custard & Cream b) At least menus comprising of five Dishes each to cover Soups (Hot& Cold) Starters. Meat dish with Vegetable& Potato dish, various sauces (Hot & Cold} c) BAKERY (Five Practical classes), Mousses etc (Simple Puddings). 18 4A. FOOD AND BEVERAGE SERVICE PRACTICALS –I L 0 T 0 P 2 C 2 Marks 100 Hrs 60 a. Opening and inspecting cleaning a restaurant : Routine Cleaning NonRoutine Cleaning b. Identification of restaurant equipments. - With Diagrams c. Special equipments used In restaurant. d. Wiping: - Glassware, Cutlery, Crockery e. Polishing silver, silvo method, burnishing method f. Arrangement and use of side board -Check list. g. Laying a table cloth h. Re-laying a table cloth i. Using a -tray j. Procedure for laying table 1. Basic a la carte 2. Basic Table D'hote 3. Continental Breakfast 4. Carte de jour k. English Break Fast 19 5A. PRACTICALS FRONT OFFICE OPERATIONS L 0 a. b. c. d. e. f. g. T 0 P 2 C 2 Marks 100 Receiving telephone calls. Familiarization of reservation tools. Receiving reservation requests. Finding room availability on Advance letting chart, updating it. Finding room availability on Density Control chart; updating it Updating Hotel diary and preparation of movement list. Handling Cancellation and Amendments. 20 Hrs 60 First Year - Second Semester 7. HOTEL FRENCH – II L 2 T 0 P 0 C 2 Marks Hrs 100 30 OBJECTIVE To create an importance of French in the hotel operations and to acquire the correct pronunciation of French terminology. To use standard phrases in French in hotel operations. To integrate the French curriculum with the core syllabus of the course. UNIT – I : Uses of Tenses - Fill in the blanks with suitable verbs given in the bracket UNIT – II : Conditional sentence - Probable Condition – Improbable Condition - Imaginary Condition UNIT – III : Vocabulary - Synonym - Antonym - Prefix - Suffix – Proper use of Adjectives –Proper use of Verbs UNIT – IV : Spoken English – Dialog between a customer and Hotel worker – Asking Questions Expression of Wishes - Expressing Commands - Requests - Greetings - Invitation - Offers – Opinions UNIT – V : Description - Describing person - Place - Things - Food - Luggage - Rooms - Room Services Narration - Experience in the Market - Buying Vegetables - Bargaining - Party - Journey A Festival - Sight Seeing OUTCOME : The student will have full knowledge of the basic grammatical structures of the French language. They should be able to read and translate information regarding time, weather,directions, shopping, food etc. Text Books: 1) G. Mauger -Cours de langue et de civilization francaise 2) A.Talukdar -Parlez a l hotel Reference Book: 1)Bhattacharya -French for Hotel Management 21 8. ENGLISH COMMUNICATION - II L 2 T 1 P 0 C 3 Marks Hrs 100 45 OBJECTIVE To enhance the communication skill of the learner in reading, writing, speaking and listening which help them to understand in a better way. Unit I – WRITING Writing reports and Memos, Paragraph writing, Coherence and Cohesion, Summary writing, Rearranging jumbled – Up sentences, Letter writing (Personal Letters, Official Letters), writing Job applications, Bio – Data, writing biographies – use of titles, Non – Verbal Devices (Bar Chart, Tables and Pie Chart) Unit – II – ANALYSIS, ARGUMENTATION AND CLASSIFICATION Comparison and Contrast and Cause and Effect relationship Exemplification, Definition, Statement- elaboration: Expanding points into paragraphs. Listing, Chronological patterning, Process Repetition, General- Specific, Specific-general Unit – III – PRINCIPLES OF EDITING Punctuation - Substitution of words - restructuring of sentences - Re-organising sentence sequence in a paragraph - Use of link words and Principles of Coherence and Cohesion. Unit - IV – SUMMARY WRITING This is to create an awareness in students regarding the organization of material—the points and sub-points, the logical connection between these points. This will include making students aware of the notions of the “main idea”,/ ”thesis statement” and the “ supporting ideas” ,with a view to training them to shorten the material, to capture the essence and present it in a precise manner. Unit – V – INTERPRETATION OF TECHNICAL DATA Students should be taught to read and interpret maps, charts, graphs. They should be able to write a paragraph based on the data given there. Unit - VI – FORMAL TECHNICAL REPORT AND BUSINESS CORRESPONDENCE Formal Technical Report: Gathering data, literature search, questionnaire and interview and creating a formal technical report. Business Correspondence: Business letters, structural elements, styles of presentation, letters of inquiry, claim and adjustment letters, letter of application for a job and calling for tenders and quotations. 22 OUTCOME: Students are expected to learn the basic use of the language and refine their pronunciation and communication skills as per the requirement of the hospitality industry. Text Books: 1. Chellammal V, 2002- Learning to communicate, Kamkhya Publications, Coimbatore. 2.Lakshminarayanan, K.R, 2002English for Technical Communication Vol. 1 & 2 SciTech Publications (India) Pvt. Ltd.. Chennai. Reference Books 1) Farhathullah, T.M. 2002. English Practice Book for Technical Communication, RBA Publications, Chennai 2) Balasubramanian, M & G. Anbalagan, 2001- English for Engineering Students RMS Anuradha Agencies, Kumbakonam. 23 9. FOOD PRODUCTION – II L T P C Marks Hrs 3 0 0 3 100 45 OBJECTIVE Food Production is an integral part of the Hospitality Industry. To prepare the students to cater to the need of the industry, it is important to inculcate in them sound knowledge of the principles of Food Production so that they can be put to use in an efficient & effective way. UNIT – I : Kitchen Organization layout and hierarchy - Kitchen layout and functions, receiving area, storage area, cold butchery, and vegetable mise en place area, cold kitchen, hot kitchen, garde manger, bakery and confectionery. The classical and new kitchen brigade, duties and responsibilities and job description of the kitchen personnel. UNIT – II : Basic preparations - Mise-en-place of all the basic preparations soups, sauces, roux, aspic, glaze, bouquet garni, mirepoix, d'uxelle, pastes masala, batters, doughs, marinades and gravies. Classification of soups, principles, garnishes, accompaniments, International soups. Importance of sauces, mother sauce, thickening agents used in a sauce, rectification of faulty sauces, other popular sauces UNIT – III : Breakfast. International and Indian menus, preparations, traditional / classical items, 'Power breakfast' & 'Brunch' concept. UNIT – IV: Basic bakery and confectionery. Principles of baking, uses of different types of oven, role of ingredients used and menu examples, ingredient proportions, various mixes, methods and temperature variations. Food Commodities - Classification using basic food chart with examples and uses in cookery Seafood, freshwater - fish, meat cookery introduction UNIT – V : Introduction to Indian cuisine - History, characteristics, different ingredients used, regional differences, equipments used, cooking methods, religious influences - Basic culinary terms-Indian and Western / International 24 OUTCOME :- The students should have full knowledge of regional cuisine of India. They should be able to prepare menus for various food outlets. Text Books: 1. Madhur Jaffrey, Pavillion -A Taste of Indi. 2. Sangeeta Bhatnagar & R.K.Saxena, Harper Collins -Dastarkhwan-e-Awadh. 3. Prashad , J.lnder Singh Kalra, Allied- Cooking with Masters. Reference Books: 1 Premjit Gill-Punjabi. 2 Pratibha Karan, HarperCollins -Hyderabadi Cuisine. 