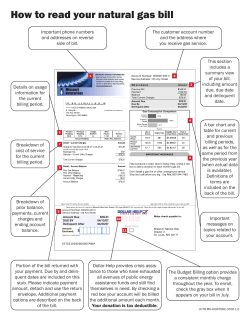
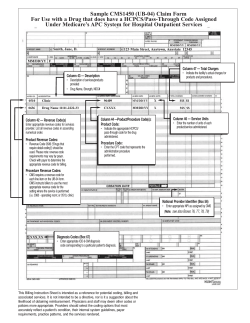
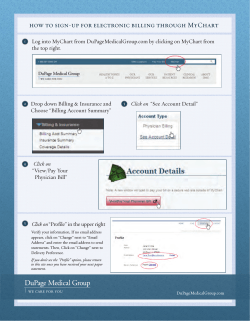
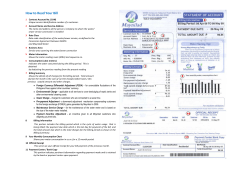
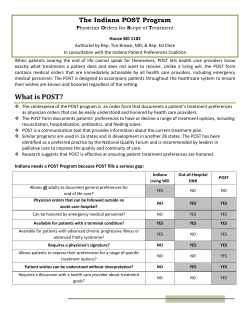
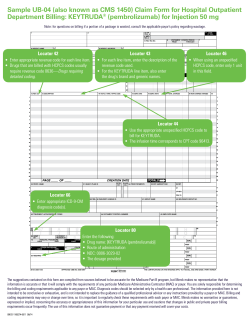
Chapter 8: Billing Instructions
I N D I A N A H E A L T H C O V E R A G E P R O G R A M S P R O V I D E R M A N U A L Chapter 8: Billing Instructions Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-1 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Current Dental Terminology (CDT) is copyrighted by the American Dental Association. 2009, 2010 American Dental Association. All rights reserved. Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) is copyright 2008 American Medical Association. All rights reserved. CPT® is a registered trademark of the American Medical Association. 8-2 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8: Revision History Document Version Number Revision Date Reason for Revisions Revisions Completed By Version 1.0 September 1999 Policies and procedures are current as of March 1, 1999 New Manual EDS Document Management Unit Version 2.0 June 2001 Policies and procedures are current as of June 1, 2000 Chapters 1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 13, 14, and Appendix A EDS Document Management Unit Version 3.0 April 2002 Policies and procedures are current as of August 1, 2001 All Chapters EDS Client Services and EDS Publications Unit Version 4.0 April 2003 Policies and procedures are current as of April 1, 2002 All Chapters EDS Client Services Unit Version 5.0 July 2004 Policies and procedures are current as of January 1, 2004 All Chapters EDS Client Services Unit Version 5.1 February 2005 Policies and procedures are current as of January 1, 2005 All Chapters EDS Publications Unit Version 6.0 December 2006 Policies and procedures are current as of April 1, 2006 All Chapters EDS Publications Unit Version 8.0 August 2008 Policies and procedures as of May 1, 2008 Semiannual Update EDS Provider Relations and Publications Units Version 8.1 February 2009 Policies and procedures as of November 1, 2008 Semiannual Update EDS Provider Relations and Publications Units Version 9.0 December 2009 Policies and procedures as of May 1, 2009 Semiannual Update EDS Provider Relations and Publications Units Version 9.1 April 22, 2010 Policies and procedures as of November 1, 2009 Semiannual Update HP Provider Relations and Publications Units Version 10.0 August 26, 2010 Policies and procedures as of May 1, 2010 Semiannual Update HP Provider Relations and Publications Units Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 • Updated Revenue Codes with Descriptions table • Updated Hospice Care Coverage section • Added Hospice Contracts 8-3 Chapter 8 Document Version Number Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Revision Date Reason for Revisions Revisions Completed By with Other Entities for Hospice-related Services section 8-4 • Added Hospice Provider Reimbursement Terms section • Added Medical Education Reimbursement section • Updated Blood Factor Products Effective for Dispense Dates of October 12, 2008, and Later table • Updated Stereotactic Radiosurgery section • Added Notification of Pregnancy Billing section • Updated Pacemakers section • Updated Hub Site Services and Billing Requirements and Special Considerations section • Updated Care Coordination Services section • Updated Diabetic Test Strips section • Added Drug-Related Medical Supplies and Medical Devices section • Updated Repair and Replacement section • Updated HCPCS Codes – DME/HME That Do Not Require PA table • Updated Capped Rental Items section • Deleted Coverage for Influenza A (H1N1) Vaccine Administration section • Updated Incontinence, Ostomy, and Urological Mail Order Supplies section Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Chapter 8 Document Version Number Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Revision Date Reason for Revisions • Updated Medicare Processed Claims Submitted to the IHCP by the Provider section • Updated HealthWatch/EPS DT Services: Coverage and Billing Procedures section • Updated Injections: Coverage and Billing Procedures section • Changed Botox Coverage and Billing Procedures section heading to Botulinum Toxin Coverage and Billing Procedures and updated section • Added Coverage of Mental Health Codes for Children’s Health Insurance Program section • Updated Managed Care Considerations: Risk-based Managed Care section • Updated Presumptive Eligibility – Package P section • Updated Antepartum Tests and Screenings Schedule table • Added Process for Completion of the Notification of Pregnancy section • Updated Prenatal Risk Assessment section • Updated Medically HighRisk Diagnoses section • Updated Lenses section • Updated VFC Vaccine Coverage and Billing Procedures section • Updated Administration Fee section Revisions Completed By 8-5 Chapter 8 Document Version Number 8-6 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Revision Date Reason for Revisions • Updated CDT Codes Allowed for Package E Members table • Updated Managed Care Considerations section • Deleted Carved-Out Services section • Updated Topical Fluoride Treatment section • Updated Radiographs section • Updated Supernumerary Tooth Extractions section • Updated CDT and CPT Codes, Including Coverage Criteria table • Updated CMS-1500 Claim Form Fields table • Updated HCPCS Codes Requiring Attachments table • Updated links to IHCP Provider Web site Revisions Completed By Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Table of Contents Chapter 8: Revision History ................................................................................. 8-3 Table of Contents ................................................................................................... 8-7 Section 1: Introduction to Billing Instructions .................................................. 8-17 General Information .......................................................................................... 8-17 Ordering Claim Forms .................................................................................. 8-18 National Provider Identifier and One-to-One Match ......................................... 8-18 Use National Provider Identifier for Referring, Rendering, or Attending Provider when Submitting Claims via Web interChange ............. 8-19 Types of Services Billed on Each Claim Form ................................................. 8-19 Paper Claim Requirements ................................................................................ 8-21 Modifiers ....................................................................................................... 8-21 National Drug Code Billing .......................................................................... 8-21 Procedure Code Partial Units ........................................................................ 8-22 Date of Service Definition ............................................................................ 8-22 Electronic Standards .......................................................................................... 8-22 Companion Guides........................................................................................ 8-22 Paper Attachment Requirements ....................................................................... 8-22 Paper Attachments with Electronic Claims ................................................... 8-23 Report Type Code ......................................................................................... 8-24 Claim Notes ....................................................................................................... 8-24 Number of Details ............................................................................................. 8-25 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions ................................................................. 8-26 Providers Using the UB-04 Claim Form ........................................................... 8-26 UB-04 Claim Form Requirements ..................................................................... 8-26 Description of Fields on the UB-04 Claim Form .............................................. 8-26 Diagnostic and Therapeutic Codes Not Reimbursable .................................. 8-54 UB-04 Claim Types........................................................................................... 8-55 Compounds – Outpatient/Outpatient Crossover............................................ 8-55 Home Health Services ....................................................................................... 8-55 Coverage ....................................................................................................... 8-55 Billing Procedures ......................................................................................... 8-55 Unit of Service .............................................................................................. 8-56 Overhead Rate ............................................................................................... 8-57 Home Health Rule Changes .............................................................................. 8-58 Multiple Visit Billing .................................................................................... 8-59 Partial Units of Service ................................................................................. 8-59 Hospital Discharge ........................................................................................ 8-59 Hospice Care Coverage ..................................................................................... 8-63 Billing Procedures ......................................................................................... 8-63 Revenue Codes.............................................................................................. 8-64 Physician Services under Revenue Codes 651 through 655 ......................... 8-67 Physician Services under Revenue Code 657 ............................................... 8-68 Prior-Authorized Physician Services ............................................................ 8-68 Hospice Contracts with Other Entities for Hospice-related Services ............ 8-68 Volunteer Physician Services........................................................................ 8-68 Emergency Services ...................................................................................... 8-68 CHOICE and Hospice Members ................................................................... 8-70 Medicare and Traditional Medicaid Eligibility Changes during the Month ............................................................................................................ 8-70 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-7 Chapter 8 Table of Contents Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Traditional Medicaid-Only – Hospice Member Who Becomes Medicare-Eligible in Nursing Facility........................................................... 8-70 Dually Eligible Medicare/Traditional Medicaid – Member in a Nursing Facility Who Becomes Traditional Medicaid-Only ........................ 8-71 Billing a Continuation Claim Using UB-04 Claim Form.............................. 8-71 Hospice Provider Reimbursement Terms ..................................................... 8-71 Inpatient Hospital Services ................................................................................ 8-73 Coverage ....................................................................................................... 8-73 Billing Procedures ......................................................................................... 8-74 Unit and Age Limitations on Inpatient Neonatal and Pediatric Critical Care Services ..................................................................................................... 8-87 Stereotactic Radiosurgery .................................................................................. 8-88 Ventricular Assist Devices ................................................................................ 8-88 Noncovered Services..................................................................................... 8-89 Prior Authorization ....................................................................................... 8-89 Coding and Billing Instructions .................................................................... 8-89 Long-Term Acute Care Facility Services .......................................................... 8-91 Long-Term Acute Care Facilities.................................................................. 8-91 Coverage ....................................................................................................... 8-92 Billing Procedures ......................................................................................... 8-92 Package C ..................................................................................................... 8-92 Nursing Facility Services .................................................................................. 8-92 Member Liability .......................................................................................... 8-93 Leave Days.................................................................................................... 8-93 Autoclosure Billing ....................................................................................... 8-94 Medicare Crossover Payment Policy ............................................................ 8-95 Nursing Facilities Not Medicare-Certified .................................................... 8-95 Intermediate Care Facility for the Mentally Retarded Services......................... 8-95 Type of Bill ................................................................................................... 8-96 Leave Days.................................................................................................... 8-96 Outpatient Services............................................................................................ 8-97 Coverage ....................................................................................................... 8-97 Billing Procedures ......................................................................................... 8-97 Package B Billing .............................................................................................. 8-97 Notification of Pregnancy Billing ..................................................................... 8-98 Outpatient Surgeries .......................................................................................... 8-99 Surgical Revenue Codes .................................................................................... 8-99 Implantable DME ............................................................................................ 8-100 Corneal Tissue ................................................................................................. 8-101 Pacemakers ...................................................................................................... 8-101 Phrenic Nerve Stimulator (Breathing Pacemaker)........................................... 8-101 Prior Authorization ..................................................................................... 8-101 Coding and Billing Instructions .................................................................. 8-102 Coverage Issues .......................................................................................... 8-102 Device Monitoring ...................................................................................... 8-103 Patient-Activated Event Recorder – Implantable Loop Recorder ................... 8-104 Coverage ..................................................................................................... 8-104 Prior Authorization ..................................................................................... 8-104 Reimbursement and Billing Instructions ..................................................... 8-104 Device Monitoring ...................................................................................... 8-105 Coverage Criteria ........................................................................................ 8-106 Intraocular Lenses ........................................................................................... 8-106 NeuroCybernetic Prosthesis System – Vagus Nerve Stimulator ..................... 8-106 Coverage Criteria for the NCP System ....................................................... 8-107 8-8 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Table of Contents Diagnosis and Procedure Codes .................................................................. 8-107 Hospital Inpatient ........................................................................................ 8-109 Physician Billing Instructions ..................................................................... 8-109 Treatment Room Visits ................................................................................... 8-110 Emergency Services ........................................................................................ 8-111 Add-on Services .............................................................................................. 8-127 Stand-alone Services ....................................................................................... 8-129 Stand-alone Laboratory Services ..................................................................... 8-131 Stand-alone Radiology Services ...................................................................... 8-131 Stand-alone Chemotherapy and Radiation Services ........................................ 8-132 Stand-alone Renal Dialysis Services ............................................................... 8-132 Composite Rate for Method I Dialysis ........................................................ 8-133 Billing Guidelines ....................................................................................... 8-133 UB-04 Completion Guidelines.................................................................... 8-134 Type of Bill Codes ...................................................................................... 8-134 Diagnosis Codes.......................................................................................... 8-134 Revenue Codes............................................................................................ 8-134 Transportation Services ................................................................................... 8-136 Outpatient Mental Health ................................................................................ 8-136 Partial Units of Service ............................................................................... 8-137 Filing UB-04 Crossover Claims ...................................................................... 8-137 Processing of Crossover Claims.................................................................. 8-137 Attachments for UB-04 Paper Claims or 837I Transaction Submissions ................................................................................................ 8-137 UB-04 Crossover Billing Procedures .......................................................... 8-138 Billing Medicare Denied Services ................................................................... 8-139 837I Electronic Transaction ............................................................................ 8-139 Companion Guides...................................................................................... 8-139 Diagnosis Codes.......................................................................................... 8-139 Additional UB-04 and 837I Admission and Duration Changes .................. 8-140 Section 3: Telemedicine ..................................................................................... 8-141 Overview ......................................................................................................... 8-141 Definitions ....................................................................................................... 8-141 Provider/Service Requirements ....................................................................... 8-141 Conditions of Payment .................................................................................... 8-142 Hub Site Services and Billing Requirements................................................... 8-142 Spoke Site Services and Billing Requirements ............................................... 8-142 Documentation Standards................................................................................ 8-143 Special Considerations .................................................................................... 8-143 Managed Care Considerations ......................................................................... 8-143 Indiana Administrative Code (IAC) ................................................................ 8-144 Rule 38. Telemedicine Services .................................................................. 8-144 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions ................. 8-147 Introduction ..................................................................................................... 8-147 Providers Using the CMS-1500 Claim Form or the 837P Transaction ............ 8-147 General Information ........................................................................................ 8-148 Claims Submission Addresses .................................................................... 8-149 CMS-1500 Paper Claim Form Requirements .................................................. 8-149 Billing and Rendering Provider Numbers ................................................... 8-149 Description of Fields on the CMS-1500 Claim Form ................................. 8-150 837P Electronic Transaction............................................................................ 8-157 Companion Guides...................................................................................... 8-157 Diagnosis Codes.......................................................................................... 8-157 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-9 Chapter 8 Table of Contents Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Modifiers ......................................................................................................... 8-157 Place of Service Codes .................................................................................... 8-171 U Modifiers ..................................................................................................... 8-173 Substitute Physicians and Locum Tenens ........................................................ 8-173 Substitute Physicians .................................................................................. 8-174 Locum Tenens Physicians ........................................................................... 8-174 Anesthesia Services ......................................................................................... 8-174 Coverage and Billing Procedures ................................................................ 8-174 Care Coordination Services ............................................................................. 8-179 Coverage and Billing Procedures ................................................................ 8-179 Prenatal Care Coordination Services .......................................................... 8-180 Care Coordination Services for Human Immunodeficiency Virus/Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome .......................................... 8-184 Chiropractic Services ...................................................................................... 8-189 Coverage and Billing Procedures ................................................................ 8-189 Diabetes Self-Care Management Training Services ........................................ 8-199 Coverage and Billing Procedures ................................................................ 8-199 Practitioners Eligible to Provide Services ................................................... 8-199 Procedure Codes and Units of Service ........................................................ 8-200 Diabetic Test Strips ..................................................................................... 8-201 Drug-Related Medical Supplies and Medical Devices................................ 8-202 Durable Medical Equipment and Home Medical Equipment .......................... 8-204 Coverage and Billing Procedures ................................................................ 8-204 Casting Supplies.......................................................................................... 8-215 Continuous Passive Motion – Continuous Passive Motion Device ............ 8-215 Cranial Remolding Orthosis........................................................................ 8-215 Home Infusion – Parenteral and Enteral Therapy Services......................... 8-216 Home Infusion – Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition Pumps .......................... 8-217 Clarification on Billing Food Thickener, HCPCS Code B4100.................. 8-218 Humidifiers, Nonheated or Heated ............................................................. 8-218 Incontinence, Ostomy, and Urological Mail Order Supplies ...................... 8-219 A4927 – Nonsterile Gloves, per 100 ........................................................... 8-222 A4930 – Gloves, Sterile, per Pair................................................................ 8-222 General Guidelines Applicable to Nonsterile and Sterile Gloves ............... 8-222 Orthopedic or Therapeutic Footwear .......................................................... 8-223 Osteogenic Bone Growth Stimulators ......................................................... 8-223 Oximetry ..................................................................................................... 8-224 Oxygen and Home Oxygen Equipment ...................................................... 8-225 Oxygen – Portable Systems ........................................................................ 8-227 Nebulizer with Compressor ........................................................................ 8-228 Phototherapy (Bilirubin Light).................................................................... 8-228 Pneumograms .............................................................................................. 8-228 Prosthetic Devices ....................................................................................... 8-229 ThAIRapy Vest™ ....................................................................................... 8-229 Trend Event Monitoring and Apnea Monitors ............................................ 8-229 Ventricular Assist Devices .......................................................................... 8-230 Wheelchairs – Motorized ............................................................................ 8-232 Wheelchairs – Nonmotorized...................................................................... 8-232 Wheelchair – Power Seating ....................................................................... 8-233 Wheelchair – Seat Cushions ....................................................................... 8-233 Wheelchair Accessories .............................................................................. 8-233 Documentation Required for Medical Supplies and Equipment ................. 8-234 Emergency Department Physicians ................................................................. 8-235 Coverage and Billing Procedures ................................................................ 8-235 8-10 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Table of Contents Evaluation and Management Services ............................................................. 8-236 Coverage and Billing Procedures ................................................................ 8-236 Consultations ................................................................................................... 8-237 Office Consultation ..................................................................................... 8-237 Inpatient Consultation ................................................................................. 8-237 Hospital Observation or Inpatient Care Services ........................................ 8-237 Family Planning Services ................................................................................ 8-238 Coverage and Billing Procedures ................................................................ 8-238 Managed Care Program Considerations...................................................... 8-240 Federally Qualified Health Centers and Rural Health Clinics ......................... 8-240 Federally Qualified Health Centers ............................................................. 8-240 Rural Health Clinics .................................................................................... 8-241 Service Coverage ........................................................................................ 8-241 FQHC and RHC Covered Services ............................................................. 8-242 Service Definition ....................................................................................... 8-244 HealthWatch/EPSDT Services ........................................................................ 8-245 Coverage and Billing Procedures ................................................................ 8-245 Managed Care Considerations .................................................................... 8-247 Hearing Aids ................................................................................................... 8-247 Coverage and Billing Procedures ................................................................ 8-247 Hearing Aid Purchase ................................................................................. 8-247 Maintenance and Repair.............................................................................. 8-247 Replacement ................................................................................................ 8-248 Audiology Services ..................................................................................... 8-248 Augmentative Communication Devices .......................................................... 8-250 Coverage and Billing Procedures ................................................................ 8-250 Reimbursement ........................................................................................... 8-250 Authorization .............................................................................................. 8-250 Trial Period ................................................................................................. 8-250 Rental Versus Purchase ............................................................................... 8-251 Repair and Replacement ............................................................................. 8-251 Rehabilitation Engineering ......................................................................... 8-251 Pneumatic Artificial Voicing Systems ............................................................ 8-251 Coverage and Billing Procedures ................................................................ 8-251 Purchase ...................................................................................................... 8-251 Home and Community-Based Services Waiver Programs .............................. 8-252 Coverage and Billing Procedures ................................................................ 8-252 Injections ......................................................................................................... 8-253 Coverage and Billing Procedures ................................................................ 8-253 Compounds – Professional Claim Types .................................................... 8-255 Botulinum Toxin Coverage and Billing Procedures ................................... 8-255 Vaccines for Children Program ................................................................... 8-257 Laboratory Services ......................................................................................... 8-258 Coverage and Billing Procedures ................................................................ 8-258 Clinical Diagnostic Laboratory Procedures ................................................ 8-258 Professional and Technical Components .................................................... 8-260 Hospital Outpatient Defined ....................................................................... 8-260 Specimen Collection ................................................................................... 8-260 Handling Conveyance ................................................................................. 8-261 Lab Panels ................................................................................................... 8-261 Interpretation of Clinical Laboratory Services ............................................ 8-261 Breast Cancer Testing ................................................................................. 8-261 Billing Requirements and Prior Authorization Criteria for Genetic Testing for Breast and Ovarian Cancer ....................................................... 8-262 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-11 Chapter 8 Table of Contents Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Lead Testing................................................................................................ 8-264 Medical and Surgical Supplies ........................................................................ 8-264 Coverage and Billing Procedures ................................................................ 8-264 Limitations on Coverage ............................................................................. 8-265 Manually Priced Supplies ........................................................................... 8-265 Medicare Part B Crossover Claims ................................................................. 8-266 Coverage and Billing Procedures ................................................................ 8-266 Medicare/Medicaid Reimbursement ........................................................... 8-266 Mental Health Services ................................................................................... 8-267 Coverage and Billing Procedures ................................................................ 8-267 Outpatient Mental Health ............................................................................ 8-267 Package C ................................................................................................... 8-269 Medicaid Rehabilitation Option Services ................................................... 8-269 Coverage of Mental Health Codes for Children’s Health Insurance Program ....................................................................................................... 8-270 Assertive Community Treatment Service ................................................... 8-275 Psychiatric Residential Treatment Facilities ............................................... 8-276 Managed Care Considerations .................................................................... 8-278 Screening and Brief Intervention Services .................................................. 8-279 Mid-Level Practitioner Services ...................................................................... 8-279 Coverage and Billing Procedures ................................................................ 8-279 Smoking Cessation Treatment Services .......................................................... 8-280 Coverage and Billing Procedures ................................................................ 8-280 Newborn Services............................................................................................ 8-282 Coverage and Billing Procedures ................................................................ 8-282 Presumptive Eligibility – Package P ............................................................... 8-284 Presumptive Eligibility Requirements ........................................................ 8-284 Qualified Provider ....................................................................................... 8-284 Billing Procedures ....................................................................................... 8-284 Obstetrical Services ......................................................................................... 8-291 Coverage and Billing Procedures ................................................................ 8-291 Antepartum Care Policy .............................................................................. 8-291 Billing for Antepartum Visits ..................................................................... 8-291 Antepartum Tests and Screenings Schedule ............................................... 8-292 Process for Completion of the Notification of Pregnancy........................... 8-295 Salivary Estriol Test for Preterm Labor Risk Assessment .......................... 8-296 Sonography ................................................................................................. 8-297 Echography ................................................................................................. 8-297 Obstetrical Delivery and Postpartum Care Billing ...................................... 8-298 Other Outpatient Office Visits .................................................................... 8-298 Normal Pregnancy ...................................................................................... 8-298 Multiple Births ............................................................................................ 8-299 High-Risk Pregnancy .................................................................................. 8-299 Additional Antepartum Visits ..................................................................... 8-304 Reimbursement ........................................................................................... 8-304 Pregnancy Services Billing Considerations ................................................ 8-304 Hoosier Healthwise Package B – Pregnancy and Urgent Care Only .......... 8-305 Proton Treatment Billing ............................................................................ 8-306 Ophthalmological Services .............................................................................. 8-306 Coverage and Billing Procedures ................................................................ 8-306 Date of Service Definition .......................................................................... 8-306 Vision Coding and the Vision Services Code Set ....................................... 8-307 Vision Procedures Limited to One Unit ...................................................... 8-307 Eye Examinations ....................................................................................... 8-309 8-12 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Table of Contents Orthoptic or Pleoptic Training, Vision Training, and Therapies Coverage Criteria ........................................................................................ 8-310 Lenses ......................................................................................................... 8-310 Frames ......................................................................................................... 8-312 Adoption of Modifiers for Replacement Eyeglasses ................................... 8-312 Written Correspondence ............................................................................. 8-313 Billing a Member for Services that have Exceeded Benefit Limitations .... 8-314 Prior Authorization ..................................................................................... 8-314 Vision Services and Managed Care ............................................................ 8-314 Podiatric Services ............................................................................................ 8-314 Coverage and Billing Procedures ................................................................ 8-314 Second Opinions ......................................................................................... 8-315 Office Visits ................................................................................................ 8-316 Surgical Services ......................................................................................... 8-316 Laboratory and X-ray Services ................................................................... 8-317 Prior Authorization ..................................................................................... 8-317 Podiatric Services and Managed Care......................................................... 8-317 Radiology Services .......................................................................................... 8-318 Coverage and Billing Procedures ................................................................ 8-318 Utilization Criteria ...................................................................................... 8-319 Computerized Tomography Scans .............................................................. 8-319 PET Scans ................................................................................................... 8-319 Radionuclide Bone Scans............................................................................ 8-320 Upper Gastrointestinal Studies .................................................................... 8-320 Hospice Providers ....................................................................................... 8-320 Renal Dialysis Physician Services ................................................................... 8-320 Coverage and Billing Procedures ................................................................ 8-320 School Corporation Services ........................................................................... 8-322 Coverage and Billing Procedures ................................................................ 8-322 Surgical Services ............................................................................................. 8-322 Coverage and Billing Procedures ................................................................ 8-322 Split Care .................................................................................................... 8-323 Therapy Services ............................................................................................. 8-327 Coverage and Billing Procedures ................................................................ 8-327 Outpatient.................................................................................................... 8-331 Hippotherapy............................................................................................... 8-331 Traumatic Brain Injury................................................................................ 8-332 Transportation Services ................................................................................... 8-335 Advanced Life Support – ALS .................................................................... 8-335 Basic Life Support – BLS ........................................................................... 8-335 Commercial or Common Ambulatory Service – CAS ................................ 8-336 Nonambulatory Service (Wheelchair Van) – NAS ..................................... 8-336 Taxi ............................................................................................................. 8-336 Rotary Air Ambulance Transportation ........................................................ 8-336 Retroactive Eligibility ................................................................................. 8-339 Definition of a Trip ..................................................................................... 8-339 Multiple Destinations .................................................................................. 8-339 Modifiers ..................................................................................................... 8-340 Prior Authorization ..................................................................................... 8-340 Twenty One-Way Trip Limitation and Exemptions.................................... 8-341 Emergency Transportation Services ........................................................... 8-341 Hospital Admission or Discharge ............................................................... 8-341 Members on Renal Dialysis or Members Residing in Nursing Homes ....... 8-341 Mileage ....................................................................................................... 8-342 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-13 Chapter 8 Table of Contents Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Mileage Units and Rounding ...................................................................... 8-342 Multiple Passengers .................................................................................... 8-343 Accompanying Parent or Attendant ............................................................ 8-343 Additional Attendant ................................................................................... 8-344 Waiting Time .............................................................................................. 8-345 Ambulance Transportation Services ........................................................... 8-345 Level of Service Rendered Versus Level of Response ............................... 8-345 Ambulance Mileage .................................................................................... 8-346 Neonatal Ambulance Transportation .......................................................... 8-346 Oxygen and Oxygen Supplies ..................................................................... 8-347 Member Copayments .................................................................................. 8-347 Exemptions to Copayments for Transportation Services ............................ 8-347 Federal Guidelines for Copayment Policy .................................................. 8-347 Package C Transportation Services ............................................................. 8-348 Risk-Based Managed Care Hoosier Healthwise Services ........................... 8-348 Noncovered Transportation Services .......................................................... 8-348 Documentation Requirements for Transportation Services ........................ 8-348 Registration Requirements .......................................................................... 8-349 Transportation Code Sets ............................................................................ 8-350 Nonambulatory Service Provider ................................................................ 8-351 Ambulance (ALS and BLS) Provider ......................................................... 8-352 Air Ambulance ............................................................................................ 8-353 Taxi Provider .............................................................................................. 8-353 Family Member Transportation Provider .................................................... 8-353 Bus Provider................................................................................................ 8-354 Vaccines for Children ...................................................................................... 8-354 Eligible Members ........................................................................................ 8-354 Provider Enrollment in the VFC Program................................................... 8-354 Vaccines for Children Forms ...................................................................... 8-355 Vaccine Storage .......................................................................................... 8-355 VFC Vaccine Coverage and Billing Procedures ......................................... 8-355 Reporting Individual Cases of Varicella (Chickenpox) .............................. 8-358 VFC and HealthWatch ................................................................................ 8-358 Provider-Purchased Vaccine ....................................................................... 8-358 Third Party Liability.................................................................................... 8-359 Package C ................................................................................................... 8-359 Children and Hoosiers Immunization Registry Program ............................ 8-360 Medical Review Team Billing Procedures ...................................................... 8-361 MRT Reimbursement for Transportation .................................................... 8-362 MRT Procedure Codes ................................................................................ 8-362 Pre-Admission Screening and Resident Review Billing Procedures ............... 8-368 Section 5: Dental Claim Form Billing Instructions ......................................... 8-371 Introduction ..................................................................................................... 8-371 Providers Using the Dental Claim Form ......................................................... 8-371 ADA 2006 Paper Claim Form Changes and Requirements ............................ 8-371 Rendering NPI Required ............................................................................. 8-372 Date of Service Definition .......................................................................... 8-372 ADA 2006 Dental Claim Form Fields ........................................................ 8-372 Description of Fields on the ADA 2006 Dental Claim Form .......................... 8-372 837D Electronic Transaction ........................................................................... 8-376 Companion Guides...................................................................................... 8-376 Billing Procedures ........................................................................................... 8-377 Current Dental Terminology Procedure Codes ........................................... 8-377 Dental Extractions ....................................................................................... 8-377 8-14 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Table of Contents Package E Billing ........................................................................................ 8-377 Attachments ..................................................................................................... 8-379 Attachment Control Number ....................................................................... 8-380 Report Type Code ....................................................................................... 8-380 Return to Provider Letter ............................................................................ 8-381 Paper Claims with Attachments .................................................................. 8-381 Managed Care Considerations .................................................................... 8-381 Services Associated with Dental Services for Hoosier Healthwise RBMC Networks ........................................................................................ 8-382 Member Eligibility Verification and Billing for Dental Services ............... 8-383 Dental Cap ....................................................................................................... 8-383 Dental Service Limitations .............................................................................. 8-386 Orthodontics................................................................................................ 8-386 Prophylaxis ................................................................................................. 8-388 Oral Evaluations.......................................................................................... 8-390 General Anesthesia ..................................................................................... 8-390 Dentures and Partials Coverage....................................................................... 8-393 Dentures and Partials .................................................................................. 8-393 Annual Dental Cap for Dentures, Relines, and Repairs .............................. 8-396 Prior Authorization ..................................................................................... 8-397 Repairs, Relines, Adjustments, Rebases of Dentures and Partials .............. 8-399 Dental Prior Authorization Form ................................................................ 8-399 Covered CDT and CPT Codes ........................................................................ 8-400 Valid Tooth Numbers ...................................................................................... 8-425 Sealants............................................................................................................ 8-428 Tooth Surface Procedure Codes ...................................................................... 8-429 Multiple Restorations Reimbursement ............................................................ 8-430 Section 6: HCBS Waiver Billing Guidelines .................................................... 8-432 Introduction ..................................................................................................... 8-432 Eligibility for HCBS Waiver Services............................................................. 8-432 Waiver Authorization .................................................................................. 8-432 Environmental Modifications...................................................................... 8-433 Special Processing Required for Home and Community-Based Services Overlapping Hospice Level of Care or Long-Term Care Discharge Dates ..... 8-435 Billing Instructions .......................................................................................... 8-435 Waiver Providers Use LPI .......................................................................... 8-435 Paid Claim Adjustments .................................................................................. 8-440 Section 7: Informed Consent Claim Attachment Instructions....................... 8-441 Abortions and Related Services....................................................................... 8-441 Documentation Requirements ..................................................................... 8-441 Medical Abortion by Oral Ingestion of Medication .................................... 8-443 Sterilization and Hysterectomy ....................................................................... 8-445 Sterilizations ............................................................................................... 8-445 Limitations .................................................................................................. 8-445 Informed Consent ............................................................................................ 8-447 Retroactive Eligibility or Failure to Provide Proof of Eligibility .................... 8-448 Consent Forms................................................................................................. 8-448 Documentation Requirements ......................................................................... 8-449 Consent Form Instructions .............................................................................. 8-449 Hysterectomy Billing ...................................................................................... 8-451 Informed Consent and Acknowledgement Statement ................................. 8-451 Retroactive Eligibility ................................................................................. 8-452 Section 8: Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System Codes ................ 8-454 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-15 Chapter 8 Table of Contents Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Fee Schedule ................................................................................................... 8-454 HCPCS Codes Requiring Attachments ........................................................... 8-454 Index ................................................................................................................... 8-471 8-16 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 1: Introduction to Billing Instructions General Information This chapter provides a comprehensive explanation of billing instructions for each claim form used by the Indiana Health Coverage Programs (IHCP). The IHCP uses the following claim forms: • UB-04 Claim Form • CMS-1500 Claim Form • American Dental Association (ADA) 2006 Claim Form • National Council for Prescription Drug Programs (NCPDP) Drug Claim Form • Indiana Medicaid Compound Prescription Claim Form Note: Claims related to Hoosier Healthwise risk-based managed care (RBMC) plans may use the above forms where applicable. Contact the appropriate managed care organization (MCO) for specific instructions. Providers can also bill claims using the 837I, 837P, or 837D transactions. This chapter includes specific guidelines for each of these transaction types. Billing instructions for the NCPDP Drug Claim Form and Compound Prescription Claim Form are available on the IHCP Web site at http://provider.indianamedicaid.com by clicking Forms on the right side of the page. The explanation of each claim form includes the following: • Types of providers using the form • Form sample • Field descriptions and field requirements • Field coding information • Unique billing instructions for each type of service billed on the form Providers can find detailed information about covered services and policy guidelines in the Indiana Administrative Code on the Web at www.state.in.us/legislative/iac/title405.html. Some supplemental programs have substantial requirements that are too lengthy to be included in this chapter. The supplemental provider manual for each program contains information about these programs. The IHCP supplemental provider manuals are available for download from the IHCP Web site at http://provider.indianamedicaid.com/general-provider-services/manuals.aspx: • Hospice Provider Manual • Medicaid Rehabilitation Option (MRO) Provider Manual • 590 Program Provider Manual • HealthWatch/Early and Periodic Screening, Diagnosis, and Testing (EPSDT) Provider Manual Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-17 Chapter 8 Section 1: Introduction to Billing Instructions Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual • Home and Community-Based Services Waiver Provider Manual • Qualified Provider Presumptive Eligibility Manual Ordering Claim Forms Providers can order UB-04, CMS-1500, and ADA 2006 Dental Claim Forms from a standard form supply company. They can also download and print UB-04 and CMS-1500 version 08-05 forms from the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) Web site at www.cms.hhs.gov. HP does not distribute supplies of these forms. Providers can download drug and compound prescription claim forms from the http://provider.indianamedicaid.com Web site in the Forms section or order them by writing to the following: HP Forms Request P.O. Box 7263 Indianapolis, IN 46207-7263 National Provider Identifier and One-to-One Match Beginning March 1, 2008, claims are denied if healthcare providers submit a claim without a billing provider National Provider Identifier (NPI). Only atypical provider claims are exempt from this requirement. Effective May 23, 2008, providers’ IHCP Legacy Provider Identifier (LPI) may appear on the claim but will not be used to process the claim. Providers are encouraged to bill with the NPI only. All healthcare providers must report their NPI on all claims and establish a one-to-one match with the service location where the patient was treated, or the claim will be denied. Three data elements are used for the standard NPI crosswalk: • Billing NPI • Billing taxonomy code • Billing provider office service location ZIP Code + 4 on file in IndianaAIM The crosswalk attempts to establish a one-to-one match with the following data elements in the following sequence: • NPI only • NPI to billing taxonomy • NPI to billing provider office service location ZIP Code + 4 • NPI to billing provider office service location five-digit ZIP Code • NPI to billing taxonomy and five-digit ZIP Code Note: Providers can view their provider profile on the Web interChange. Additional information about the Web interChange can be found in Chapter 3 of this manual. 8-18 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 1: Introduction to Billing Instructions Use National Provider Identifier for Referring, Rendering, or Attending Provider when Submitting Claims via Web interChange Nonatypical providers that submit medical (CMS-1500 format) claims via Web interChange receive an error message when the LPI and NPI are entered for the referring or rendering provider. To resolve the error, remove the LPI from all fields on Web interChange; report only the NPI for the referring or rendering provider. Nonatypical providers that submit institutional (UB-04 format) claims via Web interChange have encountered an error message when entering the attending physician license number in the Attending Prov NPI field. Please note that only the NPI is accepted in this field; the license number of the attending physician should not be entered on the claim. Types of Services Billed on Each Claim Form Tables 8.1 to 8.3 illustrate the types of services billed on each claim form. Table 8.1 – UB-04 Claim Form Provider Types Types of Services Ambulatory surgical centers (ASCs) Outpatient surgical services End-stage renal disease (ESRD) clinics Renal dialysis services Home health agencies (HHAs) Home health services Hospices Hospice facility services (except waiver services) Hospitals Inpatient facility services (acute, psychiatric, and rehabilitation) Outpatient facility services Renal dialysis services Outpatient radiological services (technical component) Outpatient laboratory services (technical component) Long-term care (LTC) facilities Nursing facility (NF) services Intermediate care facility for the mentally retarded (ICF/MR) facility services Community residential facility for the developmentally disabled (CRF/DD) facility services (this type of facility may also be called a small ICF/MR) Long Term Acute Care (LTAC) Rehabilitation hospital facilities Rehabilitation facility services Traumatic brain injury services Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-19 Chapter 8 Section 1: Introduction to Billing Instructions Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Table 8.2 – CMS-1500 Claim Form Provider Types 8-20 Types of Services Advanced practice nurses Midwife services Nurse practitioner services Nurse anesthetist services Audiologists Audiology services Case managers Care coordination services Chiropractors Chiropractic services Clinics Family planning services Federally Qualified Health Center (FQHC) services Medical services Nurse practitioner services Rural health clinic (RHC) services Therapy services Surgical services Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetist (CRNA) Nurse anesthetist services Dentists Oral surgery Durable medical equipment (DME) and home medical equipment (HME) dealers DME/HME Medical supplies Oxygen Freestanding radiology facilities Radiological services, professional component, technical component, or global component Hearing aid dealers Hearing aids Laboratories Laboratory services-professional component Mental health providers Medicaid Rehabilitation Option (MRO) services Outpatient mental health services Mid-level practitioners Anesthesiology assistant services Physician assistant services Advanced practice nurse credentialed in psychiatric or mental health nursing Opticians Optical services Optometrists Optometric services Physicians – Medical Doctor (MD) and Doctor of Osteopathy (DO) Anesthesia services Laboratory services Medical services – professional component Mental health services Radiological services Renal dialysis services Surgical services Podiatrists Podiatric services Public health agencies Medical services Psychiatric Residential Treatment Facilities (PRTF) Behavioral Health Residential Treatment Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 1: Introduction to Billing Instructions Provider Types Types of Services School corporations Therapy services – physical, occupational, speech, and mental health Therapists Therapy services – physical, occupational, speech, and audiology Transportation providers Transportation services Waiver providers Waiver services Table 8.3 – ADA 2006 Dental Claim Form Provider Types Types of Services Dentists Dental services Medical Clinics Dental services Dental Clinics Dental services Other Dental Providers Dental services Paper Claim Requirements This section describes revisions to paper claim submission requirements that are applicable to more than one claim type. These changes are required to bring paper claim requirements into compliance with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) electronic claim transaction requirements. Modifiers The paper CMS-1500 and UB-04 claim forms and the electronic 837P and 837I transactions accept four modifiers per procedure code. There are currently no modifiers approved for use with the Current Dental Terminology (CDT®) code set on the dental claim form. National Drug Code Billing The Federal Deficit Reduction Act of 2005 mandates that IHCP require the submission of National Drug Codes (NDCs) on claims submitted with certain procedure codes for physician-administered drugs. This mandate affects all providers submitting electronic or paper claims for procedure-coded drugs. Because the State may pay up to the 20 percent Medicare B copayment for dually eligible individuals, the NDC will also be required on Medicare crossover claims for all applicable procedure codes. Please contact your vendor to make the necessary software changes. The NDC is required on the CMS-1500 paper claim form, Web interChange, and 837P electronic transactions for submission on all claims. Requirements for the CMS-1500 paper claim form are explained in Section 4 of this chapter. The NDC is required on the UB-04 paper claim form, Web interChange, and 837I electronic transactions for submission on all claims. Requirements for the UB-04 paper claim form are explained in Section 2 of this chapter. All providers are encouraged to monitor future bulletins and banner pages for updates about NDC reporting. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-21 Chapter 8 Section 1: Introduction to Billing Instructions Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual The IHCP is not changing reimbursement policy pertaining to procedure-coded, physicianadministered drugs at this time. Claims for such drugs continue to be priced by using the submitted procedure code and procedure code units. The sole exception is that manually priced J and Q codes will be priced by using the submitted NDC. Procedure Code Partial Units The ADA 2006 and CMS-1500 paper claim forms and the 837 Dental (837D) and 837P transactions allow partial units for procedure codes that accommodate fractional units. Each procedure code quantity allows for two decimal places when submitting partial units. Note: Providers can submit Current Procedural Terminology (CPT®) and Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS) codes on the UB04 claim form or 837I transaction using only whole units. Date of Service Definition All claims must reflect a date of service. The date of service is the date the specific services were actually supplied, dispensed, or rendered to the patient. For example, when rendering services for space maintainers or dentures, the date of service must reflect the date the appliance or denture is delivered to the patient. This requirement is applicable to all IHCP-covered services. Electronic Standards HIPAA specifically names several electronic standards that must be followed when certain healthcare information is exchanged. These standards are published as National Electronic Data Interchange Transaction Set Implementation Guides. They are commonly called Implementation Guides (IGs). An addendum to most IGs has been published and must be used to properly implement each transaction. The IGs are available for download through the Washington Publishing Company Web site at http://wpc-edi.com. Companion Guides The IHCP has developed technical companion guides to assist application developers during the implementation process. Information contained in the IHCP Companion Guides is intended only to supplement the adopted IGs and provide guidance and clarification as it applies to the IHCP. The IHCP Companion Guides are never intended to modify, contradict, or reinterpret the rules established by the IGs. The Companion Guides are located on the IHCP Web site at http://provider.indianamedicaid.com in the EDI Solutions section. Paper Attachment Requirements The IHCP accepts paper attachments with electronic claims (837I, 837P, and 837D). Web interChange claims follow the same attachment requirements. 8-22 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 1: Introduction to Billing Instructions Paper Attachments with Electronic Claims When an 837 or Web interChange claim transaction requires the submission of additional documentation, providers can submit the documentation as a paper attachment. When a provider elects to send a paper attachment with an 837 or Web interChange transaction, the provider must include the following information: • Attachment Transmission Code – Required to indicate whether an electronic claim has paper documentation to support the billed services. This code defines the timing and transmission method or format of reports and how they are sent. Attachment Transmission Code, Data Element 756, on the 837 transaction provides this value. The IHCP only accepts paper attachments for electronic or paper claims by mail. This Attachment Transmission Code is BM (by mail). • Attachment Report Type Code – Indicates the type of attachment that the provider is sending to the IHCP to support the 837 or Web interChange claim data. The code indicates the title or contents of a document, report, or supporting item. Enter this code in Report Type Code, Data Element 755. For a complete listing of Attachment Report Type Codes, refer to the specific 837 or Web interChange claim transaction implementation guide. • Attachment control number (ACN) – This code identifies each attachment. The ACN is created by the provider and can be numbers, letters, or a combination of letters and numbers. ACNs can be up to 30 characters in length. Enter this code in Attachment Control Number, Data Element 67. Providers must adhere to the following instructions when submitting paper attachments for electronic claims: • Each paper attachment submitted for an 837 or Web interChange transaction must include a provider-assigned ACN. Assign a unique ACN for each type of attachment within a claim. Write the corresponding ACN on each page of the document. Once an ACN has been used, it cannot be used again, even if the same claim is resubmitted at a later date. • Providers must send an IHCP Claims Attachment Cover Sheet for attachments associated with a specific claim. Each claim must have its own attachment cover sheet. Providers can find a copy of the IHCP Claim Attachment Cover Sheet on the IHCP Web site at http://provider.indianamedicaid.com in the Forms section. The provider must complete the following information on the IHCP Claims Attachment Cover Sheet: - Billing provider name and service location address and ZIP Code + 4 - Billing provider National Provider Identifier (NPI) or Legacy Provider Identifier (LPI) and service location • Only atypical providers can use LPI and service location - Date(s) of service of the claim - IHCP member identification number (RID) - The ACN for each attachment for the claim - Number of pages associated with each attachment (not including the cover page) • Providers can submit a maximum of 20 ACNs with each attachment cover sheet. • The ACN must be unique per document type. Documents cannot be shared between claims. • Attachments not processed within 45 calendar days of the date posted on the provider’s Remittance Advice will be denied. Providers must mail paper attachments to the IHCP at the following address: HP Claims Attachments P.O. Box 7259 Indianapolis, IN 46207 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-23 Chapter 8 Section 1: Introduction to Billing Instructions Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual The HP Claims Support Unit reviews each Claims Attachment Cover Sheet for completeness and accuracy of the number of ACNs to the number of attachments. If errors are found, HP returns the cover sheet and attachments to the provider for correction and resubmission. If the provider does not mail the attachments within 45 days of claim submission, the claims are automatically denied. If the provider has submitted the attachments, but one specific attachment needed for processing is missing from the batch, the claim or service line denies. Report Type Code For processing, providers must also use the Report Type Code indicating the type of attachment that they are sending. Report Type Codes are as follows: • B4 – Referral Form – Used by Surveillance and Utilization Review (SUR) for the Right Choices Program • DA – Dental Models – Used by SUR and submitted only upon request • DG – Diagnostic Report – Used by PA and SUR • EB – Explanation of Benefits – Used by TPL, Resolutions, and SUR • OB – Operative Note – Used by PA, Resolutions, Medical Policy, and SUR • P6 – Periodontal Charts – Used for specific periodontal procedures • RR – Radiology Reports – Used by PA, Medical Policy, and SUR • RB – Radiology Films – Used by PA and SUR • OZ – Support Data for Claim – The following are uses for progress notes: - Invoices (Manual Pricing) - Durable Medical Equipment delivery tickets - Transportation run tickets - Sterilization/Hysterectomy consent forms - Spend-down Form 8A - Past filing limit documentation - PA request/response copies - Environmental modification service requests - Consultation reports Claim Notes IndianaAIM accepts claim note information in electronic 837 claim transactions and retrieves the information for review during processing. This feature reduces the number of attachments that must be sent with claims. Also, in some instances, use of the claim note may assist with the adjudication of claims. For example, when postoperative care is performed within one day of surgery, providers can submit supporting information in the claim note segment rather than sending an attachment. When a provider submits claims electronically via an 837 transaction or Web interChange claim submission, the following is true for claim notes: • 8-24 At the header level, the IHCP accepts 20 claim notes for the 837D transaction, 10 claim notes for the 837I transaction, and one claim note for the 837P transaction. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 1: Introduction to Billing Instructions • At the detail level, the IHCP allows 10 claim notes on the 837D transaction and one claim note on the 837P transaction. • The IHCP does not support detail level claim notes on the 837I transaction. • Claim note codes identify the functional area or purpose for which the note applies: - ADD – Additional Information - CER – Certification Narrative (header only) - DCP – Goals, Rehabilitation Potential, or Discharge Plans - DGN – Diagnosis Description (header only) - PMT – Payment - TPO – Third Party Organization Notes Number of Details IndianaAIM complies with HIPAA standards for details as follows: • 837I – 450 details (the maximum number of details for Medicare) • 837D – 50 details • 837P – 50 details Note: The IHCP accepts as many as 5,000 Claim (CLM) segments per ST – SE. Web interChange also accommodates these limitations. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-25 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Providers Using the UB-04 Claim Form The following types of providers use the UB-04 claim form when billing services to the Indiana Health Coverage Programs (IHCP): • Ambulatory surgery center (ASC) • End-stage renal disease (ESRD) clinic • Home health agency (HHA) • Hospice provider • Hospital • Long-term care (LTC) facility • Rehabilitation hospital facility Note: Hospital pharmacy take-home, direct care services performed by a physician, and transportation services provided in a hospital are not billed on a UB-04 claim form. UB-04 Claim Form Requirements This section provides a brief overview of the requirements to complete the UB-04 claim form. The IHCP no longer accepts the UB-92 claim form. These instructions are effective for paper claim submission starting April 1, 2007. Noncompliant UB04 paper claims submitted for processing after March 1, 2008, will be returned to the provider. Providers that have been assigned a National Provider Identifier (NPI) should include their NPI on the paper claim form. For more instructions about NPI requirements, see the National Provider Identifier and One-to-One Match section. Description of Fields on the UB-04 Claim Form This section explains the completion of the UB-04 claim form. Some information is required to complete the claim form, while other information is optional. Note: These instructions apply to the IHCP guidelines only and are not intended to replace instructions issued by the National Uniform Billing Committee (NUBC). The NUBC instruction manual can be accessed at http://www.nubc.org. With the implementation of the UB-04 paper claim form, the IHCP accepts as many as 66 lines for any one paper claim. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-26 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions The UB-04 paper claims form does not have a designated signature field. Therefore, all providers must have the Claim Certification Statement for Signature on File form with the IHCP for the UB-04 claim form to be processed. The Claim Certification Statement for Signature on File form can be obtained on the Forms page of the IHCP Web site at http://provider.indianamedicaid.com/general-provider-services/forms.aspx. Table 8.4 indicates in bold type if a field is Required or Required, if applicable. Optional and Not applicable information is displayed in normal type. Specific instructions applicable to a particular provider type are included. The table describes each form locator by referring to the number found in the left corner of each box on the UB-04 claim form. These boxes contain the data elements. The chart provides basic information about UB-04 claim fields. Where necessary, the chart notes specific directions applicable to a particular provider type: • Accommodation rates are always in units of full days. • A day begins at midnight and ends 24 hours later. • Any part of a day, including the day of admission, counts as a full day, except the following: - The day of discharge is not counted as a day unless the member is readmitted by midnight on the same day. - The day of death is the day of discharge and is not counted. • A period of inpatient care that includes at least one night in a hospital and is reimbursable under the IHCP is considered an inpatient stay; however, if fewer than 24 hours, then outpatient observation should be billed. Providers should use the UB-04 billing manual conventions unless otherwise specified. Table 8.4 gives field information for the UB-04 claim form. Table 8.5 lists revenue codes with descriptions. Table 8.4 – UB-04 Claim Form Locator Descriptions Form Field Narrative Description/Explanation PLEASE REMIT PAYMENT TO – Enter the billing provider office service location name, address, and the expanded ZIP Code+4 format. Required. 1 Note: If the Postal Service provides an expanded ZIP Code for a geographic area, this expanded ZIP Code must be entered on the claim form. 2 UNLABELED FIELD – Not applicable. 3a PATIENT CONTROL NO. – Enter the internal patient tracking number. Optional. 3b MEDICAL RECORD NUMBER – Enter the number assigned to the patient’s medical or health record by the provider. Optional. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-27 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Form Field Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Narrative Description/Explanation TYPE OF BILL – Enter the code indicating the specific type of bill. This three-digit code requires one digit from each of the following categories in the following sequence and all positions must be fully coded. Required. 4 Hospice bill type is 822. • First position – Type of Facility • Second position – Bill Classification • Third position – Frequency Note: See http://provider.indianamedicaid.com/media/30947/type_of_bill_table.pdf for a current list of Type of Bill codes. The National Uniform Billing Committee (NUBC) maintains this code set, which is considered an external code set by the HIPAA requirements. Therefore, the IHCP is not responsible for updating the type of bill code set. It is the provider’s responsibility to monitor the changes made to this external code set. 5 FED. TAX NO. – Not applicable. 6 STATEMENT COVERS PERIOD, FROM/THROUGH – Enter the beginning and ending service dates included on this bill. For all services rendered on a single day, use the FROM and THROUGH dates. Indicate dates in MMDDYY format, such as 122506. Required. 7 UNLABELED FIELD – Not applicable. 8a PATIENT IDENTIFIER – Not applicable. Report recipient ID in field 60. 8b PATIENT NAME – Last name, first name, and middle initial of the member. Required. 9a PATIENT ADDRESS – STREET – Enter the member’s street address. Optional. 9b PATIENT ADDRESS – CITY – Enter the member’s city. Optional. 9c PATIENT ADDRESS – STATE – Enter the member’s two-alpha character state abbreviation. Optional. 9d PATIENT ADDRESS – ZIP CODE – Enter the member’s ZIP Code. Optional. 9e PATIENT ADDRESS – COUNTRY CODE – Enter the three-character country code, if other than USA. Optional. 10 BIRTHDATE – Enter the member’s date of birth in an MMDDYY format. Optional. 11 SEX – Enter the member’s gender. M for Male, F for Female. Optional. 12 ADMISSION DATE – Enter the date the patient was admitted to inpatient care in a MMDDYY format. Required for inpatient and LTC. 13 ADMISSION HOUR – Enter the hour during which the patient was admitted for inpatient care. Required for inpatient. Admission Hour Code Structure Code 8-28 Time Frame a.m. Code Time Frame p.m. 00 12 a.m. – 12:59 a.m. 12 12 p.m. – 12:59 p.m. 01 1 a.m. – 1:59 a.m. 13 1 p.m. – 1:59 p.m. 02 2 a.m. – 2:59 a.m. 14 2 p.m. – 2:59 p.m. 03 3 a.m. – 3:59 a.m. 15 3 p.m. – 3:59 p.m. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Form Field 14 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Narrative Description/Explanation 04 4 a.m. – 4:59 a.m. 16 4 p.m. – 4:59 p.m. 05 5 a.m. – 5:59 a.m. 17 5 p.m. – 5:59 p.m. 06 6 a.m. – 6:59 a.m. 18 6 p.m. – 6:59 p.m. 07 7 a.m. – 7:59 a.m. 19 7 p.m. – 7:59 p.m. 08 8 a.m. – 8:59 a.m. 20 8 p.m. – 8:59 p.m. 09 9 a.m. – 9:59 a.m. 21 9 p.m. – 9:59 p.m. 10 10 a.m. – 10:59 a.m. 22 10 p.m. – 10:59 p.m. 11 11 a.m. – 11:59 a.m. 23 11 p.m. – 11:59 p.m. 99 Hour Unknown ADMISSION TYPE – Enter the code indicating the priority of this admission. Required for inpatient and LTC. Admission Codes Code Description 1 Emergency 2 Urgent 3 Elective 4 Newborn 5 Trauma Center 15 ADMISSION SRC – Optional. 16 (DHR) DISCHARGE HOUR – Enter the hour during which the patient was discharged from inpatient care. Valid values are the same as form field 13. Optional. 17 STATUS – Enter the code indicating the member discharge status as of the ending service date of the period covered on this bill. Required for inpatient and LTC. Patient Status Codes Code Description 01 Discharged to home or self-care, routine discharge 02 Discharged or transferred to another short-term general hospital for inpatient care 03 Discharged or transferred to skilled nursing facility (SNF) 04 Discharged or transferred to an intermediate care facility (ICF) 05 Discharged or transferred to a designated cancer center or children’s hospital Note Description effective September 30, 2009, for claims with discharge dates on or after April 1, 2008. 06 Discharged or transferred to home under care of organized home health service organization 07 Left against medical advice or discontinued care 08 Discharged or transferred to home under care of a home intravenous provider Note: Patient status code 08 is changed from active to inactive effective for claims received on or after September 30, 2009, for claims with discharge dates on or after October 1, 2005. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-29 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Form Field Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Narrative Description/Explanation 20 Expired 30 Still a patient 43 Discharged or transferred to a federal healthcare facility 50 Discharged to hospice – home 51 Discharged to hospice – medical facility 61 Discharged or transferred within this institution to hospital-based Medicare swing bed 62 Discharged or transferred to another rehabilitation facility including discharge planning units of hospital 63 Discharged or transferred to a long-term care hospital Note: Long-term care facility changed to long-term care hospital for claims with a date of receipt September 30, 2009 and after. 64 Discharged or transferred to a nursing facility – Medicaid-certified but not Medicare-certified 65 Discharged or transferred to a psychiatric hospital or psychiatric distinct part unit of a hospital 66 Discharged or transferred to a critical access hospital (effective January 1, 2006) 70 Discharged or transferred to another type of healthcare institution not defined elsewhere in the code list Note: Effective September 30, 2009, for claims with discharge dates on or after April 1, 2008. 18 – 24 Seven maximum allowed 71 Discharged, transferred, or referred to another institution for outpatient services when specified by the discharge plan of care 72 Discharged, transferred, or referred within this facility for outpatient services when specified by the discharge plan of care CONDITION CODES – Enter the applicable code to identify conditions relating to this bill that may affect processing. A maximum of seven codes can be entered. Required, if applicable. The IHCP uses the following codes: Condition Codes Code Description 02 Condition is employment related 03 Patient covered by insurance not reflected here 05 Lien is filed 07 Medicare hospice by nonhospice provider Accommodation Code Code 40 Description Same-day transfer Prospective Payment Codes Code 8-30 Description 61 Cost outlier 82 Noncovered by other insurance Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Form Field Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Narrative Description/Explanation Special Program Indicator Codes Code Description A7 Induced abortion, danger to life A8 Induced abortion, victim of rape or incest 25 – 28 CONDITION CODES – Not used. 29 ACDT STATE – Enter the state where the accident occurred. Optional. 30 Unlabeled Field – Not applicable. 31a – 34b OCCURRENCE CODE and DATE – Enter the applicable code and associated date to identify significant events relating to this bill that may affect processing. Dates are entered in an MMDDYY format. A maximum of eight codes and associated dates can be entered. Required, if applicable. The IHCP uses the following codes: Occurrence Codes Code Description 01 Auto accident 02 No-fault insurance involved – including auto accident or other 03 Accident or tort liability 04 Accident or employment related 05 Other accident 06 Crime victim 25 Date benefits terminated by primary payer 27 Date home health plan established or last reviewed 50 Previous hospital discharge – This code is used to bypass prior authorization (PA) editing when certain nursing and therapy services are to be conducted during the initial period following a hospital discharge. The discharge orders must include the requirement for such services. Details can be found in the applicable sections of the Indiana Administrative Code (IAC). 51 Date of discharge – This code is used to show the date of discharge from the hospital confinement being billed, the date of discharge from a long-term care facility, or the date of discharge from home health care, as appropriate. Note: Effective July 1, 2004, when billing for a date of service that is the same as the date of death, hospice providers must bill occurrence code 51. 52 Initial examination – This code is used to show that an initial examination or initial evaluation is being billed in a hospital setting. This code bypasses certain PA editing. Details can be found in the applicable sections of the IAC. 53 Therapy evaluation, HHA – This code is used to show HHA billing for initial therapy evaluations. This code exempts the evaluation from PA editing. Revenue codes specific to therapy evaluations must be billed. Details can be found in the applicable section of the IAC. 61 Home health overhead amount – one per day 62 Home health overhead amount – two per day; occurrence code not valid for dates of service on or after July 1, 2008 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-31 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Form Field 35a–36b Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Narrative Description/Explanation 63 Home health overhead amount – three per day; occurrence code not valid for dates of service on or after July 1, 2008 64 Home health overhead amount – four per day; occurrence code not valid for dates of service on or after July 1, 2008 65 Home health overhead amount – five per day; occurrence code not valid for dates of service on or after July 1, 2008 66 Home health overhead amount – six per day; occurrence code not valid for dates of service on or after July 1, 2008 OCCURRENCE SPAN CODE, FROM/THROUGH – Enter the code and associated dates for significant events relating to this bill. Each Occurrence Span Code must be accompanied by the span From and Through date. The only valid home health overhead Occurrence Span Code is 61. Optional. Occurrence Span Code Code 61 Description Home health overhead amount – one per day 37 UNLABELED FIELD – Enter the Care Select primary medical provider (PMP) two-character alphanumeric certification code for dates of service rendered. Required for IHCP members enrolled in Care Select when the service is not rendered by the member’s PMP, with exception of outpatient laboratory, pathology, radiology, and therapy services performed in a hospital setting for Care Select members. The bypass of these outpatient hospital services is based on the revenue codes being billed. Revenue codes and descriptions that bypass the two-digit PMP certification code are denoted in Table 8.5: Revenue Codes with Descriptions. Report the PMP NPI in field 78 for claim reimbursement of these hospital services. 38 UNLABELED FIELD – Not applicable. 39a – 41d VALUE CODES – Use these fields to identify Medicare Remittance Notice (MRN) information. The following value codes must be used along with the appropriate dollar or unit amounts for each. Required, if applicable. 42 8-32 • Value Code A1 – Medicare deductible amount • Value Code A2 – Medicare coinsurance amount • Value Code 06 – Medicare blood deductible amount • Value Code 80 – IHCP covered days REV. CD. – Enter the applicable revenue code that identifies the specific accommodation, ancillary service, or billing calculation. The appropriate three-digit, numeric revenue code must be entered to explain each charge entered in form field 47. Refer to the IAC for covered services, limitations, and medical policy rules. Use the specific revenue code when available. Required. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Form Field 43 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Narrative Description/Explanation DESCRIPTION – Enter a narrative description of the related revenue code category on this bill. Abbreviations may be used. Only one description per line. Optional. 1. Enter the NDC qualifier of N4 in the first two positions on the left side of the field. 2. Enter the NDC 11-digit numeric code in the ‘5-4-2’ format. Do not include hyphens. 3. Enter the NDC Unit of Measurement Qualifier. - F2 – International Unit - GR – Gram - ML – Milliliter - UN – Unit 4. Enter the NDC Quantity (administered amount) with up to three decimal places, such as 1234.567. REQUIRED for NDC billing for Revenue codes 634, 635, and 636 when applicable. 44 HCPCS/RATES – Use the Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS) code applicable to the service provided. Only one service code per line is permitted. Required for home health, outpatient, and ASC services. This field is also used to identify procedure code modifiers. Provide the appropriate modifier, as applicable. Up to four modifiers are allowed for each procedure code. This is a 13-character field. Required, if applicable. 45 SERV. DATE – Provide the date the indicated outpatient service was rendered. Required for home health, hospice, independent laboratories, dialysis, ASC, and outpatient. Creation Date Field 45, line 23 – enter the date the bill is submitted. Required. 46 SERV. UNITS – Provide the number of units corresponding to the revenue code or procedure code submitted. Seven digits are allowed. Units must be billed using whole numbers. Required. 47 TOTAL CHARGES – Enter the total charges pertaining to the related revenue code for the STATEMENT COVERS PERIOD. Enter the sum of all charges billed reflected in field 47, line 23. The sum should be entered only on the last page of the claim. Ten digits are allowed per line, such as 99999999.99. Required. 48 NON-COVERED CHARGES – Not applicable. Information entered in this field, and applied to the bill, results in an out-of-balance bill and subsequent denial. Do not enter information in this field. 49 UNLABELED FIELD – Not applicable. 50A–55C FORM FIELDS 50A-55C – Medicare is always listed first (50A), if applicable. Other insurers, such as a Medicare supplement (commercial insurer), are listed in the second form field (50b), if applicable. The IHCP information is listed last (50C). EXCEPTION: Section 5-1 notes that the IHCP is primary to Children’s Special Health Care Services (CSHCS) and Victim Assistance coverage. Required, if applicable. FORM FIELDS 50A-C – Such as Medicare, Medicare supplement, and Traditional Medicaid. Required, if applicable. 50A PAYER – Enter the Medicare carrier’s name. Required, if applicable. 50B PAYER – Enter the third-party carrier’s name (including Medicare Replacement/HMO) and additional payer names. Required, if applicable. 50C PAYER – Enter the applicable IHCP, such as Traditional Medicaid or 590 Program. Required. 51A–51C HEALTH PLAN ID – The Payer C, billing IHCP provider number is entered in fields 56 and/or 57. Provider numbers pertaining to 50A, Medicare Payer, or 50B, TPL Payer, are optional. 52A–52C REL INFO – Not applicable. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-33 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Form Field Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Narrative Description/Explanation 53A–53C ASG BEN – Mark Y for yes, benefits assigned. The IHCP Provider Agreement includes details about accepting payment for services. Optional. 54A–54C PRIOR PAYMENTS – Enter the amount paid by the carrier entered in form fields 50A-C. Required, if applicable. Note: When a third-party liability (TPL) carrier makes payment on a claim, the explanation of benefits (EOB) is not required. If the Medicare payment is greater than zero, the MRN is not required. 55A–55C EST. AMOUNT DUE – Not applicable. 55C EST. AMOUNT DUE – Enter the amount billed. Calculate the estimated amount due by subtracting the amounts in fields 54A-C from form field 47, Revenue Code 001, Total Charge Amount. This field accommodates 10 digits, such as 99999999.99. Required. 56 NPI – Enter the 10-digit NPI for the billing provider. The billing physician’s taxonomy should be entered in field 81CCa. Required for healthcare providers. 57A OTHER PROVIDER ID – Effective October 1, 2009, healthcare providers no longer enter the Legacy Provider Identifier (LPI) in this field. 57C Other Provider ID – Atypical providers enter the LPI for the billing provider. The LPI includes nine numeric characters and one alpha character for the service location. 58A–58C INSURED’S NAME – Enter member’s last name, first name, and middle initial. IHCP member information is required. Enter TPL information. Required, if applicable. 59A–59C P. REL – Not applicable. 60A–60C INSURED’S UNIQUE ID – Enter the member’s identification number for the respective payers entered in form fields 50A-C. The 12-digit member identification (RID) number is required in form field 60c. Other carrier information is required, if applicable. 61A–61C GROUP NAME – Enter the name of the group or plan through which insurance is provided to the member by the respective payers entered in form fields 50A-C. Required, if applicable. 62A–62C INSURANCE GROUP NO. – Enter the identification number, control number, or code assigned by the carrier or administrator to identify the group under which the individual is covered; see form fields 50A-B. Enter the policy number as well. Required, if applicable. 63A–63C TREATMENT AUTHORIZATION CODES – Enter the number that indicates the payer authorized the treatment covered by this bill. Optional. 64A–64C DOCUMENT CONTROL NUMBER – Not applicable. 65A–65C EMPLOYER NAME – Enter the name of the employer that might or does provide healthcare coverage for the insured individual identified in form field 58. Required, if applicable. 66 DX – Not applicable. 8-34 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Form Field 67 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Narrative Description/Explanation PRIN. DIAG. CD – Provide the International Classification of Diseases, 9th Edition Clinical Modification (ICD-9-CM) code describing the principal diagnosis, for example, the condition established after study to be chiefly responsible for the admission of the patient for care. Required for inpatient, outpatient, LTC, hospice, ASC, and home health. Enter present on admission (POA) in the shaded area of field 67: • Y (for yes) – Present at the time of inpatient admission. • N (for no) –Not present at the time of inpatient admission. • U (for unknown) – The documentation is insufficient to determine if the condition was present at the time of inpatient admission. • W (for clinically undetermined) –The provider is unable to clinically determine whether the condition was present at the time of inpatient admission. • 1 (one) (for unreported/not used) –Diagnosis is exempt from POA reporting. Note: The International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Edition, Clinical Modifications (ICD9-CM) Official Guidelines for Coding and Reporting includes a list of diagnosis codes that are exempt from POA reporting. Use POA indicator 1 only for codes on the list. 67A-Q OTHER DIAGNOSIS CODES – Provide the ICD-9-CM codes corresponding to additional conditions that coexist at the time of admission, or that develop subsequently, and that have an effect on the treatment received or the length of stay. Required, if applicable, for inpatient, outpatient, hospice, ASC, and home health. Enter POA in the shaded areas of field 67A-Q: • Y (for yes) – Present at the time of inpatient admission. • N (for no) – Not present at the time of inpatient admission. • U (for unknown) – The documentation is insufficient to determine if the condition was present at the time of inpatient admission. • W (for clinically undetermined) – The provider is unable to clinically determine whether the condition was present at the time of inpatient admission. • 1 (one) (for unreported/not used) – Diagnosis is exempt from POA reporting. Note: The International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Edition, Clinical Modifications (ICD9-CM) Official Guidelines for Coding and Reporting includes a list of diagnosis codes that are exempt from POA reporting. Use POA indicator 1 only for codes on the list. 68 UNLABELED FIELD – Not applicable. 69 ADM. DIAG. CD – Enter the ICD-9-CM code provided at the time of admission as stated by the physician. Required for inpatient and LTC. 70 PATIENT REASON DX – Enter the ICD-9-CM code that reflects the patient’s reason for visit at the time of outpatient registration. Optional for outpatient. 71 PPS CODE – Not applicable. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-35 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Form Field Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Narrative Description/Explanation 72 ECI (E-CODE) – If used, use the appropriate E-code provided at the time of admission as stated by the physician. The E-code indicates the external cause of injury, poisoning, or adverse effect. Required, if applicable. The IHCP does not require a POA indicator in the External Cause of Injury field locator 72. If a POA indicator is entered in the External Cause of Injury field, it will be ignored and not used for AP DRG grouping. 73 UNLABELED FIELD – Not applicable. 74 PRINCIPAL PROCEDURE CODE/DATE – Use the ICD-9-CM procedure code that identifies the principal procedure performed during the period covered by this claim, and the date the principal procedure described on the claim was performed. Required for inpatient procedures. 74a-e OTHER PROCEDURE CODE/DATE – Use the ICD-9-CM procedure codes identifying all significant procedures other than the principal procedure, and the dates, identified by code, the procedures were performed. Report the codes that are most important for the encounter and specifically any therapeutic procedures closely related to the principal diagnosis. Required, when appropriate, for inpatient procedures. 75 UNLABELED FIELD – Not applicable. 76 ATTENDING PHYS. ID – Enter the attending physician’s 10-digit numeric NPI. The attending physician’s taxonomy should be entered in field 81CCb. Required for inpatient, outpatient, ASC, and LTC. 77 OPERATING PHYS ID – Enter the operating physician’s 10-digit numeric NPI. Required for inpatient. 78 OTHER – Enter other physician’s (referring/PMP physician) 10-digit numeric NPI. Required for IHCP members enrolled in Care Select. 79 OTHER – Not applicable. 80 REMARKS – Use this field for claim note text. Provide information, using as many as 80 characters that may be helpful in further describing the services rendered. Optional. Note: The Claim Note Text field is not used systematically for claim processing at this time, but may be used by the Claim Resolutions Unit for more information if the claims suspend for review during processing. 81CC a, b 8-36 ADDITIONAL CODES – Enter B3 taxonomy qualifier and corresponding 10-digit alphanumeric taxonomy code. Optional. Taxonomy may be needed to establish a one-to-one NPI/LPI match if the provider has multiple locations. 