Learning goals: Clickers - "the greatest new teaching tool since chalk:"
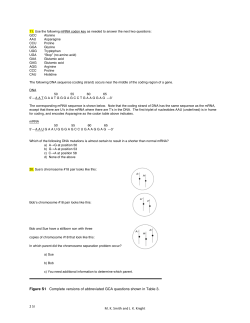
Clickers - "the greatest new teaching tool since chalk:" How to use and not misuse audience response systems December 1, 2007 1. Evidence for the benefits of active learning in general. 2. How clickers can be used effectively. 3. Side benefits of clicker use. 4. The down side: some common problems with using clickers. 5. Writing good clicker questions. 6. Write your own clicker questions. • explain and defend the pedagogical advantages of using clickers in large classes. • design effective clicker questions that assess conceptual understanding, not just note-taking skills or memorization. Outline -- Break -- After this workshop, participants should be able to: • design classes that address necessary content while allowing time for clicker discussions and other student-centered activities. Bill Wood Department of MCD Biology University of Colorado, Boulder ASCB 2007, Education Workshop Learning goals: Clickers How to use: Press On/Off button. The blue POWER light should come on. To vote, press A, B, etc. The VOTE STATUS light will flash green if your vote was recorded successfully, flash red if not (let me know and we'll give you another clicker). To change your vote, just press another key. That's it! These are RF clickers; receiver unit plugs into my computer USB port. 1 Demographics I am a A) K-12 teacher B) College faculty at a P.U.I. C) College faculty at a research university Clickers Have you used clickers before, as an instructor or a student? A) Yes B) No D) Non-tenure track college faculty E) Student or postdoc Origins and development of clickers 1. Why Clickers? (and other student-centered active-learning activities in class as opposed to traditional lecture)? Some evidence that they work 2 The idea of active learning is not new 主动学习/Active Learning 我听, 我忘记。 我看, 我记住。 我做, 我理解。 - 孔子 I hear, and I forget. I see, and I remember. I do, and I understand. - Confucius, ~ 450 BCE How can learning gains be measured? Measure conceptual understanding using the same set of assessment questions*: As a pre-test, before the start of a course, and again as a post-test, perhaps imbedded in the final exam. Then calculate a normalized learning gain for each student: Normalized % Learning Gain = (post-test minus pre-test) x 100 (100 minus pre-test) *A carefully designed, validated test, not just the final exam! Now you're in a position to do . . . Average normalized gains for students of a single instructor, teaching the same physics course over several semesters in two different styles Scientific Teaching! Passive Active Make course changes, introduce innovative approaches, and measure the effects on learning. Robert Beichner and Jeffrey Saul (2004), SCALE-UP Program, Dept. of Physics, N.C.S.U., recent NSF CCLI Conference Proceedings 3 Comparison of student normalized learning gains in traditional and interactive-engagement courses Number of students Interactive-engagement vs traditional methods: A sixthousand student survey of mechanics test data for introductory physics courses traditional interactive interactive Average normalized learning gain Traditional: n=14 courses Interactive: n=74 courses Richard R. Hake, Department of Physics, Indiana University, Bloomington, Indiana Am. J. Phys. 66: 64 (1998) % normalized learning gain Developmental biology,a required course for majors, ~70 junior and senior undergraduates, taught in Fall '03, Spr. 04,and Spr. 05 by Jennifer Knight and Bill Wood (Cell Biol Educ 4: 298310, 2005). A. Traditional (F'03) Distribution of learning gains by course grade achieved 2. Effective use of clickers: Identifying misconceptions Number of students Assessing conceptual understanding Normalized learning gain range (%) B. Interactive (S'04) Number of students Normalized learning gain range (%) 4 Clicker question: Electron micrograph of a gene caught in the act of transcription The molecules making up the mass of the wood that forms during growth of a tree are derived primarily from DNA A) sunlight. B) the air. C) the seed. D) the soil. mRNAs Left Right Which way is transcription going? A) left to right. B) right to left. (Adapted from Diane Ebert-May) 3 1 2 Three identical plates of radish seeds are incubated under three different conditions, with results as shown. How will the dry weights of the three plates compare at the end of the experiment? A) 1 < 2 < 3 B) 1 < 3 < 2 C) 1 = 3 < 2 D) 3 < 1 < 2 E) 1 = 2 = 3 (Adapted from Diane Ebert-May) 1 1.46 g 2 1.63 g 3 1.20 g Three identical plates of radish seeds are incubated under three different conditions, with results as shown. How will the dry weights of the three plates compare at the end of the experiment? A) 1 < 2 < 3 B) 1 < 3 < 2 C) 1 = 3 < 2 D) 3 < 1 < 2 E) 1 = 2 = 3 5 Example 2. Effective use of clickers: Identifying misconceptions Assessing conceptual understanding The facts and the concept of maternal effects in C. elegans Using "peer instruction" Lecture presentation: a mixture of facts and concepts: oogenesis maternal mRNAs and proteins genetic consequences if they're essential in embryonic development The gonad and early cleavages in the embryo Clicker question: If a strict