HOW TO INSTALL WINDOWS XP.
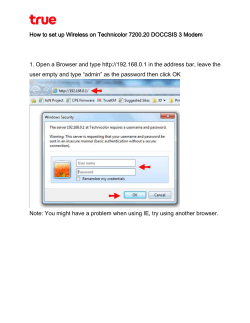
1. HOW TO INSTALL WINDOWS XP. This procedure demonstrates how to install Windows XP Professional. The procedure to install Windows XP home edition is very similar to the professional edition. Since Windows XP Pro is more advanced operating system, it will be used to demonstrate the installation procedure. The best way install Windows XP is to do a clean install. It is not difficult to perform a clean installation. Before you perform the installation I recommend that you check Windows XP Compatibility List to ensure that your hardware is supported by XP. If your hardware is not on the compatibility list you can check your hardware manufactures website to download the drivers for Windows XP. Save all the necessary drivers onto floppy disks or CD before you start the installation. All versions of Windows XP CD are bootable. In order to boot from CD/DVD-ROM you need to set the boot sequence. Look for the boot sequence under your BIOS setup and make sure that the first boot device is set to CD/DVD-ROM. You can then perform the following steps to install Windows XP: Step 1 - Start your PC and place your Windows XP CD in your CD/DVD-ROM drive. Your PC should automatically detect the CD and you will get a message saying "Press any key to boot from CD". Soon as computer starts booting from the CD your will get the following screen: Step 2 - At this stage it will ask you to press F6 if you want to install a third party Raid or SCSI driver. If you are using a an IDE Hard Drive then you do not need to press F6. If you are using a SCSI or SATA Hard drive then you must press F6 otherwise Windows will not detect your Hard Drive during the installation. Please make sure you have the Raid drivers on a floppy disk. Normally the drivers are supplied on a CD which you can copy to a floppy disk ready to be installed. If you are not sure how to do this then please read your motherboard manuals for more information. Step 3 - Press S to specify that you want to install additional device. Step 4 - You will be asked to insert the floppy disk with the Raid or SCSI drivers. Press enter after you have inserted the disk. Step 5 - You will see a list of Raid drivers for your HDD. Select the correct driver for your device and press enter. Step 6 - You will then get a Windows XP Professional Setup screen. You have the option to do a new Windows install, Repair previous install or quit. Since we are doing a new install we just press Enter to continue. Step 7 - You will be presented with the End User Licensing Agreement. Press F8 to accept and continue Step 8 - This step is very important. Here we will create the partition where Windows will be installed. If you have a brand new unformatted drive you will get a screen similar to below. In our case the drive size is 8190MB. We can choose to install Windows in this drive without creating a partition, hence use the entire size of the drive. If you wish to do this you can just press enter and Windows will automatically partition and format the drive as one large drive. However for this demonstration I will create two partitions. The first partition will be 6000MB (C: drive) and second partition would be 2180MB (E: drive). By creating two partitions we can have one which stores Windows and Applications and the other which stores our data. So in the future if anything goes wrong with our Windows install such as virus or spyware we can reinstall Windows on C: drive and our data on E: drive will not be touched. Please note you can choose whatever size partition your like. For example if you have 500GB hard drive you can have two partitions of 250GB each. Press C to create a partition. Step 8 - Windows will show the total size of the hard drive and ask you how much you want to allocate for the partition you are about to create. I will choose 6000MB. You will then get the screen below. Notice it shows C: Partition 1 followed by the size 6000 MB. This indicates the partition has been created. We still have an unpartitioned space of 2189MB. Next highlight the unpartitioned space by pressing down the arrow key. Then press C to create another partition. You will see the total space available for the new partition. Just choose all the space left over, in our case 2180MB. Step 9 - Now you will see both partition listed. Partition 1 (C: Drive) 6000MB and Partition 2 (E: Drive) 2180MB. You will also have 8MB of unpartitioned space. Don't worry about that. Just leave it how its is. Windows normally has some unpartitioned space. You might wonder what happened to D: drive. Windows has automatically allocated D: drive to CD/DVD-ROM. Select Partition 1 (C: Drive) and press Enter. Step 10 - Choose format the partition using NTFS file system. This is the recommended file system. If the hard drive has been formatted before then you can choose quick NTFS format. We chose NTFS because it offers many security features, supports larger drive size, and bigger size files. Windows will now start formatting drive C: and start copying setup files as shown on the two images below: Step 11 - After the setup has completed copying the files the computer will restart. Leave the XP CD in the drive but this time DO NOT press any key when the message "Press any key to boot from CD" is displayed. In few seconds setup will continue. Windows XP Setup wizard will guide you through the setup process of gathering information about your computer. Step 12 - Choose your region and language. Step 13 - Type in your name and organization. Step 14. Enter your product key. Step 15 - Name the computer, and enter an Administrator password. Don't forget to write down your Administrator password. Step 16 - Enter the correct date, time and choose your time zone. Step 17 - For the network setting choose typical and press next. Step 18 - Choose workgroup or domain name. If you are not a member of a domain then leave the default settings and press next. Windows will restart again and adjust the display. Step 19 - Finally Windows will start and present you with a Welcome screen. Click next to continue. Step 