81CC a – first box B3 qualifier, second box taxonomy code for billing provider from field 56 81CC b – first box B3 qualifier, second box taxonomy code for attending provider from field 76 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Figure 8.1 – UB-04 Claim Form Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-37 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Table 8.5 – Revenue Codes with Descriptions Revenue Code Description 1 Total charge 100 All inclusive room and board plus ancillary 101 All inclusive room and board 11X Room and board – private (medical or general) 110 General 111 Medical/surgical/gynecological 112 Obstetrics 113 Pediatric 114 Psychiatric 115 Hospice 116 Detoxification 117 Oncology 118 Rehabilitation 119 Other 12X Room and board – semiprivate (two beds) (medical or general) 120 General 121 Medical/surgical/gynecological 122 Obstetrics 123 Pediatric 124 Psychiatric 125 Hospice 126 Detoxification 127 Oncology 128 Rehabilitation 129 Other 13X Room and board – semiprivate three to four beds 130 General 131 Medical/surgical/gynecological 132 Obstetrics 133 Pediatric 134 Psychiatric 135 Hospice 136 Detoxification 137 Oncology 138 Rehabilitation 139 Other 8-38 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Revenue Code Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Description 14X Room and board – private (deluxe) 140 General 141 Medical/surgical/gynecological 142 Obstetrics 143 Pediatric 144 Psychiatric 145 Hospice 146 Detoxification 147 Oncology 148 Rehabilitation 149 Other 15X Room and board – ward (medical or general) 150 General 151 Medical/surgical/gynecological 152 Obstetrics 153 Pediatric 154 Psychiatric 155 Hospice 156 Detoxification 157 Oncology 158 Rehabilitation 159 Other 16X Room and board – other 160 General 164 Sterile environment 167 Self-care 169 Other 17X Nursery 170 General classification 171 Newborn – Level I 172 Newborn – Level II 173 Newborn – Level III 174 Newborn – Level IV 175 Neonatal intensive care 179 Other 18X Leave of absence 180 General Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-39 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Revenue Code Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Description 181 Patient convenience – No charges billed 182 Patient convenience – Charges billable 183 Therapeutic leave 184 From ICF/MR for any purpose 185 From nursing home for hospitalization 189 Other leave of absence 19x Subacute Care 190 General 191 Subacute Care – Level I 192 Subacute Care – Level II 193 Subacute Care – Level III 194 Subacute Care – Level IV 199 Other Subacute Care 20X Intensive care 200 General 201 Surgical 202 Medical 203 Pediatric 204 Psychiatric 206 Intermediate Intensive Care Unit (ICU) 207 Burn care 208 Trauma 209 Other intensive care 21X Coronary care 210 General 211 Myocardial infarction 212 Pulmonary care 213 Heart transplant 214 Intermediate Coronary Care Unit (CCU) 219 Other coronary care 22X Special charges 220 General 221 Admission charge 222 Technical support charge 223 UR service charge 224 Late discharge, medically necessary 229 Other special charges 8-40 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Revenue Code Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Description 23X Incremental nursing care rate 230 General 231 Nursery 232 Obstetrics 233 ICU 234 CCU 235 Hospice 239 Other 24X All inclusive ancillary 240 General 241 Basic 242 Comprehensive 243 Specialty 249 Other all inclusive ancillary 25X Pharmacy 250 General 251 Generic drugs 252 Nongeneric drugs 253 Take-home drugs 254 Drugs/incidental to other diagnosis services 255 Drugs/incidental to radiology 256 Experimental drugs 257 Nonprescription 258 Intravenous (IV) solutions 259 Other pharmacy 26X IV therapy 260 General 261 Infusion pump 262 Pharmacy services 263 Drug/supply delivery 264 Supplies 269 Other IV therapy 27X Medical/surgical supplies and devices 270 General 271 Nonsterile supply 272 Sterile supply 273 Take home supplies Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-41 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Revenue Code Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Description 274 Prosthetic/orthotic devices 275 Pacemaker 276 Intraocular lens 277 Oxygen – take home 278 Other implants 279 Other supplies/devices 28X Oncology 280 General 289 Other oncology 29X Durable medical equipment (other than renal) 290 General 291 Rental 292 Purchase of new DME 293 Purchase of used DME 294 Supply/drugs for DME effectiveness (HHAs only) 299 Other equipment 30X Laboratory 300 General 301 Chemistry 302 Immunology 303 Renal patient (home) 304 Nonroutine dialysis 305 Hematology 306 Bacteriology and microbiology 307 Urology 309 Other laboratory 31X Laboratory pathological 310 General 311 Cytology 312 Histology 314 Biopsy 319 Other 32X Radiology – diagnostic 320 General 321 Angiocardiography 322 Arthrography 323 Arteriography 8-42 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Revenue Code Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Description 324 Chest X-ray 329 Other 33X Radiology – therapeutic and/or chemotherapy administration 330 General 331 Chemotherapy administration – injected 332 Chemotherapy administration – oral 333 Radiation therapy 335 Chemotherapy administration – IV 339 Other 34X Nuclear medicine 340 General 341 Diagnostic 342 Therapeutic 343 Diagnostic radiopharmaceuticals 344 Therapeutic radiopharmaceuticals 349 Other 35X CT Scan (Computed Tomographic Scan) 350 General 351 Head scan 352 Body scan 359 Other CT scans 36X Operating room services 360 General 361 Minor surgery 362 Organ transplant other than kidney 367 Kidney transplant 369 Other operating room services 37X Anesthesia 370 General 371 Anesthesia incident to radiology 372 Anesthesia incident to other diagnostic services 374 Acupuncture 379 Other anesthesia 38X Pints Blood 380 General 381 Packed red cells 382 Whole blood Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-43 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Revenue Code Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Description 383 Plasma 384 Platelets 385 Leukocytes 386 Other components 387 Other derivatives (cryoprecipitates) 389 Other blood 39X Blood and blood component administration, processing, and storage 390 General 391 Administration 392 Processing and Storage 399 Other processing and storage 40X Other 400 General 401 Diagnostic mammography 402 Ultrasound 403 Screening mammography 404 Positron Emission Tomography (PET) 409 Other 41X Treatments – respiratory services 410 General 412 Inhalation services 413 Hyperbaric oxygen therapy 419 Other respiratory services 42X Treatments – physical therapy 420 General 421 Visit charge 422 Hourly charge 423 Group rate 424 Evaluation or reevaluation 429 Other physical therapy 43X Treatments – occupational therapy 430 General 431 Visit charge 432 Hourly charge 433 Group rate 434 Evaluation or reevaluation 439 Other occupational therapy 8-44 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Revenue Code Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Description 44X Treatments – speech-language pathology 440 General 441 Visit charge 442 Hourly charge 443 Group rate 444 Evaluation or reevaluation 449 Other speech-language pathology 45X Emergency room 450 General 451 Emergency medical screening service (EMTALA) 454 ER beyond EMTALA screening 456 Urgent Care 459 Other ER 46X Pulmonary function 460 General 469 Other pulmonary function 47X Audiology 470 General 471 Diagnostic 472 Treatment 479 Other audiology 48X Cardiology 480 General 481 Cardiac cath lab 482 Stress test 483 Echocardiology 489 Other cardiology 49X Ambulatory surgical care 490 General 499 Other ambulatory surgical care 50X Outpatient services 500 General 509 Other outpatient services 51X Clinic 510 General 511 Chronic pain center 512 Dental clinic Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-45 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Revenue Code Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Description 513 Psychiatric clinic 514 OB/GYN clinic 515 Pediatric clinic 516 Urgent care clinic 517 Family practice clinic 519 Other clinic 52X Freestanding clinic 520 General 521 Rural health clinic (RHC) 522 Rural health – home 523 Family practice clinic 524 Visit by RHC/Federally Qualified Health Center (FQHC) practitioner to a member in a covered part A stay at SNF 525 Visit by RHC/FQHC practitioner to a member in an SNF (not covered Part A stay) 526 Urgent care clinic 527 Visit nurse service to a member’s home in a home health shortage area 528 Visit by RHC/FQHC practitioner to other non-RHC/FQHC site 529 Other freestanding clinic 53X Osteopathic services 530 General 531 Osteopathic therapy 539 Other osteopathic services 54X Ambulance 540 General 541 Ambulance supplies 542 Ambulance medical transport 543 Ambulance heart mobile 544 Ambulance oxygen 545 Air ambulance 546 Neonatal ambulance services 547 Pharmacy 548 Telephone transmission EKG 549 Other ambulance 55X Skilled nursing 550 General 551 Visit charge 552 Hourly charge 8-46 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Revenue Code Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Description 559 Other skilled nursing 56X Medical social services 560 General 561 Visit charge 562 Hourly charge 569 Other medical social services 57X Home health aide (home health) 570 General 571 Visit charge 572 Hourly charge 579 Other home health aide 58X Home health visits, home health only 580 General 581 Visit charge 582 Hourly charge 583 Assessment 589 Other home health 59X Home health, units of service 590 General 599 Units of service/home health/other 60X Rental months oxygen (home health) 600 General 601 Oxygen – stationary equipment/supplies/contents 602 Oxygen – stationary equipment/supplies/under 1 liter per minute (LPM) 603 Oxygen – stationary equipment/supplies/over 4 LPM 604 Oxygen – portable add-on 609 Oxygen – other 61X Magnetic Resonance Technology (MRT) 610 Magnetic resonance technology 611 MRI – brain/brain stem 612 MRI – spinal cord/spine 614 MRT – other 615 Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) – head and neck 616 MRA – lower extremities 618 MRA – other 619 MRI – other 62X Medical and surgical supplies Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-47 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Revenue Code Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Description 621 Supplies incident to radiology 622 Supplies incident to other diagnostic services 623 Surgical dressings 624 Food and Drug Administration (FDA) investigational devices 63X Pharmacy 631 Single-source drugs 632 Multiple-source drugs 633 Restrictive prescription 634 Epoetin (EPO), less than 10,000 units 635 EPO, 10,000 or more units 636 Drugs requiring detailed coding 637 Self-administrable drugs not requiring detailed coding 64X Home IV therapy services 640 General 641 Nonroutine nursing, central line 642 IV site care, central line 643 IV start/change, peripheral line 644 Nonroutine nursing, peripheral line 645 Training patient/caregiver, central line 646 Training, disabled patient, central line 647 Training, patient/caregiver, peripheral line 648 Training, disabled patient, peripheral line 649 Other IV therapy services 65X Hospice service 650 General 651 Routine home care 652 Continuous home care 653 Hospice services/routine home care delivered in nursing home 654 Hospice services/continuous home care delivered in nursing home 655 Inpatient respite care 656 General inpatient care (nonrespite) 657 Physician services 658 Hospice room and board – nursing facility 659 Other hospice 66X Respite care 660 General 661 Hourly charge/nursing 8-48 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Revenue Code Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Description 662 Hourly charge/aide/homemaker/companion 663 Daily respite care 669 Other respite care 67X Outpatient special residence charges 670 General 671 Hospital-based 672 Contracted 679 Other special residence charges 68X Trauma response 681 Level I 682 Level II 683 Level III 684 Level IV 689 Other trauma response 70X Cast room 700 General 71X Recovery room 710 General 719 Other recovery room 72X Labor room/delivery 720 General 721 Labor 722 Delivery 723 Circumcision 724 Birthing center 729 Other labor room/delivery 73X Electrocardiogram (EKG/ECG) 730 General 731 Holter monitor 732 Telemetry 739 Other EKG/ECG 74X EEG (electroencephalogram) 740 General 749 Other EEG 75X Gastrointestinal services 750 General 759 Other gastrointestinal Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-49 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Revenue Code Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Description 76X Treatment/observation room 760 General 761 Treatment Room 762 Observation Room 769 Other Treatment/Observation Room 77X Preventive care services 770 General 771 Vaccine administration 779 Other preventive care service 78X Telemedicine 780 General 789 Other telemedicine 79X Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT) 790 General 799 Other Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy 80X Inpatient renal dialysis 800 General 801 Inpatient hemodialysis 802 Inpatient peritoneal (Non-CAPD) 803 Inpatient continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD) 804 Continuous cycling peritoneal dialysis (CCPD) 809 Other inpatient dialysis 81X Acquisition of body components 810 General 811 Living donor 812 Cadaver donor 813 Unknown donor 814 Unsuccessful organ search – donor bank charges 815 Heart/cadaver 816 Heart/other 817 Liver/acquisition 819 Other donor 82X Hemodialysis – outpatient or home 820 General 821 Hemodialysis/composite or other rate 822 Home supplies 823 Home equipment 8-50 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Revenue Code Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Description 824 Maintenance – 100 percent 825 Support services 828 Hemodialysis home/supervision 829 Other outpatient hemodialysis 83X Peritoneal dialysis – outpatient or home 830 General 831 Peritoneal/composite or other rate 832 Home supplies 833 Home equipment 834 Maintenance – 100 percent 835 Support services 839 Other outpatient peritoneal dialysis 84X CAPD – outpatient or home 840 General 841 CAPD/composite or other rate 842 Home supplies 843 Home equipment 844 Maintenance 100 percent 845 Support services 849 Other outpatient CAPD 85X CCPD – outpatient or home 850 General 851 CCPD/composite or other rate 852 Home supplies 853 Home equipment 854 Maintenance – 100 percent 855 Support services 859 Other outpatient CCPD 88X Dialysis 880 General 881 Ultrafiltration 882 Home dialysis aid visit 889 Miscellaneous dialysis/other 890 Donor bank 891 Bone 892 Organ other than kidney 893 Skin Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-51 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Revenue Code Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Description 899 Other 89X Other donor bank 90X Behavioral health treatments/services 900 General 901 Electroshock treatment 902 Milieu treatment 903 Play therapy 904 Activity therapy 905 Intensive outpatient services – psychiatric 906 Intensive outpatient services – chemical dependency 907 Community behavioral health program (day treatment) 909 Psych treatment (other) 91X Behavioral health treatments/services 910 General 911 Rehabilitation 912 Partial hospitalization – less intensive 913 Partial hospitalization – intensive 914 Individual therapy 915 Group therapy 916 Family therapy 917 Biofeedback 918 Testing 919 Other behavioral health treatments/services 92X Other diagnostic services 920 General 921 Peripheral vascular lab 922 Electromyelogram 923 Pap smear 924 Allergy test 925 Pregnancy test 929 Other diagnostic services 93X Medical rehabilitation day program 931 Half day 932 Full day 94X Other therapeutic services 941 Recreational therapy 942 Education/training 8-52 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Revenue Code Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Description 943 Cardiac rehabilitation 944 Drug rehabilitation 945 Alcohol rehabilitation 946 Complex medical equipment – routine 947 Complex medical equipment – ancillary 948 Pulmonary rehabilitation 949 Other therapeutic services 95X Other therapeutic services 951 Athletic training 952 Kinesiotherapy 96X Professional fees 960 General 961 Psychiatric 962 Ophthalmologist 963 Anesthesiologist (MD) 964 Anesthetist (CRNA) 969 Other professional fees 97X Professional fees 970 General 971 Laboratory 972 Radiology/diagnostic 973 Therapeutic radiology 974 Radiology/nuclear medicine 975 Operating room 976 Respiratory therapy 977 Physical therapy 978 Occupational therapy 979 Speech therapy 98X 980 981 982 983 984 985 986 987 988 Professional fees General Emergency room Outpatient services Clinic Medical social services EKG EEG Hospital visit Consultation Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-53 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Revenue Code Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Description 989 Private duty nurse 99X 990 991 992 993 994 995 996 997 998 999 Patient convenience items General Cafeteria/guest tray Private linen service Telephone/telegraph TV/radio Nonpatient room rentals Late discharge charge Admission kits Beauty shop/barber Other patient convenience items Diagnostic and Therapeutic Codes Not Reimbursable Under revenue codes 92x – Other Diagnostic Services and 94x – Other Therapeutic Services, the IHCP does not reimburse revenue codes 920, 929, 940, 941, 942, 944, 945, 946, 947, or 949. Providers must use an appropriate revenue code that is descriptive of the service or where the service was performed. Table 8.6 shows a list of nonreimbursable codes under 92x and 94x. Table 8.6 – Diagnostic and Therapeutic Services Not Reimbursable by the IHCP Revenue Code Description 920 Other Diagnostic Services – General 929 Other Diagnostic Service – Other Diagnostic Service 940 Other Therapeutic Service – General 941 Other Therapeutic Service – Recreational Therapy 942 Other Therapeutic Service – Education/Training 944 Other Therapeutic Service – Drug Rehabilitation 945 Other Therapeutic Service – Alcohol Rehabilitation 946 Other Therapeutic Service – Complex Medical Equipment – Routine 947 Other Therapeutic Service – Complex Medical Equipment – Ancillary 949 Other Therapeutic Service – Additional Therapeutic Services Therapeutic and diagnostic injections are performed within a number of treatment centers in a hospital, including but not limited to an operating room (360), emergency room (450), or clinic (510). Similar to Medicare policy, IHCP policy requires that hospitals report these injections under the revenue code for the treatment center where injections are performed. This is also consistent with rate setting for treatment rooms as costs for injections were considered when establishing treatment room rates. Injections are included in the reimbursement of the treatment room when other services are provided. However, if a patient is treated and only received the injection service, the provider will be reimbursed the flat fee of the appropriately billed treatment room revenue code. Claims using the 8-54 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions revenue codes in the 92x and 94x series listed above may have previously denied with Explanation of Benefits (EOB) code 4014 – No pricing segment on file. Claims billed with these revenue codes now deny with EOB code 4107 – Revenue code is not appropriate or not covered for the type of service being provided. UB-04 Claim Types When billing National Drug Codes (NDCs) that have one procedure code but that involve multiple NDCs, providers will no longer need to use the KP and KQ modifiers. Providers will bill the claim with the appropriate NDC for the drug they are dispensing on separate detail lines. For example, if a provider administers 150 mg of Synagis, most likely a 50 mg vial plus a 100 mg vial would be used. These two vials have different NDCs but one procedure code; therefore the item would be billed with two detail lines for the same procedure code and the corresponding NDCs. This change includes crossover claims as well. Compounds – Outpatient/Outpatient Crossover When billing any compound drugs that require an NDC, providers must bill the appropriate NDC for each procedure code. Providers will receive payment for all valid NDCs included in the compound drugs. Home Health Services Coverage Home health services are available to IHCP members medically confined to the home, when services are ordered in writing from a physician and performed in accordance with the written plan of care. It is important to note that there is a distinction between the Medicare home health definition of “homebound” and Indiana Medicaid’s definition of “homebound.” The Medicaid program serves a more expansive age range than the Medicare program. Home health services may be provided to those who are medically confined to the home, including IHCP members who, because of illness or injury, are unable to leave home without the assistance of another person or an assistive device, or for whom leaving home is contrary to medical advice. As such, Medicaid members may work, attend school outside the home, and leave the home with assistance of another person or an assistive device, such as a wheelchair or walker. Home health services can be provided if medically necessary to assist in these day-to-day functions. The following sections provide specific billing procedures for home health services. Providers should refer to Rule 16, 405 IAC 5-16-3, home health agency services limitations, for detailed information about coverage and PA requirements. Billing Procedures Submit home health claims electronically, or mail to the following address for processing: HP Home Health Claims P.O. Box 7271 Indianapolis, IN 46207-7271 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-55 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Note: For risk-based managed care (RBMC) members, bill the appropriate managed care organization (MCO). Contact information can be found in Chapter 1 of this manual. Home health providers follow the general billing directions for completing the UB-04 claim form with the exception of the service date, local codes, and the additional type of bill codes. In field 44, HCPCS/RATES, providers must enter the HCPCS/CPT code for the service provided, not the rate. Table 8.7 lists revenue codes and the crosswalked HCPCS/CPT codes. Table 8.7 – Revenue Codes/HCPCS/CPT Codes Revenue Code HCPCS/ CPT Code Revenue Code HCPCS/ CPT Code Revenue Code HCPCS Code 420 G0151 421 G0151 422 G0151 423 G0151 424 97001 429 G0151 430 G0152 431 G0152 432 G0152 433 G0152 434 97003 439 G0152 440 G0153 441 G0153 442 G0153 443 G0153 444 92506 449 G0153 552 99600 TE 552 99600 TD 559 S9349 559 99601, 99602 572 99600 Unit of Service Each line item identifies services billed using HCPCS codes and service dates. Providers must bill each date of service as a separate line item and bill each level of service, such as registered nurse (RN) or licensed practical nurse (LPN), provided on the same date as a separate line item. The procedure code description defines the unit of service. When home health providers perform the same service, such as multiple RN visits on the same date of service, they must bill those services on the same claim form and on one detail with the total number of units of services provided. Billing separate lines for the same service with the same date of service causes claims to be denied as exact duplicates. The Office of Medicaid Policy and Planning (OMPP) sets the rate for each procedure code. The billing units of home health visits for therapists, home health aides, LPNs, and RNs are as follows: • For therapy visits – If the therapist is in the home eight minutes or more, the provider can round the visit up to the 15-minute unit of service. If the therapist is in the home for seven minutes or less, the provider cannot round this up and therefore cannot bill for it. Therapy codes are measured as one unit equals 15 minutes. • For home health aides, LPN, or RN visits – If the home health aide, LPN, or RN is in the home for fewer than 29 minutes, providers can bill for the entire first hour only if they provided a service. For subsequent hours in the home, providers should use the partial unit procedure as outlined in the subsection of this chapter titled Partial Units of Service. Nursing services are measured as one unit equals one hour. If the therapist, home health aide, LPN, or RN enters the home and the member refuses service, providers cannot bill for any unit of service. Overheads are linked with reimbursement for services provided. Because providers rendered no service, they cannot be reimbursed for the overhead. 8-56 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Overhead Rate For services rendered prior to July 1, 2008 – for each encounter at the home, regardless of the type of service provided or the number of members serviced – home health providers receive an overhead rate for administrative costs and a staffing reimbursement component, depending on the type and number of units of service provided. The OMPP calculates the overhead rates and staffing reimbursement. These rates are the same for all agencies. An encounter occurs when an RN, LPN, home health aide, or therapist enters a home, provides services to one or more members within that home, and then leaves, thereby completing the encounter. When more than one member receives home health services in a single household, providers must coordinate care in the most efficient manner. Providers must report multiple-care member situations on PA requests. Providers may only bill one overhead per provider, per recipient per day. Effective for claims with dates of service on or after July 1, 2008, occurrence codes 62 – 66, are no longer active. Home health claims billed with occurrence codes 62 – 66, and a date of service on or after July 1, 2008, will be denied with the following Explanation of Benefit (EOB) code: 0515 - The overhead fee is not on file for the dates of service indicated or the home health occurrence code is invalid for the date of service. Please verify and resubmit. Occurrence codes 62 – 66 are active for claims that are billed or adjusted with dates of service through June 30, 2008. Providers use the UB-04 occurrence code, occurrence date, and occurrence span for fields 31-34, a–b, on the UB-04 to indicate the appropriate overhead fees. Use the following six codes to identify the overhead rate: • Code 61 indicates that one encounter with the member occurred on the date shown. • Code 62 indicates that two encounters occurred on the date shown: - These may be the same service or a combination of services provided on one day. - Example: One skilled nurse encounter and one home health aide encounter, or two home health aide encounters of care. Occurrence code not valid for dates of service on or after July 1, 2008. • Code 63 indicates that three encounters occurred on the date shown: - These may be the same service or a combination of services provided on one day. - Example: One physical therapy encounter, one skilled nurse encounter, and one home health aide encounter. Occurrence code not valid for dates of service on or after July 1, 2008. • Code 64 indicates that four encounters occurred on the date shown: - These may be the same service or a combination of services provided on one day. - Example: In limited pediatric cases, the need for more than three overhead charges in one 24hour period may occur. Occurrence code not valid for dates of service on or after July 1, 2008. • Code 65 indicates that five encounters occurred on the date shown: - These may be the same service or a combination of services provided on one day. - Example: In limited pediatric cases, the need for more than four overhead charges in one 24hour period may occur. Occurrence code not valid for dates of service on or after July 1, 2008. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-57 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions • Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Code 66 indicates that six encounters occurred on the date shown: - These may be the same service or a combination of services provided on one day. - Example: In limited pediatric cases, the need for more than five overhead charges in one 24hour period may occur. Occurrence code not valid for dates of service on or after July 1, 2008. Note: Use codes 64–66 only in exceptional circumstances. The OMPP closely monitors these codes. If the OMPP overpays a provider for overhead component occurrences, the provider is responsible for completing a paper adjustment form or an electronic void or replacement. Occurrence codes 64, 65, and 66 are not valid for dates of service on or after July 1, 2008. • If the dates of service billed are not consecutive, the provider should enter the correct occurrence code corresponding to each date of service billed on the UB-04 in the occurrence code and occurrence date fields 31-34 (a-b on the paper UB-04 claim form). • If the dates of service billed are consecutive, and one encounter was provided per day, enter occurrence code 61 and the dates of service being billed in the occurrence span code field 35 a-b. • Providers cannot use occurrence codes 62 - 66 in the occurrence span code field. Providers that submit more than one UB-04 claim form in a multiple-member care situation should submit only one form with the overhead attached. As long as the overhead is attached to only one member, it does not matter to which member it is attached. Note: Providers should not add the dollar figures associated with the overhead rates to the claim when calculating total charges. The Remittance Advice (RA) or the 835 transaction automatically reflects the appropriate overhead amounts. Home Health Rule Changes Effective July 1, 2008, pursuant to 405 IAC 1-4.2-4 (a) (1) home health agency reimbursement for State fiscal year 2009 forward will result in one overhead cost rate per provider, per recipient, per day. Home health agency rates for State fiscal year 2009 and after will be based on a new rate-setting methodology that is based on 95 percent of the unweighted median as the basis for rates. See 405 IAC 1-4.2-4 (b). The State fiscal year 2008 reimbursement methodology expired June 30, 2008. (LSA Document #07-31, Section 5.) Table 8.8 – Home Health Services Code 8-58 Service No Code Overhead 99600 TD Registered Nurse (RN) 99600 TE Licensed Practical Nurse (LPN) 99600 Home Health Aide G0151 Physical Therapy G0152 Occupational Therapy G0153 Speech Therapy Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Multiple Visit Billing When providers make multiple visits for the same prior authorized service to a member in one day, providers should bill all visits on the same claim form and on one detail with the total number of units of service provided. If providers bill these services on separate claim forms or on separate claim details, the IHCP denies one or more of the services as a duplicate service. In the event additional hours of the same service are identified after a claim has been adjudicated and paid, providers must submit a paid claim adjustment. Procedures for submitting a paid claim adjustment are in Chapter 11 of this manual. Home health agency providers should be aware that rotating personnel in the home merely to increase billing is not appropriate. Example A home health agency sent an RN to a member’s home in the morning and an LPN to the same home in the evening of July 15, 2009. The nurse performed two hours of RN services in the morning, and a second nurse performed two hours of LPN services in the evening of July 15, 2009. Detail 1: Revenue Code 552 with HCPCS 99600 TD. Date of Service is 7/15/09 and 2 in the units of service. Detail 2: Revenue Code 552 with HCPCS 99600 TE. Date of Service is 7/15/09 and 2 in the units of service. Note: In this example, providers will bill for only one overhead for dates of service July 1, 2009, and after, by entering a 61 occurrence code with a corresponding date of 7/15/09 in fields 31a-34b and 35a-36b on the UB-04 claim form. Partial Units of Service Providers must round partial units of service to the nearest whole unit when calculating reimbursement. Round up any partial unit of service of 30 minutes or more to the next highest unit, and round down any partial unit of service of 29 minutes or less to the next lowest unit. Nursing services are measured as one unit of service equals 60 minutes, while therapies are measured as one unit equals 15 minutes. • Example 1: 85 minutes spent on billable patient care activities is rounded down to one unit. • Example 2: 95 minutes spent on billable patient care activities is rounded up to two units. Hospital Discharge Providers can perform certain services without PA following IHCP member discharge from a hospital, if the parameters meet those outlined in the IAC. Within the constraints in several IAC rules, the following apply: Note: For members enrolled in Hoosier Healthwise or Care Select, providers should refer to Chapter 6 for additional information about PA. • Providers may perform home health services without PA when an RN, LPN, or home health aide performs the service, if the service does not exceed 120 units within 30 calendar days following hospital discharge. - The physician must order services in writing prior to the patient’s hospital discharge. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-59 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions - Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual The patient must be homebound. • Any combination of therapy services ordered in writing by a physician cannot continue beyond 30 units in 30 calendar days without PA. - The physician must order services in writing prior to the patient’s hospital discharge. - The patient must be homebound. • Services must be within the limits specified in 405 IAC 5-16-3. • Providers should use occurrence code 50 with the corresponding date of discharge in the occurrence code and occurrence date fields 31-34, a–b on the UB-04, to bypass PA requirements associated with the previously mentioned parameters. • Use occurrence code 53 to show HHA billing for initial therapy evaluations. This code exempts evaluations from PA editing. Providers must bill revenue codes specific to therapy evaluations. • When a provider bills for services exceeding the aforementioned parameters, and the provider has not received PA for additional units, IndianaAIM automatically denies or cuts back units on the RA. • The IHCP does not require PA for an emergency visit, but providers must request a Prior Authorization System Update from the PA Department to continue service provision. Billing Procedures for Home Infusion and Enteral Therapy Services Four provider types may bill for home infusion and enteral therapy services and supplies: • Durable medical equipment (DME) • Home medical equipment (HME) • Home health agencies (HHAs) • Pharmacies Home infusion includes the following: • Enteral feeding within, or by way of, the intestine • Enteral tube feeding that includes the provision of nutritional requirements through a tube into the stomach or small intestine • Parenteral therapy that includes any route other than the alimentary canal such as intravenous, subcutaneous, intramuscular, or mucosal • Total parenteral nutrition therapy (TPN) When providers bill for home infusion and enteral therapy, they should bill the following three components separately: 8-60 • DME and HME providers bill all supplies, equipment, and formulas required to administer home infusion and enteral therapy on a CMS-1500 claim form or 837P transaction using the appropriate HCPCS code. • HHAs bill only for services provided in the home by an RN or LPN on the UB-04 claim form or 837I transaction using the appropriate HCPCS codes. • Pharmacies bill for compound drugs or any drugs used in parenteral therapy on an IFSSA Drug Claim Form using the appropriate National Drug Code (NDC). Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Billing Procedures for Home Tocolytic Infusion Therapy Using a Home Uterine Monitoring Device HHAs may bill all three components using the proper billing forms and appropriate codes if the HHA maintains multiple enrollments as an HHA, Pharmacy and DME, or HME provider. Only those HHAs that meet the following guidelines are allowed to bill for home tocolytic infusion therapy using a home uterine monitoring device. At a minimum, the HHA must have staff that can perform the following: • Contact the patient’s physician at least weekly for updates on patient condition and compliance. • Provide home health care to pregnant women 24 hours a day, seven days a week. • Provide patient education about uterine contractions and other subtle symptoms of preterm labor. • Provide pharmacological consultation about the use of tocolytics and individualized patient dosing 24 hours a day, seven days a week. • Provide the patient with a tocolytic infusion pump and a uterine monitoring device, including setup and delivery; provide patient education about the use of the equipment; and be available to troubleshoot the equipment 24 hours a day, seven days a week. To qualify for this therapy, the member must meet the following conditions: • Be at least 24 to 34 weeks gestation. • Be in current preterm labor. Preterm labor is defined as greater than or equal to six contractions per hour. • Have a cervical dilation of greater than or equal to one centimeter, or an effacement of greater than or equal to 75 percent. • Have direct home telephone access to providers, which means having a working telephone. • Have experienced secondary failure to wean from infused tocolytics, or have failed oral therapy and requires continued infusion therapy. • Have an obstetrician or gynecologist (OB/GYN) as the referring physician or if not, have had a consultation with an OB/GYN. Three codes, S9349, 99601, and 99602, are assigned to home tocolytic infusion therapy using a home monitoring device. Code S9349 denotes the total global package of services with home health agencies providing all the components under home tocolytic infusion therapy. S9349 covers the following items: • Home uterine monitor • Skilled nursing services that include the following: - Initial nursing assessment - Instructions given to the patient about the proper use of the monitoring equipment - Home visits as needed to monitor signs and symptoms of preterm labor - Twenty-four-hour telephone support for troubleshooting on the monitoring equipment, for pharmacological support, and for patient symptoms • Ambulatory infusion pump Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-61 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual • Tocolytic drugs • All other supplies necessary to maintain a patient at home on this therapy including the following: - Conductive paste or gel - Dressings - Extra batteries for infusion pump - Sharps container - Site kits - Syringes - Tubing - Other supplies This global package also includes any costs involved in transmitting reports to the physician electronically, such as a fax or telephone modem. Codes 99601 and 99602 are used if a member meets the criteria for home tocolytic infusion therapy and the agency is providing the home uterine monitoring and skilled nursing components of the therapy only (rather than the entire package noted in S9349). When the home health agency bills 99601 and 99602, the tocolytic drugs and other supplies must be supplied and billed separately through another provider. The home health agency should provide only the home uterine monitor and the skilled nursing components of the home tocolytic infusion therapy. The home health agency may bill 99601 for the first two hours of therapy and bill 99602 for each additional hour of therapy, up to 22 additional hours for each 24-hour period. Codes 99601 and 99602 cover the following items: • Home uterine monitor • Skilled nursing services that include the following: - Initial nursing assessment - Instructions given to the patient about the proper use of the monitor - Home visits to monitor signs and symptoms of preterm labor - Twenty-four hour telephone support for troubleshooting the monitoring equipment and for reporting patient symptoms • This package also includes any costs involved in transmitting reports to the physician electronically, such as fax or telephone modem. Or providers can write to the following address to request PA: ADVANTAGE Health Solutions Prior Authorization Department P. O. Box 40789 Indianapolis, IN 46240 Note: For RBMC or Care Select members, contact the appropriate managed care entity (MCE) to obtain PA. The contact information can be found in Chapter 1 of this manual. 8-62 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions HHAs can bill for S9349, 99601, and 99602 using standard home health care billing guidelines. All supplies for each therapy are bundled into a daily rate, and HHAs are not allowed to bill separately for any supplies associated with these therapies and are not allowed to bill an overhead charge when daily infusion services do not include an actual encounter in the home. Providers are allowed to bill one unit of service daily and should use revenue code 559 when billing S9349, 99601, and 99602. Cases of premature labor treated with oral medication only, or requests for home uterine monitoring devices alone for the purpose of screening high-risk pregnancies, do not qualify for inclusion under the established criteria and are not approved. Members who receive only oral medications or who require only home uterine monitoring devices do not qualify for inclusion under the established criteria for tocolytic infusion therapy. Note: The OMPP closely monitors overhead billing associated with these procedure codes and where abuse is found, initiates recoupment efforts. Hospice Care Coverage IHCP members in need of hospice care must be eligible for program services, must have a prognosis of six months or less to live, and must elect hospice services. Available hospice services include, but are not limited to, palliative care for physical, psychological, social, and spiritual needs of the patient. Hospices can provide hospice care to an IHCP member in an inpatient setting or in the member’s home. Hospice providers must first be enrolled in the IHCP before the IHCP can reimburse them for services rendered. Note: Hospice providers should ensure that Hoosier Healthwise and Care Select members disenroll from the respective program before the member elects the hospice benefit. Billing Procedures Mail hospice claims to the following address for processing: HP Hospice Claims P.O. Box 7271 Indianapolis, IN 46207-7271 Hospice providers follow the general directions for completing the UB-04 claim form and use the following hospice-specific information to fill in the claim form. Refer to the Hospice Provider Manual on the IHCP Web site at http://provider.indianamedicaid.com for complete coverage information and billing instructions. Hospice providers are paid a per diem at the hospice level of care they are providing. Hospice providers should bill only one hospice revenue code per day. Revenue codes 183, 185, and 657 are the only revenue codes that can be billed on the same day as another hospice revenue code. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-63 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Revenue Codes Providers should use a code from the following applicable revenue codes for hospice care: Revenue Code 183: Nursing Facility Bed Hold for Hospice Therapeutic Leave Days • The hospice provider receives 50 percent of the 95 percent nursing facility (NF) case mix rate for the room and board rate associated with therapeutic leave of absence days. • A total of 18 therapeutic leave of absence days are allowed per patient, per calendar year. • One day equals one unit of service. • Revenue code 183 may be billed on the same day as other hospice revenue codes Revenue Code 185: Nursing Facility Bed Hold Policy for Hospitalization for Services Unrelated to the Terminal Illness of the Hospice Member • The hospice provider receives 50 percent of the 95 percent NF case mix rate associated with each hospitalization up to 15 days per occurrence. • One day equals one unit of service. • Revenue code 185 may be billed on the same day as other hospice revenue codes. Revenue Code 651: Routine Home Care Delivered in a Private Home • The IHCP pays the hospice at the routine home care rate for each day the member is at home, under the care of the hospice provider, and not receiving continuous home care. • The IHCP pays this rate without regard to the volume or intensity of routine home care services on any given day. • One day equals one unit of service. Note: When an IHCP-only hospice member, residing in his or her private home, is admitted to an NF for treatment of a nonterminal condition, the hospice provider must continue to bill for hospice services using revenue codes 653 or 654 while the hospice member is in the facility. When the hospice patient has resumed residence in his or her private home, the hospice provider must bill the IHCP using hospice review codes 651 or 652 for those dates of service following the discharge from the facility. Revenue Code 652: Continuous Home Care Delivered in a Private Home 8-64 • The provider gives continuous home care only during a period of crisis. • A period of crisis occurs when a patient requires continuous care, primarily nursing care, to achieve palliation and management of acute medical symptoms. • The provider must provide a minimum of eight hours of care during a 24-hour day that begins and ends at midnight. • An RN or LPN must provide care for more than half the total time. This care need not be continuous and uninterrupted. • Less skilled care needed continuously to enable the member to remain at home is covered as routine home care. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions • Divide the continuous home care per diem rate by 24 hours to calculate an hourly rate. For every hour or part of an hour of continuous care furnished, the IHCP reimburses the hourly rate to the hospice provider, up to 24 hours a day. • One hour equals one unit of service. Revenue Code 653: Routine Home Care Delivered in a Nursing Facility • The IHCP pays the hospice provider at the routine home care rate for each day the member is in an NF under the care of the hospice provider and not receiving continuous home care. • The IHCP pays this rate without regard to the volume or intensity of routine home care service on any given day. • In addition, the IHCP pays the hospice provider 95 percent of the lowest NF per diem to cover room and board costs incurred by the contracted NF. The provider should bill only normal and customary routine home care amounts as the billed amount; IndianaAIM calculates 95 percent of the lowest NF per diem and pays accordingly. • Nursing facility room and board are not billable for the date of death. • Providers also cannot bill for NF room and board for the date the member is physically discharged from the NF. • One day equals one unit of service. Revenue Code 654: Continuous Home Care Delivered in a Nursing Facility • As in the private home setting, divide the continuous home care rate by 24 hours to calculate an hourly rate. For every hour or part of an hour of continuous care furnished, the IHCP reimburses the hourly rate to the hospice provider, up to 24 hours a day. • All limitations listed for the private home setting also apply in the NF setting. • In addition, the IHCP pays the hospice an additional 95 percent of the NF case mix rate to cover room and board costs incurred by the contracted NF. • Providers cannot bill for NF room and board for the date of death. • Providers also cannot bill for NF room and board for the date the member is physically discharged from the NF. • One hour equals one unit of service. Revenue Code 655: Inpatient Respite Care • The IHCP pays the hospice provider at the inpatient respite care rate for each day the member is in an approved inpatient facility and is receiving respite care. • Respite care is short-term inpatient care provided to the member only when necessary to relieve the family members or other people caring for the member. Respite care may be provided only on an occasional basis. • The IHCP pays for respite care for a maximum of five consecutive days at a time, including the date of admission but not counting the day of discharge. • The IHCP pays for the sixth and any subsequent days at the routine home care rate. • This service applies only to members who normally reside in private homes. • The additional amount for room and board is not available for members receiving respite care. • One day equals one unit of service. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-65 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions • Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual According to 405 IAC 1-16-2(i), when a recipient is receiving general inpatient or inpatient respite care, the applicable inpatient rate (general or respite) is paid for the date of admission and all subsequent inpatient days except the day on which the patient is discharged. For the day of discharge, the appropriate home care rate is paid unless the patient dies as an inpatient. In the case where the member is discharged deceased, the applicable inpatient rate (general or respite) is paid for the date of discharge. Revenue Code 656: General Inpatient Hospice Care • The IHCP pays the hospice provider at the general inpatient hospice rate for each day the member is in an approved inpatient hospice facility and is receiving general inpatient hospice care for pain control, or acute or chronic symptom management, that cannot be managed in other settings. • This service applies only to members who normally reside in private homes. • The additional amount for room and board is not available for members receiving respite care. • One day equals one unit of service. • According to 405 IAC 1-16-2(i), when a recipient is receiving general inpatient or inpatient respite care, the applicable inpatient rate (general or respite) is paid for the date of admission and all subsequent inpatient days except the day on which the patient is discharged. For the day of discharge, the appropriate home care rate is paid unless the patient dies as an inpatient. In the case where the member is discharged deceased, the applicable inpatient rate (general or respite) is paid for the date of discharge. Revenue Code 657: Hospice Direct Care Physician Services • The IHCP reimburses on a fee-for-service (FFS) basis for physician services provided by a physician who is an employee of the hospice provider or subcontracted by the hospice. The hospice provider bills for these services under the hospice NPI. • Providers can bill this revenue code on the same day as other hospice revenue codes. • One day equals one unit of service. Revenue Code 659: Dually Eligible Nursing Facility Members Only • Use this revenue code for dually eligible members residing in an NF. • This code represents the room and board portion of the hospice per diem. • The IHCP pays the hospice provider an additional 95 percent of the NF case mix rate to cover room and board costs incurred by the contracted NF. • Revenue code 659 must not be billed with the following hospice-related revenue codes: 651, 652, 653, 654, 655, and 656. • Providers cannot bill for NF room and board for the date of death. • Providers also cannot bill for NF room and board for the date the member is physically discharged from the nursing facility. • One day equals one unit of service. Use of Condition Code 07 by Nonhospice Providers Billing Medicare for Nonterminal Conditions for a Medicare Hospice Beneficiary For Medicare beneficiaries, the Medicare Program specifies that nonhospice providers bill Medicare directly by using condition code 07 when the nonhospice provider delivers Medicare-covered services 8-66 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions to treat the nonterminal condition of a Medicare hospice beneficiary. This policy also applies to dually eligible Medicare and IHCP hospice members because the IHCP is the payer of last resort. The nonhospice provider must bill Medicare using condition code 07 in fields 18-24 on the UB-04. The Medicare Program stipulates that nonhospice providers are subject to recovery of overpayments and possible referral for fraud and abuse investigation if a pattern of incorrect use of condition code 07 is determined. Hospice or NF providers with questions about proper use of condition code 07 or a case-specific question involving a Medicare hospice beneficiary, whether the member is Medicare only or a dually eligible Medicare and IHCP hospice member, may contact the Medicare Part A Intermediary for Indiana at 1-800-633-4227. Because the IHCP is the payer of last resort, hospice providers and nursing facilities serving dually eligible Medicare and IHCP hospice members must bill Medicare first for nonhospice services, according to the parameters established by Medicare. Hospice Care in Group Homes Medicaid-eligible group home members can elect the Medicaid hospice program per the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS). The hospice should bill Medicaid for the hospice services and the group home can bill Medicaid directly for the group home per diem rate. Claims for Group homes were denied by IndianaAIM with error code 2027 – Hospice Recipient Being Billed for Non-Hospice Services. IndianaAIM has been updated and group homes should not encounter any denials for error code 2027. Hospice and group home providers should coordinate the overall care for the group home member. It is the responsibility of the hospice to provide all hospice-covered services in frequency and scope to care for the terminal illness and related conditions. Furthermore, the hospice should not delegate any hospice core services to group home staff. Any questions about the Medicaid hospice program should be directed to Family and Social Services Administration (FSSA) Division of Aging at (317) 233-1956. Physician Services under Revenue Codes 651 through 655 Reimbursement for Physician Services The basic payment rates for hospice care represent full reimbursement to the hospice provider for covered services related to the treatment of the patient’s terminal illness. Covered services include the administrative and general activities performed by physicians who are employees of, or working under arrangements made with, the hospice provider. The physician who serves as the medical director and the physician member of the hospice interdisciplinary group generally performs the following group activities: • Establishment of governing policies • Participation in the establishment of plans of care • Periodic review and update of plans of care • Supervision of care and services The costs for these services are included in the reimbursement rates for the following: • Continuous home care, revenue code 652 or 654 • Inpatient respite care, revenue code 655 • Routine home care, revenue code 651 or 653 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-67 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Physician Services under Revenue Code 657 Bill reimbursement for a hospice-employed physician’s direct patient services, not rendered by a hospice physician volunteer, as an additional service by the hospice provider, using the hospice NPI. The hospice may bill only direct patient care physician services. Laboratory and X-ray services are included in the hospice daily rates. Prior-Authorized Physician Services The IHCP reimburses a physician’s direct patient services not rendered by a hospice physician volunteer as an additional payment, in accordance with the usual IHCP reimbursement methodology for physician services. The hospice must not bill these services under the hospice NPI. An attending physician may bill only the physician’s personal professional services. Do not include the costs for services, such as laboratory or X-ray, on the attending physician’s billed charges when those services relate to the terminal condition. Include these costs in the daily hospice care rates because they are expressly the responsibility of the hospice provider. Providers may bill independent physician services on the CMS-1500 claim form or 837P transaction. Hospice Contracts with Other Entities for Hospice-related Services State statute requires the IHCP hospice program to mirror the coverage and reimbursement methodology of the Medicare hospice program. Medicare and Medicaid certified hospice providers must be certified by Medicare and licensed by ISDH before enrollment in the IHCP. They are required to comply with the the Medicare hospice Conditions of Participation at 42 CFR Part 418. The hospice provider is required to adhere to certain contractual responsibilities when entering a contract with a nonhospice provider for a service related to the member’s terminal illness or related conditions. The contract requires the nonhospice provider to bill the hospice for those services at the fair market value rate noted in the contract. The nonhospice provider must not bill the IHCP for those services separately, because this would be duplicate billing and subject the nonhospice provider to recoupment. Volunteer Physician Services Volunteer physician services are excluded from reimbursement. However, a physician who provides volunteer services to a hospice may receive reimbursement for nonvolunteer services provided to hospice patients. In determining which services are furnished on a volunteer basis and which are not, a physician must treat IHCP patients on the same basis as other hospice patients. For example, a physician cannot designate all physician services rendered to non-IHCP patients as volunteer services, and at the same time seek payment for all physician services rendered to IHCP patients. Emergency Services If emergency services are related to the terminal illness, and the hospice member has not revoked the hospice benefit, the hospice provider is responsible for hospital and transportation charges associated with all emergency services provided. If the emergency services are unrelated to the terminal illness, the IHCP may reimburse the transportation and hospital claims associated with the emergency services. 8-68 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Billing the Programs as the Payer of Last Resort The IHCP is always the payer of last resort. Therefore, the hospice provider must first bill other payer sources before billing the IHCP. The following scenarios for Traditional Medicaid-only hospice members and dually eligible Medicare and Traditional Medicaid hospice members provide guidelines for hospice providers. Traditional Medicaid-Only – Hospice Member Residing in the Private Home If the Traditional Medicaid-only hospice member has private insurance, the hospice provider must first bill the private insurance for hospice services. When the private insurance company denies or partially pays the claim, the hospice provider can bill the IHCP for the remaining balance for hospice services. If the private insurance company has denied payment for hospice services, in whole or in part, the hospice provider must complete a UB-04, and send, as an attachment to the claim, a copy of the notice from the private insurance company that outlines the denial of payment for those dates of service. On receipt of the attachment, the IHCP processes the claim for payment. Traditional Medicaid-Only – Hospice Member Residing in a Nursing Facility If the Traditional Medicaid-only hospice member has private insurance, the hospice provider must bill the private insurance company first for the hospice services and the room and board services. When the private insurance company denies or partially pays the claim, the hospice provider bills the IHCP for the remaining balance of the hospice services and the room and board services. The hospice provider must attach to the UB-04 a copy of the notice from the private insurance company that outlines denial of payment for those dates of service. On receipt of the UB-04, the IHCP processes the claim for payment. If the member has private insurance, the hospice provider must bill the private insurance company first, and then bill Medicare for the outstanding balance, according to the guidelines established by Medicare. When billing for a date of service that is the same as the date of death, hospice providers must bill occurrence code 51 in field 31 of the UB-04 claim form, along with the date of death. The IHCP only pays for hospice services for the date of death when the services are billed with occurrence code 51 and revenue codes 653 and 654. If providers bill revenue codes 653 and 654 without occurrence code 51, the claim denies. When providers bill revenue code 659, the claim denies even if it is billed with occurrence code 51. Dually Eligible Medicare and Traditional Medicaid – Hospice Member Residing in a Private Home For the dually eligible Medicare and Traditional Medicaid hospice member, the hospice provider must bill Medicare for the hospice services and the IHCP for the outstanding balance. Dually Eligible Medicare and Traditional Medicaid Hospice Member Residing in a Nursing Facility If a dually eligible Medicare hospice member has private insurance, Medicare and Traditional Medicaid require that the hospice provider bill the private insurance company first for the hospice services and the room and board services. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-69 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual If the private insurance company denies payment, in whole or in part, for the hospice services, the hospice provider must then bill Medicare for the outstanding balance according to the billing guidelines established by Medicare. If the private insurance company denies payment, in whole or in part, for the NF room and board services, the hospice provider must bill the IHCP for the outstanding balance. The hospice provider must attach to the UB-04 a copy of the notice from the private insurance company that outlines denial of payment for those dates of service. CHOICE and Hospice Members The Community and Home Option to Institutional Care for the Elderly and Disabled (CHOICE) Program is a state-funded program administered by the Division of Aging (DA). Because CHOICE is funded 100 percent by the state of Indiana, DA stipulates that CHOICE is the payer of last resort. Providers must bill the IHCP and any other insurance carrier prior to submitting charges to the CHOICE Program. Medicare and Traditional Medicaid Eligibility Changes during the Month A Traditional Medicaid-only hospice member residing in an NF may become Medicare-eligible during a one-month billing period. Inversely, a dually eligible Medicare and Traditional Medicaid hospice member residing in an NF may become a Traditional Medicaid-only hospice member during a onemonth billing period. The change in eligibility status changes how the hospice provider completes the UB-04 for those dates of service. Traditional Medicaid-Only – Hospice Member Who Becomes Medicare-Eligible in Nursing Facility The hospice provider must complete the necessary paperwork to enroll the Traditional Medicaid-only hospice member in the Medicare hospice benefit once the member has become Medicare eligible. The hospice provider must also submit the Change in Status of Medicaid Hospice Patient form to the appropriate MCO or care management organization (CMO) Hospice Authorization Unit to inform the IHCP that the member has become Medicare eligible. The following example provides guidelines for completing the UB-04 claim form for this scenario. For this example, July 15 is the date the individual is considered dually eligible for Medicare and Traditional Medicaid. The hospice provider plans to bill the IHCP for the entire month of July. From July 1 to July 14, the hospice member was a Traditional Medicaid-only member, so the hospice provider must bill using revenue code 653 or revenue code 654 for those dates of service. Revenue codes 653 and 654 include the additional room and board per diem to cover costs incurred by the contracted NF. From July 15 to July 31, the hospice member is considered dually eligible for Medicare and Traditional Medicaid, and the hospice provider must bill using revenue code 659 for the additional room and board per diem for those dates of service. The hospice provider must bill Medicare for the hospice services. 8-70 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Dually Eligible Medicare/Traditional Medicaid – Member in a Nursing Facility Who Becomes Traditional Medicaid-Only The hospice provider must complete the Change in Status of Medicaid Hospice Patient form to inform the IHCP that the individual is no longer Medicare-eligible. The hospice provider must submit the Change in Status of Medicaid Hospice Patient form to the appropriate MCO or CMO Hospice Authorization Unit. The following example provides guidelines for completing the UB-04 for this scenario. For this example, July 15 is the date the member is eligible for Traditional Medicaid only. The hospice provider plans to bill the IHCP for the entire month of July. From July 1 through July 14, the hospice member is dually eligible for Medicare and Traditional Medicaid, so the hospice provider must bill the IHCP using revenue code 659 for the additional room and board per diem for these dates of service. The hospice provider must bill Medicare for the hospice services. From July 15 through July 31, the hospice member is eligible for Traditional Medicaid only, so the hospice provider must bill the IHCP for the hospice services and the additional room and board per diem for these dates of service. The hospice provider must use revenue codes 653 or 654 for those dates of service. Revenue codes 653 and 654 include the additional room and board per diem to cover costs incurred by the contracted NF. Billing a Continuation Claim Using UB-04 Claim Form The UB-04 claim form has 22 lines; therefore, providers cannot bill an entire month on one page. The hospice provider can prepare a continuation claim, which is a claim with more than one UB-04 claim form completed as if it is one claim, to be processed for payment by the IHCP. Continuation claims cannot be more than three pages long and contain 66 detail lines. The hospice provider must complete the continuation claim as follows: • Mark the UB-04 claim form page numbers in the area provided on line 23. • Complete the first 22 lines on page one of the UB-04 claim form. • Do not subtotal the first page of the claim. Total only the last page of the continuation claim, or IndianaAIM reads the claim as two claims rather than one. • Complete the subsequent UB-04 claims form for the remaining dates of service of the month. • Provide a grand total for the continuation claim on the last page of the UB-04 claim form in the space provided at the bottom of field locator 47. If hospice providers prefer not to complete a continuation claim, they can complete separate UB-04 claim forms. The hospice provider completes a second UB-04 claim form for the remaining days of service of the month, totals the daily amounts, and enters the total charges in the space provided for a grand total on each form. Hospice Provider Reimbursement Terms It is not mandatory for nursing facility (NF) providers to reserve beds; however, the OMPP continues to reimburse hospice providers at one-half the NF case mix reimbursement rate for reserving NF beds for hospice members, when the occupancy criteria are met as set forth in 405 IAC 5-34-12. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-71 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual It is the hospice agency’s responsibility to confirm the NF occupancy percentage on the date that the leave of absence begins. Hospice providers can bill the IHCP for leave days only when the NF occupancy percentage is at 90 percent or greater on the day the leave begins. If the NF occupancy percentage falls below 90 percent following the date the leave began, the hospice provider can continue to bill the 50 percent of the NF’s case mix reimbursement rate for the entire hospital or therapeutic leave. When the NF occupancy is below 90 percent on the date that the leave of absence begins, the hospice agency should use revenue code 180 to bill the IHCP for leave days. Revenue code 180 is a nonpaid revenue code used to generate an IHCP denial, and it can be used when charging a resident or legal guardian for nonreimbursed bed-hold days. The explanation of benefits (EOB) detail for revenue code 180 lists the claim as denied, with EOB 4215 – Leave days not a covered service for this bill type – nursing facility occupancy less than 90 percent. When a member who receives hospice services and resides in a nursing facility has dual eligibility, the hospice provider must bill claims to the IHCP using revenue code 659 – Hospice services/other/dual eligibility NF recipients only. A member is considered dually eligible if he or she is enrolled in both Medicare and Medicaid. The member may also have other commercial insurance. When verifying member eligibility, members who are dually eligible will be listed as being qualified Medicare beneficiaries (QMB-Also). When a member who receives hospice services and resides in a nursing facility is not dually eligible (not a QMB), the hospice provider must bill claims to the IHCP using revenue code 653 – Hospice services/routine home care delivered in a nursing facility or 654 – Hospice services/continuous home care delivered in a nursing facility. The provider must use revenue code 653 or 654 even if the member has other commercial insurance and Medicaid. If other insurance pays for the hospice care services in full, the hospice provider shall only receive payment from the IHCP for room and board services. If other insurance and the IHCP reimbursed the provider for hospice care services, the provider was overpaid and must refund the overpayment to the IHCP. To refund the overpayment, the provider must complete a Hospice Accounts Receivable Refund Adjustment form. The form is located on the following page of the IHCP Web site: http://provider.indianamedicaid.com/provider-specific-information/hospice/forms.aspx. Mail the completed form and a check for the overpayment amount to: HP Refunds P.O. Box 2303 Dept. 130 Indianapolis, IN 46206-2303 The following example shows how to calculate the amount of an overpayment for revenue code 653 or 654. Table 8.9 – Nursing Home Room and Board Calculation Nursing Home Room and Board Level of Care Letter Represented 8-72 Description Amount A Nursing Home’s Room and Board Rate $136.98 B Payment Percentage of the Room and Board Rate 95 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Nursing Home Room and Board Level of Care Letter Represented Description Amount C Medicaid Reimbursement Per Day (A*B=C) $130.13 D Number of Days in the Month E Total Reimbursement Amount for the Month (C*D=E) $4,034.03 F Patient Liability for the Month $1,019.00 G Total Medicaid Reimbursement for Room and Board (E-F=G) $3,015.03 31 Table 8.10 – Hospice Routine Healthcare Calculation Hospice Routine Healthcare Letter Represented Description Amount A Routine Home Care Rate for the County of the Provider $126.92 B Number of Days in the Month C Medicaid Hospice Reimbursement for the Month (A*B=C) $3,934.52 D Amount Paid by Third-party Liability $3,410.00 E Total Medicaid Reimbursed for Hospice (C-D=E) 31 $524.52 In this example, the provider received the full hospice reimbursement (Table 8.10, line C) of $3,934.52 and no reimbursement for Room and Board (Table 8.9, line G.) The IHCP should have reimbursed the provider $3,539.55 (Total Medicaid Reimbursement for Room and Board, $3,015.03, plus the Total Medicaid Reimbursement for Hospice, $524.52). The provider was overpaid and must refund the IHCP $394.97 ($3,934.52 minus $3,539.55). Note: An individual form must be completed for each claim that is being refunded. Inpatient Hospital Services Coverage Inpatient services, such as acute care, mental health, and rehabilitation care, are covered when the services are provided or prescribed by a physician, and when the services are medically necessary for the diagnosis or treatment of the member’s condition. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-73 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Billing Procedures Mail inpatient hospital claims to the following address for processing: HP Inpatient Hospital Claims P.O. Box 7271 Indianapolis, IN 46207-7271 Note: For RBMC members, bill the appropriate MCO. Specified Coding Level The IHCP adheres to the coding guidelines published in the Coding Clinic for ICD-9-CM, a publication of the American Hospital Association, Central Office. The following clarifications may assist providers using the UB-04 claim form: • Use the highest level of specificity when billing diagnostic and procedure codes. • Assign three-digit codes only if no four-digit codes are within that code category. • Assign four-digit codes only if no fifth-digit subclassification is available for that category. • Assign the fifth-digit subclassification code for those categories where a fifth digit exists. • Use the codes labeled other specified or not elsewhere classified (NEC), unspecified, or not otherwise specified (NOS) only when the diagnostic statement or a thorough review of the medical record does not provide adequate information to permit assignment of a more specific code. • Use the code assignment for other or NEC when the information at hand specifies a condition but no separate code for that condition is provided. • Use unspecified or NOS when the information at hand does not permit either a more specific or other code assignment. Revenue Code Itemization Although the IHCP reimburses inpatient hospital services using a diagnosis-related group (DRG)/Level of Care (LOC) methodology, the IHCP requires a complete itemization of services performed using appropriate revenue codes in field 42. The revenue code reveals crucial information about the type of service provided during the inpatient stay. Therefore, providers need to ensure that each claim properly identifies the appropriate revenue code. The revenue code that is used must reflect the setting in which the care was delivered. For example, providers must use revenue code 20X to submit a claim for services provided to patients admitted to an Intensive Care Unit. Continued Bill If a complete itemization of services requires multiple UB-04 claim forms, providers must enter the total charges on the last page of the bill, not at the bottom of each UB-04 claim form: 8-74 • Mark the UB-04 claim form page number in the area provided on line 23. As many as three pages can be submitted as one claim. • Complete the first 22 lines on page one of the UB-04 claim form. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions • Do not subtotal the first page of the claim. Total only the last page of the continuation claim, or IndianaAIM reads the claim as two claims rather than one. • Complete the subsequent UB-04 claim forms for the remaining dates of service of the month. Provide a grand total for the continuation claim on the last page of the UB-04 claim form in the space provided at the bottom of field 47. Medical Education Reimbursement The change in medical education reimbursement is effective for encounter or shadow claims (claims that are forwarded to HP after being adjudicated by a managed care organization) received from the MCOs with a From Date of Service of January 1, 2010, and after. Based upon shadow claims data received from the MCOs, HP Enterprise Services processes and issues the medical education payments to the hospitals. All medical education payment calculations are made once the MCO has posted the claim payment information, and the shadow claim has been posted to IndianaAIM. Providers should allow 30 – 45 calendar days from the time the MCO has processed the claim for the medical education payment to be posted to the fee-for-service Remittance Advice from HP. Definition of Principal Diagnosis The principal diagnosis is defined as the condition established, after study, that is chiefly responsible for the admission of the patient to the hospital. When providers bill for inpatient services, form field 69 requires the principal diagnosis. Note: The IHCP prohibits use of V codes as a principal diagnosis on a UB-04 claim form, except when using V codes as a principal diagnosis code for newborns, rehabilitation, or chemotherapy. Reporting Other Diagnoses Providers can enter additional diagnosis codes in fields 67 A-Q to indicate all conditions that coexist at the time of admission, that develop subsequently, or that affect the treatment received or length of stay. Providers must exclude diagnoses that relate to an earlier episode and have no bearing on the current hospital stay. The IHCP defines other diagnoses as additional conditions that affect patient care in terms of requiring the following: • Clinical evaluation • Diagnostic procedures • Extended length of hospital stay • Increased nursing care or monitoring • Therapeutic treatment Inpatient Blood Factor Claims Indiana Medicaid will reimburse providers for claims for blood factor products administered during inpatient hospital stays at the lowest of the following: • Estimated Acquisition Cost (84 percent of the Average Wholesale Price) Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-75 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual • Inpatient blood factor – State maximum allowable cost (MAC) • Submitted charge Effective for claims with administration dates on or after October 12, 2008, blood factor that is used during inpatient hospital stays should now be billed separately from the inpatient hospital diagnosisrelated group or Level of Care claim. If a patient is admitted prior to October 12, 2008, and blood factor is administered prior to October 12, 2008, the charges should remain on the inpatient claim. Hospitals are prohibited from submitting any charges for blood factor administered on or after October 12, 2008, during inpatient hospital stays on their UB-04 claims. Instead, hospitals should submit their claims for blood factor used during inpatient hospital stays on the CMS-1500 claim form and should include both the NDC and the NDC quantity of the blood factor on the claims. Hospitals should use their NPIs for their facility on their CMS-1500 claim forms. Claims with quantities greater than 9,999.99 units must be special batched because the NDC code will be the same for each detail and will deny for duplicates. These claims must be sent to the following address for special handling: HP Provider Written Correspondence P.O. Box 7263 Indianapolis, IN 46207-7263 The Place of Service (POS) entered in field 24B must be 21 – Inpatient Hospital for blood factor administered during an inpatient hospital stay. If Medicare covers the blood factor product, the provider cannot bill it separately. If Medicare does not cover the blood factor product, the provider needs to attach documentation, such as an MRN, to the claim to show where the factor charges are denied or not covered under Medicare. Table 8.11 – Blood Factor Products Effective for Dispense Dates of October 12, 2008, and Later NDC 8-76 Procedure Code Blood Factor Product 00944294410 J7192 ADVATE 1,201-1,800 UNITS VIAL 00944294510 J7192 ADVATE 1,801-2,400 UNITS VIAL 00944294610 J7192 ADVATE 2,400-3,600 UNITS VIAL 00944294110 J7192 ADVATE 200-400 UNITS VIAL 00944294210 J7192 ADVATE 401-800 UNITS VIAL 00944294310 J7192 ADVATE 801-1,200 UNITS VIAL 68516460002 J7190 ALPHANATE 1,000-1,500 UNITS VL 68516460302 J7190 ALPHANATE 1,000-400 UNIT VIAL 68516460402 J7190 ALPHANATE 1,500-600 UNIT VIAL 68516460101 J7190 ALPHANATE 250-100 UNIT VIAL 68516460001 J7190 ALPHANATE 250-500 UNIT VIAL 68516460201 J7190 ALPHANATE 500-200 UNIT VIAL 68516360005 J7193 ALPHANINE SD 1,000 UNITS VIAL 68516360202 J7193 ALPHANINE SD 1,000 UNITS VIAL 68516360006 J7193 ALPHANINE SD 1,500 UNITS VIAL Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual NDC Procedure Code Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Blood Factor Product 68516360302 J7193 ALPHANINE SD 1,500 UNITS VIAL 68516360002 J7193 ALPHANINE SD 250-1,500 UNIT VL 68516360004 J7193 ALPHANINE SD 500 UNITS VIAL 05 68516360102 J7193 ALPHANINE SD 500 UNITS VIAL 06 64193024402 J7194 BEBULIN VH IMMUNO 200-1,200 UNIT 58394000105 J7195 BENEFIX 1,000 UNIT VIAL 58394000106 J7195 BENEFIX 1,000 UNIT VIAL 58394000101 J7195 BENEFIX 1,000 UNITS VIAL 58394000802 J7195 BENEFIX 2,000 UNIT VIAL 58394000803 J7195 BENEFIX 2,000 UNIT VIAL 58394000301 J7195 BENEFIX 250 UNIT VIAL 58394000305 J7195 BENEFIX 250 UNIT VIAL 58394000306 J7195 BENEFIX 250 UNIT VIAL 58394000201 J7195 BENEFIX 500 UNIT VIAL 58394000205 J7195 BENEFIX 500 UNIT VIAL 58394000206 J7195 BENEFIX 500 UNIT VIAL 64193022205 J7198 FEIBA VH IMMUNO 1,750-3,250 IU 64193022203 J7198 FEIBA VH IMMUNO 400-650 UNITS 64193022204 J7198 FEIBA VH IMMUNO 651-1,200 UNIT 64193022302 J7198 FEIBA NF 400-650 UNIT VIAL 07/ 64193022402 J7198 FEIBA NF 651-1200 UNIT VIAL 07 64193022502 J7198 FEIBA NF 1750-3250 UNIT VIAL 0 00053813004 J7192 HELIXATE FS 1,000 UNITS VIAL 00053813005 J7192 HELIXATE FS 2,000 UNIT VIAL 00053813001 J7192 HELIXATE FS 250 UNIT VIAL 00053813002 J7192 HELIXATE FS 500 UNIT VIAL 00053813302 J7192 HELIXATE FS 1,000 UNITS VIAL 00053813402 J7192 HELIXATE FS 2,000 UNIT VIAL 00053813102 J7192 HELIXATE FS 250 UNIT VIAL 00053813202 J7192 HELIXATE FS 500 UNIT VIAL 00053813502 J7192 HELIXATE FS 3,000 UNITS VIAL 00944293301 J7190 HEMOFIL M 1,701-2,000 UNITS VL 00944293504 J7190 HEMOFIL M 1,701-2,000 UNITS VL 00944293001 J7190 HEMOFIL M 220-400 UNITS VIAL 00944293501 J7190 HEMOFIL M 220-400 UNITS VIAL 00944293101 J7190 HEMOFIL M 401-800 UNITS VIAL 00944293502 J7190 HEMOFIL M 401-800 UNITS VIAL 00944293201 J7190 HEMOFIL M 801-1,700 UNITS VIAL Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-77 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions NDC 8-78 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Procedure Code Blood Factor Product 00944293503 J7190 HEMOFIL M 801-1,700 UNITS VIAL 00053762010 J7187 HUMATE-P 1,000 UNITS KIT 00053761510 J7187 HUMATE-P 1,200 UNITS KIT 00053762020 J7187 HUMATE-P 2,000 UNITS KIT 00053761520 J7187 HUMATE-P 2,400 UNITS KIT 00053762005 J7187 HUMATE-P 500 UNITS KIT 00053761505 J7187 HUMATE-P 600 UNITS KIT 63833061602 J7187 HUMATE-P 1,200 UNITS KIT A 63833061702 J7187 HUMATE-P 2,400 UNITS KIT A 63833061502 J7187 HUMATE-P 600 UNITS KIT A 55688010602 J7191 HYATE:C 400-700 UNIT VIAL 13533066550 J7190 KOATE-DVI 1,000 UNITS KIT 13533066520 J7190 KOATE-DVI 250 UNIT KIT 13533066530 J7190 KOATE-DVI 500 UNITS KIT 00026037250 J7192 KOGENATE FS 1,000 UNITS VIAL 00026037950 J7192 KOGENATE FS 1,000 UNITS VIAL 00026378550 J7192 KOGENATE FS 1,000 UNITS VIAL 00026379550 J7192 KOGENATE FS 1,000 UNITS VIAL 00026378660 J7192 KOGENATE FS 2,000 UNIT VIAL 00026379660 J7192 KOGENATE FS 2,000 UNIT VIAL 00026037220 J7192 KOGENATE FS 250 UNIT VIAL 00026037920 J7192 KOGENATE FS 250 UNITS VIAL 00026378220 J7192 KOGENATE FS 250 UNIT VIAL 00026379220 J7192 KOGENATE FS 250 UNITS VIAL 00026378770 J7192 KOGENATE FS 3,000 UNIT VIAL 00026379770 J7192 KOGENATE FS 3,000 UNIT VIAL 00026037230 J7192 KOGENATE FS 500 UNIT VIAL 00026037930 J7192 KOGENATE FS 500 UNITS VIAL 00026379330 J7192 KOGENATE FS 500 UNIT VIAL 00026378330 J7192 KOGENATE FS 500 UNITS VIAL 00944130410 J7190 MONARC-M 1,701-2,000 UNITS VL 00944130110 J7190 MONARC-M 220-400 UNITS VIAL 00944130210 J7190 MONARC-M 401-800 UNITS VIAL 00944130310 J7190 MONARC-M 801-1,700 UNITS VIAL 00053765604 J7190 MONOCLATE-P 1,000 UNITS KIT 00053765605 J7190 MONOCLATE-P 1,500 UNITS KIT 00053765601 J7190 MONOCLATE-P 250 UNIT KIT 00053765602 J7190 MONOCLATE-P 500AHFU KIT Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual NDC Procedure Code Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Blood Factor Product 00053766804 J7193 MONONINE 1,000 UNITS VIAL 00053766802 J7193 MONONINE 500 UNITS VIAL 00169706001 J7189 NOVOSEVEN 1,200 MCG VIAL 00169706101 J7189 NOVOSEVEN 2,400 MCG VIAL 00169706201 J7189 NOVOSEVEN 4,800 MCG VIAL 00169701001 J7189 NOVOSEVEN RT 1,000 MCG VIAL 00169702001 J7189 NOVOSEVEN RT 2,000 MCG VIAL 00169705001 J7189 NOVOSEVEN RT 5,000 MCG VIAL 68516320004 J7194 PROFILNINE SD 1,000 UNITS VIAL 68516320202 J7194 PROFILNINE SD 1,000 UNITS VIAL 68516320003 J7194 PROFILNINE SD 1,000-1,500 UNIT 68516320005 J7194 PROFILNINE SD 1,500 UNITS VIAL 68516320302 J7194 PROFILNINE SD 1,500 UNITS VIAL 68516320002 J7194 PROFILNINE SD 500 UNITS VIAL 68516320101 J7194 PROFILNINE SD 500 UNITS VIAL 00944283110 J7192 RECOMBINATE 220-400 UNIT VIAL 00944293810 J7192 RECOMBINATE 220-400 UNIT VIAL 00944283210 J7192 RECOMBINATE 401-800 UNIT VIAL 00944293802 J7192 RECOMBINATE 401-800 UNIT VIAL 00944283310 J7192 RECOMBINATE 801-1,240 UNIT VL 00944293803 J7192 RECOMBINATE 801-1,240 UNIT VL 58394000502 J7192 REFACTO 1,000 UNITS VIAL 58394000504 J7192 REFACTO 1,000 UNITS VIAL 58394001102 J7192 REFACTO 2,000 UNITS VIAL 58394001104 J7192 REFACTO 2,000 UNITS VIAL 58394000702 J7192 REFACTO 250 UNITS VIAL 58394000704 J7192 REFACTO 250 UNITS VIAL 58394000602 J7192 REFACTO 500 UNITS VIAL 58394000604 J7192 REFACTO 500 UNITS VIAL 67467018102 C9267 WILATE 900-900 UNIT KIT 67467018101 C9267 WILATE 450-450 UNIT KIT 58394001401 J7185 XYNTHA 1,000 UNIT KIT 58394001501 J7185 XYNTHA 2,000 UNIT KIT 58394001201 J7185 XYNTHA 250 UNIT KIT 58394001301 J7185 XYNTHA 500 UNIT KIT Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-79 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Present on Admission Indicators and Hospital-Acquired Conditions Effective for inpatient and inpatient crossover claims with a ‘From’ date of service on or after October 1, 2009, the IHCP adopted a hospital-acquired conditions (HAC) policy for Medicaid claims using our existing version 18.0 of the All Patient Diagnosis-Related Group (AP DRG) grouper. Hospitals are required to report whether each diagnosis on a Medicaid claim was present on admission. Claims submitted without the required present on admission (POA) indicators will be denied. For claims containing secondary diagnoses that are included in the list of HACs in Table 8.12 and for which the condition was not present on admission, the HAC secondary diagnosis will not be used for AP DRG grouping. That is, the claim will be paid as though any secondary diagnoses included in Table 8.12 were not present on the claim. Table 8.12 – Final HAC List as Published in FFY 2009 Final Rule Applicable ICD-9 Codes CC – Complicating Condition MCC – Major Complicating Condition Description Foreign Object Retained After Surgery 998.4 (CC) and 998.7 (CC) Air Embolism 999.1 (MCC) Blood Incompatibility 999.6 (CC) Pressure Ulcers Stages III and IV 707.23 (MCC) and 707.24 (MCC) Falls and Trauma CC/MCC codes within these ranges: • Fractures • 800 – 829 • Dislocations • 830 – 839 • Intracranial Injuries • 850 – 854 • Crushing Injuries • 925 – 929 • Burns • 940 – 949 • Electric Shock Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) • 991 – 994 996.64 (CC), and excludes the following from acting as a CC/MCC: • CC – 112.2, 590.10, 590.3, 590.80, 590.81, 595.0, 597.0, 599.0 Vascular Catheter-Associated Infection • MCC – 590.11, 590.2 999.31 (CC) Manifestations of Poor Glycemic Control MCC – • 250.10 – 250.13 • 250.20 – 250.23 • 249.10 – 249.11 • 249.20 – 249.21 CC – • 8-80 251.0 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Applicable ICD-9 Codes CC – Complicating Condition MCC – Major Complicating Condition Description Surgical Site Infection, Mediastinitis After Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG) 519.2 (MCC) and one of the following procedure codes: Surgical Site Infection Following Certain Orthopedic Procedures • 36.10 – 36.19 999.67 (CC) or 998.59 (CC) and one of the following procedure codes: Surgical Site Infection Following Bariatric Surgery for Obesity Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)/ Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Following Certain Orthopedic Procedures • 81.01 – 81.08 • 81.23 – 81.24 • 81.31 – 81.38 • 81.83 • 81.85 278.01 and 998.59 (CC) and one of the following procedure codes: • 44.38 • 44.39 • 44.95 453.40 – 453.42 (MCC) or 415.11 (MCC) or 415.19 (MCC) and one of the following procedure codes: • 81.54 • 00.85 – 00.87 • 81.51 – 81.52 Notes: If a claim contains a hospital-acquired condition diagnosis with a POA indicator of “U” or “N,” the HAC diagnosis will be suppressed when the claim processes through the DRG grouper. The OMPP will not pay the complicating condition/major complicating condition (CC/MCC) for HACs. The POA indicator of “1” is only applicable to diagnoses exempt from POA reporting and should not be applied to any codes on the HAC list. Any claims using the POA indicator of “1” with a nonexempt diagnosis will deny, and providers will need to correct and resubmit the claim for reimbursement. Claims containing HAC diagnoses with POA indicators of “Y” or “W” will process through the AP DRG grouper and process per normal inpatient policy. Claims submitted by a nonexempt hospital that do not include a POA indicator for the principal and any secondary diagnoses will be denied. The provider will need to correct and resubmit the claim. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-81 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Exempt Hospitals POA indicator reporting is mandatory for all Medicaid claims involving inpatient admission to general acute care hospitals with a primary specialty of Acute Care – 010. However, the following types of hospitals are EXEMPT from the Medicaid HAC policy and POA indicator reporting: • Critical access hospitals (CAHs) • Long-term acute care hospitals (LTACs) (primary specialty 013) • Inpatient psychiatric hospitals (primary specialty 011) • Inpatient rehabilitation facilities (primary specialty 012) Psychiatric or rehabilitation units of acute care hospitals, also known as a distinct part of an acute care hospital, enrolled with primary specialty 010 are required to submit the POA indicator on their claims. The list of critical access hospitals was identified using information obtained from Medicare. Hospitals that are not sure of their CAH status should contact the HP Provider Enrollment Department at 1-877707-5750 for confirmation. Present on Admission Indicator POA is defined as “present” at the time the order for inpatient admission occurs. Conditions that develop during an outpatient encounter, including emergency department, observation, or outpatient surgery, are considered POA. A POA indicator must be assigned to principal and secondary diagnoses (as defined in Section II of the Official Guidelines for Coding and Reporting). The CMS does not require a POA indicator for an external cause of injury code unless it is being reported as an “other diagnosis.” Therefore, the IHCP does not require a POA indicator in the External Cause of Injury field locator 72. If a POA indicator is entered in the External Cause of Injury field, it will be ignored and not used for AP DRG grouping. Common POA Explanations of Benefits The following table lists common POA explanations of benefits (EOBs). Table 8.13 – Common POA EOBs EOB Code EOB Description 4250 The Principal Diagnosis POA Indicator is Missing or Invalid – this edit will post to the claim when the provider has omitted the POA or submitted an invalid POA indicator. 4251-4275 The Secondary Diagnosis POA is Missing or Invalid – these EOBs will post to the claim for secondary diagnoses 1-24 if the POA is missing or invalid. The specific diagnosis field will be identified in the EOB message. Example: • 4251 – First Secondary Diagnosis POA Missing or Invalid • 4252 – Second Secondary Diagnosis POA Missing or Invalid Hospital Acquired Condition List The current list of HACs was published by the CMS in the August 19, 2008, FFY 2009 Inpatient Prospective Payment System final rule (73 FR 48471) and includes diagnoses listed in Chapter 8. The IHCP will continue to follow CMS’ HAC determinations, including any future additions or changes to 8-82 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions the current list of HAC conditions, as well as diagnosis codes that are exempt from HAC reporting. The list of exempt diagnosis codes can be found in the ICD-9-CM Official Guidelines for Coding and Reporting, effective October 1, 2008, at http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/icd9/icdguide08.pdf. Medicare Exhaust Claims Benefits Exhausted Prior to Inpatient Admission The IHCP reimburses acute care hospitals for dually eligible (Medicare and Medicaid) IHCP members who exhaust their inpatient hospital Medicare Part A benefits prior to admission to acute care hospitals. When a Medicare Part A stay is exhausted by Medicare prior to admission, providers must bill the date of admission through the date of discharge on the UB-04 claim form. Do not bill the IHCP for partial inpatient stays. The Medicare Remittance Notification (MRN) must be submitted with the claim to show benefits were exhausted prior to the date of admission. Providers must bill services payable to Medicare Part B before billing the exhaust claim to Medicaid. Because these claims are considered Medicaid primary claims, all IHCP filing limit rules apply. Refer to Chapter 10 for information about waiving filing limit procedures and supplying appropriate documentation for claim adjudication. Benefits Exhausted During an Inpatient Stay When a dually eligible member exhausts Medicare Part A benefits during an inpatient stay, the claim automatically crosses over from Medicare and adjudicates according to the IHCP inpatient crossover reimbursement methodology. Once the coinsurance and deductible amounts are considered, no additional payment will be made on the claim. This is also true for claims that do not automatically cross over but are submitted via the Web or paper. The IHCP will continue to reimburse Medicare Part B charges, as long as the revenue codes billed on the Medicare Part A and B claims are not the same. If the same revenue codes appear on both claims, the claim will deny for duplicate billing. Medicare Replacement Plans Claim Submission Instructions The following instructions apply when submitting claims for service adjudicated by a Medicare health maintenance organization (HMO) replacement plan: • Submit claims to the regular IHCP claims process address. Do not send the claims to the medical or institutional crossover post office boxes. - CMS-1500 claims: Enter the payment received from the Medicare replacement plan in field 29, not field 22. Do not enter any amounts in field 22. - UB-04 claims: Enter the payment received from the Medicare replacement plan in the Prior Payment form locators 54 A through C, as appropriate. Enter the words “Replacement Plan” in the Payer Name form locators 50A through 50C, as appropriate. Do not enter any reference to Medicare in Payer Name form locators, as this causes the claim to be treated as a crossover claim. - With every claim form, submit a copy of the Medicare replacement plan Remittance Advice (RA), Medicare Remittance Notice (MRN), or the explanation of payment/benefits from the replacement policy carrier. - The words “Medicare Replacement Policy” must be written on the top of the claim form and on the top of the attachments submitted with the claim. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-83 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions • Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Claims may be submitted electronically using the above process. The words “Medicare Replacement Policy” must be written at the top of the attachment. These claims are processed as third-party liability (TPL) claims. Standard Medicaid prior authorization rules apply to these claims, as do timely filing limits. Observation Billing Providers can retain members for more than one 23-hour observation period when the member has not met criteria for admission but the treating physician believes that allowing the member to leave the facility would likely put the member at serious risk. This observation period can last not more than three days or 72 hours and is billed as an outpatient claim. For all services rendered as outpatient procedures and prior to admission, providers must bill with a date of service corresponding to the date the procedure was performed in fields 74 and 74a-e of the UB-04. Transfers Because special payment policies apply to certain transfer cases that are to be reimbursed using the DRG payment methodology, it is important for providers to identify the transferring hospital on the UB-04 claim form. Indicate the following to identify the transferring hospital in field 17: 8-84 • Patient status 02 – Discharged or transferred to another short-term general hospital for inpatient care. • Patient status 03 – Discharged or transferred to skilled nursing facility (SNF). • Patient status 04 – Discharged or transferred to an intermediate care facility (ICF). • Patient status 05 – Discharged or transferred to a designated cancer center or children’s hospital. • Patient status 06 – Discharged or transferred to home under care of organized home health service organization. • Patient status 08 – Discharged or transferred to home under care of a home intravenous provider. • Patient status 43 – Discharged or transferred to a federal healthcare facility. • Patient status 61 – Discharged or transferred within this institution to hospital-based Medicare swing bed. • Patient status 62 – Discharged or transferred to another rehabilitation facility including discharge planning units of hospital. • Patient status 63 – Discharged or transferred to a long-term care hospital. • Patient status 64 – Discharged or transferred to a nursing facility – Medicaid-certified but not Medicare-certified. • Patient status 65 – Discharged or transferred to a psychiatric hospital or psychiatric distinct part unit of a hospital. • Patient status 66 – Discharged or transferred to a critical access hospital. • Patient status 70 – Discharged or transferred to another type of healthcare institution not defined elsewhere in code list. • Patient status 71 – Discharged, transferred, or referred to another institution for outpatient services when specified by the discharge plan of care. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions • Patient status 72 – Discharged, transferred, or referred within this facility for outpatient services when specified by the discharge plan of care. • Providers are not to bill separately for two DRG reimbursed inpatient stays when a member is transferred from one unit of the hospital to another unit within the same inpatient facility. Inpatient transfer claims from one inpatient unit of the hospital to another inpatient unit should be billed on one claim form as they are to be considered part of the same episode of care. Exclusions to this policy are claims priced according to the Level of Care (LOC) reimbursement methodology. Providers must combine the original admission and subsequent return stay on one claim for billing purposes. Transfer claims continue to be subject to retrospective review to ensure appropriate billing and payment. Also, claims for patients that are transferred within 24 hours of admission are to be billed as outpatient claims. Claims grouping to DRG 639 – Neonate, transferred < 5 days old, born here, and DRG 640 – Neonate, transferred < 5 days old, not born here, are exempt from this policy. Special payment policies apply to transfer cases paid using the DRG methodology. The receiving hospital, or transferee hospital, is reimbursed according to the DRG or Level of Care (LOC) methodology, whichever is applicable. Transferring hospitals are reimbursed a DRG-prorated daily rate for each day, not to exceed the full DRG amount. The IHCP calculates the DRG daily rate by dividing the DRG rate by the average length of stay. The full payment to the transferring hospital is the sum of the DRG daily rate, the capital per diem rate (up to the DRG average length of stay), and the medical education per diem rate (up to the DRG average length of stay). Transferring hospitals are eligible for outlier payments. To ensure accurate reimbursement for transfer cases, the appropriate discharge status code of 02, 05, 62, 63, 65, 66, and 70 must be placed in the UB-04 form locator 17 on the claim form. For detailed reimbursement information about transfers and readmissions, refer to Chapter 7 of this manual. Inpatient Claims for Spend-down Members Spanning Multiple Months When a spend-down member has an inpatient stay that spans multiple months, and the date of the discharge is the first day of a month, the claims are denied for explanation of benefits (EOB) 3005 – The claim covers multiple months and spend-down has not been met for all months billed on the claim. Submit these claims to the Written Correspondence Unit for processing along with an attached cover letter referencing this process. Submit claims that span multiple months with a date of discharge that is not the first of the month to the normal claims address. For dates of service prior to January 1, 2006, submit an 8A Form attached for each month in which the member was in the facility on the spenddown met date. Effective January 1, 2006, inpatient claims with dates of services that span more than one month are prorated on a daily basis, not counting the discharge date. Spend-down is credited in each month based on the number of days of service reported on the claim for each month minus the day of discharge. The reimbursement is based on the total claim allowed minus the sum of the spend-down credits. Inpatient Mental Health 405 IAC 5-20-1 (b) (c) (d) states that PA is required for all inpatient psychiatric admissions, including admissions for substance abuse. The IHCP reimburses providers for inpatient psychiatric services provided to an eligible individual between 22 and 65 years old only in a certified psychiatric hospital of 16 beds or less. If the member is 22 years old, and began receiving inpatient psychiatric services immediately before the member’s 22nd birthday, inpatient psychiatric services are available. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-85 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual According to 405 IAC 5-20-3, a psychiatric hospital must meet the following conditions to be reimbursed for inpatient mental health services: • The facility must be enrolled in the IHCP. • The facility must maintain special medical records for psychiatric hospitals as required by 42 CFR 482.61. • The facility must provide services under the direction of a licensed physician. • The facility must meet federal certification standards for psychiatric hospitals. • The facility must meet utilization review requirements. The IHCP also reimburses providers for reserving beds in a psychiatric hospital but not in a general acute care hospital for hospitalization of Traditional Medicaid members, as well as for reserving beds for a therapeutic leave of absence. In both instances, the IHCP reimburses the facility at one-half the regular per diem rate. 405 IAC 5-20-2 provides specific criteria about the reservation of beds in an inpatient psychiatric facility in Appendix A, Rule 20. The IHCP reimburses for inpatient psychiatric services provided by facilities that are freestanding, or distinct parts at an all-inclusive, statewide per diem rate that includes routine, ancillary, and capital costs. The IHCP bases reimbursement for substance abuse and chemical dependency admissions on DRG payment methodology. Direct care services of physicians, including psychiatric evaluations, are excluded from the per diem rate and are billable separately by the rendering provider on the CMS-1500 claim form or 837P transaction. The per diem rate includes all other supplies and services provided to patients in inpatient psychiatric facilities, including services of health service providers in psychology (HSPP), clinical psychologists, and clinical social workers, regardless of whether salaried, contracted, or independent providers, and providers cannot bill these supplies and services separately. All mental health service admissions, including admissions for substance abuse and chemical dependency regardless of the setting, require a Certification of Need, Form 1261A. For nonemergency admissions, the IHCP must receive the 1261A form within 10 working days of the admission. For emergency admissions, the IHCP must receive the 1261A form within 14 working days of the admission. The 1261A form must include detailed information to document the admission. If the 1261A form does not meet the requirements, any claim associated with the admission is denied. Chapter 6 provides specific information about obtaining PA for inpatient psychiatric admissions. Providers must submit inpatient psychiatric claims using the revenue code that has been authorized for this admission. Up to and including date of service December 31, 2006, the IHCP carves out of the RBMC network any mental health services, including substance abuse treatment, rendered in freestanding psychiatric hospitals and pays them on an FFS basis. The carved-out definition in the Carved-Out Services subsection later in this chapter provides additional information. Providers should bill claims for mental health services in a freestanding psychiatric hospital on a UB-04 claim form; these claims are not the financial responsibility of the MCO. Inpatient mental health services, including substance abuse treatment, provided to RBMC network members in acute care facilities are the responsibility of the MCO in which the member is enrolled. On and after January 1, 2007, these services are the responsibility of the MCO in which the member belongs, excluding PRTF services and MRO services, which will continue to be carved out. 8-86 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Inpatient Mental Health and Substance Abuse Services Package C The IHCP covers inpatient mental health and substance abuse services when the services are medically necessary for the diagnosis or treatment of the member’s condition, except when provided in a mental health institution with more than 16 beds. Coding Claims for Premature Newborns Coding claims for premature newborns requires birth weight for the proper DRG assignment. The fifth digit of diagnosis codes 764 and 765 indicates birth weight. Use the following fifth-digit subclassification with categories 764 and 765 to denote birth weight. Table 8.14 lists birth weight codes. Table 8.14 – Birth Weight Codes Code Birth Weight 0 Unspecified weight 1 Less than 500 grams 2 500 grams – 749 grams 3 750 grams – 999 grams 4 1,000 grams – 1,249 grams 5 1,250 grams – 1,499 grams 6 1,500 grams – 1,749 grams 7 1,750 grams – 1,999 grams 8 2,000 grams – 2,499 grams 9 2,500 grams and over Do not use these codes as principal diagnosis codes. When a premature infant transfers to another hospital for observation, not for treatment for a specific illness, the receiving provider must enter the diagnosis code V71.8 – observation for other suspected conditions as the principal diagnosis. Unit and Age Limitations on Inpatient Neonatal and Pediatric Critical Care Services Current Procedural Terminology (CPT®) Code 99298 – Subsequent intensive care, per day, for the evaluation and management of the recovering very low birth weight infant (present body weight less than 1500 grams). This CPT code is limited to one unit per day. CPT Code 99300 – Subsequent intensive care, per day, for the evaluation and management of the recovering infant (present body weight less than 2501-5000 grams). This CPT code is limited to one unit per day. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-87 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual CPT Code 99295 – Initial neonatal critical care, per day, for the evaluation and management of a critically ill neonate, 28 days of age or less. This CPT code has an age limit of 0-1 year of age. This CPT code is limited to one unit per day. CPT Code 99296 – Subsequent inpatient neonatal critical care, per day, for the evaluation and management of a critically ill neonate, 28 days of age or less. This code has an age limit of 0-1 year of age. This CPT code is limited to one unit per day. CPT Code 99293 – Initial inpatient pediatric critical care, per day, for the evaluation and management of a critically ill infant or young child, 29 days through 24 months of age. This code has an age limit of 0-2 years of age. This CPT code is limited to one unit per day. CPT Code 99294 – Subsequent inpatient pediatric critical care, per day, for the evaluation and management of a critically ill infant or young child, 29 days through 24 months of age. This code has an age limit of 0-2 years of age. This CPT code is limited to one unit per day. Providers rendering services under the RBMC program should also follow IHCP policy and CPT coding guidelines when billing these procedure codes. Stereotactic Radiosurgery The IHCP currently covers several types of Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS) as represented by HCPCS codes G0173, G0251, G0339, G0340, and 77301U5. In addition, the IHCP covers preoperative planning under HCPCS code G0243 and 77301U5. Reimbursement for physician services is bundled into the preoperative planning service. Ventricular Assist Devices The IHCP has instituted changes to the medical necessity criteria for ventricular assist devices (VADs) and considers them medically necessary under the following conditions: 8-88 • The IHCP covers treatment of postcardiotomy cardiogenic shock when ventricular dysfunction continues after maximum medical therapy or as a means of myocardial recovery support for individuals who are unable to be weaned from cardiopulmonary bypass with maximal inotropic support and use of an intra-aortic balloon pump. • The IHCP covers bridge-to-transplant for members who meet the following criteria: - The member must be at risk of imminent death from nonreversible left ventricular failure (NYHA Class III or IV). - The member has received prior authorization for a heart transplant (excluding dual eligible members). - The member is listed as a candidate for heart transplantation by a Medicare- and Medicaidapproved heart transplant center. - If the VAD is implanted at a different site than the Medicare- and Medicaid-approved transplant center, the implanting site must receive written permission from the Medicare- or Medicaid-approved center where the patient is listed for transplant prior to implantation of the VAD. • The IHCP covers destination therapy for members who meet the following criteria: - The member must not be a candidate for a heart transplant. - The member must have chronic end-stage heart failure (NYHA Class IV) for at least 90 days, and have a life expectancy of fewer than two years. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual - - - Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions The member’s Class IV heart failure symptoms must have failed to respond to optimal medical therapy for at least 60 of the last 90 days. Medical therapy must include salt restriction, diuretics, digitalis, beta-blockers, and angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) or angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors (if tolerated). Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction (LVEF) must be less than 25 percent. The member has demonstrated functional limitation with a peak oxygen consumption of less than 12ml/kg/min; or continued need for IV inotropic therapy due to symptomatic hypotension, decreasing renal function, or worsening pulmonary congestion. The member has the appropriate body size (greater than or equal to 1.5m2) to support the Left Ventricular Assist Device (LVAD) implantation. VAD implantation must occur at a Medicare- and Medicaid-approved heart transplant center. A VAD is a covered service for postcardiotomy cardiogenic shock or bridge-to-transplant only if it has received approval from the FDA for the intended purpose, and only if it is used according to the FDAapproved labeling instructions for that intended purpose. A VAD is a covered service for destination therapy only if it has received approval from the FDA for destination therapy or as a bridge-totransplant, or has been implanted as part of an FDA investigational device exemption trial for one of these two indications. Noncovered Services • VADs are noncovered for all conditions not listed above. • Use of a non-FDA-approved VAD is considered investigational and is a noncovered service. • The artificial heart (for example, AbioCor, CardioWest) as a replacement heart for a diseased heart is noncovered by the IHCP. Prior Authorization VADs and their surgical implantation do not require PA. However, members who receive bridge-totransplant or destination therapy, and who can continue therapy on an outpatient basis, require accessory equipment for use with the VAD. The patient supplies and replacement equipment for the VAD require PA. Coding and Billing Instructions Tables 8.15 to 8.17 list the appropriate codes for billing implantation and removal of the VADs. The tables include the following: • Table 8.15 lists the diagnosis codes appropriate for implantation of a VAD. The diagnosis code should be billed on the UB-04 claim form with the corresponding ICD-9-CM procedure code. • Table 8.16 lists the applicable ICD-9-CM procedure codes for implantation, repair, and removal of a VAD. The ICD-9-CM code must be billed on the UB-04 claim form and is incorporated into the DRG payment. • Table 8.17 lists the applicable CPT codes for the physician component of the implantation and removal of a VAD. The CPT code should be billed on a CMS-1500 claim form or 837P electronic transaction. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-89 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual The DRG for hospital inpatients using the VAD system includes the following codes and equipment, which are not separately reimbursable: • ICD-9-CM diagnoses (primary, secondary, tertiary, as appropriate) • ICD-9-CM procedures • VAD (included in the ICD-9-CM procedure code) • Stationary power base and display module (capital purchase by the hospital) • Rechargeable batteries and harness (for untethered systems) • Miscellaneous supplies Table 8.15 – ICD-9-CM Diagnosis Codes Code Description 410.xx Acute myocardial infarction 411.1 Intermediate coronary syndrome 411.81 Acute coronary occlusion without myocardial infarction 414.9 Chronic ischemic heart disease, unspecified 422.xx Acute myocarditis in diseases classified elsewhere 425.x Cardiomyopathy 426.xx Conduction disorders 427.xx Cardiac dysrhythmias 428.xx Heart failure 429.4 Functional disturbances following cardiac surgery 785.51 Cardiogenic shock 997.1 Cardiac complications Note: xx represents diagnosis code placeholders. For example, 410.xx means all diagnoses in the 410 series are applicable. Table 8.16 – ICD-9 Procedure Codes Code Description 37.63 Repair of heart assist system Replacement of parts of an existing VAD 37.64 Removal of heart assist system 37.65 Implant of external heart assist system Device (outside the body but connected to heart) with external circulation and pump Includes open chest procedure for cannula attachments 8-90 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Code 37.66 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Description Insertion of implantable heart assist system Device directly connected to the heart and implanted in the upper left quadrant of peritoneal cavity Includes the following: • Axial flow heart assist system • Diagonal pump heart assist system • LVAD • Pulsatile heart assist system • Right ventricular assist device (RVAD) • Rotary pump heart assist system • Transportable, implantable heart assist system • VAD, not otherwise specified Table 8.17 – CPT Procedure Codes Code Description 33975 Insertion of ventricular assist device; extracorporeal, single ventricle 33976 Insertion of ventricular assist device; extracorporeal, biventricular 33977 Removal of ventricular assist device; extracorporeal, single ventricle 33978 Removal of ventricular assist device; extracorporeal, biventricular 33979 Insertion of ventricular assist device, implantable, intracorporeal, single ventricle 33980 Removal of ventricular assist device, implantable intracorporeal, single ventricle 0048T Implantation of a ventricular assist device, extracorporeal, percutaneous transseptal access, single or dual cannulation 0049T Prolonged extracorporeal percutaneous transseptal ventricular assist device, greater than 24 hours, each subsequent 24 hours period 0050T Removal of a ventricular assist device, extracorporeal, percutaneous transseptal access, single or dual cannulation Long-Term Acute Care Facility Services Long-Term Acute Care Facilities Long-term acute care (LTAC) facilities must submit charges on a UB-04 claim form. The billing provider must use the revenue code 101 – All-inclusive room and board for the PA process and include it on the UB-04 claim form. The discharging hospital must enter the patient status code 63 in field 17 on the UB-04 claim form. This indicates the status of the patient as of the ending service date when the patient was discharged or transferred to a long-term care facility. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-91 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Coverage Inpatient long-term care (LTC) services are available to IHCP members who meet the threshold of nursing care needs required for admission to, or continued stay in, an IHCP-certified nursing facility. Additional information about LTC coverage and billing procedures is located in Chapter 14 of this manual. Billing Procedures Instructions for billing LTC facility services are separated into two subsections, based on the type of facility rendering the service. This section outlines billing instructions for NFs and intermediate care facilities for the mentally retarded (ICFs/MR). For detailed information about reimbursement for LTC facilities, refer to Chapter 7. Providers should mail LTC paper claims to the following address for processing: HP Nursing Home Claims P.O. Box 7271 Indianapolis, IN 46207-7271 NFs and ICFs/MR may bill using the UB-04, electronic 837I transaction, or Web interChange claim formats. If submitting paper claims, NFs must follow the general instructions for completing the UB04 claim form, as well as the specific instructions that follow. Package C LTC facility services are not covered for Package C members. Nursing Facility Services NFs bill for room and board charges using the applicable room and board revenue code. Acceptable room and board revenue codes include 110, 120, and 130. Revenue codes 180, 183, and 185 for leaveof-absence days are also acceptable. The OMPP uses a case mix reimbursement methodology based on the Resource Utilization Group (RUG)-III Classification of that member. The facility must maintain documentation in the medical record that substantiates the physical or behavior needs of the member as identified on the minimum data set (MDS). The RUG-III Classification is based on the MDS. All longterm care providers must have a State-approved Form 450B or OMPP Form 450B SA/DE on file in IndianaAIM for the appropriate provider number before billing services provided to a member. Nursing facilities cannot bill separately for medical and nonmedical supply items, personal care items, or therapies. Providers can bill parenteral or enteral services and therapies received by Medicare- and Traditional Medicaid-eligible members to Medicare and, subsequently, the IHCP as crossover claims on the appropriate claim form for these services. Inpatient care crossover services must be billed on the UB-04, 837 electronic, or Web interChange institutional claim format. Any inappropriate billing and reimbursement is subject to recoupment by the Surveillance and Utilization Review (SUR) Department. Providers can bill short-term stays of less than 30 days on discharge of the patient. Providers can bill long-term stays of 30 days or more monthly, or more frequently if desired. 8-92 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Member Liability Member liability is the term applied to the monetary amount that a Traditional Medicaid resident must contribute toward monthly care in the NF. The term personal resource contribution also indicates member liability. Calculating and assigning the member liability amount is a function of the local county office of the Division of Family Resources (DFR). Member information, including member liability or personal resource contribution reflected in IndianaAIM, is updated daily from the information relayed by the Indiana Client Eligibility System (ICES) at the county offices. Providers must apply current income to current needs. As an example, a Social Security benefit check received in October must be applied to October charges. The only exception is the direct deposit benefit check that is sometimes recorded by the bank at the end of one month instead of early in the next month when it would normally be received. Because most resources are available on a calendar month basis, all accounts that involve resource deductions must be billed on a calendar month basis, for example, June 1 through June 30, or July 1 through July 31. Note: Deduct patient resources from the payment in the month that the resources are received. The IHCP automatically deducts the member’s liability amount from the total reimbursement of the claim. The provider must not indicate the resource contribution anywhere on the claim form. When a member transfers between facilities during a billing period, the member liability is deducted from the first claim received and processed by IndianaAIM. Therefore, the facilities involved in the transfer must coordinate any liability deductions. Leave Days The IHCP reimburses for reserved beds for members provided that the criteria in 405 IAC 5-31-8 is met. Providers should use the appropriate room and board revenue code for the days the member was a patient in the NF, and they should use the applicable leave-of-absence revenue code for the days the member was out of the NF. The IHCP only reimburses for bed-hold days to nursing facilities that have occupancy rates of 90 percent or greater. This policy change is addressed in 405 IAC 5-31-8. To determine eligibility for IHCP payment for bed-hold days, each nursing facility must determine the occupancy rate as of the date that an IHCP resident leaves the facility for hospital or therapeutic leave. If the facility’s occupancy rate is equal to or greater than 90 percent as of the date the IHCP resident leaves the facility for hospital or therapeutic leave, the facility is permitted to receive IHCP reimbursement for the bed-hold days for the duration of that resident’s leave of absence, subject to the limitations prescribed by 405 IAC 5-31-8. If the facility’s occupancy rate is less than 90 percent, the facility is not permitted to receive IHCP reimbursement for any bed-hold days for the duration of that resident’s leave of absence. The facility must code for leave days using the revenue codes as indicated in Table 8.18. For internal recordkeeping purposes, facilities must continue to submit claims for bed-hold days regardless of whether those leave days are eligible for IHCP payment. Bed-hold days not eligible for payment must be billed using revenue code 180. The bed-hold days appear on the explanation of benefits (EOB) as a payment denial but still allow the OMPP to track unpaid leave days. Bill bed-hold days eligible for IHCP payment pursuant to 405 IAC 5-31-8 using either revenue code 183 or 185, as applicable. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-93 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Code any leave day, whether eligible for payment or not, on the claim using one of the codes listed in Table 8.18. Table 8.18 – Bed-Hold Revenue Codes Revenue Code Description 180 Bed-hold days not eligible for payment 183 Therapeutic bed-hold days eligible for payment 185 Hospital bed-hold days eligible for payment The types of reimbursed leave days are as follows: • Hospitalization – Must be ordered by the physician for treatment of an acute condition that cannot be treated in the NF. The total length of time allowed for payment of a reserved bed for a single hospital stay is 15 consecutive days. Providers must use revenue code 185 to denote a leave of absence for hospitalization. The IHCP reimburses leave days at one-half the case mix room and board rate. To determine the leave day rate, divide the case mix per diem rate in half. • Therapeutic Leave of Absence – Must be for therapeutic reasons, as prescribed by the attending physician and as indicated in the member’s plan of care. The maximum total length of time allotted for therapeutic leave in a calendar year is 30 days for any NF resident. Providers must use revenue code 183 to denote a therapeutic leave of absence. Autoclosure Billing To ensure that IHCP members receive all benefits to which they are entitled, it is the responsibility of each LTC provider to properly document the discharge of residents in a timely manner. Since January 1998, IndianaAIM has used the patient status code from the UB-04 claim form (locator box 22, STAT) to close the member’s Level of Care (LOC) segment. This eliminates the need for submitting written discharge information to the OMPP. If the LOC is not updated, it prevents members from receiving services, such as supplies and pharmacy prescription fulfillment, upon discharge from LTC facilities. Providers should be aware that overpayments to facilities are subject to recoupment. The following discharge status codes are the only valid codes for members who are discharged from LTC facilities: • 01 – Discharged to home or self-care, routine discharge • 02 – Discharged or transferred to another short-term general hospital for inpatient care • 05 – Discharged or transferred to a designated cancer center or children’s hospital • 07 – Left against medical advice or discontinued care • 08 – Discharged or transferred to home under care of a home intravenous provider • 20 – Expired LTC providers do not receive reimbursement for the date of discharge. Therefore, it is imperative that LTC providers carefully complete the UB-04 claim form to ensure that the “Through Date of Service” (TDOS) in field locator 6 on the claim form accurately reflects the actual date of discharge for the member. 8-94 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Medicare Crossover Payment Policy The IHCP makes a payment only when the Medicare payment amount is less than the IHCP rate on file at the time HP processes the crossover claim. This change in payment policy for Medicare crossover claims is addressed in 405 IAC 1-18-2. A paid claim can have an amount of $0. See Chapter 14 of this manual for more information. When a nursing facility resident elects Medicare benefits for room and board at the beginning of the month, the nursing facility collects liability at the beginning of the month, as if the resident was not using Medicare days. If the resident uses Medicare room and board benefits for the entire month, the nursing facility places the liability collected at the beginning of the month in the resident’s personal needs allowance account. If the resident uses Medicare benefits for room and board for several months, this may put the resident over personal resources. In this case, the nursing facility must notify the county caseworker, who will redetermine the financial eligibility of the resident and may end-date the resident’s IHCP eligibility until personal resources are again exhausted. The resident may then reapply for Medicaid and must complete a new Form 450B. If the resident uses only a portion of the month for Medicare room and board benefits, the liability collected by the nursing facility is only for the days that Medicaid paid the nursing facility room and board. The nursing facility places the remaining liability in the resident’s personal needs allowance account. If the dollar amount in the personal needs account exceeds the limit allowed, the nursing facility must notify the county caseworker. Nursing Facilities Not Medicare-Certified IHCP-enrolled nursing facilities that are not Medicare-certified must comply with the following: • The nursing facility must use the Certification Statement available on the Web at http://provider.indianamedicaid.com to certify to the OMPP that it will not request payment from the IHCP for services rendered to dually eligible IHCP members who are eligible to receive Medicare Part A nursing facility benefits. For as long as a nursing facility elects not to become Medicare-certified, the NF must submit this certification annually to the OMPP’s rate-setting contractor, Myers and Stauffer, LC. NFs must send the Certification Statement with the facility’s regularly scheduled cost report submission. • The nursing facility must maintain clinical, payment, and benefit records in sufficient detail to substantiate to the OMPP that a member for whom IHCP payment was requested is not also entitled to or eligible for Medicare Part A nursing facility benefits. The facility must contact the Medicare fiscal intermediary to determine the availability of Medicare. Intermediate Care Facility for the Mentally Retarded Services Intermediate care facilities for the mentally retarded (ICFs/MR) are divided into three distinct categories: • Small ICF/MR – Four to eight beds and are commonly referred to as community residential facilities for the developmentally disabled (CRF/DD) - Basic developmental - Child rearing - Child-rearing residences with specialized programs - Developmental training - Intensive training - Sheltered living - Small behavioral management residences for children - Small extensive needs medical residences for adults Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-95 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions • Large, private ICF/MR – More than eight beds • State-operated facilities – More than eight beds Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual ICFs/MR bill for room and board charges using the applicable room and board revenue code. Acceptable room and board revenue codes include 100, 110, 120, and 130. The ICF/MR reimbursement rate is an inclusive rate. Therefore, ICFs/MR cannot bill separately for medical and nonmedical supply items, personal care items, or therapies. The small ICF/MR reimbursement rate also includes day services as part of the inclusive rate. However, ICFs/MR can bill separately when billing crossover claims. Any inappropriate billing or reimbursement is subject to recoupment by the SUR Department. Type of Bill Providers must use type of bill 66X in form field 4 of the UB-04 claim form to denote a large or Stateowned ICF/MR. Type of bill 67X denotes a group home or small ICF/MR. Leave Days Reimbursement is available for reserving beds for members in a private or State-operated ICF/MR, provided that the criteria set out in 405 IAC 5-13-6 is met. Providers must use the appropriate room and board revenue code for the days the member was a patient in the ICF/MR and use the applicable leave of absence revenue code for the days the member was out of the ICF/MR. The two types of reimbursed leave days are as follows: 8-96 • Hospitalization – Must be ordered by the physician for treatment of an acute condition that cannot be treated in the facility. The total time allowed for payment of a reserved bed for a single hospital stay is 15 consecutive days. If the member requires hospitalization longer than 15 consecutive days, then the member must be discharged from the ICF/MR. If the member is discharged from the ICF/MR following a hospitalization in excess of 15 consecutive days, then the ICF/MR is still responsible for appropriate discharge planning. Discharge planning is required if the ICF/MR does not intend to provide ongoing services following the hospitalization for those members who continue to require ICF/MR Level of Care services. The facility must maintain a physician’s order for hospitalization in the member’s file at the facility. Providers must use revenue code 185 to denote a leave of absence for hospitalization. • Therapeutic Leave of Absence – Must be for therapeutic reasons, as prescribed by the attending physician and as indicated in the member’s habilitation plan. The maximum total length of time allotted for therapeutic leaves in any calendar year is 60 days per member residing in an ICF/MR. The leave days need not be consecutive. If the member is absent for more than 60 days per year, then no further reimbursement is available to reserve a bed for that member in that year. The facility must maintain a physician’s order for the therapeutic leave in the member’s file at the facility. Providers must use revenue code 183 to denote a therapeutic leave of absence. • Use Revenue code 180 when the hold days are not eligible for payment. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Outpatient Services Coverage Outpatient services are services provided to members who are not registered as inpatients in an acute care or psychiatric hospital. Outpatient services include surgery, therapy, laboratory, radiology, chemotherapy, renal dialysis, clinic, treatment room, and emergency department care. The IHCP covers outpatient services when such services are provided or prescribed by a physician and when the services are medically necessary for the diagnosis or treatment of the member’s condition. The member’s medical condition, as described and documented in the medical record by the primary or attending physician, must justify the intensity of service provided. The four categories of service within the defined outpatient hospital prospective payment system are as follows: • Outpatient surgeries • Treatment room visits • Stand-alone services • Add-on services Medicare and Medicaid The IHCP developed the coverage policies, reimbursement policies, and billing requirements of the Outpatient Prospective Payment System. The IHCP does not intend for these policies and requirements to mirror the policies and procedures of the Medicare program. Billing Procedures Mail outpatient claims to the following address for processing: HP Outpatient Claims P.O. Box 7271 Indianapolis, IN 46207-7271 Note: RBMC members must bill the appropriate MCO. The following clarifications may assist providers using the UB-04 claim form. Detailed information about reimbursement for outpatient services is in Chapter 7 of this manual. Package B Billing Services for Hoosier Healthwise Package B must comply with the following restrictions: • The IHCP does not reimburse for any services other than pregnancy-related services. • The IHCP pays for drugs prescribed for indications directly related to the pregnancy in accordance with IAC restrictions. In addition to drug coverage, transportation, family planning, routine prenatal care, delivery, and postpartum care, the IHCP reimburses providers for a condition that may complicate the pregnancy. In other words, the IHCP covers a service provided to a pregnant woman for the treatment of a chronic or Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-97 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual abnormal disorder, as identified by ICD-9-CM diagnosis codes 649.00 – 649.04, 649.10 – 649.14, 649.20 – 649.21, 649.23 – 649.24, 649.30 – 649.34, 649.40 – 649.44, 649.50 – 649.51, 649.53, 649.60 – 649.64, 649.70 – 649.71, and 649.73, as well as urgent care. The IHCP defines a condition that may complicate the pregnancy as any condition manifesting itself by symptoms of sufficient severity that the absence of medical attention could reasonably be expected to result in a deterioration of the patient’s condition or a need for a higher level of care. The IHCP does not dictate to physicians conditions that may or may not complicate a pregnancy. Therefore, if the physician determines that the illness or injury could complicate the pregnancy or have an adverse effect on the outcome of the pregnancy, the IHCP covers the care provided for that illness or injury. Providers should list a pregnancy diagnosis code as the primary diagnosis code and identify the illness or injury being treated as the secondary diagnosis code if the condition is considered a risk of complication of the pregnancy. When billing for emergency services, providers must appropriately code claims as emergency. The primary diagnosis code must be pregnancy-related, or IHCP denies the claim. Providers must indicate the pregnancy-related diagnosis code in primary diagnosis field 67 on the UB-04 claim form. If the pregnancy diagnosis does not adequately address the specific reason for the visit or care, providers must also include the visit or care diagnosis as a secondary or tertiary diagnosis on the claim form. If a Package B member receives a sterilization procedure following delivery, the primary diagnosis code must be pregnancy with voluntary sterilization as a secondary diagnosis. The member must complete consent forms, and the provider must send them with the claim. See Informed Consent Claim Attachment Instructions section. Notification of Pregnancy Billing Effective December 1, 2009, hospitals can submit claims for Notification of Pregnancy (NOP). Submit claims for NOP using the UB-04 claim form to the appropriate managed care organization following the guidelines below for reimbursement. To be eligible for reimbursement of an NOP: 1. The NOP must be submitted via Web interChange no more than five calendar days from the date the risk assessment was completed. The NOP cannot be a duplicate of a previously submitted NOP, and the member’s gestation must be 29 weeks or less. 2. NOP claim forms from hospitals must be coded with the following: - Revenue Code 960 - CPT® code 99354 and modifier TH Note: The revenue code, CPT code, and modifier must be billed together to be reimbursed the NOP fee when billed on the UB claim form. Duplicate NOPs will not be reimbursed. For more information on submitting a NOP through Web interChange, see the Process for Completion of the Notification of Pregnancy section. 8-98 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Outpatient Surgeries The IHCP reimburses an all-inclusive flat fee that includes all related procedures for outpatient surgeries provided in either a hospital or an ambulatory surgical center (ASC) . The IHCP reimburses for outpatient surgeries provided in a number of settings including an operating room, treatment room, emergency department, or clinic. Surgical Revenue Codes Surgical revenue codes are generally defined as 36X and 49X. The revenue codes for treatment rooms, such as 45X, 51X, 52X, 70X, 71X, 72X, and 76X, are defined as surgical revenue codes when accompanied by a surgical CPT or HCPCS code. The IHCP then reimburses these revenue codes at the appropriate ASC rate. If the provider performs no surgical procedure, the provider must submit the revenue code without a CPT or HCPCS code. The IHCP then reimburses these services at the treatment room rate. Providers combine all charges and services associated with the surgical procedure as an all-inclusive charge on one line item. Component billing of any related services is not appropriate and is denied. Note: The IHCP does not allow add-on or stand-alone services with any surgical revenue codes. Reimbursement is based on the assignment of the CPT code to one of 16 ASC groups. Reimbursement rates have been established for each ASC group that is reflective of the average cost for procedures within the group. Please note that the assignment of CPT codes to ASC groups may not be the same as the assignment formally used by the Medicare program. Table 8.19 identifies the ASC groups. Table 8.19 – ASC Groups ASC Group Group 1 Group 2 Group 3 Group 4 Group 5 Group 6 Group 7 Group 8 A – Extensive B – Complicated C – Intermediate D – Simple E – Moderate F – Minimal G – Drug Eluting Stents T – Telemedicine Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-99 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual The IHCP reimburses a maximum of two units of service regardless of the number of incisions. The IHCP reimburses the procedure with the highest ASC rate at 100 percent of that rate, and it reimburses the procedure with the second highest ASC rate or bilateral procedure at 50 percent of the respective ASC rate. All other procedures are denied. To denote multiple surgeries, the provider must list the appropriate revenue code and CPT code as two separate detail line items on the claim form. Providers must bill outpatient surgeries provided in either a hospital or an ASC on a UB-04 claim form. Combine all charges and services associated with the surgical procedure as an all-inclusive charge on each line item. The appropriate CPT surgical procedure code (10000 through 69999) must accompany one of the revenue codes listed in Table 8.20: Table 8.20 – Revenue Codes Revenue Code Description 36X Operating room services 45X Emergency department 49X Ambulatory surgical care 51X Clinic 52X Freestanding clinic 70X Cast room 71X Recovery room 72X Labor/delivery room 76X Treatment/observation room Providers must include all outpatient services provided on the day of the surgery on a single claim. Include the charges for any other services provided on the day of the surgery with the charge for the surgery, as described above. Add-on or stand-alone services are not separately reimbursable. Implantable DME The cost of certain implantable durable medical equipment is separately reimbursable for outpatient claims. Some of these items require prior authorization (see Chapter 6 for more information about PA). Providers should submit claims for these items on the CMS-1500 claim form or 837P transaction. Submit only these items on the CMS-1500 claim form or 837P transaction. The IHCP permits only these items to have separate reimbursement. Table 8.21 lists the implantable durable medical equipment. Table 8.21 – Implantable Medical Equipment Category 8-100 Type Notes Cardiac Pacemakers Single-chamber C1786, C2619 Cardiac Pacemakers Dual-chamber C1785, C2620 Cardiac Pacemakers Other than singleor dual-chamber C2621 Implantable Loop Recorders N/A See Patient-Activated Event Recorder— Implantable Loop Recorder. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Category Phrenic Nerve Stimulators New Technology Intraocular Lenses Vagal Nerve Stimulators Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Type N/A N/A N/A Implantable Infusion Pumps Nonprogrammable Implantable Infusion Pumps Programmable Notes See Phrenic Nerve Stimulator (Breathing Pacemaker). See Intraocular Lenses. See NeuroCybernetic Prosthesis System – Vagus Nerve Stimulator. Corneal Tissue The cost associated with corneal tissue acquisition, HCPCS code V2785 – Processing, preserving, and transporting corneal tissue, is separately reimbursable from the ASC rate for outpatient corneal transplant procedures. Submit claims for this item on the CMS-1500 claim form or through the 837P transaction. Make sure to attach a copy of the invoice from the eye bank or organ procurement organization showing the actual cost of acquiring the tissue. Providers must follow current policy for submitting paper attachments with the 837P transaction. Effective December 15, 2006, HCPCS code V2785 is reimbursed 100 percent of the cost invoice. Pacemakers Effective December 15, 2006, when the implantation is performed in an outpatient surgical setting, IHCP reimburses the cost of single- and dual-chamber pacemakers identified in Table 8.21 in addition to the ASC rate. The facility purchasing the pacemaker must submit, as an attachment to the CMS1500 or 837P electronic transaction, a manufacturer’s cost invoice showing the purchase price for the pacemaker. The IHCP reimburses the provider at 100 percent of the cost invoice for this device. Phrenic Nerve Stimulator (Breathing Pacemaker) IHCP began covering the phrenic nerve stimulator (breathing pacemaker) effective for claims with dates of service of October 26, 2000. Specific coverage criteria have been developed and must be met for reimbursement to be made. This section provides coverage and billing information to allow providers to submit claims for this device. This device is an electrophrenic pacemaker for pacing the diaphragm. The device consists of an external radio frequency transmitter, an antenna, a subcutaneous radio receiver, and a bipolar platinum nerve electrode. Diaphragmatic pacing (intermittent electrical stimulation of the phrenic nerves) offers freedom from mechanical ventilation for patients who need long-term ventilation, and have a functionally intact phrenic nerve and chest-wall stability. Prior Authorization Prior authorization (PA) is required for this device and its implantation, whether the device is implanted on an inpatient or an outpatient basis. One or more of the following ICD-9-CM diagnosis codes must be used when submitting requests for PA. Members with these diagnoses who are Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-101 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual ventilator dependent and have a tracheostomy due to partial or complete respiratory insufficiency are considered candidates for this device, subject to review. • 344.0-344.9 includes quadriplegia and quadraparesis of all types • 780.51 and 780.53—nonobstructive sleep apnea • 786.09—congenital respiratory abnormalities, other Coding and Billing Instructions For inpatient billing of the implantation of the device, the appropriate DRG will be used. The claim for the device must be submitted as a durable medical equipment (DME) item on a CMS-1500 claim form. When the device is implanted as an outpatient procedure, the revenue code 360 with CPT code 33282 should be used on the UB-04 claim form and the device billed as a DME item on a CMS-1500 claim form. The decision for either outpatient or inpatient status is made by the physician and determined by the assessment of complicating factors and their severity at the time the procedure is planned. The hospital providing the equipment for implantation must be enrolled as a DME provider with a DME Legacy Provider Identifier (LPI). Table 8.22 provides the CPT codes and description information to use when submitting claims either as an inpatient or outpatient. Table 8.22 − CPT Codes for Inpatient and Outpatient Claims CPT Code 64577 64585 95970 95974 Description Incision for implantation of neurostimulator electrodes; autonomic nerve Revision or removal of peripheral neurostimulator electrodes Initial programming Intraoperative or subsequent programming, first hour Coverage Issues Patient Selection The primary objective of implanting the phrenic nerve stimulator is to allow the member to return to a home environment from a skilled nursing facility and be more independent. Therefore, the following criteria are mandatory for prospective candidates requesting this device: • Functional lungs and diaphragm muscle • Absence of infection • A clear and adequate upper airway (including nasopharynx, pharynx, larynx) • Family support that includes an unpaid, physical care giver of adequate quality and the availability of nursing and medical care 8-102 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Medical Review Documentation Prior authorization for medical necessity is required for this device and its implantation. The equipment is costly and requires preoperative testing of the components and thorough education of the member and his or her caregivers concerning its use. Medical Policy Criteria 1. Members who qualify for this device will demonstrate life-threatening oxygen depletion when respiration is unassisted. 2. For stable, nonacute quadriplegics and other members with spinal-cord or brain-stem injuries [ICD9-CM 344(00-09) diagnosis codes], all the following criteria must be met: – Patient is oriented to name, date, and place. – Patient’s mobility will be improved. Patient will be able to be out of bed and be mobile per wheelchair, which may include employment or attending school. Increased mobility will allow the patient to function without interference of large equipment. – Patient’s skin integrity will be better maintained because of increased mobility. – Patient has capacity to be productive. He or she will more easily perform cognitive tasks within physical limitations. – Patient will be better able to eat and swallow. 3. For nonobstructive (or central) sleep apnea (ICD-9-CM 780.51, 780.53 diagnosis codes) only when other treatments have failed. The following criteria must be met: – The requesting physician will present sleep studies demonstrating life-threatening respiratory cycles when the patient is asleep. – The member must have a diagnosis of central sleep apnea and have failed to maintain an appropriate PO2 level (oxygen partial pressure) with continuous positive air pressure (CPAP) and bilevel continuous positive airway pressure (BiPAP) treatments. – Documentation by a specialist in otolaryngology or pulmonology of treatment attempts will accompany the prior authorization request. – The breathing pacemaker should never be recommended for treatment of obstructive sleep apnea. 4. Documentation indicating medical necessity for the appropriate diagnosis will be submitted prior to surgical implantation of the stimulator wires. Device Monitoring Medical device tracking regulations of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration require that the manufacturer of the device be notified when the following occurs: • Diaphragm pacing system is implanted • Diaphragm pacing receiver or electrode is explanted (date, name, mailing address, and telephone number of the explanting physician are to be included) • Diaphragm pacing patient dies • Diaphragm pacing device is returned • Diaphragm pacing device is permanently retired from use or otherwise permanently discarded Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-103 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Patient-Activated Event Recorder – Implantable Loop Recorder The IHCP reimburses for the insertion and programming of the patient-activated event recorder – implantable loop recorder (ILR).This change is effective for claims with service dates of October 26, 2000, or after. Claims should be billed with the ICD-9 diagnosis code that supports medical necessity, 780.2 – Syncope and collapse. This section provides details about coverage and billing of the patientactivated event recorder – ILR, also referred to as the implantable loop recorder. Coverage IHCP covers the patient-activated event recorder – ILR for use after a syncopal event. The device may be implanted at any of three places of service including inpatient, outpatient, or physician’s office. The device may not be implanted in the same member more often than every two years or 24 months. The recorder activator is furnished with the system and is not separately reimbursed. Prior Authorization Neither the implantation of the device nor the patient-activated event recorder – ILR require prior authorization (PA), but will be subject to retrospective review according to IHCP criteria. If a replacement recorder activator is needed, PA is required. Reimbursement and Billing Instructions The procedure code for the implantation of the patient-activated event recorder – ILR is CPT code 33282. The code for the removal of this device is 33284. These procedure codes have a 90-day global postoperative care designation for which care related to the surgical procedure is not separately reimbursable unless such care is nonroutine, such as treatment of complications. If the procedure is performed when the patient is an inpatient for a related problem, submit a UB-04 using the ICD-9-CM code 780.2 – Syncope and collapse as one of the diagnosis codes on the claim form. If the procedure is performed as an outpatient, submit a UB-04 using revenue code 360 and the CPT code 33282 for implantation. The device itself should be billed on a CMS-1500 using code E0616, and 780.2 – Syncope and collapse as the primary diagnosis code. Use CPT code 33284 with revenue code 360 to bill for removal of the device. Physician’s charges for the surgery should be billed on a CMS-1500. If the procedure is performed in a physician’s office, the physician should bill CPT code 33282 for implantation and E0616 for the device. Both codes are billed on the CMS-1500. Table 8.23 illustrates coding for each place of service: 8-104 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Table 8.23 − Place of Service Codes Inpatient Outpatient Physician’s Office UB-04 UB-04 (and CMS-1500 if billing for device) CMS-1500 ICD-9-CM Diagnosis Code 780.2 – Syncope and Collapse 780.2 – Syncope and Collapse 780.2 – Syncope and Collapse Revenue and CPT Codes Revenue code – 360 CPT code not necessary Revenue code – 360 CPT code – 33282 for insertion CPT code – 33284 for removal Revenue code not needed CPT code – 33282 for insertion CPT code – 33284 for removal Not needed On CMS-1500 – E0616 E0616 Type of Claim HCPCS Code Table 8.24 illustrates the codes for implantation and the device. Providers must bill their usual and customary charges on the claim form. Insertion of the device carries a 90-day global surgery designation with no assistant surgeon required. Table 8.24 − Loop Recorder System Implantation Codes Code Description 33282 Implantation of patient-activated cardiac event recorder 33284 Removal of an implantable, patient-activated cardiac event recorder 93727 Electronic analysis of ILR system (includes retrieval of recorded and stored ECG data, physician review, and interpretation of retrieved ECG data and reprogramming) E0616 Implantable cardiac event recorder memory, activator, and programmer. (The programmer is furnished by the manufacturer, to the physician, for use in the office for reading saved information in the recorder.) E1399 Recorder activator (replacement) Device Monitoring The CPT code for analysis of information collected by the recorder is 93727 and should be billed only subsequent to the date of insertion. Initial analysis and monitoring is included in the fee for insertion; therefore, code 93727 may not be billed on the date of insertion. The programmer used to program the patient-activated event recorder – ILR – to retrieve, display, and print stored data is furnished to the physician, but remains the property of the manufacturer. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-105 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Coverage Criteria Coverage criteria include the following: • • • A patient-activated event recorder – ILR is covered only if a definitive diagnosis has not been made after meeting all the following conditions: – Complete history and physical examination – Electrocardiogram (ECG) – Two negative or nondiagnostic 30-day presymptom memory loop patient demand recordings (may be either single- or multiple-event recordings, with or without 24-hour attended monitoring) – Negative or nondiagnostic tilt-table testing – Negative or nondiagnostic electophysiological testing The patient must be capable of activating the hand-held telemetry unit. The patient-activated event recorder – ILR is not covered for the following: – Patients with presyncopal episodes – Patients failing to fulfill the indications for coverage in this policy – Patients for whom compliance or lifestyle make use of the external monitoring systems inappropriate • Removal of a patient-activated event recorder – ILR on the same day as the insertion of a cardiac pacemaker is considered part of the pacemaker insertion procedure and is not reimbursed separately. • Only one patient-activated event recorder – ILR is covered for a given patient in any two-year time period. • ECG analyses obtained during device insertion for signal quality and amplification purposes are considered part of the implant procedure and are not reimbursed separately. Intraocular Lenses New Technology Intraocular lenses (NTIOL) are intraocular lenses (IOLs) that the CMS has identified as being superior to other IOLs of the same category because of a demonstrated decrease in postoperative complications. Providers should use the appropriate HCPCS V-code. Any facility reimbursed at an ASC rate should submit claims for surgical insertions of IOLs using the Physician’s CPT code 66983, 66984, 66985, or 66986 and the appropriate revenue code on a UB-04 claim form. The NTIOL claim must be submitted on a separate CMS-1500 claim form using the facility’s durable medical equipment (DME) NPI. NeuroCybernetic Prosthesis System – Vagus Nerve Stimulator Effective October 23, 2000, the IHCP will reimburse for the NeuroCybernetic Prosthesis (NCP) System, a vagus nerve stimulator. This system works as a pacemaker for the brain. The NCP System is indicated for use as an adjunctive therapy in reducing the frequency of seizures in adults and adolescents older than 12 years old with partial-onset seizures that are refractory to anti-epileptic medications, and for which surgery has failed or is not recommended. 8-106 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Coverage Criteria for the NCP System The IHCP has approved the following criteria: • Coverage of the NCP System is effective for dates of service on or after October 23, 2000. Reimbursement for implantation, revision, programming and reprogramming, and removal of the vagus nerve stimulator device is available under the IHCP for members older than 12 years old with medically intractable partial-onset seizures. These members are not otherwise surgical candidates. Providers are required to perform this procedure on an outpatient basis whenever medically possible. Implantation procedures and equipment will require prior authorization with documentation of medical necessity. In situations where complicating factors require this procedure to be performed on an inpatient basis, medical history and records should support the need for the inpatient admission. Prior authorization will not be required by the hospital for the inpatient admission or the device (included in the DRG reimbursement). The device cannot be billed separately for inpatients. Prior authorization must be obtained by the physician for the implantation procedures regardless of setting. The prior authorization request must be submitted with the following information: • Documentation that an evaluation has been made by a neurologist • Documentation of the member’s type of epilepsy • Documentation that the member’s seizures are medically intractable (member continues with an unacceptable number of seizures with adequate treatment with two or more anti-epileptic drugs (AEDs) for a period of at least 12 months) • Documentation that the member is not an intracranial surgical candidate or that surgery has been unsuccessful (for example, the member is not a surgical candidate due to multiple epileptic foci) Members with diagnoses of ominous prognosis or other limiting factors would not be considered appropriate candidates for the implantation of the vagus nerve stimulator (for example, members with an absent left vagus nerve, severe mental retardation, cerebral palsy, stroke, progressive fatal neurologic disease, or progressive fatal medical disease). Diagnosis and Procedure Codes The following diagnosis and procedure codes are to be used when billing for the implantation, revision, programming and reprogramming, and removal of the vagus nerve stimulator device. Table 8.25 – ICD-9 Diagnosis Codes for Vagus Nerve Stimulator Device Code Description 345.41 Partial epilepsy with impairment of consciousness 345.51 Partial epilepsy without impairment of consciousness Table 8.26 – ICD-9 Procedure Codes for Vagus Nerve Stimulator Device Code Description 04.92 Implantation or replacement of peripheral neurostimulator 04.93 Removal of peripheral neurostimulator Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-107 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Table 8.27 – Surgeon CPT Procedure Codes for Vagus Nerve Stimulator Device Code Description 64573 Incision for implantation of neurostimulator electrodes; cranial nerve 64553 Percutaneous implantation of neurostimulator electrodes; cranial nerve 61885 Incision and subcutaneous placement of cranial neurostimulator pulse generator or receiver, direct or indirect coupling, with connection to a single electrode array 64585 Revision or removal of peripheral neurostimulator electrodes 61888 Revision or removal of cranial neurostimulator pulse generator or receiver Table 8.28 – Neurologist CPT Procedure Codes for Vagus Nerve Stimulator Device Code Description 95970 Electronic analysis of implanted neurostimulator pulse generator system (for example, rate, pulse amplitude and duration, configuration of wave form, battery status, electrode selectability, output modulation, cycling, impedance, and patient compliance measurements); simple or complex neurostimulator pulse generator, without programming 95974 Complex cranial nerve neurostimulator pulse generator/transmitter, with intraoperative or subsequent programming, with or without nerve-interface testing, first hour 95975 Complex cranial nerve neurostimulator pulse generator/transmitter, with intraoperative or subsequent programming, with or without nerve interface testing, each additional 30 minutes after first hour (list separately in addition to code for primary procedure) Hospital Outpatient and Freestanding Ambulatory Surgical Center Billing Instructions • For claims from hospital outpatient and ambulatory surgical centers, revenue codes 360 or 490 should be used on the UB-04 claim form. • Table 8.29 indicates the procedure codes to be used when billing for the incision, implantation, revision, or removal of the vagus stimulator. The CPT code must be billed in conjunction with the appropriate revenue code on the UB-04 claim form. Table 8.29 – CPT Procedure Codes for Vagus Nerve Stimulator Device Category Implantation CPT Code 64573 64553 8-108 PA Required Description Incision for implantation of neurostimulator electrodes; cranial nerve Yes Percutaneous implantation of neurostimulator electrodes; cranial nerve Yes Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Category Revision/ Removal CPT Code Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Description PA Required 61885 Incision and subcutaneous placement of cranial neurostimulator pulse generator and or receiver, direct or indirect coupling with connection to a single electrode array Yes 64585 Revision or removal of peripheral neurostimulator electrodes No 61888 Revision or removal of cranial neurostimulator pulse generator or receiver No The surgical procedure involves two separate incisions. Therefore, 64573 and 61885 or 64553 and 61885 CPT codes should be used. Reimbursement is based on 100 percent of the highest ASC group and 50 percent for the second highest ASC group (no additional reimbursement is available for three or more procedures). Additional reimbursement, separate from the ASC rate for the implantation procedure performed in an outpatient setting, will be allowed for the cost of the device. Providers are to bill their usual and customary charge for this device and will be reimbursed the lesser of the submitted charges for the device or the maximum fee amount. The device must be billed on a CMS-1500 claim form using a DME provider number, and prior authorization must be obtained. Note: Providers may not separately bill for individual components when implanting the complete system. If a provider does not have a DME provider number, the provider can obtain an application on the Indiana Medicaid Web site at http://provider.indianamedicaid.com in the provider enrollment section. Additional information can be found in Chapter 4 of the manual. Hospital Inpatient In situations where a complicating factor is present and the patient requires admission to the hospital for the procedure, the procedure and equipment will be reimbursed according to the appropriate DRG payment. Prior authorization is not required for the admission or the device, which is included in the DRG reimbursement. The physician for the surgical procedure must obtain prior authorization. The hospital stay must be billed on the UB-04 claim form and must include a secondary diagnosis indicating a complicating factor that necessitated inpatient admission. Hospitals cannot receive additional reimbursement outside the DRG payment for the cost of the device. DRG payments for inpatient procedures with complicating factors include reimbursement for the device. Physician Billing Instructions Physicians will bill professional services on the CMS-1500 claim form, using the appropriate procedure codes in the following tables. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-109 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Table 8.30 – Procedure Codes for Vagus Nerve Stimulator Device Category Implanting Revision/Removal CPT Code PA Required Description 64573 Incision for implantation of neurostimulator electrodes; cranial nerve Yes 64553 Percutaneous implantation of neurostimulator electrodes; cranial nerve Yes 61885 Incision and subcutaneous placement of cranial neurostimulator pulse generator and/or receiver, direct or indirect coupling with connection to a single electrode array Yes 64585 Revision or removal of peripheral neurostimulator electrodes No 61888 Revision or removal of cranial neurostimulator pulse generator or receiver No Note: Surgeons will use the above codes. Anesthesia practitioners will use the above codes using the appropriate modifier(s). The following codes in Table 8.31 should be used by the neurologist for interrogation and programming services performed on patients with implants. Table 8.31 – Interrogation and Programming Services Codes for Implant Patients Code PA Required Description 95970 Electronic analysis of implanted neurostimulator pulse generator system (for example, rate, pulse amplitude and duration, configuration of wave form, battery status, electrode selectability, output modulation, cycling, impedance and patient compliance measurements); simple or complex neurostimulator pulse generator, without programming. No 95974 Complex cranial nerve neurostimulator pulse generator/transmitter, with intraoperative or subsequent programming, with or without nerve interface testing, first hour. No 95975 Complex cranial nerve neurostimulator pulse generator/transmitter, with intraoperative or subsequent programming, with or without nerve interface testing; each additional 30 minutes after first hour (list separately in addition to code for primary procedure). No Treatment Room Visits For purposes of the IHCP’s outpatient prospective payment system, treatment rooms include emergency department, clinic, cast room, labor and delivery room, recovery room, and observation room. 8-110 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions The IHCP reimburses emergency department services for the treatment of ill and injured persons that require immediate unscheduled medical or surgical care. The IHCP reimburses clinic services for diagnostic, preventative, curative, and rehabilitative services provided to ambulatory patients. Reimbursable observation services are furnished by a hospital on the hospital’s premises, including the use of a bed and periodic monitoring by a hospital’s nursing staff, and are reasonable and necessary to evaluate the patient’s condition or determine the need for possible admission to the hospital as an inpatient. When surgeries are performed in a treatment room, the appropriate CPT code should accompany the revenue code, and reimbursement is based on the ASC methodology. Facilities should otherwise not use a surgical CPT code in addition to the treatment room revenue code. Treatment room services are reimbursed at a flat rate that includes most drugs and supplies. Reimbursement is limited to one unit per day, per patient, per provider. Services must be billed on the UB-04 claim form using the appropriate revenue code. The treatment room revenue codes are listed in Table 8.32. Table 8.32 – Treatment Room Services Revenue Code Description 45X Emergency department 51X Clinic 52X Freestanding clinic 70X Cast room 72X Labor/delivery room 76X Treatment/observation room Providers may bill stand-alone services in conjunction with treatment room services. Stand-alone services include therapies, dialysis, radiology, and laboratory services. The IHCP allows certain add-on services, described below, if they are billed in conjunction with a treatment room. These are 255 (Drugs Incident to Radiology), 258 (IV Solutions), 29X (DME), 370 (Anesthesia), 38X (Blood), 39X (Blood Storage and Processing), and 62X (Diagnostic Supplies). All other add-on services are denied if billed in conjunction with a treatment room service. Emergency Services Facility payment for services rendered in the emergency department is the same statewide flat rate for an emergency diagnosis and for a nonemergency diagnosis. While authorization is not required for emergencies, the IHCP may not cover nonauthorized services rendered to a Care Select member without an emergency diagnosis. The IHCP may suspend these claims for review to determine whether the provider met the prudent layperson standard for an emergency medical condition. If the review determines that the provider did not meet the prudent layperson standard, the claim is denied. If the provider did meet the prudent layperson standard, the IHCP pays only revenue code 45X, as long as the primary medical provider (PMP) NPI is indicated in field 78 of the UB-04 claim form. The IHCP reimburses revenue codes 70X, 71X, 72X, and 76X at a flat rate regardless of the diagnosis code on the claim. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-111 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual For a service to be considered an emergency, the provider must enter the applicable emergency diagnosis code as the principal diagnosis in field 67 on the UB-04. Note For members enrolled in an MCO, providers must contact the member’s MCO for more specific guidelines. Table 8.33 shows a comprehensive list of all diagnosis codes considered emergency for outpatient reimbursement. Table 8.33 – Emergency Diagnosis Codes 0010 0011 0019 0020 0021 0022 0023 0029 0030 0031 0032 00320 00321 00322 00323 00324 00329 0038 0039 0040 0041 0042 0043 0048 0049 0050 0051 0052 0053 0054 0058 00581 0059 0060 0063 0064 00640 00641 0065 0070 0071 0072 0073 0075 0078 0079 0080 00800 00801 00802 00803 00804 00809 0081 0082 0083 00841 00842 00843 00844 00845 00846 00847 00849 0085 0086 00861 00862 00863 00865 00866 00867 00869 0088 0090 0091 0092 0093 0116 01160 01161 01162 01163 01164 01165 01166 01170 01171 01172 01173 01174 01175 01176 01200 01201 01202 01203 01204 01205 01206 0130 01300 01301 01302 01303 01304 01305 01306 0131 01310 01311 01312 01313 01314 01315 01316 0132 01320 01321 01322 01323 01324 01325 01326 0133 01330 01331 01332 01333 01334 01335 01336 01340 01342 01343 01344 01346 01350 01351 01352 01353 01354 01355 01356 01360 01361 01362 01363 01364 01365 01366 01380 01381 01382 01383 01384 01385 01386 01390 01391 01392 01393 01394 01395 01396 01400 01401 01402 01403 01404 01405 01406 01660 01661 0180 01800 01801 01802 01803 01804 01805 01806 01880 01881 01882 01883 01884 01885 01886 0188 0189 01890 01891 01892 01893 01894 01895 01896 0200 0201 0202 0203 0204 0205 0208 0209 0210 0211 0212 0213 0218 0219 0220 0221 0222 0223 0228 0229 0230 0231 0232 0233 0238 0239 024 025 0260 0261 0269 0270 0271 0272 0278 0279 0310 0320 0321 0323 03281 03282 03283 03284 03285 03289 0329 0338 0339 0341 0360 0361 0362 0363 0364 03640 03641 03642 03643 0368 03681 03682 03689 0369 037 038 0380 0381 03819 0382 0383 0384 03840 03841 03842 03843 03844 03849 0388 0389 039 0390 0391 0392 0393 0394 0398 0399 0400 04041 04042 04500 04501 04502 04503 0451 04510 04511 04512 04513 0452 04520 04521 04522 04523 04590 04591 04592 04593 0470 0471 0478 8-112 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions 0479 0490 0491 0498 0499 0520 0521 0522 0527 0528 0530 05320 05321 05322 0543 0545 05472 0550 0551 0560 05600 05601 05609 05821 05829 0620 06200 0621 0622 0623 0624 0625 0628 0629 0630 06300 0631 06310 0632 06331 0638 06380 0639 064 06400 06640 06641 06642 06649 0700 0701 0702 07020 0703 07030 0704 07041 07042 07043 07044 07049 0705 07051 0706 07070 07071 0709 071 0720 0721 0722 0723 07271 0730 0740 0741 0742 07420 07421 07422 07423 0786 07982 08240 08241 08249 09487 09817 09882 09883 09884 09886 1000 10081 101 1040 1100 1101 1102 1103 1104 1105 1106 1120 1121 1122 1123 1124 1125 1141 1142 1143 1144 1145 1150 1151 1200 1201 1202 1203 1230 1231 1232 1233 1234 1235 1236 1280 1281 1303 1304 1305 13101 13102 13103 1340 1341 1342 135 1360 1361 1362 13621 13629 1363 1364 1365 1390 1391 1400 1401 1403 1404 1405 1406 1500 1501 1502 1503 1504 1505 1570 1571 1572 1573 1574 1600 1601 1602 1603 1604 1605 1640 1641 1642 1643 1650 1710 1712 1713 1714 1715 1716 1720 1721 1722 1723 1724 1725 1726 1730 1731 1732 1733 1734 1735 1736 1740 1741 1742 1743 1744 1745 1746 1978 200 202 203 208 20922 20966 20967 210 211 213 220 223 228 229 23873 24200 24201 24210 24211 24220 24221 24230 24231 24240 24241 24280 24281 24290 24291 2450 2451 2463 24911 24920 24921 24930 24931 24940 24941 24950 24951 24960 24961 24970 24971 24980 24981 24990 24991 25010 25011 25012 25013 25020 25021 25022 25023 2503 25030 25031 25032 25033 25040 25041 25042 25043 25050 25051 25052 25053 25060 25061 25062 25063 25070 25071 25072 25073 25080 25081 25082 25083 25090 25091 25092 25093 2510 2511 2512 260 261 2630 27542 2760 2761 2762 2763 2764 27650 27651 27652 2766 2767 2768 2769 2774 27950 27951 27952 27953 2800 2809 2810 28242 28262 28264 28311 2832 2851 2870 28804 28850 28851 28860 2893 28952 28953 28981 28982 28983 28984 2903 29041 2908 2910 2913 29181 2920 29211 29212 2922 29281 29282 29283 29284 2929 2930 29381 29382 29530 29531 29532 29533 29534 29540 29541 29542 29543 29544 29590 29591 29592 29593 29594 29600 29601 29602 29603 29604 29605 29610 29611 29612 29613 29614 29615 2970 2982 2983 2984 2988 2989 30000 30001 30002 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-113 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual 30010 30011 30012 30013 30015 3004 3005 3007 30081 30082 3010 30112 3013 30150 30151 30159 3016 3017 30276 30300 30301 30302 30390 30391 30392 30400 30401 30402 30410 30411 30412 30420 30421 30422 30430 30431 30432 30440 30441 30442 30450 30451 30452 30460 30461 30462 30470 30471 30472 30480 30481 30482 30490 30491 30492 30500 30501 30502 30520 30521 30522 30530 30531 30532 30540 30541 30542 30550 30551 30552 30560 30561 30562 30570 30571 30572 30580 30581 30582 30590 30591 30592 3060 3061 3062 3063 3064 30650 30651 30652 30653 3068 3071 3073 30750 30751 30752 30754 30759 30780 30781 3079 3080 3082 3091 30921 30981 3102 311 320 3200 3201 3202 3203 3207 32081 32082 32089 3209 3210 3211 3212 3213 3214 3218 3220 3221 3222 3229 32301 32302 3231 3232 32341 32342 32351 32352 32361 32362 32363 32371 32372 32381 32382 3239 3240 3241 3249 326 33181 3321 3333 33372 33383 33520 33720 33721 33722 33729 3373 33811 33818 33819 33900 33901 33902 33903 33904 33905 33909 33910 33911 33912 33920 33921 33922 3393 33941 33942 33943 33944 33981 33983 33984 33985 33989 340 34120 34121 34122 34500 34501 34510 34511 3452 3453 34540 34541 34550 34551 34560 34561 34570 34571 34580 34581 34590 34591 34600 34601 34602 34603 34610 34611 34612 34613 34620 34621 34622 34630 34631 34632 34633 34640 34641 34642 34643 34650 34651 34652 34653 34660 34661 34662 34663 34670 34671 34672 34673 34680 34681 34682 34683 34690 34692 34693 3481 3482 34830 34831 34839 3484 3485 3490 3491 34931 34981 34982 3501 3502 3508 3509 3510 3518 3519 3530 3548 3549 3550 35571 35579 3570 3575 3576 3577 35782 35800 35801 35981 3593 36001 36002 36011 36012 36100 36101 36102 36103 36104 36105 36106 36107 3612 36181 36189 3619 36211 36214 36218 36230 36231 36232 36233 36234 36235 36236 36237 3624 36240 36241 36242 36243 36281 36283 36284 36400 36510 36520 36521 36522 36523 36524 36840 37000 37003 37034 37040 37200 37201 37202 37220 37230 37300 37313 37331 37332 37400 37410 37481 37482 37600 37601 37602 37603 37604 37700 37701 37850 37900 37963 38000 38001 38010 38011 38012 3804 3810 38100 38101 38102 38103 38104 38105 38106 38151 38160 3819 38200 38201 38202 38300 38301 38400 38401 38610 38630 38650 38830 38860 38870 3910 3911 3912 3918 3919 3980 39890 39891 4010 4011 8-114 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions 4019 40200 40201 40211 40291 40300 40301 40400 40401 40402 40403 40411 40413 40493 40501 4082 4100 41000 41001 41002 4101 41010 41011 41012 41020 41021 41022 41030 41031 41032 41040 41041 41042 41050 41051 41052 41061 41062 41070 41071 41072 41080 41081 41082 41090 41091 41092 4110 4111 41181 41189 412 4130 4131 4139 41401 41402 41403 41404 41407 41410 41411 41412 41419 4142 4143 4148 4150 41511 41512 41519 4160 4162 4171 4200 4209 42090 42091 42099 4210 4211 4219 4220 42290 42291 42292 42293 42299 4230 4231 4232 4233 4238 4239 4251 4260 42610 42611 42612 42613 4262 4263 4264 4265 42650 42651 42652 42653 42654 4266 4267 42681 42689 4269 4270 4271 4272 42731 42732 4274 42741 42742 4275 42760 42761 42769 42781 42789 4279 4280 4281 42820 42821 42823 42830 42831 42832 42833 42840 42841 42842 42843 4289 4290 4291 4292 4295 42981 42983 430 431 4320 4321 4329 43300 43301 43310 43311 43320 43321 43330 43331 43380 43381 43390 43391 43400 43401 43410 43411 43490 43491 436 4372 4373 44020 44024 4404 44101 44102 44103 4411 4412 4413 4414 4415 4416 4430 4431 44321 44322 44323 44324 44329 4440 4441 44421 44422 44481 44489 4449 44501 44502 44581 44589 4470 4472 4476 449 4510 4511 45111 45119 4512 45181 45182 45183 45184 45189 4519 452 4530 4531 4532 4533 45340 45341 45342 45350 45351 45352 4536 45371 45372 45373 45374 45375 45376 45377 45379 45381 45382 45383 45384 45385 45386 45387 45389 4539 4540 4541 4550 4552 4554 4555 4560 4561 45620 45621 4570 4572 4580 4590 460 4610 4611 4612 4613 4618 4619 462 463 46400 46410 46411 46420 46421 46430 46431 4644 46450 4650 4660 46611 46619 475 47821 47824 47825 47826 4786 47871 47875 47879 4800 4801 4802 4803 4808 4809 481 4820 4821 4822 48230 48231 48232 48239 4828 48281 48282 48283 48284 48289 4829 4830 4831 4838 4841 4843 4845 4846 4847 4848 485 486 4870 4871 4878 4880 4881 49122 49300 49301 49302 4931 49310 49311 49312 49320 49321 49322 49381 49382 49390 49391 49392 4940 4941 4957 4958 4959 500 5060 5061 5063 5070 5071 5078 5080 5100 5109 5110 5111 5118 51181 51189 5119 5120 5121 5128 5130 5131 5171 5173 5180 5181 5184 5185 5187 51881 51882 51884 51900 51902 51911 5192 5194 52181 52300 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-115 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual 52301 52333 52462 52564 5272 5273 5281 5283 5290 5301 53010 53011 53013 53019 53021 5303 5304 5307 53082 53086 53087 53100 53101 5311 53110 53111 5312 53120 53121 5313 53130 53131 53140 53141 53150 53151 53160 53161 5319 5320 53200 53201 5321 53210 53211 5322 53220 53221 53240 53241 53250 53251 53260 53261 5329 53300 53301 53310 53311 53320 53321 53340 53341 53350 53351 53360 53361 53400 53401 53410 53411 53420 53421 53430 53431 53440 53441 53450 53451 53460 53461 53500 53501 53530 53531 53540 53541 53550 53551 53560 53561 53570 53571 5362 53640 53641 53642 53649 5371 53784 5400 5401 5409 541 542 55000 55001 55002 55003 55010 55011 55012 55013 55090 55091 55092 55093 55100 55101 55102 55103 5511 55120 55121 55129 5513 5518 5519 55200 55201 55202 55203 5521 55220 55221 55229 5523 5528 5529 55300 55301 55302 55303 5531 55320 55321 55329 5533 5538 5550 5551 5552 5560 5561 5562 5563 5564 5565 5566 5569 5570 5571 5581 5582 5600 5601 5602 56030 56031 56039 56081 56089 5609 56201 56202 56203 56211 56212 56213 56400 5641 5642 5643 5650 5651 566 5670 5671 56721 56722 56723 56729 56731 56738 56739 56781 56782 56789 5679 56881 5691 5693 56941 56942 56944 5695 56960 56961 56969 56981 56983 56985 56986 56987 570 5711 5720 5721 5722 5723 5724 5728 5731 5732 5733 5734 57400 57401 57410 57411 57430 57431 57440 57441 57460 57461 57470 57471 57481 57490 57491 5750 5751 57510 57511 57512 5752 5753 5754 5760 5761 5762 5763 5770 578 5780 5781 5789 5800 5804 58081 58089 5809 5810 5811 5812 5813 58181 58189 5819 5830 5831 5832 5834 5836 5837 58381 58389 5839 5845 5846 5847 5848 5849 5856 5901 59010 59011 5902 5903 5908 59080 5909 591 5920 5921 5929 5933 5934 5935 59381 5942 5948 5949 5950 5959 5960 5962 59651 59653 59654 5966 5967 59780 59800 59801 5981 5982 5988 5989 5990 5996 59960 59969 5997 59970 59971 59972 60001 60011 60021 60091 6010 6013 6021 6039 6040 60490 60491 6071 6072 6073 60781 60782 60783 60785 60820 60821 60822 60823 60824 60883 6110 61171 61172 6140 6142 6143 6144 6145 6150 6160 61610 6162 6163 6164 6173 6190 6191 6201 6205 6206 6207 6208 6214 6233 6236 6250 6252 6253 6262 6267 62929 632 63300 63301 63310 63311 63320 63321 8-116 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions 63380 63381 63390 63391 63400 63401 63402 63410 63411 63412 63420 63421 63422 63430 63431 63432 63440 63441 63442 63450 63451 63452 63460 63461 63462 63470 63471 63472 63480 63481 63482 63490 63491 63492 63500 63501 63502 63510 63511 63512 63520 63521 63522 63530 63531 63532 63540 63541 63542 63550 63551 63552 63560 63561 63562 63570 63571 63572 63580 63581 63582 63600 63601 63602 63610 63611 63612 63620 63621 63622 63630 63631 63632 63640 63641 63642 63650 63651 63652 63660 63661 63662 63670 63671 63672 63680 63681 63682 63700 63701 63702 63710 63711 63712 63720 63721 63722 63730 63731 63732 63740 63741 63742 63750 63751 63752 63760 63761 63762 63770 63771 63772 63780 63781 63782 6380 6381 6382 6383 6384 6385 6386 6387 6388 6390 6391 6392 6393 6394 6395 6396 6398 6399 64000 64001 64003 64080 64081 64083 64090 64091 64093 64100 64101 64103 64110 64111 64113 64120 64121 64123 64130 64131 64133 64180 64181 64183 64190 64191 64193 64200 64201 64202 64203 64204 64210 64211 64212 64213 64214 64220 64221 64222 64223 64224 64230 64231 64232 64233 64234 64240 64241 64242 64243 64244 64250 64251 64252 64253 64254 64260 64261 64262 64263 64264 64270 64271 64272 64273 64274 64290 64291 64292 64294 64310 64311 64313 64320 64321 64323 64380 64381 64383 64390 64391 64393 64400 64403 64410 64413 64420 64421 64670 64671 64673 64680 64681 64682 64683 64684 64830 64831 64832 64833 64834 64930 64931 64932 64933 64962 64963 64964 650 65170 65171 65173 65281 6529 65293 654 65453 65550 65570 65571 65573 65630 65631 65633 65640 65641 65643 65670 65671 65673 65680 65681 65683 65691 65693 65701 65703 65810 65811 65813 65840 65841 65843 660 66083 66190 66191 66193 66200 66201 66203 66210 66211 66213 66220 66221 66223 66230 66231 66233 66300 66301 66303 66310 66311 66313 66320 66323 66331 66333 6634 66340 66341 66343 6635 66350 66351 66353 66360 66361 66363 66380 66381 66383 6639 66390 66391 66393 6640 66400 66401 66404 6641 66410 66411 66414 6642 66420 66421 66424 66430 66431 66434 66440 66441 66444 66450 66451 66454 66480 66481 66484 6649 66490 66491 66494 66500 66501 66503 66510 66511 66512 66514 66520 66522 66524 66530 66531 66534 66540 66541 66544 66550 66551 66554 66560 66561 66564 66570 66571 66572 66574 66580 66581 66584 66590 66591 66592 66593 66594 66600 66602 66604 66610 66612 66614 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-117 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual 66620 66622 66624 66630 66632 66634 66700 66702 66704 66710 66712 66714 66800 66801 66802 66803 66804 66810 66811 66812 66813 66814 66820 66821 66822 66823 66824 66880 66881 66882 66883 66884 66890 66891 66892 66893 66894 66900 66901 66902 66903 66904 66910 66911 66912 66913 66914 66920 66921 66922 66923 66924 66930 66932 66934 66940 66941 66942 66943 66944 66950 66951 66960 66961 66970 66971 66980 66981 66982 66983 66984 66990 66991 66992 66993 66994 67000 67002 67004 67010 67012 67014 67020 67022 67024 67030 67032 67034 67080 67082 67084 67110 67111 67112 67113 67114 67120 67121 67122 67123 67124 6713 67130 67131 67133 67140 67142 67144 67150 67151 67152 67153 67154 67200 67202 67204 67300 67301 67302 67303 67304 67310 67311 67312 67313 67314 67320 67321 67322 67323 67324 67330 67331 67332 67333 67334 67380 67381 67382 67383 67384 67400 67401 67402 67403 67404 67410 67412 67414 67420 67422 67424 67430 67432 67434 67440 67442 67444 67450 67451 67452 67453 67454 67480 67482 67484 67490 67492 67494 67500 67501 67502 67503 67504 67510 67511 67512 67513 67514 67520 67521 67522 67523 67524 67580 67581 67583 67584 67590 67591 67592 67593 67594 677 6801 6802 6803 6804 6805 6806 6807 6808 68100 68101 68102 68110 6820 6821 6822 6823 6824 6825 6826 6827 684 6850 6851 68600 68601 6910 6923 6924 6926 69271 69272 69276 69277 69281 69282 69283 69284 69289 6929 6930 6931 6938 6939 6940 6941 6942 6943 6944 6945 6946 6948 6949 6950 6951 69510 69512 69513 69514 69515 6952 6953 6954 69555 69556 69557 69558 69559 69581 7021 7041 7051 70583 7062 7070 70700 70701 70702 70703 70704 70705 70706 70707 70709 70710 70711 70712 70713 70714 70715 70719 70720 70722 70723 70724 7078 7079 7080 7104 71100 71101 71102 71103 71104 71105 71106 71107 71108 71109 7136 7140 7141 7142 71430 71431 71432 71433 71740 7175 71800 71801 71802 71803 71804 71805 71807 71808 71809 71830 71832 71833 71834 71835 71836 71837 71838 71839 71900 71901 71902 71903 71904 71905 71906 71907 71908 71909 71910 71911 71912 71913 71914 71915 71916 71917 71918 71919 71920 71921 71922 71923 71924 71925 71926 71927 71928 71929 720 7220 72210 72211 7222 7224 72251 72252 7226 7227 72270 72271 72272 72273 7228 72280 72281 72282 72283 72290 72291 72292 72293 7231 7234 7235 7245 7246 725 72610 8-118 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions 72631 72632 72633 72700 7272 7273 72760 72761 72762 72763 72764 72765 72766 72767 72768 7280 72883 72886 72888 7291 7292 72930 73000 73001 73002 73003 73004 73005 73006 73007 73008 73009 73030 73031 73032 73033 73034 73035 73036 73037 73038 73039 7327 73310 73311 73312 73313 73314 73315 73316 73319 73381 73382 73397 73398 75242 76062 76063 76064 76077 76078 7614 7620 7621 7624 7625 76384 76400 76410 76420 76490 76500 76510 76520 76521 76522 76523 76524 76525 76526 76527 76528 76529 76621 76622 7670 76711 76719 7672 7673 7674 7675 7676 7677 7678 7679 7680 7681 7682 7683 7684 7685 7686 76870 76871 76872 76873 7689 769 7700 77010 77012 77013 77014 77015 77016 77017 77018 7702 7703 7704 77081 77082 77083 77084 77085 77086 77087 77088 77089 771 7710 7711 7712 77181 77182 77183 7720 77210 7722 7723 7724 7725 7726 7728 7729 7730 7731 7732 7733 7734 7735 7742 77430 77431 77439 7744 7745 7746 7747 7751 7752 7753 7754 7755 7756 7757 7758 77581 77589 7759 7760 7761 7762 7763 7764 7765 7766 7767 7768 7769 7771 7772 7773 7774 7775 77750 77751 77752 77753 7776 7778 7779 7780 7781 7782 7783 7784 7786 7790 7791 7792 77931 77932 77933 77934 7794 7795 7796 77981 77982 77984 77985 78002 78003 78009 7801 7802 7803 78031 78032 78039 7804 7806 78060 78061 78062 78063 78064 78065 78071 7814 7816 7817 7824 7825 7827 783 7840 7841 7842 78442 7847 7848 785 7850 7852 7854 78550 78551 78552 78559 7856 786 78600 78601 78602 78605 78606 78607 78609 7862 7863 78650 78651 78652 78659 7868 7880 7881 7882 78820 78821 78829 78900 78901 78902 78903 78904 78905 78906 78907 78909 7897 79001 7907 7908 79093 79531 7980 7981 7982 7989 79901 79902 7991 79921 79922 79923 79924 79925 79929 7994 80000 80001 80002 80003 80004 80005 80006 80009 80010 80011 80012 80013 80014 80015 80016 80019 80020 80021 80022 80023 80024 80025 80026 80029 80030 80031 80032 80033 80034 80035 80036 80039 80040 80041 80042 80043 80044 80045 80046 80049 80050 80051 80052 80053 80054 80055 80056 80059 80060 80061 80062 80063 80064 80065 80066 80069 80070 80071 80072 80073 80074 80075 80076 80079 80080 80081 80082 80083 80084 80085 80086 80089 80090 80091 80092 80093 80094 80095 80096 80099 80100 80101 80102 80103 80104 80105 80106 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-119 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual 80109 80110 80111 80112 80113 80114 80115 80116 80119 80120 80121 80122 80123 80124 80125 80126 80129 80130 80131 80132 80133 80134 80135 80136 80139 80140 80141 80142 80143 80144 80145 80146 80149 80150 80151 80152 80153 80154 80155 80156 80159 80160 80161 80162 80163 80164 80165 80166 80169 80170 80171 80172 80173 80174 80175 80176 80179 80180 80181 80182 80183 80184 80185 80186 80189 80190 80191 80192 80193 80194 80195 80196 80199 802 8020 8021 80220 80221 80222 80223 80224 80225 80226 80227 80228 80229 80230 80231 80232 80233 80234 80235 80236 80237 80238 80239 8024 8025 8026 8027 8028 8029 80300 80301 80302 80303 80304 80305 80306 80309 80310 80311 80312 80313 80314 80315 80316 80319 80320 80321 80322 80323 80324 80325 80326 80329 80330 80331 80332 80333 80334 80335 80336 80339 80340 80341 80342 80343 80344 80345 80346 80349 80350 80351 80352 80353 80354 80355 80356 80359 80360 80361 80362 80363 80364 80365 80366 80369 80370 80371 80372 80373 80374 80375 80376 80379 80380 80381 80382 80383 80384 80385 80386 80389 80390 80391 80392 80393 80394 80395 80396 80399 80400 80401 80402 80403 80404 80405 80406 80409 80410 80411 80412 80413 80414 80415 80416 80419 80420 80421 80422 80423 80424 80425 80426 80429 80430 80431 80432 80433 80434 80435 80436 80439 80440 80441 80442 80443 80444 80445 80446 80449 80450 80451 80452 80453 80454 80455 80456 80459 80460 80461 80462 80463 80464 80465 80466 80469 80470 80471 80472 80473 80474 80475 80476 80479 80480 80481 80482 80483 80484 80485 80486 80489 80490 80491 80492 80493 80494 80495 80496 80499 80500 80501 80502 80503 80504 80505 80506 80507 80508 80510 80511 80512 80513 80514 80515 80516 80517 80518 8052 8053 8054 8055 8056 8057 8058 8059 8060 80600 80601 80602 80603 80604 80605 80606 80607 80608 80609 8061 80610 80611 80612 80613 80614 80615 80616 80617 80618 80619 80620 80621 80622 80623 80624 80625 80626 80627 80628 80629 80630 80631 80632 80633 80634 80635 80636 80637 80638 80639 8064 8065 80660 80661 80662 80669 80670 80671 80672 80679 8068 8069 80700 80701 80702 80703 80704 80705 80706 80707 80708 80709 80710 80711 80712 80713 80714 80715 80716 80717 80718 80719 8072 8073 8074 8075 8076 8080 8081 8082 8083 80841 80842 80843 80849 80851 80852 80853 80859 8088 8089 8090 8091 81000 81001 81002 81003 81010 81011 81012 8-120 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions 81013 81100 81101 81102 81103 81109 81110 81111 81112 81113 81119 812 81200 81201 81202 81203 81209 81210 81211 81212 81213 81219 81220 81221 81230 81231 81240 81241 81242 81243 81244 81249 81250 81251 81252 81253 81254 81259 81300 81301 81302 81303 81304 81305 81306 81307 81308 81310 81311 81312 81313 81314 81315 81316 81317 81318 81320 81321 81322 81323 81330 81331 81332 81333 81340 81341 81342 81343 81344 81345 81346 81347 81350 81351 81352 81353 81354 81380 81381 81382 81383 81390 81391 81392 81393 81400 81401 81402 81403 81404 81405 81406 81407 81408 81409 81410 81411 81412 81413 81414 81415 81416 81417 81418 81419 81500 81501 81502 81503 81504 81509 81510 81511 81512 81513 81514 81519 81600 81601 81602 81603 81610 81611 81612 81613 8170 8171 8181 8190 8191 82000 82001 82002 82003 82009 82010 82011 82012 82013 82019 82020 82021 82022 82030 82031 82032 8208 8209 82100 82101 82110 82111 82120 82121 82122 82123 82129 82130 82131 82132 82133 82139 8220 8221 82300 82301 82302 82310 82311 82312 82320 82321 82322 82330 82331 82332 82340 82341 82342 82380 82381 82382 82390 82391 82392 8240 8241 8242 8243 8244 8245 8246 8247 8248 8249 8250 8251 82520 82521 82522 82523 82524 82525 82529 82530 82531 82532 82533 82534 82535 82539 8260 8261 8270 8271 8280 8281 8290 8291 8300 8301 83100 83101 83102 83103 83104 83109 83110 83111 83112 83113 83114 83119 83200 83201 83202 83203 83204 83209 83210 83211 83212 83213 83214 83219 8322 833 83300 83301 83302 83303 83304 83305 83309 83310 83311 83312 83313 83314 83315 83319 83400 83401 83402 83410 83411 83412 83500 83501 83502 83503 83510 83511 83512 83513 8360 8361 8362 8363 8364 83650 83651 83652 83653 83654 83659 83660 83661 83662 83663 83664 83669 8370 8371 83800 83801 83802 83803 83804 83805 83806 83809 83810 83811 83812 83813 83814 83815 83816 83819 83900 83901 83902 83903 83904 83905 83906 83907 83908 83910 83911 83912 83913 83914 83915 83916 83917 83918 83920 83921 83930 83931 83940 83941 83942 83949 83950 83951 83952 83959 83961 83969 83971 83979 8398 8399 8400 8401 8402 8403 8404 8405 8406 8407 8408 8409 8410 8411 8412 8413 8418 8419 84200 84201 84202 84209 84210 84211 84212 84213 84219 8431 8438 8439 8440 8441 8442 8443 8448 8449 84500 84501 84502 84503 84509 84510 84511 84512 84513 84519 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-121 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual 8460 8461 8462 8463 8468 8469 8470 8471 8472 8473 8474 8479 8480 8481 8482 8483 84840 84841 84842 84849 8485 8488 8489 8500 85011 85012 8502 8503 8504 8505 8509 85100 85101 85102 85103 85104 85105 85106 85109 85110 85111 85112 85113 85114 85115 85116 85119 85120 85121 85122 85123 85124 85125 85126 85129 85130 85131 85132 85133 85134 85135 85136 85139 85140 85141 85142 85143 85144 85145 85146 85149 85150 85151 85152 85153 85154 85155 85156 85159 85160 85161 85162 85163 85164 85165 85166 85169 85170 85171 85172 85173 85174 85175 85176 85179 85180 85181 85182 85183 85184 85185 85186 85189 85190 85191 85192 85193 85194 85195 85196 85199 85200 85201 85202 85203 85204 85205 85206 85209 85210 85211 85212 85213 85214 85215 85216 85219 85220 85221 85222 85223 85224 85225 85226 85229 85230 85231 85232 85233 85234 85235 85236 85239 85240 85241 85242 85243 85244 85245 85246 85249 85250 85251 85252 85253 85254 85255 85256 85259 85300 85301 85302 85303 85304 85305 85306 85309 85310 85311 85312 85313 85314 85315 85316 85319 85400 85401 85402 85403 85404 85405 85406 85409 85410 85411 85412 85413 85414 85415 85416 85419 860 8600 8601 8602 8603 8604 8605 86100 86101 86102 86103 86110 86111 86112 86113 86120 86121 86122 86130 86131 86132 8620 8621 86221 86222 86229 86231 86232 86239 8628 8629 8630 8631 86320 86321 86329 86330 86331 86339 86340 86341 86342 86343 86344 86345 86346 86349 86350 86351 86352 86353 86354 86355 86356 86359 86380 86381 86382 86383 86384 86385 86389 86390 86391 86392 86393 86394 86395 86399 86400 86401 86402 86403 86404 86405 86409 86410 86411 86412 86413 86414 86415 86419 86500 86501 86502 86503 86504 86509 86510 86511 86512 86513 86514 86519 86600 86601 86602 86603 86610 86611 86612 86613 8670 8671 8672 8673 8674 8675 8676 8677 8678 8679 86800 86801 86802 86803 86804 86809 86810 86811 86812 86813 86814 86819 869 8690 8691 8700 8701 8702 8703 8704 8708 8709 8710 8711 8712 8713 8714 8715 8716 8717 8719 872 87200 87201 87202 87210 87211 87212 87261 87262 87263 87264 87269 87271 87272 87273 87274 87279 8728 8729 8730 8731 87320 87321 87322 87323 87329 87330 87331 87332 87333 87339 87340 87341 87342 87343 87344 87349 87350 87351 87352 87353 87354 87359 87360 87361 87362 87363 87364 87365 87369 87370 87371 87372 87373 87374 8-122 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions 87375 87379 8738 8739 87400 87401 87402 87410 87411 87412 8742 8743 8744 8745 8748 8749 8750 8751 8760 8761 8770 8771 8780 8781 8782 8783 8784 8785 8786 8787 8788 8789 8790 8791 8792 8793 8794 8795 8796 8797 8798 8799 88000 88001 88002 88003 88009 88010 88011 88012 88013 88019 88020 88021 88022 88023 88029 88100 88101 88102 88110 88111 88112 88120 88121 88122 8820 8821 8822 8830 8831 8832 8840 8841 8842 8850 8851 8860 8861 8870 8871 8872 8873 8874 8875 8876 8877 8900 8901 8902 8910 8911 8912 8920 8921 8922 8930 8931 8932 8940 8941 8942 8950 8951 8960 8961 8962 8963 8970 8971 8972 8973 8974 8975 8976 8977 90000 90001 90002 90003 9001 90081 90082 90089 9009 9010 9011 9012 9013 90140 90141 90142 90181 90182 90183 90189 9019 9020 90210 90211 90219 90220 90221 90222 90223 90224 90225 90226 90227 90229 9023 90231 90232 90233 90234 90239 90240 90241 90242 90249 90250 90251 90252 90253 90254 90255 90256 90259 90281 90282 90287 90289 9029 903 90300 90301 90302 9031 9032 9033 9034 9035 9038 9039 9040 9041 9042 9043 90440 90441 90442 90450 90451 90452 90453 90454 9046 9047 9048 9049 9050 9051 9052 9053 9054 9055 9056 9057 9058 9059 9060 9061 9062 9063 9064 9065 9066 9067 9068 9069 9070 9071 9072 9073 9074 9075 9079 9080 9081 9082 9083 9084 9085 9086 9089 9090 9091 9092 9093 9094 9095 9099 910 9100 9101 9102 9103 9104 9105 9106 9107 9108 9109 9110 9111 9112 9113 9114 9115 9116 9117 9118 9119 9120 9121 9122 9123 9124 9125 9126 9127 9128 9129 9130 9131 9132 9133 9134 9135 9136 9137 9138 9139 9140 9141 9142 9143 9144 9145 9146 9147 9148 9149 9150 9151 9152 9153 9154 9155 9156 9157 9158 9159 9160 9161 9162 9163 9164 9165 9166 9167 9168 9169 9170 9171 9172 9173 9174 9175 9176 9177 9178 9179 9180 9181 9182 9189 9190 9191 9192 9193 9194 9195 9196 9197 9198 9199 920 9210 9211 9212 9213 9219 9220 9221 9222 9223 92231 92232 92233 9224 9228 9229 92300 92301 92302 92303 92309 92310 92311 92320 92321 9233 9238 9239 92400 92401 92410 92411 92420 92421 9243 9244 9245 9248 9249 9251 9252 9260 92611 92612 92619 9268 9269 92700 92701 92702 92703 92709 92710 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-123 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual 92711 92720 92721 9273 9278 9279 92800 92801 92810 92811 92820 92821 9283 9288 9289 9290 9299 9300 9301 9302 9308 9309 931 932 933 9330 9331 9340 9341 9348 9349 9350 936 937 938 9390 9391 9392 9393 9399 940 9400 9401 9402 9403 9404 9405 9409 94100 94101 94102 94103 94104 94105 94106 94107 94108 94109 94110 94111 94112 94113 94114 94115 94116 94117 94118 94119 94120 94121 94122 94123 94124 94125 94126 94127 94128 94129 94130 94131 94132 94133 94134 94135 94136 94137 94138 94139 94140 94141 94142 94143 94144 94145 94146 94147 94148 94149 94150 94151 94152 94153 94154 94155 94156 94157 94158 94159 942 94200 94201 94202 94203 94204 94205 94209 94210 94211 94212 94213 94214 94215 94219 94220 94221 94222 94223 94224 94225 94229 94230 94231 94232 94233 94234 94235 94239 94240 94241 94242 94243 94244 94245 94249 94250 94251 94252 94253 94254 94255 94259 94300 94301 94302 94303 94304 94305 94306 94309 94310 94311 94312 94313 94314 94315 94316 94319 94320 94321 94322 94323 94324 94325 94326 94329 94330 94331 94332 94333 94334 94335 94336 94339 94340 94341 94342 94343 94344 94345 94346 94349 94350 94351 94352 94353 94354 94355 94356 94359 94400 94401 94402 94403 94404 94405 94406 94407 94408 94410 94411 94412 94413 94414 94415 94416 94417 94418 94420 94421 94422 94423 94424 94425 94426 94427 94428 94430 94431 94432 94433 94434 94435 94436 94437 94438 94440 94441 94442 94443 94444 94445 94446 94447 94448 94450 94451 94452 94453 94454 94455 94456 94457 94458 94500 94501 94502 94503 94504 94505 94506 94509 94510 94511 94512 94513 94514 94515 94516 94519 94520 94521 94522 94523 94524 94525 94526 94529 94530 94531 94532 94533 94534 94535 94536 94539 94540 94541 94542 94543 94544 94545 94546 94549 94550 94551 94552 94553 94554 94555 94556 94559 9460 9461 9462 9463 9464 9465 9470 9471 9472 9473 9474 9478 9479 94800 9481 94810 94811 94820 94821 94822 94830 94831 94832 94833 94840 94841 94842 94843 94844 94850 94851 94852 94853 94854 94855 94860 94861 94862 94863 94864 94865 94866 9487 94870 94871 94872 94873 94874 94875 94876 94877 94880 94881 94882 94883 94884 94885 94886 94887 94888 94890 94891 94892 94893 94894 94895 94896 94897 94898 94899 9490 9491 9492 9493 9494 9495 9500 9501 9502 9503 9509 9510 9511 9512 9513 9514 9515 9516 9517 8-124 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions 9518 9519 9520 95200 95201 95202 95203 95204 95205 95206 95207 95208 95209 95210 95211 95212 95213 95214 95215 95216 95217 95218 95219 9522 9523 9524 9528 9529 9530 9531 9532 9533 9534 9535 9538 9539 9540 9541 9548 9549 9550 9551 9552 9553 9554 9555 9556 9557 9558 9559 9560 9561 9562 9563 9564 9565 9568 9569 9570 9571 9578 9579 9580 9581 9582 9583 9584 9585 9586 9587 9588 95890 95891 95892 95893 95899 95901 95909 95911 95912 95913 95914 95919 9592 9593 9594 9595 9596 9597 9598 9599 9600 9601 9602 9603 9604 9605 9606 9607 9608 9609 9610 9611 9612 9613 9614 9615 9616 9617 9618 9619 9620 9621 9622 9623 9624 9625 9626 9627 9628 9629 9630 9631 9632 9633 9634 9635 9638 9639 9640 9641 9642 9643 9644 9645 9646 9647 9648 9649 96500 96501 96502 96509 9651 9654 9655 96561 96569 9657 9658 9659 9660 9661 9662 9663 9664 9670 9671 9672 9673 9674 9675 9676 9678 9679 9680 9681 9682 9683 9684 9685 9686 9687 9689 96900 96901 96902 96903 96904 96905 96909 9691 9692 9693 9694 9695 9696 96970 96971 96972 96973 96979 9698 9699 9700 9701 9708 9709 9710 9711 9712 9713 9719 9720 9721 9722 9723 9724 9725 9726 9727 9728 9729 9730 9731 9732 9733 9734 9735 9736 9738 9739 9740 9741 9742 9743 9744 9745 9746 9747 9750 9751 9752 9753 9754 9755 9756 9757 9758 9760 9761 9762 9763 9764 9765 9766 9767 9768 9769 9770 9771 9772 9773 9774 9778 9779 9780 9781 9782 9783 9784 9785 9786 9788 9789 9790 9791 9792 9793 9794 9795 9796 9797 9799 9800 9801 9802 9803 9808 9809 981 9820 9821 9822 9823 9824 9828 9830 9831 9832 9839 9840 9841 9848 9849 9850 9852 9853 9854 9855 9856 9858 9859 986 9870 9871 9872 9873 9874 9875 9876 9877 9878 9879 9880 9881 9882 9888 9889 9890 9891 9892 9893 9894 9895 9896 9897 98981 98982 98983 98984 98989 9899 990 9910 9911 9912 9913 9914 9915 9916 9918 9919 9920 9921 9922 9923 9924 9925 9926 9927 9928 9929 9930 9931 9932 9933 9934 9938 9939 9940 9941 9942 9943 9944 9945 9946 9947 9948 9949 9950 9951 99520 99521 99522 99523 99524 99527 99529 9953 9954 99550 99551 99552 99553 99554 99555 99559 99560 99561 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-125 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual 99562 99563 99564 99565 99566 99567 99568 99569 9957 99580 99581 99582 99583 99584 99585 99586 99589 99590 99591 99592 99593 99594 99600 99601 99602 99603 99604 99609 9961 9962 99631 99632 99639 99640 99641 99642 99643 99644 99645 99646 99647 99649 99651 99652 99653 99654 99656 99657 99659 99660 99661 99662 99663 99664 99665 99666 99667 99668 99669 99670 99671 99672 99673 99674 99675 99676 99677 99678 99679 99680 99681 99682 99683 99684 99685 99686 99687 99689 99690 99691 99692 99693 99694 99695 99696 99699 99700 99701 99702 99709 9971 9972 9973 99731 99739 9974 9975 99760 99761 99762 99769 99791 99799 9980 99811 99812 99813 9982 99830 99831 99832 99833 9984 99851 99859 9986 9987 99881 99882 99883 99889 9989 9990 9991 9992 99931 99939 9994 9995 9997 9998 99981 99982 99988 99989 9999 E8000 E8001 E8002 E8003 E8008 E8009 E8010 E8011 E8012 E8013 E8018 E8019 E8020 E8021 E8022 E8023 E8028 E8029 E8030 E8031 E8032 E8033 E8038 E8039 E8040 E8041 E8042 E8043 E8048 E8049 E8050 E8051 E8052 E8053 E8058 E8059 E8060 E8061 E8062 E8063 E8068 E8069 E8070 E8071 E8072 E8073 E8078 E8079 E8100 E8101 E8102 E8103 E8104 E8105 E8106 E8107 E8108 E8109 E8110 E8111 E8112 E8113 E8114 E8115 E8116 E8117 E8118 E8119 E8120 E8121 E8122 E8123 E8124 E8125 E8126 E8127 E8128 E8129 E8130 E8131 E8132 E8133 E8134 E8135 E8136 E8137 E8138 E8139 E8140 E8141 E8142 E8143 E8144 E8145 E8146 E8147 E8148 E8149 E8150 E8151 E8152 E8153 E8154 E8155 E8156 E8157 E8158 E8159 E8160 E8161 E8162 E8163 E8164 E8165 E8166 E8167 E8168 E8169 E8170 E8171 E8172 E8173 E8174 E8175 E8176 E8177 E8178 E8179 E8180 E8181 E8182 E8183 E8184 E8185 E8177 E8178 E8179 E8180 E8181 E8182 E8183 E8184 E8185 E8187 E8188 E8189 E8190 E8191 E8192 E8193 E8194 E8195 E8196 E8197 E8198 E8199 E8200 E8201 E8202 E8203 E8204 E8205 E8206 E8207 E8208 E8209 E8210 E8211 E8212 E8213 E8214 E8215 E8216 E8217 E8218 E8220 E8221 E8222 E8223 E8224 E8225 E8226 E8227 E8228 E8229 E8230 E8231 E8232 E8233 E8234 E8235 E8236 E8238 E8239 E8240 E8241 E8242 E8243 E8244 E8245 E8246 E8247 E8248 E8249 E8250 E8251 E8252 E8253 E8254 E8255 E8256 E8257 E8258 E8259 E8260 E8261 E8262 E8263 E8264 E8268 E8269 E8270 E8272 E8273 E8274 E8278 E8279 E8280 E8282 E8284 E8288 E8289 E8290 E8294 E8298 E8299 E8300 E8301 E8302 E8303 E8304 E8305 E8306 E8307 E8308 E8309 E8310 E8311 E8312 E8313 E8314 E8315 E8316 E8317 8-126 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions E8318 E8319 E8320 E8321 E8322 E8323 E8324 E8325 E8326 E8327 E8328 E8329 E8330 E8331 E8332 E8333 E8334 E8335 E8336 E8337 E8338 E8339 E8340 E8341 E8342 E8343 E8344 E8345 E8346 E8348 E8349 E8350 E8351 E8352 E8353 E8354 E8355 E8356 E8358 E8359 E8360 E8361 E8362 E8363 E8364 E8365 E8366 E8368 E8369 E8370 E8371 E8372 E8373 E8374 E8375 E8376 E8378 E8379 E8380 E8381 E8382 E8383 E8384 E8385 E8386 E8388 E8389 E8501 E8502 E8503 E8504 E8505 E8506 E8507 E8508 E8509 E851 E852 E8520 E8521 E8522 E8523 E8524 E8525 E8528 E8529 E853 E8530 E8531 E8532 E8538 E8539 E854 E8540 E8541 E8542 E8543 E855 E8550 E8551 E8552 E8553 E8554 E8555 E8556 E8558 E8559 E856 E857 E858 E8580 E8581 E8582 E8583 E8584 E8585 E8586 E8588 E8589 E860 E8600 E8601 E8602 E8603 E8604 E8608 E8609 E861 E8610 E8611 E8612 E8613 E8614 E8615 E8616 E8619 E862 E8620 E8621 E8622 E8623 E8624 E8629 E863 E8630 E8631 E8632 E8633 E8634 E8635 E8636 E8637 E8638 E8639 E864 E8640 E8641 E8642 E8643 E8644 E865 E8650 E8651 E8652 E8653 E8655 E8658 E8659 E866 E8660 E8661 E8662 E8663 E8664 E8665 E8666 E8667 E8668 E8669 E867 E8680 E8681 E8682 E8683 E8688 E8689 E869 E8690 E8691 E8692 E8693 E8698 E8699 E8850 E8880 E8881 E8888 E8889 E8980 E9173 E9174 E9175 E9176 E9177 E9178 E9225 E9557 E9790 E9791 E9792 E9793 E9794 E9795 E9796 E9797 E9798 E9799 E9857 E999 V1253 V1254 V0181 V0182 V0189 V4321 V4322 V4614 V6284 V8701 V8732 V9796 Add-on Services The IHCP reimburses add-on services at a flat statewide rate when billed with a stand-alone procedure. Table 8.34 lists add-on services. Note: Add-on services are not allowed with any surgical revenue codes. Table 8.34 – Add-on Services Revenue Code Description 250 Pharmacy – general 251 Generic drugs 252 Brand drugs 253 Take-home drugs Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-127 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Revenue Code 8-128 Description 254 Drugs incident to other diagnostic procedures 255 Drugs incident to radiology 256 Drugs experimental 257 Nonprescription drugs 258 IV solutions 259 Other pharmacy 270 Med/surg supply – general 271 Nonsterile supply 272 Sterile supply 273 Take-home supplies 274 Prosthetic/orthotic devices 275 Pacemaker 276 Intraocular lens 277 Oxygen – take home 278 Other implants 279 Other supplies/devices 290 DME – general classification 291 DME – rental 292 DME – new 293 Purchase of used DME 299 Other med equipment 370 Anesthesia – general 371 Anesthesia – incident to radiology 372 Anesthesia – incident to other diagnostic services 374 Anesthesia – acupuncture 379 Anesthesia – other 380 Blood pints blood 381 Packed red cells 382 Blood – whole 383 Blood – plasma 384 Blood – platelets 385 Blood – leucocytes 386 Blood – other components 387 Blood – other derivatives 389 Blood – other Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Revenue Code Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Description 390 Blood storage and process – general 391 Blood administration 399 Other blood processing 621 Supplies incident to radiology 622 Supplies incident to other diagnostic 623 Supplies incidental to other diagnostic 624 FDA investigational devices Add-on services are separately reimbursable in conjunction with a stand-alone procedure. Certain addon services are also separately reimbursable if billed in conjunction with a treatment room. These are 255 (Drugs Incident to Radiology), 258 (IV Solutions), 29X (DME), 370 (Anesthesia), 38X (Blood), 39X (Blood Storage and Processing), and 62X (Diagnostic Supplies). All other add-on services are denied if billed in conjunction with a treatment room service. Add-on services are not separately reimbursable if provided on the same day as an outpatient surgery. Stand-alone Services Stand-alone services include therapies, diagnostic testing, dialysis, laboratory, and radiology procedures performed in an outpatient setting. Providers can bill stand-alone services separately or in conjunction with treatment room services. Stand-alone services are not separately reimbursable with outpatient surgeries if provided on the same day as the surgery. The IHCP reimburses stand-alone services at an established flat statewide rate and reimburses laboratory and radiology services at the lower of the submitted charge or the fee schedule amount. The IHCP allows a maximum of one unit of service, per revenue code, for each date of service, except for lab and radiology. Providers must bill services on the UB-04 claim form. Table 8.35 lists the revenue codes for stand-alone services. Table 8.35 – Stand-alone Services Revenue Code Description 260 IV therapy – general 261 IV therapy – infusion pump 269 IV therapy – other 28X Oncology 30X Laboratory 31X Laboratory pathological 32X Radiology – diagnostic 33X Radiology – therapeutic 34X Nuclear medicine 35X CT scan 40X Other imaging service Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-129 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Revenue Code 8-130 Description 410 Respiratory services – general 412 Inhalation services 413 Hyperbaric oxygen therapy 419 Other respiratory 42X Physical therapy 43X Occupational therapy 44X Speech-language pathology 460 Pulmonary function – general 469 Other pulmonary function 47X Audiology 481 Cardiac catheter laboratory 482 Stress test 483 Echocardiology 489 Other cardiology 61X MRT 634 EPO, less than 10,000 units 635 EPO, 10,000 units or more 636 Drugs requiring detailed coding 730 Electrocardiogram (EKG/ECG) 731 EKG/ECG – holter monitor 732 EKG/ECG – telemetry 739 Other EKG/ECG 740 Electroencephalogram (EEG) 749 EEG – other 75X Gastrointestinal services 780 Telemedicine 79X Extracoporeal shockwave therapy 820 Hemodialysis OP/home – general 821 Hemodialysis OP/home – composite 823 Hemodialysis – home equipment 825 Hemodialysis – support services 829 Other OP hemodialysis 830 Peritoneal dialysis – general 831 Peritoneal dialysis – composite 832 Peritoneal – home supplies 833 Peritoneal – home equipment Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Revenue Code Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Description 841 CAPD OP/home – composite 851 CCPD OP/home – composite 890 Donor bank – general 921 Peripheral vascular lab 922 Electromyelogram 923 Pap smear 924 Allergy test 925 Pregnancy test 94X Therapeutic services 943 Cardiac rehabilitation Stand-alone Laboratory Services A physician or other practitioner authorized to do so under state law must order laboratory services in writing. Laboratories performing the services must bill the IHCP directly unless otherwise approved. Providers may submit only one claim when providing multiple laboratory services. Hospitals must bill laboratory services using the most appropriate HCPCS code. Revenue codes billed without the appropriate HCPCS procedure code are denied. Providers must bill the professional component of a laboratory service performed in an outpatient hospital setting on the CMS-1500 claim form or an 837P transaction with the appropriate HCPCS code and 26 modifier. Refer to the CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions section of this chapter for specific CMS-1500 billing instructions. Stand-alone Radiology Services A physician, or other practitioner authorized to do so under state law, must order radiology services in writing. Facilities must bill the IHCP directly. Hospitals billing under the provider type of “01” should bill only the technical component (TC) for radiology services provided in an outpatient hospital setting on the UB-04 claim form. No TC modifier is necessary for provider type 01. Providers must bill radiology revenue codes in conjunction with the appropriate HCPCS procedure code. Revenue codes billed without the appropriate HCPCS procedure code are denied. For radiology procedures, do not fragment and bill them separately. Providers must bill the professional component of a radiology service performed in an outpatient hospital setting with the appropriate HCPCS code and 26 modifier on the CMS-1500 claim form or 837P transaction. Freestanding radiology facilities must bill the technical and/or professional components of a radiology service on the CMS-1500 claim form or 837P transaction with the appropriate HCPCS code. If the freestanding radiology facility performed both components of the service, a modifier is not necessary. If the radiology facility performed only one component, the applicable 26 or TC modifier is necessary. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-131 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual The CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions section of this chapter provides specific CMS-1500 billing instructions. Stand-alone Chemotherapy and Radiation Services Bill all outpatient hospital chemotherapy and radiation treatment services on the UB-04 claim form or 837I transaction. Chemotherapy services consist of four components: • Administration of chemotherapy agent • Chemotherapy agent • Intravenous (IV) solution and equipment • Treatment room services Each of the four components is separately reimbursable when chemotherapy is administered, using the following code combinations: • Administration of chemotherapy agent – Bill using revenue codes 331, 332, or 335. The appropriate CPT chemotherapy codes are 96401 through 96549. • Chemotherapy agent – Bill using revenue code 636 – Drugs requiring detailed coding, along with the appropriate HCPCS code. • IV solution and equipment – Bill using revenue code 258 for the IV solution and revenue code 261 for IV equipment. • Treatment room services – Bill using revenue codes 45X, 483, 51X, 52X, or 76X. Radiation Treatment Services consist of two components: • Administration of radiation treatment • Treatment room services Both components are separately reimbursable, using the following code combinations: • Administration of radiation treatment – Bill using revenue codes 330, 333, or 339, along with the appropriate CPT radiation treatment code, 77261 through 77799. • Treatment room services – Bill using revenue codes 45X, 483, 51X, 52X, or 76X. Note: When chemotherapy and radiation treatment services are rendered on the same day, bill all applicable components to the IHCP. Stand-alone Renal Dialysis Services This section addresses billing requirements for hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis services rendered in a hospital outpatient setting in independent renal dialysis facilities called end-stage renal disease (ESRD) dialysis facilities; or in a patient’s home. 8-132 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Composite Rate for Method I Dialysis Patients who have ESRD, a chronic condition with kidney impairment considered irreversible and permanent, require a regular course of dialysis or a kidney transplant to maintain life. The IHCP reimburses for routine dialysis. The cost of dialysis treatments includes overhead costs, personnel services, administrative services (includes nursing staff members, social worker, and dietician), equipment and supplies, ESRD-related laboratory tests, certain injectable drugs, and biologicals. The composite rate for dialysis is the charge for the actual treatment or dialysis session. Routine laboratory charges are included in the fee for hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis and, as such, are not billed separately. However, the IHCP covers nonroutine lab services when billed separately if medical justification is indicated. The composite rate also includes all durable and disposable items and medical supplies necessary for the effective performance of a patient’s dialysis. Supplies include, but are not limited to, the following: • Forceps • Syringes • Alcohol wipes • Needles • Topical anesthetics • Rubber gloves • Dialysate heaters • Dialysate • Connecting tubes The composite rate covers certain parenteral items used in the dialysis procedure; therefore, these items cannot be billed separately. The following drugs are included under the composite rate: • Heparin • Protamine • Mannitol • Saline • Pressor drugs • Glucose • Dextrose • Antihistamines • Antiarrhythmics • Antihypertensives Billing Guidelines The following billing guidelines are for hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis and are used in the following settings: • Hospital outpatient • Independent renal dialysis facilities (ESRD dialysis facilities) • Patient’s home (some are Method II) Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-133 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Providers of dialysis services must use the UB-04 claim form to submit claims to the IHCP. The IHCP allows providers to bill for the drugs associated with renal dialysis services on the CMS-1500 claim form. Providers must bill all services provided by the ESRD facility on the UB-04 claim form. For IHCP-only claims, providers must bill each date-specific service separately on the UB-04 claim form. For example, if the patient receives 15 dialysis treatments in the month, enter 15 detail lines of revenue code 821 on the UB-04 claim form with the specific service date in field 45. This is true for all other services provided during the month. UB-04 Completion Guidelines The UB-04 claim form has 22 lines; therefore, providers cannot bill an entire month on one page. Providers can prepare a continuation claim, which is a claim with more than one UB-04 claim form completed, as if it is one claim to be processed for payment by the IHCP. Continuation claims cannot be more than three pages. Providers must complete the continuation claim as follows: 1. Complete the first 22 lines on page one of the UB-04 claim form. 2. Mark the UB-04 claim form page numbers in the area provided on line 23. 3. Do not subtotal the first page of the claim. Total only the last page of the continuation claim, or IndianaAIM reads the claim as two claims rather than one. 4. Complete the subsequent UB-04 claim forms for the remaining dates of service of the month, numbering each page in the area provided on line 23. 