3 Ms. Thangam Philip, Orient Longman- Modern Cookery for Teaching & Trade 25 10. FOOD AND BEVERAGE SERVICE – II L 3 T 0 P 0 C 3 Marks 100 Hrs 45 OBJECTIVE The courses will give the students a comprehensive knowledge and develop technical skills in the basic aspects of food and non-alcoholic beverage service operations in the Hotel Industry. UNIT – I : Types Of Meals, set ups Brunch, Lunch, Hi-Tea, Dinner, Supper Elevenses and others Breakfast-Introduction, Types, Service Methods, a la carte and TDH set ups – Brunch – Lunch - Hi-Tea – Dinner – Supper - Elevenses and others UNIT – II : Menu- Introduction - Types-Ala Carte & Table D'hote - Menu Planning, considerations and constraints - Menu Terms - Menu Design UNIT – III : Classical French Menu – All seventeen courses. Classical Foods & its Accompaniments with Cover Indian regional dishes, accompaniments and service, Types of equipment used for serving each course. UNIT – IV: Control Methods - Billing Methods-Duplicate & Triplicate System, KOTs & BOTs, Computerised K.O.T's - Necessity and functions of a control system, F&B Control cycle & monitoring UNIT-V : Non - Alcoholic Beverages – Classification - Hot Beverages-Types, Production, Service Cold Beverages-Types, Production, Service - Food & Beverage Terminology related to the inputs of the semester 26 OUT COME :- The students should be well versed with different wines, alcoholic beverages. They should know the manufacturing process, classification, storage and service. They should also know about room service. Text Books : 1. Sudhir Andrews, Tata McGraw Hill- Food & Beverage Service Training Manual 2. Lillicrap& Cousins -Food & Beverage Service 3. John Fuller -Modern Restaurant Service 4. Brian Varghese -Food & Beverage Service Management 5. Brown, Heppner &Deegan -Introduction F& B Service 6. Brian Varghese -Professional Food & Beverage Service Management Reference Books: 1. Peter Jones & Cassel -Food Service Operations 2. Joyce Rubash -Master Dictionary of Food & Wine 3. JaksaKivela-Menu planning, Hospitality Press 4. Lipinski- The Restaurant (From Concept to Operation) 5. Sergio Andrioli& Peter Douglas, Heinemann- Professional Food Service 6. John Drysale -Profitable Menu Planning 27 11. ACCOMMODATION OPERATION – I L 3 T 0 P 0 C 3 Marks 100 Hrs 45 OBJECTIVE The subject aims to establish the importance of House Keeping and its role in the hospitality Industry. It also prepares the student to acquire basic knowledge and skills necessary for different tasks and aspects of housekeeping. UNIT – I: HOUSEKEEPING AS A DEPARTMENT & ORGANISATION STRUCTURE OF HOUSEKEEPING DEPARTMENT In the hotel - In other institutions: to be applied in a slight different set of Circumstances - Interdepartmental co-operation & co-ordination of Housekeeping Different sections of Housekeeping departments. Small hotels, Medium hotels, large hotels - Duties & responsibilities of Executive Housekeeping - Duties & responsibilities of Housekeeping Staff. UNIT – II : FUNCTIONS OF HOUSEKEEPING DEPARTMENT Area of cleaning – Security - Dealing with guests - Brief notes on Lost & Found - Baby sitting - Services and facilities offered by various hotels. UNIT – III : ROUTINE SERVICES Cleaning of Checkout roam - Cleaning of Occupied Room - Cleaning of Vacant Room Evening service UNIT – IV : CLEANING EQUIPMENT General considerations & selections - Classification & Types of equipments, Floor trolley, Vacuum Cleaner etc. - Method of use & mechanism for each type - Care & maintenance. UNIT-V CLEANING AGENTS: Phenyle Acids Glass Cleaner Liquid Soap Toilet Cleaner 28 Out Come : The student should be able to fix the position and the value of each housekeeping staff in the hotel organization. The Student should become familiar with the equipment and agents needed in the housekeeping department. He/She should also become through with all the practices and procedures. Text Books : 1. Sudhir Andrews, Tata McGraw Hill -Hotel Housekeeping. 2. Tucker Schneider, VNR-The Professional Housekeeper 3. Martin Jones, Wiley -Professional Management of Housekeeping Operations. 4. Rosemary Hurst, Heinemann-House Keeping Management for Hotels Reference Books: 1. Joan C. Branson & Margaret Lennox, ELBS- Hotel, Hostel & Hospital House Keeping. 2. David . Allen, Hutchinson Accommodation & Cleaning Services, Vol I & II. 3. Margaret Kappa &Aleta Nitschke -Managing House Keeping Operation. 4. First Aid, St. John Ambulance Association, New Delhi 29 12. HOTEL ACCOUNTS L 2 T 0 P 0 C 2 Marks 100 Hrs 30 OBJECTIVE: This subject intends to impart students the basic knowledge of Hotel Accounting required for the Hospitality Management and to prepare them to comprehend and utilize this knowledge for the day-to-day operations of the organization. UNIT – I : ACCOUNTING THEORY Business Transaction and Basic Terminology, Need To Study Accounting, Accounting functions, Purpose of Accounting Records, Accounting Principles - Concepts and Conventions. UNIT – II : ACCOUNT RECORDS Principles of Double Entry System, Journal Entries, Ledger, Subsidiary Books - Cash, Sales & Purchase books, Bank Reconciliation statement. Financial Statements - Basic Financial Statements, Trial Balance, Preparation of Final Accounts, Basic Adjustments to final Accounts, Methods of Presenting Final Accounts Practical Problem. UNIT – III : Depreciation Reserves and Provisions - Meaning, basic Methods. Depreciation - Meaning and definition of depreciation‐causes of depreciation‐methods of depreciation ‐ straight mine method‐written down value method UNIT – IV: Inventory valuation - Introduction ‐ Need ‐ Nature ‐ Purpose of inventory valuation‐Inventory costing methods‐FIFO‐LIFO UNIT – V: Departmental accounting - Meaning and definition of departmental accounting‐Objectives‐allocation and apportionment of expenses‐Inter departmental transfer‐working out problems - Analysis of financial statement - flow statement – Preparation of Problems in fund flow statement - Auditing‐meaning and definition of auditing‐types of auditing‐advantages & limitations of auditing Outcome: The student will understand the need of accounts in hotel industry. 30 Text Books: 1) S.N.Maheswari -Principles of accounting 2) R.C.Gupta -Advanced accounting 3) M.C.Shukla and T.S.Grewal and S.C.Gupta -Advanced Accounting 4) Jain and Narang -Advanced Accounting Reference Books: 1) S.A. Siddiqui -Comprehensive Accountancy 2) I, N.D. Kapoor- A Complete Course in Accounting Volume 3) R.C. Chawla& C. Juneja -Double-Entry Book-Keeping. 4) T.S. Grewal -Introduction to Accountancy. 31 9A. FOOD PRODUCTION PRACTICALS – II L 0 T 0 P 3 C 3 Marks 100 Hrs 90 Basic sauce preparations and few (2-4) commonly used derivatives* Preparation of traditional / classical Indian, English and continental breakfast dishes*. Preparation of three course simple Indian menus and Indian snacks / high tea items* Preparation of basic continental cookery-stews, sauces, soups, and basic fish preparations.* *The institutions / universities adopting this syllabus must ensure that for all Food Production practical sessions the list of names of preparations / dishes, sets of menus, method (if needs to be specified) should be specifically mentioned for standardized teaching and evaluation. This may be done by constituting a team of experts to compile the details keeping the local conditions in mind. 32 10A. FOOD AND BEVERAGE SERVICE PRACTICALS – II L 0 a) b) c) d) e) f) g) h) i) j) T 0 P 2 Breakfast Table Lay-up. TDH & A la Carte Cover Restaurant Reservation System Receiving the guests Sequence of Service Silver Service Crumbing, Clearing , Presenting the bill Side board Organization Taking an Order-Food & Making a KO T. Writing a Menu in French & its Equivalent in English Service of Cold & Hot - Non Alcoholic Beverages 33 C 2 Marks 100 Hrs 60 11A. ACCOMMODATION OPERATION PRACTICALS – I L 0 T 0 P 2 C 2 Marks 100 Hrs 60 a. Introduction, identification, uses and care of hand tools, cleaning" Equipments and cleaning agents (Paste chart I drawing as applicable} b. Basic cleaning procedure in Guest room: 1. Check-out room, 2. Occupied room, 3. Vacant room, 4. Evening service c. Procedure for Bed making: 1. Day Bed, 2. Night Bed 34 Second Year – Third Semester 12. FOOD PRODUCTION – III L 4 T 0 P 0 C 4 Marks 100 Hrs 60 OBJECTIVE Based on the sound knowledge of commodities and principles and methods of cooking it is desired to prepare students to evolve good understanding and prepare Indian regional menus in large quantities to suit the occasion. The course further introduces the students to the concepts of bakery & confectionery. UNIT – I - REGIONAL CUISINE A detailed study on North and South Indian regional cuisine : Goa, Kashmir, Kerala, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Tamilnadu, Assam, Bengal, Ingredients used. Traditional preparation methods, Utensils and accompaniments. UNIT – II - QUANTITY FOOD PRODUCTION Introduction to Large scale commercial cooking, contract catering, Industrial catering, Institutional catering, Layout of a large quantity kitchen, staff hierarchy, production workflow UNIT – III : MENU DESIGNING Banquet menus- planning, indenting, costing, forecasting, recipes, pre-preparation and cooking techniques. UNIT – IV : STORES Principles of storage, Types of stores, Layout of Dry and cold room, Staff