Sample Risk Ranking Tools Qualitative measure of consequence
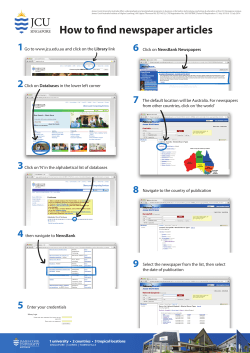
BSBOHS403B IDENTIFY HAZARDS AND ASSESS OHS RISKS – Element 4.4 Prioritise risk Sample Risk Ranking Tools 1 AS/NZS4360:1999 Risk Management (Appendix) (Standards Australia, 1999) Qualitative measure of consequence Level Descriptor Example detail description Description should be modified to suit the needs of the organisation and activity 1 2 Insignificant Minor 3 Moderate 4 Major 5 Catastrophic No injuries, low financial loss First aid treatment, on-site release immediately contained, medium financial loss Medical treatment required, on-site release contained with outside assistance, high financial loss Extensive injuries, loss of production capability, off site release with no detrimental effects, major financial loss Death, toxic release off site with detrimental effect, huge financial loss Qualitative measures of likelihood Level A B C D E Descriptor Almost certain Likely Possible Unlikely Rare Description Is expected to occur in most circumstances Will probably occur in most circumstances Might occur at some time Could occur at some time May occur only in exceptional circumstances Qualitative risk analysis matrix – level of risk Likelihood Insig’ant 1 A B C D E Almost certain Likely Moderate Unlikely Rare H M L L L Minor 2 H H M L L Consequence Moderate Major 3 4 E E H E H E M H M H Catastrophic 5 E E E E H Number of categories should reflect the needs of the risk being assessed Where: E: H: M: L: extreme risk; immediate action required high risk; senior management attention needed moderate risk; management responsibility must be specified low risk; manage by routine procedures. Refer also to Section 6 of the Risk management handbook. (Standards Australia, 2004) PAGE 1 SAFETYLINE INSTITUTE FEBRUARY 2012 BSBOHS403B IDENTIFY HAZARDS AND ASSESS OHS RISKS – Element 4.4 Prioritise risk 2 Nomogram (Kinney & Wiruth, 1976) Table 1 T Table 2 To use the nomogram: 1. identify the estimated value for the variables likelihood and exposure draw a straight line through the estimated value of each variable and extend the line to the tie line 2. estimate the possible consequences 3. draw a straight line from the point on the tie line through the estimated possible consequences and extend the line to the risk score Then if required: 4. transfer the resultant risk score to Table 2 5. estimate the risk reduction 6. draw a straight line to join the values for risk score and reduction and extend the line through the tie line 7. estimate the costs for correction 8. draw a line from the point on the tie line through the estimated costs for correction to the justification factor PAGE 2 SAFETYLINE INSTITUTE FEBRUARY 2012 BSBOHS403B IDENTIFY HAZARDS AND ASSESS OHS RISKS – Element 4.4 Prioritise risk References Kinney, G. F., & Wiruth, A. D. (1976). Practical Risk Analysis for Safety Management. China Lake, CA: NWC Technical Publication 5865, Naval Weapons Centre. Standards Australia. (1999). AS/NZS 4360:1999 Risk Management: Standards Association of Australia. Standards Australia. (2004). HB 436:2004 Risk Management Guidelines Companion to AS/NZS4360:2004. Sydney: Standards Australia International Ltd. PAGE 3 SAFETYLINE INSTITUTE FEBRUARY 2012
© Copyright 2026