3/24/2014 What is your CDI IQ?
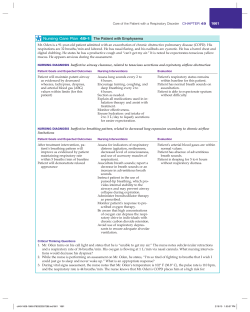
3/24/2014 What is your CDI IQ? Clinical Documentation Improvement Strategies for LTC Leah Killian-Smith, BA, NHA, RHIA ©Pathway Health 2013 Objectives • Be able to educate your staff on concepts for documenting accurately • Understand the differences in charting for ICD-10-CM • Recognize documentation requirements that will reduce risk of audits • Gain skills to maintain regulatory compliance with charting in ICD-10-CM ©Pathway Health 2013 1 3/24/2014 Documentation is important Critical for patient care Legal document Audit purposes Validates care provided Decreases chance of claim denial Compliance with CMS, state, and local rules & regulations • Impacts coding, billing, & reimbursement • • • • • • ©Pathway Health 2013 4 What Has Changed? • ↑ Clinical Needs of patients • ↑ Scrutiny from regulators / survey outcomes • Implementation of documentation based payment systems • ↑ Litigation & Legal Challenges • ↑ Audits (ZIPC, UPIC, RAC) ©Pathway Health 2013 5 CMS Rule • F514 (2 CFR 483.75(l),Clinical Records – Determine whether the clinical records: – Accurately and completely document the resident's status, the care and – services provided in accordance with current professional standards and practices; and – Provide a basis for determining and managing the resident's progress – including response to treatment, change in condition, and changes in treatment ©Pathway Health 2013 6 2 3/24/2014 Similarities • Symbols, Code First, Use additional code • Includes & Excludes • Code to highest level of specificity • Adherence to HIPAA & Official Guidelines • Non-specific codes still available • Inconsistent, missing, or conflicting documentation must be resolved by provider ©Pathway Health 2013 7 Similarities • Use of Coding Books or E-Encoder • Tabular List similar to ICD-9 with some exceptions • Main Terms – Indented Sub-terms • Alphabetical Index of external causes • Table of Neoplasms • Table of Drugs & Chemicals • Conventions, Abbreviations, Punctuation 8 ©Pathway Health 2013 Structure of Codes □□□•□□□ □ Category Etiology, Anatomical Site, Severity Extension ©Pathway Health 2013 3 3/24/2014 Examples of Structure • S52 – Fx of Forearm • S52.5 – Fx lower end of radius • S52.52 – Torus Fx of lower end of radius • S52.521 – Torus Fx of lower end of R radius • S52.521D – Torus Fx of lower end of R radius, subsequent care ©Pathway Health 2013 Differences • More Codes! 17,000 versus 68,000 • More codes in the different categories • Diabetes – 59 to 200+ • Pressure Ulcers – 9 to 125 • Pathologic Fractures – 8 to 150 Codes are longer now (3-7 versus 3-5) All codes begin with a letter (except “u”) Code extensions are available for injuries & external causes Combo codes are available for diagnoses & symptoms ©Pathway Health 2013 11 Differences • Increased precision with diagnoses • Full diagnostic titles for each code • More flexibility in incorporating advances in medicine & technology • Uses more current & up to date med terms • Laterality Added (left and right, both) ©Pathway Health 2013 12 4 3/24/2014 Specificity in Documentation Condition ICD‐9 ICD‐10 • Essential HTN • 401.9 – Essential HTN, unspecified • I10 – Essential primary HTN • Asthma with acute exacerbation • 493.92 – Asthma unspecified with acute exacerbation • J45.21 – mild intermittent asthma with acute exacerbation < 2 weeks or J45.31: >2 weeks or J45.41: Daily ©Pathway Health 2013 Final Rule • Modifications to HIPAA Electronic Health Transaction Standards – http://edocket.access.gpo.gov/2009/pdf/E9740.pdf • Modifications to Medical Data Code Set – http://edocket/access.gpo.gov/2009/pdf/E9.743.pdf • Final Compliance Date – www.gpo.gov/fdsys/pkg/FR-2012-0905/pdf/2012-21238.pdf ©Pathway Health 2013 Official Guidance • Official Coding Guidelines – http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/icd/icd10cm _guidelines_2014.pdf • Conventions in the Coding Manual – Take precedence if conflict in instructions • Chapter Specific Guidelines – Some chapters have specific rules – Example: Diabetes ©Pathway Health 2013 15 5 3/24/2014 Complete Record • Accurate & functional representation of the actual experience of the individual in the facility • Enough information to show the facility knows the status of the patient • Plan of care identified to meet the resident’s identified conditions • Effects of the care provided • Picture of the resident and response to treatment ©Pathway Health 2013 16 Complete Record cont…… • Main purpose is continuity of care • Other important reasons – Clinical – Administrative – Financial – Regulatory – Legal ©Pathway Health 2013 17 Duplication / Redundant Info • Duplication of information in the record – Inefficient – Creates conflicting / contraindications that can lead to errors – Diminishes the credibility of the record • Answer – Create a list of documentation elements that you currently collect on each for and by each discipline ©Pathway Health 2013 18 6 3/24/2014 Admission Record / Face Sheet • Some states have certain regulations for field specificity • Demographics • Contact information • Financial & insurance information • Professionals involved in patient’s care • Diagnoses ©Pathway Health 2013 19 Assessments • Data collection • Evaluation • Conclusion – come to a decision as to the clinical conclusions based on the data collected • Conclusion – interpreting and documenting conclusion based on data collected • Plan / recommendations / intervention ©Pathway Health 2013 20 RAI / MDS • The documentation supports the coding of the MDS in the assessment reference period • The CAAs should be used as a foundation to create the plan of care • Section I of the MDS – Coding diagnoses – Triggers 3 CAAs (visual function, psychosocial well being, dehydration / fluid maintenance) – Can affect our payment ©Pathway Health 2013 21 7 3/24/2014 MDS Section I Diagnoses Pneumonia Septicemia Diabetes Multiple Sclerosis Parkinson’s Aphasia Cerebral Palsy Hemiplegia Asthma COPD Hemiparesis Quadriplegia Respiratory Failure ©Pathway Health 2013 22 Payment Categories Affected Special Care High Special Care Low Clinically Complex ©Pathway Health 2013 23 Charting Content Picture of the resident Resident’s perception of progress Observations & assessment of staff Communication with resident, families, providers • Response to interventions / treatment • Change toward achieving goals • • • • ©Pathway Health 2013 24 8 3/24/2014 Determining Principle Dx • Section II of Official Coding Guidelines – The condition established after study to be chiefly responsible for occasioning the admission of the patient to the hospital for care – The application of the UHDDS definitions has been expanded to include all nonoutpatient settings including LTC ©Pathway Health 2013 25 Determining Secondary Dx • Section III of the Official Coding Guidelines – Additional conditions that affect patient care in terms of: • • • • • • Clinical evaluation Therapeutic treatment Diagnostic procedures Extended length of hospital stay Increased nursing care Increased nursing monitoring ©Pathway Health 2013 26 Determining Secondary Dx • Section I of the MDS – Intent – To code diseases that have a relationship to the resident’s current functional status, cognitive status, mood and behavior status, medical treatments, nursing monitoring and risk of death. To generate an updated, accurate picture of the resident’s health status ©Pathway Health 2013 27 9 3/24/2014 Data in CDI 1. Data the organization produces – – – – – Review LTC data by Specialty diagnosis Medicare RUG Low case mix High risk 2. Data others produce about the organization ©Pathway Health 2013 28 Criteria to screen data • Normative data (comparing ourselves to others) Quality Measures • Regulatory guidance (F Tags and State Licensure Rules and Regulations) • Organizational Benchmarks (Our QA or QAPI initiatives) ©Pathway Health 2013 29 Transfer data • How is our information when we send a patient to the hospital