Hierarchy, Guidelines for efficient storage, control procedures, Inventory Procedures, EOQ, Reorder levels, Bin Cards, Form and formats, Function of a stores manager. UNIT – V : CUTS OF MEAT & MEAT COOKERY Cuts of beef, pork, lamb, chicken, SPS, menus examples, methods of cooking each cut, Cold cuts, ham, bacon, common types of ham, preparation, menu examples, selection, storage points Food Commodities Classification with examples and uses in cookery : Pressed meats, Smoked Meats, classification of milk and milkproducts including cheese. Classification and International cheese. UNIT – VI : MENU PLANNING Introduction, types of Menus, French classical menus, International menus, Menu terms, Factors that affect menu planning. Accompaniments, garnishes and Salads For all French classical menus, Classical vegetable accompaniments, classical potato preparation, classical garnishes : Indian, Asian and western foods. Accompaniments for popular international dishes. Classification of salads, types, dressings, examples, Parts of a salad, principles, and vegetable based, meat based, pasta based, sea food, pulses, cereals etc. 35 UNIT – VII :BASIC BAKERY AND CONFECTIONARY Types of dough, types of cake batters, cookies, classical breakfasr rolls, examples of bakery and confectionary product, names and description Convenience food and Fast foods Characteristics, types- Indian and western, Menu examples, equipment used, differences, Role of convenience foods in fast food operations, advantages and disadvantages of convenience food, labour& cost saving aspect. OUTCOME: The Students will get an idea how to design a menu and about bulk cooking for big Parties. Text Books: 1) Madhur Jaffrey, Pavillion -A Taste of India. 2) SangeetaBhatnagar&R.K.Saxena, Harper Collins -Dastarkhwan-e-Awadh 3) Prashad , J.lnder Singh Kalra,HarperCollins, Zaika, SonyaAtalSapru -Cooking with Masters. Reference Books: 1) Premjit Gill -Punjabi Cuisine 2) Pratibha Karan, HarperCollins -Hyderabadi Cuisine 3) Ms. Thangam Philip, Orient Longman -Modern Cookery for Teaching & Trade. 4) Wazwaan, Rocky Mohan, Roli& Janssen , Friberg- The Professional Pastry Chef 36 13. FOOD AND BEVERAGE SERVICE – III L 4 T 0 P 0 C 4 Marks 100 Hrs 60 OBJECTIVE The courses will give a comprehensive knowledge of the various alcoholic beverage used in the Hospitality Industry. It will give an insight into their history, manufacture, classification, and also to develop technical and specialized skills in the service of the same. UNIT – I : ROOM SERVICE Introduction, general principles, pitfalls to be avoided - Cycle of Service, scheduling and staffing, Room service menu planning - Forms & formats, order taking, thumb rules, suggestive selling, breakfast cards - Layout & Setup of Common Meals, use of technology for better room service - Time management - lead time from order taking to clearance UNIT – II : ALCOHOLIC BEVERAGES Introduction, definitions and classification Wines – Classification - Viticultures Viticulture Methods - Vinification-Still, Sparkling, Aromatized & Fortified Wines - Vine Diseases - Wines-France, Italy, Spain, Portugal, South Africa, Australia, lndia& California Food & Wine Harmony - Wine glasses and equipment - Storage and service of wine UNIT – III: BEERS Introduction - Ingredients Used – Production - Types and Brands, Indian and International - Service, bottled, canned and draught beers - Other Fermented &Brewed Beverages – Sake - Cider – Perry - Alcohol Free Wines UNIT – IV : SPIRITS Introduction to Spirits (Whisky, Brandy, Rum, Vodka, Gin &Tequila) - Spirits- Types, Production, Brands- Indian and International & Service - Other Alcoholic BeveragesAbsinthe, Ouza Aquavit, Silvovitz, Arrack, Feni, Grappa, Calvados Etc, LIQUEURS Types – Production - Brands & Service - Indian and International COCKTAILS Introduction, History, Types & Preparation. - Classic Cocktails -Recipes, costing, innovative cocktails & mocktails - Cocktail Bar Equipment, garnishes, decorative accessories - Terms related to alcoholic beverages - Interaction with guests, suggestive selling 37 UNIT – V : BAR Introduction, bar stocks maintenance - Types, Layout, Equipments Used, Control Methods & Licenses - Staffing, job description, job specification - Bar Planning and Designing & Bar Menus, costing, corkage TOBACCO Types – Production - Brands, storage & Service - Food & Beverage Terminology related to the inputs of the semester OUTCOME: The students will gain knowledge on the preparation method of alcoholic drinks and there Advantages and Dis-advantages. Text Books: 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) Sudhir Andrews -Food & Beverage Service Training Manual Lillicrap& Cousins -Food & Beverage Service John Fuller-Modern Restaurant Service Brian Varghese-Food & Beverage Service Management Brown, Heppner &Deegan-Introduction F& B Service Brian Varghese -Professional Food & Beverage Service Management H.Berberoglu -The World Of Wines, Spirits & Beers Reference Books: 1) Andrew, Dunkin & Cousins-Beverage Book 2) Lipinski-Professional Guide to Alcoholic Beverages 3) Lipinski & Lipinski -Alcoholic Beverages 4) Peter Jones & Cassel- Food Service Operations 5) Joyce Rubash -Master Dictionary of Food & Wine 6) BD &L -New york Bartenders Guide 7) Warner -Mr. Boston's Bartender & Party Guide 8) John Kivela- Menu planning 9) Lipinski -The Restaurant (From Concept to Operation) 10) Sergio Andrioli& Peter Douglas -Professional Food Service 11) Costas Katsigris -Bar & Beverage Book 12) John Drysale -Profitable Menu Planning 38 14. FRONT OFFICE OPERATION – II L 3 T 0 P 0 C 3 Marks 100 Hrs 45 OBJECTIVE This course aims to establish the importance of Front Office operations within the hospitality Industry .It also prepares the student to acquire basic skills and knowledge necessary to successfully identify the required standards in this area and to consider all aspects of cost control and establishing profitability. UNIT – I - RESERVATIONS Reservation methods - Reservation inquiring Group - reservation The Reservations - record Reservation confirmation - Reservation maintenance Reservation reports Reservation - Considerations UNIT – II - REGISTRATION Pre-registration activities - Registration activity - The registration record - Room and rate assignment- FITs, Groups, Crew, Indian & Foreign - Method of payment Issuing the room key - Fulfilling special requests - Creative options - Change of room - Over-booking cases UNIT – III: FRONT OFFICE RESPONSIBILITIES Front office communication - Interdepartmental communication - Guest services Guest relations - Dealing with emergencies: medical, death, theft, robbery, fire, bomb threats etc.. UNIT – IV : FRONT OFFICE COMPUTER OPERATION Basics of computer - Application of property management system - Reservations Registration – Cashiering - Night audit UNIT – V : FRONT OFFICE SECURITY FUNCTIONS Role of Front Office in Hotel Security - Check in : use of metal detectors, validators, scanty baggage handling - Keys control : ELS (Electronic Cards), Handling Grand Master / Master key, lost & found & damaged keys, use of key cards - Guest & staff movement & access control - Protection of funds, safe deposit boxes Out Come : Students should gain knowledge of various sections and functions of front office and their procedures. They should be able to Hand various tools and equipments of the front office. 39 Text Books: 1) Colin Dix &Chirs Baird -Front office operations 2) James Bardi, VNR -Hotel Front office management 3) Kasavana& Brooks- Managing front office operations 4) Sudhir Andrews, Tata McGraw Hill -Front office training manual 5) Raymond S Schmidgall -Managerial accounting and hospitality accounting 6) Michael Kasavana and Cahell -Managing computers in hospitality industry Reference Books: 1) Michael Kasavana, CBI-VNR -Effective Front Office Operation. 2) J.R.S.Beavis&S.Medlik, Heinemann Professional- A Manual of Hotel Reception. 3) Colin Dix, Pitman -Accommodation Operation - Front Office4) Sue Baker& Jeremy Huyton Continuum- Principles of Hotel Front Office Operations, 5) Peter Abott& Sue Lewry, Butterworth Heinemann-- Front Office Procedures, Social Skills and Management. 