20 - Choose 'help protect my PC by turning on automatic updates now' and press next. Step 21 - Will this computer connect to the internet directly, or through a network? If you are connected to a router or LAN then choose: 'Yes, this computer will connect through a local area network or home network'. If you have dial up modem choose: 'No, this computer will connect directly to the internet'. Then click Next. Step 22 - Ready to activate Windows? Choose yes if you wish to active Windows over the internet now. Choose no if you want to activate Windows at a later stage. Step 23 - Add users that will sign on to this computer and click next. Step 24 - You will get a Thank you screen to confirm setup is complete. Click finish. Step 25. Log in, to your PC for the first time. Step 26 - You now need to check the device manager to confirm that all the drivers has been loaded or if there are any conflicts. From the start menu select Start -> Settings -> Control Panel. Click on the System icon and then from the System Properties window select the Hardware tab, then click on Device Manager. If there are any yellow exclamation mark "!" next to any of the listed device, it means that no drivers or incorrect drivers has been loaded for that device. In our case we have a Video Controller (VGA card) which has no drivers installed. Your hardware should come with manufacturer supplied drivers. You need to install these drivers using the automatic setup program provided by the manufacturer or you need to manually install these drivers. If you do not have the drivers, check the manufacturers website to download them. To install a driver manually use the following procedure: (a) From the device manager double click on the device containing the exclamation mark. (b) This would open a device properties window. (c) Click on the Driver tab. (d) Click Update Driver button. The Wizard for updating device driver pops up as shown below: You now get two options. The first option provides an automatic search for the required driver. The second option allows you to specify the location of the driver. If you don't know the locations of the driver choose the automatic search which would find the required driver from the manufacturer supplied CD or Floppy disk. Windows would install the required driver and may ask you to restart the system for the changes to take effect. Use this procedure to install drivers for all the devices that contain an exclamation mark. Windows is completely setup when there are no more exclamation marks in the device manager. After logon, take a few minutes to validate your copy of Windows. Validation gives you accessto hundreds of free downloads from the Microsoft Download Center. To learn about the new features Windows XP provides, click the Start button, click All Programs, click Accessories, and then click Tour Windows XP. 2.TROUBLESHOOTING WINDOWS 7 WIRELESS NETWORKING PROBLEMS With that said, let’s get started by checking the basics. You should begin by closing any applications or other windows that you have open, as we don’t want anything to inadvertently interfere with the diagnostic process. After doing so, open the Control Panel and double click on the Network and Internet icon. Next, open the Network and Sharing Center and click on the Change Adapter settings link. At this point, you should see a window that lists all of the network adapters that are installed in your PC. In most cases, there will be a wired, and a wireless adapter as shown in Figure A. Figure A: You should see a listing for your wireless network adapter Ultimately, whether or not you see a listing for the wired network adapter is irrelevant. It is the wireless adapter that really counts. If you don’t see your wireless network adapter listed, then this is the source of your connectivity problems. There are several potential underlying causes for an unlisted wireless network adapter. The most common causes involve an incorrect or missing device driver. The listing for the network adapter might also be missing if the network card is not enabled at the hardware level. If you are using a PC card, PCI card, or a USB based Wi-Fi card, then solving the problem might be as simple as making sure that your network adapter is plugged in tightly. If you are using a laptop with an integrated wireless NIC, then you should take a moment to make sure that the NIC has been turned on. I just want to start with the basics before I move on to some of the more advanced troubleshooting techniques. Besides, I myself have fallen victim to a disabled wireless NIC. One night, I was doing some work and needed to switch to a spare battery. I hit a switch on the bottom of the laptop that I thought would eject my battery. Imagine my surprise when I realized that it was really a switch to enable and disable the network adapter. Almost all laptops have such a switch (or a button). The FAA does not allow Wi-Fi connections to be used on airplanes, so laptop manufacturers provide a switch that can be used to disable the adapter. However, every manufacturer puts the switch in a different place. I presently own five different laptops, and while they all have mechanisms for disabling the Wi-Fi connection, no two of the machines do it in the same way. Just as a wireless NIC can be disabled through a switch or a button, it is also possible to enable or disable it through Windows. Keep in mind though, that in order for a wireless NIC to function, it must be enabled at both the hardware and at the operating system level. With that said, watch what happens in Figure B when I right click on my wireless network adapter. As you can see in the figure, the shortcut menu contains an option to disable the adapter. When I disable the adapter, the wireless connection’s icon changes to reflect the fact that it has been disabled, as shown in Figure C. You can re-enable the connection by right clicking on it, and choosing the Enable option from the shortcut menu. Figure B: You can disable a wireless connection by right clicking on it, and choosing the Disable option Figure C: The connection’s icon changes to reflect the fact that it has been disabled. 