or when we call a physician with a new or exacerbated problem? • What tools do we use? – Standardized forms – Interact tools – Transfer forms ©Pathway Health 2013 30 10 3/24/2014 Top Diagnoses in LTC • • • • • • • • CVA / Stroke / CVD Mental disorders Respiratory diseases Neoplasms Chronic kidney disease / Diabetes Orthopedic aftercare CAD / CHF / HTN Arthritis ©Pathway Health 2013 31 Medicare Charting • Worksheets are helpful • Reduce risk of denials and audits • Prove the resident needed & received skilled services on a daily basis – Nursing or therapy • Nursing should have documentation in addition to therapy to address how skills learned in therapy area applied on the nursing unit. ©Pathway Health 2013 32 Physical & Occupational Therapy • For ADLs (Bed Mobility, Eating, Transferring, Toilet Use) • How does the resident perform activities of daily living? • Even though therapy is covering for a specific diagnosis, nursing still needs to document on skilled needs ©Pathway Health 2013 33 11 3/24/2014 Speech Therapy • How does the resident communicate and make needs known? • Skilled nursing interventions used to compensate for speech deficits • Ability to swallow foods and skilled nursing interventions used to compensate for impaired swallowing abilities ©Pathway Health 2013 34 Diabetes • Document insulin injections daily • Order changes and physician visits • Skilled nursing interventions used to teach resident self administration • Outcome of resident teaching • Signs and symptoms associated with fluctuating blood sugars ©Pathway Health 2013 35 Respiratory Diseases • • • • • Skilled tracheostomy care Sreath sounds over all lung aspects Respiration rate, rhythm, and quality Effectiveness of respiratory treatments Resident comfort level as it relates to respiratory status ©Pathway Health 2013 36 12 3/24/2014 Respiratory Diseases • Changes in level of care, anxiety, or mental status changes • Each incident of suctioning or any other invasive technique • Overall condition as it relates to his/her respiratory status and any skilled nursing used to aid in comfort and improve overall status ©Pathway Health 2013 37 IM or IV Medications • Nature of medication used (indication for use) • Nursing skills and observations used in administration of the medication • Effectiveness of medication and any observed side effects • How resident tolerated therapy (infiltration, fluid volume overload, pain, phlebitis, etc) ©Pathway Health 2013 38 Gastrostomy • Amount of fluids delivered • Ability to communicate and make needs known to staff • How resident tolerates tube feeding, any adverse effects to tube feeding – Diarrhea – Abdominal distension – Cardiac symptoms – Abnormal lung sounds ©Pathway Health 2013 39 13 3/24/2014 Gastrostomy • Type of ostomy care provided around the tube site • Condition of tube site • Clinical necessity for G-Tube, J-Tube, NG-Tube ©Pathway Health 2013 40 Surgical Wounds • Location and nature of wound • Pain associated with wound and interventions for pain management • Nursing interventions and observations of healing process • Drainage, areas of erythema, warmth • Response to any treatments • Weekly at least! ©Pathway Health 2013 41 GU Complications • Nature of resident condition that warrants use of straight catheterization technique • Use of sterile technique during catheter administration • Resident teaching due to catheter use • Clinical conditions present that require skilled nursing observation such as frequency, dysuria, indicators of UTI, etc ©Pathway Health 2013 42 14 3/24/2014 Respiratory Therapy Skilled tracheostomy care provided Breath sounds & overall lung aspects Respiratory rate, rhythm, quality Effectiveness of respiratory treatments Resident comfort level as it relates to respiratory status • Changes in level of consciousness, anxiety, or other mental status changes • • • • • ©Pathway Health 2013 43 Respiratory Status • Each incident of suctioning and any other invasive techniques • Overall condition as it