40 15. HOTEL ENGINEERING L 2 T 0 P 0 C 2 Marks 100 Hrs 30 OBJECTIVE The subject will provide information regarding the basic services and different types of systems in hotel industry. This will help the students to understand plan, co-ordinate and integrate the functions of engineering departments for over all operations and assist in the management of hotel. UNIT – I : TYPES OF MAINTENANCE Preventive and Breakdown – Comparisons - Contract maintenance - Advantages and disadvantages - Types of contract - Price rate - Jump sum contract - Rate contract Service contract. UNIT – II : EQUIPMENT REPLACEMENT POLICIES Circumstances under which equipment are generally replaced – Inadequacy – Obsoiescence - Excessive maintenance - Declining efficiency UNIT – III : WASTE DISPOSAL &POLLUTION CONTROL Disposal of waste various methods - Sewage treatment plant - Water Pollution - Sewage Pollution - Air Pollution and Noise pollution related to hotel industry Energy Conservative - Energy conservative methods in different departments of a hotel. UNIT-IV: "Meters" - Voltmeter - Ammeter, Multi Meter, Tester and Test Lamp – Hard Drill / Power Drill / Switches and Sockets – Multi plug - Adaptor and Ballast Florescent Tube - Lamp UNIT – V "Burner" - LPG – precaution of handling LPG – Low pressure Burner – High Pressure Burner - LPG Regulator and adopter. "Electricity" - Conductor -Insulator – Resistance, Difference between AC & DC Power Supply - Single Phase & Three Phase Power Supply – Open Circuit - Closed Circuit - Short Circuit. "Fuels" - Types of Fuels used in Hotel industry - Advantages and Disadvantages of Fuel Types OUTCOME: The student will gain knowledge on how to use the equipment and also how well they can maintain equipment without any repair. 41 Text Books: 1) Barrie and rockliff London -Practical maintenance and equipment for hoteliers, Licenses and Caterers by D.C. Gladweli. 2) M R Frank D Borcnik –John Wiley and sons, New York-Maintenance and Engineering for lodging and food service Facilities 3) Frank D Borcnik –John wiley and sons, New York-.The management of Maintenance and Engineering Systems in Hospitality industry Reference Books: 1) M Satyanarayan&Lalitha Raman – Himalaya Publishing House, Bombay, 400004.Management operations Research 2) Michael H Redlin and David M -Managing Hospitality Engineering Systems Stipnuk – The Educational institute of the American Hotel & motel Association. 3) Robert E Aullach- Energy and Water Resources Management –The Education Institute of the American Hotel & Motel Association. 42 16. COMPUTER APPLICATIONS L 2 T 1 P 0 C 3 Marks Hrs 100 45 OBJECTIVE The subject aims to give a basic knowledge of computers and its operations and enables the student to operate the computer with enough practice to get confidence. UNIT – I : INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTERS Computer, Block Diagram, Components of a computer system, generation of computers, programming languages, generation of languages, storage devices, floppy disks, CD ROM's UNIT – II : OPERATING SYSTEMS Introduction, Functions, types, Components, Case Studies - DOS, Windows UNIT – III : INTRODUCTION TO DBMS Data, Data types, Advantages, Creating a database, Searching, Sorting, Indexing, Writing simple programmes, overview of MS Access, LINUX UNIT – IV : WORD PROCESSING, SPREAD SHEETS AND PRESENTATIONS MS OFFICE, Features of MS WORD, Editing Commands and Mail merge. spreadsheet, Features, Formulae and functions? If Statement, preparing sample worksheets, Different graphs, Features of POWERPOINT. Preparing a presentation Preparing an Organization chart UNIT – V : INTRODUCTION TO INTERNET What is Internet, Network, Network of Networks, WWW, Search Engines, e-mail, websites, Introduction to e-commerce, Creation of email account, search engine. PRACTICALS DOS, WINDOWS MS WORD MS EXCEL MS POWERPOINT INTERNET USAGE Out Come: The student will be able to understand the basics of computers and use the windows application 43 Text Books: 1) V.Rajaraman, Prentice Hall India -Fundamental of Computers, 2) Lonnie E. Moseley & David M. Boodey, BPB Publication-.Mastering Microsoft Office Reference Books: 1) Arora& Bhatia Excels books- Management Information System 2) O’Brien James Tata McGraw Hills -Management Information System 3) S. Sadagopal Prentice Hall -Management Information System 4) Foundation Course in Front Office 44 12A.FOOD PRODUCTION PRACTICAL – III L 0 T 0 P 3 C 3 Marks 100 Hrs 90 a) Preparation of gravies and commonly used Indian masalas b) Regional cookery of India c) Karnataka, Tamilnadu, Kerala, Andhra Pradesh, Gujrathi, Lucknow, Moghlai, Punjabi, Bengali, Hyderabadi and Kashmiri cuisines with proper accompaniments like chutney, Indian breads rice preparations etc d) Tandoor cooking e) Planning elaborate Indian menus upto 40 portions f) The institutions / universities adopting this syllabus must ensure that for all Food Production practical sessions the list of names of preparations / dishes, sets of menus, recipes should be specifically mentioned for standardized teaching and evaluation. This may be done by constituting a team of experts to compile the details keeping the local conditions in mind. 45 13A. FOOD AND BEVERAGE SERVICE PRACTICAL – III L 0 a) b) c) d) e) f) g) T 0 P 3 C 3 Room Service Tray & Trolley Lay-Up and service. Room Service Amenities Set-up In Rooms. Functional & Floor Layouts for room service Conducting Briefing/De-Briefing for F & B outlets Taking an Order for Beverages. Service Of Beer, Sake and Other Fermented & Brewed Beverages. Service Of Sparkling, Aromatized, Fortified, Still Wines. Set up a table with Prepared Menu with wines. 46 Marks 100 Hrs 90 14A. FRONT OFFICE PRACTICAL – III L 0 a) b) c) d) e) f) g) h) i) T 0 P 2 C 2 Marks 100 Hrs 60 How to handle inquiries, suggestive selling How to convert inquiries to valid reservations Preparing and filling up reservation forms Role play of accepting reservations, walking a guest and complaint handling for bumped reservations Reservation handling by computers. Actual computer lab work with the PMS Preparing and filling up registration card Role play for different check ins as - Walk in, FIT, FFFIT, Corporate, VIP, CIP and Groups Role play on guest complaint handling, critical and dangerous situation handling Operating FIDELIO/IDS-PMS system in computer lab. Familiarization of all options 47 Second Year – Fourth Semester 17. ADVANCE FOOD PRODUCTION – IV L 4 T 0 P 0 C 4 Marks 100 Hrs 60 OBJECTIVE Food Production is an integral part of the Hospitality Industry. To prepare the students to cater to the need of the industry, it is important to inculcate in them sound knowledge of the principles of Food Production so that they can be put to use in an efficient & effective way. UNIT – I : RE-CHAUFFER COOKERY Food Commodities - Classification with examples and uses in cookery Nuts and oil seeds, fats and oils classification, sweetening agents, spices and condiments leavening agents, herbs, essences, flavours and food colouring agents, raising agents, brighteners, gels and modified starches used in bakery. UNIT – II : Sandwiches, rolls, burgers, pizzas, hot dogs, foot longs. Types, preparations, selection of spreads, fillings, classical sandwiches, canapés. Presentation styles and appropriate garnishes and accompaniments UNIT – III : KITCHEN MANAGEMENT Work-flow, lay-out, stewarding, staffing, stores management, indenting, production planning, new product development, use of internet and other latest technologies in food production. Food Styling - General principles, modern and special innovative garnishes, accompaniments, decorations and concept development UNIT – IV : BANQUETING PREPARATIONS Types of banquets, themes, production, menu preparation Low calorie food, advantages, disadvantages, menu examples, preparation. Out -door Catering Concept, principles, limitations, menus, planning, check list and precautions UNIT – V : COOK CHILL SYSTEMS Purpose of chilling food, cook chill process, finishing kitchens, distribution of cook chill and types of containers to preserve food. Cook freeze system Preparation of food for freezing, storage of frozen food, transport of frozen food, reheating of frozen or cooked food. Advantages of cook freeze over cook chill. 