maternal-effect embryonic-lethal mutation is segregating in a mating population of C. elegans, the viability of an embryo will depend on A) its genotype. B) the genotype of its maternal parent. C) the genotype of its paternal parent. D) the genotypes of both parents. G 8.43 > 90% usually get the right answer 6 Maternal-effect lethal mutants P0 +/+ F1 m/+ Maternal-effect lethal mutants mutagenize Question: If m is a strict maternal-effect recessive mutation: P0 +/+ A) m/m embryo will live. F1 m/+ F2 +/+ live mutagenize A) m/m embryo will live. B) m/m embryo will die. F2 F2 embryo will +/+ live m/+ live m/m ? Question: If m is a strict maternal-effect recessive mutation: B) m/m embryo will die. F2 embryo will m/+ live m/m ? initial individual answers n=70 Maternal-effect lethal mutants What to do when you find out that half the class doesn’t understand? P0 +/+ F1 m/+ F2 +/+ live mutagenize Question: If m is a strict maternal-effect recessive mutation: A) m/m embryo will live. B) m/m embryo will die. Embryo will m/+ live m/m ? initial individual answers after group discussion n=70 7 What to do when you find out that half the class doesn’t understand? Don't forget to discuss what happened ! Peer instruction works! E. Mazur, Peer Instruction, A Users Manual, Prentice-Hall, 1996) 2. Effective use of clickers: Identifying misconceptions Assessing conceptual understanding Using "peer instruction" Teaching sequential information Making a KO mouse. First, engineer ES cells: go through the molecular biology In fact, you need two selectable markers • To select for a construct that has actually inserted into a specific location, have to use some tricks • Positive selection: neomycin resistance: construct contains neo resistance gene; any cell that has incorporated the construct (even randomly) will be resistant to neomycin • Negative selection: thymidine kinase (TK) from the herpes virus. If a cell contains the TK gene, it will be killed by the drug gancylovir YFG Neor YFG TK 8 Then go through the breeding steps Remember, the ES cells are from a black mouse The black coat color allele is dominant Then step through the entire sequence of steps with clicker questions to test comprehension You transfect ES cells from a black mouse (dominant marker) with this construct : Neor TK YFG YFG Following transfection, the culture will include a) cells that have lost the transgene without inserting it b) cells that have inserted the transgene by homologous recombination at the YFG locus c) cells that have inserted the transgene at another locus by end-joining to a nicked strand followed by DNA repair. 1) In non-selective growth medium (no neomycin or gancyclovir) the most frequent class of cells will be ___. 2) In medium containing gancyclovir alone, the most frequent class of cells will be ___. G 4.21 YFG Neor YFG TK a) cells that have lost the transgene without inserting it b) cells that have inserted the transgene by homologous recombination at the YFG locus c) cells that have inserted the transgene at another locus by end-joining to a nicked strand followed by DNA repair. 5. You inject embryonic stem cells that have undergone homologous recombination at the YFG locus into blastocysts obtained from a mated white mouse and reimplant them into pseudopregnant white females. When she gives birth to offspring (Po mice): 3) In medium containing neomycin alone, the most frequent class of cells will be ___ . a) all will be variegated (both black and white patches of coat color). b) a few may be white, but the majority will be variegated. c) some will be white, some will be variegated. 4) In medium containing neomycin and gancyclovir, the most frequent class will be ___. 9 6. You mate a variegated (chimeric) female mouse to a white male, and examine their offspring (F1) for coat color and the presence of the knocked out YFG. Which of the following statements is true? (Remember: the white mice are homozygous black –/black –; black coat color is dominant, and the gene is on a different chromosome from YFG). a) All of the black offspring are homozygous for the transgene (YFG-/YFG-) b) Some of the black offspring are homozygous for the transgene (YFG-/YFG-) 3. Some side benefits of clicker use Impromptu quizzes Attendance records - setting and keeping Obtaining demographic information Monitoring performance of individual students Getting honest answers to touchy questions c) All of the black offspring are heterozygous for the transgene (YFG-/YFG+) d) All of the black offspring are homozygous normal (YFG+/YFG+) e) Some of the black offspring are heterozygous for the transgene (YFG-/YFG+) How are you finding this workshop so far? A) Fascinating and useful B) Somewhat interesting. C) Boring. D) A waste of time. Benefits of clickers For you, the student: • Responses are anonymous • Instant comparison to your peers • You’re active and engaged ! For me, the instructor: • I know you’re there (later) • I can find out how you answered (later) • Students come to class • I know instantly what fraction of you didn’t understand ! 