relates to respiratory status and any skilled nursing interventions used to aid in comfort and improve overall status ©Pathway Health 2013 44 Pressure Ulcers • Condition of wound(s) • Response to current treatment • Nursing interventions to prevent further ulcer development • Consumption amounts of meals and fluids, BMI • Skin condition including poor skin turgor, bruises, rashes, cyanosis, redness, edema, other abnormality ©Pathway Health 2013 45 15 3/24/2014 Pressure Ulcers • Interventions implemented due to abnormal lab values (low H&H, low serum, albumin, low Fe+ levels, etc) • Dietary interventions implemented such as increased vitamin C and protein foods offered • Weekly documentation • Look to change treatment if no improvement in 14 days - NPUAP ©Pathway Health 2013 46 Nursing Rehabilitation • Outcome of insulin injection instruction • Outcome of colostomy/ileostomy training • Outcome of catheter care training • Outcome of self wound care training • Outcome of medication self administration training • Outcome of stump care training • Outcome of bowel & bladder training ©Pathway Health 2013 47 Medical Complexity • Cerebral Palsy, Multiple Sclerosis, Quadriplegia • Fever and (vomiting, weight loss, tube feeding, pneumonia, dehydration) • Comatose • Septicemia • Burns • End Stage Disease • Dehydration ©Pathway Health 2013 48 16 3/24/2014 Medical Complexity • Hemiplegia / Paresis AND ADL dependence • Internal Bleeding • Chemotherapy • Dialysis • Transfusions • Oxygen therapy • Radiation therapy • Neurologic ©Pathway Health 2013 49 Medical Complexity • • • • • • • • GI CV General Infection on Foot Unstable neurological status Unstable GI status Unstable cardiovascular status Unstable condition requiring skilled medication administration ©Pathway Health 2013 50 Cognition & Behaviors • • • • Cognitive Loss Signs of Depression Behavior Symptoms Present Hallucinations or Delusions Present ©Pathway Health 2013 51 17 3/24/2014 Documentation Audits • Concurrent – Most helpful to ensure accurate clinical information and proper reimbursement • Retrospective – Most helpful for quality assurance activities ©Pathway Health 2013 52 The IDT • • • • • • • Medical Director Business Office HIM Compliance / Medicare / MDS Therapy Nursing Leadership Ancillary Departments ©Pathway Health 2013 53 IDT Documentation Functions • Report quality issues to QA Committee • Promote CDI for quality & reimbursement • Provide ongoing education • Review case mix ongoing • Participates in claim check review • Creates & updates documentation tools • Audits for complete & accurate documentation ©Pathway Health 2013 54 18 3/24/2014 Training on Documentation • Formal education – Assess the staff members current level of formal training such as: • • • • • • Degree or certification Medical Terminology Anatomy & Physiology Pathophysiology Pharmacology Psychology / Abnormal Psychology ©Pathway Health 2013 55 Training on Documentation • Determine what training your staff members have had to date: – Class room trainig by staff development – Online learning – (Readilearning, webinars, Silver Chair, etc) – Orientation (class room and hands on with another employee that does the same job or similar) ©Pathway Health 2013 56 Training on Documentation • Determine what training is needed for your staff members – By diagnosis – By specialty program (CCU) – By identifying any deficient practice or quality issues – By identifying reimbursement issues ©Pathway Health 2013 57 19 3/24/2014 References • AHIMA – American Health Information Management Association • NPUAP – National Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel • CMS – Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services • CDC – Centers for Disease Control • CDI – Clinical Documentation Improvement Manual - AHIMA ©Pathway Health 2013 58 Thank you for your time! Leah Killian‐Smith, BA, NHA, RHIA AHIMA Approved ICD‐10‐CM/PCS Trainer www.pathwayhealth.com 651‐407‐8699 ©Pathway Health 2013 59 20
© Copyright 2026