48 MISCELLANEOUS Power breakfasts, brunches and lunches, High teas, cocktail snacks, theme menus, food festivals, other new or non-conventional catering concepts Airline and Cruise liner meal planning OUTCOME: The student will know how to operate a banquet kitchen, pantry and menu planning for big banquet parties. Text Book: 1) Hamlyn Publishing Chocolate, Carolyn Humphries-The Wilton Ways of Cake Decorations Reference Books: 1) Cavendish House -International Cook Book, 2) Time - Life Series - The Cooking of Various countries 49 18. ADVANCE FOOD AND BEVERAGE SERVICE – IV L T P 4 0 0 C 4 Marks 100 Hrs 60 OBJECTIVE The students will gain a comprehensive knowledge and develop technical skills in aspects of Specialized Food and Beverage services. UNIT – I : FUNCTION CATERING Introduction - Types of Function - Function Administration & Organization-Booking Procedure, Menus, Function contracts, Seating Arrangements UNIT – II : INTERNATIONAL CUISINES, CLASSICAL DISHES / MENUS / SERVICE Mediterranean – Oriental – Polynesian - Far East – American – French - Kosher UNIT – III : GUERIDON SERVICE Introduction - History, Types, Staffing, Equipments Used, Ingredients Used - Common preparations - Flambé dishes, Carving, Salad making etc. - Trolley service - Beverages, Starters, High tea, Desserts etc. UNIT – IV : KITCHEN STEWARDING AND ANCILLARY AREAS Introduction - Staffing, equipment & layout - Kitchen Stewarding Operations Inventory/Records maintenance - Analysing strengths and weaknesses of catering outlets vis-a-vis competition - parameters, decision making on basis of the analysis Traditional Indian service - South Indian (wedding & functions), Thali service (Lay-out & sequence) and other regional cuisines for special occasions. - Food & Beverage Terminology related to the inputs of the semester UNIT-V : HANDLING OF SPECIAL EQUIPMENTS Introduction, usage of special equipments. Advantages and disadvantages of the special equipments. 50 OUTCOME: The student will gain knowledge on handing special equipments and different types of set up for banquet parties. Text Books: 1) Sudhir Andrews- Food & Beverage Service Training Manual 2) Lillicrap& Cousins- Food & Beverage Service 3) John Fuller -Modern Restaurant Service 4) Brian Varghese -Food & Beverage Service Management 5) Brown, Heppner &Deegan -Introduction F& B Service 6) Brian Varghese- Professional Food & Beverage Service Management Reference Books: 1) H.Berberoglu- The World Of Wines, Spirits & Beers 2) Andrew, Dunkin & Cousins-Beverage Book 3) Lipinski-Professional Guide to Alcoholic Beverages 4) Lipinski & Lipinski -Alcoholic Beverages 5) Peter Jones & Cassel -Food Service Operations 6) Joyce Rubash-Master Dictionary of Food & Wine 7) BD &L -New york Bartenders Guide 8) Warner -Mr. Boston's Bartender & Party Guide 51 19. ACCOMMODATION OPERATION – II L 2 T 0 P 0 C 2 Marks 100 Hrs 30 OBJECTIVE This course aims to establish the importance of Accommodation operations within the hospitality Industry .It also prepares the student to acquire basic skills and knowledge necessary to successfully identify the required standards in this area and to consider all aspects of cost control and establishing profitability. UNIT – I : CLEANING OF PUBLIC AREAS Cleaning process - Cleaning and upkeep of Public areas (Lobby, Cloak rooms/Restaurant/bar/banquet Halls/Administration offices/Lifts and Elevators/Staircase/back areas/Front areas/Corridor) UNIT – II : SAFETY AWARENESS AND FIRST AID & SAFEGAURDING ASSETS Concept and Importance - Safety: Accidents, Fires (Cause, Procedure, Accident report form) - Security: Security of Guest/Staff/Public areas/Rooms/Back office areas - First Aid: Concept and Emergency Procedures (Heart Attack, Fits, Burns, Fainting, Fractures, Scalds, Artificial respiration) - Concerns for safety and security in Housekeeping operations - Concept of Safeguarding assets - Theft: Employee, guest, external persons Security in Hotel guest rooms UNIT – III : PEST CONTROL & HOUSEKEEPING SUPERVISION Types of pests - Control procedures - Importance of inspection - Check-list for inspection - Typical areas usually neglected where special attention is required - Selfsupervision techniques for cleaning staff - Degree of discretion / delegation to cleaning staff UNIT – IV : LINEN/ UNIFORM / TAILOR ROOM Layout - Types of Linen, sizes and Linen exchange procedure - Selection of linen Storage Facilities and conditions - Par stock: Factors affecting par stock, calculation of par stock - Discard Management - Linen Inventory system - Uniform designing: Importance, types, characteristics, selection, par stock - Function of Tailor room UNIT – V : CLEANING OF GUEST ROOMS Daily cleaning of (Occupied/Departure/Vacant/Under repair/VIP rooms - Weekly cleaning/spring cleaning - Evening service - Systems & procedures involved - Forms and Formats - Guest room cleaning - Replenishment of Guest supplies and amenities Out Come : The student should be able to fix the position and the value of each housekeeping staff in the hotel organization. The Student should become familiar with the 52 equipment and agents needed in the housekeeping department. He/She should also become through with all the practices and procedures. Text Books : 1) Sudhir Andrews, Tata McGraw Hill-Hotel Housekeeping 2) Tucker Schneider, VNR-The Professional Housekeeper 3) Martin Jones, Wiley- Professional Management of Housekeeping Operations Reference Books: 1) Rosemary Hurst, Heinemann -House Keeping Management for Hotels 2) Joan C. Branson & Margaret Lennox, ELBS -Hotel, Hostel & Hospital House Keeping 3) David . Allen, Hutchinson- Accommodation & Cleaning Services, Vol I & II 4) Margaret Kappa &Aleta -Managing House Keeping Operation, 53 20. NUTRITION AND FOOD SCIENCE L 2 T 0 P 0 C 2 Marks 100 Hrs 30 OBJECTIVE This course aims to develop awareness of the importance of hygiene, sanitation and food safety in hotel industry. UNIT – I : INTRODUCTION Food & its relation to health, Objectives in the study of nutrition Major Nutrients : Their characteristics, functions, metabolism, food sources, deficiencies, Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, Vitamins & Minerals UNIT – II : CLASSIFICATION OF RAW MATERIALS INTO FOOD GROUPS Cereals, Pulses, Milk & milk products, milk borne disease pasteurization and boiling preservation of milk, Eggs, Meat varieties, preservatives, cooking poultry white and red meat, Fish, cooking, disease produced by fish, Fruit & Vegetables, Nuts & dried fruits, Sweet foods & sweetening agents, Spices & condiments, emulsions, colloids, flavour and browning. UNIT - III : EFFECT OF HEAT ON FOOD Effect of cooking on- Nutritive value of food, Pigments and texture. Method of retention of Nutrients. UNIT – IV : WATER Definition, Dietary sources (visible, invisible), functions of water, role of water In maintaining health (water balance). UNIT – V : Balanced Diet / Menu planning: Definition, importance of balanced diet, RDA for various nutrients – age, gender, physiological state, planning of nutritionally balanced meals based upon the three food group system, factors affecting meal planning, critical evaluation of few meals served at the Institutes/Hotels based on the principle of meal planning, calculation of nutritive value of dishes/ meals. Basics of In-valid cookery and therapeutic diets. 54 Outcome:-The student will understand the correlation between food microbiology, its Importance and nutrition. Text Books: 1) F. P. Anita -Clinical dietetics & nutrition 2) Dr. M Swaminathan- Food science chemistry & experimental foods 3) H. Robinson -Normal and therapeutic nutrition 4) Anna K Joshna -Microbiology 5) Dr. M. Swaminathan -Food & Nutrition Reference Books: 1) A. V. S. S. Rama Rao -A text book of Bio chemistry 2) Mohinseth, SurjeetMulhan -Catering Management an integrated approach 3) Manay&ShalaksharaSwamy- Food facts & principles 4) SumathiMudambi -Food science 5) Nutritive value of Indian foods. Indian Council of Medical Research 6) Mudambi&Rajgopal 4th edition 2001-Fundamentals of food and nutrition 7) P.J.Fellows -Principles of Food Technology 55 21. PERSONALITY DEVELOPMENT L 2 T 0 P 0 C 2 Marks 100 Hrs 30 OBJECTIVE To develop the personality and communication skills of the student, so as to prepare them for campus interviews and challenges in personal and professional life. UNIT – I : INTRODUCTION Life Cycle Approach to Development - Social and Cultural Context in Human Development - Culture and Human Development - Cognitive Development Emotional and Social Development - Development Concerns during Adolescence early youth and adulthood - Problems of aging - .Problems and Issues of Human Development in the Indian Context - Suggested practicum activities: Observation skills - · Models of parenting - · Study of generational studies through internet - · Study collection and theories of mind UNIT – II : SELF-ESTEEM, SELF-CONCEPT, SELF-ACCEPTANCE AND PERSONALITY DEVELOPMENT Accept themselves as they are with all their