10 4. The down side: problems with clickers For those who have used clickers in teaching, how successful did you and your students find them in facilitating learning? A) Highly successful. B) Somewhat successful. C) Not much of an effect. D) They had a negative impact on the course. E) They were a waste of time and effort. Some students may have had bad experiences with clickers prior to your course Clickers? (asked at the start of a recent course) 4. The down side: problems with clickers Economics a) I love using clickers. Technical problems b) I like using clickers. Points for credit or participation, or both? c) I’m neutral about clickers. Testing memorization or note-taking is boring! d) I don’t like using clickers. Clicker discussions take time; e) I hate using clickers. how can I still "cover" everything? 11 Less is more . . . Students don't have to learn many of the facts we ask them to know; they can find them easily later when they need them. It's not all-or-nothing: even incremental change from lecturing toward active learning can result in significantly increased learning gains. Students can learn a lot more in your course than just what you tell them. We must put more of the responsibility for content learning on the students. http://webphysics.iupui.edu/jitt/jitt.html (Just Google JiTT) Just-in-Time Teaching puts more of the responsibility for content learning on the students. Instructor assigns pre-class work to be submitted online. Instructor can assess it in advance, determine the level of understanding, and plan use of class time accordingly. Students may object, but . . . They need to learn how to learn, to reason, to assimilate information for themselves, to critically evaluate the information they encounter, and to understand how science is done, much more than they need to know a lot of factual knowledge. More active learning is a step in the right direction. 12 Why clickers can fail to please 5. Writing good clicker questions (It's not trivial) Factual recall questions are neither fun nor particularly helpful. Good clicker questions: are "EnGauging" are conceptual See Beatty et al. article in your folder Bloom's Taxonomy of the Cognitive Domain (levels of understanding) 6. Evaluation: think critically about and defend a position 5. Synthesis: transform, combine ideas to create something new 4. Analysis: break down concepts into parts 3. Application: apply comprehension to unfamiliar situations 2. Comprehension: demonstrate understanding of ideas, concepts Bloom's Taxonomy of the Cognitive Domain 6. Evaluation: think critically about and defend a position Judge, Justify, Defend, Criticize, Evaluate 5. Synthesis: transform, combine ideas to create something new Develop, Create, Propose, Design, Invent 4. Analysis: break down concepts into parts Compare, Contrast, Distinguish 3. Application: apply comprehension to unfamiliar situations Apply, Use, Compute, Solve, Predict 2. Comprehension: demonstrate understanding of ideas, concepts Restate, Explain, Summarize, Interpret, Describe 1. Factual Knowledge: remember and recall factual information Define, List, State, Name, Cite 1. Factual Knowledge: remember and recall factual information Adapted from Allen, D. and Tanner, K., Cell Biol. Educ. 1: 63-67 (2002) 13 Bloom's Taxonomy of the Cognitive Domain Example: Questions from a virology course 2. Comprehension: demonstrate understanding of ideas, concepts Restate, Explain, Summarize, Interpret, Describe, Explain how the life cycle of a lytic animal virus proceeds. 1. Factual Knowledge: remember and recall factual information Define, List, State, Name, Cite Name the coat components of a typical lytic animal virus. From Allen, D. and Tanner, K., Cell Biol. Educ. 1: 63-67 (2002) Bloom's Taxonomy of the Cognitive Domain 6. Evaluation: think critically about and defend a position Judge, Justify, Defend, Criticize, Evaluate Would you argue that viruses are alive? Why or why not? 5. Synthesis: transform ideas into something new Develop, Create, Propose, Design, Invent Propose a way in which viruses could be used to treat a human disease. 4. Analysis: break down concepts into parts Compare, Contrast, Distinguish What distinguishes the replication processes of RNA and DNA viruses? 3. Application: apply comprehension to unfamiliar situations Apply, Use, Compute, Solve, Predict Based on your knowledge of viral life cycles, what effects would you predict anti-viral drugs might have on viruses? From Allen, D. and Tanner, K., Cell Biol. Educ. 1: 63-67 (2002) Bloom's Taxonomy of the Cognitive Domain 6. Evaluation: think critically about and defend a position 5. Synthesis: transform, combine ideas to create something new 4. Analysis: break down concepts into parts 3. Application: apply comprehension to unfamiliar situations 2. Comprehension: demonstrate understanding of ideas, concepts Most questions on biology exams! 