3. EVENT VIEWER FOR WINDOWS XP Application log The application log contains events logged by programs. For example, a database program may record a file error in the application log. Events that are written to the application log are determined by the developers of the software program. Warning An event that is not necessarily significant, however, may indicate the possible occurrence of a future problem. For example, a Warning message is logged when disk space starts to run low. Error An event that describes a significant problem, such as the failure of a critical task. Error events may involve data loss or loss of functionality. For example, an Error event is logged if a service fails to load during startup. 4.HOW TO FAST THE SPEED OF COMPUTER WINDOWS XP In today’s world the most common problem related with PC as everybody is after speed only in order to make it up to your expected speed there are some easy options available with the help of disk clean up which will delete the unwanted or unused files from the computer and fasten the speed of your PC. After clicking OK Disc Cleanup will start and take few minutes to complete the whole process as a result of that system will run smoothly afterwards 5. HOW TO CREATE USER ACCOUNT WINDOWS XP 1. To open User Accounts, click the Start button , click Control Panel, click User Accounts and Family Safety, and then click User Accounts. 2. Click Manage another account. If you're prompted for an administrator password or confirmation, type the password or provide confirmation. 3. Click Create a new account. 4. Type the name you want to give the user account, click an account type, and then click Create Account. In order to create User Account you need to follow these steps. 6.HOW TO OPTIMISE THE COMPUTER PERFORMANCE 6.1 STEP 1 – JUMP TO WINDOWS 7 Both Windows XP and Windows Vista come from an era in which SSDs were not widespread. They do not support the TRIM command which is important to boost systems’ performance and life spans. TRIM allows Windows 7 to tell the SSD which files should be deleted and completely erases the corresponding data blocks. The moment a file is deleted from an SSD, Windows 7 not only updates the file system (as it normally would) but also informs the SSD which data blocks can be removed. These blocks are marked as free so that Windows and third-party programs can use them. On a mechanical hard disk, this happens automatically, but on SSDs (without support for the TRIM command), data blocks need to be completely erased before they can be used again—this causes a loss in performance. Windows 7 (and it’s bigger server brother “Windows Server 2008 R2″) are the only Microsoft operating systems that support the essential TRIM command. 6.2 STEP 2 – MAKE SURE THAT TRIM IS ENABLED While Windows 7 officially supports TRIM, there have been cases in which it’s not enabled (or maybe not supported). To see if TRIM is enabled, open up a command prompt by clicking on the Start orb and typing “cmd” into the search bar. Right-click on the first result (“cmd”) and click “Run as administrator”. Next, type in the command “Fsutil behavior query disable delete notify”. Hit Enter. If this returns the result “= 0″, you’re good to go! Otherwise, TRIM isn’t supported and needs to be enabled. Try entering the command “fsutil behavior set Disable Delete Notify 0″. If that doesn’t help, a firmware upgrade might be necessary to enable TRIM. 6.3 STEP 3 – DO NOT DEFRAG YOUR SSD Defragmentation is one of the more useful steps to keep your hard disk at its best. However, with SSD, defragmentation is not necessary. Read operations are incredibly fast throughout the entire disk. Thanks to the flash-based nature of SSDs, it simply doesn’t matter if data is stored in a noncontiguous manner. What most users don’t know is that defragmentation can actually be harmful to the SSD as the thousands of disk operations that occur during defrag reduce the life span of solid state cells. By default, Windows 7 should automatically disable its scheduled defragmentation—but unfortunately, I’ve seen too many cases where the built-in Disk Defragmenter was still enabled, despite the fact that an SSD was built-in! Users should make sure that it’s disabled. Here’s how: Go to the Start menu and click on “All Programs”, “Accessories”, “System Tools” and “Disk Defragmenter”. This can be even easier regulated with the new Tune Up version Tune Up Utilities 2012. It recognizes the SSD drive and excludes it automatically from defragmentation. Go to “Turn off schedule” and make sure that Windows does not defragment your SSD drive (probably drive C :). 7.FASTEN YOUR SPEED REMOVING TEMPORARY In order to run the computer smoothly with accurate speed there is an option in the search bar where we need to write %temp% and we will receive so many temporary files in front of us .You need to select all files and delete it with the help of delete option. In order to fasten your computer please delete all the files which has been saved on your Computer as a temporary files .By doing this your PC will start working fast with a normal speed. 8.FASTEN YOUR SPEED BY DISABLING THE MSCONFIG MS Config is a powerful tool that allows you to enable/disable the programs that start when Windows boots up. 9.HOW TO FIND HIDDEN VIRUS OR MALACIOUS JUNK FILES In order to find hidden virus we need to follow steps given below with the help of screen shots given. Click Apply and OK. 10.HOW TO INCREASE VIRTUAL MEMORY In order to increase the Virtual Memory or to know about the real status of the memory we need to follow steps mentioned through screen shots: You need to disable automatically and need to double click on paging the size for each drive. Double click on set option and then increase the size in the desired drive. 11.HOW TO ADD PRINTER This is the way you could be able to add your Printer and will run smoothly. THANKS MICROSOFTSUPPORTUSA
© Copyright 2026





![[WCR-300S] How to Change the Wireless Network Name(SSID)](http://cdn1.abcdocz.com/store/data/000232989_1-c13ffbaf9a88e423608ef46454e68925-250x500.png)