strengths and weaknesses to live as fuller and richer persons, fully alive and human - Positive Thinking - have the right perception of life - soft and tender minded to tough minded individuals - weak, negative individuals to men and women of strength. UNIT – III : MOTIVATION AND ACTUALIZATION Energizing and directing their efforts toward a meaningfulGoal - self-directed performing out of their own needs, desires and aspirations - Goal Setting - the different types of goals - setting goals and striving Meaning and Attitude to Success - unpredictability and satisfaction with oneself and one’s achievements - proper attitude Problem Solving - Problems in terms of their past decisions - consequences of such decisions and then choose a more satisfying alternative UNIT – IV : DECISION MAKING Result of events and circumstances that happen - decisions are crucial for personal growth - Time Management - importance of time in their lives - judicious use of time and how if used effectively to achieve their goals – Leadership - nature and types of leadership - enumeration of the characteristics of good leadership leadership role with courage and confidence - Team work – dynamic work with Team - ways and means of them building – imbibe the skills of working as a member of a team 56 UNIT – V : COPING MECHANISM Coping with Shyness – How to overcome - Coping with Depression - meaning and nature of depression - symptoms of depression and the causes - how to overcome the ways to overcome depression - Coping with Fear - various kinds of fear - how to handle fear and overcome the same - Coping with Failure - accept experiences of failure as part of life - worthy getting upset about - Coping with Criticism - Criticism in an inevitable reality - Coping with Conflict - Conflict is a fact of life – distinction between constructive - destructive conflicts - strategies to manage conflict - Coping with Change - change that is inevitable - attitude of flexibility to adjust - Coping with Study -study is the most important part of the curriculum - deal with methodically OUTCOME: The student will Gain knowledge Self motivation, problem solving and how to present themselves in front of others. Text Books: 1. R. Gairns and S. Redman, - Working with words - Cambridge University Press,London 2. BookDeff/Jones, Foundation Books (Cambridge University Press), Delhi. Meanings into Words-Upper Intermediate Students 3. A.J. Thomson and A.V. Martinet, OUP, Delhi-.A Practical English Grammar 4. Margaret M. Maison, Orient Longman, New Delhi -Examine your English . 5. W.J. Ball. Longman -A Practical Guide to Colloquial Idom . Reference Books: 1. L.A. ill, Oxford -A guide to correct English . 2. H.whitehall, Longman- Structural Essentials of english. 3. B.D. Graver, OUP, Delhi- Advanced English Practice 4. Public Speaking, Sudha Publication Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi. 5. Group Discussion, Sudha Publication Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi. 57 17A-FOOD PRODUCTION PRACTICALS – IV L T P C Marks Hrs 0 0 3 3 100 90 a) Regional Indian cookery b) Preparation of Salads, centerpiece, cold cuts and sandwiches c) Preparation of Basic Bakery and Confectionery d) Biscuit dough, Bread dough, Cake batters, Puff pastry dough, Croissants, Danish pastry, e) Doughnuts, Different Bread preparation. Pancakes, Cold and hot desserts. The institutions / universities adopting this syllabus must ensure that for all Food Production practical sessions the list of names of preparations / dishes, sets of menus, recipes should be specifically mentioned for standardized teaching and evaluation. This may be done by constituting a team of experts to compile the details keeping the local conditions inmind. 58 18A-FOOD AND BEVERAGE SERVICE PRACTICALS – IV L T P 0 0 3 a) Service of Spirits & Liqueurs b) Bar set up and operations c) Cocktail/ Mocktail Preparation d) Presentation and service e) Service of Cigars & cigarettes 59 C 3 Marks 100 Hrs 90 19A- ACCOMMODATION OPERATION PRACTICAL – II L T P C Marks 0 0 2 2 100 a) Room Attendant Trolley b) Bed Making c) Turn down service d) Cleaning of guest rooms - departure, occupied, vacant e) Cleaning of public areas f) Inspection of guest rooms & public areas with the help of checklist g) First aid 60 Hrs 60 Third Year – Fifth Semester 22. FOOD AND BEVERAGE MANAGEMENT L 2 T 0 P 0 C 2 Marks 100 OBJECTIVE The student will gain comprehensive knowledge on various aspects of control procedures, adopted by the food and Beverage department. UNIT – I : COST DYNAMICS a) Elements of Cost b) Classification of Cost UNIT – II : SALES CONCEPTS a) Various Sales Concept b) Uses of Sales Concept UNIT – III : INVENTORY CONTROL a) Importance b) Objective c) Method d) Levels and Technique e) Perpetual Inventory f) Monthly Inventory g) Pricing of Commodities h) Comparison of Physical and Perpetual Inventory UNIT – IV: BEVERAGE CONTROL a) Purchasing b) Receiving c) Storing d) Issuing e) Production Control f) Standard Recipe g) Standard Portion Size h) Bar Frauds i) Books maintained j) Beverage Control 61 Hrs 30 UNIT –V: SALES CONTROL a) Procedure of Cash Control b) Machine System c) ECR d) NCR e) Preset Machines f) POS g) Reports h) Thefts i) Cash Handling UNIT – VI : BUDGETARY CONTROL a) Define Budget b) Define Budgetary Control c) Objectives d) Frame Work e) Key Factors f) Types of Budget g) Budgetary Control OUTCOME: The student will gain knowledge about different types control procedure adopted in the hotel industry. Text Books: 1. controlPaul R .Dittma, JeraldG.Giffin -Principles of food, beverage and labor cost 2. Hodder and Stoughton-Profitable food and beverage management 3. Roy and wood-Strategic questions in food and beverage management Reference Books: 1. Jones and erricks-The management of food and beverage management 2. Paul Morrison, Heinruys and Brian Morrison -Cost management for food and beverage operations 3. Paul Culler -The food and beverage manager 62 23-PROJECT WORK & REPORT L 0 T 3 P 3 C 6 Marks 100 Hrs 135 OBJECTIVE To enable the student to apply the knowledge and skills acquired in the many facets of Hotel Operations, learn to analyse data situations at logical decisions. The student will be required to undertake a research on any topic related to hospitality Formulating The length of the report may be 150 double spaced pages (excused appendices and annexure) 10% variation on either side is permitted. Guidelines List of contents of the research Chapter I - Introduction Chapter II Scope, Objective, Methodology, and limitation of the research Chapter III data analysis Chapter IV results and discussion Chapter V recommendation Chapter VI annexure, exhibits, and bibliography Submission of the report Three copies of the report have to be submitted before the due date as specified by the college. The original copies should be submitted to the university through the college concerned. The College copy is to be retained by the college and the personal copy should be duly signed by the faculty guide and Principal or HOD of the HM Department. The student should carry the personal copy to the Viva Voce The Student should also carry the following: Duly signed personal copy of the project Examination Hall ticket College Identity card Dress code should be formal OUTCOME: The student would have gained adequate knowledge on the project which he would be doing. 63 24- TRAVEL AND TOURISM L 3 T 0 P 0 C 3 Marks 100 Hrs 45 OBJECTIVE To inculcate a sense of importance and establish a link between the tourism industry and the hotel industry and to highlight tourism industry as an alternative career path UNIT-I Economics of Tourism Origin and objectives of tourism, Elements of tourism, Scope of tourism, nature of tourism, Travel motivations, job opportunities and employment generation, Govt. revenue and foreign currency exchange, economic growth based on tourists statistics, economic benefit of tourism UNIT-II Tourism products and resources Architectural heritage of India, Islamic and inter European influence, Culture and iconography of India, Painting and music of India, Classical and folk arts of India, Fairs and festivals of India, Natural and other tourism resources. UNIT-III Tourism planning and development Tourism policy formation, Types of tourism planning, Steps o tourism planning, Role of international organizations planning, Tourism policy of India, Tourism in Tamilnadu and its Policy, Participation of public and private sector in planning UNIT-IV Tourism Marketing Introduction, Market segmentation of tourism, Marketing mix in tourism, Advertising and publicity, Selection of media, Travel writings Sales report, Public relations and its importance in travel marketing, Marketing and its objectives, Types of marketing research, distribution channels of tourism marketing. UNIT-V Socio Economic impact of tourism 64 International understanding and tourism, National integration and tourism, Protection of arts and folk arts, Improvement of human relationships, Infrastructure development, Water pollution, Air pollution, Noise Pollution, Ecological destruction, Environment OUTCOME: The student will understand the importance of Tourism industry in the Hospitality Industry Text Books: 1. Mills & Morrison- The tourism system –An introductory text 2. Gunclare A -Tourism planning . 