Dean S. Barron twobluecats.com The Ohio State University, May 19 -22, 2010
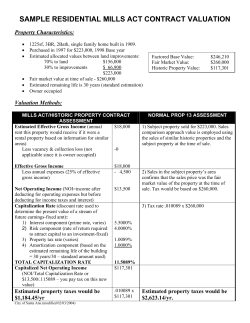
Dean S. Barron twobluecats.com Presented at Conference on Nonparametric Statistics and Statistical Learning, The Ohio State University, May 19 -22, 2010 Dean S. Barron President twobluecats.com [email protected] A two sample test based on rotationally superimposable permutations Pawprints: A Cyclical Approach Based On Kolmogoroff-Smirnoff Conference on Nonparametric Statistics and Statistical Learning The Blackwell and Pfahl Conference Center The Ohio State University May 19 -22, 2010 Pfahl 202 (Contributed) Nonparametric Tests Thursday 20 May 2010 Dean S. Barron twobluecats.com Presented at Conference on Nonparametric Statistics and Statistical Learning, The Ohio State University, May 19 -22, 2010 Table 2.1. Sequences with four consecutive drawn from one population, n=8 location of maximum maximum id sequence (n/2)*ks consecutive significant consecutive run run 11112222 4 4 initial and final yes 1 11122221 3 4 interior no 5 11222211 2 4 interior no 15 12222111 3 4 interior no 35 21111222 3 4 interior no 36 22111122 2 4 interior no 56 22211112 3 4 interior no 66 22221111 4 4 initial and final yes 70 Dean S. Barron twobluecats.com Presented at Conference on Nonparametric Statistics and Statistical Learning, The Ohio State University, May 19 -22, 2010 id=1 KS=1.00 griffe=11112222 1 id=5 KS=0.75 griffe=11122221 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 2 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 Figure 2.1. Circular representations. Green arrows are the sequence starts. Definition 1. A unique permutation is called a griffe. Definition 2. Operation רis defined as the set of n rotations רk of griffes by 360k/n degrees, for corresponding k=0, ... ,n-1. This forms a cyclic abelian group by applying each of the n rotations to a griffe. When present, the duplicate resultant transformed permutations are deleted to form a reduced set. Definition 3. Each such reduced set of griffes is called a patte. This process is performed on every griffe, resulting in n!/[(n/2)!(n/2)!] pattes. When present, the duplicate pattes are deleted to form a reduced set. Definition 4. The reduced set of pattes is called a pawprint. Each griffe has associated with it its original KS-value, called KSgriffe. Since each set is comprised of equivalent data set sequences, the highest KS-value within a patte is substituted for the original KS-value for each member griffe. This maximum KS-value is called, KSpatte. Dean S. Barron twobluecats.com Presented at Conference on Nonparametric Statistics and Statistical Learning, The Ohio State University, May 19 -22, 2010 Table 3.1. Operation, ר, for n=8. ר0 ר1 ר2 ר3 ר4 ר5 ר6 ר7 ר0 ר1 ר2 ר3 ר4 ר5 ר6 ר7 ר0 ר1 ר2 ר3 ר4 ר5 ר6 ר7 ר1 ר2 ר3 ר4 ר5 ר6 ר7 ר0 ר2 ר3 ר4 ר5 ר6 ר7 ר0 ר1 ר3 ר4 ר5 ר6 ר7 ר0 ר1 ר2 ר4 ר5 ר6 ר7 ר0 ר1 ר2 ר3 ר5 ר6 ר7 ר0 ר1 ר2 ר3 ר4 ר6 ר7 ר0 ר1 ר2 ר3 ר4 ר5 ר7 ר0 ר1 ר2 ר3 ר4 ר5 ר6 Dean S. Barron twobluecats.com Presented at Conference on Nonparametric Statistics and Statistical Learning, The Ohio State University, May 19 -22, 2010 Table 3.2. Duplicate generated pattes from two griffes from n=8 11112222 11122221 ר0 ר1 ר2 ר3 ר4 ר5 ר6 ר7 11112222 11122221 11122221 11222211 11222211 12222111 12222111 22221111 22221111 22211112 22211112 22111122 22111122 21111222 21111222 11112222 Table 3.3. Aligned duplicate generated pattes from two griffes from n=8 11112222 11122221 11112222 11122221 11222211 12222111 22221111 22211112 22111122 21111222 x x x x x x x x ר0 ר1 ר2 ר3 ר4 ר5 ר6 ר7 x x x x x x x x ר7 ר0 ר1 ר2 ר3 ר4 ר5 ר6 Two of these 10 pattes themselves contain duplicate griffes (Table 3.4). The elimination of these elemental degenerative duplicates (light blue shading) results in one patte of two griffes, and one patte of four griffes; the remaining eight pattes consist of the full eight griffes. Thus, the remaining pattes are disjoint. Table 3.4. The two pattes with degenerative duplicate griffes, n=8. 