Male and Female Reproductive Systems
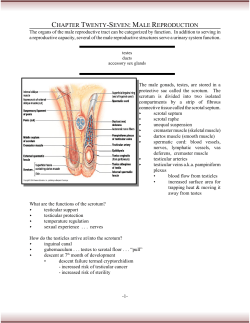
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS! MALE AND FEMALE HEALTH MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Ejaculatory Ducts Cowper’s Gland Male Reproductive System DEFINITIONS: (EXTERNAL) Penis: The male organ for sexual intercourse, reproduction, and urination. The reproductive purpose of the penis is to deposit semen in the vagina during sexual intercourse. Scrotum: A sac-like pouch located behind the penis that holds each testical and helps regulate temperature for sperm production. DEFINITIONS: (INTERNAL) Testicles/Testes: The two testes are small organs about the size of a peach pit that lie in the scrotum and produce sperm and the hormone testosterone. The testicles are the male sex gland. Epididymis: Tightly coiled tube where sperm are stored. From here sperm are transported to the Vas Deferens. DEFINITIONS: (INTERNAL) Vas Deferens: Two long, thin tubes that serve as a passageway. Transports sperm from the Epididymis to the urethra. Urethra: A dual purpose tube that both semen and urine pass through to leave the body. Semen and urine never mix. DEFINITIONS: (INTERNAL) Seminal Vesicles: Two small glands that secrete a mucous fluid that nourishes and enables the sperm to move. Prostate Gland: Walnut-sized gland beneath the bladder. The gland secretes an alkaline fluid that neutralizes the acid found in the male urethra and the female reproductive tract. DEFINITIONS: (INTERNAL) Cowper’s Gland: Two small pea-sized glands located beneath the prostate gland on both sides of the base of the penis. They secrete a clear, sticky fluid that is alkaline to help neutralize the acidity of the urethra. Ejaculatory Ducts: These are formed by the fusion of the vas deferens and the seminal vesicles. The ejaculatory ducts empty into the urethra. SPERM PRODUCTION AND EJACULATION 1. Sperm made in testicles 2. Sperm matures in epididymis 3. Sperm travel up vas deferens 4. Sperm mix with seminal fluid to make semen 5. Sperm leave the penis (ejaculation) WHAT ELSE DO YOU KNOW ABOUT SPERM PRODUCTION? QUESTIONS? DISCUSS FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Female Reproductive System-External Fallopian Tube Uterus Cervix Vagina Ovary Female Reproductive SystemInternal (front view and side view, missing left leg) DEFINITIONS: (EXTERNAL) Vulva: The general term to describe all the external female sex organs. Urethra: Below the clitoris, the opening to the bladder. Clitoris: The center of sexual sensation. It is composed of many sensitive nerve endings. DEFINITIONS: (EXTERNAL) Labia Majora: Two folds of skin running that form around the vaginal opening. The labia majora meet and fold together forming protection for the genitals. Covered with pubic hair. Labia Minora: Two smaller folds of tissue which lie just within the labia majora. Join at the top, forming a hood over the clitoris. DEFINITIONS: (INTERNAL) Hymen: A thin ring of tissue covering the opening to the vagina. It is the dividing line between external and internal sex organs. Vagina: Female organ of intercourse, it is actually an empty passageway leading from the vaginal opening to the uterus. It is usually 3-4 inches. The vaginal walls can stretch greatly. DEFINITIONS: (INTERNAL) Cervix: The neck or opening of the uterus. A normal healthy cervix is the strongest muscle in the body. Uterus: The uterus is a hollow, muscular organ shaped somewhat like an upside-down pear. The uterus has one main function – to protect and nourish a fetus. The walls of the uterus stretch much like a balloon that is blown up. DEFINITIONS: (INTERNAL) Fallopian Tubes: Two tubes shaped like arched bridges, on either side of the uterus. They are about the size of cooked spaghetti. The fallopian tubes carry egg cells toward the uterus and sperm cells toward the egg cell. They are the location for fertilization. DEFINITIONS: (INTERNAL) Ovaries: Two solid egg-shaped structures about the size of peach pits. They are the counterpart of the male testicles. They have two main functions: 1-produce female estrogen and progesterone. 2- to store and release the ova or female egg cell. MENSTRUATION 1. Lining of uterus us shed (day 1 of menstrual flow) • Usually lasts 5-7 days • Made up of blood and tissues • About 4-12 teaspoons 2. Lining of uterus thickens with blood and other tissues 3. Ovulation occurs (egg released from ovary) 4. Egg travels through fallopian tube 5. Egg enters the uterus 6. Egg dissolves if unfertilized 7. Lining of uterus is shed (day 1 of menstrual flow) WHAT ELSE DO YOU KNOW ABOUT MENSTRUATION? QUESTIONS? DISCUSS
© Copyright 2026