3. Venkitaraman R -Archeology . 4. Luniya B -Indian culture . Reference Books: 1. Manoj Das -India and tourist paradise 2. A.K. Bhatia- Tourism Development 3. R.N. Kaul -Dimensions of tourism 4. P.N. Seth- Tourism Management 5. Jagmohan Negi -International Travel & Tourism. 65 25-OPTIONAL SUBJECT ( FP, F&BS, AO, FOO) L T 4 2 P 0 C 6 Marks 100 Hrs 90 Depending on the elective subject the student will be given theory and practical knowledge to appear in the interviews. FOOD PRODUCTION OBJECTIVE This course enables the student to acquire administrative and managerial skills and to familiarize them with the current trends in the Food Production Operations, like standard operating procedures and software applications while sharpening their culinary skills. UNIT-I Deserts Frozen Deserts, Classification, Types & methods of preparation care uses, Hot Puddings – Methods of preparation, care, uses, Ice- creams, methods, types, Indian Specialty Deserts UNIT-II Chocolate making Manufacturing & processing of chocolate, Types of chocolate, Preparations & care in chocolate work, Fillings & toppings – preparation, method, care in preparation, presentation, and storage. UNIT-III Personal Management in the Kitchen Developing a good food production team (Desirable attributes for staff at various levels of hierarchy), Allocation of work, Task Analysis, Duty roaster Time & motion study in kitchen, Production, planning, scheduling & budgeting UNIT-IV Kitchen Administration Aims of Control, Maintaining records / registers / logbook, Communication with other departments, Conduction meetings, Liasing with customers / guests 66 UNIT-V Production Management Buying Knowledge, Specification buying, Scope of Purchases, Production planning & scheduling, Production quality & quantity control UNIT-VI Budgetary Control Objectives, Types of budgets, Basic stages in preparation of budgets, Pricing consideration, Menu engineering, UNIT-VII Product Research & Development Testing of new recipes and equipment, Developing new recipes, Food trials, Organoleptic and sensory evaluation OUTCOME: The Student will be fully equipped with the adequate knowledge about the production department. Reference Books: 1.) Meera John Jacob -Fruit and Vegetable Carving 2.) Frederic H. Sonneschmidt & John Nicolas- The Art of Grade Manager 3.) Published by Wiley & Sons Inc-The Professional Chef – ( The Culinary Institute of America) 4.) David Paul Larousse -The Professional Grade Manager 5.) Brenda Purton- The Art of Sugar Craft – Sugar Paste 6.) Brenda Purton- The Art of Sugar Craft – Royal Icing 7.) Jill Smith- Practical Computing a Guide for Hotel and Catering students – Publisher – Heinemann Professional Publishing Ltd. 8.) Cassell- People and the Hotel and Catering Industry 9.) Practical Computing – A guide for Hotel and catering Students FOOD AND BEVERAGE SERVICE OBJECTIVE This course enables the student to gain a better understanding of the role of Food and Beverage Management in the context of overall catering operations. To Familiarize the student with the current trends in hospitality operations like Standard Operating Procedures and Software Applications UNIT-I Chapter 1 Meal Experience 67 Introduction, Eating Out, Food and Drink, Variety of service, Level of Services, Interior design and atmosphere, Expectation and identification, F & B Service employees, Trends in eating out. UNIT-II Managing quality in Food & Beverage Operations Definition and importance, Approaches to quality management, Managing quality UNIT-III Budgetary Control Objectives, Types of Budgets, Basic stages in preparation of budgets, Pricing consideration, Menu pricing, Menu engineering UNIT-IV F & B Management in Fast Food and Popular Catering Introduction, Basic policies – Financial marketing and Catering, Organizing and Staffing, Control and performance measurement. UNIT-V F & B Management in Hotels & Restaurants Introduction, Basic Policies – Financial marketing and Catering, Organizing and Staffing, Control and performance measurement, Production planning & scheduling, Production quality & quantity control UNIT-VI F & B Management in Industrial Catering Introduction, Basic policies – Financial marketing and Catering, Organizing and Staffing, Control and performance measurement OBJECTIVE : The student will gain a deep and thorough knowledge about the food and beverage department. REFRENCE BOOKS: 1.) Dennis Lillicrap and John Cousins- Food & Beverage Service 2.) Bernard Davis, Andrew Lockwood and Sally Stone-Food & Beverage Management 3.) Richard Kotas -Food & Beverage Control 4.) Brain Varghese- Food & Beverage Service Management 5.) Lipinski -The Restaurant (From Concept to Operation) 6.) Sudhir Andrews -Food & Beverage Service Training Manual 7.) Jill Smith -Practical Computing – A guide for Hotel and students -Heinemann Profes. Publishing 68 ACCOMMODATION OPERATION OBJECTIVE The subject aims to establish the importance of accommodation management and Front Office with in the hospitality industry. It equips the student to acquire knowledge & skills with respect to various management aspects of housekeeping Division and front office Division. UNIT-I Operations Management Effective use of cleaning practices and Front Office, Operations – SOP’s at housekeeping and front office department, Effective use and control of supplies & equipment, Establishing standards, monitoring performance, corrective action in Rooms Division. UNIT-II Personnel Management in Accommodations Operations Calculating Staff Requirement, Duty Rotas, Selection & Requirement of employees – Attributes for staff at various levels of hierarchy, Time & Motion study, work study & work measurements UNIT-III Financial Management & cost control Preparation of Budget, Revenue Budget for Front Office, Expense Budget for House keeping Department, Budgets : Types – fixed, flexible, zero base, Measures to reduce operating cost & labour cost UNIT-IV Environmental Practices in Housekeeping Eco friendly cleaning supplies, Waste reductions programme, Recycling of materials UNIT-V Use of computer technology in Rooms Division MIS – Management Information System, Software used in Hotels, Reports generated at Front Desk and Housekeeping, Rooms Status Report, Sales Mix Report, Revenue Report, Guest History UNIT-VI Yield Management Concept ARR & Rev PAR, Definition & importance of Yield Management Forecasting 69 OUTCOME: The student will gain a deep and thorough knowledge about the Accommodation Operation department and the Front Office department. Reference Books: 1. Georgina Tucker, Schneider, Mary Scoviak- Professionals Housekeeper 2. Matt. A. Casado ( Wiley)-Professional Management of H.K. operations FRONT OFFICE OPERATION OBJECTIVE The subject aims to establish the importance of Front Office with in the hospitality industry. It equips the student to acquire knowledge & skills with respect to various management aspects of front office Division. Unit -I Computers in Front Office Handling PMS, Generation of reports / Night audit, Internet / E- Commerce Websites of our hotels and other hotels, Collect addresses of search engines for browsing & updates, Working knowledge of computers to assist in installation of software related to Front Office Unit-II Charting credit policies / floor limits and billing procedures Handling Travellers cheques, foreign currencies, credit cards, fake currencies & procedures UNIT-III Financial Management & cost control Preparation of Budget, Revenue Budget for Front Office, Expense Budget for House keeping Department, Budgets : Types – fixed, flexible, zero base, Measures to reduce operating