12121212 22112211 ר0 ר1 ר2 ר3 ר4 ר5 ר6 ר7 12121212 11221122 21212121 12211221 12121212 22112211 21212121 21122112 12121212 11221122 21212121 12211221 12121212 22112211 21212121 21122112 Note: Light blue shading indicates degenerative duplicates. Dean S. Barron twobluecats.com Presented at Conference on Nonparametric Statistics and Statistical Learning, The Ohio State University, May 19 -22, 2010 Table 3.6 KS PP significance grid, n=8 PP significant KS significant 0 0 1 total 1 68 2 70 total 0 0 0 68 2 70 Dean S. Barron twobluecats.com Presented at Conference on Nonparametric Statistics and Statistical Learning, The Ohio State University, May 19 -22, 2010 Table 3.7. KSgriffe KS patte grid, n=10 (n/2)*KS (n/2)*PP 1 2 3 4 5 total 2 30 0 0 0 32 1 0 30 84 16 0 130 2 0 0 36 30 4 70 3 0 0 0 14 4 18 4 0 0 0 0 2 5 2 2 60 120 60 252 total 10 Note: Light blue areas represent sequences which are statistically significant. Dean S. Barron twobluecats.com Presented at Conference on Nonparametric Statistics and Statistical Learning, The Ohio State University, May 19 -22, 2010 Table 3.10. KS PP significance grid, n=10 PP significant KS significant 0 0 1 total 1 242 0 242 8 2 10 total 250 2 252 Dean S. Barron twobluecats.com Presented at Conference on Nonparametric Statistics and Statistical Learning, The Ohio State University, May 19 -22, 2010 Table 3.13. KS PP grid, linearized, 2≤n≤30. KS KS KS not sign not sign sign n PP PP PP not sign sign not sign 2 0 0 2 6 0 0 4 20 0 0 6 68 0 2 8 242 8 0 10 894 6 18 12 3278 126 0 14 12512 118 150 16 45946 1042 820 18 180818 1658 1258 20 678218 12584 6732 22 2537728 81420 32844 24 9846592 93548 336908 26 38476962 886158 280098 28 1095330 2919720 30 149950590 KS sign PP sign 0 0 0 0 2 6 28 90 812 1022 7898 52164 123552 473382 1151880 KS sign 0 0 0 2 2 24 28 240 1632 2280 14630 85008 460460 753480 4071600 PP sign 0 0 0 0 10 12 154 208 1854 2680 20482 133584 217100 1359540 2247210 n griffes 2 6 20 70 252 924 3432 12870 48620 184756 705432 2704156 10400600 40116600 155117520 Dean S. Barron twobluecats.com Presented at Conference on Nonparametric Statistics and Statistical Learning, The Ohio State University, May 19 -22, 2010 Daily Average Temperature Februrary 2000 90 80 70 60 o temp/ F 50 40 30 20 10 0 01 05 09 anchorage Figure 4.1. Graph of eurostate data (REF210) 13 17 day honolulu paris 21 25 brussels 29 Dean S. Barron twobluecats.com Presented at Conference on Nonparametric Statistics and Statistical Learning, The Ohio State University, May 19 -22, 2010 Table 4.1. Comparison of power, β, for eurostate data at α=0.05 n n1=n2 n/N KScrit KSmin KSmax βKS PP βPP 4 0.0690 4 2 4 0.1120 8 4 0 5 0.0862 5 3 5 0.0518 5 1.0000 10 6 0.1034 5 3 6 0.1936 6 1.0000 12 7 0.1207 6 4 7 0.1020 7 1.0000 14 8 0.1379 6 4 8 0.2529 8 1.0000 16 9 0.1552 6 5 9 0.4703 9 1.0000 18 10 0.1724 7 5 10 0.2973 10 1.0000 20 11 0.1897 7 6 11 0.5045 11 1.0000 22 12 0.2069 7 6 12 0.7470 12 1.0000 24 13 0.2241 7 7 13 1.0000 13 1.0000 26 14 0.2414 8 7 14 0.7598 14 1.0000 28 15 0.2586 8 8 15 1.0000 15 1.0000 30 29 0.5000 11 15 29 1.0000 29 1.0000 58 58 1.0000 15 29 29 1.0000 29 1.0000 116 Note: N=58. Blue area represents region where KSmin≥KScrit, universally. Pink area represents region where PPcrit does not exist. KScrit (REF209). Dean S. Barron twobluecats.com Presented at Conference on Nonparametric Statistics and Statistical Learning, The Ohio State University, May 19 -22, 2010 Relative Efficiency Pawprints to Kolmogoroff-Smirnoff eurostate data 4.50 Relative Efficiency, e 4.00 3.50 3.00 2.50 2.00 1.50 1.00 0.50 0.00 0.0000 0.2500 0.5000 0.7500 beta alpha=0.01 alpha=0.05 alpha=0.10 Figure 4.2. Graph of relative efficiency for eurostate data. lim alpha --> 0 1.0000 Dean S. Barron twobluecats.com Presented at Conference on Nonparametric Statistics and Statistical Learning, The Ohio State University, May 19 -22, 2010 Table 4.2. Asymptotic Relative Efficiency, e, for β=1 for eurostate data z L α kscritn116 ks n pp n e 1.23 0.902972 0.1 14 22 10 2.20 1.36 0.950512 0.05 15 30 10 3.00 1.63 0.990154 0.01 18 42 14 3.00 1.95 0.999004 0.001 22 62 18 3.44 2.23 0.999904 0.0001 25 78 22 3.55 2.47 0.99999 0.00001 27 98 24 4.08 2.70 0.999999 0.000001 30 118 28 4.21 2.90 0.9999999 0.0000001 32 n/a 32 n/a Note: Pink areas represent level at which relative efficiency is not defined. z and L are from Smirnoff (REF202).
© Copyright 2026