1. Factual Knowledge: remember and recall factual information The 5-minute university Guido Sarducci, from Saturday Nite Live, ~1982 14 Why clickers can fail to please Factual recall questions are neither fun nor particularly helpful. Good clicker questions: are "EnGauging" are conceptual include plausible distractors based on common misconceptions can't be easily "gamed" See Beatty et al. article in your folder Is this question testing conceptual knowledge? Multiple choice questions must be validated! A heritable disease that primarily affects women and not men is most likely caused by: a) a mutation in a gene on the X chromosome. b) a mutation in a gene on a non-sex chromosome (autosome). c) Without additional information, either answer (a) or (b) is possible. Answer: c Is this question testing conceptual knowledge? Multiple choice questions must be validated! A heritable disease that primarily affects women and not men is most likely caused by: a) a mutation in a gene on the X chromosome. b) a mutation in a gene on a non-sex chromosome (autosome). c) Without additional information, either answer (a) or (b) is possible. Answer: c B- : "When I see 'most likely' it has to be one of the answers that is listed." [I.e. either a) or b)] C- : "My test taking experience tells me not to answer c), I should just pick one or the other, so I will go with a)." 6. Workshop exercise: Try writing your own clicker questions A : I would have only answered c) at the beginning of the class because I didn’t know the right answer… 15 Writing your own clicker questions • Form groups of 3-5, • Agree on one or two concepts you know students have difficulty with. • Write one or two multiple choice clicker questions to assess student if possible with colleagues who teach the same area of biology. understanding of this concept, with distractors based on your knowledge of common misconceptions, following Beatty's suggestions. • Try to write questions that assess "higher" Bloom's levels of conceptual understanding, not just factual recall. • Pass questions in to me (or email them?: [email protected]). I'll choose a few and put them up on the screen so we can try them out and then discuss them. Following are questions from workshop participants Which of the following is least likely to result in change in phenotype? a. Insertion 10 nucleotides in the TATA box b. Insertion of a G nucleotide in Exon 2. c. D e letion of 37 nucleotides in the center of Intron 1 d. Insertion of AUG in the 5’UTR Diagram of typical gene from Gilbert's development text, would not transfer from PC to Mac. soma Motor neuron electrode If a neuron is stimulated by depolarization half-way along the length of the axon, which way will an action potential travel? terminal Muscle A) Right toward terminal B) Left toward soma C) Both directions D) You can't generate an action potential in this situation E) None of the above. Two individuals in a 4-person pedigree show a particular trait. Which pair of affected individuals (if any) would rule out an X-linked dominant mode of inheritance? A) Mom and daughter B) Mom and son C) Dad and daughter D) Dad and son E) None of the above 16 Taxol stabilizes microtubules, preventing their depolymerization. If taxol were added to a synchronized population of cells that had just competed S phase, what would happen? A) Cells will not be able to assemble a metaphase spindle. B) Cells will be able to assemble a spindle, but won't be able to separate their chromosomes. Increasing the substrate concentration for an enzyme-catalyzed reaction has effects on A) Vmax sometimes B) Vo sometimes C) Km sometimes D) Keq sometimes C) Cells will be able to separate their chromosomes but won't be able to execute cytokinesis. Which of these diets causes weight loss by forcing the metabolism of Krebs cycle intermediates? A) Raw food diet. A single chromosome from one of your somatic cells is likely to be B) Vegan diet (no meat) A) Identical to a chromosome from a somatic cell in your mother or father. C) Atkins diet (no carbohydrates) B) Derived from both your parents. D) Caloric restriction (nutritious diet but low calories). C) Derived from both your maternal or paternal grandparents. D) Derived from both your maternal and paternal grandmothers or grandmothers. 17 You are interested in amplifying a section of DNA from a template containing the following sequence: 5'A A T T C G G T T G A T T C A A A T T T A T G G G C C T A C G A T 3’ Which of the following primer pairs would amplify a product from this template? (note that the convention is that, given no other indication, nucleotide sequences are written 5’ to 3’) A) B) C) D) E) TTAA AATT AATT AATT TTAA and and and and and TAGC CGAT TAGC ATCG ATCG If you change a valine to a phenyalanine in the interior of a protein, what would be the most likely effect on the protein’s structure? A) It will stabilize the protein because of the additional bonds formed by phenylalanine. B) It will disrupt the structure because of steric effects. C) It will have no effect because they are both nonpolar. D) It will disrupt the protein because valine is polar and phenylalanine is nonpolar. E) It will disrupt the protein because phenylalanine is polar and valine is nonpolar. If you mate a homozygous wild type fruit fly with a fly that is homozygous for recessive mutations that cause brown eyes and shriveled wings, then cross their F1 offspring, you would expect a ratio of 9 wild type: 3 red eyes and shriveled wings: 3 brown eyes and normal wings: 1 brown eyes and shriveled wings. The most likely explanation for this result is: A) Both mutants cause heterozygous lethality. B) One gene is X-chromosome linked C) The two genes are linked. D) There was recombination between the two genes. 18
© Copyright 2026