cost & labour cost Unit-IV Front Office Statistics Budget estimates of revised budgets, Marketing & hotel sales statistics, MIS and related graphs / Segmentation, SWOT Analysis and action plan, Mock report generation Unit-V 70 Interpersonal Skills and handling conflicts Transactional analysis, Ego states, Life positions, Conflict handling techniques Communications in accommodation management OUTCOME: The student will gain a deep and thorough knowledge about the Front Office department. Reference Books: 1. Linsley Deveaur, Marcel Escoffer- Front Office Management & Operations 2. Gary Vallen, Jereme, Vallen -Check in – Check out 3. Michel Kasavana, Richard M Brooks- Managing Front Office Operations 71 26- HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT L 3 T 0 P 0 C 3 Marks 100 Hrs 45 OBJECTIVE The understanding of Human Resources Management will help the students in identifying the significance and its role in the Hotel & Catering Industry. It will also help them to develop an attitude for positive Human Behaviour at work. UNIT - I : HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT Meaning, Nature, Objectives, Scope and functions the Philosophy and policy of the HRMDepartment structure and functions- Managerial and operating functions- HRM as a profession – Environmental influence of HRM. UNIT – II : HUMAN RESOURCE PLANNING Manpower planning- strategy consideration of planning- job analysis- job specificationjob description- Approaches to job design- job simplification- job enlargement- job rotation – job enrichment- Absenteeism and labour turnover- Recruitment & selection: Recruitment policy- problems- source of recruitment- recruitment policies in Indiaselect in – placement and induction- promotions and transfers- demotions and separations. UNIT – III : TRAINING & DEVELOPMENT TRAINING Need and importance- steps in training programme- evaluation of training programmes – concept of management development programme – techniques of training and development – group discussion – conferences and seminar case studies- role playingbusiness games- sensitivity training- stages of career development. UNIT – IV : WAGE & SALARY ADMINISTRATION Compensation plan- job evaluation- individual- group- incentives- bonus- fringe benefits- performance appraisal- meaning- need and importance- objectives- methods and modern techniques of performance appraisal- requisite of good appraisal planproblems in performance appraisal. UNIT - V : QUALITY OF WORKING LIFE Issues in quality of working life- obstacles in QWL- quality circles- management by objectivesTrade union- structure- objectives, policies, growth of trade union in Indiajoint consultation and employee participation in management – collective bargaining OBJECTIVE: The student will get knowledge about the managing manpower and the recruitment procedures in the hospitality industry. 72 Text Books: 1. E.B. Flippo -Personnel Management 2. C.B.Memoria -Personnel Management Reference Books: 1. Gary Dessler- Human resource Management 2. K Aswathappa -Human Resourse Management - 5th edition TMG 73 25A-OPTIONALSUBJECT PRACTICAL (FP, F&BS, AO, FO) L T P C 0 0 5 5 Marks 100 Hrs 150 Depending on the elective subject the student will be given theory and practical knowledge to appear in the interviews. All semester’s theory and practical will be considered for the exams. (As per the student’s choice) For the food production they can specialize in any one cuisine which the student prefer to do.( Indian, Chinese, multi cuisine, French, Mexican, Italian or continental.) For the food and beverage service they can specialize in bar management and control and restaurant management. Accommodation operation will go through from the beginning of the semester till end and the interview point of view the training will be given. Front Office operation will go through from the beginning of the semester till end and the interview point of view the training will be given. 74 Third Year – Sixth Semester 27-INDUSTRIAL TRAINING AND INDUSTRIAL REPORT L T P C 0 8 8 16 OBJECTIVE Marks 100 Hrs 360 The Industrial Training enables students to relate the knowledge and skills acquired in the classroom with systems, standards and practices prevalent in the Industry. Each student has to undergo Industrial Exposure Training of 10 weeks duration The Training will be given in the following departments of any Hotel of national or global reputed. 1. Front Office (2 weeks) 2. Housekeeping (2 weeks) 3. F & B Production (3 weeks) 4. F & B Service (3 Weeks) After the completion of training the students shall immediately be submitting an industrial exposure training report within two weeks time. This Report shall also carry Two hundred marks. The marks shall be awarded by the concerned training coordinator of the college, based on the viva and the report submitted by the student. Each student has to have a certificate of successful completion of training. OUTCOME: The student will get a sound knowledge about the hospitality industry by getting trained in the industry and by completing the Industrial training report. 75 28-SALES AND MARKETING L 3 T 0 P 0 C 3 Marks 100 Hrs 45 OBJECTIVES The subject aims to make the students understand importance of marketing in Hospitality Industry, concepts of the marketing, buying behaviors, market segmentation and marketing mix strategies for effective marketing of the hotel industry. UNIT‐I : Fundamentals of marketing Definition of markets, marketing and selling‐The marketing concept –methods and scope of marketing market segmentations‐basis of market segmentations‐Types market information research(MIS)‐Difference between MIS and Marketing research. UNIT‐II : Introduction to market mix Product‐New product development‐product life cycle‐branding Price‐ factors influencing pricing decisions‐types of pricing. Place ‐ distribution‐channels of distribution. Promotion‐Promotional mix‐types of media UNIT‐III Introduction to promotional activities‐advertising‐aims of advertising‐advantages and disadvantages of advertising‐pre-testing and post testing methods UNIT-IV Sales promotion Introduction –Types of sales persons -role of sales person UNIT-V International marketing-International marketing -emergence of global marketing significance of international marketing for developing countries-liberalizationrole of foreign MNC OUTCOME: The student will gain knowledge about how to sell a product or how to market a product . 76 Text Book: 1. Philip Kotler-Marketing management Reference Books: 1. Rajan Nair -Marketing management. 2. D.D.Sharma -Marketing Management. 77 29-EVENT MANAGEMENT L T 3 1 P 0 C 4 MARKS 100 HRS 60 OBJECTIVE This course enables the student to develop and understand the necessity of the event management in Hospitality Industry. UNIT – I : The events business a. Definition and frame work b. Categories and typologies c. Historical context and precedence d. Characteristics of events UNIT – II : The market demands of events a. Introduction b. Size and scope of the event c. Determinants and motivation d. The structure of demand for event UNIT – III : The events business; supply and suppliers a. Introduction b. The structure of event service – public sector c. The structure of event service - private sector d. Companies and their duties e. Voluntary bodies, committees and individuals UNIT – IV : Managing events a. Making a start b. Introduction c. Getting organized d. Event feasibility – finding and testing an idea e. The screening process f. Progressing the idea UNIT - V : Event planning a. Introduction b. The planning process c. Objectives, environmental search and information gathering d. Demand and operational planning 78 e. Financial planning f. Marketing planning g. Getting it together UNIT – VI : The event – venue finding, logistics and ambience a. Introduction b. Finding the venue c. Logistics – supplies, transport and distribution d. Catering e. Drink services f. Backdrop and staging g. Lightening h. Sound and communication i. Amenities and cleaning j. Creating the ambience UNIT – VII : Marketing and public relations for events a. Introduction b. The target market c. How to influence the target market d. Marketing plan e. Marketing for a new event OUTCOME: The student will understand the necessity of event management in the hospitality industry. Reference Books: 1. Anton shone, Pryn proxy- “successful Event Management” 2nd edition 2. Allen J, Etobicoke -Event planning 79
© Copyright 2026