5. Provide a grand total for the continuation claim on the last page of the UB-04 claim form in the space provided at the bottom of field 47. Providers that prefer not to complete a continuation claim can complete separate UB-04 claim forms. Type of Bill Codes Providers must use the following Type of Bill codes when submitting claims for renal dialysis: • Freestanding renal dialysis facilities (ESRDs) should use Type of Bill code 721. • Outpatient hospital renal dialysis facilities should use Type of Bill code 131. • Inpatient renal dialysis services should be billed with Type of Bill code 111. Diagnosis Codes • 584 – Acute renal failure • 585.x – Chronic renal failure • 586 – Renal failure unspecified Revenue Codes • 8-134 Dialysis Sessions – Hemodialysis sessions are reimbursable at an established flat statewide rate. These services represent the number of hemodialysis sessions. “Outpatient or home” and “units of service” reflect the number of actual sessions rendered (one per day). Use Revenue Codes 82X, 83X, 84X, and 85X. - Revenue category 82X: 821 – hemodialysis/composite or other rate. This revenue code represents the number of hemodialysis sessions, outpatient or home, rendered per day. Providers should indicate a “1” in field 46, Service Units, on the UB-04 claim form. The IHCP Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual - - - Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions allows only one unit per date of service. For ESRD providers, Revenue Code category 82X cannot be billed on the same claim with 83X, 84X, and 85X. Revenue category 83X: 831 – peritoneal dialysis/composite or other rate. This revenue code represents the number of peritoneal dialysis sessions performed in the outpatient or home setting. Providers should indicate a “1” in field 46, Service Units, on the UB-04 claim form. The IHCP allows only one unit per date of service. Revenue category 84X: 841 – CAPD/composite or other rate. This revenue code represents the charges for continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis, using the patient’s peritoneal membrane as a dialyzer, which is performed in the home or outpatient setting. Providers should indicate a “1” in field 46, Service Units on the UB-04 claim form. The IHCP allows only one unit per date of service. For ESRD providers, Revenue Code category 82X cannot be billed on the same claim with 83X, 84X, and 85X. Revenue category 85X: 851 – CCPD/composite or other rate. This revenue code represents the charges for continuous cycling peritoneal dialysis performed in an outpatient or home setting. Providers should indicate a “1” in field 46, Service Units on the UB-04 claim form. The IHCP allows only one unit per date of service. Note: Providers can submit claims for revenue codes 820, 821, 830, 831, 840, 841, 849, 850, 851, and 881with more than one unit of service on a detail line. When multiple units span multiple days, providers must indicate the date range in the Statement Covers Period field. If providers do not include the date range in this field, the claim may be denied. • Administration of Epoetin – Providers must use the following revenue codes with the appropriate HCPCS J code when billing for the administration of Epoetin in a hospital outpatient or ESRD setting. The IHCP currently allows payment for HCPCS codes J0885 or J0886 for patients with a hematocrit range of less than 20 to 40 and above. - 634 Epoetin, less than 10,000 units - 635 Epoetin, 10,000 or more units • Drugs Requiring Detailed Coding – Revenue Code 636 is used with the appropriate HCPCS code to report charges for drugs and biological products requiring specific identification. Submit Revenue Code 636 in field 42 on the UB-04 claim form. Providers must submit the appropriate HCPCS code, including J codes, identifying the specific drug injected, in field 44. In field 46 on the UB-04 claim form, submit the number of units administered. • Laboratory Services – The composite rate for hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis includes routine laboratory charges; therefore, providers cannot bill separately for them. However, the IHCP covers nonroutine lab services when billed separately, if medical justification is indicated. Use Revenue Code category 30X with the appropriate HCPCS code. Laboratory tests included in the composite rate and their anticipated frequency include the following: - Per Treatment – All hematocrit, hemoglobin, and clotting times furnished incident to dialysis treatments - Weekly – Prothrombin time for patients on anticoagulant therapy, serum creatinine, and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) - Monthly – Serum calcium, serum bicarbonate, alkaline phosphatase, serum potassium, serum phosphorous, aspartate aminotransferase (AST, formerly SGOT), serum chloride, total protein, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), complete blood count (CBC), and serum albumin - Nonroutine lab services – The IHCP covers nonroutine lab services when billed separately, if medical justification is indicated. Use revenue code category 30X with the appropriate HCPCS code. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-135 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Note: The facility performing the dialysis treatment must bill all laboratory services performed. An independent lab cannot bill labs for dialysis patients separately. These independent labs should be contracted with the dialysis facility to perform the actual tests and cannot bill the IHCP separately for their services. • Supplies – The composite rate includes all durable and disposable items and medical supplies necessary for the effective performance of a patient’s dialysis. However, providers can use revenue code 270 to bill supplies outside the list of those included in the composite rate. Supplies are not paid if billed in conjunction with treatment room revenue codes. Supply revenue codes are denied if billed without an HCPCS surgical procedure code or if billed in conjunction with treatment room revenue codes 45X, 51X, 52X, 70X, 71X, 72X, and 76X, also billed without an HCPCS surgical procedure code. Providers can bill revenue code 270 with multiple units only when the member has any of the following renal diagnoses – 584.x, 585.x, or 586 – and when the service is directly related to the dialysis service. This is subject to postpayment review and recoupment. Transportation Services Providers may not bill transportation services on the UB-04 claim form. Providers must obtain a separate provider number to bill transportation services. These services must be billed on the CMS1500 claim form or 837P transaction. To enroll as a transportation provider, providers can access http://provider.indianamedicaid.com/become-a-provider/enroll-as-a-provider.aspx to enroll online or download a Provider Enrollment Application. Providers can also contact HP Provider Enrollment at 1877-707-5750. Chapter 4 of this manual provides specific enrollment information and criteria. Specific billing information for transportation services is provided in the Transportation Services section in this chapter. Outpatient Mental Health As required by the House Enrolled Act (HEA) 1396, the Covered Services Rule, 405 IAC 5-20, and 405 IAC 5-21, providers cannot use revenue codes 500, 510, 90X, 91X, and 96X to bill covered outpatient mental health hospital services. Hospitals can bill for the facility use associated with these services by billing the appropriate clinic or treatment room revenue code. Providers must bill all professional services associated with outpatient mental health services on the CMS-1500 claim form or 837P transaction. Up to and including date of service December 31, 2006, outpatient mental health services, including substance abuse and chemical dependency services rendered in freestanding psychiatric hospitals, are carved out of the RBMC delivery system and paid on an FFS basis. The carved-out definition in the Carved-Out Services subsection of this chapter provides further information. Bill claims for mental health services in a freestanding psychiatric hospital on a UB-04 claim form or 837I transaction. These claims are not the financial responsibility of the MCOs. Outpatient mental health services, including substance abuse treatment, provided to members in an RBMC delivery system in acute care facilities are the MCO’s financial responsibility. On and after January 1, 2007, these services will no longer be carved out, excluding services for PRTF and MRO services. 8-136 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Partial Units of Service Providers must round partial units of service to the nearest whole unit when calculating reimbursement. For example, if a unit of service equals 15 minutes, a minimum of eight minutes must be provided to bill for one unit. Filing UB-04 Crossover Claims Processing of Crossover Claims This section provides clarification of the billing procedures providers must follow when submitting paper UB-04 crossover claims to HP. The IHCP requires direct submission of crossover claims when a claim does not cross over automatically from Medicare. A claim may not cross over for the following reasons: • The Medicare carrier or intermediary is not National Government Services (previously known as AdminaStar Federal of Indiana) or is not a carrier that has a partnership agreement with HP. • Medicare does not reimburse the claim. Medicare denies payment because the service is not covered or does not meet the Medicare medical necessity criteria. • The IHCP provider file does not reflect the Medicare provider number. Chapter 4 of this manual provides additional information. • The provider has no record of a claim crossing over automatically within 60 days after the claim is reimbursed by the Medicare intermediary. • The provider is not a Medicare provider and does not accept assignment to bill the IHCP for dual eligible members. • Some ASCs must bill services to Medicare on a CMS-1500 claim form or 837P transaction with the SG modifier. If the services fail to cross over, the provider must submit the claim on a paper UB-04 claim form with a copy of the MRN. Attachments for UB-04 Paper Claims or 837I Transaction Submissions Mail paper crossover claims to the following address for processing: HP Institutional Crossover Claims P.O. Box 7271 Indianapolis, IN 46207-7271 The following guidelines are required to ensure appropriate processing of Medicare and IHCP-related claims: • Providers must not submit Medicare denied services on the claim form or electronic transaction with Medicare paid services. Providers must split the claim and group all denied line items on one claim or electronic transaction and all paid line items on another. It is critical that providers attach a copy of the MRN to the paper claim or send it as an attachment for the 837I transaction containing the Medicare denied services. • Applicable documentation for third-party liability or spend-down information should be submitted with the paper claim or sent as an attachment for the electronic 837I transaction. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-137 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Note: EOB codes 0512 and 0545 state that a claim submitted after the one-year filing limit without acceptable documentation does not apply to a crossover claim when Medicare made a payment. Specifically, EOBs 0512 and 0545 are bypassed for cases in which Traditional Medicaid is paying the coinsurance and deductible amounts. If Medicare denies a claim, EOB codes 0512 and 0545 apply to the Traditional Medicaid claim. UB-04 Crossover Billing Procedures Providers should follow the general directions for filling out the UB-04 claim form when filing crossover claims. Providers can also submit crossover claims electronically using the electronic 837I transaction or through Web interChange. The following billing instructions help to ensure accurate processing of all UB-04 Medicare crossover claims: • Use fields 39-41 to indicate a value code of A1 to reflect the Medicare deductible amount, a value code of A2 to reflect the Medicare coinsurance amount, and a value code of 06 to reflect the blood deductible amount. Use a value code of 80 to reflect covered days. • Use fields 50a–54a to reflect Medicare information only. Use form field 54a to indicate the Medicare paid amount. Do not include the Medicare allowed amount or contract adjustment amount in field 54. Do not include Medicare Replacement/HMO policy information in these fields. Note: If the Medicare paid amount is greater than the billed amount, indicate the correct dollar values in the fields. Then reflect the estimated amount due as $0 in form field 55c. This amount does not have a negative impact on the payment of a crossover claim. • Fields 50b–54b are reserved for Medicare supplement carrier information. Use form field 54b to denote any Medicare supplemental carrier or third-party liability payment information, which includes Medicare Replacement/HMO policy information. • Use field 55c to reflect the amount calculated in the following equation: - Total claim amount - Medicare paid (54a) - Medicare supplement or third-party liability (54b) = Est. Amount Due (55c) - Automated Spend-down outpatient hospital claims that span more than one month are credited to spend-down based on individual dates of services as reported on the detail lines of the claim. Note: Leave fields 55a and 55b blank. The amount in form field 55c is not necessarily equal to the coinsurance and deductible amounts present on the Medicare MRN, but is calculated using the correct data for each of the fields. • Field 67, Principal Diagnosis Code, and field 69, Admitting Diagnosis Code, are required for all inpatient claims, including LTC and hospice. Complete these fields to avoid claim denial. • Field 45, Service Date, is required for all outpatient, hospice, renal dialysis, and home health claims. The date in field 45 populates the statement From and Through dates for the aforementioned claim types. EOB code 264 – Date-of-service is missing, posts with a denial on all claims submitted without this required information. 8-138 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Billing Medicare Denied Services If Medicare does not pay a detail, the IHCP does not consider the detail a crossover claim. Providers must bill this detail separately using a UB-04 claim form or the 837I transaction. Providers must attach copies of the MRN and any applicable third-party EOBs when submitting these types of claims. Note: Providers cannot submit paid and denied charges on the same claim form or electronic transaction. Providers must submit the paid portion of the Medicare charges as a crossover claim, and they must submit denied Medicare charges as a separate claim or transaction. Line items submitted on incorrect claim forms are denied. 837I Electronic Transaction Providers must use the standard 837I format to submit electronic institutional claims. These standards are published in the 837I Implementation Guides (IGs). An addenda to most IGs has been published and must be used to properly implement each transaction. The IGs are available for download through the Washington Publishing Company Web site at http://wpc-edi.com. Companion Guides The IHCP has developed technical companion guides to assist application developers during the implementation process. Information contained in the IHCP Companion Guides is intended only to supplement the adopted IGs and provide guidance and clarification as the guides apply to the IHCP. IHCP Companion Guides are never intended to modify, contradict, or reinterpret the rules established by the IGs. The Companion Guides are located on the IHCP Web site at http://provider.indianamedicaid.com in the EDI Solutions section. Some data elements that providers submit may not be used in processing the 837I transaction; however, they may be returned in other transactions, such as the 277 Claim Status Request and Response or the 835 Remittance Advice transactions. These data elements are necessary for processing, and failure to append these data elements may result in claim suspension or denial. Providers may submit as many as 48 occurrence (span) codes and dates. IndianaAIM accepts as many as 24 occurrence codes and 24 occurrence span dates. Diagnosis Codes Providers may submit as many as 27 ICD-9-CM five-digit diagnosis codes on the 837I. IndianaAIM accepts admit, primary, E-code, and 24 secondary diagnosis codes. The provider uses these codes to describe the medical condition of the patient, and the IHCP uses them to process the transaction. The IHCP processes the first 11 diagnosis codes including the principal, admission, and additional diagnosis codes submitted. This rule applies to paper claims and 837I transaction submissions. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-139 Chapter 8 Section 2: UB-04 Billing Instructions Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Additional UB-04 and 837I Admission and Duration Changes The following requirements apply to the UB-04 claim form and the 837I transaction: • Always include an admitting code for inpatient claims. • Always enter accommodation rates in full units. • A day begins at midnight and ends 24 hours later. For long-term care (LTC), a part of a day, including day of admission, counts as a full day if the member is not readmitted to the hospital by midnight on the same day. The day of death is the day of discharge and is not counted for inpatient or LTC services. Hospice services can include the day of death as a billable date for the hospice portion of the claim when the member resides in a nursing facility. The date of discharge or death is not payable for the room and board portion of the hospice claim when the member resides in a nursing facility. • Always include an admitting code for inpatient claims. • Always include principal, admitting, and E-codes for all claims except religious, nonmedical claims and hospital, other. 8-140 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 3: Telemedicine Overview Effective April 1, 2007, telemedicine services are covered by the Indiana Health Coverage Programs (IHCP). This section discusses applicable coverage parameters and billing guidelines. Telemedicine services are covered by Medicaid within the parameters specified in rule 405 IAC 5-38, which is presented in the Indiana Administrative Code (IAC) section. Definitions • Hub Site – Location of the physician or provider rendering consultation services. • Spoke Site – Location where the patient is physically located when services are provided. • Interactive Television (IATV) – Videoconferencing equipment at the hub and spoke sites that allows real-time, interactive, and face-to-face consultation. • Store and Forward – Electronic transmission of medical information for subsequent review by another health care provider. Only IATV is separately reimbursed by the IHCP. Store-and-forward technology to facilitate other reimbursable services is allowed; however, separate reimbursement of the spoke-site payment will not be provided for this technology because of restrictions in 405 IAC 5-38-2(4). Note: Telemedicine is not the use of the following: (1) Telephone transmitter for transtelephonic monitoring; or (2) Telephone or any other means of communication for consultation from one provider to another Provider/Service Requirements The following service or provider types are not permitted to be reimbursed for telemedicine per 405 IAC 5-38: • Ambulatory surgical centers • Outpatient surgical services • Home health agencies or services • Radiological services • Laboratory services • Long-term care facilities, including nursing facilities, intermediate care facilities, or community residential facilities for the developmentally disabled • Anesthesia services or nurse anesthetist services • Audiological services • Chiropractic services Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-141 Chapter 8 Section 3: Telemedicine Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual • Care coordination services • Durable medical equipment (DME), medical supplies, hearing aids, or oxygen • Optical or optometric services • Podiatric services • Services billed by school corporations • Physical or speech therapy services • Transportation services • Services provided under a Medicaid waiver Conditions of Payment 1. IHCP reimburses for telemedicine services only when the hub and spoke sites are greater than 20 miles apart. 2. The member must be present and able to participate in the visit. 3. For a medical professional to receive reimbursement for professional services in addition to payment for spoke services, medical necessity must be documented. If it is medically necessary for a medical professional to be with the member at the spoke site, the spoke site is permitted to bill an evaluation and management code in addition to the fee for spoke services. Adequate documentation must be maintained in the patient’s medical record to support the need for the provider’s presence at the spoke site during the visit. Documentation is subject to postpayment review. 4. The audio and visual quality of the transmission must meet the needs of the physician located at the hub site. The IATV technology must meet generally accepted standards to allow the physician at the hub site to render medical decisions. Hub Site Services and Billing Requirements The following Current Procedural Terminology (CPT®) codes are reimbursable for providers that render services via telemedicine at the hub site. Modifier GT – Via interactive audio and video telecommunications system must be used to denote telemedicine services. The payment amount is equal to the current fee schedule amount for the following services: • Consultations – 99241 to 99245 and 99251 to 99255 • Office or other outpatient visit – 99201 to 99205 and 99211 to 99215 • Individual psychotherapy – 90804 to 90809 • Psychiatric diagnostic interview – 90801 • Pharmacologic management – 90862 • End-stage renal disease (ESRD) services – 90951 to 90970 Spoke Site Services and Billing Requirements The following Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS) code and revenue code are reimbursable for providers that render services via telemedicine at the spoke site. Modifier GT – Via interactive audio and video telecommunications system must be used to denote telemedicine services. 8-142 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 3: Telemedicine The payment amount is equal to the current fee schedule amount for HCPCS code Q3014 Telehealth originating site facility fee. 1. Spoke services are reimbursed using HCPCS code Q3014 – Telehealth originating site facility fee. The GT modifier must be used to denote telemedicine services. 2. Revenue code 780 represents telemedicine services. If a different, separately reimbursable treatment room revenue code is provided on the same day as the telemedicine consultation, the appropriate treatment room revenue code should also be included on the claim. Documentation must be maintained in the patient’s record to indicate that services were provided separate from the telemedicine visit. 3. If spoke site services are provided in a physician’s office and other services are provided on the same date as the spoke service, the medical professional should bill Q3014 as a separate line item from other professional services. Documentation Standards 1. Documentation must be maintained at the hub and spoke locations to substantiate the services provided. Documentation must indicate the services were rendered via telemedicine. 2. Documentation must clearly indicate the location of the hub and spoke sites. 3. All other IHCP documentation guidelines for services rendered via telemedicine apply, such as chart notes and start and stop times. Documentation must be available for postpayment review. 4. Providers must have written protocols for circumstances when the member must have a hands-on visit with the consulting provider. The member should always be given the choice between a traditional clinical encounter versus a telemedicine visit. Appropriate consent from the member must be obtained by the spoke site and maintained at the hub and spoke sites. Special Considerations 1. When ongoing services are provided, the member should be seen by a physician for a traditional clinical evaluation at least once a year, unless otherwise stated in policy. In addition, the hub physician should coordinate with the patient’s primary care physician. 2. The existing service limitations for office visits are applicable. All telemedicine consultations billed using the codes listed in the Hub Site Services and Billing Requirements section will be counted against the office visit limit. Third-party liability (TPL), spend-down, managed care, and all other considerations apply. 3. Reimbursement for ESRD-related services under HCPCS codes 90951 to 90970 is permitted in the telemedicine setting. The IHCP requires at least one monthly visit for ESRD-related services to be a traditional clinical encounter to examine the vascular access site. 4. Federally Qualified Health Centers (FQHCs) or rural health clinics (RHCs) are only reimbursed for hands-on services and are therefore not permitted to bill for telemedicine services. Managed Care Considerations Refer questions to the appropriate managed care organization (MCO) for risk-based managed care considerations. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-143 Chapter 8 Section 3: Telemedicine Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual FQHCs and RHCs may submit claims to an MCO as fee-for-service and receive reconciliation review through Myers & Stauffer, which, in coordination with the Office of Medicaid Policy and Planning (OMPP), determines billable and nonbillable services. Indiana Administrative Code (IAC) Rule 38. Telemedicine Services 405 IAC 5-38-1 General provisions Authority: IC 12-8-6-5; IC 12-15-1-10; IC 12-15-21-2; IC 12-15-21-3 Affected: IC 12-13-7-3; IC 12-15 Sec. 1. (a) Telemedicine services refer to a specific method of delivery of certain services, including medical exams and consultations, which are already reimbursed by Medicaid. Telemedicine uses videoconferencing equipment allowing a medical provider to render an exam or other service to a patient at distant location. Telemedicine services are covered by Medicaid within the parameters specified in this rule. (b) Telemedicine is not the use of a: (1) telephone transmitter for transtelephonic monitoring; or (2) telephone or any other means of communication, consultation from one (1) doctor to another. (Office of the Secretary of Family and Social Services; 405 IAC 5-38-1; filed Feb 28, 2007, 2:42 p.m.: 20070328-IR-405060029FRA readopted filed Sep 19, 2007, 12:16 p.m.: 20071010-IR-405070311RFA) 405 IAC 5-38-2 Definitions Authority: IC 12-8-6-5; IC 12-15-1-10; IC 12-15-21-2; IC 12-15-21-3 Affected: IC 12-13-7-3; IC 12-15 Sec. 2. The following definitions apply throughout this rule: (1) “Hub site” means the location of the physician or provider rendering consultation services. (2) “Interactive television” or “IATV” means the videoconferencing equipment at the hub and spoke site that allows real time, face-to-face consultation. (3) “Spoke site” means the location where the patient is physically located when services are provided. (4) “Store and forward” means the electronic transmission of medical information for subsequent review by a health care provider at the hub site. Restrictions placed on store and forward reimbursement in this rule shall not disallow the permissible use of store and forward technology to facilitate reimbursable services. (Office of the Secretary of Family and Social Services; 405 IAC 5-38-2; filed Feb 28, 2007, 2:42 p.m.: 20070328-IR-405060029FRA; readopted filed Sep 19, 2007, 12:16 p.m.: 20071010-IR405070311RFA) 8-144 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 3: Telemedicine 405 IAC 5-38-3 Description of service Authority: IC 12-8-6-5; IC 12-15-1-10; IC 12-15-21-2; IC 12-15-21-3 Affected: IC 12-13-7-3; IC 12-15 Sec. 3. (a) In any telemedicine encounter, there will be the following: (1) A hub site. (2) A spoke site. (3) An attendant to connect the patient to the specialist at the hub site. (4) A computer or television monitor to allow the patient to have: (A) real-time; (B) interactive; and (C) face-to-face communication with the hub specialist/consultant via IATV technology. (b) Services may be rendered in an inpatient, outpatient, or office setting. (Office of the Secretary of Family and Social Services; 405 IAC 5-38-3; filed Feb 28, 2007, 2:42 p.m.: 20070328-IR405060029FRA; readopted filed Sep 19, 2007, 12:16 p.m.: 20071010-IR-405070311RFA) 405 IAC 5-38-4 Limitations Authority: IC 12-8-6-5; IC 12-15-1-10; IC 12-15-21-2; IC 12-15-21-3 Affected: IC 12-13-7-3; IC 12-15 Sec. 4. Telemedicine shall be limited by the following conditions: (1) The patient must be: (A) physically present at the spoke site; and (B) participate in the visit. (2) The physician or practitioner who will be examining the patient from the hub site must determine if it is medically necessary for a medical professional to be at the spoke site. Separate reimbursement for a provider at the spoke site is payable only if that provider’s presence is medically necessary. Adequate documentation must be maintained in the patient’s medical record to support the need for the provider’s presence at the spoke site during the visit. Such documentation is subject to postpayment review. If a health care provider’s presence at the spoke site is medically necessary, billing of the appropriate evaluation and management code is permitted. (3) Reimbursement for telemedicine services is available only when the hub and spoke sites are greater than twenty (20) miles apart. Adequate documentation must be maintained as service is subject to postpayment review. (4) Store and forward technology is not reimbursable by Medicaid. The use of store and forward technology is permissible as defined under section 2(4) of this rule. (5) The following service or provider types may not be reimbursed for telemedicine: (A) Ambulatory surgical centers. (B) Outpatient surgical services. (C) Home health agencies or services. (D) Radiological services. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-145 Chapter 8 Section 3: Telemedicine Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual (E) Laboratory services. (F) Long term care facilities, including nursing facilities, intermediate care facilities, or community residential facilities for the developmentally disabled. (G) Anesthesia services or nurse anesthetist services. (H) Audiological services. (I) Chiropractic services. (J) Care coordination services. (K) DME, medical supplies, hearing aids, or oxygen. (L) Optical or optometric services. (M) Podiatric services. (N) Services billed by school corporations. (O) Physical or speech therapy services. (P) Transportation services. (Q) Services provided under a Medicaid waiver. (Office of the Secretary of Family and Social Services; 405 IAC 5-38-4; filed Feb 28, 2007, 2:42 p.m.: 20070328-IR-405060029FRA; readopted filed Sep 19, 2007, 12:16 p.m.: 20071010-IR405070311RFA) 8-146 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Introduction This document refers to the CMS-1500, Health Insurance Claim Form as CMS-1500 claim form, and it refers to the 837P Health Care Claim: Professional Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) transaction as 837P or 837P transaction throughout this document. Providers should refer to the Indiana Health Coverage Programs (IHCP) Companion Guides for specific information about electronic billing. View the HIPAA Companion Guides from the IHCP Web site at http://provider.indianamedicaid.com/general-provider-services/electronic-data-interchange-(edi)solutions/ihcp-companion-guides.aspx. The paper claim form billing instructions align the paper claim process with the electronic claim requirements mandated by the HIPAA Administrative Simplification requirements. Providers should refer to the appropriate transaction implementation guide and IHCP Companion Guide for information about the 837P transaction. Providers Using the CMS-1500 Claim Form or the 837P Transaction The following is a list of provider types and services covered that are billed using the CMS-1500 claim form or 837P transaction: • Advanced practice nurses – midwife services, nurse practitioner services, nurse anesthetist services, and clinical nurse specialists • Audiologists – audiology services • Case managers – care coordination services • Certified registered nurse anesthetist (CRNA) • Chiropractors – chiropractic services • Clinics – family planning services, Federally Qualified Health Center (FQHC) services, medical services, nurse practitioner services, rural health center (RHC) services, therapy services, and surgical services • Dentists – oral surgery • Diabetes self-management • Durable medical equipment (DME), home medical equipment (HME), and supply dealers – DME, medical supplies, and oxygen • Early and Periodic Screening, Diagnosis, and Treatment (EPSDT) service providers • Freestanding radiology facilities – radiological services, professional component or global • Hearing aid dealers – hearing aids • Laboratories – lab services, professional component • Mental health providers – Medicaid Rehabilitation Option (MRO) services, outpatient mental health services Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-147 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions • Mid-level practitioners – anesthesiology assistant services, physician assistant services, independent practice school psychologists, and advanced practice nurses under IC 25-23-1-1(b)(3), credentialed in psychiatric or mental health nursing by the American Nurses Credentialing Center – billing under the supervising physician rendering National Provider Identifier (NPI). • Opticians – optical services • Optometrists – optometric services • Pharmacies – supplies • Physicians, medical doctors, and doctors of osteopathy – anesthesiology services, lab services, professional component, medical services, mental health services, radiology services, renal dialysis services, surgical services • Podiatrists – podiatric services • Public health agencies – medical services • School corporations – therapy services: physical, occupational, speech, mental health • Therapists – therapy services: physical, occupational, speech, audiology • Transportation provider – transportation services, including hospital-based ambulance services • Waiver providers – waiver services General Information The IHCP uses the International Classification of Diseases-9th Edition-Clinical Modification (ICD-9CM) and Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS) Level I and II coding systems. Each coding system is described as follows: • ICD-9-CM codes Volume 1 is numeric diagnosis codes, Volume 2 is an alphabetic index, and Volume 3 is a tabular list of codes and an alphabetic index for procedures. • Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS) Level I codes are Current Procedural Terminology® (CPT) numeric codes and modifiers created by the American Medical Association (AMA). • HCPCS Level II codes are A through V alphanumeric codes and modifiers created by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) and are found in the HCPCS manual. These codes identify products, supplies, materials, and services that are not included in the CPT code book. Except where otherwise noted, the IHCP uses coding practices created and published by these entities. Coding exceptions and clarifications are noted throughout the remainder of this chapter. Additional exceptions related to the Medicare resource-based relative value (RBRVS) reimbursement system are noted in Chapter 7 of this manual. Providers should always monitor all bulletins, banner page articles, and newsletter articles for future coding information and clarification of billing practices. 8-148 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Claims Submission Addresses Mail all claims, including those that have passed the filing limit, to one of the following addresses: HP CMS-1500 Claims P.O. Box 7269 Indianapolis, IN 46207-7269 HP Medical Crossover Claims P.O. Box 7267 Indianapolis, IN 46207-7267 Note: For risk-based managed care (RBMC) members, providers should send claims to the appropriate managed care organization (MCO) unless otherwise indicated. CMS-1500 Paper Claim Form Requirements This section provides a brief overview for completing the CMS-1500 claim form version 08-05. Note: Providers are encouraged to submit claims on the standard red-ink form to expedite claim processing and improve the accuracy of data entry. Billing and Rendering Provider Numbers The following are the four provider classifications: 1. Billing – A practitioner or facility operating under a unique taxpayer identification number (TIN). The TIN may be the practitioner’s Social Security number (SSN) or a Federal Employer Identification Number (FEIN), but a sole proprietor’s TIN may not be shared or used by any other practitioner, group, or facility. 2. Group – Any practice with one or more practitioners (rendering providers) sharing a common TIN. A group may be a corporation or partnership, or any other legally defined business entity. The group must have members linked to the business, and these members are identified as rendering (the person performing the service) providers. 3. Rendering – The provider that performs the services. Reimbursement for these services is paid to the group and reported on the group’s TIN. 4. Dual – A provider that is a billing and rendering provider. The provider is enrolled as a billing provider at one or more locations, and is also a member of a group or groups at one or more locations. It is imperative that providers enter only the NPI in field 33a on the CMS-1500. Placement of more than one NPI in this field could result in reimbursement of the claim to the wrong provider. For more instructions about NPI requirements, see the National Provider Identifier and One-to-One Match section in Section 1 of this chapter. Note: Atypical providers (nonmedical service providers) will continue to bill using the Legacy Provider Identifier (LPI) in field 33b with the 1D qualifier. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-149 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions When the rendering provider’s NPI appears in form field 33a on the CMS-1500, and the IHCP makes a payment to the rendering provider, the rendering provider must refund the incorrect payment. Mail refunds to the following IHCP address: HP Refunds P.O. Box 1937, Dept. 104 Indianapolis, IN 46206-1937 Description of Fields on the CMS-1500 Claim Form This section explains the CMS-1500 claim form and the 837P transaction. Some information is required on the form and other information is optional. The field chart in Table 8.36 indicates if a field is Required or Required, if applicable. Optional and Not applicable information is displayed in normal type. Specific instructions applicable to a particular provider type are included. The table describes each form locator by referring to the number found in the left corner of each box on the CMS-1500 claim form. These boxes contain the data elements. IndianaAIM processes a maximum of six service lines per paper CMS-1500 claim form and 50 service lines on the 837P. Figure 8.2 shows a sample copy of the CMS-1500, Version 08-05 claim form. Table 8.36 − CMS-1500, Version 08-05 Claim Form Locator Descriptions Form Locator Narrative Description/Explanation 1 INSURANCE CARRIER SELECTION – Enter X for Traditional Medicaid. Required. 1a INSURED’S I.D. NUMBER (FOR PROGRAM IN ITEM 1) – Enter the member IHCP identification (RID) number. Must be 12 digits. Required. 2 PATIENT’S NAME (Last Name, First Name, Middle Initial) – Provide the member’s last name, first name, and middle initial obtained from the Automated Voice Response (AVR) system, electronic claim submission (ECS), Omni, or Web interChange verification. Required. 3 PATIENT’S BIRTH DATE – Enter the member’s birth date in MMDDYY format. Optional. SEX – Enter an X in the appropriate box. Optional. 4 INSURED’S NAME (Last Name, First Name, Middle Initial) – Not applicable. 5 PATIENT’S ADDRESS (No., Street), CITY, STATE, ZIP CODE, TELEPHONE (include Area Code) – Enter the member’s complete address information. Optional. 6 PATIENT RELATIONSHIP TO INSURED – Not applicable. 7 INSURED’S ADDRESS (No., Street), city, state, ZIP Code, telephone (include area code) – Not applicable. 8 PATIENT STATUS – Enter X in the appropriate box. Optional. 9 OTHER INSURED’S NAME (Last Name, First Name, Middle Initial) – If other insurance is available, and the policyholder is other than the member shown in fields 1a and 2, enter the policyholder’s name. Required, if applicable. 9a OTHER INSURED’S POLICY OR GROUP NUMBER – If other insurance is available, and the policyholder is other than the member noted in fields 1a and 2, enter the policyholder’s policy and group number. Required, if applicable. 8-150 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Form Locator Narrative Description/Explanation 9b OTHER INSURED’S DATE OF BIRTH – If other insurance is available, and the policyholder is other than the member shown in fields 1a and 2, enter the requested policyholder birth date in MMDDYY format. Optional. SEX – Enter X in the appropriate box. Optional. 9c EMPLOYER’S NAME OR SCHOOL NAME – If other insurance is available, and the policyholder is other than the member shown in fields 1a and 2, enter the requested policyholder information. Required, if applicable. 9d INSURANCE PLAN NAME OR PROGRAM NAME – If other insurance is available, and the policyholder is other than the member shown in field 1a and 2, enter the policyholder’s insurance plan name or program name information. Required, if applicable. 10 IS PATIENT’S CONDITION RELATED TO – Enter X in the appropriate box in each of the three categories. This information is needed for follow-up third-party recovery actions. Required, if applicable. 10a EMPLOYMENT (CURRENT OR PREVIOUS) – Enter X in the appropriate box. Required, if applicable. 10b AUTO ACCIDENT – Enter X in the appropriate box. Required, if applicable. PLACE (State) – Enter the two-character state code. Required, if applicable. 10c OTHER ACCIDENT – Enter X in the appropriate box. Required, if applicable. 10d RESERVED FOR LOCAL USE – Not applicable. Fields 11 and 11a through 11d are used to enter member insurance information. 11 INSURED’S POLICY GROUP OR FECA NUMBER – Enter the member’s policy and group number of the other insurance. Required, if applicable. 11a INSURED’S DATE OF BIRTH – Enter the member’s birth date in MMDDYY format. Required, if applicable. SEX – Enter an X in the appropriate sex box. Required, if applicable. 11b EMPLOYER’S NAME OR SCHOOL NAME – Enter the requested member information. Required, if applicable. 11c INSURANCE PLAN NAME OR PROGRAM NAME – Enter the member’s insurance plan name or program name. Required, if applicable. 11d IS THERE ANOTHER HEALTH BENEFIT PLAN? Enter X in the appropriate box. If the response is Yes, complete fields 9a–9d. Required, if applicable. 12 PATIENT’S OR AUTHORIZED PERSON’S SIGNATURE – Not applicable. 13 INSURED’S OR AUTHORIZED PERSON’S SIGNATURE – Not applicable. 14 DATE OF CURRENT ILLNESS (First symptom date) OR INJURY (Accident date) OR PREGNANCY (LMP date) – Enter the date of the last menstrual period (LMP) for pregnancy-related services in MMDDYY format. Required for payment for pregnancy-related services. 15 IF PATIENT HAS HAD SAME OR SIMILAR ILLNESS, GIVE FIRST DATE – Enter date in MMDDYY format. Optional. 16 DATES PATIENT UNABLE TO WORK IN CURRENT OCCUPATION – If field 10a is Yes, enter the applicable FROM and TO dates in a MMDDYY format. Required, if applicable. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-151 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Form Locator Narrative Description/Explanation NAME OF REFERRING PROVIDER OR OTHER SOURCE – Enter the name of the referring physician. Required, if applicable. For waiver-related services, enter the provider name of the case manager. Required for Care Select PMP. 17 Note: The term referring provider includes those physicians primarily responsible for the authorization of treatment for lock-in or restricted card members. 17a ID NUMBER OF REFERRING PROVIDER, ORDERING PROVIDER OR OTHER SOURCE – Enter the qualifier in the first shaded box of 17a, indicating what the number reported in the second shaded box of 17a represents. Atypical providers should report the IHCP LPI provider number in the second box of 17a. Healthcare providers should report the taxonomy code in the second box of 17a. The qualifier is required when entering the IHCP LPI provider number or taxonomy. Qualifiers to report to IHCP: 1D is the qualifier that applies to the IHCP provider number, also called the LPI for the atypical nonhealthcare provider. The LPI includes nine numeric characters and one alpha character for the service location. ZZ is the qualifier that applies to the provider taxonomy code. The taxonomy code includes 10 alphanumeric characters. Taxonomy may be needed to establish a one-to-one NPI/LPI match if the provider has multiple locations. Required when applicable and for any waiver-related services. 17b NPI – Enter the 10-digit numeric NPI of the referring provider, ordering provider, or other source. Required when applicable and for Care Select PMPs. 18 HOSPITALIZATION DATES RELATED TO CURRENT SERVICES – Enter the requested FROM and TO dates in MMDDYY format. Required, if applicable. 19 RESERVED FOR LOCAL USE – Enter the Care Select primary medical provider (PMP) two-digit alphanumeric certification code. Required for Care Select members when the physician rendering care is not the PMP or a physician in the PMP’s group or a clinic. Note: Report the PMP qualifier and ID number in 17a. 20 OUTSIDE LAB? – Not applicable. CHARGES – Not applicable. 21.1 to 21.4. DIAGNOSIS OR NATURE OF ILLNESS OR INJURY – Complete fields 21.1, 21.2, 21.3, and/or 21.4 to field 24E by detail line. Enter the ICD-9-CM diagnosis codes in priority order. A total of four codes can be entered. At least one diagnosis code is required for all claims except those for waiver, transportation, and medical equipment and supply services. Required. 22 MEDICAID RESUBMISSION CODE, ORIGINAL REF. NO. – Applicable for Medicare Part B crossover claims only. For crossover claims, the combined total of the Medicare coinsurance, deductible, and psych reduction must be reported on the left side of field 22 under the heading Code. The Medicare paid amount (actual dollars received from Medicare) must be submitted in field 22 on the right side under the heading Original Ref No. Required, if applicable. 23 PRIOR AUTHORIZATION NUMBER – The prior authorization (PA) number is not required, but entry is recommended to assist in tracking services that require PA. Optional. Note: Date of service is the date the specific services were actually supplied, dispensed, or rendered to the patient. For services requiring authorization, the FROM date of service cannot be prior to the date the service was authorized. The TO date of service cannot exceed the date the specific service was terminated. 8-152 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Form Locator Narrative Description/Explanation 24A to 24I Top Half – Shaded Area NATIONAL DRUG CODE INFORMATION – The shaded portion of fields 24A to 24I is used to report NDC information. Required as of August 1, 2007. To report this information, begin at field 24A as follows: 1. Enter the NDC qualifier of N4 2. Enter the NDC 11-digit numeric code 3. Enter the drug description 4. Enter the NDC Unit qualifier • F2 – International Unit • GR – Gram • ML – Milliliter • UN – Unit 5. Enter the NDC Quantity (Administered Amount) in the format 9999.99 24A Bottom Half DATE OF SERVICE – Provide the FROM and TO dates in MMDDYY format. Up to six FROM and TO dates are allowed per form. Required. 24B PLACE OF SERVICE – Use the POS code for the facility where services were rendered. Required. For a complete listing of POS codes, go to http://www.cms.hhs.gov/PlaceofServiceCodes/03_POSDatabase.asp. 24C EMG – Emergency indicator. This field indicates services were for emergency care for service lines with a CPT or HCPCS code in field 24D. Enter Y or N. Required, if applicable. 24D PROCEDURES, SERVICES, OR SUPPLIES CPT/HCPCS – Use the appropriate procedure code for the service rendered. Only one procedure code is provided on each claim form service line. Required. MODIFIER – Use the appropriate modifier, if applicable. Up to four modifiers are allowed for each procedure code. Required, if applicable. 24E DIAGNOSIS CODE – Enter number 1–4 corresponding to the applicable diagnosis codes in field 21. A minimum of one, and a maximum of four, diagnosis code references can be entered on each line. Required. 24F $ CHARGES – Enter the total amount charged for the procedure performed, based on the number of units indicated in field 24G. The charged amount is the sum of the total units multiplied by the single unit charge. Each line is computed independently of other lines. This is a 10-digit field. Required. 24G DAYS OR UNITS – Provide the number of units being claimed for the procedure code. Six digits are allowed, and 9999.99 units is the maximum that can be submitted. The procedure code may be submitted in partial units, if applicable. Required. 24H EPSDT Family Plan – If the patient is pregnant, indicate with a P in this field on each applicable line. Required, if applicable. 24I Top Half – Shaded Area RENDERING ID QUALIFIER – Enter the qualifier indicating what the number reported in the shaded area of 24J represents – 1D for IHCP LPI rendering provider number or ZZ for rendering provider taxonomy code. 1D is the qualifier that applies to the IHCP provider number (LPI) for atypical nonhealthcare providers. The LPI includes nine numeric characters. Atypical providers (for example, certain transportation and waiver service providers) are required to submit their LPIs. ZZ is the qualifier that applies to the provider taxonomy code. The taxonomy code includes 10 alphanumeric characters. The taxonomy code may be required for a one-to-one match. Taxonomy – Enter the taxonomy code of the rendering provider. Taxonomy may be needed to establish a one-to-one NPI/LPI match if the provider has multiple locations. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-153 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Form Locator Narrative Description/Explanation 24J Top Half – Shaded Area RENDERING PROVIDER ID – Enter either the LPI if entering the 1D qualifier in 24I or the taxonomy if entering the ZZ qualifier in 24I for the Rendering Provider ID. Required, if applicable. LPI – The entire nine-digit LPI must be used. If billing for case management, the case manager’s number must be entered here. Taxonomy – Enter the taxonomy code of the rendering provider. Optional unless required for a oneto-one match. 24J Bottom Half RENDERING PROVIDER NPI – Enter the NPI of the rendering provider. Required if applicable. 25 FEDERAL TAX I.D. NUMBER – Not applicable. 26 PATIENT’S ACCOUNT NO. – Enter the internal patient tracking number. Optional. 27 ACCEPT ASSIGNMENT? – The IHCP Provider Agreement includes details about accepting payment for services. Optional. 28 TOTAL CHARGE – Enter the total of all service line charges in column 24F. This is a 10-digit field, such as 99999999.99. Required. 29 AMOUNT PAID – Enter the payment received from any other source, excluding the 8A deductible and the Medicare paid amount. All applicable items are combined and the total entered in this field. This is a 10-digit field. Required, if applicable. Other insurance – Enter the amount paid by the other insurer. If the other insurer was billed but paid zero, enter 0 in this field. Attach denials to the claim form when submitting the claim for adjudication. 30 BALANCE DUE – TOTAL CHARGE (field 28) – AMOUNT PAID (field 29) = BALANCE DUE (field 30). This is a 10-digit field, such as 99999999.99. Required. 31 SIGNATURE OF PHYSICIAN OR SUPPLIER INCLUDING DEGREES OR CREDENTIALS – An authorized person, someone designated by the agency or organization, must sign and date the claim. A signature stamp is acceptable; however, a typed name is not. Providers that have signed the Signature on File certification form will have their claims processed when a signature is omitted from this field. The form is available on the IHCP Web site, Provider Services page at http://provider.indianamedicaid.com/become-a-provider/enroll-as-a-provider.aspx. Required if applicable. DATE – Enter the date the claim was filed. Required. 32 SERVICE FACILITY LOCATION INFORMATION – Enter the provider’s name and address where the services were rendered, if other than home or office. This field is optional, but it helps HP contact the provider, if necessary. Optional. 32a SERVICE FACILITY LOCATION NPI – Not applicable. 32b SERVICE FACILITY LOCATION QUALIFIER AND ID NUMBER – Not applicable. 33 BILLING PROVIDER INFO & PH # – Enter the billing provider office location name, address, and the ZIP Code+4. Required. Note: If the U.S. Postal Service provides an expanded ZIP Code (ZIP Code + 4) for a geographic area, this expanded ZIP Code must be entered on the claim form. 33a BILLING PROVIDER NPI – Enter the billing provider NPI. Required. 8-154 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Form Locator 33b Narrative Description/Explanation BILLING PROVIDER QUALIFIER AND ID NUMBER – Healthcare providers may enter a billing provider qualifier of ZZ and taxonomy code. Taxonomy may be needed to establish a one-toone NPI/LPI match if the provider has multiple locations. If the billing provider is an atypical provider, enter the qualifier 1D and the LPI. Required. Note: Qualifiers are ZZ = Taxonomy and 1D = LPI Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-155 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Figure 8.2 – CMS-1500 Claim Form 8-156 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions 837P Electronic Transaction Providers must use the standard 837P format to submit electronic institutional claims. These standards are published in the 837P Implementation Guides (IGs). An addendum to most IGs has been published and must be used to properly implement each transaction. The IGs are available for download through the Washington Publishing Company Web site at http://wpc-edi.com. Companion Guides The IHCP has developed technical companion guides to assist application developers during the implementation process. Information contained in the IHCP Companion Guides is only intended to supplement the adopted IGs and provide guidance and clarification as it applies to the IHCP. Companion guides are never intended to modify, contradict, or reinterpret the rules established by the IGs. The companion guides are located on the IHCP Web site at http://provider.indianamedicaid.com/general-provider-services/electronic-data-interchange-(edi)solutions/ihcp-companion-guides.aspx in the EDI Solutions section. Some data elements that providers submit may not be used in processing the 837P transaction; however, those data elements may be returned in other transactions, such as the 277 Claim Status Request and Response or the 835 Remittance Advice transactions. These data elements are necessary for processing, and failure to append these data elements may result in claim suspension or claim denial. Paper data requirements should mirror or be modified to mirror that of the 837P implementation guide and current claim processing requirements. Paper and electronic billing procedures must also be aligned for the provider. It is not necessary to maintain separate manuals and procedure rules. Diagnosis Codes Providers may submit up to eight ICD-9-CM five-digit diagnosis codes. Providers use these codes to describe the medical condition of the patient, and the IHCP uses them for processing the transaction. The IHCP processes the first four diagnosis codes. This rule applies to paper and electronic claims submissions. Modifiers IndianaAIM accepts procedure modifiers for providers billing on the CMS-1500 claim form or 837P. Modifiers allow greater flexibility in billing the type or degree of services rendered, and the IHCP encourages providers to incorporate modifiers into their IHCP billing practices. The IHCP recognizes CPT and HCPCS modifiers. Note: The only modifiers mandatory for IHCP usage are pricing, processing, anesthesia, physical status, and medical direction modifiers. However, providers should always include any modifier that is applicable according to correct coding criteria. The modifiers are categorized according to type. Table 8.37 lists the definition for each modifier type. Table 8.38 lists the CMS-1500 modifiers. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-157 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Table 8.37 – Types of Modifiers Type Definition Informational Used for reference. Procedure code linkage is not required for these modifiers. Pricing Used to read a fee segment. A rate is linked to the procedure code modifier combination. These modifiers must be linked to the procedure code in IndianaAIM. Processing Used to modify a fee segment by a percent or by a dollar amount. These modifiers must be linked to the procedure code in IndianaAIM. Review Causes a claim to suspend for review. Procedure code linkage is not required for these modifiers. Anesthesia Used to route the claim through the anesthesia pricing logic. These modifiers must be linked to the procedure code in IndianaAIM. Physical Status Used to modify the anesthesia units submitted on the claim form. These modifiers must be linked to the procedure code in IndianaAIM. Medical Direction Used in anesthesia processing. Procedure code linkage is not required for these modifiers. Table 8.38 – CMS-1500 Modifiers Modifier 8-158 Type Description 21 Informational Prolonged evaluation and management (E/M) services 22 Review Unusual procedural services 23 Anesthesia Unusual anesthesia, general anesthesia not usually required 24 Informational Unrelated E/M service by the same physician during a postoperative period 25 Informational Significant, separately identifiable E/M service by the same physician on the same day of a procedure or other service 26 Pricing Professional component 27 Informational Multiple outpatient hospital E/M encounters on the same date 32 Informational Mandated services, not covered 47 Informational Anesthesia by a surgeon 50 Processing Bilateral procedure 51 Informational Multiple procedures 52 Informational Reduced services 53 Informational Discontinued procedure 54 Processing Surgical care only 55 Processing Postoperative management only 56 Processing Preoperative management only 57 Informational Decision for surgery 58 Informational Staged or related procedure or service by the same physician during the postoperative period Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Modifier Type Description 59 Informational Distinct procedural service 62 Processing Two surgeons 63 Informational Procedure performed on infants less than 4 kg 66 Processing Surgical team 73 Informational Discontinued outpatient hospital/ambulatory surgical center (ASC) procedure prior to the administration of anesthesia 74 Informational Discontinued outpatient hospital/ASC procedure after the administration of anesthesia 76 Informational Repeat procedure by same physician 77 Informational Repeat procedure by another physician 78 Informational Return to the operating room for a related procedure during the postoperative period 79 Informational Unrelated procedure or service by the same physician during the postoperative period 80 Processing Assistant surgeon 81 Processing Minimum assistant surgeon 82 Processing Assistant surgeon (when qualified resident surgeon not available) 8P Informational Performance modifier in OS 90 Informational Reference (outside) laboratory 91 Informational Repeat clinical diagnostic laboratory test 99 Review Multiple modifiers A1 Informational Dressing for one wound A2 Informational Dressing for two wounds A3 Informational Dressing for three wounds A4 Informational Dressing for four wounds A5 Informational Dressing for five wounds A6 Informational Dressing for six wounds A7 Informational Dressing for seven wounds A8 Informational Dressing for eight wounds A9 Informational Dressing for nine wounds AA Anesthesia Anesthesia services performed personally by anesthesiologist AD Medical Direction Medical supervision by a physician, more than four concurrent anesthesia procedures AE Informational Registered dietician AF Informational Specialty physician AG Informational Primary physician AH Processing Clinical psychologist AJ Processing Clinical social worker Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-159 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Modifier 8-160 Type Description AK Processing Nonparticipating physician AM Informational Physician, team member service AP Informational Ophthalmological examination AQ Informational Physician service in an unlisted health professional shortage area (HPSA) AR Informational Physician scarcity area AS Processing Physician assistant, nurse practitioner, or clinical nurse specialist (CNS) services for assistant at surgery AT Informational Acute treatment (used when reporting service 98940, 98941, or 98942) AU Informational Item furnished in conjunction with a urological, ostomy, or tracheostomy supply AV Informational Item furnished in conjunction with a prosthetic device, prosthetic or orthotic AW Informational Item furnished in conjunction with a surgical dressing AX Informational Item furnished in conjunction with dialysis services BA Informational Item furnished in conjunction with parenteral enteral nutrition (PEN) services BL Informational Special acquisition of blood and blood products BO Informational Orally administered nutrition, not by feeding tube BP Informational The member has been informed of the purchase and rental options and elected to purchase the item BR Informational The member has been informed of the purchase and rental options and has elected to rent the item BU Informational The member has been informed of the purchase and rental options, and after 30 days has not informed the supplier of his or her decision CA Informational Procedure only payable in the inpatient setting when performed emergently on an outpatient who expires prior to admission CB Informational Service ordered by renal dialysis facility (RDF) physician as part of end-stage renal dialysis (ESRD) beneficiary’s dialysis CC Informational Procedure code change (use “cc” when the procedure code submitted was changed for administrative reasons or because an incorrect code was filed) CD Informational Automated Multi-Channel Chemistry (AMCC) test for ESRD or MCP CE Informational Medical necessity AMCC test separate reimbursement CF Informational AMCC test not composite rate CR Informational Catastrophe/disaster related DE Informational From diagnosis (DX) site to facility DH Informational Origin – diagnostic or therapeutic Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Modifier Type Description DN Informational Origin – diagnostic or therapeutic DR Informational Origin – diagnostic or therapeutic E1 Informational Upper left, eyelid E2 Informational Lower left, eyelid E3 Informational Upper right, eyelid E4 Informational Lower right, eyelid EA Informational Erythropoiesis Stimulating Agents (ESA), anemia, chemo induced EB Informational ESA, anemia, radio induced EC Informational ESA, anemia, nonchemo/radio ED Informational Hematocrit (Hct) greater than 39 percent or hemoglobin (Hgb) greater than 13 g = 3 cycle From facility to DX site EE Informational From facility to another EG Informational From residential facility to hospital based dialysis facility EH Informational From facility to hospital EI Informational From residence to facility to transfer EJ Informational From residential facility to nonhospital-based dialysis facility Subsequent claim for defined course of therapy, such as epoetin (EPO), sodium hyaloronate, infliximab EM Informational Emergency reserve supply – for end-stage renal disease (ESRD) benefit only EN Informational From facility to skilled nursing facility (SNF) EP Informational From residence facility to doctor’s office Service provided as part of Medicaid Early and Periodic Screening, Diagnosis, and Treatment (EPSDT) program ER Informational From facility to residence ES Informational From residence facility to accident ET Informational Emergency services EX Informational From facility to hospital EY Informational No physician or other licensed healthcare provider order for this item or service F1 Informational Left hand, second digit F2 Informational Left hand, third digit F3 Informational Left hand, fourth digit F4 Informational Left hand, fifth digit F5 Informational Right hand, thumb F6 Informational Right hand, second digit F7 Informational Right hand, third digit Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-161 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Modifier 8-162 Type Description F8 Informational Right hand, fourth digit F9 Informational Right hand, fifth digit FA Informational Left hand, thumb FB Informational Item provided without cost to provider, supplier, or practitioner FC Informational Part credit, replaced device FP Informational Service provided as part of an IHCP family planning program G1 Informational Most recent urea reduction ratio (URR) reading of less than 60 G2 Informational Most recent URR reading of 60 to 64.9 G3 Informational Most recent URR reading of 65 to 69.9 G4 Informational Most recent URR reading of 70 to 74.9 G5 Informational Most recent URR reading of 75 or greater G6 Informational ESRD patient for whom less than six dialysis sessions have been provided in one month G7 Informational Pregnancy resulted from rape or incest, or pregnancy certified by physician as life threatening G8 Informational Monitored anesthesia care (MAC) for deep complex, complicated, or markedly invasive surgical procedure G9 Informational MAC for a patient who has history of severe cardiopulmonary condition GA Informational Waiver of liability statement on file GB Informational Claim being resubmitted because it is no longer covered under a global payment demonstration GC Informational Service has been performed in part by a resident under the direction of a teaching physician GD Informational Hospital-based dialysis facility to a diagnostic or therapeutic site GE Informational Service has been performed by a resident without the presence of a teaching physician, under the primary care exception GG Informational Performance and payment of screening mammogram and diagnostic mammogram on the same patient, same day GH Informational Diagnostic mammogram converted from screening mammogram on same day GJ Informational OPT OUT physician or practitioner emergency or urgent service GK Informational Actual Item/Service ordered by physician, item associated with GA or GZ modifier GL Informational Medically unnecessary upgrade provided instead of standard item, no charge, no advance member notice (ABN) GM Informational Multiple patients on one ambulance trip Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Modifier Type Description GN Informational Service delivered under an outpatient speech language pathology plan of care GO Informational Service delivered under an outpatient occupational therapy plan of care GP Informational Service delivered under an outpatient physical therapy plan of care GQ Informational Via asynchronous telecommunications system GR Informational Hospital-based dialysis facility to residence GS Informational Dosage of EPO or darbepoietin alfa has been reduced 25 percent of preceding month’s dosage GT Informational Via interactive audio and video telecommunication systems GV Informational Attending physician not employed or paid under arrangement by the patient’s hospice provider GW Informational Service not related to the hospice patient’s terminal condition GY Informational Item or service statutorily excluded or does not meet the definition of any Medicare benefit GZ Informational Item or service expected to be denied as not reasonable and necessary H9 Informational Court ordered HA Informational Child/adolescent program HB Informational Adult program, nongeriatric HC Informational Adult program, geriatric HD Informational Pregnant/parenting women’s program HE Processing Mental health program HF Informational Substance abuse program HG Informational Opioid addiction treatment program HH Informational Integrated mental health/substance abuse program HI Informational Integrated mental health and mental retardation/developmental disabilities program HJ Informational Employee assistance program HK Informational Specialized mental health programs for high-risk populations HL Informational Intern HM Processing Less than bachelor degree level HN Informational Bachelor’s degree level HO Informational Master’s degree level HP Informational Doctoral level HQ Informational Group setting HR Informational Family/couple with client present HS Informational Family/couple without client present Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-163 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Modifier 8-164 Type Description HT Informational Multi-disciplinary team HU Informational Funded by child welfare agency HV Informational Funded state addictions agency HW Informational Funded by state mental health agency HX Informational Funded by county/local agency HY Informational Funded by juvenile justice agency HZ Informational Funded by criminal justice agency J1 Informational Competitive acquisition program (CAP) no-pay submission for a prescription number J2 Informational CAP, restocking of emergency drugs after emergency administration J3 Informational CAP, drug not available through CAP as written, reimbursed under average sales price methodology JA Informational Administered intravenous JB Informational Administered subcutaneous JD Informational Nonhospital-based dialysis to DX JE Informational Nonhospital-based dialysis to residence JG Informational From nonhospital-based dialysis to hospital-based dialysis facility JH Informational Nonhospital-based dialysis to hospital JI Informational From nonhospital-based dialysis facility to site of transfer between types of ambulance JJ Informational From nonhospital-based dialysis to nonhospital-based dialysis JN Informational Nonhospital dialysis to SNF JP Informational Nonhospital dialysis to doctor of medicine (MD) office JR Informational Nonhospital dialysis to residence JS Informational From nonhospital-based dialysis to accident JW Informational Drug amount discarded/not administered to any patient JX Informational From nonhospital-based dialysis to inter stop K0 Informational Lower extremity prosthesis functional level 0 K1 Informational Lower extremity prosthesis functional level 1 K2 Informational Lower extremity prosthesis functional level 2 K3 Informational Lower extremity prosthesis functional level 3 K4 Informational Lower extremity prosthesis functional level 4 KA Informational Add-on option/accessory for wheelchair KB Informational Beneficiary Requested Upgrade for ABN, more than four modifiers identified on claim KB Informational Beneficiary Requested Upgrade for ABN, more than four modifiers identified on claim Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Modifier Type Description KC Informational Replacement of special power wheelchair interface KD Informational Drug or biological infused through DME KF Informational Item designated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as Class III device KH Informational Durable medical equipment, prosthetics, orthotics, and other supplies (DMEPOS) item, initial claim, purchase or first month rental KI Informational DMEPOS item, second or third month rental KJ Informational DMEPOS item, parenteral enteral nutrition (PEN), pump or capped rental, months four to 15 KL Informational DMEPOS item delivered via mail KM Pricing Replacement of facial prosthesis including new impression/moulage KN Pricing Replacement of facial prosthesis using previous master model KO Informational Single drug unit dose formulation KP Informational First drug of a multiple drug unit dose formulation KQ Informational Second or subsequent drug of a multiple drug unit dose formulation KR Informational Rental item, billing for partial month KS Informational Glucose monitor supply for diabetic member not treated with insulin KT Informational Beneficiary resides bidding area KV Informational DMEPOS item, professional service KX Informational Specific required documentation on file KZ Informational New coverage not implemented by managed care LC Informational Left circumflex coronary artery LD Informational Left anterior descending coronary artery LL Informational Lease rental-use when DME equipment rental is applied against the purchase price LR Informational Laboratory round trip LS Informational FDA monitored intraocular lens implant LT Informational Procedures performed on the left side of the body M2 Informational Medicare secondary payer MP Informational Multiple patients seen MS Informational Six-month DME maintenance and service fee for reasonable and necessary parts and labor not covered under any manufacturer or supplier warranty ND NE NG Informational Informational Informational From SNF to DX site From SNF to a resident SNF to hospital-based dialysis facility Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-165 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions 8-166 Modifier NH NI NJ NN NP NR Type Informational Informational Informational Informational Informational Informational Description NS NU NX P1 P2 P3 P4 Informational Pricing Informational Physical status Physical status Physical status Physical status P5 Physical status P6 Physical status Physical status PD Informational From MD to diagnostic site PE Informational From a physician’s office to a residential, domiciliary, or custodial facility From MD office to residence PG Informational From MD office to hospital-based dialysis PH Informational From MD office to hospital PI Informational From MD to transfer between types of ambulance PJ Informational From MD to nonhospital-based dialysis PL Informational Progressive additional lenses PN Informational From MD office to SNF PP Informational From one MD office to another PR Informational From MD office to residence PS Informational From MD office to scene of accident PX Informational From MD office to hospital Q0 Informational Invest clinical research Q1 Informational Routine clinical service provided in a clinical research study that is an approved clinical research study Q2 Informational CMS Office of Research, Development, and Information (ORDI) demonstration project procedure or service Q3 Informational Live kidney donor: surgery and related services Q4 Informational Service for ordering/referring physician qualifies as a service exemption From SNF to hospital From SNF to transfer between types of ambulance SNF to nonhospital-based dialysis From SNF to SNF From SNF to MD office New when rented – DME which was new at the time of rental is subsequently purchased From SNF to residence From SNF to scene of accident New durable medical equipment purchase From SNF to hospital with stop at MD office A normal healthy patient A patient with mild systemic disease A patient with severe systemic disease A patient with severe systemic disease that is a constant threat to life A moribund patient who is not expected to survive without the operation Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Modifier Type Description Q5 Informational Service furnished by a substitute physician under a reciprocal billing arrangement Q6 Informational Service furnished by a locum tenens physician Q7 Informational One class A finding Q8 Informational Two class B findings Q9 Informational One class B and two class C findings QA Informational FDA investigational device exception QB Informational Physician providing services in a rural health professional shortage area (HPSA) QC Informational Single channel monitoring QD Informational Recording and storage in solid state memory by a digital recorder QE Informational Prescribed amount of oxygen less than one liter per minute (LPM) QF Informational Prescribed amount of oxygen exceeds four LPM QG Informational Prescribed amount of oxygen greater than four LPM QH Informational Conserving device is being used with an oxygen delivery system QJ Informational Services or items provided to a prisoner or patient in state or local custody; however, the state or local government, as applicable, meets the requirements in 42 CFR 411.4 (b) QK Processing Medical direction of two, three, or four concurrent anesthesia procedures involving qualified individuals QL Informational Patient pronounced dead after ambulance called QM Informational Ambulance service provided under arrangement by a provider of services QN Informational Ambulance service furnished directly by a provider of services QP Informational Documentation is on file showing that the laboratory test(s) was ordered individually or ordered as a CPT-recognized panel other than automated profile codes 80002-80019, G0058, G0059, and G0060 QQ Informational Claim submitted with a statement of intent QR Informational Item or service provided in a Medicare-specified study QS Informational Monitored anesthesia care service QT Informational Recording and storage on tape by an analog tape recorder QU Informational Physician providing services in urban HPSA QV Informational Item or service provided as routine care in a Medicare qualifying clinical trial QW Informational Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA) waived test Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-167 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Modifier 8-168 Type Description QX Processing Certified registered nurse anesthetist (CRNA) service, with medical direction by a physician, for services on or after January 1, 1992 QY Informational Anesthesiologist medically directs one CRNA QZ Anesthesia CRNA service, without medical direction by a physician, for services on and after December 1, 1992 RC Informational Right coronary artery RD Informational From a residence to a designated diagnostic or therapeutic site other than a physician’s office or hospital when these are used as origin codes RE Informational From residence to custodial facility RH Informational From residence to hospital RG Informational Residence to hospital-based dialysis RI Informational From residence to site of transfer between types of ambulance RJ Informational Residence to nonhospital dialysis facility RN Informational From residence to SNF RP Informational Replacement and repair for dates of service on or before December 31, 2008 RR Pricing Rental of durable medical equipment RT Informational Describes procedures performed on the right side of the body RX Informational From residence to hospital with an intermediate stop at MD office SA Informational Nurse practitioner rendering service in collaboration with a physician SB Informational Nurse midwife SC Informational Medically necessary service or supply SD Informational Services provided by registered nurse with specialized, highly technical home infusion training SE Informational State-funded program or services SF Informational Second opinion ordered by a professional review organization SG Informational Ambulatory surgical center (ASC) facility service SH Informational Second concurrently administered infusion therapy SI Informational From accident to site of transfer between types of ambulance SJ Informational Third or more concurrently administered infusion therapy SK Informational Member of high-risk population (use only with codes for immunization) SL Informational State-supplied vaccine SM Informational Second surgical opinion SN Informational Third surgical option Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Modifier Type Description SP Informational From accident to MD office SQ Informational Item ordered by home health SR Informational From scene of accident to residence SS Informational Home infusion services provided in the infusion suite of the IV therapy provider ST Informational Related to trauma or injury SU Informational Procedure performed in physician’s office SV Informational Pharmaceuticals delivered to patient’s home but not utilized SW Informational Services provided by a certified diabetic educator SX Informational From the scene of an accident or acute event to a hospital with an intermediate stop at a physician’s office SY Informational Persons who are in close contact with member of high-risk population T1 Informational Left foot, second digit T2 Informational Left foot, third digit T3 Informational Left foot, fourth digit T4 Informational Left foot, fifth digit T5 Informational Right foot, great toe T6 Informational Right foot, second digit T7 Informational Right foot, third digit T8 Informational Right foot, fourth digit T9 Informational Right foot, fifth digit TA Informational Left foot, great toe TC Pricing Technical component TD Informational Registered nurse (RN) TE Informational Licensed practical nurse (LPN)/licensed vocational nurse (LVN) TG TH TJ TK TL TM TN TP TQ Pricing Informational Informational Informational Informational Informational Informational Informational Informational Complex/high tech level of care Obstetrical treatment/services – prenatal or postpartum Program group, child and/or adolescent Extra patient or passenger, nonambulance Early intervention/individualized family service plan Individualized education program Rural/outside providers’ customary service area Medical transport, unloaded vehicle Basic life support transport by a volunteer ambulance provider TR Informational School-based individualized education program services, provided outside the public school district responsible for the student Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-169 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Modifier Type Description TS Informational Follow-up service TT Informational Individualized service provided to more than one patient in same setting TU Informational Special payment rate, overtime TV Informational Special payment rates, holidays/weekends TW Informational Backup equipment U1 Informational Medicaid Level of Care 1, as defined by each state U2 Informational Medicaid Level of Care 2, as defined by each state U3 Informational Medicaid Level of Care 3, as defined by each state U4 Informational Medicaid Level of Care 4, as defined by each state U5 Informational Medicaid Level of Care 5, as defined by each state U6 Informational Medicaid Level of Care 6, as defined by each state U7 Informational Medicaid Level of Care 7, as defined by each state U8 Informational Medicaid Level of Care 8, as defined by each state Note: The U8 modifier is used for the replacement and repair of glasses for dates of service on or after January 1, 2009. 8-170 U9 Informational Medicaid Level of Care 9, as defined by each state UA Informational Medicaid Level of Care 10, as defined by each state UB Informational Medicaid Level of Care 11, as defined by each state UC Informational Medicaid Level of Care 12, as defined by each state UD Pricing Disease management education UE Pricing Used durable medical equipment UF Informational Services provided in the morning UG Informational Services provided in the afternoon UH Informational Services provided in the evening UJ Informational Services provided in the night UK Informational Services provided on behalf of the client to someone other than the client (collateral relationship) UN Processing Two patients served UP Processing Three patients served UQ Processing Four patients served UR Processing Five patients served US Processing Six or more patients served VP Informational Aphakic patient Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Use single-character modifiers in combination for ambulance transportation to report services to the CMS. The first character indicates the transport’s place of origin, and the second character indicates the destination. Table 8.39 lists the modifiers used for ambulance transports. Table 8.39 – Modifiers – Ambulance Transport Modifier Description D Diagnostic or therapeutic site, other than P or H E Residential, domiciliary, or custodial facility (nursing home, not SNF) G Hospital-based dialysis facility (hospital or hospital-related) H Hospital I Site of transfer between types of ambulance (for example, airport or helicopter pad) J Nonhospital-based dialysis facility N Skilled nursing facility (SNF) P Physician’s office – includes health maintenance organization (HMO) nonhospital facility, clinic, and so forth R Residence S Scene of accident or acute event X Intermediate stop at physician’s office en route to the hospital (can only be used as a designation code in the second position of a modifier) Note: CMS does not require the designation of the four positron emission tomography (PET) scan modifiers (N, E, P, and S). Place of Service Codes Table 8.40 lists the Place of Service codes. Table 8.40 – Place of Service Codes Place of Service Code(s) Place of Service Name 01 Pharmacy 02 Unassigned 03 School 04 Homeless Shelter 05 Indian Health Service Freestanding Facility 06 Indian Health Service Provider-based Facility 07 Tribal 638 Freestanding Facility 08 Tribal 638 Provider-based Facility 11 Office 12 Home 13 Assisted Living Facility Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-171 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Place of Service Code(s) 8-172 Place of Service Name 14 Group Home 15 Mobile Unit 16-19 Unassigned 20 Urgent Care Facility 21 Inpatient Hospital 22 Outpatient Hospital 23 Emergency Room 24 Ambulatory Surgical Center 25 Birthing Center 26 Military Treatment Facility 27-30 Unassigned 31 Skilled Nursing Facility 32 Nursing Facility 33 Custodial Care Facility 34 Hospice 35-40 Unassigned 41 Ambulance – Land 42 Ambulance – Air or Water 43-48 Unassigned 49 Independent Clinic 50 Federally Qualified Health Center 51 Inpatient Psychiatric Facility 52 Psychiatric Facility – Partial Hospitalization 53 Community Mental Health Center 54 Intermediate Care Facility/Mentally Retarded 55 Residential Substance Abuse Treatment Facility 56 Psychiatric Residential Treatment Center 57 Nonresidential Substance Abuse Treatment Facility 58-59 Unassigned 60 Mass Immunization Center 61 Comprehensive Inpatient Rehabilitation Facility 62 Comprehensive Outpatient Rehabilitation Facility 63-64 Unassigned 65 End-Stage Renal Disease Treatment Facility 66-70 Unassigned 71 Public Health Clinic 72 Rural Health Clinic 73-80 Unassigned Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Place of Service Code(s) Place of Service Name 81 Independent Laboratory 82-98 Unassigned 99 Other Place of Service When similar services are rendered to the same member at multiple service locations on a single date of service, it is acceptable to bill the total units on a single line item using a single place of service (POS). Documentation in the medical record must contain the more specific POS for each service rendered. For example: A community mental health center (CMHC) provides four units of case management services to a member in the office at 10 a.m. on July 10, 2009, and on the same day provides an additional three units of case management at 3 p.m. in the member’s home. The CMHC may bill for seven units of service on one detail of the claim at POS 11 (office) and document in the medical record the number of units rendered at each individual POS. All providers must follow established policy and coding guidelines for their specialty. Fee-for-service FQHC or RHC providers should bill only one encounter per IHCP member, per provider, per day unless the diagnosis differs. RBMC may have other specific reimbursement guidelines. Providers rendering services in the RBMC delivery system should contact the MCO with whom they are contracted for information about the billing of multiple service locations. U Modifiers The Office of Medicaid Policy and Planning (OMPP) has specifically designated U modifiers for the use of Medicaid as defined by state. Modifiers U1 through U9 and UA through UD are defined as “Medicaid Level of Care 1 – 13, as defined by each state.” The IHCP uses many of these modifiers for dual purposes. A U modifier indicates that a procedure was altered by circumstance, but not changed in meaning. U modifiers are two-character numeric or alphanumeric codes that providers add to the end of a CPT/HCPCS code. The IHCP accepts up to four procedure code modifiers on all professional claims, paper and electronic CMS-1500, and electronic 837P transactions. Waiver providers must utilize the modifier U7 for all waiver services. Providers should use modifier U7 even if other modifiers are required in the procedure code and modifier combination. Failure to add the U7 modifier and any other required modifier may result in claim denial or an incorrect payment. Substitute Physicians and Locum Tenens Substitute physicians and locum tenens may fill in for a member’s regular physician. The regular physician may be the member’s primary care physician or primary medical provider (PMP), or a specialist that a member sees on a regular basis. The substitute physician or locum tenens must be the same discipline as the regular physician. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-173 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Substitute Physicians A substitute physician is a physician who is asked by the regular physician to see a member in a reciprocal agreement when the regular physician is unavailable to see the member. A substitute physician may be asked to see a member if the regular physician is not available or on call. The substitute arrangement does not apply to physicians in the same medical group with claims submitted in the name of the medical group. In addition, a substitute physician arrangement should not exceed 14 days. In a substitute physician arrangement, the regular physician reciprocates the substitute physician either by paying the substitute the amount received for the service rendered or by providing the same service in return. In a substitute physician arrangement, the regular physician and the substitute physician must be enrolled as an IHCP provider. In field 24D of the CMS-1500 claim form, enter the modifier Q5 to indicate that a substitute physician rendered the services. Locum Tenens Physicians Providers can create a locum tenens arrangement when the regular physician must leave his or her practice due to illness, vacation, or medical education opportunity and does not want to leave his or her patients without service during this period. Providers use the locum tenens arrangement in a single or a group practice, but the locum tenens physician cannot be a member of the group in which the regular physician is a member. The locum tenens physician usually has no practice of his or her own and moves from area to area as needed. The physician is usually paid a fixed per diem amount with the status of an independent contractor, not an employee. The locum tenens physician must meet all the requirements for practice in Indiana as well as all the hospital or other institutional credentialing requirements prior to providing services to IHCP members. The practitioner providing locum tenens services is not required to be an IHCP provider. The regular physician’s office must maintain documentation of the locum tenens arrangement, including what services were rendered and when they were provided. The regular physician’s office personnel submit claims for the locum tenens services using the regular physician’s NPI and modifier Q6 in form field 24D of the CMS-1500 claim form. Locum tenens arrangements should not exceed 90 consecutive days. If the physician is away from his or her practice for more than 90 days, a new locum tenens would be necessary. If a locum tenens provider remains in the same practice for more than 90 days, he or she must enroll as an IHCP provider. Anesthesia Services The Administrative Simplification requirements of HIPAA mandated adopting the standards for the anesthesia CPT codes. Providers submit anesthesia services using anesthesia CPT codes 00100 through 01999. Providers must submit anesthesia charges using the anesthesia CPT code that corresponds to the surgical procedure performed. Coverage and Billing Procedures The following types of anesthesia are eligible for separate reimbursement under the IHCP, when provided by a physician other than the operating surgeon: • Epidural • Field block 8-174 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions • Inhalation • Intravenous • Nerve block • Regional • Spinal General, regional, or epidural anesthesia administered by the same provider performing the surgical or obstetrical delivery procedure is not reimbursable, because it is included in the surgical delivery fee. When billing regional anesthesia as the anesthesia type for a given surgical procedure that is performed by a qualified anesthesia professional, providers bill regional anesthesia in the same manner as a general anesthetic, such as base units plus time, and it will be reimbursed the same way. Do not use the bilateral procedure code modifier 50 in conjunction with anesthesia modifiers. Time Providers should indicate the actual time of the service rendered, in minutes, in field 24G of the CMS1500 claim form. IndianaAIM calculates the time units, and it allows one unit for each 15-minute period or fraction thereof. Time starts when the anesthesiologist or certified registered nurse anesthetist (CRNA) begins preparing the patient for the procedure in the operating room or other appropriate area. Starting to count time when the preoperative examination occurs is not appropriate. The IHCP reimbursement of the preoperative exam is included in the base units. Time ends when the anesthesiologist or CRNA releases the patient to the postoperative unit and is no longer in constant attendance. Base Units The IHCP has assigned relative value units (RVUs) or base unit values to each CPT code that would normally allow for anesthesia services. Note: Providers do not report the base units on claims. IndianaAIM automatically determines the base units for the procedure code as submitted on the CMS1500 claim form or the 837P transaction. Additional Units IndianaAIM, the claims processing system, recognizes and calculates additional units for the following: • Patient age – IndianaAIM applies additional units to the base units for members under 1 year of age or more than 70 years old. • Procedure code 99140 – Providers should bill this service on a separate line item of the claim to indicate that the anesthesia provided was complicated by emergency conditions. • Physical status – Providers should utilize the appropriate status modifier to denote any conditions described in the modifier descriptions listed in Table 8.41. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-175 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Table 8.41 – Status Modifiers – Anesthesia Modifier P1 P2 P3 P4 P5 P6 Description A normal healthy patient for an elective operation A patient with mild systemic disease A patient with severe systemic disease A patient with a severe systemic disease that is a constant threat to life A moribund patient who is not expected to survive without the operation. A declared brain-dead patient whose organs are being removed for donor purposes. Elective 0 units 0 units 1 unit 2 units 3 units 0 units Utilization Anesthesiologists performing the following procedures must bill with the AA modifier and must bill these procedures in units: • 36555 – Insertion of nontunneled centrally inserted central venous catheter; under 5 years of age • 36620 – Arterial catheterization or cannulation for sampling, monitoring, or transfusion (separate procedure); percutaneous • 36625 – Arterial catheterization or cannulation for sampling, monitoring, or transfusion (separate procedure); cutdown • 93503 – Insertion and placement of flow directed catheter (for example, Swan-Ganz) for monitoring purposes • 99116 – Anesthesia complicated by utilization of total body hypothermia (list separately in addition to code for primary anesthesia procedure) • 99183 – Physician attendance and supervision of hyperbaric oxygen therapy, per session • 99185 – Hypothermia; regional Do not bill procedure code 99140 – Anesthesia complicated by emergency conditions (specify) with the AA modifier. Anesthesia Reimbursement IndianaAIM converts minutes to units (one unit equals 15 minutes) and adds the assigned base units in addition to units for modifying circumstances for a total unit value times the anesthesia conversion factor. Base Units + Time Units + Additional Units for age (if applicable) + Additional Units for physical status modifiers (as applicable) x Anesthesia Conversion Factor = Anesthesia Reimbursement Rate Providers can add additional reimbursement to the anesthesia reimbursement rate if billing CPT codes for emergency (99140) or other qualifying circumstances. The current IHCP anesthesia conversion factor is $13.88. 8-176 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Medical Direction and Certified Registered Nurse Anesthesiologist Billing Requirements Anesthesia services that are medically directed by an anesthesiologist are priced at 30 percent of the allowed rate. Anesthesia services that are rendered by a certified registered nurse anesthesiologist (CRNA) are priced at 60 percent of the allowed amount. CRNAs enrolled in the IHCP provider program must use anesthesia CPT codes (00100-01999). CRNAs that bill with their individual rendering NPI must not use modifiers listed in Table 8.42. Anesthesia procedure code modifiers listed in Table 8.42 must be reported to identify services rendered by CRNAs not enrolled in the IHCP and the anesthesiologist providing medical direction. According to 405 IAC 5-10-3 (i), reimbursement is available for medical direction of a procedure involving an anesthetist only when the direction is by an anesthesiologist, and only when the anesthesiologist medically directs two, three, or four concurrent procedures involving qualified anesthetists. Reimbursement is not available for medical direction in cases in which an anesthesiologist is concurrently administering anesthesia and providing medical direction. Table 8.42 – Procedure Code Modifiers – Anesthesia (CRNAs) Modifier Description QS Monitored anesthesia care services QX CRNA with medical direction by a physician QZ CRNA without medical direction by a physician QK Medical direction of two, three, or four concurrent anesthesia procedures involving qualified individuals Note: CRNA providers use the same physical status modifiers that apply to the anesthesiologist. Anesthesiologists billing for medical direction should use the QK modifier. An anesthesiologist involved in medically directing more than one and up to four procedures cannot be personally performing procedures at the same time. Criteria for medical direction include the following: • Ensure that only qualified individuals administer the anesthesia • Monitor anesthesia at frequent intervals • Participate in the most demanding portions of the procedures, including induction and emergence, if applicable • Perform the preoperative evaluation • Perform the postoperative evaluation • Prescribe anesthesia plan • Remain immediately available and not performing other services concurrently Anesthesia for Vaginal or Cesarean Delivery Providers billing anesthesia services for labor and delivery use the anesthesia CPT vaginal or cesarean delivery CPT codes. This method of billing is the same for any other surgery and for obstetrical Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-177 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions anesthesia, regardless of the type of anesthesia provided (such as general or regional), including epidural anesthesia. When the anesthesiologist starts an epidural for labor, and switching to a general anesthetic for the delivery becomes necessary, combine and bill the total time for the procedure performed, such as vaginal delivery or cesarean section (C-section). Base RVUs are in IndianaAIM for providers, and providers do not list them on the CMS-1500 claim form or 837P transaction. However, the actual time of the procedure should be indicated in minutes in field 24G on the CMS-1500 claim form. The same method of billing applies to anesthesia for all services. IndianaAIM calculates total units by adding base RVUs to the number of time units, which are calculated by the system, based on the number of minutes billed on the claim. IndianaAIM converts each 15-minute block of time to one time unit. However, for procedure codes 01960 and 01967, IndianaAIM calculates one time unit for each 15-minute block of time billed in the first hour of service and, for subsequent hours of service, calculates one unit of service for every 60-minute block of time or portion billed. When a provider, other than the surgeon or obstetrician, bills for epidural anesthesia, the IHCP reimburses that provider in the same manner as for general anesthesia. Table 8.43 is a list of applicable vaginal and cesarean delivery CPT codes. Table 8.43 – Procedure Codes – Vaginal or Cesarean Delivery CPT Procedure Code Description 01960 Anesthesia for vaginal delivery only 01961 Anesthesia for cesarean delivery only 01962 Anesthesia for urgent hysterectomy following delivery 01963 Anesthesia for cesarean hysterectomy without any labor analgesia/anesthesia care 01965 Anesthesia for incomplete or missed abortion procedures 01966 Anesthesia for induced abortion procedures 01967 Neuraxial labor analgesia or anesthesia for planned vaginal delivery (this includes any repeat subarachnoid needle placement and drug injection and/or any necessary replacement of an epidural catheter during labor) 01968 Anesthesia for cesarean delivery following neuraxial labor analgesia/anesthesia (list separately in addition to code for primary procedure performed) 01969 Anesthesia for cesarean hysterectomy following neuraxial labor analgesia/anesthesia (list separately in addition to code for primary procedure performed) Monitored Anesthesia Monitored anesthesia care (MAC) involves the intraoperative monitoring of a patient’s vital signs in anticipation of the need for administration of general anesthesia or the development of adverse physiological patient reaction to the surgical procedure. MAC also includes the performance of a preanesthetic examination and evaluation, prescription of the anesthesia care required, administration of 8-178 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions any necessary oral or parenteral medications (such as Atropine, Demerol, or Valium), and the provision of indicated postoperative anesthesia care. The IHCP allows payment for medically reasonable and necessary MAC services on the same basis as other anesthesia services. Providers must append the QS modifier to the appropriate CPT code in addition to other applicable modifiers to identify the services as monitored anesthesia care. General Anesthesia for Dental Procedures The IHCP covers general anesthesia for dental procedures for members 21 years old and older if the procedure is performed in an inpatient or hospital outpatient setting. The IHCP does not cover general anesthesia for dental procedures performed in a dentist’s office. Adult dental patients who may qualify for hospital or surgical center general anesthesia include, but are not limited to, adults with the following medical conditions: • Mental incapacitation, such that the member’s ability to cooperate with procedures is impaired, including mental retardation and organic brain disease • Previously demonstrated idiosyncratic or severe reactions to IV sedation medication • Seizure disorders • Severe physical disorders affecting the tongue or jaw movements • Significant psychiatric disorders resulting in impairment of the member’s ability to cooperate with the procedures Regional Anesthesia (Epidural, Nerve Block, Spinal) Regional anesthesia or nerve blocks involve blocking nerve impulses with a local anesthetic, steroid, narcotic, or other agent. Physicians administer a nerve block, and it requires special techniques and attention, especially during the initial phase of instituting the block. Providers should bill nerve blocks performed as a surgical procedure for the treatment of a condition, such as chronic pain with the appropriate nerve block code, quantity of one, with no anesthesia modifier. General, regional, or epidural anesthesia administered by the same provider performing the surgical or obstetrical delivery procedure is not reimbursable, because it is included in the surgical delivery fee. Postoperative Pain Management Services The IHCP reimburses for postoperative epidural catheter management services using procedure code 01996. The IHCP does not pay separately for procedure code 01996 on the same day the epidural is placed. Rather, providers should bill this code on subsequent days when the epidural is actually being managed. Providers should use this code for daily management of patients receiving continuous epidural, subdural, or subarachnoid analgesia. The IHCP limits this procedure to one unit of service for each day of management. Procedure code 01996 is only reimbursable during active administration of the drug. Providers should not append a modifier when this procedure is monitored by an anesthesia provider. Care Coordination Services Coverage and Billing Procedures Care coordination is the process that integrates services according to an individual’s needs. This process includes comprehensive assessment, development of an individualized service plan, linking Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-179 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions individuals with services, monitoring services received, and measuring individual progress and evaluation. It also includes development of collaborative arrangements among service providers that are simultaneously serving the individual’s needs, resulting in an integrated system of services. The IHCP, in collaboration with the Indiana State Department of Health (ISDH), promote the Pregnancy Care Coordination Programs. The IFSSA in collaboration with the ISDH promotes the HIV/AIDS Care Coordination Programs. Notes: Providers interested in becoming prenatal care coordinators should contact HP for further information about certification. Providers interested in becoming HIV/AIDS care coordinators should contact the ISDH for more information about certification. Care coordination services may obtain the Care Coordination Outcome Report form from the IHCP Web site at http://provider.indianamedicaid.com/general-provider-services/forms.aspx or by calling HP Customer Assistance at (317) 655-3240 in the local area or toll free at 1-800-577-1278. Care coordination services are available for enrolled IHCP members who have Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) or Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS), are pregnant, have a mental illness diagnosis, or have an emotional disturbance. IHCP members must be enrolled in the IHCP to be eligible for the services to be paid. Providers can verify eligibility for a member through the Eligibility Verification System (EVS). Failure to do so may result in denial of payment. The member’s name must appear on the claim form exactly as it appears in the eligibility file. The IHCP reminds providers to check eligibility every time they render a service. Care coordination services are not covered for Package C members. The IHCP allows reimbursement on a fee-for-service (FFS) basis. Eligible members may receive care coordination services only from an appropriate and enrolled care coordination provider. There is a oneyear claim filing limit from the date of service. Third-Party Liability (Private Insurance) and Care Coordination Claims For HIV/AIDS care coordination services, providers must use diagnosis code 042 – HIV/AIDS and procedure code G9012 – Other Specified Case Management. Providers must bill a principal diagnosis code of V68.9 – Unspecified administrative purpose for care coordination claims, and providers should use it only for HIV/AIDS. Federal regulations require the IHCP to be the payer of last resort; however, it is rare for insurance to cover care coordination services. Therefore, the IHCP does not require that any provider file for reimbursement from third-party insurers. The claims can be submitted directly to the IHCP. Prenatal Care Coordination Services Note: Payment for care coordination services must not duplicate payments made to public agencies or private entities under other program authorities for the same purpose. Care coordination services provide case management services for pregnant women. Care coordination is an active, ongoing process of assisting the member to identify, access, and use community resources and coordinating the services to meet individual needs. This includes locating service sources, making appointments for services, arranging transportation to services, and following up to verify appointments or reschedule appointments for women whose pregnancies are at risk for low birth weight or poor pregnancy outcome. Pregnant women identified as high-risk patients due to medical or 8-180 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions psychosocial conditions may also receive pregnancy care coordination services through the IHCP. For more information, refer to 405 IAC 5-11. Enrollment of Prenatal Care Coordinators Reimbursement is available for care coordination services provided to eligible pregnant women by any of the following professionals: • Physician licensed by the State under IC 25-22.5-1 • Registered nurse licensed by the State • Social worker with a baccalaureate or master’s degree from a school accredited by the Council on Social Work Education or a social worker certified by the State • Dietitian registered with the Commission on Dietetic Registration of the American Dietetic Association • Community health worker under the supervision of one of the professionals listed Additional information about enrollment is included in Chapter 4 of this manual. Care Coordination Services Risk Assessment Form Providers must keep record of a risk assessment in the member’s file to substantiate services beyond the initial assessment. If the provider deems a pregnancy not at risk during the initial assessment, but later factors put the outcome at risk, services can be resumed. Providers must maintain documentation of the hig risk pregnancy in the member’s file. All the forms used to document prenatal care coordination services are available on the IHCP Web site at http://provider.indianamedicaid.com. Providers use pregnancy care coordination services to prevent preterm or poor pregnancy outcomes by facilitating the linking of the pregnant women to all necessary services, including medical, health promotion, and social services. Physicians, registered nurses, social workers, and registered dietitians with certified training in pregnancy case management can provide these services on a trimester basis, including the following services: • Follow-up activities to ensure services were received • Home visits, including the initial and postpartum home visit • Referral to social service agencies Prenatal Care Coordination and Managed Care If the initial assessment indicates a high-risk condition that could potentially result in a poor pregnancy outcome, members can receive prenatal care coordination services as an intervention. Once the pregnancy has been identified as being high-risk, the prenatal care coordinator must conduct additional prenatal reassessments to gather vital information about the pregnancy. The Outcome Report, which is to be completed during the final postpartum visit, is used to assess mother and baby’s health resulting from individualized services delivered throughout the high-risk pregnancy. Care Select pregnancy care coordination services require PMP authorization. In field 19 of the CMS1500 claim form or 837P transaction, providers must indicate the two-character certification code, provided by the PMP. For RBMC members assigned to an MCO, providers must contact the MCO for further information. MCO contact information is included in Chapter 1. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-181 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Statewide Mandatory Risk-Based Managed Care Impact on Prenatal Care Coordination RBMC for all Hoosier Healthwise members expanded across Indiana in 2005. Prenatal Care Coordination (PNCC) Program providers should monitor IHCP providers throughout Indiana. The PNCC Program providers must contract with Hoosier Healthwise MCOs in their county to continue to receive reimbursement for services. The MCO maintains responsibility for the delivery and payment of PNCC services for its members. The IHCP encourages prenatal care coordinators to contract with all MCOs in their county. There are three state MCOs. The Indiana PNCC Program is being standardized to facilitate contracting and providing services with the three MCOs. Note: Reimbursement rate for prenatal care coordinator services remains unchanged. Reimbursement for the appropriate ICD-9 code, billed on a CMS-1500 claim form, is a maximum of $240 per qualifying member. Providers submit billing to the member’s MCO. Data for the mandatory Medicaid Prenatal Outcome Report form that is attached to the Postpartum Assessment Form billing form is now incorporated into the standardized assessment forms to facilitate data gathering. The IHCP requires that all certified prenatal care coordinators and community health workers use the mandatory standardized Combined Initial and Reassessment Prenatal Care Coordination Assessment Form (CIRPNCCAF), the Postpartum Assessment Form (PPAF), and Medicaid Prenatal Outcome Report. Also, use the following forms when required: • Care Coordination Outcome Report: Providers use this form to report statistical data for care coordination services in Indiana. In the past, the Care Coordination Outcome Report was completed by the care coordinator and submitted with the postpartum visit billing claim when sent to HP. Prenatal care coordinators no longer send claims or outcome reports to HP unless a client is a member of Care Select or not enrolled in an MCO. With RBMC mandatory in all counties, providers send assessment forms to the MCO in which the member is enrolled. To cut down on reports received by the MCOs, the data found on the Care Coordination Outcome Report has been incorporated into the CIRPNCCAF and the PPAF. Note: The areas highlighted in gray on the CIRPNCCAF and the PPAF contain information previously included on the Medicaid Prenatal Outcome Report. A copy of the appropriate assessment form is faxed to the MCO at the time of each claim. The outcome information is collected throughout the pregnancy and postpartum period. Contact each MCO for specific information on transmission of assessment forms. • Prenatal Risk Assessment Form: PNCC services that will be reimbursed by the IHCP include a prenatal risk assessment, one initial assessment and follow-up, one reassessment and follow-up per trimester occurring after the initial assessment, and one postpartum assessment. In the past, PNCC providers used suggested forms for each of these assessments. To standardize the PNCC Program, all providers are required to complete the CIRPNCCAF and the PPAF. The Prenatal Risk Assessment Form is available on the IHCP Web site Forms page at http://provider.indianamedicaid.com/general-provider-services/forms.aspx. Access all forms on the Forms page of the IHCP Web site at http://provider.indianamedicaid.com/general-provider-services/forms.aspx. 8-182 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions For inquiries about the Combined Initial and Reassessment Prenatal Care Coordination Assessment Form or the Postpartum Assessment Form, providers should contact each MCO or call the following number: Indiana State Department of Health at (317) 233-1344 Procedure Codes for Billing Prenatal Care Coordination Services H1000 – Initial Assessment This service must occur during the prenatal period. The billing limit for this code is one unit per pregnancy and must include the following: • Case finding risk assessment; care plan development; two encounters, one of which must be a home visit; coordination, referral, and linkage to appropriate support services; and follow-up monitoring • Documentation including an Initial Assessment form and an individual care plan H1004 – Reassessment The billing limit for this code is one unit per trimester, following the trimester of initial assessment. • Available only for at-risk pregnancies • Includes review and update of care plan; coordination referral and linkage to appropriate support services; two encounters, one of which must be either a home visit or a visit at the care coordinator’s office; and follow-up monitoring. Document this with a Reassessment form and a follow-up record. 99501 – Home Visit for Postnatal Assessment and Follow-up Care The billing limit for this code is one unit per child per pregnancy. • Must be completed within 60 days postpartum, preferably within two weeks. • Must follow an initial assessment and is only reimbursable for a pregnancy determined to be atrisk. • Includes a home visit referral and linkage to appropriate support services. A copy of the Care Coordination Outcome Report is available online at http://provider.indianamedicaid.com/generalprovider-services/forms.aspx. • Must be documented by a Care Coordination Outcome Report. Attach a completed copy of the Care Coordination Outcome Report to the claim for the postpartum visit submitted for payment. Providers should document multiple births on the claim form to explain duplicate billing of postpartum assessment and outcome services. For claims for multiple births, providers must attach the Care Coordination Outcome Report to the claim for the postpartum visit for each child born of the pregnancy. Care Coordination Outcome Report The IHCP uses a Prenatal Care Coordination Outcome Report form to report statistical data for care coordination services in Indiana. Use the expanded Care Coordination Outcome Report during the postpartum visit to assess and report postpartum and newborn results. The postpartum visit (99502) is the only service that requires a copy of the Care Coordination Outcome Report form to be completed Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-183 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions by the care coordinator and submitted with the claim when billing for the visit. The Care Coordination Outcome Report is available from the IHCP Web site at http://provider.indianamedicaid.com/general-provider-services/forms.aspx. Care Coordination Services for Human Immunodeficiency Virus/Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome The IHCP provides targeted case management or care coordination services to members with HIV and AIDS, available statewide. Definition of Service HIV and AIDS care coordination is a specialized form of case management for members with HIV infection. Care coordination consists of goal-oriented activities that locate, create, facilitate access to, coordinate, and monitor the full range of HIV-related health and human services. The purpose is to encourage the cost-effective use of medical and community resources and to promote the well-being of the individual while ensuring the individual’s freedom of choice. To ensure freedom of choice, the individual signs a Freedom of Choice/Intent to Participate Form acknowledging an understanding of the services provided and identifying the chosen care coordination provider. Care coordination services are those that assist Traditional Medicaid-eligible individuals from the targeted group to access needed medical, psychological, social, educational, and other services. Member Eligibility To be eligible for reimbursement for care coordination, a member must be a Traditional Medicaid, Hoosier Healthwise, or Care Select member and have a documented HIV infection. Medical documentation or verification of medical diagnosis of HIV infection must be in the member’s care coordination file. Providers can verify the diagnosis with the following types of documentation: • Confidential, positive HIV test result • A physician’s statement • Hospital discharge statement or other medical reports that verify the diagnosis • Medical prescription for AZT, ddI, or ddC, or copy of approval for participation in the AIDS Drug Assistance Program (ADAP) or the Early Intervention Program (EIP) Enrollment of HIV and AIDS Care Coordinators To receive reimbursement for HIV and AIDS care coordination services, the service provider must be enrolled in the IHCP. Refer to Chapter 4 for provider enrollment requirements and information. Procedure Code for Billing HIV/AIDS Care Coordination The IHCP policy for billing HIV care coordination services states that providers must use primary diagnosis code 042 – HIV/AIDS and procedure code G9012 – Other Specified Case Management. HIV and AIDS care coordination services are self-referral services under the Hoosier Healthwise and Care Select programs. HIV/AIDS care coordination claims are not subject to managed care edits; therefore, there is no requirement for a PMP’s certification code and NPI on the CMS-1500 claim form or the 837P transaction. Providers serving members in the RBMC delivery system should contact the appropriate managed care organization for claim filing requirements. One unit of service equals 15 minutes. 8-184 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Restrictions • As determined by the Assessment of Intensity of Care Coordination/Worksheet for Data Entry form, care coordination services must not exceed a maximum of 128 units, or 32 hours, per calendar quarter, or three-month period, per member. Note: The following provides information about the Assessment of Intensity of Care Coordination/Worksheet for Data Entry form: – Developed to substantiate the need for higher intensity levels of service as well as to collect data. – Completed at the beginning of each quarter to determine the maximum number of hours allowed per member. – Expected that most members use between six and one-half hours and nine hours per quarter and some use less. – Anticipated that few members require more than nine hours per quarter. – Describes the supporting factors for the number of care coordination hours used. Substantiate supporting factors through self-report, medical records, caregiver records, other agency reports, or physical observation. Document substantiation in the member’s file. • When providers reach the maximum level of hours allowed in a given quarter, submit a new and updated Assessment of Intensity of Care Coordination/Worksheet for Data Entry form to request additional hours. • Eligible members may receive HIV and AIDS care coordination services that are reimbursable by the IHCP from only one HIV and AIDS care coordination service provider. Care Coordination Services Provider Requirements The following are care coordination service provider requirements: • Each year, service providers must take required updated training about the nature of HIV infection and institutional and community intervention resources. • Service providers must maintain written documentation of all services provided. Documentation is subject to postpayment review and audit by the OMPP or its contracted agent. • Service providers must provide care coordination services that are structured and time-goal oriented. • Service providers must develop a plan of care for each member that reflects individual needs and includes strategies, outcome objectives, and time frames for each individual who receives care coordination services. Providers must update the plan of care at least annually to reflect changing needs. • The IHCP requires service providers to keep comprehensive records on all members on forms approved by the OMPP and the Division of Disability, Aging, and Rehabilitative Services (DDARS). The following records must be available in each member’s file and updated annually if applicable: - Determination of eligibility - Documentation of a verified diagnosis of HIV infection Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-185 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions - - Intake form Assessment and reevaluation of the member’s present problems, indications of medical and physical status, indications of psychological status, quality of social supports, living arrangements, and status of other relevant factors Documentation of service provider referrals Progress notes Comprehensive plan of care Documentation of member and service provider contacts, including face-to-face contacts Signed release-of-information form • Service providers must permit access to and examination of records by those authorized by the OMPP, its agent, or federal personnel. Providers must maintain records for seven years and perform record destruction, such as burning or shredding documents, in a confidential manner. • Service providers must develop the member’s plan of care on or before the 30th day following the date of the initial intake process. At least annually, providers must complete reevaluations and update the plan of care. Providers must maintain ongoing contacts either face-to-face or by telephone with the member or member’s representative at least once every 30 days from the date of the initial intake process. If providers cannot maintain contact, they must make notation of attempted contacts and the process used in the file to determine whether services continue. • The IHCP requires service providers to engage in face-to-face consultations with members or member representatives at least once every 90 days, measured from the date of the initial intake process, at a place mutually agreed on by both parties. • Service providers must have sufficient care coordination, support, and administrative staff to meet the service demands in the area, allowing for a reasonable care coordinator to member ratio. The recommended national standard ratio for HIV and AIDS care coordination is 1:35. • Service providers must obtain input about member service satisfaction from members, summarize this input at least annually, and have this information available for review. • The IHCP requires service providers to provide quarterly reports to the DDARS on the approved forms. • Service providers must have the data collection and analysis capability required to prepare monthly statistical reports concerning member demographics, including but not limited to: age, race, sex, risk exposure category, and other relevant data in a format approved by the DDARS. • Service providers must develop and maintain a current list of support services in the community available to members who are HIV infected, as well as established referral mechanisms. • The IHCP requires service providers to maintain member files in a secure area to protect member confidentiality. Information stored on computerized data systems must have password protection. Providers must adopt and adhere to a written policy protecting confidentiality that states that all information about the member is confidential information. The service provider cannot use any information obtained about the member in any way except as necessary for the proper discharge of responsibilities. Providers must treat all information, such as personal facts and circumstances concerning the member, as privileged communication and cannot divulge it without the written consent of the member or the member’s legal representative. • Service providers ensure that services are available to all eligible members regardless of age, race, sex, sexual orientation or preference, ethnicity, religion, national origin, or handicap. • Service providers must comply with licensing and accreditation standards as required by the OMPP or its agent. 8-186 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions • Service providers determine whether the member is eligible for services in accordance with the OMPP and the DDARS established policy and procedures. • Service providers comply with procedures for administrative review of the appeals of applicants and members. • The IHCP requires service providers to prepare and submit claims in accordance with stated policies and procedures of the OMPP or its agent. HIV/AIDS Care Coordination Services by Care Coordinators The following are the approved activities of the care coordinator: • Intake and assessment – The care coordinator completes a Freedom of Choice/Intent to Participate Form, an intake and an assessment on the areas in the following list, and an Assessment of Care Coordination/Worksheet for Data Entry form: - Presenting problems - Medical and physical status - Indicators of psychosocial status - Indicators of developmental and intellectual status - Living arrangements - Status of other relevant factors • Plan of Care Development – Based on the information gathered in the assessment, the care coordinator and the member develop a comprehensive plan of care using the following techniques. The care coordinator must develop the plan of care on or before the 30th day after the date of the initial intake: - Prioritizing the needs identified in the assessment - Developing outcome goals that address identified needs - Identifying factors that may impinge on the implementation of the plan of care - Proposing and discussing preliminary strategies for meeting outcome goals and obtaining signed approval from the member or the member’s legal representative - Specifying the time frame for meeting outcome goals - Developing evaluation criteria to measure whether outcome goals are being met - Identifying specific services, costs, and sources of payment - Contracting with the member or the member’s legal representative to apportion the rights and responsibilities between the member and the care coordinator - Developing procedures for emergency situations • Implementation – The care coordinator negotiates agreements with service providers, coordinates delivery of service, maintains the member’s record, and implements the plan of care developed with the member or member representative. The care coordinator works to ensure nonduplication and cost-effectiveness of services, and maintains member records in accordance with reporting requirements. The care coordinator acts as a facilitator in resolving access problems that arise in implementing the plan of care and acts as an advocate for the development of new services. • Monitoring – The care coordinator ensures implementation of the services identified in the plan of care by monitoring planned interventions in a timely fashion and obtaining confirmation of scheduled interventions by the member, the service provider, or both. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-187 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions • Evaluation – The care coordinator periodically engages in the following activities to measure the quality and the effectiveness of the plan of care: - Analysis of information generated through the monitoring function, such as quality and effectiveness of interventions, appropriateness of goals and strategies, the member’s legal representative’s commitment to participate in the plan of care, and the member or member’s legal representative’s satisfaction with the plan of care. - Comparison of plan of care objectives with actual outcomes of the intervention. • Reevaluation – The care coordinator makes scheduled reevaluations to the plan of care in view of continuing or changing needs of the member based on the periodic evaluation. Evaluations and reevaluations require ongoing contact with the member. As part of the reevaluation process and in addition to the following list, the care coordinator completes the Assessment of Care Coordination/Worksheet for Data Entry Form at the beginning of every quarter, starting with the date of the initial assessment. When there is a change in member needs, the care coordinator does the following: - Revises the plan of care outcome goals - Reevaluates the priority of member needs - Revises the plan of care strategies - Realigns technical service resources - Proposes and discusses new strategies for meeting outcome goals subject to member or representative approval - Specifies new time frames for meeting outcome goals - Enters into a new contract with the member or representative to reapportion the rights and responsibilities of the member and the care coordinator • Termination – On reevaluation of the plan of care, the care coordinator and the member or the member’s legal representative determine whether services should continue. The decision is made based on whether the following is true: - Care coordination services are still required. - The member or member’s legal representative elects to continue care coordination services. - The member or representative is upholding his or her contracted agreement set forth in the plan of care. - The member or representative is cooperating with the agreed-upon plan of care. - The member is aggressive or noncooperative with the care coordinator. Billable versus nonbillable activities – Any of the activities of care coordination are billable when provided on behalf of a specific member. Progress notes written the same day as a care coordination service are billable. Nonbillable activities include time spent completing or reviewing claim forms for care coordination, implicit paperwork, and activities not related to a particular member. The reimbursement rate includes administrative expenses, which are therefore not billable. Transporting members, general provider recruitment, and ongoing counseling are not billable. HIV/AIDS Care Coordination and Managed Care HIV/AIDS care coordination services are self-referral services under the Hoosier Healthwise and Care Select programs. Providers serving Hoosier Healthwise members in the RBMC delivery system should contact the appropriate MCO for filing these claims. MCO contact information is included in Chapter 1. 8-188 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions HIV/AIDS care coordination claims are not subject to managed care edits; therefore, there is no requirement for a PMP’s certification code and NPI on the CMS-1500 claim form or the 837P transaction. Chiropractic Services Coverage and Billing Procedures The IHCP provides coverage for chiropractic services for members when the services are provided by a licensed chiropractor. Services such as office visits, physical medicine treatments, laboratory, X-ray, and muscle testing are available to all IHCP members pursuant to restrictions outlined in the individual’s benefit package when necessitated by a condition-related diagnosis. The following sections outline additional coverage, billing, and PA information for chiropractic services. Package C The IHCP provides reimbursement for covered services provided by a licensed chiropractor when rendered within the scope of the practice. Office visits are limited to five visits and 14 therapeutic physical medicine treatments per member, per calendar year. Additional treatments may be covered if the provider obtains PA based on medical necessity. Package B The IHCP provides reimbursement for medically necessary pregnancy-related chiropractic services. Providers must submit claims for Package B members with one of the diagnosis codes listed in Table 8.44 as the primary diagnosis, followed by the appropriate chiropractic diagnosis code and chiropractic procedure code. Table 8.44 – ICD-9-CM Diagnosis Codes for Package B for Chiropractic Services Diagnosis Code Description 646.93 Unspecified complication of pregnancy – antepartum condition or complication 648.73 Bone and joint disorders of the back, pelvis, and lower limbs – antepartum condition or complication 648.93 Other current conditions classified elsewhere – antepartum condition or complication IHCP Members The IHCP limits reimbursement to a total of 50 office visits and spinal manipulation or physical medicine treatments per member per calendar year. As part of this limitation, the IHCP reimburses for no more than five office visits out of the total 50 treatment or office visits per member per calendar year. Reimbursement is not available for durable medical equipment (DME) provided by chiropractors. Additionally, reimbursement is not available for the following types of extended or comprehensive office visits: • New patient detailed • New patient comprehensive • Established patient detailed • Established patient comprehensive Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-189 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions The IHCP does not cover electromyogram (EMG) testing for chiropractors. A visit code is reportable on the same date as a manipulative treatment only if the visit constitutes a significant, separately identifiable E/M service. The visit code is then billed with the 25 modifier. The service must be above and beyond the usual and preservice and postservice work associated with a manipulation service. Medical record documentation supporting the need for an office visit, in addition to the manipulation treatment, must be maintained by the provider and is subject to postpayment review. When requested, chiropractors must provide the actual X-ray films previously taken at no cost to IHCP members. The IHCP does not reimburse for additional X-rays that could be necessitated by the failure of a practitioner to forward X-rays or related documentation to a chiropractic provider when requested. Chiropractors are entitled to receive X-rays from other providers at no charge to the member upon the member’s written request to the other providers and upon reasonable notice. The IHCP limits claim payment for chiropractic practitioners (specialty 150) to the CPT procedure codes and ICD-9-CM diagnosis codes as listed in the following tables. Tables 8.45 through 8.50 identify the procedure codes that chiropractors should bill to the IHCP. Table 8.45 – Covered IHCP Chiropractic Codes for Office Visits CPT Code Description 99201 Office or other outpatient visit for evaluation and management of new patient; problems are self-limited or minor 99202 Office or other outpatient visit for evaluation and management of new patient; presenting problems are of low or moderate severity 99203 Office or other outpatient visit for evaluation and management of new patient; presenting problems are of moderate severity 99211 Office or other outpatient visit for the evaluation and management of an established patient; presenting problem(s) are minimal 99212 Office or other outpatient visit for the evaluation and management of an established patient; presenting problem(s) are self-limited or minor 99213 Office or other outpatient visit for the evaluation and management of an established patient; presenting problem(s) are low to moderate severity Table 8.46 – Covered IHCP Chiropractic Codes for Manipulative Treatment CPT Code Description 98940 Chiropractic manipulative treatment (CMT); spinal, one to two regions 98941 CMT, spinal, three to four regions 98942 CMT, spinal, five regions 98943 CMT, extraspinal, one or more regions Chiropractors may perform laboratory tests that fall within their scope of practice for the state of Indiana, IC 25-10-1 and Title 846, which include blood analysis and urinalysis. 8-190 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Table 8.47 – Covered IHCP Chiropractic Codes for Radiology CPT Code Description 72010 Radiologic examination, spine, entire, survey study, anteroposterior and lateral 72020 Radiologic examination, spine, single view, specify level 72040 Radiologic examination, spine, cervical; two or three views 72050 Radiologic examination, spine, cervical; minimum of four views 72052 Radiologic examination, spine, cervical; complete, including oblique and flexion and/or extension studies 72069 Radiologic examination, spine, thoracolumbar, standing (scoliosis) 72070 Radiologic examination, spine; thoracic, two views 72072 Radiologic examination, spine; thoracic, three views 72074 Radiologic examination, spine; thoracic, minimum of four views 72080 Radiologic examination, spine; thoracolumbar, two views 72090 Radiologic examination, spine; scoliosis study, including supine and erect studies 72100 Radiologic examination, spine, lumbosacral; two or three views 72110 Radiologic examination, spine, lumbosacral; minimum of four views 72114 Radiologic examination, spine, lumbosacral; complete, including bending view 72120 Radiologic examination, spine, lumbosacral; bending view only, minimum of four views 72170 Radiologic examination, pelvis; one or two views 72190 Radiologic examination, pelvis; complete, minimum of three views 72200 Radiologic examination, sacroiliac joints; less than three views 72202 Radiologic examination, sacroiliac joints; three or more views 72220 Radiologic examination, sacrum and coccyx, minimum of two views 73000 Radiologic examination; clavicle, complete 73010 Radiologic examination; scapula, complete 73020 Radiologic examination, shoulder; one view 73030 Radiologic examination, shoulder; complete, minimum of two views 73050 Radiologic examination; acromioclavicular joints, bilateral, with or without weighted distraction 73060 Radiologic examination; humerus, minimum of two views 73070 Radiologic examination, elbow, anteroposterior and lateral views 73080 Radiologic examination, elbow, complete, minimum of three views 73090 Radiologic examination; forearm, two views 73100 Radiologic examination, wrist; two views 73110 Radiologic examination, wrist; complete, minimum of three views 73120 Radiologic examination, hand; two views 73130 Radiologic examination, hand; minimum of three views Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-191 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions CPT Code Description 73140 Radiologic examination, finger(s), minimum of two views 73500 Radiologic examination, hip, unilateral; one view 73510 Radiologic examination, hip, complete, minimum of two views 73520 Radiologic examination, hips, bilateral, minimum of two views of each hip, including anteroposterior view of pelvis 73550 Radiologic examination, femur, two views 73560 Radiologic examination, knee; one or two views 73562 Radiologic examination, knee; three views 73564 Radiologic examination, knee; complete, four or more views 73565 Radiologic examination, knee; both knees, standing, anteroposterior 73590 Radiologic examination; tibia and fibula, two views 73600 Radiologic examination, ankle; two views 73610 Radiologic examination, ankle; complete, minimum of three views 73620 Radiologic examination, foot; two views 73630 Radiologic examination, foot; complete, minimum of three views 73650 Radiologic examination; calcaneus, minimum of two views 73660 Radiologic examination, toe(s), minimum of two views Table 8.48 – Covered Chiropractic Codes for Physical Medicine Services CPT Code 8-192 Description 95831 Muscle testing, manual (separate procedure) with report; extremity (excluding hand) or trunk 95832 Muscle testing, manual (separate procedure) with report; hand with or without comparison with normal side 97010 Application of a modality to one or more areas; hot or cold packs 97012 Application of a modality to one or more areas; traction, mechanical 97014 Application of a modality to one or more areas; electrical stimulation (unattended) 97016 Application of a modality to one or more areas; vasopneumatic devices 97018 Application of a modality to one or more areas; paraffin bath 97022 Application of a modality to one or more areas; whirlpool 97024 Application of a modality to one or more areas; diathermy 97026 Application of a modality to one or more areas; infrared 97028 Application of a modality to one or more areas; ultraviolet 97032 Application of modality to one or more areas; electrical stimulation (manual), each 15 minutes 97033 Application of modality to one or more areas; iontophoresis, each 15 minutes Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions CPT Code Description 97034 Application of modality to one or more areas; contrast baths, each 15 minutes 97035 Application of modality to one or more areas; ultrasound, each 15 minutes 97036 Application of modality to one or more areas; Hubbard tank, each 15 minutes 97039 Physical medicine treatment to one area; unlisted modality (specify type and time if constant attendance) 97110 Therapeutic procedure, one or more areas, each 15 minutes; therapeutic exercises to develop strength and endurance, range of motion and flexibility 97112 Therapeutic procedure, one or more areas, each 15 minutes; therapeutic exercises to develop strength and endurance, range of motion and flexibility; neuromuscular reduction of movement, balance, coordination, kinesthetic sense, posture, and/or proprioception for sitting and/or standing activities 97113 Therapeutic procedure, one or more areas, each 15 minutes; therapeutic exercises to develop strength and endurance, range of motion and flexibility; aquatic therapy with therapeutic exercises 97116 Therapeutic procedure, one or more areas, each 15 minutes; therapeutic exercises to develop strength and endurance, range of motion and flexibility; gait training (including stair climbing) 97124 Therapeutic procedure, one or more areas, each 15 minutes; therapeutic exercises to develop strength and endurance, range of motion and flexibility; massage, including effleurage, pestrissage, and/or tapotement (stroking, compression, percussion) 97139 Therapeutic procedure, one or more areas, each 15 minutes; therapeutic exercises to develop strength and endurance, range of motion and flexibility; unlisted procedure (specify) 97140 Manual therapy techniques (for example, mobilization/manipulation, manual lymphatic drainage, manual traction), one or more regions, each 15 minutes Table 8.49 identifies the appropriate primary ICD-9-CM diagnosis codes for billing chiropractic services to the IHCP. Table 8.49 – Primary ICD-9-CM Codes for Chiropractic Services Diagnosis Code Description 739.0 Occipitocervical (Occ-C1) 739.1 Cervical (C1-C7) 739.2 Thoracic (T1-T12) 739.3 Lumbar (L1-L5) 739.4 Sacral (S) 739.5 Pelvic region 739.6 Lower extremities 739.7 Upper extremities 739.8 Rib cage Table 8.50 identifies the secondary diagnosis codes that chiropractors should bill to the IHCP. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-193 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Table 8.50 – Secondary ICD-9-CM Codes for Chiropractic Services Diagnosis Code 8-194 Description 307.81 Tension headache 333.83 Spasmodic torticollis 346.00 Classical migraine without mention of intractable migraine 346.01 Classical migraine with intractable migraine, so stated 346.02 Migraine with aura, without mention of intractable migraine with status migrainosus 346.03 Migraine with aura, with intractable migraine, so stated, with status migrainosus 346.10 Common migraine without mention of intractable migraine 346.11 Common migraine with intractable migraine, so stated 346.20 Variants of migraine without mention of intractable migraine 346.21 Variants of migraine with intractable migraine, so stated 346.31 Hemiplegic migraine, with intractable migraine, so stated, without mention of status migrainosus 346.32 Hemiplegic migraine, without mention of intractable migraine with status migrainosus 346.33 Hemiplegic migraine, with intractable migraine, so stated, with status migrainosus 346.40 Menstrual migraine, without mention of intractable migraine without mention of status migrainosus 346.41 Menstrual migraine, with intractable migraine, so stated, without mention of status migrainosus 346.42 Menstrual migraine, without mention of intractable migraine with status migrainosus 346.43 Menstrual migraine, with intractable migraine, so stated, with status migrainosus 346.50 Persistent migraine aura without cerebral infarction, without mention of intractable migraine without mention of status migrainosus 346.51 Persistent migraine aura without cerebral infarction, with intractable migraine, so stated, without mention of status migrainosus 346.52 Persistent migraine aura without cerebral infarction, without mention of intractable migraine with status migrainosus 346.53 Persistent migraine aura without cerebral infarction, with intractable migraine, so stated, with status migrainosus 346.60 Persistent migraine aura with cerebral infarction, without mention of intractable migraine without mention of status migrainosus 346.61 Persistent migraine aura with cerebral infarction, with intractable migraine, so stated, without mention of status migrainosus 346.62 Persistent migraine aura with cerebral infarction, without mention of intractable migraine with status migrainosus 346.63 Persistent migraine aura with cerebral infarction, with intractable migraine, so stated, with status migrainosus 346.70 Chronic migraine without aura, without mention of intractable migraine without mention of status migrainosus Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Diagnosis Code Description 346.71 Chronic migraine without aura, with intractable migraine, so stated, without mention of status migrainosus 346.72 Chronic migraine without aura, without mention of intractable migraine with status migrainosus 346.73 Chronic migraine without aura, with intractable migraine, so stated, with status migrainosus 346.80 Other forms of migraine without mention of intractable migraine 346.81 Other forms of migraine with intractable migraine, so stated 346.82 Other forms of migraine, without mention of intractable migraine with status migrainosus 346.83 Other forms of migraine, with intractable migraine, so stated, with status migrainosus 346.90 Migraine, unspecified, without mention of intractable migraine 346.91 Migraine, unspecified, with intractable migraine, so stated 346.92 Migraine, unspecified, without mention of intractable migraine with status migrainosus 346.93 Migraine, unspecified, with intractable migraine, so stated, with status migrainosus 353.0 Brachial plexus lesions 353.1 Lumbosacral plexus lesions 353.2 Cervical root lesions, not elsewhere classified 353.3 Thoracic root lesions, not elsewhere classified 353.4 Lumbosacral root lesions, not elsewhere classified 353.8 Other nerve root and plexus disorders 353.9 Unspecified nerve root and plexus disorder 354.4 Causalgia of upper limb 354.8 Other mononeuritis of upper limb 354.9 Mononeuritis of upper limb, unspecified 646.93 Preg compl nos-antepart 648.73 Bone disorder-antepartum 648.93 Oth curr cond-antepartum 719.40 Pain in joint, site unspecified 719.48 Pain in joint, other specified site 719.49 Pain in joint, multiple site 720.0 Ankylosing spondylitis 720.1 Spinal enthesopathy 721.0 Cervical spondylosis without myelopathy 721.1 Thoracic spondylosis without myelopathy 721.3 Lumbosacral spondylosis without myelopathy 721.6 Anklyosing vertebral hyperostosis 721.7 Traumatic spondylopathy Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-195 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Diagnosis Code 8-196 Description 721.90 Spondylosis of unspecified site without mention of myelopathy 722.0 Displacement of cervical intervertebral disc without myelopathy 722.10 Displacement of lumbar intervertebral disc without myelopathy 722.11 Displacement of thoracic intervertebral disc without myelopathy 722.2 Displacement of intervertebral disc, site unspecified, without myelopathy 722.30 Schmorl’s nodes, unspecified region 722.31 Schmorl’s nodes, thoracic region 722.32 Schmorl’s nodes, lumbar region 722.4 Degeneration of cervical intervertebral disc 722.51 Degeneration of thoracic or thoracolumbar intervertebral disc 722.52 Degeneration of lumbar or lumbosacral intervertebral disc 722.6 Degeneration if intervertebral disc, site unspecified 722.80 Postlaminectomy syndrome, unspecified region 722.81 Postlaminectomy syndrome, cervical region 722.82 Postlaminectomy syndrome, thoracic region 722.83 Postlaminectomy syndrome, lumbar region 722.90 Other and unspecified disc disorder, unspecified region 722.91 Other and unspecified disc disorder, cervical region 722.92 Other and unspecified disc disorder, thoracic region 722.93 Other and unspecified disc disorder, lumbar region 723.0 Spinal stenosis in cervical region 723.1 Cervicalgia 723.2 Cervicocranial syndrome 723.3 Cervicobrachial syndrome (diffuse) 723.4 Brachia neuritis or radiculitis, NOS 723.5 Torticollis, unspecified 723.8 Other syndromes affecting cervical region 723.9 Unspecified musculoskeletal disorders and symptoms referable to neck 724.00 Spinal stenosis, unspecified region 724.01 Spinal stenosis, thoracic region 724.02 Spinal stenosis, lumbar region 724.09 Spinal stenosis of other region 724.1 Pain in thoracic spine 724.2 Lumbago 724.3 Sciatica 724.4 Thoracic or lumbosacral neuritis or radiculitis, unspecified 724.5 Backache, unspecified Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Diagnosis Code Description 724.6 Disorders of sacrum 724.70 Unspecified disorders of coccyx 724.79 Other disorders of coccyx, coccygodynia 724.8 Other symptoms referable to back, facet syndrome 724.9 Other unspecified back disorders 728.71 Plantar fascial fibromatosis 728.85 Spasm of muscle 729.1 Myalgia and myositis, unspecified 729.4 Fascilitis, unspecified 732.0 Juvenile osteochondrosis of spine 737.0 Adolescent postural kyphosis 737.10 Kyphosis (acquired) (postural) 737.12 Kyphosis (acquired), postlaminectomy 737.19 Kyphosis (acquired), other 737.20 Lordosis (acquired) (postural) 737.21 Lordosis (acquired), postlaminectomy 737.22 Lordosis (acquired), other postsurgical lordosis 737.29 Lordosis (acquired), other 737.30 Kyphoscoliosis and scoliosis – scoliosis (and kyphoscoliosis), idiopathic 737.31 Kyphoscoliosis and scoliosis – resolving infantile idiopathic scoliosis 737.32 Kyphoscoliosis and scoliosis – progressive infantile idiopathic scoliosis 737.34 Kyphoscoliosis and scoliosis – thoracongenic scoliosis 737.39 Kyphoscoliosis and scoliosis – other 737.40 Curvature of spine associated with other conditions – curvature of spine, unspecified 737.41 Curvature of spine associated with other conditions – kyphosis 737.42 Curvature of spine associated with other conditions – lordosis 737.43 Curvature of spine associated with other conditions – scoliosis 737.8 Other curvatures of spine 737.9 Unspecified curvature of spine 738.4 Acquired spondylolisthesis 739.0 Nonallopath lesion – head 739.1 Nonallopath lesion – cervical 739.2 Nonallopath lesion – thoracic 739.3 Nonallopath lesion – lumbar 739.4 Nonallopath lesion – saral 739.5 Nonallopath lesion – pelvic 739.6 Nonallopath lesion – lower extrem Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-197 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Diagnosis Code 8-198 Description 739.7 Nonallopath lesion – upper extrem 739.8 Nonallopath lesion – rib cage 754.1 Congenital torticollis 754.2 Certain congenital musculoskeletal deformities of spine (lordosis, scoliosis) 756.11 Spondylolysis, lumbrosacral region 756.12 Spondylolisthesis 784.0 Headache 839.00 Cervical vertebra dislocation, closed – cervical vertebra, unspecified 839.01 Cervical vertebra dislocation, closed – first cervical vertebra 839.02 Cervical vertebra dislocation, closed – second cervical vertebra 839.03 Cervical vertebra dislocation, closed – third cervical vertebra 839.04 Cervical vertebra dislocation, closed – fourth cervical vertebra 839.05 Cervical vertebra dislocation, closed – fifth cervical vertebra 839.06 Cervical vertebra dislocation, closed – sixth cervical vertebra 839.07 Cervical vertebra dislocation, closed – seventh cervical vertebra 839.08 Cervical vertebra dislocation, closed – multiple cervical vertebra 839.20 Lumbar vertebra dislocation, closed 839.21 Thoracic vertebra dislocation, closed 846.0 Sprains and strains of lumbosacral (joint) (ligament) 846.1 Sprains and strains of sacroiliac ligament 846.2 Sprains and strains of sacrospinatus (ligament) 846.3 Sprains and strains of sacrotuberous (ligament) 846.8 Sprains and strains of other specified sites of sacroiliac region 846.9 Sprains and strains of unspecified site of sacroiliac region 847.0 Sprains and strains of other and unspecified parts of back – neck 847.1 Sprains and strains of other and unspecified parts of back – thoracic 847.2 Sprains and strains of other and unspecified parts of back – lumbar 847.3 Sprains and strains of other and unspecified parts of back – sacrum 847.4 Sprains and strains of other and unspecified parts of back – coccyx 847.9 Sprains and strains of other and unspecified parts of back – unspecified site of back 907.3 Late effect of injury to nerve root(s), spinal plexus(es), and other nerves of trunk 953.0 Injury to cervical nerve root 953.1 Injury to dorsal nerve root 953.2 Injury to lumbar nerve root 953.3 Injury to sacral nerve root 953.4 Injury to brachial plexus 953.5 Injury to lumbrosacral plexus Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Diagnosis Code Description 956.0 Injury to sciatic nerve 956.1 Injury to nerve of pelvic girdle and lower limb – femoral nerve 956.2 Injury to nerve of pelvic girdle and lower limb – posterior tibial nerve 956.3 Injury to nerve of pelvic girdle and lower limb – peroneal nerve 956.4 Injury to nerve of pelvic girdle and lower limb – cutaneous sensory nerve, lower limb 956.5 Injury to nerve of pelvic girdle and lower limb – other specified nerve(s) of pelvic girdle and lower limb 956.8 Injury to nerve of pelvic girdle and lower limb – multiple nerves of pelvic girdle and lower limb 956.9 Injury to nerve of pelvic girdle and lower limb – unspecified nerve of pelvic girdle and lower limb Diabetes Self-Care Management Training Services Coverage and Billing Procedures The IHCP covers diabetes self-care management training services. The IHCP defines self-care management training as services provided in accordance with the terms and provisions of IC 27-814.5(6). The IHCP intends these services to enable the patient, or enhance the patient’s ability to properly manage a diabetic condition, thereby optimizing the therapeutic regimen. The following are examples of diabetes self-care management training activities: • Nutrition • Medication counseling • Blood glucose self-monitoring • Insulin injection • Foot, skin, and dental care The IHCP limits coverage to eight units per member, per rolling calendar year. Providers can prior authorize additional units. One unit is equal to 30 minutes. The IHCP covers diabetes self-management training services for Package C members. Note: For RBMC members, send claims to the appropriate MCO. Practitioners Eligible to Provide Services Healthcare practitioners, licensed, registered, or certified under applicable Indiana law, with specialized training in the management of diabetes that meets community standards, must provide the diabetes self-care management training services. Practitioners eligible to provide diabetes self-management training services, but not currently enrolled as IHCP providers, can obtain additional information in Chapter 4. Eligible practitioners, such as pharmacists, who work for or own IHCP-enrolled pharmacies should bill for services rendered through Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-199 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions the enrolled entity where services are provided. MCO contact information is included in Chapter 1, Section 2. The following are examples of IHCP practitioners who may enroll and bill for direct care services or supervision of services: • Audiologists • Chiropractors • Dentists • Hearing aid dealers • Nurses • Occupational therapists • Optometrists • Pharmacists • Physical therapists • Physicians • Respiratory therapists • Speech and language pathologists The following are examples of IHCP practitioners who may not enroll in the IHCP. Practitioners in this list must bill under the supervising practitioner’s IHCP NPI: • Athletic trainers • Dietitians • Environmental health specialists • Health facility administrators • Marriage and family therapists • Physician assistants • Psychologists • Social workers Providers are not entitled to reimbursement for any services provided to the general public at no charge. Adherence to this program parameter is closely monitored by the Surveillance Utilization Review (SUR) Department. Procedure Codes and Units of Service Providers must bill for the service only on the CMS-1500 or 837P transaction using procedure code G0108 – Diabetes outpatient self-management training services, indiv, or G0109 – Diabetes selfmanagement training service, group session. One unit of G0108 or G0109 is equal to 30 minutes of service. Providers should not round up to the next unit. Instead, providers should accumulate billable time equivalent to whole units and then bill. Limit service to eight units per member, or the equivalent of four hours, per rolling calendar year, applicable under any of the following circumstances: • Receipt of a diagnosis of diabetes • Receipt of a diagnosis that represents a significant change in the member’s symptoms or condition • Re-education or refresher training 8-200 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Providers can request authorization for additional units through the standard PA process. The IHCP reviews the documentation for additional requested units of service for evidence of medical necessity. Providers should bill the usual and customary charge for the units of service rendered. Billing and rendering practitioners should maintain sufficient documentation of the respective functions to substantiate the medical necessity of the service rendered and the provision of the service itself. This requirement is in accordance with existing policies and regulations. Physicians and podiatrists ordering the service should maintain documentation in the usual manner. Examples of documentation that the provider of the service should maintain include (but are not limited to) written orders for the service, date rendering the service, amount of time used for the training session, general content of the training session, units of service billed, charge amount, pertinent patient history and clinical data, and practitioner notes from the training sessions. Diabetic Test Strips The IHCP accepts Medicare crossover claims for diabetic test strip procedure codes with dates of service that span 90 days. Providers can use Web interChange to submit these claims electronically. The affected procedure codes and descriptions are listed in Table 8.51. Table 8.51 – HCPCS Codes for Diabetic Testing HCPCS Code Description A4233 Replacement battery, alkaline (other than J cell), for use with medically necessary home blood glucose monitor owned by patient, each A4234 Replacement battery, alkaline, J Cell, for use with medically necessary home blood glucose monitor owned by patient, each A4235 Replacement battery, lithium, for use with medically necessary home blood glucose monitor owned by patient, each A4236 Replacement battery, silver oxide, for use with medically necessary home blood glucose monitor owned by patient, each A4244 Alcohol or peroxide, per pint A4245 Alcohol wipes, per box A4246 Betadine or phisohex solution, per pint A4247 Betadine or iodine swabs/wipes, per box A4250 Urine test or reagent strips or tablets (100 tablets or strips) A4253 Blood glucose test or reagent strips, per 50 strips A4253 Billed with modifier NU, now crosses over from Medicare A4255 Platforms for home blood glucose monitor, 50 per box A4256 Normal, low, and high calibrator solution/chips A4257 Replacement lens shield cartridge for use with laser skin piercing device, each A4258 Spring-powered device for lancet, each A4259 Lancets, per box of 100 Effective February 1, 2007, a maximum quantity limitation is placed on HCPCS codes A4253 and A4259. Providers are permitted to bill as many as four units of A4253 or 200 strips per 30 days, effective for claims with dates of service on or after January 1,2010 Additional units of A4253 deny Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-201 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions unless PA is obtained. Providers are permitted to bill as many as two units of A4259 (200 lancets) per 30 days effective for claims with date of service on or after January 1,2010. Additional units of A4259 deny unless PA is obtained. The following PA criteria is required for additional units of A4253 and A4259: • A signed statement of medical necessity • A clear medical recommendation of the number of additional units required to meet the patient’s medical need • A hemoglobin A1C test dated within 90 days prior to the request for additional units Drug-Related Medical Supplies and Medical Devices Some drug-related medical supplies and medical devices are reimbursed on an FFS basis. Table 8.52 lists drug-related medical supplies and medical devices that are paid for by the FFS medical benefit for all Hoosier Healthwise (HHW) and Healthy Indiana Plan (HIP) health plan members for claims with dates of service on or after December 31, 2009. These claims should be billed on the CMS-1500 claim form or an 837P transaction. Services must be provided by an IHCP-enrolled pharmacy or DME provider. This list is subject to change. Providers will be notified via an IHCP provider bulletin or other formal communication at least 45 calendar days prior to the change. Only the drug-related medical supplies and medical devices listed below are reimbursable by the FFS medical benefit. Claims submitted to the FFS, HHW, or HIP health plan pharmacy benefits with dates of service on or after December 31, 2009, will be denied. Table 8.52 – Drug-Related Medical Supplies and Medical Devices Procedure Code 8-202 Description A4210 Needle free injection device A4211 Supplies for self administered injection A4245 Alcohol wipes, per box A4206 Syringe with needle; sterile, 1cc or less, each A4207 Sterile 2cc, each A4208 Sterile 3cc, each A4209 Sterile 5cc or greater, each A4213 Syringe, sterile, 20cc or greater, each A4215 Needle, sterile, any size, each A4233 Replacement battery, alkaline (other than J cell), for use with medically necessary home blood glucose monitor owned by patient, each A4234 Replacement battery, alkaline, J cell, for use with medically necessary home blood glucose monitor owned by patient, each A4235 Replacement battery, lithium, for use with medically necessary home blood glucose monitor owned by patient, each A4236 Replacement battery, silver oxide, for use with medically necessary home blood glucose monitor owned by patient, each Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Procedure Code Description A4244 Alcohol or peroxide, per pint A4250 Urine test or reagent strips or tablets (100 tablets or strips) A4253 Blood glucose test or reagent strips for home blood glucose monitor, per 50 strips A4256 Normal, low, and high calibrator solutions/chips A4258 Lancet device A4259 Lancets, per box of 100 A4261 Cervical cap for contraceptive use A4266 Diaphragm for contraceptive use A4267* Contraceptive supply, condom, male, each A4268* Contraceptive supply, condom, female, each A4269* Contraceptive supply, spermicide (e.g., foam, gel), each A4627 Spacer, bag or reservoir, with or without mask, for use with metered dose inhaler A7018 Water, distilled, used with large volume nebulizer, 1000 ml E0607 Home blood glucose monitor E2100 Blood glucose monitor with integrated voice synthesizer E2101 Blood glucose monitor with integrated S8101 Holding Chamber or spacer for use with an inhaler or nebulizer; with mask S8100 Holding chamber or spacer for use with an inhaler or nebulizer without mask * Not covered by Healthy Indiana Plan The HHW and HIP health plans remain responsible for the following services: • Procedure-coded drugs billed by entities other than IHCP-enrolled pharmacy providers • Medical supplies and medical devices not included in Table 8.52 • DME • Enteral or oral nutritional supplements Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-203 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Durable Medical Equipment and Home Medical Equipment Coverage and Billing Procedures 405 IAC 5-19-2, IC 25-26-21 defines durable medical equipment (DME) and home medical equipment (HME) as equipment that can withstand repeated use, is primarily and customarily used to serve a medical purpose, and generally is not useful to a member in the absence of illness or injury. For all DME or HME, a physician must make the order for the equipment or supply in writing. The written order must be maintained on file for retrospective review purposes. For items that the OMPP has identified as requiring frequent or substantial servicing, reimbursement is limited to rentals only and does not reimburse for a purchase of the item. For Package C, the IHCP covers medical supplies and equipment, including prosthetic devices, implants, and hearing aids, when medically necessary. The benefit limit 407 IAC 3-6-1 on DME and HME for Package C members is a maximum benefit of $2,000 per year, or $5,000 per lifetime, for DME. This does not include eyeglasses. Members can purchase or rent the equipment, depending on which is more cost-efficient. The IHCP does not reimburse claims for medical supplies, nonmedical supplies, and routine DME or HME items for members residing in long-term care facilities. Long-term care facilities include nursing facilities, intermediate care facilities for the mentally retarded (ICFs/MR), and community residential facilities for the developmentally disabled (CRFs/DD). The IHCP policy stipulates that providers cannot bill the IHCP directly for medical supplies, nonmedical supplies, or routine DME or HME items provided to an IHCP member residing in a long-term care facility. The facility per diem rate includes the costs for these services, and the medical supplier or DME or HME company should bill the long-term care facility directly for such services. For further information, refer to 405 IAC 5-13-3 and 405 IAC 5-31-4. Providers that use HCPCS codes for medical supplies, nonmedical supplies, or routine DME items billed to the IHCP for members residing in long-term care facilities, receive a denial with explanation of benefit (EOB) code 2034 – Medical and nonmedical supplies and routine DME items are covered in the per diem rate paid to the long term care facility and may not be billed separately to the IHCP. The IHCP reimburses for DME or HME equipment, services, and supplies within one of the classifications listed in Table 8.53. Table 8.53 – DME/HME Classification Codes DME Classification Number 8-204 DME Classification Name 1 Capped rental items 2 Inexpensive or other routinely purchased items 3 Items requiring frequent or substantial servicing 4 Customized items 5 Prosthetic and orthotic devices 6 Oxygen and oxygen equipment Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Manually Priced Supplies, DME, and HME For DME or HME services, equipment, and supplies that providers bill with a nonspecific HCPCS code with a description, such as unspecified, unclassified, or miscellaneous, the IHCP bases reimbursement on manual pricing. An example of a manually priced HCPCS code is E1399 – durable medical equipment – miscellaneous. Payment for manually priced HCPCS codes, related to DME or HME services, is specific to the item being billed. Providers must submit documentation supporting the cost of the item, including a listing of all materials. The IHCP determines reimbursement using the following guidelines: • If the provider submits an itemized sales invoice from the manufacturer listing all materials or supplies purchased and showing the price paid for individual items, the IHCP reimburses the claim at the billed amount, up to 30 percent above the invoice amount. The IHCP does not accept a manufacturer’s price list as proof of purchase price for this level of reimbursement. • If a provider submits a retail price list from the manufacturer, the IHCP reimburses the claim at 90 percent of the price on the manufacturer’s retail price list, not to exceed the billed amount. • If the provider submits a copy of the provider’s own retail price list or an invoice from the provider’s own company, which indicates the price that a provider charges the general public for products or supplies, the IHCP reimburses the claim at 90 percent of the invoice or price list, not to exceed the billed amount. • Providers must identify on each attachment which service corresponds to the procedure code and amount identified on the claim form. • Invoices must be within one year from the date of service (DOS). Providers must not bill more than their usual and customary charge for any item. When providers request prior authorization for miscellaneous services, they must include an itemized list of materials in the PA request. For any item providers identify under a miscellaneous code on the PA form, they must identify a specific number of units for billing purposes and claim adjudication. Repair and Replacement Provisions related to the repair of purchased DME or HME and replacement of DME or HME items are outlined in 405 IAC 5-19-4 and 405 IAC 5-19-5. The rules are summarized as follows: • Repair of purchased DME/HME may require PA based on the HCPCS codes billed. • The IHCP does not pay for repair of equipment still under warranty. The IHCP does not authorize payment for repair necessitated by member misuse or abuse, whether intentional or unintentional. The provider must obtain documentation from the member stating the member understands the service is noncovered by IHCP, and the member will assume responsibility for the repairs. • Repairs for rental equipment are the responsibility of the rental provider. • The IHCP does not cover payment for maintenance charges of properly functioning equipment. • Repair costs for DME or HME included in a long-term care (LTC) facility’s per diem rate are not separately reimbursable. • The IHCP does not authorize replacement of large DME or HME items more than once every five years per member. The IHCP allows more frequent replacement only if there is a change in the Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-205 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions member’s medical needs, documented in writing, significant enough to warrant a different type of equipment. Procedure code K0739 – Repair or nonroutine service for durable medical equipment other than oxygen equipment requiring the skill of a technician, labor component, per 15 minutes is a replacement code for E1340 – Repair or nonroutine service for durable medical equipment requiring the skill of a technician, labor component, per 15 minutes and is covered effective January 1, 2010. Rental Versus Purchase Providers should base their decision to rent or purchase DME or HME on the least expensive option available for the anticipated period of need. DME or HME items purchased with IHCP funds become the property of the OMPP. Providers must notify the local county office of the Division of Family Resources (DFR) to make arrangements to return the equipment when a member no longer needs the equipment. Prior Authorization Items including, but not limited to, the following are examples of DME and HME that require prior authorization when medically necessary: • Hospital beds • Wheelchairs • Ventilators • Heated and nonheated humidifiers • Oxygen • Patient lifts • Standers • Wheelchair seat cushions • Power seating systems The IHCP requires PA for all DME and HME rented or purchased with IHCP funds, as set forth in 405 IAC 5-19-6, except for oxygen and supplies and equipment for delivery to nursing facility (NF) residents, included in the per diem. This requirement excludes parenteral infusion pumps when used in conjunction with parenteral hyperalimentation, including central venous catheters, codes B9004 and B9006. Table 8.54 lists the HCPCS codes for DME and HME that do not require PA. Note: For RBMC members, contact the appropriate MCO for PA. Table 8.54 – HCPCS Codes – DME/HME That Do Not Require PA DME/HME 8-206 HCPCS Codes Surgical/elastic support hose A4490 – A4510 A6530 – A6544 Battery, heavy duty; replacement for patient-owned ventilator A4611 Battery cables; replacement for patient-owned ventilator A4612 Battery charger; replacement for patient-owned ventilator A4613 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions DME/HME HCPCS Codes Nasal cannula A4615 Breathing circuits A4618 Oxygen tubing A4616 Oxygen mouthpiece A4617 Oxygen face tent A4619 Oxygen concentration mask A4620 Tracheostomy mask/collar A7525, A7526 Crutches E0110 – E0117 Canes E0100, E0105 Walkers E0130 – E0159 Commodes E0163 – E0175 Decubitis Care E0181 – E0191, E0199 Bilirubin light E0202 Heat/cold application E0200 – E0239 Bath and toilet aids E0240 – E0248 Bedpans E0275, E0276 Urinals E0325, E0326 Oximeter for blood oxygen levels E0445 Humidifiers E0550 – E0560 Compressors E0565 Nebulizers E0570 – E0585 Suction pumps E0600 Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) device E0601 Vaporizers E0605 Monitoring equipment E0607 Apnea monitors E0618, E0619 Pacemaker monitor E0610, E0615 Patient lifts E0621 Pneumatic compressors E0650 – E0673 Belt/harness E0700 Restraints E0710 IV Poles E0776 Parenteral infusion pumps E0779, E0781 – E0791 Traction E0840, E0849, E0850, E0855,E0860, E0870, E0880,E0890, E0900 Trapeze equipment E0910 – E0948 Wheelchair accessories E0950 – E0952, Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-207 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions DME/HME Rollabout chair E1031 Dialysis equipment E1510 – E1699 Jaw motion rehab system E1700 – E1702 Repairs and replacement supplies K0739 Cervical collars L0120 – L0174 Thoracic-lumbar-sacral orthosis (TLSO) L0450 – L0492 Lumbar-sacral orthosis L0621 – L0640 Back supportive devices, such as corsets L0970 – L0976 Orthotics for scoliosis L1000 – L1520 Lower limb orthotics L1600 – L2038 Torsion control orthotics L2040 – L2090 Fracture orthotics L2106 – L2397, Q4001 – Q4051 Knee additions L2405 – L2550 Pelvic-thoracic control L2570 – L2680 Abduction bars L3650 – L3805, L3807 Additions to upper limb L3810 – L3901 External power orthotics L3902 – L3904 Wrist/hand orthosis L3905 – L3954, L3956 Upper limb orthosis L3960 – L3969 Additions to mobile arm supports L3970 – L3974, L3978 Upper limb fracture orthosis L3980 – L3999 Orthotic repairs L4000 – L4210 Ancillary orthotic services L4350 – L4380, L4386 Prosthetic procedures L5000 – L8049 Hernia trusses L8300 – L8330 Prosthetic socks L8400 – L8499 Artificial larynx L8500 Tracheostomy speaking valve L8501 Prosthetic implants L8603 – L8670 Medical and Surgical Supplies 8-208 HCPCS Codes E0959, E0960 – E0961, E0966, E0970, E0971, E0978 – E0980, E0994 , E0995, E0997, E0998, E2601 HCPCS Codes Vascular catheters A4305 Slings A4565 Supplies for oxygen and related respiratory equipment A4611 – A4629 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions DME/HME HCPCS Codes Supplies for other DME A4630 – A4640 Supplies for ESRD A4653, A4660, A4663, A4911, A4680, A4690 Enteral and parenteral therapy B9000, B9002, B9004, B9006 Optometric Services Prosthetic eyes HCPCS Codes V2623 – V2629 The physician must provide a written, signed prescription describing the item needed, as well as the quantity required, for the member to receive the equipment. The rendering provider, as well as the physician ordering the services or the durable medical equipment, must keep appropriate documentation on file. The above procedures are intended to streamline the PA process. The SUR Department evaluates provider profiles and performs retrospective reviews of services no longer requiring PA. Notes: All services provided to 590 Program members with a billed amount greater than $500 per procedure require PA. For residents of nursing facilities and ICFs/MR, the IHCP reimburses the items in Table 8.54 only through the approved per diem rate for the facility. Administrative staff of the facilities should be aware that these changes to the PA requirements do not affect the reimbursement rule that includes supplies and DME/HME items in the provider’s per diem rate. Under no circumstances should the facility provider or any other provider bill separately for DME/HME and supply items that are included in the per diem. Customized Items The IHCP defines custom equipment as equipment uniquely constructed or substantially modified to meet the specific needs of an individual patient. For example, the IHCP would consider a customized molded seating system, billed using code E1399, as a customized item. Due to the unique aspects, providers cannot group these items with similar items for purposes of payment. Suppliers must submit documentation of the costs of the item, including the cost of labor and types of materials used in customizing the item. They must attach a materials and labor itemization and a manufacturer’s cost invoice to the claim when submitted for payment. The IHCP reviews each item on the invoice when calculating the reimbursement amount for all customized items. The IHCP reimburses the materials needed for repair at 30 percent above the manufacturer’s cost to the provider. The IHCP considers the following factors when reviewing PA requests for customized equipment: • The costs and changes for construction of the item can vary widely from one patient to another. Some items, while individually constructed, may have standard costs and charges. Providers can most often identify and bill these items using existing HCPCS codes, and the items are not considered custom equipment. • A wheelchair assembled by a supplier or ordered from a manufacturer that makes available special features, modifications, or components cannot be considered a customized wheelchair. The HCPCS contains many different codes to categorize wheelchairs. The IHCP may make additional Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-209 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions payment for modifications such as attachments to convert a wheelchair to a one-arm drive, brake extensions, wheelchair hand rims, and antitipping devices. Capped Rental Items The IHCP limits certain procedure codes to 15 months of continuous rental. The IHCP defines continuous rental as rental without interruption for a period of more than 60 days. A change in provider does not cause an interruption in the rental period. Providers should bill DME and HME rentals on the CMS-1500 or 837P transaction. The IHCP handles claims submitted for rental of DME and HME in the following manner: • The allowed charge is the lower of the IHCP rental fee schedule amount or the actual submitted charge. • The IHCP pays claims until the number of rental payments made to date reaches the capped rental number of 15 months. • The IHCP evaluates requests for approval of DME/HME capped rental items for documentation of long-term need. In long-term situations, the IHCP may make a decision to purchase the item. • The procedure codes listed in Table 8.55 are subject to the 15-month capped rental period. The use of a piece of equipment during a rental period may be interrupted; however, if the patient resumes use of the equipment within 60 days of the last payment, the original 15-month period remains active. If the interruption period exceeds the 60-day period, and the interruption reasons are justified, providers must submit a new PA request to begin a new 15-month rental period. The supplier must document the reason for the greater-than-60-day break in the rental period on the Indiana Prior Review and Authorization Request form. Justification for a break in the rental period more than 60 days may include the following: • Change in medical necessity • Hospitalization • Nursing facility stay A physician must provide justification. Unless the IHCP receives a new PA requesting a new rental period, the original 15-month period remains active. A change in the provider does not result in a new 15-month rental period. If a member becomes inactive for a period of more than 60 days, the IHCP requires a new PA to resume services. Table 8.55 lists the procedure codes that are subject to the 15-month capped rental period. Table 8.55 – Procedure Codes – DME/HME Capped Rental Items B9000* B9002* B9004* B9006* E0165 E0168 E0170 E0171 E0181* E0182* E0186* E0187* E0196 E0218* E0221* E0231* E0232* E0235* E0236* E0250 E0251 E0255 E0256 E0260 E0261 E0265 E0266 E0277 E0290 E0292 E0293 E0294 E0295 E0297 E0296 E0301 E0302 E0303 E0305 E0316 E0371 E0372 E0373 E0445* E0459 E0462* E0481 E0482 E0483 E0550* E0565* E0571* E0572* E0574* E0585* E0600* E0601* E0603 E0606 E0607* E0617 E0618* E0619* 8-210 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions E0630 E0635 E0636 E0638 E0641 E0740 E0744 E0745 E0770 E0749 E0779* E0781* E0784 E0791* E0910* E0920* E0930* E0940* E0941 E0946* E0955 E0956 E0957 E0958* E0959 E0960 E0967 E0968 E0969 E0970 E0971 E0973 E0974 E0978 E0980 E0981 E0982 E0983 E0984 E1014 E1015 E1016 E1020 E1028 E1030 E1031* E1035 E1037 E1038 E1039 E1050 E1060 E1070 E1083 E1084 E1085 E1086 E1087 E1088 E1089 E1090 E1092 E1093 E1100 E1110 E1130 E1140 E1150 E1160 E1161 E1170 E1171 E1172 E1180 E1190 E1195 E1200 E1221 E1222 E1223 E1224 E1225 E1228 E1231 E1232 E1233 E1234 E1235 E1236 E1237 E1238 E1240 E1250 E1260 E1270 E1280 E1285 E1290 E1295 E1800 E1801 E1802 E1805 E1806 E1810 E1811 E1815 E1816 E1818 E1821 E1825 E1830 E1840 E1902 E2000* E2100 E2101 E2202 E2203 E2204 E2209 E2210 E2211 E2212 E2213 E2214 E2215 E2216 E2218 E2219 E2220 E2221 E2222 E2223 E2224 E2225 E2226 E2340 E2341 E2343 E2360 E2361 E2362 E2363 E2364 E2365 E2366 E2371 E2372 E2373 E2374 E2376 E2381 K0011 K0010 K0012 K0014 K0606 K0733 K0800 K0801 K0802 K0806 K0807 K0808 K0812 K0813 K0814 K0815 K0816 K0820 K0821 K0822 K0823 K0824 K0825 K0826 K0827 K0829 K0830 K0831 K0835 K0836 K0837 K0838 K0839 K0840 K0841 K0842 K0843 K0848 K0849 K0850 K0851 K0852 K0853 K0854 K0855 K0856 K0857 K0858 K0859 K0860 K0861 K0862 K0863 K0864 K0868 K0869 K0870 K0871 K0877 K0878 K0879 K0880 K0884 K0885 K0886 K0899 K0890 K0891 K0898 * These codes do not require PA. The IHCP denies claims submitted using these procedure codes with rental in excess of 15 months. Capped rental items are also subject to replacement or servicing when certain criteria are met. The IHCP does not authorize replacement of capped rental items more often than once every five years per member, unless there is a change in the member’s medical needs, documented in writing, significant enough to warrant a different type of equipment. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-211 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions As indicated above, the IHCP makes rental payments through the 15th month. At the end of the 15month rental period, the IHCP considers the DME/HME equipment purchased, and in accordance with 405 IAC 5-19-8, the equipment becomes the property of the OMPP. During the capped rental period, the equipment supplier must supply and service the item for as long as the member continues to need it at no additional charge to the IHCP. However, subject to prior approval parameters, for repairs not covered by warranty, the IHCP does not reimburse more frequently than six months after the 15th month and every six months thereafter, for as long as the equipment is medically necessary. Providers should use HCPCS code E1399 – Durable medical equipment, miscellaneous to bill DME materials that do not have a specific HCPCS code available. HME providers should bill labor costs associated with servicing and repairs with HCPCS code K0739 – Repair or nonroutine service for durable medical equipment other than oxygen equipment requiring the skill of a technician, labor component, per 15 minutes. Providers must attach a materials and labor itemization to the claim when submitting it for payment. The IHCP makes no payment for rental for any month the patient is in an institution that does not qualify as his or her home, or is outside the United States for an entire month. However, if the patient is at home on the first day of a rental month, the IHCP may make payment for the entire rental month. Similarly, if a member returns an item of rental equipment to the supplier before the end of a payment month, the IHCP may make payment for the entire rental month. Items Requiring Frequent or Substantial Servicing For items requiring frequent or substantial servicing, the IHCP reimburses providers for rental payments only, as long as the equipment is deemed medically necessary. The IHCP denies claims for the purchase of these items. As noted in 405 IAC 5-19-4, repair of rental items is the responsibility of the rental provider. Table 8.56 represents a list of equipment and supplies requiring frequent or substantial servicing that are available on a rental basis. The IHCP denies these codes if providers bill them as a purchase. This list is not all-inclusive. Table 8.56 – Procedure Codes Classified as Frequent and Substantial Servicing by the IHCP Procedure Code Description E0450 Volume ventilator, stationary or portable, with backup rate feature, used with invasive interface (such as tracheostomy tube) E0460 Negative pressure ventilator, portable or stationary E0461 Volume control ventilator, without pressure support mode; may include pressure control mode, used with noninvasive interface (such as mask) E0500 IPPB machine, all types, with built-in nebulization; manual or automatic valves; internal or external power source E0575 Nebulizer, ultrasonic, large volume E0935 Continuous passive motion exercise device for use on knee only The IHCP does not allow any provider to bill the IHCP for medical or nonmedical supplies and equipment or therapies provided to residents in LTC facilities. The IHCP rules for separate billing and reimbursement also exclude food supplements, nutritional supplements, and infant formulas. The IHCP includes all medical and nonmedical supplies, routine medical equipment, and therapies in the NF per diem rate. 8-212 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Ancillary and Therapy Billing for LTC Facility Residents Providers can bill parenteral and enteral services and therapies received by dual-eligible members (Medicare and Traditional Medicaid, as well as Care Select) to Medicare and the IHCP as crossovers, and the provider must submit these on the UB-04 claim form. Automatic External Defibrillators and Wearable Cardioverter Defibrillators The IHCP covers two types of automatic external defibrillators (AEDs) with PA for individual use. The IHCP covers the AED, E0617 – External defibrillator with integrated electrocardiogram analysis and the wearable cardioverter defibrillator (WCD), K0606 – Automatic external defibrillator, with integrated electrocardiogram analysis, garment type. The AED (E0617) is similar to a manual defibrillator, except the AED detects and analyzes heart rhythms automatically. Various manufacturers make the AED devices. Each device uses a battery pack and electrode defibrillator pads, and the initial supplies are usually included with the device. The WCD (K0606) consists of a vest-like or garment-like device worn under a patient’s clothing that holds a monitor, electrodes, a battery, and a small alarm module. The monitor is designed to automatically sense abnormal heart rhythms and deliver electrical therapy through the electrodes after alerting the patient to avoid improper defibrillation. Nonwearable components include a battery charger, a computer modem, a modem cable, a computer cable, WCDNET, and the diagnostic test. WCDNET is a secure Web-based data storage and retrieval system that allows the physician to access the patient’s electrocardiogram (ECG) data stored by the WCD monitor. The physician uses the diagnostic tester to program the WCD to identify specific heart rates and rhythms for data storage. Additional components included with the WCD are a second battery to be used when the first is charging and an extra garment for use when the first is cleaned. The AED (E0617) and WCD (K0606) are indicated for members who normally are candidates for an implanted cardioverter defibrillator (ICD), but for whom an ICD is contraindicated or needs to be removed. Members use these devices for an average time of approximately two to three months, although some members awaiting transplant have used the device for more than one year. The IHCP covers either an AED (E0617) or a WCD (K0606), based on the physician’s clinical assessment of the member’s medical needs. Table 8.57 lists examples of factors that providers may consider when choosing which defibrillator is most appropriate for the member. Table 8.57– Defibrillator Factors Factors for Choosing E0617 Inability to wear a WCD vest due to obesity Skin irritation from wearing electrodes 24 hours per day Limited or lack of mobility Availability of an assistant to operate the AED Factors for Choosing K0606 Lack of assistant who can operate an AED Frequency that the member is away from home Mobility of the member Frequently unstable heart rhythms Tables 8.58 and 8.59 list the HCPCS code and description for the WCD, AED, and accessories. The WCD and the AED are capped rental items. K0607 and K0608 are inexpensive and routinely purchased items. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-213 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Table 8.58 – Wearable Cardioverter Defibrillator HCPCS Code K0607* Description Automatic external defibrillator with integrated electrocardiogram analysis, garment type Replacement battery for AED, garment type only K0608 Replacement garment for use with AED garment type only, each K0609* Replacement electrodes for use with AED, garment type only K0606 *Note: These HCPCS codes are used for the automatic external defibrillator and wearable cardioverter defibrillator. Table 8.59 – Automatic External Defibrillator HCPCS Code E0617 K0607* K0609* Description External defibrillator with integrated electrocardiogram analysis Replacement battery for AED, garment type only Replacement electrodes for use with AED, garment type only *Note: These HCPCS codes are used for the automatic external defibrillator and wearable cardioverter defibrillator. Prior Authorization Criteria for Accessories K0607 – K0609 The IHCP bases PA criteria for accessories on the estimated average life expectancies of the accessories. AED (E0617) and WCD (K0606) use the accessories replacement batteries, K0607, and replacement electrodes, K0609. K0607 – Replacement Battery 1. The member must currently be renting or have purchased an AED (E0617) or WCD (K0606 with integrated electrocardiogram analysis, garment type). 2. The battery being replaced must be at least 11 months old or completely discharged. K0608 – Replacement Garment (only for WCD) 1. The member must currently be renting or have purchased a WCD with integrated electrocardiogram analysis, garment type (K0606). 2. The garment must be damaged or worn beyond repair and have been in use at least five months. K0609 – Replacement Electrodes 1. The member must currently be renting or have purchased an AED (E0617) or the WCD with integrated electrocardiogram analysis, garment type (K0606). 2. The electrodes being replaced must have been used for at least 22 months, or the provider must prove that the equipment is broken or damaged beyond repair. 8-214 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Casting Supplies The IHCP allows reimbursement for cast supplies in conjunction with the initial fracture care service. The IHCP also allows cast supplies when billed in conjunction with the application of a cast, strap, or splint, when billing CPT codes 29000 through 29799, when applied initially, without restorative fracture care, or when applied as a replacement when restorative care has been previously provided. When the application of a cast, strap, or splint is an initial service, providers can bill CPT code 99070 – supplies and materials in combination with the appropriate casting CPT code 29000 through 29799, and the appropriate CPT E/M code. Continuous Passive Motion – Continuous Passive Motion Device The following information outlines the billing parameters for a continuous passive motion (CPM) device: • PA is not required. • Units of service: One unit of service equals one day. For CPM devices, the billing code is HCPCS code E0935, and providers must append the modifier RR. Cranial Remolding Orthosis The IHCP considers HCPCS code S1040 for cranial remolding orthosis to be medically necessary for members aged 4 to 24 months with benign positional plagiocephaly, plagiocephaly with torticollis, brachycephaly, dolichocephaly, and scaphocephaly due to conditions such as in utero or intra partum molding, premature or multiple births, and supine positioning. A pediatrician, general surgeon with a specialty in pediatrics, pediatric surgeon, craniofacial surgeon, or craniofacial anomalies team member must sign the prescription for the cranial remolding orthosis. The prescribing physician must document the medical necessity and prior authorization criteria in the patient’s chart. The prescribing physician must sign the prior authorization form, but the prescribing physician or DME or HME supplier may also submit it. Providers must meet the following prior authorization criteria for the cranial remolding orthosis to be considered for approval for IHCP members between 4 months and 24 months of age: • Providers must submit documentation that shows the member received a minimum of a two-month trial of aggressive repositioning and stretching exercises recommended by the American Academy of Pediatrics and has failed to improve. Exercise should include at least four of the following activities: - Alternating back and side sleeping - Supervising “tummy time” - Rearranging the crib relative to the primary light source - Limiting time spent in a supine position - Limiting time in strollers, carriers, and swings - Rotating activity - Exercising neck motion The member must meet one of the following criteria: • Moderate to severe positional plagiocephaly, with or without torticollis, documented by an anthropometric asymmetry greater than 6 mm in the measurement of the cranial base, cranial vault, or orbitotragial depth Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-215 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions • Brachycephaly documented by a cephalic index 2 standard deviations above or below the mean (approximately 78 percent) • Scaphocephy or dolichochaly in premature or breech infants with a cephalic index significantly less than 78 percent • Further correction or asymmetry for members after surgical treatment of craniosynostosis, considered on a case-by-case basis • Moderate to severe residual plagiocephaly after surgical correction of plagiocephaly - The pediatric neurosurgeon or craniofacial surgeon who performed the corrective procedure must provide documentation of medical necessity. The IHCP considers treatment for approval on a case-by-case basis for members aged 12 months to 24 months with severe plagiocephaly and who are considered to have a reasonable likelihood of continued skull growth. A pediatric neurosurgeon, craniofacial surgeon, or craniofacial anomalies team member must provide documentation of medical necessity. The member must have documented trial of repositioning and stretching exercises as described in the first criteria to be considered for approval. The following are contraindications to receiving cranial remolding orthosis: • Members older than 24 months old • Unmanaged hydrocephalus • Craniosynostosis Home Infusion – Parenteral and Enteral Therapy Services The billing procedures listed in this section apply to parenteral and enteral therapy when provided in a member’s home. Enteral therapy may include enteral feeding within or by way of the intestine, or enteral tube feeding that includes the provision of nutritional requirements through a tube into the stomach or small intestine. Parenteral therapy includes any route other than the alimentary canal such as intravenous, subcutaneous, intramuscular, or mucosal, and total parenteral nutrition (TPN). The following three provider types may bill for these services: • HME and DME medical supply dealers • Home health agencies • Pharmacies Providers must bill separately for the components for home infusion and enteral therapy. Pharmacies must bill for compounded prescriptions or any drugs used in parenteral therapy on the appropriate Compound Prescription Claim Form or National Council for Prescription Drug Programs (NCPDP) Pharmacy Drug Claim Form or via the NCPDP 5.1 transaction using the appropriate National Drug Code(s) (NDC). HME providers bill all supplies and formulas used for home infusion and enteral therapy on the CMS-1500 claim form or 837P transaction using the appropriate HCPCS codes. Home health agencies bill services provided by an RN, LPN, or home health aide on a UB-04 claim form or 837I transaction using the appropriate HCPCS codes for services provided. Providers must bill the IHCP for such services using HCPCS codes billed on the CMS-1500 claim form. Providers enrolled as multiple provider types, such as pharmacy, DME, HME, and home health agencies, can bill all three components using the proper billing forms and appropriate codes. A home health agency (HHA) that is dually enrolled as a pharmacy provider must submit all compound drugs and any drugs used in parenteral therapy on a drug claim form or via the NCPDP 5.1 transaction using the appropriate NDC. 8-216 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Note: When an HHA that is dually enrolled as a pharmacy bills claims for parenteral therapy containing drugs on the CMS-1500 or the 837P transaction, the IHCP may subject those claims to postpayment audit and recoupment. The IHCP does not routinely use HCPCS S codes when other national codes are available for the same services. The IHCP does not reimburse HCPCS S codes for home infusion therapy and enteral therapy, with the exception of S9349 – Home tocolytic infusion therapy. Providers must separately bill the appropriate national codes, using the proper billing format, to receive reimbursement for services described in HCPCS S codes for home therapy, including home infusion and enteral therapy. Home Infusion – Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition Pumps Parenteral and enteral pumps (PEN) are not in the capped rental fee schedule category; however, the payment policies are similar. The IHCP makes no more than 15 monthly rental payments, just as with the capped rental. At the end of the 15-month rental period, the pump becomes the property of the IHCP. If there is medical necessity for rental of the pump past the 15-month rental limit, the supplier is entitled to periodic servicing payments. Necessary servicing of pumps may include repairs that require specialized testing equipment not available to the member or nursing home. The IHCP pays for only actual servicing. However, providers must get prior authorization for reimbursement for repair or servicing not covered by warranty. When requesting PA for repair services, providers must include an itemized list of materials and labor with the PA request. Providers must attach a materials and labor itemization plus a manufacturer’s invoice to the claim submitted for payment. The IHCP reimburses the materials needed for repair at 30 percent above the manufacturer’s cost to the provider. For enteral pumps, the IHCP pays no more than one-half the rental payment every six months, beginning six months after the last rental payment. For parenteral pumps, the IHCP pays no more than one-half the rental payment every three months, beginning three months after the last rental payment. The supplier should keep written proof of servicing of enteral and parenteral pumps on file. PEN pumps include HCPCS codes B9000, B9002, B9004, and B9006. The IHCP requires the Certification of Medical Necessity (CMN) for all PEN pumps. Providers must submit a copy of the CMN with the initial, and each subsequent, PA request for enteral nutrition items. The IHCP does not require PA for HCPCS codes B9002 – Enteral Nutrition Infusion Pump – with Alarm and B9000 – Enteral Nutrition Infusion Pump – without Alarm. The IHCP does not require PA for the total parenteral nutrition or infusion pumps when used in conjunction with parenteral hyperalimentation, including central venous catheters. The IHCP requires PA for enteral nutrition. The IHCP requires a CMN for enteral nutrition and allows someone other than the ordering physician to complete it. However, the ordering physician must review for the accuracy of the information, sign, and date the CMN to indicate agreement. Providers should photocopy CMN forms, because the contractor does not supply this form as a routine item. Providers must submit a copy of the CMN with each PA request (including the initial request) for enteral nutrition items. After the initial PA of enteral nutrition items, the IHCP requires subsequent PA after three, nine, and 18 months of therapy to document the member’s continued need for therapy. After two years, the IHCP determines the need for further PA on a case-by-case basis. If the member does not medically require enteral nutrition services for two consecutive months, the IHCP requires a new PA, and the required extension schedule starts again. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-217 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions For the initial PA or extensions of initial PA, providers must include additional documentation to support medical necessity of the following orders: • The need for special nutrients • The need for total caloric intake less than 20 cal/kg/day or greater than 35 cal/kg/day • The need for a pump Table 8.60 represents a comprehensive list of the parenteral nutrition solution, kit, and pump HCPCS codes. View the IHCP fee schedule at http://provider.indianamedicaid.com for a comprehensive list of covered procedures. Table 8.60 – HCPCS Codes – Parenteral Nutrition Solution/Kit/Pump B4164 B4185 B4199 B4224 B9004 B4168 B4189 B4216 B5000 B9006 B4176 B4193 B4220 B5100 B9999 B4180 B4197 B4222 B5200 E0776 Table 8.61 lists HCPCS codes that the IHCP covers for enteral nutrition formula, kit, tubing, and pump. View the IHCP fee schedule at http://provider.indianamedicaid.com for a comprehensive list of covered procedures. Table 8.61 – HCPCS Codes – Enteral Nutrition Formula/Kit/Tubing/Pump B4034 B4082 B4152 B9000 B4035 B4083 B4153 B9002 B4036 B4150 B4154 B9998 B4081 B4149 B4155 E0776 Clarification on Billing Food Thickener, HCPCS Code B4100 Nutritional supplements are not considered drugs or biologics. Please report them to the IHCP with the appropriate HCPCS code on the CMS-1500 paper claim form or using the 837P electronic transaction. According to the HIPAA, only drugs and biologics may be reported on the pharmacy claim form with an NDC. The policy for billing changed effective April 3, 2003, and the IHCP discontinued coverage of nutritional supplements billed with an NDC when billed on a drug claim form. B4100 (Food Thickener, administered orally, per oz), requires prior authorization and must be billed on a CMS-1500 claim form. Humidifiers, Nonheated or Heated The IHCP covers a nonheated (E0561) or a heated (E0562) humidifier for use with a noninvasive respiratory assistive device (RAD) (E0470 an E0471) or a CPAP (E0601), when ordered by a physician, based on medical necessity, and subject to prior authorization. Providers must meet the following criteria for reimbursement: • The IHCP considers humidifiers E0561 and E0562 for use with a RAD or a CPAP for coverage only when physician documentation supports the medical necessity of the humidifier. • Documentation must indicate that the member is suffering from nosebleeds, extreme dryness of the upper airways, or other conditions that interfere with compliance or use of the RAD or a CPAP, and that the humidifier could improve this condition. 8-218 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions HCPCS codes E0561 and E0562 are single patient use devices, categorized as inexpensive and routinely purchased items available for purchase only for Traditional Medicaid members. The IHCP covers rental temporarily for crossover claims only and no longer requires a rental trial period before purchase of nonheated or heated humidifiers. Incontinence, Ostomy, and Urological Mail Order Supplies The IHCP contracted with three vendors to provide incontinence, ostomy, urological, and other supplies including diapers, underpads, ostomy bags, and gloves. The contracted vendors are listed below: • Binson’s Home Health Care Centers www.binsons.com Telephone: 1-888-217-9610 • Healthcare Products Delivery (HPD), Inc. www.hpdinc.net Telephone: 1-800-291-8011 • J&B Medical Supply Company www.jandbmedical.com Telephone: 1-866-674-5850 Effective June 1, 2008, all fee-for-service members, which include those in the Traditional Medicaid and Care Select programs, are required to obtain incontinence, ostomy, and urological supplies through mail order from one of the contracted providers. Claims for supplies from noncontracted providers received on or after June 1, 2008, are systematically denied. Members enrolled in the 590 Program, Medical Review Team (MRT), First Steps, Pre-Admission Screening and Resident Review (PASRR), Long Term Care (LTC), and RBMC programs are excluded from this policy change. Members with Medicare or third-party insurance must follow the guidelines of Medicare and/or their primary insurance plan to receive reimbursement of these products. Crossover claims and claims with a third-party payment amount indicated for these supplies are not affected by this policy change. If Medicare or the primary carrier does not cover this type of service, the claims will process following Medicaid rules as though Medicaid is primary. In this case, claims from a noncontracted vendor will be denied. Table 8.62 lists the procedure codes for supplies affected by this change. Claims for these supplies will be denied if billed by noncontracted providers on and after June 1, 2008. Table 8.62 – Procedure Codes Covered Under Contract T4521 T4526 T4531 T4536 T4542 A4313 A4321 A4331 T4522 T4527 T4532 T4537 T4543 A4314 A4322 A4332 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Covered Procedure Codes T4523 T4528 T4533 T4539 A4310 A4315 A4326 A4333 T4524 T4529 T4534 T4540 A4311 A4316 A4327 A4334 T4525 T4530 T4535 T4541 A4312 A4320 A4328 A4338 8-219 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions A4340 A4352 A4357 A4366 A4372 A4378 A4383 A4389 A4394 A4399 A4407 A4412 A4417 A4423 A4428 A4433 A5053 A5063 A5082 A5113 A4344 A4353 A4358 A4367 A4373 A4379 A4384 A4390 A4395 A4400 A4408 A4413 A4418 A4424 A4429 A4434 A5054 A5071 A5093 A5114 Covered Procedure Codes A4346 A4354 A4361 A4368 A4375 A4380 A4385 A4391 A4396 A4404 A4409 A4414 A4419 A4425 A4430 A4458 A5055 A5072 A5102 A5126 A4349 A4355 A4362 A4369 A4376 A4381 A4387 A4392 A4397 A4405 A4410 A4415 A4420 A4426 A4431 A5051 A5061 A5073 A5105 A5131 A4351 A4356 A4363 A4371 A4377 A4382 A4388 A4393 A4398 A4406 A4411 A4416 A4422 A4427 A4432 A5052 A5062 A5081 A5112 There are instances when the use of tapes, adhesives, gloves, and other supplies are not related to incontinence, ostomy, or urological conditions. IHCP members will not be restricted to purchasing the supplies listed below only through mail order from one of the three contracted vendors. Therefore, the following codes are billable by appropriate providers: • A4364 (adhesive liquid) • A4456 (adhesive remover wipes) • A4402 (lubricant) • A4450 and A4452 (tape) • A4455 (adhesive remover) • A4927 (gloves) • A5120, A5121, and A5122 (skin barrier) For members with a primary payer, the following apply: • Incontinence supplies are covered for members 3 years old or older. • A maximum of $162.50 is allowed per member per month for all incontinence supplies. • A maximum of $1,950 is allowed per member per rolling calendar year for all incontinence supplies is assigned. • Providers may only supply such services to an IHCP member in 30-day increments. Incontinence supplies for members in LTC facilities are reimbursed through the per diem rate for the facility and cannot be billed separately by the facility, a pharmacy, or other provider. Providers must work with families to provide cost-effective supplies that meet the needs of the member. 8-220 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Documentation Required for All Incontinence Supplies The IHCP requires documentation of medical necessity for all incontinence supplies. The physician should maintain documentation of the medical necessity for the supplies in the patient’s record. The supplier must maintain a signed physician’s order in the IHCP member’s record for audit purposes. The order must include a start and stop date and a detailed list of the incontinence supplies ordered. Providers must renew the physician’s order annually at minimum. For example, an order written on February 15, 2008, is effective for a maximum of 12 months through February 14, 2009. The supplier must obtain a new order to cover dates of service starting February 15, 2009, through February 14, 2010. The supplier must have a current order to initiate or continue the provision of supplies to an IHCP member. In addition to the signed physician’s order, the supplier must maintain documentation of proof of delivery. Documentation must include the date of delivery, address of delivery, and signature of the IHCP member, caregiver, or family member who received the supplies. Incontinence Supplies for Group Homes, Intermediate Care Facilities for the Mentally Retarded, and Long-Term Care Facility Residents Please note that the IHCP reimburses incontinence supplies for members residing in group homes, intermediate care facilities for the mentally retarded, and LTC facilities through the per diem rate for the facility, and the facility or any other provider cannot bill separately. Out-of-State Providers The following designated cities are exempt from the out-of-state prior authorization (PA) rules: • Danville, Illinois • Watseka, Illinois • Louisville, Kentucky • Owensboro, Kentucky • Sturgis, Michigan • Cincinnati, Ohio • Hamilton, Ohio • Harrison, Ohio • Oxford, Ohio • Chicago, Illinois* *Note: Effective January 5, 2007, the city of Chicago was added to this list. Chicago medical providers need to follow the same prior authorization rules as instate providers for all members in the Care Select and Traditional Medicaid programs. See Chapter 6 for information about the prior authorization process. This change includes all active providers with locations in the ZIP Codes of 606XX, 607XX, and 608XX. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-221 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions A4927 – Nonsterile Gloves, per 100 One unit of A4927 equals 100 gloves. Partial units of A4927 (less than 100 gloves) must be billed using the appropriate decimal indicator for the number of gloves. For example, 50 gloves would be billed as 0.50 units. Billing for more than one unit may result in an incorrect payment amount. Per IHCP guidelines, code A4927 is limited to five units per month (one unit = 100 gloves). Providers are reminded that nonsterile gloves are only reimbursable when used by the patient, family, or other nonpaid caregiver. Examples of a medical need for a nonsterile glove include, but are not limited to, the following uses: • A bowel program requiring manual evacuation • An ostomy care program • A wound care program Note: The IHCP does not separately reimburse providers for nonsterile gloves supplied for end-stage renal disease (ESRD)/dialysis services. Payment for gloves is included in the payment for dialysis services. Payment for gloves is included in the nursing facility per diem rate; therefore, gloves are not separately billable by either the nursing facility or another provider. A4930 – Gloves, Sterile, per Pair Sterile gloves are reimbursable when medically necessary using procedure code A4930 – Gloves, sterile, per pair. Sterile gloves are often included in sterile procedure kits, such as catheter insertion kits and suture removal kits. Items in these kits are not billed separately. General Guidelines Applicable to Nonsterile and Sterile Gloves Documentation of medical need is required for all gloves, nonsterile and sterile. The supplier must maintain a signed physician’s order in the patient record with a start and stop date, frequency of treatment, and type of treatment that makes the gloves medically necessary. Documentation must indicate the reason the physician ordered the gloves as part of the plan of care. Physicians must renew their orders at least every 12 months to ensure ongoing need for gloves. Providers are reminded that code A4927 should not be used for billing gloves supplied for ESRD/dialysis services. Reimbursement for these gloves is included in the payment for dialysis services. Nonsterile gloves will be reimbursed only when used by the patient, family, or other nonpaid caregiver. Providers cannot bill the IHCP for any amount that exceeds their usual and customary charge to the general public. Providers should bill single nonsterile gloves in partial units by completing form locator 24G on the CMS-1500 claim form or Service Unit Count, Data Element 380 on the 837P electronic transaction. The partial unit is billed by using the appropriate decimal indicator for the number of gloves used. For example, two gloves would be billed as 0.02; 40 gloves would be billed as 0.40. 8-222 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Orthopedic or Therapeutic Footwear With a physician’s written order, the IHCP provides reimbursement for members of all ages for the following: • Corrective features built into shoes such as heels, lifts, wedges, arch supports, and inserts • Orthopedic footwear, such as, shoes, boots, and sandals • Orthopedic shoe additions If a member currently has a brace, the IHCP covers the shoes and supportive devices if providers document continued medical necessity. The IHCP also provides coverage for therapeutic shoes for members with severe diabetic foot disease. The HCPCS codes listed in Table 8.63 are the only codes that providers can use to bill for these services. Providers should not use these codes in any other circumstances. Table 8.63 – HCPCS Codes – Therapeutic Shoes for Severe Diabetic Foot Disease A5500 A5501 A5503 A5504 A5505 A5506 A5507 A5508 A5510 A5512 A5513 The IHCP’s policy mirrors Medicare’s coverage of inserts and diabetic shoes. The IHCP allows for one of the following: • One pair of custom molded shoes (A5501) and two additional pairs of inserts (A5512 or A5513) • One pair of depth shoes (A5500) and three pairs of inserts (A5512 or A5513) The member is eligible for a total of three pairs of inserts each calendar year. A5512 has a maximum unit of six per date of service. A5513 has a maximum unit of two per date of service. If the provider dispenses inserts independently of diabetic shoes, the member must have appropriate footwear into which to place the insert. Providers should submit claims using the appropriate HCPCS codes with one unit of service for each code. If a member needs shoes and inserts, providers should submit claims using the appropriate HCPCS codes with two as the unit of service for each code. The IHCP considers payment for the certification of the need for therapeutic shoes and the prescription of the shoes to be included in the office visit or consultation payment. Providers cannot bill for encounters for the sole purpose of dispensing or fitting shoes. The IHCP makes no payment for an office visit or consultation provided on the same day as the fitting or dispensing of shoes by the same physician. Osteogenic Bone Growth Stimulators The IHCP covers osteogenic bone growth stimulators (OBGS) with prior authorization. The equipment requires thorough education to the member and his or her caregivers. OBGS are inexpensive and routinely purchased DME. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-223 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Noninvasive Stimulators – E0747 and E0748 The IHCP covers the noninvasive stimulator devices only for the following indications: • Nonunion of long bone fractures • Congenital pseudoarthroses • As an adjunct to spinal fusion surgery for patients at high risk of pseudarthrosis due to previously failed spinal fusion at the same site, or for those undergoing multiple-level fusion - A multiple-level fusion involves three or more vertebrae. Invasive or Implantable Stimulator – E0749 The IHCP covers the implantable invasive stimulator for the following indications: • Nonunion of long bone fractures • As an adjunct to spinal fusion surgery for patients at high risk of pseudarthrosis due to previously failed spinal fusion at the same site, or for those undergoing multiple-level fusion - A multiple-level fusion involves three or more vertebrae. Ultrasound Stimulator – E0760 The IHCP covers the ultrasound stimulator for the following indications: • Nonunion of a fracture documented by a minimum of two sets of radiographs obtained prior to starting treatment with the ultrasound stimulator, separated by a minimum of 90 days, each including multiple views of the fracture site, and with a written interpretation by a physician stating that there has been no clinically significant evidence of the fracture healing between two sets of radiographs • Not concurrent use with other noninvasive osteogenic devices This policy relates to nonunion fractures. The diagnosis of a nonunion fracture must meet the following criteria: • Serial radiographs must confirm that the fracture healing has ceased for three or more months prior to starting treatment with an osteogenic stimulator. • Serial radiographs must include a minimum of two sets of radiographs, each including multiple views of the fracture site separated by a minimum of 90 days. The IHCP excludes nonunions of the skull, vertebrae, and those that are tumor-related from coverage. The IHCP does not cover treatment for fresh fractures and nonunion associated with osteomyelitis. Oximetry The following information outlines the billing parameters for oximetry: • PA is not required. • Use procedure code 94762 – one unit of service equals one day for billing oximetry service on a daily basis, up to and including a maximum of eight units of service per month. • Use HCPCS code E0445 RR – one unit of service equals one month for billing oximetry service monthly, such as more than eight units per month. Purchase of an Oximetry System, E0445 NU, is 8-224 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions appropriate for an expected long-term need where the cost to purchase the system is less than the expected monthly rental charges. Oxygen and Home Oxygen Equipment Oxygen and oxygen equipment reimbursement includes the system for furnishing oxygen, the vessels that store the oxygen, the tubing and administration sets that allow the safe delivery of the oxygen, and the oxygen contents. The oxygen and oxygen equipment classification does not fall under capped rental guidelines. Medical necessity is the determining criteria. Only rented oxygen systems, HCPCS codes E0424, E0431, E0434, E0439, E1390, E1405, and E1406, are reimbursable. The IHCP includes oxygen contents HCPCS codes E0441 through E0444 in the rental allowance and reimburses them separately only when the IHCP, or another third-party payer, has purchased an oxygen system and rented or purchased only a portable oxygen system. The IHCP also includes accessories, including but not limited to cannulas, masks, and tubing, HCPCS codes A4615, A4616, A4619, A4620, A7525, and A7526, in the allowance for rented systems; and does not allow separate billing of these unless they are used with a purchased oxygen system. For all oxygen codes, one unit equals one month. Providers must indicate one month of service by including a 1 in the Units of Service field on the CMS-1500 or 837 transaction. Spare tanks of oxygen or emergency oxygen inhalators will be denied as medically unnecessary, because they are considered precautionary and not therapeutic in nature. The facility, pharmacy, or other provider cannot bill the IHCP for oxygen, oxygen equipment, and supplies for oxygen delivery for the usual care and treatment of members in LTC facilities. The IHCP reimburses for these in the facility per diem rate. The IHCP requires PA for nonstandard equipment and associated repair costs. Providers can bill separately for these. Facilities cannot require members to purchase or rent such equipment with the member’s personal funds. Prior Authorization Requirements The IHCP requires PA for all oxygen and associated equipment and supplies, including concentrators and portable oxygen equipment, for members receiving oxygen services in a home setting. The ordering physician must complete, sign, and date a CMN and submit it with the PA request for members receiving service at home. The IHCP accepts the same CMN for oxygen currently accepted by Medicare. Providers must keep the CMN or CMS 484.2 on file. Providers should use this form for initial PA, subsequent PA extensions, and changes in the prescriptions. The IHCP does not require a separate order because the order information is incorporated in the CMN. Providers should photocopy CMN forms because the contractor does not supply this form as a routine item. Note: For RBMC members, contact the appropriate MCO for PA. The IHCP requires PA renewals at least annually. Providers should submit a new PA and CMN whenever there is a change in the oxygen prescription, such as an increase or decrease in oxygen flow rate or different equipment ordered, or if there is a change in the attending physician. In addition, the IHCP may require subsequent extensions in individual cases. The IHCP uses Medicare’s coverage criteria and medical policy to determine medical necessity for prior approval. The following coverage and payment rules apply to oxygen therapy when supplied for Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-225 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions members in the home setting. The IHCP requires recertification three months after initial certification for inpatients in the following cases: • For inpatient members whose arterial PO2 was 56 mm Hg or greater or whose oxygen saturation was 89 percent or greater on the initial certification. • For inpatient members whose physician’s initial estimate of length of need for oxygen was one to three months. • If the first situation applies, repeat testing must be performed between the 61st and the 90th days of home oxygen therapy. For members for whom the IHCP does not require recertification at three months, the IHCP requires recertification at 12 months after the initial certification. The IHCP requires initial certification and three-month recertification when the initial PO2 is 56mm Hg or greater or oxygen saturation is 89 percent or greater. Documentation must include the results of a recently performed arterial blood gas (ABG) or oximetry test. The IHCP does not require retesting for recertification at 12 months, but providers must include on the form the results of the most recent ABG or oximetry test representing the patient’s chronic stable state. The form must specify whether tests were performed while on room air or on oxygen and specify the amount. The form must specify whether the patient was at rest, sleeping, or exercising when the test was performed. Coverage and Payment Rules The IHCP covers home oxygen therapy only for patients with significant hypoxemia in the chronic stable state, provided the following are met: • The attending physician has determined that the patient has a severe lung disease or hypoxiarelated symptoms that might be expected to improve with oxygen. • The patient’s blood gas levels indicate the need for oxygen therapy. • The physician has tried or considered alternative treatment measures and has deemed them clinically ineffective. Note: The IHCP accepts transcutaneous oximetry in lieu of arterial or capillary blood gases for oxygen monitoring. A physician or provider other than a DME supplier, certified to conduct such tests, must conduct the measurement of these tests. The IHCP does not extend this prohibition to tests conducted by a hospital that may also be furnishing home oxygen therapy to the patient directly or through an associated organization. The patient needs to meet the criteria in one of the following categories to receive approval of home oxygen therapy: Group I Criteria – The patient meets the criteria with any of the following: • An arterial PO2 at or below 55mm Hg or an arterial oxygen saturation at or below 88 percent, taken at rest. • The IHCP provides coverage only for nocturnal use of oxygen in the following cases: - The patient demonstrates an arterial PO2 at or below 55 mm Hg or an arterial oxygen saturation at or below 88 percent taken during sleep, and the patient demonstrates an arterial PO2 at or above 56mm Hg or an arterial oxygen saturation at or above 89 percent while awake. - The patient demonstrates a greater than normal fall in oxygen level during sleep, a decrease in arterial PO2 more than 10mm Hg, or a decrease in arterial oxygen saturation of more than 5 8-226 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions percent, associated with symptoms or signs reasonably attributable to hypoxemia, such as cor pulmonale, P pulmonale on EKG, documented pulmonary hypertension, and erythrocytosis. • The IHCP provides coverage only during exercise if the patient demonstrates an arterial PO2 at or below 55mm Hg or an arterial oxygen saturation at or below 88 percent (taken during exercise) and an arterial PO2 at or above 56mm Hg or an arterial oxygen saturation at or above 89 percent (taken during the day while at rest). In this case, the IHCP provides supplemental oxygen during exercise if it is documented that the use of oxygen improves the hypoxemia that was demonstrated during exercise when the patient was breathing room air. Group II Criteria – The patient meets the criteria when the patient demonstrates an arterial PO2 of 56 to 59mm Hg or an arterial blood oxygen saturation of 89 percent and any of the following: • Dependent edema suggesting congestive heart failure • Pulmonary hypertension or cor pulmonale, determined by measurement of pulmonary artery pressure, gated blood pool scan, echocardiogram, or P pulmonale on EKG, P wave greater than 3mm in standard leads II, III, or AVF • Erythrocythemia with a hematocrit greater than 56 percent Group III Criteria – The IHCP requires additional documentation to substantiate use of oxygen when the patient demonstrates an arterial PO2 level at or above 60mm Hg or arterial blood oxygen saturation at or above 90 percent. Providers should ensure that additional documentation appears on the PA form or an attached form, indicating the type, frequency, and severity of incidents or episodes. Examples include, but are not limited to, the following: • Apnea conditions • Bronchopulmonary dysplasia • Cerebral Palsy • Cyanotic congenital heart disease • Episodic attacks of acute and severe asthma • Intermittent cyanosis or dyspnea documented by clinical observation • Intermittent upper airway obstruction • Neuromuscular disorders extensive enough to affect pharyngeal and chest muscles and that clinically interfere with normal breathing • Severe recurrent attacks of epilepsy • Significant mental retardation with repetitive episodes of respiratory difficulties • Tracheal laryngeal malacia The IHCP may give PA to patients who fall into Group III for three, six, or 12 months, depending on the medical necessity demonstrated in the documentation provided. If not waived, the IHCP determines whether to require retesting using ABG or transcutaneous oximetry readings when and if authorization is granted. Providers must include such results, or the results of the latest ABG or oximetry readings, on the CMN form when submitted with the new PA request. Oxygen – Portable Systems The IHCP covers a portable oxygen system if the patient is mobile within the home. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-227 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions The IHCP does not reimburse for spare tanks of oxygen or emergency oxygen inhalators as medically unnecessary because they are precautionary and not therapeutic in nature. The IHCP does not cover respiratory therapists’ services under the DME benefit. Nebulizer with Compressor The following information outlines the billing parameters for a nebulizer with compressor: • PA not required, unless a new rental purchase • Units: - For purchase, one unit equals one nebulizer - For rental, one unit equals one month Table 8.64 lists billing codes and parameters for nebulizers with compressors. Table 8.64 – Billing Codes and Parameters – Nebulizer with Compressor Procedure Code Modifier Description E0570 NU Purchase E0570 RR Rental Phototherapy (Bilirubin Light) The following information outlines the billing parameters for phototherapy: • PA is not required. • One unit of service equals one day. This service is limited to 15 units per lifetime of the member. Table 8.65 lists billing codes and parameters for phototherapy. Table 8.65 – Billing Codes and Parameters – Phototherapy Procedure Code E0202 Modifier RR Description Rental Pneumograms Providers should bill pneumograms using CPT code 94772 – Circadian respiratory pattern recording (pediatric pneumogram), 12 to 24 hour continuous recording, infant. The IHCP does not require prior authorization for pneumograms. The IHCP considers one pneumogram, with any number of channels, to be one unit. The IHCP does not separately reimburse for oximetry during a pneumogram because it is included in the pneumogram reimbursement. CPT code 94772 includes technical and professional components of service. Providers should use modifier TC when billing only the technical component, or modifier 26 when billing only the professional component. Table 8.66 lists billing codes and parameters for pneumograms. 8-228 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Table 8.66 – Billing Codes and Parameters – Pneumograms Procedure Code/Modifier Description 94772 Circadian respiratory pattern recording (pediatric pneumogram), 12 to 24 hour continuous recording, infant 94772 TC Technical component only 94772 26 Professional component only Prosthetic Devices The IHCP reimburses for prosthetic devices under the following conditions: • A physician, optometrist, or dentist must order all prosthetic devices in writing. • When the basic prosthesis is approved, all customizing features are exempt from PA. Glasses do not require PA. • The IHCP does not cover prosthetic devices dispensed for purely cosmetic reasons, such as contact lenses, hairpieces, or makeup. ThAIRapy Vest™ The IHCP covers the ThAIRapy Vest™ device for use only for cystic fibrosis. The ThAIRapy Vest™ is a mechanical device that uses a vest and a generator to assist in loosening bronchial secretions and clearing the airway. All requests for this DME device require PA with an appropriate clinical summary and physician prescription. The vest and generator components of the ThAIRapy Vest™ are only authorized as a purchase. The IHCP requires rental of the generator and hoses for the ThAIRapy Vest for three months prior to purchase of these components. Trend Event Monitoring and Apnea Monitors The IHCP covers trend event monitoring with an apnea monitor that has recording features. HCPCS code E0619 is billed for the actual monitor. Providers must use the appropriate CPT code for monitoring, recording, transmission, and interpretation to bill for these services. Table 8.67 shows current coding options. Providers should use HCPCS code E0618 when a member requires an apnea monitor without a recording feature. Table 8.67 – Coding for Trend Event Monitoring and Apnea Monitors Procedure Code Description E0618 RR (Rental) Apnea monitor without recording feature E0618 NU (Purchase) Apnea monitor without recording feature E0619 RR (Rental) Apnea monitor with recording features E0619 NU (Purchase) Apnea monitor with recording features Patient demands single or multiple event recording with pre-symptom memory loop, per 30 day period of time; includes transmission, physician review, and interpretation 93268 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-229 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Procedure Code Description 93270 Recording (includes hook-up, recording, and disconnection) 93271 Monitoring, receipt of transmissions, and analysis 93272 Physician review and interpretation only Ventricular Assist Devices Effective May 1, 2006, the IHCP instituted changes in the medical necessity criteria for ventricular assist devices (VADs) and considers them medically necessary under the following conditions. The IHCP covers treatment of postcardiotomy cardiogenic shock when ventricular dysfunction continues after maximum medical therapy or as a means of myocardial recovery support for individuals who are unable to be weaned from cardiopulmonary bypass with maximal inotropic support and use of an intra-aortic balloon pump. The IHCP covers bridge-to-transplant for members who meet the following criteria: • The member must be at risk of imminent death from nonreversible left ventricular failure (NYHA Class III or IV). • The member has received prior authorization for a heart transplant (excluding dual eligible members). • The member is listed as a candidate for heart transplantation by a Medicare- and/or Medicaidapproved heart transplant center. • If the VAD is implanted at a different site than the Medicare- and/or Medicaid-approved transplant center, the implanting site must receive written permission from the Medicare- and/or Medicaidapproved center where the patient is listed for transplant prior to implantation of the VAD. The IHCP covers destination therapy for members who meet the following criteria: • The member must not be a candidate for a heart transplant. • The member must have chronic end-stage heart failure (NYHA Class IV) for at least 90 days, and have a life expectancy of less than two years. • The member’s Class IV heart failure symptoms must have failed to respond to optimal medical therapy for at least 60 of the last 90 days. Medical therapy must include salt restriction, diuretics, digitalis, beta-blockers, and ARBs or ACE inhibitors (if tolerated). • Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction (LVEF) must be less than 25 percent. • The member has demonstrated functional limitation with a peak oxygen consumption of less than 12ml/kg/min; or continued need for IV inotropic therapy due to symptomatic hypotension, decreasing renal function, or worsening pulmonary congestion. • The member has the appropriate body size (greater than or equal to 1.5m2) to support the Left Ventricular Assist Device (LVAD) implantation. • VAD implantation must occur at a Medicare- or Medicaid-approved heart transplant center. A VAD is a covered service for postcardiotomy cardiogenic shock or bridge-to-transplant only if it has received approval from the FDA for the intended purpose, and only if it is used according to the FDAapproved labeling instructions for that intended purpose. A VAD is a covered service for destination therapy only if it has received approval from the FDA for destination therapy or as a bridge-totransplant, or has been implanted as part of an FDA investigational device exemption trial for one of these two indications. 8-230 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Noncovered Services • VADs are noncovered for all conditions not listed above. • Use of a non-FDA approved VAD is considered investigational and a noncovered service. • The artificial heart (for example, AbioCor, CardioWest) as a replacement heart for a diseased heart is noncovered by the IHCP. Prior Authorization VADs and their surgical implantation do not require PA. However, members who receive bridge-totransplant or destination therapy, and who can continue therapy on an outpatient basis, require accessory equipment for use with the VAD. The patient supplies and replacement equipment for the VAD require PA. Stationary Power Base and Display Module The power base is the electrical supply unit for the VAD. It provides tethered functioning of the VAD by powering the VAD and simultaneously recharging the batteries. The display module provides pump functioning information for the physician to evaluate patient status. The hospital or DME provider purchases the power base as a capital expense and loans it to the member. The hospital or DME provider is reimbursed a rental payment while the equipment is used on an outpatient basis by the member. The physician must submit a PA request for HCPCS code L9900 – Orthotic and prosthetic supply, accessory, and/or service component of another HCPCS L code and modifier RR – Rental use. Patient Supplies and Replacement Equipment PA is required for patient supplies and replacement equipment. Patient supplies and replacement equipment include the system controller, rechargeable batteries, travel case, shower kit, and other miscellaneous supplies. The hospital or DME provider must supply the replacement parts. IHCP-covered services for implantation of VADs for postcardiotomy cardiogenic shock, bridge-totransplant, and destination therapy are subject to postpayment review. Providers must maintain documentation in the member’s medical record that indicates that all criteria listed above have been met for implantation of a VAD. If all the criteria for implantation are not satisfied, reimbursement of funds may be recouped, including surgical fees, professional fees, and equipment costs. Billing Instructions for Outpatient Equipment Utilizing the CMS-1500 Claim Form 1. PA must be obtained for VAD accessory equipment for outpatient therapy. 2. The description of the power unit and display module should be entered on a detail line with HCPCS code L9900, placed in locator 24d of the CMS-1500 claim form. The total rental price may not exceed the purchase price. 3. The description of the replacement supplies should be placed on a second detail line with the appropriate HCPCS code in locator 24d of the CMS-1500 claim form. 4. An invoice for each detail must accompany the CMS-1500 claim form when submitted. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-231 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Wheelchairs – Motorized Providers should determine which of the codes is the most appropriate to use, based on the Wheelchair Product Classification List published by Medicare’s Statistical Analysis Durable Medical Equipment Regional Carrier (SADMERC). This listing itemizes the manufacturers and specific power wheelchair models and details the exact HCPCS code associated with each product and model type. Providers cannot bill separately for programmable electronic systems that come standard on the specific motorized or power wheelchair model provided because the total reimbursement for the motorized or power wheelchair with programmable electronics (K0011) is all-inclusive under that code. Effective for claims with dates of service July 18, 2003, or after, the IHCP allows separate reimbursement only for programmable electronic system upgrades, determined to be medically necessary for the patient, made on motorized/power wheelchair bases. Any such upgrades must have PA, and providers must bill them under HCPCS code K0108 with a KA modifier. Providers must bill the wheelchair base with HCPCS code K0014. For claims submission, providers must attach a cost invoice or retail price invoice to document the cost or price of the wheelchair base and the upgraded electronic system. The IHCP allows separate reimbursement only if an electronic system is an upgrade to a system that comes standard on a specific wheelchair model. Certain patients may need adaptive switch controls such as a sip and puff, or patients with degenerative diseases whose prognosis could worsen in the future may need additional drive controls and programming not available on the basic one-drive electronic system. In this instance, a physiatrist must confirm the medical necessity to support the need of the programmable electronic system upgrade and the physician must document it in the patient record, as well as on a completed IHCP medical clearance form for motorized/power wheelchairs. Documentation requirements for motorized or power wheelchairs are described in more detail in Chapter 6 of this manual. The IHCP covers motorized wheelchairs only when the member is enrolled in a school, sheltered workshop, or work setting, or if the member is left alone for a significant period of time. Providers must document that the member can safely operate the vehicle and that the member does not have the upper extremity function necessary to operate a manual wheelchair. A physical medicine and rehabilitation practitioner (physiatrist) must complete a medical clearance form for the IHCP to consider requests for power wheelchairs or similar motorized equipment for approval. A physiatrist must review the medical necessity documentation and sign the medical clearance forms. The IHCP does not require that the member initially be seen by the physiatrist, but only that the physiatrist reviews the documentation supporting the request for a motorized or power wheelchair. However, a physiatrist must review the medical necessity form, and approve and sign the medical clearance form prior to submitting the form to the appropriate MCO or CMO PA Department. The IHCP requires a member to see the physiatrist only if the physiatrist requests to see the member after a review of the documentation. Additionally, the IHCP does not require that the physiatrist be located within a certain distance of the physician or the member. If the physiatrist requests to see the member after reviewing the documentation, the member is then required to travel to visit the physiatrist. Wheelchairs – Nonmotorized The IHCP covers purchase of a nonmotorized wheelchair or motorized wheelchair subject to prior authorization review. Requests for nonmotorized wheelchairs or similar motorized vehicles require that the provider submits a medical clearance with the PA request before the IHCP reviews the request. The IHCP includes standard nonmotorized wheelchairs in the per diem rate, for LTC facilities, per 405 IAC 5-13-3-4 and 405 IAC 5-13-3-7. Requests should be submitted to the appropriate MCO for approval only if there is a medical necessity for the custom wheelchair. For example, if the member’s diagnosis requires sitting in a particular upright position due to a breathing difficulty, the member may 8-232 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions need a customized wheelchair. Providers must follow the normal PA process using IHCP PA and medical clearance forms. LTC members receive 24-hour care in a nursing facility. This care includes safety, propulsion, evaluation of the member for skin breakdown, and an active plan of care to prevent and treat decubitus ulcers. Therefore, providers should not request custom wheelchairs for the sole purpose of providing safety, preventing decubitus ulcers, allowing self-propulsion, or providing restraint. Wheelchair – Power Seating The IHCP has determined HCPCS codes E1002, E1003, E1004, E1005, E1006, E1007, and E1008 for power seating systems; E1009 and E1010 for power-elevating leg rests; and E2310 and E2311 for electric connectors to be medically necessary items. The IHCP covers these HCPCS codes as inexpensive and routinely purchased items for rental or purchase with prior authorization. Wheelchair – Seat Cushions The IHCP deleted the HCPCS K codes K0650-K0658 on December 31, 2004, and crosswalked them to HCPCS codes E2601-E2610. The HCPCS E codes became nonreimbursable after September 30, 2004. For dates of service on or after September 1, 2006, the following codes are reimbursable for adjustable seat cushions: • K0734 – Skin protection wheelchair seat cushion, adjustable, width less than 22 inches, any depth • K0735 – Skin protection wheelchair seat cushion, adjustable, width 22 inches or greater, any depth • K0736 – Skin protection and positioning wheelchair seat cushion, adjustable, width less than 22 inches, any depth • K0737 – Skin protection and positioning wheelchair seat cushion, adjustable, width 22 inches or greater, any depth Adjustable cushions are purchase-only items. Providers must attach the NU modifier when billing adjustable seat cushions. The adjustable cushions do not have to be listed on the Statistical Analysis Durable Medical Equipment Regional Carrier (SADMERC) classification list to be reimbursed by the IHCP. Wheelchair Accessories Providers must use HCPCS code E1028 – Wheelchair accessory, manual swingaway, retractable or removable mounting hardware for joystick, other control interface or positioning accessory, for PA and billing. The IHCP denies requests for approval of the universal headrest plate using HCPCS code E1399 – Durable medical equipment, miscellaneous for appropriate coding. Providers should submit their usual and customary charge using HCPCS code E1028. Reimbursement of the universal headrest plates are subject to the following PA criteria: • The IHCP covers universal headrest plates when the initial headrest ordered for a new wheelchair does not meet the member’s needs upon the first or subsequent fittings. On the PA request, the provider must document the brand name and model of the original headrest, and include an explanation of why the headrest did not meet the member’s needs. In addition, the provider must indicate the brand name and model of the subsequent headrest that will be used on the wheelchair. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-233 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions • The IHCP covers universal headrest plates for a used wheelchair if the member’s condition changes, and the wheelchair back is not predrilled for the headrest. The provider must provide documentation of the medical necessity for the headrest. • The IHCP covers replacement universal headrest plates with documentation of an explanation for the replacement (for example, the plate is damaged due to high tone or spasticity of the patient). The IHCP does not cover universal headrest plates for the initial headrest ordered for use on a new wheelchair. The wheelchair back should be predrilled to accommodate the headrest initially ordered with the wheelchair. Documentation Required for Medical Supplies and Equipment All medical supplies and equipment require a written order by a physician, optometrist, or dentist. According to the Indiana Administrative Code (IAC) citation 405 IAC 5-19-1, “medical supplies shall be for a specific medical purpose, not incidental or general purpose usage.” Verbal orders, communicated by the prescriber to the supplier, are permitted when appropriately documented; however, verbal orders must be followed up with written orders. Suppliers must maintain the written physician’s order to support medical necessity during postpayment review. The IHCP has identified instances when medical supplies were dispensed in excess of medically reasonable and necessary amounts. This information serves to clarify the IHCP standards for prescribing and dispensing medical supplies, including but not limited to items such as surgical dressings, catheters, and ostomy bags. This information does not eliminate any other IHCP requirements for DME and medical supplies at the time services are rendered. Prescribers of DME, HME, and Medical Supplies Physicians must be aware that their signature on an order for DME, HME, and medical supplies authorizes those items to be dispensed to the patient. When writing an order for such items, the physician must consider the following questions: • Are specific instructions, such as frequency of use, directions for use, duration of need, and so forth, listed on the order? • Is the quantity authorized by the physician medically reasonable and necessary for the patient’s medical condition? The prescriber is also responsible for maintaining documentation in the member’s medical record that supports the medical necessity of specific DME, HME, and medical supplies prescribed. To ensure that the appropriate quantity and type of item are dispensed, it is especially important that the written order be detailed. Providing a detailed written order does not eliminate the need for other IHCP requirements in effect at the time services are rendered. The written order for DME, HME, and medical supplies should include, at a minimum, the following information, when applicable: • Patient’s name • Date ordered • Physician’s signature • Area of body for use (for items that may be appropriate for multiple sites) • Type and size of the product • Quantity intended for use • Frequency of use (for example, change dressing three times per day) • Anticipated duration of need 8-234 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions • Indication of refill authorization and the number of refills - As needed or PRN (when necessary), refill authorization must be medically necessary and reasonable. - The need for long-term use must be documented in the patient’s medical record. Note: Orders and physician signatures may be verified retrospectively by the OMPP or the designated contractor. Suppliers of DME, HME, and Medical Supplies Suppliers of DME, HME, and medical supplies must maintain the prescriber’s written order in the member’s medical record. Suppliers are responsible for ensuring that the written order contains the necessary information to complete the order. If the physician’s order lacks information necessary to accurately dispense the appropriate, specific DME, HME, and medical supplies, including type or quantity, the supplier must contact the physician’s office for written clarification. Suppliers must maintain the written physician’s order to support medical necessity during postpayment review. Note: The IHCP requires that Medicaid providers maintain medical records for a period of seven years, per 405 IAC 1-5-1. Services may be subject to recoupment if the physician orders are modified after the service is rendered or if orders are obtained after the provision of service. Emergency Department Physicians Coverage and Billing Procedures The IHCP provides coverage to emergency department physicians who render emergency services to IHCP eligible members. This section provides additional information about billing procedures for emergency department physicians. IC 12-15-15-2.5 (P.L. 153-1995) addresses reimbursement of emergency department physicians. In accordance with this, Care Select members no longer require PMP authorization for federally required medical screening examinations performed by a physician in the emergency department of a hospital. Providers must bill one of the CPT codes listed in Table 8.68, reflecting the appropriate level of screening exam, on a CMS-1500 or 837P transaction. Table 8.68 – CPT Codes – Appropriate Level of Screening Exam CPT Codes 99281 99282 99283 Definitions Emergency department visit – Level 1 Emergency department visit – Level 2 Emergency department visit – Level 3 For related services provided to Care Select members such as facility charge, lab, and X-ray that do not have an emergency diagnosis and emergency indicator on the claim, the IHCP may suspend the claim for review to determine whether the prudent layperson standard has been met if the claim does not contain the PMP authorization. The authorization consists of the PMP NPI and the two-digit Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-235 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions certification code. If the IHCP review determines that the prudent layperson standard has not been met, the IHCP will deny the claim. Note: For members enrolled in the RBMC delivery system, providers must contact the member’s MCO for more specific guidelines. Evaluation and Management Services Coverage and Billing Procedures The purpose of this section of the billing instructions chapter is to provide the most current policy, billing criteria, and reimbursement information for submitting claims for Evaluation and Management (E/M) services. The IHCP offers reimbursement for office visits limited to a maximum of 30 per year, per IHCP member, without PA, and subject to the restrictions in Section 2 of this rule. The rules set in 405 IAC 5-9-1 apply to E/M services. The E/M codes in Table 8.69 are subject to this limitation. Table 8.69 – Evaluation and Management Services Codes Subject to Limitation CPT Code 99201-99215 99241-99245 99381-99397 Per 405 IAC 5-9-2, office visits should be appropriate to the diagnosis and treatment given and properly coded. Providers must submit professional services rendered during the course of a hospital confinement on the CMS-1500 or 837P transaction. The IHCP reimburses in accordance with the appropriate professional fee schedule. The inpatient diagnosis-related group (DRG) reimbursement methodology does not provide payment for physician fees, including hospital-based physician fees. New patient office visits are limited to one visit per member, per provider within a three-year period. For purposes of this subsection, new patient means one patient who has not received any professional services from the provider or another provider of the same specialty that belongs to the same group practice. If a physician uses an emergency department as a substitute for the physician’s office for nonemergency services, providers should bill these visits with a CPT code usually used for a visit in the office with the site of service indicated. The IHCP will apply a site of service reduction in the reimbursement. If a provider performs a surgical procedure during the course of an office visit, the IHCP generally considers that the surgical fee includes the office visit. However, the provider may report the visit separately for the following reasons: the provider has never seen the member prior to the surgical procedure, the provider determines whether to perform surgery during the evaluation of the patient, or the patient is seen for evaluation of a separate clinical condition. Providers must use the following modifiers with the E/M visit code to identify these exceptional services. Use modifier 25 to show that there was a significant, separately identifiable E/M service by the same physician on the same day of a procedure. Use modifier 57 to show that an E/M service 8-236 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions resulted in the initial decision to perform surgery. The medical record must include appropriate documentation to substantiate the need for an office visit code in addition to the procedure code on the same date of service. Consultations The IHCP reimburses for the following two categories of consultation: • Office or other outpatient consultation • Inpatient consultation Office Consultation A consultation is a type of service provided by a physician whose opinion or advice about evaluation and management of a specific problem is requested by another physician or other appropriate source. A physician consultant may initiate diagnostic or therapeutic services. Providers should not use consultation codes for the evaluation of a self-referred or nonphysician-referred patient. A consultation implies collaboration between the requesting and the consulting physician. Providers should use consultation codes 99241– 99245. Providers should use office visit codes for established patients, 99211–99215, to report follow-up visits in the consultant’s office or other outpatient facility initiated by the physician consultant. When the attending physician receives an additional request for an opinion or advice about a new problem and documents it in the medical record, the provider may use the office consultation codes again. When the provider is billing consultation codes, the medical record must contain written documentation of the request for consultation by the requesting physician. The provider should maintain this documentation in the patient’s medical record at the requesting and receiving physician’s office. When a provider performs a consultation, the consulting physician customarily responds in writing to the requesting physician about the opinion or advice of the consulting physician. Providers may bill a maximum of one unit per patient per day for procedure code 99051 – Service(s) provided in the office during regularly scheduled evening, weekend, or holiday office hours, in addition to basic service. Evening hours are defined as routinely scheduled after 5 p.m. in the prevailing time zone. Providers may only bill for the following holidays, which represent days when physician offices are generally closed for the day: New Year’s Day, Memorial Day, Independence Day, Labor Day, Thanksgiving Day, and Christmas Day. When billing for 99051, please document in the medical chart the time, date, or holiday, as applicable. All other billing requirements will remain unchanged. Inpatient Consultation The IHCP recognizes CPT codes 99251–99255 for inpatient consultations with new or established patients in the inpatient hospital setting. Consultants may report only one consultation per admission. Providers must document the request for consultation. Subsequent services are reported using Subsequent Hospital Care Codes 99231–99233. Hospital Observation or Inpatient Care Services The IHCP recognizes CPT codes 99234–99236 for observation or inpatient hospital care services provided to patients admitted and discharged on the same date of service. When a patient is admitted to the hospital from observation status on the same date, the physician should report only the initial hospital care code. The initial hospital care code includes all services related to the observation status Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-237 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions services the physician provided on the same date of an inpatient admission. The IHCP recognizes CPT codes 99217, 99218–99220 or 99221–99223, and 99238–99239 for patients admitted for observation or inpatient care and discharged on a different date. Hospital Discharge Services Providers should report hospital discharge day management by using CPT codes 99238 or 99239, depending on the amount of time spent discharging the patient. Providers should document this amount of time in the medical record to substantiate the code being billed. For a patient admitted and discharged from observation or inpatient status on the same date, report the service using CPT codes 99234–99236. Providers should report separately for hospital discharge services, using CPT codes 99238 and 99239, performed on the same day as an NF admission by the same provider. Critical Care Services The IHCP recognizes CPT codes 99291–99296 for reporting critical care services performed by a physician. The IHCP has adopted the guidelines set forth in the CPT manual, and providers can find a complete definition of critical care services in the current version of the CPT manual. Family Planning Services Coverage and Billing Procedures Family planning services are those services provided to individuals of childbearing age to temporarily or permanently prevent or delay pregnancy. Family planning services include the following: • Diagnosis and treatment of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), if medically indicated • Follow-up care for complications associated with contraceptive methods issued by the family planning provider • Health education and counseling necessary to make informed choices and understand contraceptive methods • Laboratory tests, if medically indicated as part of the decision-making process for choice of contraceptive methods • Limited history and physical examination • Pregnancy testing and counseling • Provision of contraceptive pills, devices, and supplies • Screening, testing, and counseling of members at risk for HIV and referral and treatment • Tubal ligation or hysteroscopic sterilization with an implant device • Vasectomy Note: Family planning services are not covered under Package P – Presumptive Eligibility. Refer to the Qualified Provider Presumptive Eligibility Manual for more information. Family planning services can include pap smears if performed according to the United States Preventative Services Task Force Guidelines. The guidelines specify cervical cancer screening every one to three years, based on the presence of risk factors such as early onset of sexual intercourse and 8-238 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions multiple sexual partners; however, pap smear annual frequency may be reduced if three or more annual smears are normal. Based on the CMS’ policies, the IHCP considers initial STD diagnosis and treatment, HIV testing, and counseling provided during a family planning encounter to be part of the family planning services. Ongoing follow-up of STDs and visits for treatment of chronic STDs are not part of family planning services. Family planning services are self-referred in each of the managed care programs, but they require appropriate HCPCS or CPT codes and ICD-9-CM diagnosis combinations for CMS-1500 or 837P billing. See Table 8.70 for family planning ICD-9-CM codes. Table 8.70 – Diagnosis Codes – Family Planning ICD-9-CM Diagnosis Codes Definition V2501 Prescription of oral contraceptives V2502 Initiation of other contraceptive measures V2503 Encounter for emergency contraceptive counseling and prescription V2509 Contraceptive management, other V251 Intrauterine device (IUD) insertion V253 Menstrual extraction V2540 Contraceptive surveillance, unspecified V2541 Contraceptive pill surveillance V2542 IUD surveillance V2543 Implantable subdermal contraceptive V2549 Contraceptive surveillance, other V255 Insertion of implantable subdermal contraceptive V258 Other specified contraceptive management V259 Contraceptive management, unspecified Providers must bill services and supplies not classified as drugs or biologicals using the CMS-1500 or 837P. Providers should bill these services using appropriate CPT or HCPCS codes and appropriate ICD-9-CM diagnosis codes for services rendered or condition treated. For example, use ICD-9-CM diagnosis codes V25.01 through V25.9 for contraceptive management, and use ICD-9-CM diagnosis code 099.53 for acute chlamydial vaginitis. Providers using CPT code 99070 for supplies dispensed during a family planning visit should identify the name of the item dispensed on the CMS-1500 or 837P, below the line item being billed. Identify the quantity or number of packages dispensed in field 24G. The amount billed should reflect the appropriate cost of the contraceptive item and should not exceed the NDC packaging price. Do not substitute CPT code 99070 if an HCPCS code exists for the item dispensed. If billing electronically, the provider can submit the NDC of the drug administration in the claim notes section of the 837 transaction, and the claim will adjudicate appropriately. Ensure that the member’s chart contains the date of the office visit, the NDC code, and name of the product dispensed, as well as the amount of the item dispensed, such as four boxes of 30 items. Providers billing for Norplant Systems must use the CPT procedure codes listed in Table 8.71. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-239 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Table 8.71 – CPT Procedure Codes for Norplant Systems Procedure Code Description 11975 Insertion, implantable contraceptive capsules 11976 Removal, implantable contraceptive capsules 11977 Removal with reinsertion, implantable contraceptive capsules In accordance with CPT Changes, An Insider’s View 2002, published by the American Medical Association, “CPT Codes 11981–11983 differ from the other implant codes 11975–11977, in that codes 11975–11977 are also a type of nonbiodegradable capsule, but are specific for contraceptive use.” Table 8.72 lists CPT codes 11981–11983 and the description for clarification. Table 8.72 – CPT Codes for Other Contraception Implants CPT Code Description 11981 Insertion, nonbiodegradable drug delivery implant 11982 Removal, nonbiodegradable drug delivery implant 11983 Removal with insertion, nonbiodegradable drug delivery implant The IHCP covers HCPCS codes J7303 – Contraceptive supply, hormone containing vaginal ring, each, and J7304 – Contraceptive supply, hormone containing patch, each, effective October 1, 2005. Providers must bill J7303 and J7304 instead of a miscellaneous supply code because these codes are more specific to the service being supplied. Limits and Restrictions for Depo-Provera Contraceptive Injection HCPCS code J1055-Injection, medroxyprogesterone acetate for contraceptive use, 150 mg. The gender indicator will be “Female.” The allowable units per date of service (DOS) will be limited to one. According to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), Depo-Provera Contraceptive Injection (CI) is a long-term contraceptive for women and is indicated only for the prevention of pregnancy. The recommended dose to women is 150 mg every three months. An appropriate HCPCS code for billing medroxyprogesterone for noncontraceptive use is J1051 – Injection, medroxyprogesterone acetate, 50 mg, which may be billed for multiple units, per member, on a single DOS. Managed Care Program Considerations Direct billing questions for Traditional IHCP and Care Select to Customer Assistance at (317) 6553240 in the Indianapolis local area or 1-800-577-1278. For Hoosier Healthwise RBMC questions, providers should contact the MCO to which the member has been assigned. Federally Qualified Health Centers and Rural Health Clinics Federally Qualified Health Centers FQHCs receive funds through the Public Health Service (PHS) and are designated as such. FQHC look-alikes meet the criteria but do not receive PHS funding and have not been given FQHC status by CMS. For information about this process, contact the Indiana Primary Health Care Association at (317) 8-240 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions 630-0845. To enroll as an FQHC, providers should forward the CMS letter, which grants the FQHC status, to the HP Provider Enrollment Unit with the completed application. The provider must also contact the IHCP’s rate-setting contractor, Myers and Stauffer, LC, to submit the proper financial documents to have a rate determined for the FQHC. Myers and Stauffer, LC forwards the rate document to the Provider Enrollment Unit so the encounter rate can be loaded into IndianaAIM. Each time the facility expands the scope of service and receives an adjustment to its encounter rate, Myers and Stauffer, LC must forward a new rate letter to the Provider Enrollment Unit to ensure that reimbursement remains accurate. In the Care Select network, FQHC provider specialties are not entitled to receive the monthly administrative fee payment. Rural Health Clinics RHCs receive their Medicare designation through CMS. The clinics must contact the ISDH to request RHC status for the IHCP. The IHCP requires all RHCs to submit finalized (reviewed or audited) cost reports and copies of their Medicare rate letters to Myers and Stauffer, LC. RHC services are defined in 42CFR 405.2411 and 42 CFR 440.20. For more information about becoming an RHC under the IHCP, contact the Indiana Department of Health, the Indiana Primary Health Care Association at (317) 630-0845, or other practice consultants. Each time the facility expands its scope of service and receives an adjustment to its encounter rate, Myers and Stauffer, LC must forward the new rate letter to the Provider Enrollment Unit to ensure that reimbursement remains accurate. In the Care Select network, RHC provider specialties are not entitled to receive the monthly administrative fee payment. Service Coverage According to 405 IAC 5-16-5, IHCP reimbursement is available to RHCs and FQHCs for services provided by the following providers: • Physician • Physician assistant • Nurse practitioner • Clinical psychologist • Clinical social worker The IHCP also provides reimbursement to RHCs and FQHCs for services provided by the following providers: • Dentist • Dental hygienist • Podiatrist • Optometrist The IHCP also reimburses for services and supplies incidental to such services, which the IHCP would otherwise cover if furnished by a physician or incident to a physician’s services. The IHCP covers services to a homebound individual only in the case of those FQHCs located in an area with a shortage of home health agencies, as determined by the OMPP. The IHCP considers any other ambulatory service included in the Medicaid state plan to be a covered FQHC service if the FQHC offers such a service. FQHC services are defined the same as services provided by RHCs. FQHCs and RHCs should contact Myers and Stauffer, LC for information about cost reports and interim cost settlements. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-241 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions FQHC and RHC Covered Services In accordance with Section 702 of the Medicare, Medicaid, and State Children’s Health Insurance Program (SCHIP) Benefits Improvement and Protection Act of 2000 (BIPA), significant changes occurred with the IHCP reimbursement methodology for FQHCs and RHCs. Billing procedures and administrative requirements also changed for fee-for-service billing for each type of facility. Providers must use the prospective payment system (PPS) methodology for claims submitted with dates of service (DOS) on or after April 1, 2003. All FQHC and RHC facilities must submit claims using HCPCS Level III codes, including the current code T1015 – (clinic, visit/encounter, all-inclusive) and Level I and Level II HCPCS procedure codes. FQHCs and RHCs continue to receive a facility-specific PPS rate determined by Myers and Stauffer, LC. Myers and Stauffer, LC forwards the specific PPS rate information to HP, and the HP Provider Enrollment Unit loads the rate for reimbursement of T1015 to the specific provider enrollment file for reimbursement. Providers must submit claims for valid FQHC and RHC encounters with a place of service of 11, 12, 31, 32, 50, or 72. Providers must use the T1015 – Clinic visit/encounter, all-inclusive code and CPT or HCPCS codes. The claim logic compares the other CPT or HCPCS codes used to a list of valid CPT and HCPCS codes approved by the OMPP. If the claim contains T1015 and one of the allowable procedure codes from the encounter criteria, the CPT or HCPCS codes correctly are denied for EOB 6096 – The CPT/HCPCS code billed is not payable according to the PPS reimbursement methodology. The encounter rate (T1015) is reimbursed according to the usual and customary charge (UCC) established by Myers and Stauffer, LC from the provider-specific rate on the provider file. The provider should not resubmit CPT or HCPCS codes separately that were denied for EOB 6096 – The CPT/HCPCS code billed is not payable according to the PPS reimbursement methodology. Providers should identify all services provided during the visit using all the appropriate CPT and HCPCS codes. If the CPT or HCPCS codes billed do not contain one of the procedure codes included in the list of allowable procedure codes from the encounter criteria for place of service 11, 12, 31, 32, 50, or 72, the claim is denied for EOB 4124 – The CPT/HCPCS code billed is not a valid encounter. Providers should not resubmit claims denied for EOB 4124 – The CPT/HCPCS code billed is not a valid encounter for payments. Additionally, claims submitted with a place of service 11, 12, 31, 32, 50, or 72 with CPT or HCPCS codes that do not have the T1015 present on the claims are denied for EOB 4121 – T1015 must be billed with a valid CPT/HCPCS code. Providers can resubmit these claims with the T1015 code properly included on the claim. The IHCP allows only one encounter per IHCP member, per provider, per day, unless the diagnosis code differs. When the IHCP determines the number of allowable encounters for that specific claim, it multiplies that number by the facility-specific PPS rate to calculate the amount paid on the claim. Providers can submit valid encounters with differing diagnosis codes for a member that exceed the allowed one encounter per day to HP for manual processing. Providers can submit claims electronically using the 837P transaction. When a provider submits claims for valid encounters submitted using the 837P transaction, those claims must contain the T1015 and the CPT/HCPCS codes for the services rendered. For services provided at these place of service locations that are not valid encounters with the appropriate provider, such as injections performed by a nurse without a corresponding visit to satisfy the valid encounter definition, providers should instead reflect the services in the facility’s cost report submitted to Myers and Stauffer, LC. Hospital Services The IHCP reimburses claims submitted with place of service 20-26 at the current reimbursement rate for each specific CPT/HCPCS code. It is not necessary for providers to include the T1015 encounter 8-242 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions code on claims with place of service 20-26. The IHCP considers these services non-FQHC/RHC services provided by the valid provider but in a setting other than an RHC/FQHC setting. Dental Services Providers should continue to bill dental claims for services provided at an FQHC or RHC on a dental claim form using Current Dental Terminology (CDT) codes. Do not include the T1015 encounter code on the dental claim form. Myers and Stauffer, LC makes settlements and reconciles dental claims to the provider-specific PPS rate through annual reconciliations. The reconciliations continue until the IndianaAIM system is adapted to the PPS methodology. Care Select Claims submitted for Care Select members require PMP authorization if the service provided to the member was not provided by the PMP. Refer to the billing information at the beginning of this section for information about submitting the paper CMS-1500 claim form. Services provided to a Care Select member, such as immunizations, at a location other than the PMP’s office require the Memorandum of Collaboration (MOC) and authorization information. If the visit does not satisfy the criteria for an encounter with a valid provider, the claim is denied. Providers can use the denial information to track these services and reflect them in the facilities cost report. Self-referral services provided at the FQHC or RHC do not require PMP authorization information when appropriately billed. These must, however, satisfy the criteria for valid encounters and include the T1015 encounter code when submitting the claim for processing. Third-Party Liability Considerations All third-party liability (TPL), patient liability, and copayments continue to apply as appropriate. Allowable EPSDT and pregnancy services provided during the encounter visit and appropriately billed continue to bypass TPL. Providers need to apply previous TPL payments and spend-down to the total amount due. The IHCP excludes all Medicare crossover claims from the PPS logic, as well as the crossover reimbursement methodology, and continues to pay coinsurance and deductible amounts. Risk-Based Managed Care Providers should continue to use CPT codes to bill claims for members in RBMC. Providers must submit the claims to the applicable managed care organization. Do not include the T1015 encounter code on these claims. Myers and Stauffer, LC reconciles all managed care claims to the providerspecific PPS rate and makes annual settlements at that time. Providers may submit requests for supplemental payment to Myers and Stauffer, LC. The MCOs must also provide data related to annual reconciliations to Myers and Stauffer, LC. Medicare Processed Claims Submitted to the IHCP by the Provider Providers can submit claims electronically using the 837I or the 837P transaction. Claims submitted using the 837P transaction must contain the T1015 and the CPT codes for the services rendered. Per the Family and Social Services Administration (FSSA) Emergency Rule LSA #02-121, all paper UB-04 claim form or electronic 837I transaction crossover claims must contain additional information on the claim form. The rule changed how the IHCP reimburses providers for crossover claims. The IHCP uses the information in the required fields on the paper UB-04 claim form or electronic 837I transaction to process claims. Fields 39 through 41 on the paper UB-04 claim form must contain value code A1 to reflect the Medicare deductible amount and value code A2 to reflect the Medicare coinsurance amount. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-243 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions To ensure correct reimbursement, the paper UB-04 claim form or the electronic 837I transaction must show Medicare as the previous payer. Additionally, the paper UB-04 claim form or electronic 837I transaction must contain the Medicare paid amount (actual dollars received from Medicare). Providers should continue to report TPL payments on the paper UB-04 claim form or the electronic 837I transaction. Providers can use the professional format to submit claims processed by Medicare that did not cross over to the IHCP. These are claims allowed by Medicare that failed to cross over and Medicare-denied claims. Providers should refer to the 837 companion guides for specific information about electronic claims transaction requirements to be used with the 837 implementation guides. For the links to the appropriate Web sites and documents, go to http://provider.indianamedicaid.com. Providers that submit claims on paper when claims do not automatically cross over from Medicare to the IHCP must submit FQHC and RHC encounter service claims on the paper CMS-1500 claim form. Submit the paper claims using CPT or HCPCS codes for FQHCs, provider-based RHCs, or independent RHCs along with the T1015 for services billed. If Medicare denied the claim, providers must attach the Medicare Remittance Notice (MRN) and make sure that the MRN is clearly marked as a Medicare MRN. If you are submitting an electronically generated MRN, you must print it in landscape format so that all information is properly and clearly labeled. Providers can submit claims electronically using the 837I or 837P transaction. Claims submitted using the 837P transaction must contain the T1015 and the CPTs for the services rendered. Provider Enrollment Considerations All physicians associated with the clinic must have an individual IHCP provider number (LPI). Provider must also report their NPI number to IHCP. The provider numbers must be linked to the FQHC or RHC. The clinic must also notify the Provider Enrollment Unit in writing when a provider is no longer associated with the FQHC or RHC so that the clinic provider profile is current. If the CMS notifies an FQHC or RHC that the FQHC or RHC status has been terminated, the provider must also send a copy of the termination to the ISDH, which then forwards it to the Provider Enrollment Unit. The provider must contact HP to request an application to enroll as a medical clinic until FQHC or RHC status is reinstated. Failure to do this will result in disenrollment as a provider and loss of any managed care members assigned to PMPs linked to that location. Physician assistants cannot obtain an IHCP rendering provider NPI number. Providers must use the supervising practitioner’s NPI number to submit claims for services rendered by these practitioners. Service Definition The IHCP defines a visit as a face-to-face encounter between a clinic patient and a physician or other provider. The IHCP considers multiple services that a provider performs during the same visit for the same or related diagnosis to be a single encounter, even though the provider can consider them separate encounters if billed independently. For example, if a patient receives a dental exam and an amalgam during the same visit, the IHCP considers it a single encounter. The IHCP considers multiple visits that occur within the same 24-hour period to be a single encounter if they are for the same diagnosis. The IHCP considers them to be multiple encounters if the diagnosis is different. For example, if the patient has an office visit in the morning and returns later the same day with the same or related diagnosis, the IHCP considers the two instances as a single encounter. However, if a patient has an office visit in the morning and returns later the same day for treatment of a fracture, two different encounters have occurred. 8-244 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Providers can bill only one unit of service on a single detail line of the paper or electronic claim form. When two valid providers see the same patient in the same day, such as a medical provider and a mental health provider, the principal diagnoses should not be the same. Providers should break down consecutive service dates so that they bill each day on a separate line. When a provider has more than one visit per day for the same member for the same provider and the diagnoses are different, the IHCP requires a manual review. Therefore, providers should submit proper documentation along with the claim to substantiate the need for additional visits. This documentation includes, but is not limited to, the following: • Visits performed at separate times of the day that indicate the times and the reasons for each visit on the face of the claim or on a claim attachment • Visits provided by different providers on the same day that indicate the type of provider that rendered each visit and denote which practitioner treated which diagnosis • Documentation in writing from the medical record that supports the medical reasons for the additional visit - This documentation includes presenting symptoms or reasons for the visit, onset of symptoms, and treatment rendered. • Documentation that the diagnosis for each encounter is different The IHCP also reimburses for services and supplies incidental to such services as would otherwise be covered if furnished by a physician or as an incident to a physician’s services. Services such as drawing blood, collecting urine specimens, performing laboratory tests, taking X-rays, filling and dispensing prescriptions, or providing optician services do not constitute encounters. Providers can include these services in the encounter reimbursement when performed in conjunction with the office visit to a valid provider. The IHCP does not reimburse for these services through claim submission if performed without a visit with a valid provider. FQHCs and RHCs can provide preventive services and encounters, care coordination, and HealthWatch services. The Care Coordination Services section in this chapter and the HealthWatch/EPSDT supplemental provider manual provide more information about those services. HealthWatch/EPSDT Services Coverage and Billing Procedures The Early and Periodic Screening, Diagnosis and Treatment (EPSDT) Program, referred to as HealthWatch/EPSDT in Indiana, is a preventive healthcare program designed to improve the overall health of IHCP eligible members from birth to 21 years old. Special emphasis is given to early detection and treatment of health issues because these efforts can reduce the risk of more costly treatment or hospitalizations that can result when detection is delayed. Because HealthWatch/EPSDT services include more components than a simple well-child office visit, reimbursement rates for HealthWatch/EPSDT screens are higher than the rates paid for well-child exams. To offer HealthWatch/EPSDT services, the provider must be licensed to perform an unclothed physical exam, as well as other screening components of the HealthWatch/EPSDT examination. A copy of the HealthWatch manual is available on the Web site at http://provider.indianamedicaid.com/general-provider-services/manuals.aspx. Medicaid-enrolled providers must furnish and document all components of the EPSDT visit to bill for the higher rate of reimbursement for EPSDT screens. To review a complete list of EPSDT requirements, refer to the HealthWatch/EPSDT Provider Manual for screening and referral details. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-245 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Table 8.73 – CPT Codes for EPSDT Visits Visits CPT® CODES EPSDT/Well Care Provide preventive care following the EPSDT guidelines and documenting the components of the screening to allow for a higher level of reimbursement. Preventive: 99381-99385 Initial/New Patient A comprehensive prenatal visit meets all of the requirements for a preventive care visit. Sick Visit plus EPSDT (two visit codes) V20.2 – Routine infant or child health check Includes: • Developmental testing of infant or child, Immunizations appropriate for age • Initial and subsequent routine newborn check 99391-99395 Established Patient Evaluation and Management: 99201-99205 New Patient 99211-99215 Established Patient Preventive/ Well Care Provide and document preventive care at any visit. Include age appropriate medical history, physical exam, and health education. ICD-9 Coding First 15 months: 99381, 99382 Initial/New Patient 99391, 99392 Established Patient 3rd- 6th years: 99382, 99383 Initial/New Patient 99392, 99393 Established Patient EPSDT visits must be billed with V20.2 and one of the CPT codes listed. These visits are eligible for additional reimbursement. Initial/New Patient EPSDT $75 • Routine vision and hearing Use additional codes to identify special screening examinations performed. Established Patient EPSDT $62 V20.2 – Routine infant or child health check Only a complete routine infant/child health check is provided. Claim must be billed with one of the CPT codes listed and a listed ICD-9 code. V70.0 – Routine general medical examination at a health care facility (excludes health checkup of infant or child) Initial/New Patient Well-child $63-69 V70.3 – V70.9 as a diagnosis Established Patient Well-child $50-56 Adolescent years: 99383-99385 Initial/New Patient 99391-99395 Established Patient Prenatal Care: 59425 and 59426 Preventive visit code and 9920399215 with modifier 25 Additional Reimbursement V20.2 must be used as the primary diagnosis for the appropriate preventive visit and multiple diagnoses for presenting problem. Sick visits depend on complexity and doctor/patient relationship (new/established) $19-65 When a member presents to a provider for a sick visit, and his or her records indicate the need for an updated EPSDT visit, physicians can include services for both visits and bill two visit codes for reimbursement of both services on the same day. Providers must maintain a complete problem-focused 8-246 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions visit exam for the presenting problem and a complete preventive visit documenting the EPSDT components of the screening exam within the member’s health records. Managed Care Considerations EPSDT is a required component of care for Hoosier Healthwise and Care Select members. If the member is in a Hoosier Healthwise RBMC network, the member’s MCO can provide information. Information on Care Select members can be obtained through the member’s CMO. Hearing Aids Coverage and Billing Procedures If a provider voluntarily provides a loaner hearing aid for a 30-day trial period, the loaner hearing aid for that 30-day trial period does not need PA. Purchase of a hearing aid becomes effective with the authorization of the PA request. Hearing Aid Purchase The IHCP provides reimbursement for the purchase, repair, or replacement of hearing aids under the following conditions: • PA is required for the purchase of hearing aids. • When a member is fitted with a hearing aid by an audiologist or a registered hearing aid specialist, the specialist must complete and submit a medical clearance and audiometric test form with the PA request form. Providers must perform professional audiology services associated with dispensing a hearing aid in accordance with the appropriate provisions of 405 IAC 5-19-13, Hearing aids, purchase. • Hearing aids purchased by the IHCP become the property of the OMPP. • The IHCP does not cover hearing aids for members with a unilateral pure tone average (500, 1,000, 2,000, or 3,000 hertz) equal to or less than 30 decibels. • The IHCP authorizes binaural aids and Contralateral Routing Of Signals (CROS) type aids only when providers can document significant, objective benefit to the member. • The IHCP covers programmable hearing aids when the member meets certain criteria. • Reimbursement of the hearing aid includes dispensing fees, which are not separately billable. • The IHCP does not reimburse for canal hearing aids. Maintenance and Repair The IHCP reimburses for the maintenance and repair of hearing aids as defined in 405 IAC 5-19-14, Hearing aids; maintenance and repairs, under the following conditions: • The IHCP does not require PA for repairs for hearing aids and ear molds; however, the IHCP does not make reimbursement for such repairs more frequently than once every 12 months. Providers can obtain PA for repairs more frequently for members under 18 years of age if the provider documents circumstances justifying the need. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-247 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions • The IHCP does not require PA for batteries, sound hooks, tubing, and cords. Providers must use the appropriate HCPCS code and indicate the number of packages in the quantity field of the CMS-1500 claim form. Note: The IHCP designates one unit of code V5266 to represent four batteries; therefore, when submitting claims to the IHCP for reimbursement, providers are to report one unit of V5266 for each package of four batteries supplied. • The IHCP does not pay for repair of hearing aids still under warranty. • The IHCP does not cover routine servicing of functional hearing aids. • The IHCP makes no payment for repair or replacement of hearing aids necessitated by member misuse or abuse, whether intentional or unintentional. Replacement The IHCP reimburses for the replacement of hearing aids as defined in 405 IAC 5-19-15, Hearing aids; replacement, and under the following conditions: • The IHCP reimburses for the replacement of hearing aids, subject to the conditions listed in the maintenance and repairs section. • Requests for replacement of hearing aids must document all the following: - Change in the member’s hearing status - Purchase date of current hearing aid - Condition of current hearing aid • The IHCP does not replace hearing aids before five years from the purchase date of a previously purchased hearing aid. Providers can prior authorize replacements more frequently for members under 18 years old, if the provider documents circumstances justifying the medical necessity (see 405 IAC 5-22-7 for more information). Audiology Services Audiology services are subject to the following restrictions: • The physician must certify in writing the need for audiology assessment or evaluation. • The audiology service must be rendered by a licensed audiologist or a person registered for his or her clinical fellowship year that is supervised by a licensed audiologist. A registered audiology aide can provide services under the direct on-site supervision of a licensed audiologist under 880 IAC 1-1. • When an audiologist or a registered hearing aid specialist fits a member with a hearing amplification device, the provider must complete a medical clearance and audiometric test form in accordance with the instructions given herein and submitted with the PA request form. Providers must ensure that the form is complete and includes the proper signatures, where indicated. • The IHCP limits audiological assessments to one assessment every three years per member. If more frequent audiological assessments are necessary, providers must obtain PA. • Provisions of audiological services are subject to the following criteria: - Audiologists should enroll in the IHCP and receive direct reimbursement for services rendered. - The contractor reviews all requests for PA on a case-by-case basis. 8-248 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions - - - - The involved professional(s) must complete the member history. The referring physician must complete Part 2 of the Medical Clearance and Audiometric Test Form no earlier than six months before providing the hearing aid. An otolaryngologist must examine children 14 years old and younger. A licensed physician can examine older members if an otolaryngologist is not available. The audiologist must conduct all testing in a sound-free enclosure. If a member is institutionalized and his or her physical or medical condition precludes testing in a sound-free enclosure, the ordering physician must verify medical confinement in the initial order for audiological testing. A licensed audiologist, clinical fellowship year audiologist, or otolaryngologist must conduct the audiological assessment. The IHCP does not reimburse for testing conducted by other professionals and cosigned by an audiologist or otolaryngologist. If the audiological evaluation reveals one or more of the following conditions, the member must be referred to an otolaryngologist for further evaluation: • Speech discrimination testing must indicate a score of less than 60 percent in either ear. • Pure tone testing must indicate an air bone gap of 15 decibels or more for two adjacent frequencies in the same ear with a speech discrimination score of less than 60 percent. The audiologist or registered hearing aid specialist must complete the hearing aid evaluation. Before the IHCP grants PA, providers must document the results of the hearing aid evaluation on the PA request and must indicate that the member can derive significant benefit from amplification. A registered hearing aid specialist must sign the hearing aid contract portion of the audiometric test form. For audiology assessments rendered more frequently than every three years, providers must obtain prior authorization and assess on a case-by-case basis, based on documented otologic disease. Note: For audiology procedures, providers cannot fragment and bill separately. The IHCP considers hearing tests, such as whispered voice and tuning fork, to be part of the general otolaryngology services and may not be reported separately. Basic comprehensive audiometry includes pure tone, air and bone threshold, and discrimination. The IHCP reimburses for all other audiometric testing procedures on an individual basis, based on the medical necessity of the test procedure. The following audiology services do not require PA: • Screening tests indicating the need for additional medical examination; however, screenings are not reimbursed separately • Initial hearing assessments • Determinations of suitability of amplification and recommendations about a hearing aid • Determinations of functional benefit gained by use of a hearing aid The facility’s established per diem rate includes audiology services provided by an NF, large private intermediate care facility for the mentally retarded (ICF/MR), or small ICF/MR. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-249 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Augmentative Communication Devices Coverage and Billing Procedures An Alternative or Augmentative Communication (AAC) device is a device or system that compensates for the loss or impairment of speech function due to a congenital condition, an acquired disability, or a progressive neurological disease. The term includes only equipment used for communication, such as electronic devices. Reimbursement The IHCP reimburses for a communication device if a medical doctor or a doctor of osteopathy orders the device in writing. The IHCP requires PA for a communication device. Requesting practitioners must include medical necessity documentation on or attached to the PA request form that is submitted. As part of the PA request, providers must submit a speech pathologist’s clinical evaluation, substantiating the medical necessity for the communication device. Authorization The IHCP grants authorization of reimbursement for a communication device only when the provider sends the following: • Documentation to substantiate that the member demonstrates sufficient mental and physical ability to benefit from the use of the system • Documentation to substantiate that, in the absence of a communication device, people outside the member’s communication environment cannot effectively understand the member • Documentation to substantiate that the provider reasonably expects that the member’s medical condition will necessitate use of the device for at least two years • Documentation that identifies all communication devices that would meet the member’s communication needs, taking into account the physical and cognitive strengths and weaknesses of the member and the member’s communication environment - The documentation should note the recommended least expensive communication device. • Documentation that the intended use of a computer or computerized device is to compensate for the member’s loss or impairment of communication function (in cases where the provider requests authorization for a computer or computerized device) Trial Period The IHCP does not require a trial period for AAC devices, but the speech-language pathologist who conducts the AAC evaluation may recommend a trial period. The IHCP approves PA for rental of an AAC device for a trial use period when the speech and language pathologist prepares a request that includes the following information: • Duration of the trial period • Examination of the AAC device during the trial period, including all the necessary components, such as mounting device, software, and switches or access control mechanism • Identification of the AAC services provider that will assist the member during the trial period 8-250 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions • Identification of the AAC services provider that will assess the trial period • Evaluation criteria specific to the member, used to determine the success or failure of the trial period • Extension of trial periods and provision of different AAC devices when requested by the speech and language pathologist responsible for evaluating the trial use period Rental Versus Purchase The IHCP contractor determines whether to rent or purchase an approved AAC device, based on the least expensive option to meet the member’s needs. The IHCP denies no AAC device to an eligible member solely because it is not available for rental. Repair and Replacement The IHCP does not authorize replacement of an augmentative communication device more often than once every five years per member, unless a documented change in the member’s medical needs arises and is significant enough to warrant a different type of equipment. Rehabilitation Engineering Subject to PA, the IHCP covers rehabilitation engineering service necessary to mount or make adjustments to a communication device. The IHCP also covers speech therapy services as medically necessary to aid the member in the effective use of a communication device, subject to this rule and 405 IAC 5-22, Nursing and Therapy Services. Pneumatic Artificial Voicing Systems Coverage and Billing Procedures For a pneumatic artificial voice system or artificial larynx, the IHCP reimburses subject to PA. The IHCP grants PA only when the provider sends the following: • Documentation to substantiate that the member demonstrates sufficient mental and physical ability to benefit from the use of the system • Documentation to substantiate that the member demonstrates sufficient articulation and language skills to benefit from the use of the system Purchase When a provider supplies a pneumatic artificial voice system or an artificial larynx to a member on an inpatient basis, the attendant costs fall under the established per diem rate for the hospital or LTC facility. The provider should not bill for attendant costs separately. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-251 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Home and Community-Based Services Waiver Programs Coverage and Billing Procedures The IHCP reimburses Home and Community-Based Services (HCBS) waiver providers for covered services they provide to waiver members using a standard, statewide rate-setting methodology. The OMPP establishes waiver service rates and rate capitations. All waiver providers, including home health agencies, should continue to bill waiver services on the CMS-1500 or 837P. Note: Providers should verify member eligibility on the 1st and 15th of the month, because member eligibility in managed care is effective on the 1st and 15th calendar days of the month. If a member is enrolled in Hoosier Healthwise, contact that member’s MCO immediately. MCO contact information is included in Chapter 1. If the member is identified as a Care Select member, contact the care management organization (CMO) to which the member is assigned. Supportive documentation is required when billing for waiver services. The documentation requirements are defined in the waiver service definition specific to the waiver service provided. The documentation must include the following: • Complete date of service, including month, day, and year • Time entry for service provided, including the time in and time out, noting a.m. and p.m., as appropriate, unless the provider chooses to use 24-hour time notations. Providers should ensure consistent notation of time, either standard notation or 24-hour notation. • Number of units of service delivered on that date. • Signature of any staff member providing the service or making entries into the documentation. Signature must include a minimum of the first initial and last name, and must include the staff member’s certification or title. To receive appropriate reimbursement, the provider must bill only the waiver services and procedure codes shown on the approved notice of action (NOA). Providers must ensure that the documentation of the service rendered and the procedure code billed are in accordance with the service definition and parameters as published in the approved waiver. In addition, the service must be authorized on the client’s NOA and listed on the member’s prior authorization file. In an institutional setting (for example, hospitalized or incarcerated), the only HCBS waiver service for which a provider can render and receive reimbursement is case management. The IHCP prohibits reimbursement for other services including, but not limited to, respite, residential habilitation and support (RHS), and behavior management while the member is institutionalized. For service providers that use electronic signatures for documentation, a specific policy must be in place on how electronic signatures will be done, controlled, and verified. Please see the Electronic Digital Signatures Act (IC 5-24) and the Uniform Electronic Transactions Act (IC 26-2-8). The State Board of Accounts has promulgated a rule at 20 IAC 3 with additional regulations. These citations are specific to documents transmitted to the state. 8-252 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Injections Coverage and Billing Procedures With the exception of vaccines available through the Vaccines for Children (VFC) Program, the IHCP calculates the maximum allowable amount for reimbursement for physician office-administered injectable drugs, using HCPCS J codes and CPT immunization codes, on the basis of the most costeffective, current, reimbursement for an appropriate NDC, identified as the benchmark NDC. The maximum allowable reimbursement is equal to Wholesale Acquisition Cost (WAC) plus 5 percent (WAC+5%) of the benchmark NDC or, if no WAC data is available, CMS’ reimbursement, which is currently Average Sales Price (ASP) plus 6 percent (ASP+6%). The maximum allowable cost corresponds to the dose in the narrative description of the HCPCS or CPT code. When the provider specifies no dose in the narrative, the reimbursement rate is set by the contractor responsible for updating the rates based on what corresponds to a typical dose for the particular code. The IHCP notifies providers through bulletins or banner pages about reimbursement rates for codes that have no dose or are dose-unspecified. For injectable drugs, vaccines that are not part of the VFC program, and vaccines typically part of the VFC program but supplied out of private stock, providers may separately bill an appropriate CPT administration code, 96372 - 96373, in addition to the HCPCS J-code or CPT drug code. If an E/M code is billed with the same date of service as an office-administered drug, the provider should not bill a drug administration code separately. Reimbursement for administration is included in the E/M code allowed amount. Separate reimbursement is allowed when the administration of the drug is the only service billed by the practitioner. In addition, if more than one injection is given on the same date of service and no E/M code is billed, providers may bill a separate administration fee for each injection using the appropriate codes. The IHCP reviews pricing for physician office-administered injectable drugs quarterly and updates pricing according to WAC data in the drug database file received from First DataBank. If no WAC data is available, Medicare’s reimbursement, currently ASP+6%, is used. The IHCP limits joint injections to three injections per joint site, per provider, per month. Claims submitted for more than three injections in a one-month period must have supporting documentation attached to indicate that the provider administered no more than four injections to a single joint site. Providers can utilize the claim note section to document that the injections are performed on different joints and indicate the site of the injection. The IHCP limits Vitamin B12 injections to one per 30 days per member. When a provider cannot use an existing CPT or HCPCS code to bill for new injectable drugs that the IHCP covers because the IHCP has not assigned a specific code, the provider should use an appropriate nonspecific CPT or HCPCS code such as J3490 – Unclassified drugs or 90749 – Unlisted immunization procedure to bill. Providers can use a nonspecific CPT or HCPCS code only when no code is available with a narrative that accurately describes the drug being administered or the drug’s route of administration. The IHCP manually prices drugs billed with a nonspecific CPT or HCPCS code, and providers must submit them with an attachment. For all CMS-1500 claims or 837P transactions billed with a nonspecific code, providers must write the NDC qualifier, NDC, NDC unit of measure, and number of units administered on the claim itself; otherwise, the IHCP must deny the claim. The IHCP reimburses for nonspecific codes at the WAC+5% – or ASP+6% if no WAC data is available – of the National Drug Code (NDC) indicated on the claim form, multiplied by the number of units administered. For electronic 837 transactions, providers can indicate the NDC for the drug dispensed in the NDC field. The NDC quantity and unit of measure must also be provided. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-253 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions The Federal Deficit Reduction Act of 2005 requires that NDCs are submitted on the CMS-1500 in the shaded area of field 24a beginning August 1, 2007. Because the State may pay up to the 20 percent Medicare B copayment for dual-eligible individuals, the NDC is required on Medicare crossover claims for all applicable procedure codes. Remittance Advice The Remittance Advice (RA) will not display the NDC submitted on the claim. The following edits will be activated as a part of claims processing: • Edit 0217 – NDC number is missing. • Edit 0218 – NDC number is not in a valid format. • Edit 0219 – Quantity dispensed or quantity billed information is missing. • Edit 4003 – Less than effective drugs are not covered under Indiana Health Coverage Programs. Note: Additional information how drugs are determined to be less than effective is located at: http://www.cms.hhs.gov/MedicaidDrugRebateProgram/12_LTEIRSDrugs.asp. A list of noncovered, less than effective drugs (DESI) is located at: http://www.cms.hhs.gov/MedicaidDrugRebateProgram/downloads/desi.pdf. • Edit 4004 – This NDC is not on file. Please verify that the NDC was filed correctly. • Edit 4007 – Noncovered NDC due to CMS Termination – Claims with an NDC that has been terminated by the CMS will not be reimbursable. • Edit 4300 – Invalid NDC to procedure code combination. • Edit 0810 – NDC Unit Qualifier (unit of measure) is missing. • Edit 1016 – Nonparticipating Manufacturer – Claims with an NDC from a nonrebating manufacturer will be denied and are not reimbursable. Note: CMS maintains a list of rebating labelers located at: http://www.cms.hhs.gov/MedicaidDrugRebateProgram/10_DrugComCon tactInfo.asp. Providers can also contact their wholesaler or drug supplier to determine if products supplied are from CMS rebating labelers. Procedure Codes Procedure codes that require the submission of the product NDC and NDC quantity, along with the procedure code and procedure code billing units, are listed on the Indiana Medicaid Web site. This list is reviewed and updated on an annual basis, or as determined by the OMPP. The procedure codes listed in the document located at http://provider.indianamedicaid.com/media/28002/pg%20154%20codes%20as%20of%205_06_08.pdf do not guarantee coverage. About the NDC Medication listed under Section 510 of the U.S. Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act is assigned a unique 11-digit, three-segment number. This number, known as the National Drug Code (NDC), identifies the labeler or vendor, product, and package size. The first segment, known as the labeler code, is assigned by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). A labeler is any firm that manufactures, repacks, or distributes a drug product. The second segment, known as the product code, 8-254 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions identifies a specific drug, strength, and dosage form of that drug. The third segment, known as the package code, identifies the package size. For purposes of meeting the new billing requirement, NDCs must be configured in what is referred to as a “5-4-2” format; the first segment must include five digits, the second segment must include four digits, the third segment must include two digits. If an NDC segment is missing a number on the product label, the appropriate number of zeros must be added at the beginning of the segment. For example, 12345-1234-12 is a correctly configured NDC. Because a zero can be a valid digit in the NDC, this can lead to confusion when trying to reformat the NDC back to its FDA standard. Example: 12345-0678-09 (11 digits) could appear as 12345-678-09 or 12345-0678-9 on the label, depending on the labeler’s configuration. To ensure proper payment of claims, the NDC must be zero-padded as appropriate. The procedure code billing units, as well as the NDC quantity, are required. To report the NDC on the CMS-1500 claim form, enter the following information into the shaded portion of fields 24A to 24H: • Enter the NDC qualifier of N4 • Enter the NDC 11-digit numeric code • Enter the drug description • Enter the NDC Unit qualifier - F2 – International Unit - GR – Gram - ML – Milliliter - UN – Unit • Enter the NDC Quantity (Administered Amount) in the format 9999.99 NDC Quantity The procedure code billing units and NDC quantity do not always have a one-to-one relationship. The NDC quantity is based on the strength of the drug administered per unit, and the designated strength of the procedure code. The NDC quantity billed must be reflective of the procedure code quantity billed on the claim. Compounds – Professional Claim Types When billing any compound drugs that require an NDC, providers must bill the appropriate NDC for each procedure code. Providers will receive payment for all valid NDCs included in the compound drugs. When billing NDCs that have one procedure code but that involve multiple NDCs, providers will no longer need to use the KP and KQ modifiers. Providers will bill the claim with the appropriate NDC for the drug they are dispensing on separate detail lines. For example, if a provider administers 150 mg of Synagis, most likely a 50 mg vial plus a 100 mg vial would be used. These two vials have different NDCs but one procedure code; therefore, the item would be billed with two detail lines for the same procedure code and the corresponding NDCs. This change includes crossover claims as well. Botulinum Toxin Coverage and Billing Procedures Currently there are three available botulinum toxin products: Botox (J0585), Dysport (J0586), and Myobloc (J0587). Providers should be aware that the potency units of these products are not interchangeable with each other and, therefore, units of biological activity of one product cannot be compared to or converted into units of other bolulinum toxin products. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-255 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Due to the short life of these products, the IHCP has developed the following policies when providers administer less than a full vial in a single treatment session. • Because botulinium toxin type A is supplied in 100 unit vials, it will be appropriate for the provider to bill the entire 100 units to Indiana Medicaid when less than 100 units are injected in a single treatment session and the balance of the product is discarded. If more than 100 units are injected in a single treatment session, and the remainder is not used for another patient, round the number of units billed on the claim up to the nearest 100 units. Whenever unused botulinium toxin type A is billed, both the amount of the agent actually administered and the amount discarded is to be documented in the patient’s medical record. • Due to the short shelf life of Myobloc, wastage of the product may be unavoidable. The IHCP has adopted the following policy for billing unused units of Myobloc. Myobloc is supplied in 2,500 units, 5,000 units, and 10,000 units. When billing for Myobloc, the provider must show the number of units given on the claim form. If a vial is split between two or more members, the provider must bill the amount of the Myobloc used for each member and bill the unused amount as wastage on the claim for the last member injected. If the provider does not split the vial between two or more members, the provider may bill the discarded portion to the IHCP. Whenever a provider bills for unused Myobloc, the provider must document the amount of agent actually administered and the amount discarded in the member’s medical record. • Similarly, the IHCP has adopted the following policy for billing unused units of Dysport (J0586). Dysport is supplied in 300 unit and 500 unit preservative-free, single-use vials. When billing for Dysport, the provider must show the number of units given on the claim form and may bill the discarded portion to the IHCP. Whenever a provider bills for unused Dysport, the provider must document the amount of agent actually administered and the amount discarded in the member’s medical record. Providers should bill botulinum toxin injections using the appropriate HCPCS codes. Table 8.74 – HCPCS Codes for Botulinum Toxin Injections HCPCS Code Code Description J0585 Injection, onabotulinumtoxina, 1 unit J0586 Injection, abobotulinumtoxina, 5 units J0587 Injection, rimabotulinumtoxinb, 100 units IHCP reimbursement for botulinum toxin injections must include one of the following CPT codes available for billing chemodenervation, listed in Table 8.75. Table 8.75 – CPT Codes for Chemodenervation for use with Botox and Myobloc Injections CPT Code Definition 42699 Unlisted procedure, salivary glands or ducts 43201 Esophagoscopy, rigid or flexible; with directed submucosal injections, any substance 43236 Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy including esophagus, stomach, and either the duodenum and/or jejunum as appropriate; with directed submucosal injection(s), any substance 46505 Chemodenervation of internal anal sphincter 53899 Unlisted procedure, urinary system 64612 Chemodenervation of muscle(s); muscle(s) innervated by facial nerve (e.g., for blepharospasm, hemifacial spasm) 8-256 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions CPT Code Definition 64613 Chemodenervation of muscle(s); cervical spinal muscles(s) (e.g. for spasmodic torticollis) 64614 Chemodenervation of muscle(s); extremity(s) and/or trunk muscle(s) (e.g., for dystonia, cerebral palsy, multiple sclerosis) 64650 Chemodenervation of eccrine glands; both axillae 64653 Chemodenervation of eccrine glands; other area(s) (eg., scalp, face, neck), per day 67345 Chemodenervation of extraocular muscle 95873 Electrical stimulation for guidance in conjunction with chemodenervation (List separately in addition to code for primary procedure) 95874 Needle electromygraphy for guidance in conjunction with chemodenervation (List separately in addition to code for primary procedure) As of July 1, 2005, the IHCP limits reimbursement for Botox and Myobloc injections to the ICD-9-CM diagnosis codes listed in Table 8.76. Table 8.76 – ICD-9-CM Diagnosis Codes for Botox and Myobloc Injections Diagnosis Codes 333.6 333.89 341.9 343.3 344.03 344.32 378.00 378.07 378.15 378.23 378.35 378.50 378.60 378.81 378.9 596.54 333.71 334.1 342.10 343.4 344.04 344.40 378.01 378.08 378.16 378.24 378.40 378.51 378.61 378.82 478.29 596.55 333.79 340 342.11 343.8 344.09 344.41 378.02 378.10 378.17 378.30 378.41 378.52 378.62 378.83 478.75 705.21 333.81 341.0 342.12 343.9 344.1 344.42 378.03 378.11 378.18 378.31 378.42 378.53 378.63 378.84 478.79 723.5 333.82 341.1 343.0 344.00 344.2 374.03 378.04 378.12 378.20 378.32 378.43 378.54 378.71 378.85 527.7 729.1 333.83 341.22 343.1 344.01 344.30 374.13 378.05 378.13 378.21 378.33 378.44 378.55 378.72 378.86 530.0 754.1 333.84 341.8 343.2 344.02 344.31 351.8 378.06 378.14 378.22 378.34 378.45 378.56 378.73 378.87 565.0 These diagnosis codes reflect medically necessary diagnoses for these injections. The IHCP also limits reimbursement of these injections to one treatment session every three months, per member, unless an additional injection is medically necessary. The medical record must contain documentation of the medical necessity for additional treatment sessions provided within a three-month period. Vaccines for Children Program The IHCP encourages providers to bill drugs on the IFSSA Drug Claim Form instead of billing unlisted codes on a CMS-1500 or 837P. Chapter 9 in this manual provides instructions for completing the IFSSA Drug Claim Form. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-257 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions The section in this chapter titled Vaccines for Children provides information about billing procedures and reimbursement for vaccines available through the VFC Program. Laboratory Services Coverage and Billing Procedures The IHCP defines a laboratory as any facility that performs laboratory testing on specimens derived from humans to provide information for the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of disease, or for information about impairment or assessment of health. Providers must order all laboratory services in writing and include a condition-related diagnosis that necessitates the laboratory services. Providers should use the pathology and laboratory guidelines noted in the CPT and HCPCS codes when billing laboratory services. To receive reimbursement from the IHCP for laboratory services falling under Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendment (CLIA) regulations, the provider must have a valid copy of the CLIA certificate on file with the contractor and must bill only lab codes allowed by the certificate. The section in Chapter 4 of this manual titled Provider Eligibility gives further information about CLIA, or the provider can contact the ISDH at (317) 233-7502. Provider types subject to CLIA rules include those in Table 8.77. Table 8.77 – CLIA Provider Types CLIA Code Description 01 Hospitals, type/specialty 010–012 04 Rehabilitation facilities 05 Home health agencies 06 Hospices 08 Clinics, type/specialty 080–085 11 Mental health, type/specialty 110–111 13 Public health agencies 14 Podiatrists 15 Chiropractors 28 Laboratories, type/specialty 280–281 30 End-stage renal disease clinics 31 Physicians, all types/specialties Refer to the CMS Web site for information about the procedures that are eligible for reimbursement under specific CLIA certificates. For more information, go to the Web site http://www.cms.hhs.gov/clia and select Categorization of Tests. Clinical Diagnostic Laboratory Procedures When billing for clinical diagnostic tests, providers must indicate the appropriate CPT or HCPCS code on the claim form. Laboratories performing services must bill the IHCP directly unless otherwise specified by the CMS. If the provider administers the procedure more than one time in the same day, the provider should bill it as only one line item, with an indication of the number of units of service given that day. 8-258 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions The IHCP reimburses for clinical diagnostic laboratory procedures, performed in a physician’s office, by an independent laboratory, or by a hospital laboratory for outpatients, on the basis of the following: • The lower of the submitted charge or the Medicare Lab Fee Schedule • The lower of the submitted charge or the RBRVS For procedures on the Medicare Fee Schedule that do not have Relative Value Units (RVUs), the IHCP reimburses based on the Medicare Clinical Laboratory Fee Schedule or manual pricing methodology, if a rate has not yet been established by Medicare. On the Medicare Fee Schedule, some procedures do not have RVUs because the procedure meets one of the following criteria: • Associated with special restrictions • Carrier-priced • Excluded from the definition of physician services • Excluded from the Medicare Fee Schedule • Noncovered by Medicare • Not valid for Medicare For laboratory procedures not covered by the Medicare Fee Schedule as not meeting the definition of physician-provided services, the IHCP reimburses from the Medicare Clinical Laboratory Fee Schedule. The IHCP reimburses through manual pricing until Medicare assigns a rate for codes for which Medicare has not yet established a specific rate, either in the Medicare Fee Schedule or in the Medicare Clinical Laboratory Fee Schedule. Clinical diagnostic laboratory services include all laboratory tests listed in codes 80048 through 89356, as well as some G, P, and Q codes listed in the HCPCS Level II Code book. Blood or blood products, blood testing, and tests involving physician interpretation are exceptions. When providers submit codes from the list of codes in Table 8.78 on the same claim form with codes corresponding to blood or blood products, the codes are not subject to pricing by the Medicare fee schedule. If providers submit the codes without charges for blood or blood products, the IHCP classifies the services as clinical diagnostic lab tests, subject to pricing by the Medicare fee schedule. Table 8.78 – CPT Codes – Blood or Blood Products CPT Code Description 86021 Antibody identification; leukocyte antibodies 86022 Antibody identification; platelet antibodies 86880 Antihuman globulin test (Coombs test); direct, each antiserum 86885 Antihuman globulin test (Coombs test); indirect, qualitative, each antiserum 86886 Antihuman globulin test (Coombs test); indirect, titer, each antiserum 86900 Blood typing; ABO 86901 Blood typing; Rh (D) 86903 Blood typing; antigen screening for compatible blood unit using reagent serum, per unit screened 86904 Blood typing; antigen screening for compatible unit using patient serum, per unit screened 86905 Blood typing; RBC antigens, other than ABO or Rh (D), each Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-259 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions CPT Code Description 86906 Blood typing; Rh phenotyping, complete 86910 Blood typing, for paternity testing, per individual; ABO, Rh and MN 86911 Blood typing, for paternity testing, per individual; each additional antigen system 86970 Pretreatment of RBCs for use in RBC antibody detection, identification, and/or compatibility testing; incubation with chemical agents or drugs, each 86971 Pretreatment of RBCs for use in RBC antibody detection, identification, and/or compatibility testing; incubation with enzymes, each 86972 Pretreatment of RBCs for use in RBC antibody detection, identification, and/or compatibility testing; by density gradient separation 86975 Pretreatment of serum for use in RBC antibody identification; incubation with drugs, each 86976 Pretreatment of serum for use in RBC antibody identification; by dilution Pretreatment of serum for use in RBC antibody identification; incubation with inhibitors, each 86977 86978 Pretreatment of serum for use in RBC antibody identification; by differential red cell absorption using patient RBCs or RBCs of known phenotype each absorption Professional and Technical Components Some clinical diagnostic laboratory procedures encompass professional and technical components of service. A physician typically performs the professional component of the lab procedure. The IHCP reimburses the physician for the professional component because the physician bills the appropriate CPT lab code along with modifier 26, professional component. When billing only the technical component, providers should append modifier TC, technical component, with the appropriate CPT lab code. When billing for professional and technical components of service, providers should use no modifiers. Providers should bill the appropriate lab code only. Look in the Federal Register under Relative Value Units and Related Information to see a list of lab codes billed using these modifiers. Hospital Outpatient Defined The IHCP defines hospital outpatient as a member who the hospital has not admitted as an inpatient but is registered in hospital records as an outpatient and receives services directly from the hospital. If personnel not employed by the hospital take a tissue sample, blood sample, or specimen and send it to the hospital for tests, the IHCP classifies the tests as nonpatient (rather than outpatient) hospital services, because the patient did not directly receive services from the hospital. Specimen Collection The IHCP allows a minimal fee for separate charges made by physicians, independent laboratories, or hospital laboratories for drawing or collecting specimens. The IHCP covers these services only when the provider draws a blood sample through venipuncture or collects a urine sample by catheterization. Providers must itemize specimen collection fees when billing for them. The IHCP allows only one charge per day for each patient for venipuncture. The IHCP allows a charge for catheterization for each patient encounter and does not limit this service per day. 8-260 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Handling Conveyance The IHCP allows a fee for physicians, chiropractors, and podiatrists for handling and conveying a specimen to a laboratory (405 IAC 5-18-2 c). The IHCP reimburses providers for no more than two conveyance fees (CPT procedure codes 99000 and 99001) on the same date of service. Providers can charge this only if the physician has an expense involved in conveyance. Lab Panels Organ or disease-oriented panels were developed to allow for coding of a group of tests. Providers are expected to bill the lab panel when all the tests listed within each panel are performed on the same date of service. When one or more of the tests within the panel are not performed on the same date of service, providers may bill each test individually. Providers may not bill for a panel and all the individual tests listed within that panel on the same day. However, tests performed in addition to those listed on the panel on the same date of service may be reported separately in addition to the panel code. Providers must follow CPT coding guidelines when reporting multiple panels. For example, providers cannot report 80048 with 80053 on the same date of service because all the same lab codes in 80048 are components of 80053. Interpretation of Clinical Laboratory Services The CMS has identified certain procedures as clinical lab tests that frequently require a laboratory physician to interpret. The physician can bill these codes with the 26 modifier. The IHCP covers consultative pathology services for clinical laboratory tests if the claim meets the following conditions: • The patient’s attending physician requested the service in writing. • The service relates to a test that lies outside the clinically significant normal or expected range in view of the condition of the patient. • The service results in a written narrative report in the patient’s medical record. • The service requires the exercise of medical judgment by the consulting physician. Hospice providers should note that they must not include costs for services, such as laboratory and Xrays, with the attending physician’s billed charges. The daily hospice care rates that the IHCP pays include these costs, and they are expressly the responsibility of the hospice provider. Breast Cancer Testing Providers should use the codes in Table 8.79 to bill HER2 protein over expression tests, HercepTest®, as an aid in assessment of patients who use trastuzumab, HERCEPTIN®. Table 8.79 – CPT Codes for HER2 Test CPT Code Description 88342 Immunohistochemistry, including tissue immunoperoxidase, each antibody 88365 Tissue in situ hybridization (e.g, FISH), each probe HER-2/neu Gene Detection Test, such as Oncor’s INFORM®, is an adjunct to existing clinical and pathological information and an aid to stratify breast cancer patients with a primary, invasive, or localized breast cancer, who are lymph node negative, for risk of recurrence or disease-related death. Providers use this test as a prognostic indicator and should use the codes in Table 8.80 to bill it. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-261 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Table 8.80 – CPT Codes for HER-2/neu Gene Detection Test CPT Code Description 83892 Molecular diagnostics; enzymatic digestion 88271 Molecular cytogenetics; DNA probe, each, for example, FISH 88274 Molecular cytogenetics; interphase in situ hybridization, analyze 25–99 cells. (Either code 88274 or 88275 should be billed.) 88275 Molecular cytogenetics; interphase in situ hybridization, analyze 100–300 cells. (Either code 88274 or 88275 should be billed.) 88291 Cytogenetics and molecular cytogenetics, interpretation and report Billing Requirements and Prior Authorization Criteria for Genetic Testing for Breast and Ovarian Cancer The IHCP reimburses for genetic testing for breast and ovarian cancer (BRCA) 1 and BRCA 2 genetic testing when medically necessary, with prior authorization (PA) billed with the appropriate HCPCS codes shown in Table 8.81 and the appropriate ICD-9-CM diagnosis codes shown in Table 8.82. The IHCP limits HCPCS codes S3820, S3822, and S3823 to once per lifetime. If the IHCP has provided reimbursement for HCPCS code S3820, the IHCP will not reimburse S3822 or S3823 for that member because S3820 represents complete BRCA 1 and BRCA 2 gene sequence analysis. IHCP reimbursement is not available for BRCA testing reported with the HCPCS codes listed in Table 8.83. However, reimbursement is available for the codes listed in Table 8.83 for genetic testing related to other types of cancer, such as pancreatic carcinoma. The IHCP gives PA for genetic testing related to breast and ovarian cancer, using the HCPCS codes listed in Table 8.81 when medically necessary in the following circumstances. Providers must submit documentation with the PA request and must maintain it in the member’s medical record. • Clinically affected individuals (invasive breast cancer or ovarian cancer at any age) meeting at least one of the following criteria: - One or more first-degree (mother, father, sister, or daughter) or second-degree (aunt, uncle, grandmother, niece, or granddaughter) relatives with invasive breast cancer diagnosed before age 50 - One or more first- or second-degree relatives with ovarian cancer - One or more first- or second-degree relatives with male breast cancer • Individuals with a personal history of at least one of the following (no family history required): - Invasive breast cancer before age 50 - Ovarian cancer at any age - Invasive breast cancer and ovarian cancer at any age - Male breast cancer at any age • Individuals with a family member (related by blood) with a known BRCA 1 or BRCA 2 mutation • Individuals with Ashkenazi (Eastern European) Jewish ancestry with invasive breast cancer at any age, or meeting any of the criteria listed above 8-262 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions The IHCP considers BRCA testing of men with breast cancer medically necessary for either of the following indications: • To assess the man’s risk of recurrent breast cancer; or • To assess the breast cancer risk of a female member where the affected male is a first- or seconddegree blood relative of that member - The IHCP considers BRCA 1 and BRCA 2 testing to assess the risk of breast or prostate cancer in men without breast cancer to be not medically necessary. Table 8.81 – HCPCS Codes to Report Genetic Testing for Breast and Ovarian Cancer Diagnoses Only Code Description Comments S3820 Complete BRCA 1 and BRCA 2 gene sequence analysis for susceptibility to breast and ovarian cancer S3820 encompasses all the testing for all the genetic variations involving BRCA 1 and BRCA 2. Testing required is more extensive than required for the specific gene variations reported by S3822 and S3823. S3822 Single mutation analysis (in individual with a known BRCA 1 or BRCA 2 mutation in the family) for susceptibility to breast and ovarian cancer S3822 designates the test required for detection of BRCA gene mutation for an individual with a family member known to have BRCA 1 or BRCA 2 mutation. S3823 Three-mutation BRCA 1 and BRCA 2 analysis for susceptibility to breast and ovarian cancer in Ashkenazi individuals S3823 reports genetic testing for individuals of Ashkenazi Jewish descent. Because there are known to be fewer and more specific changes in this population group, the amount of testing required is significantly less than for the general population. Table 8.82 – ICD-9-CM Codes Supporting Medical Necessity Code Description 174.0 Malignant neoplasm of female breast; nipple and areola 174.1 Malignant neoplasm of female breast; central portion 174.2 Malignant neoplasm of female breast; upper-inner quadrant 174.3 Malignant neoplasm of female breast; lower-inner quadrant 174.4 Malignant neoplasm of female breast; upper-outer quadrant 174.5 Malignant neoplasm of female breast; lower quadrant 174.6 Malignant neoplasm of female breast; axillary tail 174.8 Malignant neoplasm of female breast; other specified sites of breast 175.0 Malignant neoplasm of male breast; nipple and areola 175.9 Malignant neoplasm of male breast; other and unspecified sites of male breast 183.0 Malignant neoplasm of ovary and other uterine adnexa; ovary 183.2 Malignant neoplasm of ovary and other uterine adnexa; fallopian tube 183.3 Malignant neoplasm of ovary and other uterine adnexa; broad ligament 183.4 Malignant neoplasm of ovary and other uterine adnexa; parametrium 183.5 Malignant neoplasm of ovary and other uterine adnexa; round ligament Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-263 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Code Description 183.8 Malignant neoplasm of ovary and other uterine adnexa; other specified sites of uterine adnexa 183.9 Malignant neoplasm of ovary and other uterine adnexa; uterine adnexa, unspecified V10.3 Personal history of malignant neoplasm; breast V10.43 Personal history of malignant neoplasm; ovary V16.3 Family history of malignant neoplasm; breast V16.41 Family history of malignant neoplasm; ovary Table 8.83 – CPT/HCPCS Codes to Report Other Genetic Testing Not to be Used for Breast and Ovarian Cancer Diagnoses Code 83891 83898 83904 Definition Molecular diagnostics; isolation or extraction of highly purified nucleic acid Molecular diagnostics; amplification of patient nucleic acid, each nucleic acid sequence Molecular diagnostics; mutation identification by sequencing, single segment, each segment 83912 S3818 S3819 Molecular diagnostics; interpretation and report Complete gene sequence analysis; BRCA 1 gene Complete gene sequence analysis; BRCA 2 gene Lead Testing For lead testing in the office setting, the coverage and reimbursement rate for code 83655 includes tests administered using filter paper and handheld testing devices. The following procedure codes and modifier combinations are effective December 1, 2007. Table 8.84 – New Codes for Lead Testing Procedure Code Description 83655 U1 Assay of lead, using filter paper 83655 U2 Assay of lead, using handheld testing device 83655 Assay of lead (venous blood) Reimbursement Rate $10.00 $5.00 $16.72 Medical and Surgical Supplies Coverage and Billing Procedures Medical and surgical supplies (medical supplies) are items that are disposable, nonreusable, and must be replaced on a frequent basis. The IHCP covers some medical supplies and does not cover others. Providers use medical supplies primarily and customarily to serve a medical purpose, and medical supplies are generally not useful to a person in the absence of an illness or an injury. To the extent that the IHCP covers a medical supply item, it is a reimbursable service only when medically necessary. A physician or a dentist must prescribe all medical supplies and must document the need for such items. Covered medical supplies include, but are not limited to, antiseptics and solutions, bandages and 8-264 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions dressing supplies, gauze pads, catheters, incontinence supplies, irrigation supplies, diabetic supplies, ostomy supplies, and respiratory and tracheotomy supplies. The IHCP requires providers to submit claims for medical supplies on the paper CMS-1500 claim form or 837P transaction using HCPCS codes. Providers should send all claims for medical supplies to HP using HCPCS codes. The IHCP denies all claims submitted on the pharmacy form, using NDCs, Health Related Item (HRI) codes, Universal Package Codes (UPCs), or Product Identification Numbers (PINs). Reimbursement for medical supplies is equal to the lower of the provider’s submitted charges (usual and customary) or the Medicaid calculated allowable for the item. The Medicaid calculated allowable for an item is the statewide fee schedule amount. Providers must include their usual and customary charge for each medical supply item when submitting claims for reimbursement. Providers should not use the Medicaid calculated allowable for their billed charge unless the Medicaid calculated allowable is equal to the amount charged by the provider to the general public. Limitations on Coverage When providers include medical supplies in LTC facility reimbursement (nursing facilities, group homes, intermediate care facilities for the mentally retarded) or otherwise include them as part of reimbursement for a medical or surgical procedure, LTC providers must always include them as part of their NF per diem. Under no circumstances should a pharmacy, LTC facility, or any other provider separately bill such supplies to the program. This requirement includes all covered medical supplies that are included in the LTC provider’s per diem rate, even if the LTC facility does not include the cost of medical supplies in its cost report. The IHCP does not reimburse for medical supplies provided in quantities greater than a one-month supply for each calendar month, except when the manufacturer packages those supplies only in larger quantities. Medical supplies must be for a specific medical purpose, not incidental or general-purpose usage. All covered sterile water products, with the exception of those required for compounded prescriptions, are included in the nursing home per diem and are, therefore, not separately reimbursable. Covered sterile water products are billable with an NDC on the pharmacy claim form. Manually Priced Supplies For medical supplies that are billed with a nonspecific HCPCS code with a description such as unspecified, unclassified, or miscellaneous, the IHCP bases reimbursement on manual pricing. Payment for manually priced HCPCS codes, related to medical supplies, is specific to the item being billed. Providers must submit documentation supporting the cost of the item, including a listing of all materials. The IHCP uses the following guidelines to determine reimbursement: • If the provider submits an itemized sales invoice from the manufacturer listing all materials or supplies purchased and showing the price paid for individual items, the IHCP reimburses the claim at the billed amount, up to 30 percent above the invoice amount. The IHCP does not accept a manufacturer’s price list as proof of purchase price for this level of reimbursement. • If a provider submits retail price lists from the manufacturer, the IHCP reimburses the claim at 90 percent of the price on the manufacturer’s retail price list but cannot exceed the billed amount. • If the provider submits a copy of the provider’s own retail price list or an invoice from the provider’s own company that indicates the price that a provider charges the general public for Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-265 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions products or supplies, the IHCP reimburses the claim at 90 percent of the invoice or price list, not to exceed the billed amount. Providers must not bill more than their usual and customary charge for any item. All nonspecific HCPCS codes may be subject to retrospective review. Medicare Part B Crossover Claims Coverage and Billing Procedures Crossover claims filed with the IHCP must comply with IHCP billing rules. Therefore, providers must bill services on the appropriate claim form. There is no filing limit for paid Medicare crossover claims. Note: Providers should bill outpatient professional charges on the CMS-1500 or 837P. Always submit ambulatory surgery center charges on a UB-04 or 837I. FQHCs, hospital-based ambulance services, and independent RHCs submit claims to the Medicare intermediary on the UB-04 or 837I, but they must submit claims to the IHCP on the CMS-1500 or 837P. Providers must submit LTC facility Medicare charges for parenteral/enteral services and therapies to the IHCP on the UB-04 claim form or 837I transaction. Refer to the UB-04 Billing Instructions section of this chapter for instructions on completing a UB-04 crossover claim form. The CMS-1500 form must contain the combined total of the Medicare coinsurance, deductible, and psych reduction when applicable, in the left side of field 22, under the heading Code. Providers must submit the Medicare paid amount (actual dollar amount received from Medicare) in field 22 on the right side, under the heading Original Ref No. Additionally, in field 29, providers must enter only a total payment amount received from a TPL, if applicable. Do not include the Medicare paid amount or contract adjustment in field 29. The IHCP requires the Medicare Remittance Notice only for claims containing a zero paid amount by Medicare. Note: Providers should submit Medicare denials through the normal claims process, because the IHCP does not consider them crossover claims. Medicare/Medicaid Reimbursement Providers must be Medicare providers and accept assignment for a claim for dually eligible members to cross over. Detailed information about Medicare-Medicaid related reimbursement appears in Chapter 5 of this manual. Atypical providers must ensure that the Medicare provider number, per service location, by individual provider and billing provider, is on file with the HP Provider Enrollment Unit. Chapter 4 of this manual provides further information about provider enrollment. 8-266 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Mental Health Services Coverage and Billing Procedures Providers furnishing mental health services to members enrolled in Care Select must follow existing PA guidelines. Some mental health services are no longer carved out and providers must submit RBMC member claims to the member’s MCO for payment. Services that require PA furnished to members enrolled in RBMC must be prior-authorized by the MCO in accordance with the MCO guidelines. Refer to http://provider.indianamedicaid.com/provider-specific-information/managedcare/hoosier-healthwise.aspx. As stated in 405 IAC 5-20-8, the IHCP also allows direct reimbursement for outpatient mental health services provided by licensed physicians, psychiatric hospitals, psychiatric wings of acute care hospitals, outpatient mental health facilities, and psychologists endorsed as health services providers in psychology (HSPP). Outpatient mental health services rendered by or under supervision of a physician or HSPP are subject to the limitations in 405 IAC 5-25 and are subject to the following limitations. Subject to PA by the OMPP or its designee, the IHCP reimburses physician- or HSPP-directed outpatient mental health services for group, family, and individual psychotherapy when services are provided by one of the following mid-level practitioners: • Advanced practice nurse under IC 25-23-1-1(b)(3), who is a licensed, registered nurse with a master’s degree in nursing, with a major in psychiatric or mental health nursing from an accredited school of nursing • Licensed psychologist • Licensed independent practice school psychologist • Licensed clinical social worker (LCSW) • Licensed marriage and family therapist • Licensed mental health counselor • A person holding a master’s degree in social work, marital and family therapy, or mental health counseling These mid-level practitioners may not be separately enrolled as individual providers to receive direct reimbursement. Mid-level practitioners can be employed by an outpatient mental health facility, clinic, or physician, or HSPP enrolled in the IHCP. The IHCP reimburses for covered services rendered. The employer or supervising psychiatrist bills for the services. The IHCP reimburses for services provided by mid-level practitioners in an outpatient mental health facility when an HSPP supervises services. Mid-level practitioners who render services must bill using the rendering NPI of the supervising practitioner and the billing NPI of the outpatient mental health clinic or facility. An HSPP may certify the diagnosis or supervise the plan of treatment. Outpatient Mental Health The physician or HSPP is responsible for certifying the diagnosis and supervising the plan of treatment described as stated in 405 IAC 5-20-8 (3) (a) (b)). The physician or HSPP must be available for emergencies and must see the patient or review the information obtained by the mid-level practitioner within seven days of the intake process. The physician or HSPP must again see the patient or review the documentation to certify the treatment plan and specific treatment modalities at intervals not to exceed 90 days during a course of treatment. The physician must document all reviews in writing. A cosignature is not sufficient. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-267 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions The IHCP requires written evidence of physician or HSPP involvement and personal evaluation to document the member’s acute medical needs. If practicing independently, a physician or an HSPP must order therapy in writing. The IHCP requires PA for mental health services provided in an outpatient or office setting that exceed 20 units per member, per provider, per rolling 12-month period. Providers must attach a current plan of treatment and progress notes explaining the necessity and effectiveness of therapy to the PA form and available for audit purposes, according to 405 IAC 5-20-8 (4). The IHCP requires PA for all units of neuropsychology and psychological testing. This applies to CPT 96101 – psychological testing, 96110 – developmental testing, 96111 – developmental testing extended, and 96118 – neuropsychological testing battery. According to 405 IAC 5-20-8(5), a physician or HSPP must provide these services. According to 405 IAC 5-20-8 (10), reimbursement is available for one unit of psychiatric diagnostic interview, CPT codes 90801 or 90802, per member, per provider, per rolling 12-month period. All additional units of psychiatric diagnostic interviews require prior authorization, except two units are allowed every rolling 12-month period when the recipient is separately evaluated by both the physician or HSPP and a mid-level practitioner. The following HCPCS codes in combination are subject to 20 units per member, per provider, per rolling 12-month period: • 90801–90802 • 90804–90815 • 90845–90857 • 96151–96153 The IHCP does not cover the following services: • Biofeedback • Broken or missed appointments • Day care • Hypnosis • Partial hospitalization, except as set in 405 IAC 5-21 CPT codes 90805, 90807, 90809, 90811, 90813, and 90815 for psychotherapy with medical evaluation and management, and CPT code 90862 for pharmacological management are medical services. Therefore, the IHCP does not reimburse clinical social workers, clinical psychologists, or any midlevel practitioners (excluding nurse practitioners and clinical nurse specialists) for these codes. For all outpatient services rendered, providers must identify and itemize services rendered on the CMS1500. The medical record documentation must identify the services and the length of time of each therapy session. Providers must make this information available for audit purposes. Providers should use the rendering NPI of the supervising practitioner (physician or HSPP) to bill psychiatric and clinical nurse specialist services. Providers must use these modifiers with the appropriate procedure code, which are as follows: • AH – Services provided by a clinical psychologist • AJ – Services provided by a clinical social worker • HE in conjunction with SA – Services provided by a nurse practitioner or clinical nurse specialist 8-268 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions • HE – Services provided by any other mid-level practitioner as addressed in the 405 IAC 5-20-8 (10) • HW – Medicaid Rehabilitation Option (MRO) services • SA – NP/CNS in a nonmental health arena For claims that providers bill for mid-level practitioner services and bill with the modifiers noted – except modifiers SA and HW, which are informational and do not impact reimbursement – the IHCP reimburses at 75 percent of the IHCP allowed amount for the procedure code identified. HSPPs do not need to use the modifier, and the IHCP reimburses them at 100 percent of the RBRVS fee. Place the modifiers in field 24D of the CMS-1500 claim form. CMHCs must continue to use the HW modifier to denote MRO services in addition to the modifiers listed above that identify the qualifications or the individual rendering the service. Place the modifiers in field 24D of the CMS-1500 claim form. Additional information about MRO services is published in the MRO Provider Manual. Package C The IHCP reimburses for 30 visits per member, per rolling calendar year for Package C members. The IHCP may cover an additional 20 visits with PA for a maximum of 50 visits per year. Medicaid Rehabilitation Option Services Medicaid Rehabilitation Option Services are clinical mental health services that the IHCP covers for individuals, families, or groups living in the community who need aid intermittently for emotional disturbances or mental illness. The IHCP reimburses for the following MRO, outpatient mental health services: • Assertive Community Treatment • Case management services • Conjoint counseling or psychotherapy • Crisis intervention • Diagnostic assessment and prehospitalization screening • Family counseling or psychotherapy • Group counseling or psychotherapy • Group training in activities of daily living • Individual counseling or psychotherapy • Medication or somatic treatment • Partial hospitalization • Prehospitalization screening • Training in activities in daily living As stated in 405 IAC 5-21, the IHCP reimburses for community mental health services for members with mental illness when the provider for those services is an enrolled mental health center that meets applicable federal, state, and local laws concerning the operation of CMHCs. Community Medicaid Rehabilitation Services include outpatient mental healthcare for the seriously mentally ill or seriously emotionally disturbed, partial hospitalization services, and case management services. Outpatient Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-269 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions mental health services may include clinical attention in the member’s home, workplace, mental health facility, emergency department, or wherever needed. A qualified mental health professional must render these services as outlined in 405 IAC 5-21-1-C-(1-5). Coverage of Mental Health Codes for Children’s Health Insurance Program Effective January 1, 2010, for dates of service on or after January 1, 2010, the IHCP will reimburse for mental health services, including Psychiatric Residential Treatment Facility (PRTF) and Medicaid Rehabilitation Option (MRO) services under Children’s Health Insurance Plan (CHIP, or Package C). This change comes as a result of Senate Enrolled Act 102. Prior authorization (PA) is required for any codes currently requiring PA for fee-for-service beneficiaries. Providers may submit claims for services that have been rendered on or after January 1, 2010. Table 8.85 shows codes for covered services rendered and billed under CHIP. The same limits and restrictions that apply to these codes under Medicaid apply to these codes covered under CHIP (Package C). Table 8.85 – Codes for Covered Services under CHIP Code/Modifier 8-270 Description H0004 HW Behavioral health counseling and therapy H0004 HW HQ Behavioral health counseling and therapy, group setting H0004 HW HR Behavioral health counseling and therapy, family/couple with client H0004 HW HS Behavioral health counseling and therapy, family/couple without the client present H0031 HW Mental health assessment, by nonphysician H0033 HW Oral medication administration, direct observation H0035 HW Mental health partial hospitalization, treatment, less than 24 hours H0040 HW Assertive community treatment program, per diem H2011 HW Crisis intervention service, per 15 minutes H2014 HW Skills training and development, per 15 minutes T1016 HW Case management, each 15 minutes T1016 HW TG Case management, second case manager 97535 Self-care/home management training 97537 Community/work reintegration training T2048 Behavioral health; long-term care residential (nonacute care in a residential treatment program where stay is typically longer than 30 days), with room and board, per diem T2048 U1 Behavioral health; long-term care residential (nonacute care in a residential treatment program where stay is typically longer than 30 days); medical leave days are limited to four (PRTF) Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Code/Modifier Description T2048 U2 Behavioral health; long-term care residential (nonacute care in a residential treatment program where stay is typically longer than 30 days); therapeutic leave days are limited to 14 (PRTF) 90801 Psychiatric diagnostic interview examination 90802 Interactive psychiatric diagnostic interview examination using play equipment, physical devices, language interpreter, or other mechanisms of communication 90804 Individual psychotherapy, insight oriented, behavior modifying and/or supportive, in an office or outpatient facility, approximately 20 to 30 minutes face-to-face with the patient 90805 Individual psychotherapy, insight oriented, behavior modifying and/or supportive, in an office or outpatient facility, approximately 20 to 30 minutes face-to-face with the patient, with medical evaluation and management services 90806 Individual psychotherapy, insight oriented, behavior modifying and/or supportive, in an office or outpatient facility, approximately 45 to 50 minutes face-to-face with the patient 90807 Individual psychotherapy, insight oriented, behavior modifying and/or supportive, in an office or outpatient facility, approximately 45 to 50 minutes face-to-face with the patient, with medical evaluation and management services 90808 Individual psychotherapy, insight oriented, behavior modifying and/or supportive, in an office or outpatient facility, approximately 75 to 80 minutes face-to-face with the patient 90809 Individual psychotherapy, insight oriented, behavior modifying and/or supportive, in an office or outpatient facility, approximately 75 to 80 minutes face-to-face with the patient, with medical evaluation and management services 90810 Individual psychotherapy, interactive, using play equipment, physical devices, language interpreter, or other mechanisms of nonverbal communication, in an office or outpatient facility, approximately 20 to 30 minutes face-toface with the patient 90811 Individual psychotherapy, interactive, using play equipment, physical devices, language interpreter, or other mechanisms of nonverbal communication, in an office or outpatient facility, approximately 20 to 30 minutes face-toface with the patient, with medical evaluation and management services Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-271 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Code/Modifier 8-272 Description 90812 Individual psychotherapy, interactive, using play equipment, physical devices, language interpreter, or other mechanisms of nonverbal communication, in an office or outpatient facility, approximately 45 to 50 minutes face-toface with the patient 90813 Individual psychotherapy, interactive, using play equipment, physical devices, language interpreter, or other mechanisms of nonverbal communication, in an office or outpatient facility, approximately 45 to 50 minutes face-toface with the patient, with medical evaluation and management services 90814 Individual psychotherapy, interactive, using play equipment, physical devices, language interpreter, or other mechanisms of nonverbal communication, in an office or outpatient facility, approximately 75 to 80 minutes face-toface with the patient 90815 Individual psychotherapy, interactive, using play equipment, physical devices, language interpreter, or other mechanisms of nonverbal communication, in an office or outpatient facility, approximately 75 to 80 minutes face-toface with the patient, with medical evaluation and management services 90816 Individual psychotherapy, insight oriented, behavior modifying and/or supportive, in an inpatient hospital, partial hospital or residential care setting, approximately 20 to 30 minutes face-to-face with the patient 90817 Individual psychotherapy, insight oriented, behavior modifying and/or supportive, in an inpatient hospital, partial hospital or residential care setting, approximately 20 to 30 minutes face-to-face with the patient, with medical evaluation and management services 90818 Individual psychotherapy, insight oriented, behavior modifying and/or supportive, in an inpatient hospital, partial hospital or residential care setting, approximately 45 to 50 minutes face-to-face with the patient 90819 Individual psychotherapy, insight oriented, behavior modifying and/or supportive, in an inpatient hospital, partial hospital or residential care setting, approximately 45 to 50 minutes face-to-face with the patient, with medical evaluation and management 90821 Individual psychotherapy, insight oriented, behavior modifying and/or supportive, in an inpatient hospital, partial hospital or residential care setting, approximately 75 to 80 minutes face-to-face with the patient 90822 Individual psychotherapy, insight oriented, behavior modifying and/or supportive, in an inpatient hospital, partial hospital or residential care setting, approximately 75 to 80 minutes face-to-face with the patient, with medical evaluation and management Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Code/Modifier Description 90823 Individual psychotherapy, interactive, using play equipment, physical devices, language interpreter, or other mechanisms of nonverbal communication, in an inpatient hospital, partial hospital or residential care setting, approximately 20 to 30 minutes face-to-face with the patient 90824 Individual psychotherapy, interactive, using play equipment, physical devices, language interpreter, or other mechanisms of nonverbal communication, in an inpatient hospital, partial hospital or residential care setting, approximately 20 to 30 minutes face-to-face with the patient, with medical evaluation and management 90826 Individual psychotherapy, interactive, using play equipment, physical devices, language interpreter, or other mechanisms of nonverbal communication, in an inpatient hospital, partial hospital or residential care setting, approximately 45 to 50 minutes face-to-face with the patient 90827 Individual psychotherapy, interactive, using play equipment, physical devices, language interpreter, or other mechanisms of nonverbal communication, in an inpatient hospital, partial hospital or residential care setting, approximately 45 to 50 minutes face-to-face with the patient with medical evaluation and management services 90828 Individual psychotherapy, interactive, using play equipment, physical devices, language interpreter, or other mechanisms of nonverbal communication, in an inpatient hospital, partial hospital or residential care setting, approximately 75 to 80 minutes face-to-face with the patient 90829 Individual psychotherapy, interactive, using play equipment, physical devices, language interpreter, or other mechanisms of nonverbal communication, in an inpatient hospital, partial hospital or residential care setting, approximately 75 to 80 minutes face-to-face with the patient, with medical evaluation and management services 90845 Psychoanalysis 90846 Family psychotherapy (without the patient present) 90847 Family psychotherapy (conjoint psychotherapy) (with patient present) 90849 Multi-family group psychotherapy 90853 Group psychotherapy (other than of a multi-family group) 90857 Interactive group psychotherapy 90862 Pharmacological management, including prescription, use, and review of medication with no more than minimal medical psychotherapy Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-273 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Code/Modifier 8-274 Description 90870 Electroconvulsive therapy (includes necessary monitoring) 90899 Unlisted psychiatric service or procedure 96101 Psychological testing (includes psycho diagnostic assessment of emotionality, intellectual abilities, personality and psychopathology, e.g, MMPI, Rorschach, WAIS), per hour of the psychologist’s or physician’s time, both face-to-face time administering tests to the patient and time interpreting these test results and preparing the report 96105 Assessment of aphasia (includes assessment of expressive and receptive speech and language function, language comprehension, speech production ability, reading, spelling, writing, e.g, by Boston Diagnostic Aphasia Examination) with interpretation and report, per hour 96110 Developmental testing; limited (e.g, Developmental Screening Test II, Early Language Milestone Screen), with interpretation and report 96111 Developmental testing; extended (includes assessment of motor, language, social, adaptive and/or cognitive functioning by standardized developmental instruments) with interpretation and report 96116 Neurobehavioral status exam (clinical assessment of thinking, reasoning, and judgment, e.g, acquired knowledge, attention, language, memory, planning and problem solving, and visual spatial abilities), per hour of the psychologist’s or physician’s time, both face-to-face time with the patient and time interpreting test results and preparing the report 96118 Neuropsychological testing (e.g, Halstead-Reitan Neuropsychological Battery, Wechsler Memory Scales and Wisconsin Card Sorting Test), per hour of the psychologist’s or physician’s time, both face-to-face time administering tests to the patient and time interpreting these test results and preparing the report 96150 Health and behavior assessment (e.g, health-focused clinical interview, behavioral observations, psycho physiological monitoring, health-oriented questionnaires), each 15 minutes face-to-face with the patient; initial assessment 96151 Health and behavior assessment (e.g, health-focused clinical interview, behavioral observations, psycho physiological monitoring, health-oriented questionnaires), each 15 minutes face-to-face with the patient; re-assessment 96152 Health and behavior intervention, each 15 minutes face-toface; individual 96153 Health and behavior intervention, each 15 minutes, face-toface; group (two or more patients) 96154 Health and behavior intervention, each 15 minutes, face-toface; family (with the patient present) Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Code/Modifier 96155 Description Health and behavior intervention, each 15 minutes, face-toface; family (without the patient present) Assertive Community Treatment Service Assertive community treatment (ACT) is an intensive mental health service for members discharged from a hospital after multiple or extended stays, or who are difficult to engage in treatment. An interdisciplinary team provides ACT services as defined under 440 IAC 5.2-2-3, and a physician must order the services. Members receiving this intensive level of community support will experience increased community tenure and decreased frequency or length of hospitalization or crisis services. The IHCP requires PA for ACT services that it covers. Before admission to an approved ACT team under 440 IAC 5.2-2-3, the ACT team psychiatrist must document and review an assessment of the member’s current medical status, psychiatric history, status at time of consideration for ACT services, and treatment plan goals. Refer to Chapter 6 of this manual for additional information about prior authorization. The IHCP requires development of an individual treatment plan that includes: medication administering and monitoring; self medication monitoring; crisis assessment and intervention; symptom assessment, management, and individual supportive therapy; substance abuse training and counseling; psychosocial rehabilitation and skill development; personal, social, and interpersonal skill training; and coordination with case management, consultation, and psycho-educational support for individuals and their families provided on behalf of the ACT member. Services must be available 24 hours a day, seven days a week with emergency response coverage, including availability of a psychiatrist. Members receiving ACT services must not attend traditional partial hospitalization programs. To meet the service standard, the ACT team must meet and discuss the services rendered, scheduled services, and progress of ACT members on a daily basis during the five-day work week. ACT teams should have a procedure in place to track daily team meeting attendance and client tracking (for example, cardex system, minutes, and so forth). Providers may submit claims for ACT services using the CMS-1500 paper claim or HIPAA-compliant electronic 837P claim. Providers may bill the IHCP for one unit of ACT service daily per approved member, provided that the ACT team meets the ACT service standard. Providers must use HCPCS level II code H0040 – ACT services, per diem and modifier HW – State mental health agency funded to bill ACT services at 100 percent of the Medicaid allowable amount. One unit of ACT service equals one 24-hour day. The ACT team psychiatrist or an HSPP who is an ACT team member must be present at the daily team meeting for the IHCP to reimburse the service code at 100 percent. When the ACT team psychiatrist or HSPP is not in attendance at the daily team meeting, the mid-level practitioner is reimbursed at 75 percent. All appropriate modifiers must be used for correct billing. Follow the billing and modifier guidelines described in this chapter for correct billing guidelines for mid-level practitioner services. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-275 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Note: The IHCP restricts MRO services to providers enrolled as Community Mental Health Centers who also meet the requirements for approval by the Division of Mental Health under IC 12-29 in accordance with 440 IAC 4. MRO enrolled providers must refer to the separate MRO Provider Manual for detailed eligibility, billing, and reimbursement information. Chapter 4 of this manual provides more information. Psychiatric Residential Treatment Facilities Coverage Provisions The IHCP reimburses for medically necessary services provided to children younger than 21 years old in a psychiatric residential treatment facility (PRTF). The IHCP also reimburses for children younger than 22 years old who began receiving PRTF services immediately before their 21st birthday. All services require prior authorization by the appropriate MCO or CMO. Note: The PRTF Model Attestation Letter Addendum has been updated to include State Survey Provider ID so that the ISDH and the OMPP can track facilities. The ISDH issues a State Survey Provider ID after reviewing the PRTF Attestation Form. Because the State Survey Provider ID is used for internal purposes, the provider should disregard this field. Additional information can be found in Chapter 4 of this manual. Managed Care Considerations Risk-based Managed Care The IHCP carves out PRTF services from the risk-based MCOs’ financial responsibility. However, MCOs must provide care coordination services and associated services related to PRTF services. These services are subject to the PA and reimbursement policies of the member’s managed care plan. Providers should verify the member’s eligibility at initial admission on the 1st and 15th of the month to determine the member’s current managed care eligibility. Care Select PRTF services do not require certification from the primary medical provider (PMP) Care Select. The appropriate CMO provides PA for PRTF placement, and providers bill claims to the IHCP. Services rendered outside the PRTF may be subject to PMP certification and PA requirements. Providers should verify the member’s eligibility before rendering services and also verify on the 1st and 15th of each month to confirm the member’s current care management eligibility. Hoosier Healthwise Package C Hoosier Healthwise Package C does not cover PRTF services. Leave Days The days of care that can be billed to the IHCP for a member admitted to a PRTF shall be expressed in units of full days. A day consists of 24 hours beginning at midnight and ending 24 hours later at midnight. For IHCP billing purposes, PRTFs are expected to follow the midnight-to-midnight method when reporting days of care for members, even if the health facility uses a different definition of a day for statistical or other purposes. 8-276 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Although it is not mandatory for facilities to reserve beds, Medicaid will reimburse for reserving beds for recipients at one-half the regular customary per diem rate, provided that criteria set forth is met for medical and therapeutic leave. These services are available to Medicaid members younger than 21 years old. In no instance will the IHCP reimburse a PRTF for reserving beds for Medicaid members when the facility has an occupancy rate of less than 90 percent. The occupancy rate shall be determined by dividing the total number of residents in licensed beds (excluding residential beds) in the psychiatric treatment facility taken from the midnight census as of the day that a Medicaid recipient takes a leave of absence, by the total number of licensed PRTF beds (excluding residential beds) in the PRTF. Medical Leave Days For members younger than 21 years old, the IHCP reimburses for medical leave days in a PRTF at one-half the regular customary per diem rate when the provider meets all the following conditions: • The physician orders hospitalization for treatment of an acute condition that cannot be treated in the PRTF. • The total length of time allowed for payment of a reserved bed in a PRTF for a single hospital stay is four consecutive days. If the member requires hospitalization longer than four consecutive days, the PRTF must discharge the member. • The PRTF must maintain a physician’s order for the hospitalization in the member’s file. • The facility has an occupancy rate of at least 90 percent. In no instance does the IHCP reimburse a PRTF for reserving beds for Medicaid members when the facility has an occupancy rate of less than 90 percent. Documentation will be subject to retrospective review. Therapeutic Leave Days For members younger than 21 years old, the IHCP reimburses for therapeutic leave days in a PRTF at one-half the regular customary per diem rate when the provider meets all the following conditions: • A leave of absence must be for therapeutic reasons as prescribed by the attending physician and as indicated in the member’s plan of care. • In a PRTF, the total length of time allotted for therapeutic leaves in any calendar year is 14 days per member. If the member is absent from the PRTF for more than 14 days per year, the IHCP makes no further reimbursement in that year for reserving a bed for therapeutic leave for that member. Therapeutic leave days do not have to be consecutive. • The facility must maintain a physician’s order for therapeutic leave in the member’s file. • The facility must have an occupancy rate of at least 90 percent. In no instance does the IHCP reimburse a PRTF for reserving beds for Medicaid members when the facility has an occupancy rate of less than 90 percent. Documentation is subject to retrospective review. Providers must submit claims for PRTF services on the CMS-1500 claim form or the 837P electronic transaction. PRTF services are reimbursed on a per diem basis. PRTF providers may bill a single date of service per detail, with consecutive dates of service per individual CMS-1500 claim form. The PRTF per diem does not include pharmaceutical supplies and physician services. The per diem rate includes the cost of all IHCP-covered psychiatric services provided to members residing in a PRTF, as well as the cost for IHCP-covered services not related to the member’s psychiatric condition if such services are performed at the PRTF. The IHCP makes separate reimbursement available only in instances where IHCP-covered services, not related to the member’s psychiatric condition, are unavailable at the PRTF and are performed at a location other than the PRTF. The PRTF per diem does not include pharmaceutical supplies and physician services, and the IHCP pays for them separately Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-277 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions from the PRTF per diem rate. These services are subject to provisions set forth in 405 IAC 5-24 and 405 IAC 5-25 respectively. Providers should use the following codes when billing for these services included in the PRTF per diem: • T2048 – For per diem services (behavioral health, long-term care residential, or nonacute care in a residential treatment facility where the stay is typically longer than 30 days). • T2048 U1 – For medical leave (behavioral health, long-term care residential, nonacute care in a residential treatment facility where the stay is typically longer than 30 days). Medical leave days are limited to four. • T2048 U2 – For therapeutic leave (behavioral health, long-term care residential, nonacute care in a residential treatment facility where the stay is typically longer than 30 days). Therapeutic leave days are limited to 14. Managed Care Considerations Risk-based Managed Care The 2007 Hoosier Healthwise MCO Procurement project carved in most behavioral health services to the RBMC program. Beginning with dates of service of January 1, 2007, services rendered by providers enrolled in the IHCP with the following provider specialties are the responsibility of the MCO: • 011 – Freestanding Psychiatric Hospital • 110 – Outpatient Mental Health Clinic • 111 – Community Mental Health Center • 112 – Psychologist • 113 – Certified Psychologist • 114 – Health Services Providers in Psychology • 115 – Certified Clinical Social Worker • 116 – Certified Social Worker • 117 – Psychiatric Nurse • 339 – Psychiatrist The carved-in behavioral health services rendered by the mental health provider specialties listed above should be billed directly to the applicable Behavioral Health Organization (BHO) subcontracted by the MCO. Behavioral health services rendered by nonmental health provider specialties should be billed to the applicable MCO. The following mental health services remain carved out of the RBMC program and are paid by HP on the fee-for-service methodology: • PRTF services rendered by a provider enrolled in the IHCP program with a specialty of 034. The MCOs retain responsibility for services outside the PRTF, including transportation, pharmacy, and other related healthcare services. MCOs are also responsible for care coordination of members receiving PRTF services. PRTF services are not covered for Package C members. • MRO services rendered by provider specialty 111 – Community Mental Health Center to individuals, families, or groups living in the community who need aid intermittently for emotional 8-278 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions disturbances or mental illness. MRO services include outpatient mental health services, partial hospitalization, case management, and Assertive Community Treatment. As with other carved-out services, the MCO remains responsible for services that may be related to the PRTF or MRO services, including but not limited to care coordination, transportation, and pharmacy services. The following services remain excluded from the Hoosier Healthwise program, and members are disenrolled from managed care upon qualification for such services: • Services in an ICF/MR • Inpatient services in a state psychiatric hospital, which are not Medicaid services, but are provided under the State’s 590 program Screening and Brief Intervention Services Beginning October 1, 2008, the IHCP began reimbursing providers for screening and brief intervention (SBI) services. SBI identifies and intervenes with individuals who are at risk for substance abuserelated problems or injuries. SBI services use established systems, such as trauma centers, emergency rooms, community clinics, and school clinics, to screen patients who are at risk for substance abuse and, if necessary, provide the patients with brief interventions or referrals to appropriate treatment. The IHCP reimburses providers when they bill procedure codes 99408 or 99409. The descriptions for the procedure codes are listed in Table 8.86. Table 8.86 – Screening and Brief Intervention Service Procedure Codes Code Description 99408 Alcohol and/or substance abuse structured screening and brief intervention services, 15-30 minutes 99409 Alcohol and/or substance abuse structured screening and brief intervention services, greater than 30 minutes The new CPT® codes were developed by the American Medical Association (AMA) to make it possible for the healthcare system to “efficiently report screening services for drug and alcohol abuse.” Providers can bill procedure code 99408 or 99409 only after an individual has been screened for alcohol or drug abuse by a healthcare professional. SBI services currently do not require prior authorization. Procedure codes 99408 and 99409 are limited to one structured screening and brief intervention per individual, every three years, when billed by the same provider. This does not count toward the number of annual office visits allowed per year for an individual. Providers can submit claims for services rendered for dates of service beginning October 1, 2008. Mid-Level Practitioner Services Coverage and Billing Procedures The proper billing procedures for billing nurse practitioner and physician assistant services are as follows: • Nurse Practitioners – The IHCP reimburses independently practicing nurse practitioners at 75 percent of the rate on file. The nurse practitioner must enter his or her rendering NPI number in Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-279 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions field 24J of the CMS-1500. The billing NPI must be entered in field 33a on the CMS-1500 claim form. • Nurse practitioners not individually enrolled in the IHCP, and clinical nurse specialists employed by physicians in a physician-directed group or clinic, bill services with the SA modifier and the physician rendering NPI in fields 24J of the CMS-1500. The billing NPI must be entered in field 33a on the CMS-1500 claim form. The IHCP reimburses them at 100 percent of the Medicaidallowed amount. • Nurse practitioners with an individual LPI and NPI and who are employed by a physician, should bill using their rendering NPI in field 24J of the CMS-1500. The NPI must be entered in field 33a on the CMS-1500 claim form. The IHCP reimburses them at 100 percent of the Medicaid allowed amount. • Providers cannot bill separately for nurse practitioner services in outpatient hospital settings and should include these services in the hospital outpatient reimbursement rate. • Physician Assistants –Providers should bill physician assistant services with the HN, bachelors degree or HO, masters degree modifier applicable to the level of education of the physician assistant. The physician rendering NPI must be entered in field 24J of the CMS-1500. The physician billing NPI must be entered in field 33a on the CMS-1500 claim form. The IHCP reimburses them at 100 percent of the Medicaid allowed amount. Physician assistants are not separately enrolled in the IHCP. However, when a physician assistant provides assistant surgeon services, the provider should use modifier AS instead of the HN or HO modifier. Reimbursement for the assistant at surgery is 20 percent of the rate on file. Providers should place modifiers in field 24D, under the modifier heading on the CMS-1500 claim form. Smoking Cessation Treatment Services Coverage and Billing Procedures Eligible Providers and Practitioners Practitioners eligible to provide smoking cessation treatment services, but not currently enrolled as IHCP providers, should contact HP Provider Enrollment at 1-877-707-5750 to request a provider enrollment application. Eligible practitioners, such as pharmacists who work for or own IHCP-enrolled pharmacies, bill for treatment services rendered through the enrolled entity where services are provided. Physician assistants, registered nurses, and psychologists who are not HSPPs bill for counseling services rendered through the enrolled entity through which services are provided. Treatment services must be prescribed by a licensed practitioner within the scope of license under Indiana law. The IHCP reimburses for smoking cessation treatment services rendered by the following licensed practitioners participating in the IHCP: • Nurse practitioner • Pharmacist • Physician • Physician’s assistant • Psychologist • Registered nurse • Dentist 8-280 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions The following practitioners cannot obtain an IHCP rendering NPI number and must bill under the supervising practitioner’s NPI number: • Physician assistant • Psychologist • Registered nurse Reimbursement The IHCP makes reimbursement for smoking cessation available for one 12-week course of treatment per member per calendar year. Treatment may include prescription of any combination of smoking cessation products and counseling. Providers can prescribe one or more modalities of treatment. Providers must include counseling in any combination of treatment. Providers must order smoking cessation treatment services for the IHCP to reimburse for the services. Practitioners ordering smoking cessation services should maintain documentation about the order in the same manner used for other covered services. The IHCP does not require PA for reimbursement for smoking cessation products or counseling. Providers of smoking cessation treatment services must obtain PMP certification for Hoosier Healthwise and Care Select enrollees. Pharmacy Providers The IHCP reimburses pharmacy providers for smoking cessation products when a licensed practitioner prescribes them within the scope of the practitioner’s license under Indiana law. For the pharmacy to be reimbursed by the IHCP for over-the-counter smoking cessation products, a licensed practitioner must prescribe them. The practitioner must prescribe all smoking cessation products for use, along with counseling, within the 12-week treatment time frame. There is a limit of 84 days of smoking cessation therapy in 365 calendar days. Pharmacies should bill for reimbursement according to the normal procedures. Note: Only patients who agree to participate in smoking cessation counseling may receive prescriptions for smoking cessation products. The prescribing practitioner may want to have the patient sign a commitment to establish a “quit date” and to participate in counseling as the first step in smoking cessation treatment. A prescription for such products serves as documentation that the prescribing practitioner has prescribed or obtained assurance from the patient that counseling occurs concurrently with the receipt of smoking cessation products. Smoking Cessation Products The list of smoking cessation products that the IHCP covers includes, but is not limited to, the following: • Sustained release buproprion products • Varenicline tartrate tablets • Nicotine replacement drug products, such as a patch, gum, or inhaler Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-281 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Counseling When providers and practitioners furnish a service to the general public at no charge, including smoking cessation counseling services, they cannot receive IHCP reimbursement for that service. The SUR Department closely monitors adherence to this program limitation. Ordering and rendering practitioners must maintain sufficient documentation of respective functions to substantiate the medical necessity of the service rendered and to substantiate the provision of the service itself; this requirement is consistent with existing IHCP policies and regulations. Providers or practitioners of counseling services must bill only on the CMS-1500 or 837P using procedure code S9075 – Smoking cessation treatment, with a primary diagnosis code of 305.1 – Tobacco use disorder. Note: Providers and practitioners must bill the usual and customary charge for the units of service rendered, and the IHCP calculates the final reimbursement amount. One unit of S9075 is 15 minutes of service. Providers should not round up to the nearest 15 minutes. Providers must perform counseling for a minimum of 30 minutes (two units) and a maximum of 150 minutes (10 units) within the 12 weeks. Providers must bill counseling in 15-minute increments. Newborn Services Coverage and Billing Procedures Newborn Blood Screening Indiana law requires newborn blood screening tests for at least eight conditions for every infant before discharge from the hospital. IC 16-41-17-2(c) identifies religious belief exception from this requirement. The hospital obtains a blood sample from the infant, even if the sample is taken at less than 48 hours, which is the time needed to obtain valid test results. The newborn screening test screens for the following: • Galactosemia • Hemoglobinopathies, including sickle cell anemia • Homocystinuria • Hypothyroidism • Maple syrup urine disease • Phenylketonuria (PKU) • Congenital adrenal hyperplasia • Biotinidase deficiency The hospital collects all blood samples on a filter paper card that must also contain information to identify the infant, the physician, the time of birth, the time of first feeding, and the time of the blood draw. The hospital sends the blood sample to the Indiana University (IU) Laboratory. 8-282 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions The IU Laboratory has a contract with the ISDH to perform laboratory analysis for newborn screening. Providers using laboratories other than the IU Laboratory to perform newborn screening analysis must discontinue the practice. To ensure that the IU Laboratory performs all newborn screening, the ISDH must coordinate all newborn screening. Providers must first determine whether IU Laboratory has obtained valid newborn screening test results for the infant. IU Laboratory results can be verified by calling 1-800-245-9137 or (317) 4916625 or (317) 491-6678. If IU Laboratory has obtained a valid test and the results are normal, the IHCP requires no further testing. If the laboratory needs to rescreen due to invalid or abnormal results, the provider must call the ISDH at 1-800-761-1271, extension 1250, to work out the best method of accomplishing the rescreening. Because hospitals are more frequently releasing newborns prior to the 48 hours needed to obtain valid newborn screen results, an increasing number of newborns require a second screen. Providers ask families to bring the newborn back to the birth hospital as an outpatient, or the hospital requests that a nurse make a follow-up visit to obtain the sample for newborn screening. In either case, the possibility arises that the hospital could bill separately for newborn screening that is already included in the DRG that the IHCP pays for the newborn hospitalization. The IHCP does not require HealthWatch/EPSDT providers to report newborn screening on the CMS1500 or 837P. The IHCP does not permit hospitals to bill separately for newborn screening. The IHCP pays the newborn hospitalization under the DRG that includes the newborn screening. Newborns should be screened at the birth hospital or the hospital of closest proximity. To avoid being charged by the IU Laboratory for a second screen, a hospital screening a newborn who was born in another Indiana hospital must indicate the name of the birth hospital on the filter paper card. If the newborn’s name or birth date has been changed, the hospital must include the original name and date of birth in the information sent to the IU Laboratory to facilitate a match and avoid a charge by the lab. Note: A child born to a woman eligible for pregnancy and urgent care only is categorically eligible at birth for full IHCP coverage, at least for the month of birth. The child’s claims must have the child’s RID number. Newborn Hearing Screening Indiana legislation mandates that every infant shall be given a physiologic hearing screening examination at the earliest feasible time for the detection of hearing impairments. The IHCP includes the cost of this screening in the IHCP DRG reimbursement rate that includes the newborn’s hospitalization. The IHCP does not allow hospitals to bill separately for initial newborn screening. Newborns must be screened at the birth hospital before the infant is discharged. Newborns who require further evaluation should be referred to First Steps. Refer to this Web site for contact information: http://www.in.gov/fssa/ddrs/2633.htm. Providers who deliver newborns not hospitalized at birth, at locations other than in the hospital, may use the appropriate CPT codes to bill for the newborn hearing screening. Use CPT code 92585 for auditory evoked potentials for evoked response audiometry and testing of the central nervous system, or evoked auditory brainstem responses (ABR). Use CPT code 92587 for evoked otoacoustic emissions (OAE); limited, single stimulus level, either transient or distortion products, or OAE. For any follow-up diagnostic testing that results from detection of possible audiological impairment via the newborn screening process, providers should bill in the same manner that they bill other audiological testing. Providers should obtain PA if applicable. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-283 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Presumptive Eligibility – Package P Presumptive Eligibility (PE) provides coverage to low-income pregnant women through a simplified application process. Presumptive Eligibility covers most pregnancy-related outpatient services while the Medicaid application process is completed. Coverage begins on the date a qualified provider (QP) determines the woman presumptively eligible using the process outlined in the Qualified Provider Presumptive Eligibility Manual. The woman’s Medicaid eligibility determination will be subsequently completed by the Division of Family Resources (DFR). Failure on behalf of the patient to cooperate with DFR to complete the Medicaid application process will result in termination of PE benefits. PE does not cover hospice, long-term care, inpatient care, labor and delivery services, abortion services, postpartum services, sterilization, and services unrelated to the pregnancy or birth outcome. These services, if determined to be pregnancy-related, may be covered if the woman is later determined eligible for Hoosier Healthwise benefits. Presumptive Eligibility Requirements To be eligible for presumptive eligibility, a pregnant woman must: • Be pregnant, as verified by a professionally administered pregnancy test • Not be a current Medicaid member • Be an Indiana resident • Be a U.S. citizen or a qualified noncitizen (defined in the Qualified Provider Presumptive Eligibility Manual) • Not be currently incarcerated • Have gross family income less than 200 percent of the federal poverty level Qualified Provider Only a QP or designee can make a determination of pregnancy for PE. A QP is a provider that meets the following criteria: 1. Enrolled as a provider in the IHCP 2. Capable of verifying pregnancy via a professionally administered pregnancy test (homeadministered tests do not meet this requirement) 3. Must attend a Qualified Provider training session provided by the Family and Social Services Administration (FSSA) or designee 4. Currently provide outpatient hospital, rural health clinic, or clinic services 5. Must have access to a printer, fax machine, and Web interChange Providers must allow PE applicants to use an office telephone to facilitate the PE and Hoosier Healthwise enrollment process. Billing Procedures Submit Presumptive Eligibility claims to the appropriate MCO as selected by the patient and/or HP fee-for-service claims. Covered PE services are similar to Package B services, except for the limited diagnosis listing below. More information about billing for Obstetrical Services and Package B is found within this chapter. Contact information for the MCOs can be found in Chapter 1 of this manual. Qualified providers follow general billing directions for completing the CMS-1500 claim form. 8-284 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Table 8.87 – Presumptive Eligibility Covered Diagnosis Codes Diagnosis Code 63300 63301 63311 63321 63381 63391 640 6400 64003 64083 6408 6409 64093 641 6410 64103 64113 64123 6413 64133 6418 64183 6419 64193 64203 64213 64223 64233 64243 64253 64263 64273 64293 643 6430 64303 6431 64313 6432 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Description ABD PREG W/O INTRAUTER PR ABD PREG W/INTRAUTER PRG TUBAL PREG W/INTRAUT PREG OVAR PREG W/INTRAUT PREG OTH ECT PREG W/INTRA PREG ECT PREG NOS W/INTRA PREG HEMORRHAGE IN EARLY PREG THREATENED ABORTION THREATENED ABORTION-ANTEP HEMORR IN EARLY PREG NECHEMORR IN EARLY PREG NECHEMORR IN EARLY PREG HEMORR IN EARLY PREG NOSANTEPART HEM & PLAC PREV PLACENTA PREVIA W/O HEM PLACENTA PREVIA W/O HEM-A PLACENTA PREV HEM-ANTEPAR PREM SEPAR PLAC-ANTEPART COAG DEF ANTEPART HEMORR COAG DEF HEMORR-ANTEPART ANTEPARTUM HEMORR NEC ANTEPART HEM NEC-ANTEPAR ANTEPARTUM HEMORR NOS ANTEPART HEM NOS-ANTEPAR ESSEN HYPERTEN-ANTEPART RENAL HYPERTEN-ANTEPART OLD HYPERTEN NEC-ANTEPAR TRANS HYPERTEN-ANTEPART MILD/NOS PREECLAMP-ANTEP SEV PREECLAMP-ANTEPARTUM ECLAMPSIA-ANTEPARTUM TOX W OLD HYPER-ANTEPART HYPERTENS NOS-ANTEPARTUM EXCESS VOMITING IN PREG MILD HYPEREMESIS GRAVIDAR MILD HYPEREMESIS GRAVID-A HYPEREM GRAV W METAB DIS HYPEREM GRAV W METAB DISLATE VOMITING PREGNANCY 8-285 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Diagnosis Code 64323 6438 64383 6439 64393 644 6440 64403 6441 64413 645 6451 64513 64523 6453 646 6460 64603 6461 64613 64623 64633 64643 64653 6463 6464 6465 64663 6467 64673 6468 64683 6469 64693 64703 64713 64723 64733 64743 64753 8-286 Description LATE VOMITING PREGNANCY-A VOMITING COMPL PREG NEC VOMITING COMPL PREGNANCYVOMITING PREGNANCY NOS VOMITING PREGNANCY NOS-AN EARLY/THREATENED LABOR THREATEN PREMATURE LABOR THREAT PREM LABOR-ANTEPAR THREATENED LABOR NEC THREAT LABOR NEC-ANTEPAR LATE PREGNANCY PROLONGED PREG POST TERM PREG, ANTEPART) PROLONG PREG, ANTEPART C/ PROLONGED PREG-ANTEPART OTHER COMPL OF PREGNANCY PAPYRACEOUS FETUS PAPYRACEOUS FET-ANTEPAR EDEMA IN PREGNANCY EDEMA IN PREG-ANTEPARTUM RENAL DIS NOS-ANTEPARTUM HABITUAL ABORT-ANTEPART NEURITIS OF PREG-ANTEPAR ASY BACTERIURIA-ANTEPART HABITUAL ABORTER PERIPHERAL NEURITIS PREG ASYMPT BACTERIURIA PREG GU INFECTION-ANTEPARTUM LIVER DISORDER IN PREG LIVER DISORDER-ANTEPART PREGNANCY COMPL NEC PREG COMPL NEC-ANTEPART PREGNANCY COMPL NOS PREG COMPL NOS-ANTEPART SYPHILIS-ANTEPARTUM GONORRHEA-ANTEPARTUM OTHER VD-ANTEPARTUM TUBERCULOSIS-ANTEPARTUM MALARIA-ANTEPARTUM RUBELLA-ANTEPARTUM Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Diagnosis Code 64763 64783 64793 64803 64813 64823 64833 64843 64853 64863 64873 6488 64883 64893 65103 65113 65123 65133 65143 65153 65163 65173 65183 65193 65203 65213 65223 65233 65243 65253 65263 65273 65283 65293 65303 65313 65323 65333 65343 65353 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Description OTH VIRAL DIS-ANTEPARTUM INFECT DIS NEC-ANTEPART INFECT NOS-ANTEPARTUM DIABETES-ANTEPARTUM THYROID DYSFUNC-ANTEPART ANEMIA-ANTEPARTUM DRUG DEPENDENCE-ANTEPART MENTAL DISORDER-ANTEPART CONGEN CV DIS-ANTEPARTUM CV DIS NEC-ANTEPARTUM BONE DISORDER-ANTEPARTUM ABN GLUC TOLERAN IN PREG ABN GLUCOSE-ANTEPARTUM OTH CURR COND-ANTEPARTUM TWIN PREGNANCY-ANTEPART TRIPLET PREG-ANTEPARTUM QUADRUPLET PREG-ANTEPART TWIN PREG FET LOSS-ANTEPA TRIPLET PREG FET LOSS-ANT QUADRUP PREG FET LOSS-ANT OTH MULT PREG FET LOSS-AN MULT GEST POST W/ANTE MULTI GEST NEC-ANTEPART MULTI GEST NOS-ANTEPART UNSTABLE LIE-ANTEPARTUM CEPHAL VERS NOS-ANTEPART BREECH PRESENT-ANTEPART TRANSV/OBLIQ LIE-ANTEPAR FACE/BROW PRES-ANTEPART HIGH HEAD TERM-ANTEPART MULT GEST MALPRES-ANTERPA PROLAPSED ARM-ANTEPART MALPOSITION NEC-ANTEPART MALPOSITION NOS-ANTEPART PELV DEFORM NOS-ANTEPART CONTRAC PELV NOS-ANTEPAR INLET CONTRACT-ANTEPART OUTLET CONTRACT-ANTEPART FETOPELV DISPROP-ANTEPART FETAL DISPROP NOS-ANTEPAR 8-287 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Diagnosis Code 65363 65373 65383 65393 65403 65413 65423 65433 65443 65453 65463 65473 65483 65493 655 65503 65513 65523 65533 65543 65553 65563 65573 65583 65593 65603 65613 65623 65633 65653 65663 65673 65683 65693 65703 65803 65843 65883 65893 65943 8-288 Description HYDROCEPH FETUS-ANTEPART OTH ABN FET DISPROP-ANTEP DISPROPOR NEC-ANTEPARTUM DISPROPOR NOS-ANTEPARTUM CONGEN ABN UTER-ANTEPART UTERINE TUMOR-ANTEPARTUM PREV C-SECT NOS-ANTEPART RETROVERT UTER-ANTEPART ABN UTERUS NEC-ANTEPART CERV INCOMPET-ANTEPARTUM ABN CERVIX NEC-ANTEPART ABNORM VAGINA-ANTEPARTUM ABNORMAL VULVA-ANTEPART ABN PELV ORG NOS-ANTEPAR FETAL ABN AFFECT MOTHER FETAL CNS MALF ORM-ANTEPA FET CHROMOS ABN-ANTERPART FAMIL HERED DIS-ANTEPART FET DAMG D/T VIRUS-ANTEP FET DAMG D/T DIS-ANTEPAR FET DAMG D/T DRUG-ANTEP RADIAT FET DAMAG-ANTEPAR DECREASED FETAL MOVEMENTS FETAL ABNORM NEC-ANTEPAR FETAL ABNORM NOS-ANTEPAR FETAL-MATERN HEM-ANTEPAR RH ISOIMMUNIZAT-ANTEPART ABO ISOIMMUNIZAT-ANTEPAR FETAL DISTRESS-ANTEPART POOR FETAL GRTH-ANTEPART EXCESS FET GRTH-ANTEPART OTH PLACENT COND-ANTEPAR FET/PLAC PROB NEC-ANTEP FET/PLAC PROB NOS-ANTEP POLYHYDRAMNIOS-ANTEPART OLIGOHYDRAMNIOS-ANTEPAR INFECT AMNIOTIC CAVITY-AN AMNIOTIC CAVITY PROB NECAMNIOTIC CAVITY PROB NOSGRAND MULTIPARITY-ANTEP Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Diagnosis Code 65953 65963 65973 66303 66313 66323 66333 66343 66353 66363 66383 66393 66503 66583 66593 67103 67113 67123 67133 67153 67183 67193 67303 67313 67323 67333 67383 67403 67503 67513 67523 67583 67593 67603 67613 67623 67633 67643 67653 67663 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Description ELDERLY PRIMIG RAVIDA-ANT OTHER ADVANCED MATERNAL A ABNORMALITY IN FETAL HEAR PROLAPSE OF CORD-ANTEPAR COMP CORD ROUND NECK-ANTE CORD ENTANGLE W COMP-ANTE CORD-ENTANGLE NEC/NOS-ANT SHORT UMBILICAL CORD-ANTE VASA PREVIA-ANTEPAR VASC LESIONS OF CORE-ANTE UMBILICAL CORD COMP NEC-A UMBILICAL CORD COMP NOS-A PRELAB RUPT UTER-ANTEPAR OB TRAUMA NEC-ANTEPARTUM OB TRAUMA NOS-ANTEPARTUM VARIC VEIN LEG-ANTEPART VARICOSE VULVA-ANTEPART THROMBOPHLEBIT-ANTEPART DEEP THROM ANTEPAR-ANTEPA THROMBOSIS NEC-ANTEPART VENOUS COMPL NEC-ANTEPAR VENOUS COMPL NOS-ANTEPAR OB AIR EMBOLISM-ANTEPART AMNIOTIC EMBOL-ANTEPART BLOOD-CLOT EMBOL-ANTEPART OB PYEMIC EMBOL-ANTEPART PULMON EMBOL NEC-ANTEPAR CEREBROVASC DIS-ANTEPART INFECT NIPPLE-ANTEPARTUM BREAST ABSCESS-ANTEPART MASTITIS-ANTEPARTUM BREAST INF NEC-ANTEPART BREAST INF NOS-ANTEPART RETRACT NIPPLE-ANTEPART CRACKED NIPPLE-ANTEPART BREAST ENGORGE-ANTEPART BREAST DIS NEC/NOW-ANTEPA LACTATION FAIL-ANTEPART SUPPR LACTATION-ANTEPART GALACTORRHEA-ANTEPARTUM 8-289 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Diagnosis Code 67683 67693 7600 7601 7602 7603 7604 7605 V189 V22 V23 V234 V238 V28 V220 V221 V222 V230 V231 V232 V233 V235 V237 V2381 V2382 V2389 V239 V2631 V2632 V2633 V280 V281 V282 V283 V284 V285 V286 V289 8-290 Description LACTAT DIS NEC-ANTEPART LACTAT DIS NOS-ANTEPART MATERN HYPERTEN AFF NB MATERN URINE DIS AFF NB MATERNAL INFEC AFF NB MATERN CIRULAT/RESPIRAT A MATERN NUTRIT DIS AFF NB MATERNAL INJURY AFF NB FH GENT DIS CARRIER NORMAL PREGNANCY SUPERVIS HIGH-RISK PREG PREG W POOR OBSTETRIC HX SUPRV HIGH-RISK PREG NEC ANTENATAL SCREENING SUPERVIS NORMAL 1ST PREG SUPERVIS OTH NORMAL PREG PREG STATE, INCIDENTAL PREG W HX OF INFERTILITY PREG W HX-TROPHOBLAS DIS PREG W HX OF ABORTION GRAND MULTIPARITY PREG W POOR REPRODUCT HX INSUFFICIENT PRENATAL CAR SUPERVISION OF HIGH RISK SUPERVISION OF HIGH RISK SUPERVISION OF OTHER HIGH SUPRV HIGH-RISK PREG NOS TEST FEM GENET DIS CAR ST OTH GENET TESTING OF FEMA GENETIC COUNSEL SCREENING-CHROMOSOM ANOM SCREEN-ALPHAFETOPROTEIN SCREEN BY AMNIOCENT NEC SCREEN-FETAL MALFORM SCREEN-FETAL RETARDATION SCREEN-ISOIMMUNIZATION SCREENING STREPTOCOCCUS B ANTENATAL SCREENING NOS Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Obstetrical Services Coverage and Billing Procedures Policies for the following pregnancy-related services are presented in this subsection: • Antepartum care policy • Other outpatient office visits • Normal pregnancy • High-risk pregnancy • Pregnancy services billing procedures • Hoosier Healthwise Package B – Pregnancy and Urgent Care Only Antepartum Care Policy To encourage comprehensive, timely, and appropriate antepartum care, providers must indicate the date of last menstrual period (LMP) in field 14 on the CMS-1500 (or Last Menstrual Period Date, Data Element 1251 on the 837P), enter the appropriate diagnosis codes in field 21 of the CMS-1500, and refer to the date of LMP in field 24E on the CMS-1500 for these pregnancy-related services. The IHCP reimburses up to 14 visits for normal antepartum care, one visit more than the 13 visits recommended by the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG). The IHCP reimburses providers for the following number of visits in a normal pregnancy: • Three visits in trimester one • Three visits in trimester two • Eight visits in trimester three Billing for Antepartum Visits Providers should bill antepartum care for pregnant members separately from the delivery and postpartum visits. Providers must individually list each antepartum visit on the CMS-1500 or 837P. Providers can submit claims after each individual visit or at the end of the respective trimester. Bill the required antepartum tests and screenings for each trimester along with the trimester visits. Bill antepartum services within a trimester within 30 days of the end of the trimester. Providers should bill each antepartum visit separately using CPT procedure codes 59425 or 59426. Submit visits four through six with the procedure code 59425 at each visit. Submit the seventh, and all subsequent visits, with procedure code 59426 at each visit. Providers may use a new or established patient E/M code, 99201–99215, for the first through third antepartum visits to accommodate the greater amount of work involved with each visit. However, providers should use the appropriate antepartum care code to bill all subsequent antepartum visits. If providers report an E/M code for the first visit, they must use the appropriate trimester modifier and expected date of delivery. To identify antepartum visits in each trimester, providers must bill one of the following modifiers in conjunction with CPT procedure code 59425, 59426, or 99201-99215 (if used for the first antepartum visit) with each specific date of service. Place the modifier following the CPT code in field 24D of the CMS-1500. Table 8.88 lists modifiers for antepartum visits. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-291 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Use the modifiers in Table 8.88, in conjunction with 59425 and 59426, to denote the appropriate trimester. Table 8.88 – Modifiers – Antepartum Visits Modifier Description U1 Trimester one – 0 through 14 weeks, 0 days U2 Trimester two – 14 weeks, one day through 28 weeks, 0 days U3 Trimester three – 28 weeks, one day, through delivery Note: The IHCP allows up to eight antepartum visits during the third trimester for a normal pregnancy, and providers can bill them along with delivery and postpartum services on the same CMS-1500 claim form or 837P transaction. Antepartum Tests and Screenings Schedule In addition to the schedule for antepartum visits, the OMPP has developed a schedule of tests and screenings highly recommended for pregnant members within each respective trimester. Providers should render other tests and screenings, such as those defined as optional, only when the person providing the service determines that the procedure is necessary. Providers can bill the tests and screenings with the appropriate antepartum care visit code on the same CMS-1500 or 837P transaction. The trimester schedules in Table 8.89 are uniform with standards established by the ACOG and the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP). Table 8.89 – Antepartum Tests and Screenings Schedule CPT Code Procedure Trimester One (three total visits) 59425* First trimester visits = three 59426* 59015 Chorionic Villa Sampling (CVS), optional for women older than 35 81000 (includes microscopy for suspected urinary tract infection), or 81002 (without microscopy), or 81001 (Urinalysis, automated with microscopy), or 81003 (Urinalysis, automated without microscopy) Urinalysis by dipstick, performed each visit; the use of the automated urinalysis is to be based on medical necessity as determined by the physician 86644 CMV antibody titer 86694 Herpes simplex test 86701 HIV test (optional) 86777 Toxoplasma antibody titer 88150, 88152-88155 Cervical cytology (Pap smear) 8-292 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions CPT Code Procedure Total obstetrical panel includes: 80055 • CBC with complete differential • Hepatitis B surface antigen • Rubella antibody titer • Syphilis test • Antibody screen, RBC • Blood typing (ABO) • Blood typing (RhD) Or instead of 80055, use the following: 85025 CBC with complete differential 87340 Hepatitis B surface antigen 86762 Rubella antibody titer 86592 Syphilis test; qualitative such as VDRL, RPR, ART 86850 Antibody screen, RBC 86900 Blood typing (ABO) 86901 Blood typing (RhD) 99354 TH Notification of Pregnancy (NOP); one NOP per member, per pregnancy is reimbursed *Use the appropriate CPT code for the number of antepartum visits: 59425 Antepartum care only; one to six visits 59426 Antepartum care only; seven or more visits CPT Code Procedure Trimester Two (three total visits) 59425* Second trimester visits = three 59426* 59000 Amniocentesis, optional for women older than 35 81000 (includes microscopy for suspected urinary tract infection), or 81002 (without microscopy), or 81001 (Urinalysis, automated with microscopy), or 81003 (Urinalysis, automated without microscopy) Urinalysis by dipstick, performed each visit; the use of the automated urinalysis is to be based on medical necessity as determined by the physician 82105 Serum alpha-fetoprotein 82947 Diabetic screening 82951 Glucose tolerance test 86644 CMV antibody titer 86694 Herpes simplex test 86777 Toxoplasma antibody titer Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-293 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions CPT Code Procedure 80055 Total obstetrical panel includes: • CBC with complete differential • Hepatitis B surface antigen • Rubella antibody titer • Syphilis test • Antibody screen, RBC • Blood typing (ABO) • Blood typing (RhD) Or instead of 80055, use the following: 85025 CBC with complete differential 87340 Hepatitis B surface antigen 86762 Rubella antibody titer 86592 Syphilis test; qualitative such as VDRL, RPR, ART 86850 Antibody screen, RBC 86900 Blood typing (ABO) 86901 Blood typing (RhD) 99354 TH Notification of Pregnancy; one NOP per member, per pregnancy is reimbursed *Use the appropriate CPT code for the number of antepartum visits: 59425 Antepartum care only; one to six visits 59426 Antepartum care only; seven or more visits Trimester Three (eight total visits) 59425* Third trimester visit = eight 59426* 81000 (includes microscopy for suspected urinary tract infection), or 81002 (without microscopy), or 81001 (Urinalysis, automated with microscopy), or 81003 (Urinalysis, automated without microscopy) Urinalysis by dipstick, performed each visit; the use of the automated urinalysis is to be based on medical necessity as determined by the physician 85025 CBC with differential 86592 Syphilis test, repeat test for patients who tested positive in first trimester 86850 Antibody test, repeat for patients who tested negative in first trimester 86644 CMV antibody titer 86694 Herpes simplex test 86777 Toxoplasma antibody titer 8-294 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions CPT Code Procedure Total obstetrical panel includes: 80055 • CBC with complete differential • Hepatitis B surface antigen • Rubella antibody titer • Syphilis test • Antibody screen, RBC • Blood typing (ABO) • Blood typing (RhD) Or instead of 80055, use the following: 85025 CBC with complete differential 87340 Hepatitis B surface antigen 86762 Rubella antibody titer 86592 Syphilis test; qualitative, such as VDRL, RPR, ART 86850 Antibody screen, RBC 86900 Blood typing (ABO) 86901 Blood typing (RhD) 99354 TH Notification of Pregnancy; one NOP per member, per pregnancy is reimbursed. The NOP is not reimbursable when the risk assessment is performed beyond 29 weeks gestation. *Use the appropriate CPT code for the number of antepartum visits: 59425 Antepartum care only; one to six visits 59426 Antepartum care only; seven or more visits Process for Completion of the Notification of Pregnancy Recognized providers complete and submit the NOP electronically using Web interChange. Once logged in, complete the following steps: 1. Select the Eligibility Inquiry function to verify the member’s eligibility. 2. On the Eligibility Inquiry screen, select the Go To NOP button to complete and submit the online form. Providers may also complete a hard-copy NOP by selecting the Print Blank NOP button. Only NOPs submitted online are reimbursable. 3. Web interChange will check for potential duplicate NOPs. If a duplicate is identified, the recognized provider will be asked to provide a reason explaining why the new NOP is not a duplicate. The recognized provider can choose from three reasons related to the prior pregnancy: (1) member abortion, (2) member preterm delivery, or (3) member miscarriage. The provider can continue the process without identifying a reason; however, the duplicate NOP will not be reimbursed. 4. The NOP can only be submitted and billed for a woman enrolled in Hoosier Healthwise risk-based managed care. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-295 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions 5. The recognized provider must submit the NOP within five calendar days from the date of the risk assessment to be reimbursed. NOPs submitted more than five days from the date of the risk assessment are not reimbursed For more information on NOP, see the NOP FAQs at http://provider.indianamedicaid.com/providerspecific-information/managed-care/notification-of-pregnancy-(nop).aspx. Billing 1. Providers may receive $60 for one NOP per member, per pregnancy. Note: Duplicate NOPs, those for the same woman and the same pregnancy, do not qualify for the $60 reimbursement. Only one NOP per member, per pregnancy is eligible for reimbursement. Recognized providers will receive a systematic message if the NOP appears to be a duplicate. 2. To be eligible for reimbursement the NOP must: - Be submitted within five calendar days of the date of service to be reimbursed. The date of service is the date the member risk assessment is completed by the recognized provider. - Be completed and submitted prior to 30 weeks of gestation. Salivary Estriol Test for Preterm Labor Risk Assessment The salivary estriol test for preterm labor risk assessment gives the provider additional information to assess the risk for preterm delivery and allows the provider to take steps to treat the patient, even when the patient does not appear to be a high risk by traditional assessment methods. Patients who may be currently missed by traditional risk assessment can be identified and treated, decreasing the chance of premature delivery and the medical impact prematurity entails. The IHCP does not require PA for the salivary estriol test. Table 8.90 shows the ICD-9-CM diagnosis codes that support medical necessity of this test. Table 8.90 – ICD-9-CM Diagnosis Codes for Salivary Estriol Test Diagnosis Code Description V23.2 Pregnancy with history of abortion V23.4 Pregnancy with other poor obstetric history V23.8 Other high-risk pregnancy 658.9 Unspecified 640.9 Unspecified hemorrhage in early pregnancy (with V23.8) 644.0 Threatened premature labor 644.03 Threatened premature labor, antepartum condition, or complication 644.13 Other threatened labor, antepartum condition or complication 654.50 Cervical incompetence 654.53 Cervical incompetence, antepartum condition or complication 654.60 Other congenital or acquired abnormality of cervix; unspecified as to episode of care 8-296 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Diagnosis Code Description 654.63 Other congenital or acquired abnormality of cervix; antepartum condition or complication 621.0 through 621.9 Disorders of uterus, not elsewhere classified The ordering physician must have supporting documentation in the patient’s medical record to support the medical necessity of any tests ordered. Note: Salivary estriol tests are indicated for use in singleton pregnancies. Billing Instructions Providers must bill the salivary estriol test using the code S3652, one unit per test. The test is appropriate for use between gestational ages 22 to 35 weeks, and providers can use it every one to two weeks. The physician’s test order and the claim must indicate modifier U2, second trimester, or Modifier U3, third trimester. The pregnancy series includes multiple tests during the third trimester of pregnancy. Providers must not bill the salivary estriol test when providing home tocolytic therapy using codes S9349, 99601, or 99602. The IHCP closely monitors use of the salivary estriol test for appropriateness of use. Sonography The IHCP reimburses for sonography performed during pregnancy when warranted by one or more of the following conditions: • Early diagnosis of ectopic or molar pregnancy • Fetal age determination if necessitated by the following: - Discrepancy in size versus fetal age - Lack of fetal growth or suspected fetal death - Fetal postmaturity syndrome - Guide for amniocentesis - Placental localization associated with abnormal bleeding - Polyhydramnios or oligohydramnios - Suspected multiple births - Suspected congenital anomaly The IHCP reimburses for sonography for fetal age determination prior to therapeutic, nonelective, abortions when the age of the fetus cannot be determined by the patient’s history and physical examination in the case of fetal demise or for missed abortion. The information may also be essential for the selection of the abortion method when the member is considering a procedure and the conditions meet the requirements of IC 16-10-3-3 for an elective abortion. Echography The IHCP does not reimburse for routine echographies. A diagnosis of normal pregnancy does not explain the reason for the echography. Documentation in the patient’s medical record must substantiate the medical need for the echography. Echographies performed to detect fetal malformations or intrauterine growth retardation should list an ICD-9-CM code from the V22 series as the primary diagnosis and an ICD-9-CM diagnosis code from the V28 series, antenatal screening as the secondary Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-297 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions diagnosis. Pregnancy-related echographies billed without a secondary diagnosis to support medical necessity of the echography are subject to recoupment. The secondary codes are as follows: • V28.3 – Screening for malformation using ultrasonics • V28.4 – Screening for fetal growth retardation using ultrasonics Obstetrical Delivery and Postpartum Care Billing Providers should bill antepartum care separately from the delivery and postpartum care. The IHCP follows CPT guidelines for obstetrical delivery billing. Delivery services include admission to the hospital, the admission history and physical examination, management of uncomplicated labor, vaginal delivery (with or without episiotomy, with or without forceps), or cesarean delivery. Medical problems complicating labor and delivery management may require additional resources, and providers should identify them by using the codes in the Evaluation and Management Services section, in addition to codes for maternity care. Therefore, providers do not bill separately for the hospital inpatient service E/M codes for initial hospital care (99221, 99222, and 99223), subsequent hospital care (99231, 99232, and 99233), and hospital discharge services (99238 and 99239), and the IHCP does reimburse for these to the practitioner billing for the obstetrical delivery. In addition, providers should not bill separately for the E/M codes for observation or inpatient care services, including admission and discharge services (99234, 99235, and 99236), and the IHCP does not reimburse to the practitioner billing for the obstetrical delivery. Any submission of E/M codes by the delivering practitioner should meet the CPT guidelines. The IHCP also allows up to two postpartum visits within 60 days postdelivery. The IHCP may reimburse the provider for up to two inpatient or outpatient postpartum visits using CPT code 59430, which is for postpartum care only. However, if providers use CPT codes 59410 or 59515 – which include delivery plus postpartum care – when billing, they can bill one additional postpartum visit using procedure code 59430. Other Outpatient Office Visits Providers can bill CPT procedure codes 99211–99215 or 99241-99245 for outpatient office visits rendered to pregnant members, if the service is related to a concurrent medical condition requiring medical care or consultative referral. Providers must identify that concurrent condition as either a primary or secondary condition by a valid ICD-9-CM diagnosis code and indicate the appropriate diagnosis reference number (1, 2, 3, or 4) in field 24E of the CMS-1500. Additionally, providers can bill the first prenatal visit with E/M codes 99201–99215, the appropriate trimester modifier, and the expected date of delivery, all indicated on the claim. For billing instructions for services rendered to IHCP Package B members, see the section titled Hoosier Healthwise Package B in this chapter. Normal Pregnancy The following diagnosis codes indicate a normal, low-risk pregnancy: • V22.0 • V22.1 8-298 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Multiple Births Multiple birth deliveries are subject to multiple surgery reimbursement. The current reimbursement policy indicated in 405 IAC 5-28-1 (g) for pricing multiple surgical procedures states that 100 percent of the global fee is reimbursed for the most expensive procedure. The second most expensive procedure is reimbursed at 50 percent of the global fee, and remaining procedures are reimbursed at 25 percent of the global fee. The IHCP reimburses for only one cesarean procedure regardless of the number of babies delivered during the cesarean section. Therefore, only one detail line with one unit of service is billed for cesarean delivery procedure codes. The IHCP reimburses for only one delivery procedure code that includes postpartum care. If there are multiple births during one delivery, the first delivery code can include postpartum care; however, any subsequent deliveries are billed with a procedure code that does not include postpartum care. If billing for multiple births when all births are vaginal deliveries, providers bill the first birth using procedure code 59409 – Vaginal delivery only (with or without episiotomy and/or forceps); 59410 – Vaginal delivery only (with or without episiotomy and/or forceps); including postpartum care; 59612 – Vaginal delivery only, after previous cesarean delivery (with or without episiotomy and/or forceps), or 59614 – Vaginal delivery only, after previous cesarean delivery (with or without episiotomy and/or forceps); including postpartum care. The second birth and any subsequent births are billed using procedure codes 59409 or 59612 with modifier 51 – Multiple procedures. When billing for one vaginal birth and one or more births by cesarean section, the cesarean birth is billed with procedure code 59514 – Cesarean delivery only or 59515 – Cesarean delivery only; including postpartum care, and the vaginal birth is billed using procedure code 59409 or 59612 with modifier 51. When billing for two or more vaginal births and one or more births by cesarean, the cesarean birth(s) are billed on one detail line with one unit of service using procedure code 59514 or 59515. The vaginal birth(s) are billed as separate details using procedure code 59409 or 59612 with modifier 51. If all births are cesarean, the cesarean births are billed using the appropriate procedure code 59514, 59515, 59620, or 59622, and one unit of service. If an assistant surgeon aids in the cesarean delivery, the service is billed using modifiers 80 and 82 to indicate the service was performed by an assistant surgeon. The reimbursement for the assistant surgeon’s services is 20 percent of the allowed amount for the cesarean delivery. Providers cannot bill the same rendering provider number for the surgeon and assistant surgeon details when billing for a cesarean delivery. If billing for assistant surgery services provided by a physician assistant, providers can bill the same rendering provider number for the surgeon and physician assistant surgery details. The detail for the physician assistant is billed with the AS modifier to indicate the service was provided by the physician assistant. The reimbursement for the physician assistant’s services is 20 percent of the allowed amount for the cesarean delivery. High-Risk Pregnancy Prenatal Risk Assessment The IHCP may also consider a pregnant woman medically high-risk if the provider identifies two relative medical conditions during a prenatal risk assessment. To document medically high-risk pregnancies, providers may do one of the following: • Use a standardized risk assessment tool (for example, ACOG Obstetric Medical History). • Use the Prenatal Risk Assessment Form available on the IHCP Web site at http://provider.indianamedicaid.com. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-299 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions • Complete and submit the Notification of Pregnancy (NOP) through Web interChange. Providers are encouraged to use the NOP, which provides a $60 reimbursement per pregnancy submission. See Process for Completion of the Notification of Pregnancy section. Psychosocially High-Risk Pregnancy For high-risk pregnancies identified for psychosocial reasons, the IHCP limits to the standard maximum 14 antepartum care visit requirement. Psychosocially high-risk pregnancies do not automatically qualify for additional antepartum visits unless another medical complication exists that is listed under the ICD-9-CM codes for high-risk pregnancies. Use the ICD-9-CM diagnosis code range V60.0 through V62.9 to indicate a high-risk pregnancy for psychosocial reasons. Medically High-Risk Pregnancy Some pregnant members have medical complications that may adversely affect the outcome of the pregnancy if not adequately treated. These complications, identified during the prenatal assessment, may place the member and the fetus in a high-risk pregnancy category that requires additional primary care management. The IHCP reimburses only physicians for medically high-risk pregnancy care. Providers may refer members identified as having medically high-risk pregnancies only to other appropriate physicians. The IHCP does not permit referrals to nonphysicians for high-risk pregnancyrelated services. Providers in the Care Select program participating in a Memorandum of Collaboration agreement may provide care for patients as defined in the agreement. To be considered a high-risk pregnancy, a woman must have at least two medical risk factors in her current pregnancy or obstetrical history that places her at risk for a preterm birth or poor pregnancy outcome. Medically High-Risk Diagnoses The following list gives examples of common high-risk pregnancy conditions. This list is included for illustrative purposes only and is not an inclusive list of all medical conditions that can complicate pregnancy. Providers may use a standardized risk assessment tool (for example, ACOG Obstetric Medical History), use the Prenatal Risk Assessment Form available on the IHCP Web site at http://provider.indianamedicaid.com, or complete and submit the Notification of Pregnancy (NOP) through Web interChange to document a high-risk pregnancy. Providers are encouraged to use the NOP, which provides a $60 reimbursement per pregnancy submissionFor billing purposes, providers must use the ICD-9-CM diagnosis code appropriate to the patient’s condition: • Abortion, second trimester, in previous pregnancy history • Active herpes or positive culture, third trimester in current pregnancy • Alloimmunization associated with fetal disease in current pregnancy • Anemia, less than 10gm Hgb or less than 30 percent Hct in current pregnancy • Asthma, on medication in current pregnancy • Bleeding, significant after 12 weeks in current pregnancy • Cervix dilated or effaced in current pregnancy or previous history of cone biopsy • Chronic bronchitis in current pregnancy • Deep venous thrombosis in current pregnancy • Diethylstilbestrol (DES) exposure in previous pregnancy history • Diabetes, gestational, diet controlled in current pregnancy 8-300 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions • Diabetes, insulin dependent in current pregnancy • Drug dependence • Eclampsia or severe pre-eclampsia in pregnancy history or present in current pregnancy • Elderly primigravida, 40 years old or older • Epilepsy, on anticonvulsants in current pregnancy • Familial genetic disorder, confirmed in current pregnancy • Gonorrhea, positive culture in current pregnancy • Grand multiparity, greater than five pregnancies with delivery • Heart disease, class III or IV, in current pregnancy • Hepatitis or chronic liver disease in current pregnancy • Hydatidiform mole in pregnancy history or vesicular mole in the immediate prior pregnancy • Hypertension, on medication in current pregnancy • Immediate prior pregnancy stillborn intrauterine death, neonatal, or post neonatal death • Incompetent cervix in previous pregnancy history • Irritable uterus, more than six contractions per hour, confirmed in current pregnancy • Low birth weight baby, less than 2,500 grams, or repetitive low birth weight babies in each pregnancy, documented • Major abdominal surgery in current pregnancy • Major congenital anomaly in previous pregnancy history • Malignancy or leukemia in current pregnancy • Multiple gestation in current pregnancy • Obesity more than 20 percent of weight for height in current pregnancy • Oligohydramnios in current pregnancy • Organ transplantation complicating current pregnancy • Placenta previa, third trimester in current pregnancy • Pneumonia in current pregnancy • Polyhydramnios in current pregnancy • Positive serology in current pregnancy • Post-term pregnancy; current pregnancy has advanced beyond 41 weeks of gestation • Preterm labor in current pregnancy and/or previous obstetric history of preterm delivery • Previous cesarean delivery • Premature rupture of membranes (PROM), confirmed in current pregnancy • Psychosis or mental retardation in current pregnancy • Pyelonephritis in current pregnancy • Renal dialysis status complicating current pregnancy • Respirator-dependent status complicating current pregnancy Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-301 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions • Rubella exposure with rising titer in current pregnancy • Sickle cell anemia, other hemoglobinopathy in current pregnancy • Spontaneous abortions, more than two, first trimester occurrences in previous pregnancy history • Thyroid disease, confirmed in current pregnancy • Trauma, requiring hospitalization in current pregnancy • Tuberculosis, active in current pregnancy • Underweight, more than 10 percent of weight for height in current pregnancy • Uterine anomaly or fibroids in current pregnancy • Weight loss greater than 10 pounds during pregnancy, continuing after 14 weeks The ICD-9-CM diagnosis codes listed in Table 8.91 represent conditions that may complicate pregnancy. These codes, when billed with prenatal office visit procedure codes 59425 and 59426, increase the maximum fee allowed for these services by $10 per visit. Providers may use a standardized risk assessment tool (for example, ACOG Obstetric Medical History), use the Prenatal Risk Assessment Form available on the IHCP Web site at http://provider.indianamedicaid.com, or complete and submit the Notification of Pregnancy (NOP) through Web interChange for these patients and retain a copy of the form in the patient’s record for retrospective review. Providers are encouraged to use the NOP, which provides a $60 reimbursement per pregnancy submission. Providers should refer patients with risk factors to a prenatal care coordinator. The IHCP provides higher reimbursement for prenatal office visits only for patients who present with medical high-risk factors. Table 8.91 – High-Risk Pregnancy – ICD-9-CM Diagnosis Codes Medical Factor Anemias, acquired and hereditary Code 282.0 – 282.9, 283.1X – 283.9, 284.0, 284.01, 284.09, 284.1, 284.2, 284.81, 284.89, 284.9, 285.0 – 285.9, 287.X, 288X, 648.20, 648.23 Medical Factor Code Obesity 649.10, 649.11, 649.12, 649.13, 649.14 Bariatric surgery status 649.20, 649.21 Other (for medical high-riskpregnancy) 255.42, 259.50, 259.51, 259.52, 276.5X, 277.30, 277.31, 277.39, 278.02, V23.1, V23.4X, V23.8X, V23.9, V60.81, V60.89, V61.07, V61.08, V61.23, V61.24, V61.25, V61.42, V62.84, V85.0, V85.2X- V85.4, Coagulation defects 649.34 Other specified complications of pregnancy 646.80, 646.83 Pregnancy with history of abortion 646.30, 646.33, V23.2 Current drug or alcohol 291.82, 304.00 – 304.93, abuse 648.30, 648.33, V61.42 8-302 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Medical Factor Current malignancy or leukemia Diabetes Code Medical Factor 140.0 – 174.9, 176.0 – 184.9, 188.0 – 214.3, 214.8 Preterm complications, history – 221.9, 223.0 – 233.3, 233.30, 233.31, 233.32, of or with current pregnancy 233.39, 233.7 – 236.3, 236.7 – 239.9 Preterm labor in current 362.07, 648.00, 648.03, pregnancy or previous 648.80, 648.83 pregnancy Code 640.00, 640.03, 640.80, 640.83, 640.90, 640.93, 641.00, 641.03, 641.10, 641.13, 641.20, 641.23, 641.30, 641.33, 641.80, 641.83, 641.90, 641.93, 658.10, 658.13, 671.30, 671.33, 760.5 644.00, 644.03, 644.10, 644.13, 644.20, 654.50, 654.53, V13.21 Epilepsy 649.40, 649.41, 649.42, 649.43, 649.44 621.34, 621.35, 624.01, 624.02, 624.09, 629.23, 648.70, 648.73, Potential structural 654.00, 654.03, 654.10, 654.13, complications of pregnancy or 654.20, 654.23, 654.50, 654.53, delivery 654.60, 654.63, 657.00, 657.03, 658.00, 658.03, 664.60, 664.61, 664.64, V13.22, V67.00 Excessive vomiting in pregnancy 643.00, 643.03, 643.10, 643.13, 643.20, 643.23, 643.80, 643.83, 643.90, 643.93 Primigravida, less than 17 years 659.40, 659.43, 659.50, 659.60, or more than 35 years 659.63, V23.81 – V23.84 History of a previous 286.0 – 286.4, 317, 318.X, pregnancy resulting in a 319, V19.5, V21.30 – congenital anomaly or V21.35, V23.4 complication to infant 041.02, 042, 079.5X, 090.X – 099.X, 488.0, 488.1, Infections affecting 567.2X – 567.8X, 616.10, pregnancy 647.33, 647.53, 655.33, 795.71, V08, V01.6 642.00, 642.03, 642.10, 642.13, 642.20, 642.23, 642.30, 642.33, 642.40, 642.43, 642.50, 642.53, 642.60, 642.63, 642.70, 642.73, 642.90, 642.93 345.00 – 345.91, 359.21359.29, 414.2, 415.12, 423.3, 426.82, 440.4, 449, 523.0 – 523.9, 646.13, Maternal diseases or history affecting 646.70, 646.73, 646.80, pregnancy 646.83, 648.10, 648.13, 648.50, 648.53, 648.60, 648.63, 656.23, V23.82, V23.84, V42.0 – V42.9 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Renal complications and infections 580.0 – 593.9, 599.6X, 639.3, 646.20, 646.23, 646.60, 646.63 Respiratory disease, history of 480.0 – 487.0, 491.0 – 491.9, or acquired 493.0X – 493.9X, V46.1X Smoking, more than 10 cigarettes per day 305.11, 648.33, V15.82 Spotting 649.50, 649.51, 649.53 8-303 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Medical Factor Code Medical Factor Code 651.00, 651.03, 651.10, 651.13, 651.20, 651.23, 651.30, 651.33, 651.40, Multiple gestation/grand 651.43, 651.50, 651.53, multipara 651.60, 651.63, 651.70, 651.71, 651.73, 651.80, 651.83, 651.90, 651.93, 659.40, 659.43, V23.3 Tobacco use 649.00, 649.01, 649.02, 649.03, 649.04 Myelogibrosis Uterine size date discrepancy 649.60, 649.61, 649.62, 649.63, 649.64 289.83 Note: Bill each trimester on separate claims. Additional Antepartum Visits Members identified as medically high-risk patients may receive additional antepartum care visits, beyond the maximum of 14 allowed for a normal pregnancy. Claims must indicate the high-risk diagnosis, the LMP, the appropriate CPT procedure code (procedure code 59425 for visits one through six, and procedure code 59426 for visits in excess of six), and the corresponding modifier. Reimbursement The IHCP recognizes that care of pregnant women in the medical high-risk category requires greater physician management, and therefore the IHCP reimburses physicians practicing obstetrics an additional $10 per prenatal visit. The additional reimbursement is available if the provider identifies and documents the specific medical high-risk factors in the medical record and indicates the high-risk diagnosis when submitting claims. Ensure that this information is easily identifiable on the medical record for audit purposes. Pregnancy Services Billing Considerations Providers must indicate the LMP in a MM/YY/DD format in field 14 for paper claim filing and in a CCYYMMDD format in the Last Menstrual Period Date, Data Element 1251 for electronic claim filing. The IHCP does not process for payment any claims for pregnancy-related services submitted without an LMP. Providers must enter the charged amount for each antepartum visit and for each postpartum visit in field 24F of the CMS-1500. Providers must indicate a pregnancy-related diagnosis code as the primary diagnosis when billing for pregnancy-related services. The IHCP limits payment for pregnancy-related services to the following ICD-9-CM diagnoses subject to PA restrictions and in accordance with Indiana Administrative Code. The primary diagnosis codes are V22.0 through V25.2 and V60.0 through V62.9. Providers must indicate the pregnancy-related diagnosis code in field 24E of the CMS-1500. Enter the pregnancy indicator P in field 24H on the CMS-1500. Diagnoses to identify supervision of a high-risk pregnancy for medical reasons are listed in the Medically High-Risk Diagnoses subsection in this chapter. 8-304 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Hoosier Healthwise Package B – Pregnancy and Urgent Care Only The IHCP pays only for abortions to terminate pregnancies resulting from rape or incest, in addition to abortions necessary to save the life of the pregnant mother. Hoosier Healthwise Package B members are entitled to coverage of services related to pregnancy, which includes prenatal, delivery, and postpartum services as well as conditions that may complicate the pregnancy. Hoosier Healthwise Package B covers most conditions that can complicate pregnancies but does not cover elective services as pregnancy-related. Additionally, Hoosier Healthwise Package B members are eligible for family planning, transportation, and pharmacy services. As with all claims, the IHCP reimburses services to Hoosier Healthwise Package B limited benefits in accordance with the Indiana Administrative Code. Note: For RBMC members, contact the appropriate MCO for additional instructions. Services for Hoosier Healthwise Package B must comply with the following restrictions: • The IHCP does not reimburse for any services other than pregnancy-related services. • The IHCP pays for drugs prescribed for indications directly related to the pregnancy in accordance with IAC restrictions. In addition to drug coverage, transportation, family planning, routine prenatal care, delivery, and postpartum care, the IHCP reimburses providers for a condition that may complicate the pregnancy. In other words, the IHCP covers a service provided to a pregnant woman for the treatment of a chronic or abnormal disorder, as identified by ICD-9-CM diagnosis codes 649.00 – 649.04, 649.10 – 649.14, 649.20 – 649.21, 649.23 – 649.24, 649.30 – 649.34, 649.40 – 649.44, 649.50 – 649.51, 649.53, 649.60 – 649.64, 649.70 – 649.71, and 649.73, as well as urgent care. The IHCP defines a condition that may complicate the pregnancy as any condition manifesting itself by symptoms of sufficient severity that the absence of medical attention could reasonably be expected to result in a deterioration of the patient’s condition or a need for a higher level of care. The IHCP does not dictate to physicians conditions that may or may not complicate a pregnancy. Therefore, if the physician determines that the illness or injury could complicate the pregnancy or have an adverse effect on the outcome of the pregnancy, the IHCP covers the care provided for that illness or injury. Physicians must use one of the diagnosis codes previously listed as the primary diagnosis on the claim. If none of the diagnosis codes are appropriate for the situation, the physician should list a pregnancy diagnosis code as the primary diagnosis code and identify the illness or injury being treated as the secondary diagnosis code. Following termination of the pregnancy, a pregnancy and urgent care only member is eligible solely for transportation, family planning, and postpartum care services. The IHCP does not reimburse for urgent care services unrelated to complications of the puerperium. This eligibility begins on the last day of pregnancy and extends through the end of the month in which the last day of the 60-day period ends. When billing for urgent care services, providers must appropriately mark and code claims as emergency. The primary diagnosis code must be pregnancy-related or the IHCP denies the claim. Providers must indicate the pregnancy-related code in field 24E on the CMS-1500 claim form. If the pregnancy diagnosis does not adequately address the specific reason for the visit or care, providers must also include the visit or care diagnosis as a secondary or tertiary diagnosis on the claim form. Providers must enter the pregnancy indicator, P, in field 24H of the CMS-1500 claim form. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-305 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions If a pregnancy and urgent care only member receives a sterilization procedure following delivery, the primary diagnosis code should be pregnancy with voluntary sterilization as a secondary diagnosis. The member must complete consent forms, and the provider must send them with the claim. Proton Treatment Billing The IHCP has determined that it is appropriate for providers to use the CPT codes listed in Table 8.92 to report the technical component only of the CPT codes noted in Table 8.92 for reporting proton treatment delivery. Therefore, effective for dates of service on or after December 1, 2006, the IHCP does not reimburse providers services reported using the CPT codes listed in Table 8.92 and billed with modifiers 26 – Professional component and TC – Technical component. Providers are advised to bill CPT codes 77520, 77522, and 77525 for the technical component only. Additionally, providers are advised to report the professional services using an appropriate CPT procedure code. Table 8.92 – Proton Treatment Delivery CPT Code 77520 77522 77525 Description Proton treatment; simple, without compensation Proton treatment; simple, with compensation Proton treatment delivery; complex Ophthalmological Services Coverage and Billing Procedures The IHCP provides reimbursement for ophthalmology services, subject to the following restrictions: • One routine vision care examination and refraction for members 18 years old and younger, per rolling calendar year • One routine vision care examination and refraction for members 19 years old and older, every two years • The member must meet the following medical necessity guidelines in at least one eye for the provision of eyeglasses (including replacement eyeglasses): - A change of 0.75 diopters for patients 6 to 42 years old - A change of 0.50 diopters prescription or change for patients more than 42 years old - An axis change of at least 15 degrees • Replacement frames and lenses only when the medical necessity guidelines are met or when necessitated by loss, theft, or damage beyond repair Date of Service Definition All claims must reflect a date of service. The date of service is the date the specific services were actually supplied, dispensed, or rendered to the patient. For example, when rendering services for space maintainers or dentures, the date of service must reflect the date the appliance or denture is delivered to the patient. This requirement is applicable to all IHCP-covered services. 8-306 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Vision Coding and the Vision Services Code Set Providers must use the appropriate CPT codes or HCPCS codes when submitting claims for vision services to the IHCP. Optometrists and opticians are subject to the vision services code set, and the IHCP reimburses them only for services listed on the code set. IHCP provider code sets are available on the IHCP Web site at http://provider.indianamedicaid.com. The IHCP considers the following services bundled and not separately billable to the IHCP or the patient: • Eyeglass cases • Fitting of eyeglasses • Neutralization of lenses • Verification of prescription Vision Procedures Limited to One Unit IHCP providers may only bill one unit, per member, per day for the procedures listed in Table 8.93. Claims that have more than one unit per day for these codes will automatically cut back and pay for one unit. Providers that have been reimbursed for more than one unit may be subject to post-payment review and possible recoupment. Table 8.93 – Eye Exams and Other Ophthalmological Services CPT Code 92002 92004 92012 92014 92018 92019 92020 92060 92065 92081 Definition Ophthalmological services: medical examination and evaluation with initiation of diagnostic and treatment program; intermediate, new patient Ophthalmological services: medical examination and evaluation with initiation of diagnostic and treatment program; comprehensive, new patient, one or more visits Ophthalmological services: medical examination and evaluation, with initiation or continuation of diagnostic and treatment program; intermediate, established patient Ophthalmological services: medical examination and evaluation, with initiation or continuation of diagnostic and treatment program; comprehensive, established patient, one or more visits Ophthalmological examination and evaluation, under general anesthesia, with or without manipulation of globe for passive range of motion or other manipulation to facilitate diagnostic examination; complete Ophthalmological examination and evaluation, under general anesthesia, with or without manipulation of globe for passive range of motion or other manipulation to facilitate diagnostic examination; limited Gonioscopy (separate procedure) Sensorimotor examination with multiple measurements of ocular deviation (such as restrictive or paretic muscle with diplopia) with interpretation and report (separate procedure) Orthoptic and/or pleoptic training, with continuing medical direction and evaluation Visual field examination, unilateral or bilateral, with interpretation and report; limited examination (such as tangent screen, Autoplot, arc perimeter, or single stimulus level automated test, such as Octopus 3 or 7 equivalent) Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-307 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions CPT Code Definition 92130 Visual field examination, unilateral or bilateral, with interpretation and report; intermediate examination (such as at least two isopters on Goldmann perimeter, or semiquantitative, automated suprathreshold screening program, Humphrey suprathreshold automatic diagnostic test, Octopus program 33) Visual field examination, unilateral or bilateral, with interpretation and report; extended examination (such as Goldmann visual fields with at least three isopters plotted and static determination within the central 30 degrees, or quantitative, automated threshold perimetry, Octopus programs G-1, 32 or 42, Humphrey visual field analyzer full threshold programs 302, 24-2, or 30/60-2) Serial tonometry (separate procedure) with multiple measurements of intraocular pressure over an extended time period with interpretation and report, same day (such as diurnal curve or medical treatment of acute elevation of intraocular pressure) Tonography with interpretation and report, recording indentation tonometer method or perilimbal suction method Tonography with water provocation 92140 Provocative tests for glaucoma, with interpretation and report, without tonography 92250 Fundus photography with interpretation and report 92260 Ophthalmodynanometry 92265 92270 Needle oculoelectromyography, one or more extraocular muscles, one or both eyes, with interpretation and report Electro-oculography with interpretation and report 92275 Electroretinography with interpretation and report 92284 Dark adaptation examination, with interpretation and report 92285 External ocular photography with interpretation and report for documentation of medical progress (such as close-up photography, slit lamp photography, goniophotography, stereophotography) Special anterior segment photography with interpretation and report; with specular endothelial microscopy and cell count Special anterior segment photography with interpretation and report; with fluorescein angiography Prescription of optical and physical characteristics of and fitting of contact lens, with medical supervision of adaptation; corneal lens for aphakia, one eye Prescription of optical and physical characteristics of and fitting of contact lens, with medical supervision of adaptation; corneal lens for aphakia, both eyes Prescription of optical and physical characteristics of and fitting of contact lens, with medical supervision of adaptation; corneoscleral lens Prescription of optical and physical characteristics of contact lens, with medical supervision of adaptation and direction of fitting by independent technician; corneal lens for aphakia, one eye Prescription of optical and physical characteristics of contact lens, with medical supervision of adaptation and direction of fitting by independent technician; corneal lens for aphakia, both eyes 92082 92083 92100 92120 92286 92287 92311 92312 92313 92315 92316 8-308 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Eye Examinations Providers should use the CPT code that best describes the examination to report eye examinations. Table 8.94 lists CPT codes for eye examinations. Table 8.94 – Eye Examination CPT Codes 99201 – 99215 99241 – 99245 99251 – 99255 92002 – 92014 The eye examination includes the following services, and providers should not bill separately for these: • Biocular measurement • External eye examination • Gross visual field testing including color vision, depth perception, or stereopsis • Routine ophthalmoscopy • Tonometry • Visual acuity determination Providers may code examinations in which counseling and coordination of care are the dominant services with the appropriate E/M code using the time factor associated with the code. Documentation in the patient’s record must include the total time of the encounter and a synopsis of the counseling topics and coordination of care efforts. Table 8.95 lists CPT codes for eye examinations including counseling and coordination. Table 8.95 – Eye Examination including Counseling and Coordination 99201 – 99215 99251 – 99255 CPT Codes 99241 – 99245 Providers can submit the following diagnostic services, if medically necessary, in addition to the eye examination: • Dark adaptation examination • Determination of a refractive state • Extended color vision examination • External ocular photography and special anterior segment photography • Fitting of contact lens for treatment of disease, limited visual field, intermediate visual field, extended visual field, serial tonometry, and tonography • Gonioscopy • Orthoptic or pleoptic training • Provocative tests for glaucoma, extended ophthalmoscopy, fluorescein angiography, indocyaninegreen angiography, fundus photography, ophthalmodynamometry, needle oculoelectromyography, and electroretinography • Scanning computerized ophthalmic diagnostic imaging • Sensorimotor examination Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-309 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Orthoptic or Pleoptic Training, Vision Training, and Therapies Coverage Criteria CPT code 92065 – Orthoptic or pleoptic training, with continuing medical direction and evaluation covers all vision training therapies. Providers should be sure to meet the following criteria: • Submit services using CPT code 92065. • Limit 92065 to one unit or visit per day. • Have a physician or an optometrist order all vision therapy services. • The physician or optometrist must document, in the medical record, a diagnosis and treatment plan and reevaluations of the need for continued treatment. Providers must document this information in the member’s medical record. • An optometrist, a physician, or a supervised certified or trained staff can perform vision therapy services. • Staff trained or certified in vision training may perform orthoptic and pleoptic training only under the direct supervision of an optometrist or physician. Direct supervision requires that the supervising physician or optometrist must be physically available at the time and the place where the vision therapy services are rendered. • Only the supervising optometrist or physician may document the treatment plan and reevaluations in the medical record. All documentation of directly supervised vision therapy services rendered by opticians, orthoptists, or staff trained in vision therapy must be cosigned by the supervising optometrist or physician in the medical record. These services are noncovered by Medicare, and providers can bill them directly to Medicaid on a CMS-1500 for dually eligible members. Lenses Providers should include prescription of lenses, when required, in 92015 – Determination of refractive state, which includes specification of lens type (monofocal, bifocal, or other), lens power, axis, prism, absorptive factor, impact resistance, and other factors. The IHCP does not provide coverage for the services listed in Table 8.96. Table 8.96 – Procedure Codes Not Covered by the IHCP Procedure Code 8-310 Description V2702 Deluxe lens feature V2744 Tint, photochromic, per lens V2750 Antireflective coating, per lens V2760 Scratch resistant coating, per lens V2781 Progressive lenses, per lens V2782 Lens, index 1.54 to 1.65 plastic or 1.60 to 1.79 glass, excludes polycarbonate, per lens V2783 Lens, index greater than or equal to 1.66 plastic, or greater than or equal to 1.80 glass, excludes polycarbonate, per lens V2786 Specialty occupational multi-focal lens, per lens Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions If a member chooses to upgrade to progressive lenses, transitional lenses, anti-reflective coating, or tint numbers other than 1 and 2, providers can bill the basic lens V code to the IHCP. Providers can bill the upgrade portion to the member only if they gave the member appropriate advance notification of noncoverage. According to 405 IAC 5-23-4 (2), the IHCP may only reimburse for tints 1 and 2. Table 8.97 – Covered Codes for Tints Code with Modifier Description V2745 U1 Tint, plastic, rose 1 or 2, per lens V2745 U2 Tint, glass, rose 1 or 2, per lens The IHCP covers safety lenses only for corneal lacerations and other severe intractable ocular or ocular adnexal disease. The IHCP developed specific criteria for polycarbonate lenses to ensure that providers use the lenses only for medically necessary conditions that require additional ocular protection for members. HCPCS code V2784–Lens, polycarbonate or equal, any index, per lens remains covered when a corrective lens is medically necessary, and if one or more of the following criteria is met: • Member has carcinoma in one eye, and the healthy eye requires a corrective lens. • Member has only one eye that requires a corrective lens. • Member has had eye surgery and still requires the use of a corrective lens. • Member has retinal detachment or is post-surgery for retinal detachment and requires a lens to correct a refractive error of one or both eyes. • Member has a cataract in one eye or is post-cataract surgery and requires a lens to correct a refractive error of one or both eyes. • Member has low vision or legal blindness in one eye with normal or near normal vision in the other eye. • Other conditions deemed medically necessary by the optometrist or ophthalmologist exist. These conditions must be such that one eye is affected by an intractable ocular condition, and the polycarbonate lens is being used to protect the remaining vision of the healthy eye. In all these situations, one or both eyes must be affected by an intractable ocular condition. The IHCP covers the polycarbonate lens only to protect the remaining vision of the healthy eye when it is medically necessary to correct a refractive error. Patient charts must support medical necessity. The IHCP monitors use of these lenses in postpayment reviews. The IHCP covers contact lenses when they are medically necessary. The IHCP does not require documentation with the claim, but providers must maintain documentation in the patient’s medical record for postpayment review. Examples of medically necessary contact lenses include, but are not limited to, patients with severe facial deformity who are physically unable to wear eyeglasses or who have severe allergy to all frame materials. The prescription of contact lens includes the specification of optical and physical characteristics such as power, size, curvature, flexibility, and gas permeability, and providers can bill with CPT codes 92310 through 92326, which is not part of the general ophthalmology services. Fitting contact lenses includes instruction and training of the wearer and incidental revision of the lenses during the training period. Providers should report follow-up of successfully fitted extended wear lenses as part of the general ophthalmological service. The IHCP does not reimburse for more than one unit for eye exams and other ophthalmologic procedures. (See Table 8.97 for codes applying to eye exams and other ophthalmological services.) Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-311 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions IHCP providers may only bill one unit, per member, per day for the codes listed in the table below. Claims that have more than one unit per day for these codes will automatically cutback and pay for one unit. Table 8.97 – Eye Exams and Other Ophthalmological Services CPT Codes 92002 92004 92012 92014 92018 92019 92020 92060 92065 92081 92082 92083 92100 92120 92130 92140 92250 92260 92265 92270 92275 92284 92285 92286 92287 92311 92312 92313 92315 92316 Frames The IHCP reimburses for frames including, but not limited to, plastic or metal. Providers should bill for frames using V2020. Providers who receive payment from the IHCP for frames may not bill the member for any additional cost above the IHCP reimbursement. The IHCP does not cover any portion of a deluxe or fancy frame purchase, except when medically necessary. Situations include, but are not limited to, special frames to accommodate a facial deformity or anomaly, allergic reaction to standard frame material, or infant and child frames. Providers must submit charges for medically necessary deluxe frames with procedure code V2025. The IHCP requires documentation outlining the medical necessity when providers submit the claim. Providers must submit an invoice for the frames with the claim. The IHCP reimburses at 90 percent of the retail price, as indicated on the invoice. If a patient chooses to upgrade to a deluxe frame, the IHCP considers the entire frame noncovered, and the provider may bill it to the patient if the provider gave proper advance notice of no coverage to the member and the member signed it. In these situations, providers should submit only the claim for the lenses to the IHCP. The IHCP does not cover the following services: • Lenses with decorative designs • Fashion tints, gradient tints, sunglasses, and photochromatic lenses - The IHCP does cover tint numbers 1 and 2, rose A, pink 1, soft lite, cruxite, and velvet lite, subject to medical necessity. • Oversized lenses larger than 61mm, except when medical necessity is documented The IHCP reimburses for lenses and other optical supplies, except frames, at the lower of the provider’s usual and customary charge or the IHCP maximum rate on file. Note: Replacement of eyeglasses beyond the indicated criteria must be medically necessary and clearly documented in the patient’s medical record. Replacement eyeglasses represent the beginning of a new limitation period. Adoption of Modifiers for Replacement Eyeglasses Repair or replacement covers the part of the eyeglasses that is broken or damaged. Patients are not entitled to a new pair of eyeglasses if the lenses and/or frames can be repaired. 8-312 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Members younger than 19 years of age who have met the medical necessity for replacement eyeglasses may be eligible for a new pair of eyeglasses one year from the date when the IHCP provided their replacement eyeglasses. Members 19 years of age and older who have met the medical necessity for replacement eyeglasses may be eligible for a new pair of eyeglasses two years from the date when the IHCP provided their replacement eyeglasses. If a member needs replacement eyeglasses due to loss, theft, or damage beyond repair prior to the established frequency limitations, providers must use the RP modifier for dates of service on or before December 31, 2008, and U8 modifier for dates of service on or after January 1, 2009, to bill for the replacement lenses and/or frames. Providers must include documentation in the member’s medical record to substantiate the need for replacement frames or lenses. Documentation that eyeglasses have been lost, stolen, or broken beyond repair must include a signed statement by the member detailing how the eyeglasses were lost, stolen, or broken. If a member needs replacement eyeglasses due to a change in prescription as specified in 405 IAC 523-4 and prior to the established frequency limitations, providers must use modifier SC when billing lenses and/or frames. Use of either modifier indicates that the appropriate documentation is on file in the patient’s record to substantiate the need to replace lenses or frames. Replacement of eyeglasses must be for medical necessity. Note: The IHCP requires modifiers only needed on claims for replacement of frames or lenses within the one- or two-year period, based on the patient’s age at the time of service; however, all eyeglasses dispensed must meet the minimum prescription requirements for the initial dispensing and each subsequent dispensing of eyeglasses. Written Correspondence Ophthalmology and optometric providers may not have the most current information available about services previously rendered to the member and paid by the IHCP. This could result in reduced reimbursement or no reimbursement for rendered services. The HP Provider Written Correspondence Unit addresses specific questions pertaining to the IHCP. Providers may write to this unit to determine whether particular members have exceeded their service limitations. Providers should allow 10 business days to receive an answer to a written inquiry. Benefit limits for optometry services are available through the Eligibility Verification System (EVS). Chapter 3 of this manual provides additional information. When providers use the Indiana Medicaid Inquiry Form, it assists the HP Provider Written Correspondence Unit in providing the timeliest response. The IHCP may return incomplete written inquiry forms for additional information. Clearly stating the reason for the inquiry enables analysts to research the issue and provide a resolution. Providers should not send inquiries to resubmit claims previously rejected. Mail all written inquiries to the following address: HP Provider Written Correspondence P.O. Box 7263 Indianapolis, IN 46207-7263 Note: For RBMC members, contact the appropriate MCO. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-313 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Download copies of the Indiana Medicaid Inquiry Form from the http://provider.indianamedicaid.com Web site or request copies from the following address: HP Forms Request P.O. Box 7263 Indianapolis, IN 46207-7263 Note: For RBMC members, contact the appropriate MCO to obtain PA. Billing a Member for Services that have Exceeded Benefit Limitations Providers may bill IHCP members for services exceeding the ophthalmology benefit limitations under the following circumstances: • If the EVS informs the provider that the limitation has already been met, the member is informed. If the member still wishes to receive the service, they are asked to sign a waiver stating that the service will not be covered because benefits have been exhausted. • If the EVS does not show that benefits have been exhausted, the provider may ask the member or their guardian to attest in writing that they have not received Medicaid covered glasses within the past one or two years (depending upon their age). The member is informed that if they are misrepresenting and the provider’s claim is denied for exceeding benefit limitations, the member will be responsible for the charges. Prior Authorization The IHCP does not require PA for vision care services except for the following provisions: • Blepharoplasty for a significant obstructive vision problem • Prosthetic device, except eyeglasses • Reconstruction or plastic surgery Vision Services and Managed Care Providers furnishing optical or ophthalmology services to members enrolled in Care Select must follow existing PA guidelines for surgical services. The IHCP makes vision care and medical services available to Care Select and Hoosier Healthwise members on a self-referral basis. Providers must submit RBMC member claims to the members’ MCO for payment. Surgeries furnished to patients enrolled in the RBMC must be prior authorized by the MCO in accordance with the MCO guidelines. Podiatric Services Coverage and Billing Procedures Routine foot care includes the following: • Cutting or removal of corns, calluses, or warts, including plantar warts • Trimming of nails, including mycotic nails 8-314 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions • Treatment of fungal, mycotic infection of the toenail is routine foot care only when the following applies: - Clinical evidence of infection of the toenail is present. - Compelling medical evidence exists, documenting that the patient either has a marked limitation of ambulation requiring active treatment of the foot or, in the case of nonambulatory patient, has a condition that is likely to result in significant medical complications in the absence of such treatment. The IHCP covers routine foot care only if a medical doctor or doctor of osteopathy has seen the patient for treatment or evaluation of a systemic disease during the six-month period prior to rendering routine foot care services. Providers must include the name and provider number of the physician in the CMS1500 in fields 17 and 17A, respectively. Providers should include the nature of the foot condition being treated on the claim form, include the diagnosis in field 21 of the CMS-1500, and referred to the diagnosis in field 24E of the CMS-1500. The IHCP covers a maximum of six routine foot care services per rolling 12-month period when the patient has one of the following: • A systemic disease of sufficient severity that treatment of the disease may pose a hazard when performed by a nonprofessional • Has had severe circulatory impairment as a result of the systemic condition or has had areas of desensitization in the legs or feet • The following is a list of the ICD-9-CM diagnosis codes that represent those systemic conditions that would justify coverage for routine foot care: - Diabetes mellitus, ICD-9-CM codes 250.00 through 250.91 - Arteriosclerotic vascular disease of extremities, ICD-9-CM code 440.20 through 440.29 - Thromboangiitis obliterans, ICD-9-CM code 443.1 - Post-phlebitis syndrome, ICD-9-CM code 459.10 through 459.19 - Polyneuropathy of the feet, ICD-9-CM codes 357.1 through 357.7 The IHCP does not cover routine foot care services for Package C. The IHCP reimburses when a podiatrist renders orthotic services covered by Medicare for all eligible members receiving Medicare and Traditional Medicaid. The IHCP requires PA for the following: • When a podiatrist prescribes or supplies corrective features built into shoes such as heels, lifts, and wedges for members 20 years old and younger. • When a podiatrist fits or supplies orthopedic shoes for members with severe diabetic foot disease, subject to the restrictions and limitations outlined in 405 IAC 5-19-10. Second Opinions The IHCP may require providers to obtain a second or third opinion substantiating the medical necessity or approach to the following surgical procedures: • Bunionectomy procedures • All surgical procedures involving the foot Refer to 405 IAC 5-8 for documentation about second opinions. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-315 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Office Visits The IHCP reimburses for podiatric office visits, subject to the following restrictions: • The IHCP limits reimbursement to one office visit, using procedure codes 99211, 99212, and 99213, per member, per 12 months, without obtaining PA. • The IHCP reimburses for new patient office visits, using procedure codes 99201, 99202, and 99203, one per member, per provider, within the last three years as defined by the CPT guidelines. • Providers can bill a visit separately only on the initial visit. For subsequent visits, the procedure performed on that date includes the reimbursement for the visits, and providers do not bill them separately. However, if a second, significant problem is addressed on a subsequent visit, the provider can report the visit code with the 25 modifier. The provider needs to send documentation indicating why the subsequent visit was required. Note: The SUR Department identified utilization issues related to podiatrists inappropriately billing multiple units of CPT® codes 99201-99203 for new patient visits and CPT codes 99211-99213 for established patient visits. The SUR Department advises all providers to carefully review claims submitted to the IHCP to ensure proper billing of units for these services. The SUR Department reviews claims to determine any inappropriate reimbursement and recoups overpayments. If a provider identifies overpayments related to these errors, the provider should file an adjustment or contact the SUR Department to arrange for repayment. Surgical Services The IHCP reimburses for the following surgical procedures without PA: • Drainage of skin abscesses of the foot • Drainage or injections of a joint or bursa of the foot • Surgical cleansing of the skin • Trimming of skin lesions of the foot, other than those identified as included in routine foot care services The IHCP reimburses for surgical procedures other than those mentioned above, performed within the scope of the podiatrist’s license, subject to PA, as specified in 405 IAC 5-26, Podiatric Services. For all surgical procedures on one or both feet performed on the same date, the IHCP pays 100 percent of the IHCP allowance for the major procedure and 50 percent of the IHCP allowance for subsequent procedures. If providers perform surgery on both feet, and if the surgery on the second foot is performed at least five days after surgery on the first foot, 100 percent allowance is payable for the second surgery. If providers perform the major surgical procedure on one toe, a time period of five days must elapse before the IHCP would again pay 100 percent of the IHCP-allowable reimbursement for subsequent surgery on the same foot. For surgery performed sooner than five days, the IHCP pays 50 percent of the IHCP-allowable reimbursement. If providers perform the major surgical procedure on one toe, a period of 30 days must elapse before the IHCP would again pay at 100 percent of IHCP-allowable reimbursement for a subsequent surgery on the same toe. For surgery performed sooner than 30 days, the IHCP reimburses 50 percent of the IHCP-allowable reimbursement. 8-316 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions For podiatric surgical procedures, including diagnostic surgical procedures, providers cannot fragment and bill separately. Generally, providers include such procedures in the major procedure. Procedures in this category include, but are not limited to, the following: • Arthroscopy or arthrotomy procedures in the same area as a major joint procedure unless the claim documents a second incision was made • Local anesthesia administered to perform the surgical or diagnostic procedure • Scope procedures used for the surgical procedure approach Laboratory and X-ray Services The IHCP reimburses a podiatrist for laboratory or X-ray services only if the services are rendered by or under the personal supervision of the podiatrist. For services ordered by a podiatrist, but performed by a laboratory or X-ray facility, the laboratory or X-ray facility bills directly to the IHCP. The IHCP may reimburse the podiatrist for collection of a specimen sent to the laboratory. The IHCP does not reimburse for comparative foot X-rays, unless prior authorized. The IHCP reimburses for the following lab and X-ray services billed by a podiatrist: • Cultures for foot infections and mycotic fungal nails for diagnostic purposes • Medically necessary presurgical testing • Sensitivity studies for treatment of infection processes Prior Authorization The IHCP requires PA for the following: • Corrective features built into shoes, such as heels, lifts, and wedges, for a member younger than 20 years old • Orthopedic shoes for members with severe diabetic foot disease, subject to the restrictions and limitations outlined in 405 IAC 5-19-10 • Palliative or hygienic care for the removal or trimming of corns, calluses, and nails covered for members with painful keratosis, diseased nails, or deformed nails (authorization covers six treatments per year) • Routine foot care in excess of six services per year for patients with diabetes mellitus, peripheral vascular disease, or peripheral neuropathy Podiatric Services and Managed Care Providers furnishing podiatric services to members enrolled in Care Select must follow existing PA guidelines. Podiatric services are available to Care Select and Hoosier Healthwise patients on a selfreferral basis. Providers should submit RBMC member claims to the member’s MCO for payment. For services that require PA furnished to members enrolled in RBMC, providers must obtain prior authorization from the MCO in accordance with the MCO guidelines. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-317 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Radiology Services Coverage and Billing Procedures Providers furnishing radiology services to members enrolled in Care Select must follow existing PA guidelines. The IHCP makes radiology services available to Care Select and Hoosier Healthwise patients on a self-referral basis. Providers submit RBMC member claims to the member’s MCO for payment. Services that require PA furnished to members enrolled in RBMC must be prior authorized by the MCO in accordance with the MCO guidelines. Some radiological procedures encompass professional and technical components of the service. A physician typically performs the professional component of the procedure. The IHCP reimburses radiology inpatient and outpatient facilities, freestanding clinics, and surgical centers for services provided to members subject to the following limitations: • The IHCP requires PA for any radiological services that exceed the use parameters set out in this section. • For a radiological service, a physician or other practitioner authorized to do so under state law must order it in writing. • The radiological service facility must bill the IHCP directly for components provided by the facility. When two practitioners separately provide a portion of the radiology service, each practitioner may bill the IHCP directly for the component provided. The IHCP reimburses a physician or other practitioner for radiological services only when that physician or practitioner directly supervised the performance of those services. • The IHCP reimburses a physician for the professional component by billing the appropriate CPT code along with Modifier 26, Professional component. When billing only the technical component, providers must use Modifier TC, Technical component, with the appropriate CPT code. When billing for professional and technical components of service, providers should use no modifiers. CPT codes for which providers should use these modifiers to bill are listed in the Federal Register under RVUs and related information. • For radiology procedures, providers cannot fragment and bill separately. Such procedures may include, but are not limited to, the following: - The IHCP does not reimburse for CPT codes for supervision and interpretation procedures when the same provider bills for the complete procedure CPT code. - If two provider specialties are performing a radiology procedure, the radiologist bills for the supervision and interpretation procedure, and the second physician bills the appropriate injection, aspiration, or biopsy procedure. • The IHCP does not reimburse for angiographic procedures performed as an integral component of a surgical procedure by the operating physician. Such procedures include, but are not limited to, the following: - Angiographic injection procedures during coronary artery bypass graft - Peripheral, percutaneous transluminal angioplasty procedures 8-318 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Utilization Criteria Criteria for the use of radiological services include consideration of the following: • Evidence that this radiologic procedure is necessary for the appropriate treatment of illness or injury • X-rays of the spinal column limited to cases of acute documented injury or a medical condition in which interpretation of X-rays would make a direct impact on the medical/surgical treatments • IHCP reimbursement for X-rays of the extremities and spine for the study of neuromusculoskeletal conditions The IHCP does not reimburse for radiology examinations of any body part taken as a routine study not necessary for the diagnosis or treatment of a medical condition. Situations generally not needing radiology services include, but are not limited to, the following: • Fluoroscopy without films • Pregnancy • Premarital examinations • Research studies • Routine physical examinations or check-ups • Screening, preoperative chest X-ray Providers must document all services related to radiological examinations in the patient’s record. Computerized Tomography Scans The IHCP may reimburse for diagnostic examination of the head (head scan) and of other parts of the body (body scans), performed by computerized tomography (CT) scanners, subject to the following restrictions: • The scan should be reasonable and necessary for the individual patient. • The provider must find use of a CT scan to be medically appropriate considering the patient’s symptoms and preliminary diagnosis. • The IHCP reimburses only for CT scans performed with equipment certified by the FDA. • The IHCP does not reimburse for whole abdomen or whole pelvis scans on greater than 20 cuts, except in staging cancer for treatment evaluation. • The IHCP does not require PA for CT scans. PET Scans If the member is an inpatient, the IHCP covers the Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scan in the DRG payment to the hospital. All claims for reimbursement of PET scans must include an appropriate ICD-9-CM diagnosis code. The HCPCS codes for PET scans represent the global service. Providers performing just one component of the test should appropriately use modifier TC (technical component) or 26 (professional component). Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-319 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions If the member is an outpatient and has services performed in the outpatient area of the hospital or a freestanding facility, the provider should bill for the PET scan as follows: • Reimbursement for professional services, reported with the appropriate CPT code, modifier 26 (professional services), and the appropriate ICD-9-CM code, and billed on a CMS-1500 or 837P electronic transaction, reimburse from the resource-based relative value scale (RBRVS) fee schedule. • Reimbursement for the appropriate CPT code, billed with the technical component (TC) and appropriate ICD-9-CM code on a UB-04 claim form, reimburse based on the statewide max rate. Radionuclide Bone Scans The IHCP reimburses for radionuclide bone scans when performed for the detection and evaluation of suspected or documented bone disease. Upper Gastrointestinal Studies The IHCP reimburses for upper gastrointestinal (GI) studies when performed for detection and evaluation of diseases of the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum. The IHCP does not cover an upper GI study for a patient with a history of duodenal or gastric ulcer disease unless the patient was recently symptomatic. The IHCP does not cover an upper GI study in the preoperative cholecystectomy patient unless symptoms indicate an upper GI abnormality in addition to cholelithiasis, or if the etiology of the abdominal pain is uncertain. Hospice Providers The attending physician’s billed charges should not include costs for services such as X-rays and laboratory. The daily hospice care rates include these costs, and they are expressly the responsibility of the hospice provider. Renal Dialysis Physician Services Coverage and Billing Procedures The IHCP uses the same criteria and coding methodology as Medicare, using HCPCS codes 9095190970 to bill for the management of ESRD dialysis services. Table 8.98 lists the HCPCS codes for ESRD. Table 8.98 – HCPCS Codes for ESRD Code 90951 8-320 Description End-stage renal disease (ESRD)-related services during the course of treatment, for patients younger than 2 years of age to include monitoring for the adequacy of nutrition, assessment of growth and development, and counseling of parents; with four or more face-to-face physician visits per month Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Code Description 09052 ESRD-related services during the course of treatment, for patients younger than 2 years of age to include monitoring for the adequacy of nutrition, assessment of growth and development, and counseling of parents; with two or three face-to-face physician visits per month 90953 ESRD-related services during the course of treatment, for patients younger than 2 years of age to include monitoring for the adequacy of nutrition, assessment of growth and development, and counseling of parents; with one face-to-face physician visit per month 90954 ESRD-related services during the course of treatment, for patients 2-11 years of age to include monitoring for the adequacy of nutrition, assessment of growth and development, and counseling of parents; with four or more face-to-face physician visits per month 90955 ESRD-related services during the course of treatment, for patients 2-11 years of age to include monitoring for the adequacy of nutrition, assessment of growth and development, and counseling of parents; with two or three face-to-face physician visits per month 90956 ESRD-related services during the course of treatment, for patients 2-11 years of age to include monitoring for the adequacy of nutrition, assessment of growth and development, and counseling of parents; with one face-to-face physician visit per month 90957 ESRD-related services during the course of treatment, for patients 12-19 years of age to include monitoring for the adequacy of nutrition, assessment of growth and development, and counseling of parents; with four or more face-to-face physician visits per month 90958 ESRD-related services during the course of treatment, for patients 12-19 years of age to include monitoring for the adequacy of nutrition, assessment of growth and development, and counseling of parents; with two or three face-to-face physician visits per month 90959 ESRD-related services during the course of treatment, for patients 12-19 years of age to include monitoring for the adequacy of nutrition, assessment of growth and development, and counseling of parents; with one face-to-face physician visit per month 90960 ESRD-related services during the course of treatment, for patients 20 years of age and older; with four or more face-to-face physician visits per month 90961 ESRD-related services during the course of treatment, for patients 20 years of age and older; with two or three face-to-face physician visits per month 90962 ESRD-related services during the course of treatment, for patients 20 years of age and over; with one face-to-face physician visit per month 90963 ESRD-related services for home dialysis patients per full month; for patients younger than 2 years of age to include monitoring for adequacy of nutrition, assessment of growth and development, and counseling of parents 90964 ESRD-related services for home dialysis patients per full month; for patients 2-11 years of age to include monitoring for adequacy of nutrition, assessment of growth and development, and counseling of parents 90965 ESRD-related services for home dialysis patients per full month; for patients 12-19 years of age to include monitoring for adequacy of nutrition, assessment of growth and development, and counseling of parents 90966 ESRD-related services for home dialysis patients per full month; for patients 20 years of age and older 90967 ESRD-related services for home dialysis (less than full month), per day; for patients younger than 2 years of age 90968 ESRD-related services for home dialysis (less than full month), per day; for patients 2-11 years of age Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-321 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Code Description 90969 ESRD-related services for home dialysis (less than full month), per day; for patients 12-19 years of age 90970 ESRD-related services for home dialysis (less than full month), per day; for patients 20 years of age and over School Corporation Services Coverage and Billing Procedures Special education services provided by a public school and contained in an Individual Education Plan (IEP) are exempt from PA and managed care referral requirements. The IEP serves as prior authorization for the service provided. The IHCP enrolls only school corporations recognized and approved by the Indiana Department of Education. Effective for dates of service on or after August 1, 1998, school corporations enrolled as IHCP providers are exempt from requirements to obtain PA and the PMP Certification Code to bill for IEP services furnished to a student in Special Education. Submit claims for IEP services provided to special education students enrolled in the Care Select on the CMS-1500 to the following address: HP CMS-1500 Claims P.O. Box 7269 Indianapolis, IN 46207-7269 If the student is enrolled in an RBMC MCO, school corporation providers must submit claims for IEP services to HP and not to the student’s MCO. Although IEP services are carved out of the IHCP managed care programs, provider cooperation is strongly encouraged to keep the PMPs informed of health-related services provided to IHCP-eligible special education students. Arrangements should be made to send progress reports or some other type of documentation to the PMP of each student to promote continuity and quality of care for each student. Surgical Services Coverage and Billing Procedures Providers furnishing surgical services to members enrolled in Care Select must follow existing PA guidelines. RBMC member claims are submitted to the patients’ MCO for payment. Services that require PA furnished to patients enrolled in RBMC must be prior authorized by the MCO in accordance with the MCO guidelines. A surgical procedure generally includes the preoperative visits performed on the same day or the day prior to the surgery for major surgical procedures, and the day of the surgical procedure for minor surgical procedures. Separate reimbursement is available for preoperative care when the provider performing the surgery has never seen the patient, or the decision to perform surgery was made during the preoperative visit. • 8-322 Modifier 57 – Decision for Surgery must be submitted on the CMS-1500 or 837P with the E/M Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions The postoperative care days for a surgical procedure include 90 days following a major surgical procedure and 10 days following a minor surgical procedure. Separate reimbursement is available for care provided during the global postoperative period unrelated to the surgical procedure, or for care not considered routine, and postoperative care for surgical complications. All levels of medical care, prior to surgical procedures, are reimbursed individually based on documentation of the patient’s medical condition. If the patient’s condition requires additional medical or surgical care outside the scope of the operating surgeon – for example, an additional surgery performed by a different specialist for a different diagnosis – on the same day, reimbursement for the medical care is considered individually. Medical visits for surgical complication are reimbursed only if medically indicated and no other physician has billed for the same or related diagnosis. The claim must indicate the specific complications and providers should attach documentation that clearly supports the medical necessity for the care provided. The medical visits are billed separately from the surgical fee. Such complications may include but are not limited to the following: • Cardiovascular complications • Comatose conditions • Elevated temperature above 38.4 degrees C, 101 degrees F, for two or more consecutive days • Medical complications, other than nausea and vomiting, due to anesthesia • Nausea and vomiting persisting more than 24 hours • Postoperative wound infection requiring specialized treatment • Renal failure Split Care Requirements for Split Care The IHCP requires a written agreement when the global surgical procedure is split among multiple providers. The conditions are the same as those for Medicare and are illustrated as follows: • Providers billing for split care must have a written agreement outlining the date care is to be turned over and the name of the provider receiving the patient. • Agreement must become part of the patient’s file. • Agreement must be submitted with any review or hearing request about the split care payment. • Modifier 54 must not be billed unless a written agreement exists. • Physician must bill the appropriate CPT code without modifier 54 or 55 if a written agreement does not exist. Split Care Billing Procedures and Reimbursement Calculation When the provider who performed the surgery does not provide any postoperative care, the provider must bill the surgical procedure code with modifier 54 – surgical care only and the actual date of the surgery. Postoperative care must be billed using the surgical procedure code with modifier 55 – postoperative management only. The dates of service must reflect the date care was assumed and relinquished and the units field must include the total number of postoperative days furnished. To ensure appropriate reimbursement when billing with modifier 55, the number of days within the date of service range Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-323 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions must equal the number of units (days) reported on the claim. For the purposes of defining postoperative care units, one unit is equal to one day of postoperative care. Note: The postoperative period begins the day after surgery. Postoperative management claims must not be submitted until the physician managing the postoperative care sees the patient for the first time. The following two examples define appropriate billing procedures for split care and show how reimbursement is calculated. The examples use procedure code 43030, a 90-day postoperative period, and allow a total of $460.48 for the global service, as shown in Table 8.99. Table 8.99 – Procedure Code 43030 Description Percentage Preoperative Modifier 9 Intraoperative +81 Total intraoperative 90 54 Postoperative 10 55 Total 100 Example 1 In this example, two physicians split the postoperative care. Physician A performs the surgical procedure and manages the patient postoperatively for 60 days, as shown in Table 8.100. Table 8.100 – Billing Physician A Physician A From Date of Service To Date of Service Procedure Code Modifier Units Billed Detail 1 10/01/2008 10/01/2008 43030 54 1 Detail 2 10/02/2008 11/30/2008 43030 55 60 Calculations are made as follows: Detail 1: Global fee of $460.48 multiplied by 0.90 (9 percent preoperative percentage + 81 percent intraoperative percentage) multiplied by 1 unit billed equals $414.43. Detail 2: Global fee of $460.48 multiplied by 0.10 equals the total postoperative allowance of $46.048 divided by 90 (number of global days assigned) equals $0.5116 per day multiplied by 60 (number of postoperative days reported) equals $30.699 or $30.70. As shown in Table 8.101, Physician B performs the balance of the postoperative care for 30 days. Table 8.101 – Billing Physician B Physician B Detail 1 8-324 From Date of Service 12/01/2008 To Date of Service 12/30/2008 Procedure Code 43030 Modifier 55 Units Billed 30 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Calculations are made as follows: Detail 1: Global fee of $460.48 multiplied by 0.10 equals the total postoperative allowance of $46.048 divided by 90 (number of global days assigned) equals $0.5116 per day multiplied by 30 (number of postoperative days reported) equals $15.348 or $15.35. When only one provider is responsible for the surgery and all the postoperative care, the provider must bill the surgical procedure, without modifier 54 or 55. The IHCP allowed amount in this case would be 100 percent of the RBRVS fee. Modifiers 54 and 55 are used only to split postoperative care between multiple providers. Example 2 In this example, the same provider bills for the surgery and all the postoperative care. Physician A performs and bills for the surgical procedure and all the postoperative care, as shown in Table 8.102. Table 8.102 – Billing Physician A Physician A Detail 1 From Date of Service 10/01/2008 To Date of Service 10/01/2008 Procedure Code 43030 Modifier Units Billed 1 Calculations are made as follows: The global fee for procedure code 43030 is $460.48. Therefore, reimbursement for this service should be made at $460.48. Exceptions and Special Billing Considerations If more than one physician in the same group practice participates in a portion of a patient’s care, included in a global surgery package, only the physician who performs the surgery can submit a bill. Split care modifiers are not applicable and the surgeon’s claim must include only the surgical procedure. Although other physicians participated in the care, all are within the same group practice. There is no need to split the reimbursement because the physician group is reimbursed the global fee. If a transfer of care does not occur, occasional post-discharge services for a physician other than the surgeon are reported with the appropriate E/M code. Modifiers are not required. If the transfer of care occurs immediately after surgery, the physician who provides the postoperative care while the patient remains in the hospital bills using subsequent hospital care codes. Once the patient is released from the hospital, the physician responsible for postoperative care bills using the surgical procedure code with modifier 55. The surgeon should bill the appropriate surgical procedure code with modifier 54. This situation can occur when an itinerant (traveling) surgeon is used. If a physician provides follow-up services during the postoperative period for minor procedures performed in the emergency department, the physician must bill the appropriate level of office visit code. The emergency department physician who performed the surgical service bills the surgical procedure code without a modifier. If the services of a physician, other than the surgeon, are required during a postoperative period for an underlying condition or medical complication, the other physician reports the appropriate E/M code, and split care modifiers are not required on the claim. For example, a cardiologist may manage the underlying cardiovascular condition during the postoperative period for a cardiovascular procedure that was performed by a cardiothoracic surgeon. If a patient is returned to surgery for a related procedure during the postoperative period and billed using modifier 78, the IHCP-allowed amount is calculated by multiplying the RBRVS fee amount by Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-325 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions the surgical care only (intraoperative) percentage on the Medicare fee schedule data base (MFSDB). In these situations, the preoperative percentage is not added to the intraoperative percentage for calculating the allowed amount described in the first example. In addition, a new postoperative period is not allowed for the related procedure. The number of postoperative days allowed following the return to surgery is equal to the number of postoperative days remaining from the original procedure. Billing certain modifiers on the same detail is restricted as follows to avoid processing issues: Modifier 54 (intraoperative) cannot be billed on the same detail as modifiers: 55, 78, 80, 81, 82, AA, P1 through P5, QJ, QK, QX, QZ, QO, QQ, X6, and W5 through W7, or the detail denies for an invalid modifier combination. Billing certain modifiers on the same detail is restricted as follows, to avoid processing issues: • Modifier 54 (intraoperative) cannot be billed on the same detail as modifiers: 55, 78, 80, 81, 82, P1 through P5, QK, QX, and QZ, or the detail denies for an invalid modifier combination. • Modifier 55 (postoperative) cannot be billed on the same detail as modifiers: 54, 78, 80, 81, 82, P1 through P5, QK, QX, and QZ, or the detail denies for an invalid modifier combination. Cosurgeons Cosurgeons must append modifier 62 to the surgical service. Modifier 62 cuts the reimbursement rate to 62.5 percent of the rate on file. Multiple procedures When two or more covered surgical procedures are performed during the same operative session, multiple surgery reductions apply to the procedures based on the following adjustments: • 100 percent of the global fee for the most expensive procedure • 50 percent of the global fee for the second most expensive procedure • 25 percent of the global fee for the remaining procedures All surgeries that are performed on the same day, by the same rendering physician, must be billed on the same claim form. Otherwise the claim may be denied and the original claim needs to be adjusted for any additional payment. Bilateral Procedures Providers submitting CMS-1500 claims or 837P transactions using modifier 50, indicating bilateral procedure, must enter only one unit in field 24G on the CMS-1500. The use of modifier 50 ensures that the procedure code is priced at the lower of 150 percent of the billed charge or the rate on file. Providers should note that if the CPT code description specifies the procedure as bilateral, modifier 50 should not be used on the CMS-1500 or 837P. Prior Authorization Chapter 6 of this manual provides additional information on PA for this service. Note: For RBMC members, contact the appropriate MCO for PA instructions. 8-326 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Therapy Services Coverage and Billing Procedures This section outlines IAC criteria for therapy services. 405 IAC 5-22-6 states that the IHCP requires prior review and authorization for all therapy services with the following exceptions: • Initial evaluations • Emergency respiratory therapy • Any combination of therapy ordered in writing prior to a member’s release or discharge from inpatient hospital care, which may continue for a period not to exceed 30 units, sessions, or visits in 30 calendar days • Deductible and copay for services covered by Medicare Part B • Oxygen equipment and supplies necessary for the delivery of oxygen with the exception of concentrators • Therapy services provided by an NF or large private or small ICF/MR, included in the facility’s per diem rate • Physical therapy, occupational therapy, and respiratory therapy ordered in writing by a physician to treat an acute medical condition, except as required in Sections 8, 10, and 11 of this rule Unless specifically indicated otherwise, the following criteria for PA of therapy services apply to occupational therapy, physical therapy, respiratory therapy, and speech pathology: • The IHCP requires written evidence of physician involvement and personal patient evaluation to document acute medical needs. A physician must order the therapy. Providers must attach a current plan of treatment and progress notes about the necessity and effectiveness of therapy to the PA request and make this available for audit. • A qualified therapist or qualified assistant under the direct supervision of the therapist, as appropriate, must provide the therapy. • Therapy must be of such a level of complexity and sophistication, and the condition of the member must be such that they require the judgment, knowledge, and skills of a qualified therapist. • The IHCP reimburses only for medically reasonable and necessary therapy. • The IHCP does not cover therapy rendered for diversional, recreational, vocational, or avocational purpose, or for the remediation of learning disabilities or developmental activities that can be conducted by nonmedical personnel. • The IHCP covers therapy for rehabilitative services for a member no longer than two years from the initiation of the therapy unless a significant change in medical condition requires longer therapy. Providers can prior authorize habilitative services for a member younger than 18 years old for a longer period on a case-by-case basis. Providers can prior authorize respiratory therapy services for a longer period on a case-by-case basis. • The IHCP does not cover maintenance therapy. • When a member is enrolled in therapy, ongoing evaluations to assess progress and redefine therapy goals are part of the therapy program. The IHCP does not separately reimburse for ongoing evaluations. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-327 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions • One hour of billed therapy must include a minimum of 45 minutes of direct patient care with the balance of the hour spent in related patient services. • The IHCP does not approve therapy services for more than one hour per day, per type of therapy. The IHCP does not prior authorize requests for therapy that duplicate other services provided to a patient. The IHCP does not authorize therapy services when they duplicate nursing services required under 410 IAC 16.2-3-4. 405 IAC 5-22-8 states that physical therapy services are subject to the following restrictions: • A licensed physical therapist or certified therapist assistant under the direct, on-site supervision of a licensed physical therapist must perform physical therapy service. Only the activities in this subdivision related to the therapy can be performed by someone other than a licensed therapist or certified therapist assistant who must be under the direct on-site supervision of a licensed physical therapist. • The IHCP allowance for the modality provided by the licensed therapist includes payment for the following services, and providers may not bill separately for them: - Assisting patients in preparation for treatment, as necessary during treatment, and at the conclusion of treatment - Assembling and disassembling equipment - Assisting a physical therapist in the performance of appropriate activities related to the treatment of the individual patient - Following established procedures pertaining to the care of equipment and supplies - Preparing, maintaining, and cleaning treatment areas and maintaining supportive areas - Transporting patients, records, equipment, and supplies in accordance with established policies and procedures - Performing established clerical procedures • The IHCP limits evaluations and reevaluations to three hours of service per member evaluation. For the initial evaluation, the IHCP does not require PA. For any additional reevaluations, the IHCP does require PA unless conducted during the initial 30 days after hospital discharge and the discharge orders include physical therapy orders. The IHCP does not authorize reevaluations more than one time per year unless the provider submits documentation indicating significant change in the patient’s condition. The provider is responsible for determining whether evaluation services have been previously provided. • Physical therapy services ordered in writing to treat an acute medical condition provided in an outpatient setting may continue for a period not to exceed 12 one-hour sessions, or visits within 30 calendar days without PA. This exception includes the provision of splints, crutches, and canes. Providers must obtain PA for additional services. • The IHCP does not require PA for physical therapy services provided by an NF or large private or small ICF/MR, which are included in the facility’s per diem rate. The IHCP does not reimburse these services separately. 405 IAC 1-11.5-2 was amended to allow for the reimbursement of services provided by certified physical therapist assistants (PTAs). This rule amends 405 IAC 5-22-8 regarding supervision requirements for services provided by certified PTAs. The PTA is precluded from performing and interpreting tests, conducting initial or subsequent assessments, and developing treatment plans. Under direct supervision, a PTA is still required to consult with the supervising physical therapist daily to review treatment. The consultation can be either face-to-face or by telephone. 8-328 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Covered Procedures for Physical Therapist Assistants Effective April 1, 2006, the IHCP has identified procedures that can be performed by a PTA and are eligible for reimbursement. Providers must bill these services with the modifier HM – Less than a bachelor’s degree. Pricing for these services will reimburse at 75 percent of the reimbursement level for a physical therapist. Table 8.103 lists the physical therapy services that PTAs may perform. Note: This information does not apply to First Steps services. Table 8.103 – Physical Therapy Services that May Be Performed by a PTA CPT Code Description 29200 Strapping; thorax 29220 Strapping; low back 29240 Strapping; shoulder 29260 Strapping; elbow or wrist 29280 Strapping; hand or finger 29505 Application of long leg splint (thigh to ankle or toes) 29515 Application of short leg splint (calf to foot) 29520 Strapping; hip 29530 Strapping; knee 29540 Strapping; ankle and/or foot 29550 Strapping; toes 29580 Strapping; Unna Boot 29590 Denis-Browne splint strapping 97010 Application of a modality to one or more areas; hot or cold compacts 97012 Application of a modality to one or more areas; traction, mechanical 97014 Application of a modality to one or more areas; electrical stimulation (unattended) 97016 Application of a modality to one or more areas; vasopneumatic devices 97018 Application of a modality to one or more areas; paraffin bath 97022 Application of a modality to one or more areas; whirlpool 97024 Application of a modality to one or more areas; diathermy 97026 Application of a modality to one or more areas; infrared 97028 Application of a modality to one or more areas; ultraviolet 97032 Application of a modality to one or more areas; electrical stimulation (manual), each 15 minutes 97033 Application of a modality to one or more areas; iontophoresis, each 15 minutes 97034 Application of a modality to one or more areas; contrast baths, each 15 minutes 97035 Application of a modality to one or more areas; ultrasound, each 15 minutes 97036 Application of a modality to one or more areas; Hubbard tank, each 15 minutes Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-329 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions CPT Code Description 97110 Therapeutic procedure, one or more areas, each 15 minutes; therapeutic exercises to develop strength and endurance, range of motion and flexibility 97112 Therapeutic procedure, one or more areas, each 15 minutes; neuromuscular reeducation of movement, balance, coordination, kinesthetic sense, posture, and/or proprioception for sitting and/or standing activities 97113 Therapeutic procedure, one or more areas, each 15 minutes; aquatic therapy with therapeutic exercise 97116 Therapeutic procedure, one or more areas, each 15 minutes; gait training (includes stair climbing) 97124 Therapeutic procedure, one or more areas, each 15 minutes; massage, including effleurage, petrissage, and/or tapotement (stroking, compression, percussion) 97140 Manual therapy techniques (such as mobilization/manipulation, manual lymphatic drainage, manual traction), one or more regions, each 15 minutes 97150 Therapeutic procedure(s), group (two or more individuals) 97760 Orthotic(s) management and training, (including assessment and fitting when not otherwise reported), upper extremity(s) and/or trunk, each 15 minutes 97761 Prosthetic training, upper and/or lower extremity(s), each 15 minutes 97530 Therapeutic activities, direct (one-on-one) patient contact by the provider (use of dynamic activities to improve functional performance), each 15 minutes. Evaluation and testing codes are excluded from this list as PTAs may not administer tests or perform evaluations. 405 IAC 5-22-10 states that respiratory therapy services are subject to the following restrictions: • The IHCP reimburses for respiratory therapy service only when performed by a licensed respiratory therapist or a certified respiratory therapy technician who is an employee or contractor of a hospital, medical agency, or clinic. • The IHCP considers the equipment necessary for rendering respiratory therapy to be part of the provider’s capital equipment. • The IHCP does not require PA for oxygen provided in an NF, because it is included in the per diem for the facility and providers cannot bill separately for it. • For respiratory therapy given on an emergency basis, the IHCP does not require PA. • For a period not to exceed 14 hours or 14 calendar days, providers can perform respiratory therapy services ordered in writing for the acute medical diagnosis of asthma, pneumonia, bronchitis, and upper respiratory infection without PA. If the member requires additional services after that date, the provider must obtain PA. • For respiratory therapy services provided by an NF or large private or small ICF/MR, which are included in the facility’s established per diem rate, the IHCP does not require PA. 405 IAC 5-22-11 states that occupational therapy services are subject to the following restrictions: • 8-330 A registered occupational therapist or a certified occupational therapy assistant under the direct on-site supervision of a registered occupational therapist must perform the occupational therapy service. The registered occupational therapist must perform the evaluation for the IHCP to reimburse the provider. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions • The IHCP limits evaluations and reevaluations to three hours of service per evaluation. For the initial evaluation, the IHCP does not require PA. For any additional reevaluations, the IHCP does require PA unless conducted during the initial 30 days after hospital discharge when the discharge orders include occupational therapy orders. The IHCP does not authorize reevaluations more than one time per year unless the provider submits documentation indicating significant change in the patient’s condition. The provider is responsible for determining whether evaluations have been previously provided. • The IHCP does not cover general strengthening exercise programs for recuperative purposes. • The IHCP does not cover passive range-of-motion services as the only or primary mode of therapy. • The IHCP does not reimburse for occupational therapy psychiatric services. • Occupational therapy services ordered in writing to treat an acute medical condition provided in an outpatient setting may continue for a period not to exceed 12 one-hour sessions, or visits in 30 calendar days without PA. This exception includes provision of splints, crutches, and canes. Providers must obtain PA for additional services. • The IHCP does not require PA for occupational therapy services provided by an NF or large private or small ICF/MR, which are included in the facility’s established per diem rate. Note: For RBMC members, contact the appropriate MCO for billing and PA instructions. The IHCP reimburses for therapy services provided outside Indiana, subject to PA as defined in 405 IAC 5-5-2. Note: The IHCP does not cover home health agency services outside Indiana. Providers should refer to the section on Home Health Services in this manual for billing guidelines related to provision of therapy by HHAs. Outpatient Outpatient providers bill occupational therapy, physical therapy, and speech therapy as stand-alone services. For these services, providers bill using the revenue code only and IHCP reimburses at a flat, statewide fee on a per-hour basis or unit billed. Providers cannot bill for fractional units for less than one hour. Providers must accumulate and report time in one-hour increments. The section Outpatient Services in Section 2 under the UB-04 Billing Instructions provides additional information. Hippotherapy The IHCP covers hippotherapy for physical therapy, effective April 1, 2005. To be covered, a licensed physical therapist must provide the services, and providers must bill for the services using the appropriate HCPCS code from the following list: • 97110 – Therapeutic exercises to develop strength and endurance, range of motion, and flexibility • 97112 – Neuromuscular reeducation of movement, balance, coordination, kinesthetic sense, posture, or proprioception for sitting and standing activities • 97530 – Therapeutic activities to improve functional performance Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-331 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions • 97533 – Sensory integrative techniques to enhance sensory processing and promote adaptive responses to environmental demands. This code can be used only for patients with a diagnosis of traumatic brain injury (TBI). A physician must order the services and include them in the patient’s treatment plan. Existing PA requirements for physical therapy apply to hippotherapy. Note: Procedure code S8940 (hippotherapy per person, equestrian, hippotherapy, per session), effective January 1, 2005, is not covered by the IHCP. Traumatic Brain Injury 405 IAC 5-29-1 (25) (I) states that cognitive rehabilitation is a noncovered service, except for the treatment of traumatic brain injury. The IHCP limits CPT code 97532 – Development of cognitive skills to improve attention, memory, problem solving (including compensatory training), direct (one-on-one) patient contact by the provider, each 15 minutes, and CPT code 97533 – Sensory integrative techniques to enhance sensory processing and promote adaptive responses to environmental demands, direct (one-on-one) patient contact by the provider, each 15 minutes, to the specific traumatic brain injury diagnoses listed in Table 8.104. Table 8.104 – Traumatic Brain Injury ICD-9-CM Codes ICD-9-CM Codes 348.1 800.01 800.02 800.03 800.04 800.05 800.06 800.09 800.10 800.11 800.12 800.13 800.14 800.15 800.16 800.19 800.20 800.21 800.22 800.23 800.24 800.25 800.26 800.29 800.30 800.31 800.32 800.33 800.34 800.35 800.36 800.39 800.40 800.41 800.42 800.43 800.44 800.45 800.46 800.49 800.50 800.51 800.52 800.53 800.54 800.55 800.56 800.59 800.60 800.61 800.62 800.63 800.64 800.65 800.66 800.69 800.70 800.71 800.72 800.73 800.74 800.75 800.76 800.79 800.80 800.81 800.82 800.83 800.84 800.85 800.86 800.89 800.90 800.91 800.92 800.93 800.94 800.95 800.96 800.99 801.00 801.01 801.02 801.03 801.04 801.05 801.06 801.09 801.10 801.11 801.12 801.13 801.14 801.15 801.16 801.19 801.20 801.21 801.22 801.23 8-332 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions ICD-9-CM Codes 801.24 801.25 801.26 801.29 801.30 801.31 801.32 801.33 801.34 801.35 801.36 801.39 801.40 801.41 801.42 801.43 801.44 801.45 801.46 801.49 801.50 801.51 801.52 801.53 801.54 801.55 801.56 801.59 801.60 801.61 801.62 801.63 801.64 801.65 801.66 801.69 801.70 801.71 801.72 801.73 801.74 801.75 801.76 801.79 801.80 801.81 801.82 801.83 801.84 801.85 801.86 801.89 801.90 801.91 801.92 801.93 801.94 801.95 801.96 801.99 803.00 803.01 803.02 803.03 803.04 803.05 803.06 803.09 803.10 803.11 803.12 803.13 803.14 803.15 803.16 803.19 803.20 803.21 803.22 803.23 803.24 803.25 803.26 803.29 803.30 803.31 803.32 803.33 803.34 803.35 803.36 803.39 803.40 803.41 803.42 803.43 803.44 803.45 803.46 803.49 803.50 803.51 803.52 803.53 803.54 803.55 803.56 803.59 803.60 803.61 803.62 803.63 803.64 803.65 803.66 803.69 803.70 803.71 803.72 803.73 803.74 803.75 803.76 803.79 803.80 803.81 803.82 803.83 803.84 803.85 803.86 803.89 803.90 803.91 803.92 803.93 803.94 803.95 803.96 803.99 804.00 804.01 804.02 804.03 804.04 804.05 804.06 804.09 804.10 804.11 804.12 804.13 804.14 804.15 804.16 804.19 804.20 804.21 804.22 804.23 804.24 804.25 804.26 804.29 804.30 804.31 804.32 804.33 804.34 804.35 804.36 804.39 804.40 804.41 804.42 804.43 804.44 804.45 804.46 804.49 804.50 804.51 804.52 804.53 804.54 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-333 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions ICD-9-CM Codes 804.55 804.56 804.59 804.60 804.61 804.62 804.63 804.64 804.65 804.66 804.69 804.70 804.71 804.72 804.73 804.74 804.75 804.76 804.79 804.80 804.81 804.82 804.83 804.84 804.85 804.86 804.89 804.90 804.91 804.92 804.93 804.94 804.95 804.96 804.99 851.00 851.01 851. 02 851.03 851.04 851.05 851.06 851.09 851.10 851.11 851.12 851.13 851.14 851.15 851.16 851.19 851.20 851.21 851.22 851.23 851.24 851.25 851.26 851.29 851.30 851.31 851.32 851.33 851.34 851.35 851.36 851.39 851.40 851.41 851.42 851.43 851.44 851.45 851.46 851.49 851.50 851.51 851.52 851.53 851.54 851.55 851.56 851.59 851.60 851.61 851.62 851.63 851.64 851.65 851.66 851.69 851.70 851.71 851.72 851.73 851.74 851.75 851.76 851.79 851.80 851.81 851.82 851.83 851.84 851.85 851.86 851.89 851.90 851.91 851.92 851.93 851.94 851.95 851.96 851.99 852.00 852.01 852.02 852.03 852.04 852.05 852.06 852.09 852.10 852.11 852.12 852.13 852.14 852.15 852.16 852.19 852.20 852.21 852.22 852.23 852.24 852.25 852.26 852.29 852.30 852.31 852.32 852.33 852.34 852.35 852.36 852.39 852.40 852.41 852.42 852.43 852.44 852.45 852.46 852.49 852.50 852.51 852.52 852.53 852.54 852.55 852.56 852.59 853.00 853.01 853.02 853.03 853.04 853.05 853.06 853.09 853.10 853.11 853.12 853.13 853.14 853.15 853.16 853.19 854.00 854.01 854.02 854.03 854.04 854.05 8-334 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions ICD-9-CM Codes 854.06 854.09 854.10 854.11 854.12 854.13 854.14 854.15 854.16 854.19 907.0 994.1 997.01 Transportation Services Advanced Life Support – ALS The Indiana Emergency Medical Services Commission (EMSC), Title 836 of the Indiana Administrative Code (IAC), defines advanced life support (ALS) as follows: Care given at the scene of an accident, act of terrorism, or illness, care given during transport, or care given at the hospital by a paramedic, emergency medical technician-intermediate, and care that is more advanced than the care usually provided by an emergency medical technician or an emergency medical technician-basic advanced. The term advanced life support may include any of the following acts of care: • Defibrillation • Endotracheal intubation • Parenteral injection of appropriate medications • Electrocardiogram interpretation • Emergency management of trauma and illness The IHCP provides reimbursement for medically necessary emergency and nonemergency ALS ambulance services when the level of service rendered meets the EMSC definition of ALS. Note: In accordance with Indiana Code (IC)16-1-31, vehicles and staff that provide emergency services must be certified by the EMSC to be eligible for reimbursement for transports involving either ALS or basic life support (BLS) services. Basic Life Support – BLS The EMSC defines BLS as the following: • Assessment of emergency patients • Administration of oxygen • Use of mechanical breathing devices • Application of antishock trousers • Performance of cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) • Application of dressings and bandage materials • Application of splinting and immobilization devices • Use of lifting and moving devices to ensure safe transport Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-335 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions • Use of an automatic or semiautomatic defibrillator • Administration of epinephrine through an auto-injector • An emergency medical technician-basic advanced may perform the following: - Electrocardiogram interpretation - Manual external defibrillation - Intravenous fluid therapy The terms basic life support and BLS services do not include invasive medical care techniques or advanced life support. The IHCP provides reimbursement for medically necessary emergency and nonemergency BLS ambulance services when the level of service rendered meets the EMSC definition of BLS. Commercial or Common Ambulatory Service – CAS The IHCP provides reimbursement for transportation of ambulatory (walking) members to or from an IHCP-covered service. Commercial or Common Ambulatory Service (CAS) transportation may be provided in any type of vehicle; however, providers must bill all transportation services according to the level of service rendered. For example, if an ambulance provides transportation of an ambulatory member but no ALS or BLS services are medically necessary for the transport of the member, the ambulance provider must bill the CAS charges. For CAS transportation, providers can bill separately for base rate, waiting time, and mileage, and receive reimbursement. Nonambulatory Service (Wheelchair Van) – NAS The IHCP reimburses for nonambulatory services (NAS) or wheelchair services when a member must travel in a wheelchair to or from an IHCP-covered service. Providers must bill claims for ambulatory members transported in a vehicle equipped to transport nonambulatory members according to the CAS level of service and rate, and they must not bill according to the vehicle type. For NAS transportation, providers can bill separately for base rate, waiting time, and mileage, and receive reimbursement. Taxi Taxi providers transport ambulatory members and may operate under authority from a local governing body (city taxi or livery license). Taxi providers whose rates are regulated by local ordinance must bill the metered or zoned rate, as established by local ordinance, and the IHCP reimburses them up to the maximum allowable fee. The IHCP reimburses taxi providers whose rates are not regulated by local ordinance at the lower of their submitted charge or the maximum allowable fee based on trip length. The IHCP does not separately reimburse taxi providers for mileage above the maximum allowable rate for the trip; however, providers must have mileage documented on the driver’s ticket by odometer readings or mapping software. Rotary Air Ambulance Transportation Base Rate and Mileage Effective for dates of service on or after December 25, 2009, the IHCP provides reimbursement for a base rate and mileage. The base rate and mileage will be reimbursed at the lower of the usual and customary charge or the IHCP established max fee. The base rate is an all-inclusive rate including coverage of treatments and services that are an integral part of care while in transit; it includes but is not limited to oxygen, drugs, supplies, reusable devices and equipment, and extra attendants. 8-336 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Table 8.105 – Rotary Air Ambulance Codes Effective December 25, 2009 Provider Specialty 261: Air Ambulance HCPCS Code Description A0431 Ambulance service, conventional air service, transport, one way (rotary wing) A0436 Rotary wing air mileage, per statute mile The air ambulance mileage rate is calculated to the nearest suitable hospital per actual loaded (patient onboard) miles flown and is expressed in statute miles (not nautical miles). Transportation providers are expected to transport members along the shortest, most efficient route to the nearest suitable hospital. All rotary air transportation providers must document mileage on the trip ticket. Providers must bill the IHCP for whole units only. Partial mileage units must be rounded to the nearest whole unit. For example, if the provider transports a member between 15.5 miles and 16.0 miles, the provider must bill 16 miles. If the provider transports the member between 15.0 and 15.4 miles, the provider must bill 15 miles. Providers are reminded that additional reimbursement is not available for multiple passengers in a rotary air ambulance, nor is separate reimbursement available for an accompanying parent/attendant in a rotary air ambulance. Prior Authorization Providers are reminded that prior authorization is required for air ambulance services. The IHCP acknowledges that PA for rotary air transport will be approved after services have been rendered due to the nature of the services. A PA request must include a brief description of the care and description of the clinical circumstances necessitating the need for the transportation. Providers must indicate that the transportation was an emergency by using the Y indicator in field 24I on the CMS-1500 or in the Emergency Indicator on the 837P. Medical Necessity Rotary air ambulance transport is a covered service when the member has a potentially life-threatening condition that does not permit the use of another form of transportation. The IHCP reimburses rotary air transportation services to a hospital facility under medically appropriate circumstances. Medical necessity is only established when the member’s condition is such that the time needed to transport a member by ground, or the instability of transportation by ground, poses a threat to the member’s survival or seriously endangers the member’s health. The list below includes examples of medical conditions in which rapid transport may be necessary. This list does not guarantee reimbursement nor is it intended to be all inclusive. Diagnosis alone does not serve as justification for reimbursement. • Intracranial bleeding requiring neurosurgical intervention • Cardiogenic shock • Burns requiring treatment in a burn center • Conditions requiring treatment in a Hyperbaric Oxygen Unit • Multiple severe injuries • Life-threatening trauma Generally, transport by rotary wing air ambulance may be necessary because the member’s condition requires rapid transport to a treatment facility, and great distances or other obstacles preclude such rapid delivery by ground transport to the nearest appropriate facility. Transport by rotary wing air ambulance may also be necessary because the member is inaccessible by a ground or water vehicle. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-337 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Air transport must be to the nearest suitable hospital. If the air transport was medically necessary but the member could have been treated at a nearer hospital than one to which they were transported, the air transportation mileage reimbursement is limited to the rate for the distance from the point of pickup to the nearer hospital. Additionally, transportation by air ambulance is covered only for transport to a hospital. Air ambulance services are not covered for transport to a facility that is not an acute care hospital. Transport to a nursing facility, a physician’s office, or a beneficiary’s home by rotary air ambulance is not reimbursable. Special Circumstances In addition to the general instructions above, additional information concerning coverage and billing is included below for three identified special circumstances – hospital-to-hospital transfers, patient expiration, and bad weather. Hospital-to-Hospital Transfer Air ambulance transport is covered for transfer of a patient from one hospital to another if the medical appropriateness criteria is met, for example, transportation by ground ambulance would endanger the member’s health, and the transferring hospital does not have adequate facilities to provide the medical services needed by the patient. Examples of such specialized medical services that are generally not available at all types of facilities may include, but are not limited to, burn care, cardiac care, trauma care, and critical care. A patient transported from one hospital to another hospital is covered only if the hospital to which the patient is transferred is the nearest one with appropriate facilities. Reimbursement is not available for transport from a hospital capable of treating the patient because the patient and/or family prefer a specific hospital or physician. Patient Expiration When the member expires, the IHCP payment amount depends on the time at which the member is pronounced dead by an individual authorized by the State to make such pronouncements. If the time of death pronouncement is prior to takeoff to point of pickup, with notice to the dispatcher and time to abort the flight, no payment is made. This includes scenarios in which the air ambulance has taxied to the runway and/or has been cleared for takeoff but has not actually taken off. If the member is pronounced dead after takeoff to point of pickup, but before the member is loaded, the appropriate air base rate (A0431) with no mileage is reimbursed. The provider should use the QL modifier when submitting such a claim (A0431 QL). If the provider bills a mileage code in conjunction with a base rate and QL modifier, the mileage code will be denied with the following audit 6194 explanation: Mileage is not payable with this service. When the member is pronounced dead after being loaded onboard but prior to or upon arrival at the receiving facility, the provider may bill for the air ambulance base rate and mileage as if the member had not expired. Table 8.106 – Billing Upon Beneficiary Death After Takeoff but Before Loading Provider Specialty 261: Air Ambulance HCPCS Code A0431 QL Description Ambulance service, conventional air service, transport, one way (rotary wing) Bad Weather Providers should note that if the flight is aborted due to bad weather or other circumstance beyond the pilot’s control any time before the beneficiary is loaded onboard, that is, prior to or after takeoff to point of pickup, the IHCP will not reimburse for the flight. If the flight is aborted due to bad weather after the beneficiary is loaded, the appropriate base and mileage codes may be reimbursed. 8-338 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Retroactive Eligibility If a member becomes retroactively eligible for IHCP coverage and notifies the provider of retroactive eligibility, the provider must follow guidelines outlined in Chapter 2 of this manual. When notified of member eligibility, the provider must refund any payments by the member for covered services (other than the IHCP Package C copayments) rendered on or after the eligibility effective date. Definition of a Trip For billing purposes, the IHCP defines a trip as transporting a member from the initial point of pickup to the drop-off point at the final destination. Transportation must be the least expensive type of transportation available that meets the medical needs of the member. Providers must bill trips according to the level of service rendered and not according to the vehicle type. Providers must bill for all transportation services provided to the same member on the same date of service on one claim form. If the provider makes a round trip for the same member, same date of service, and same level of base code, the provider should submit both runs on the same detail with two units of service to indicate a round trip. Additionally, the provider must bill all mileage for the trip on the one detail with the total number of miles associated for the round trip. If the provider transports a member on the same date of service but with different trip levels (for example, the to trip was a CAS trip, and the return trip was a NAS trip with mileage for each base), the provider must bill these base trips on two different claim forms with the corresponding mileage for each base. Note: In the Units field on the CMS-1500 or Service Unit Count field on the 837P, the provider must use a 1 with the base unit code to indicate a one-way trip and a 2 to indicate a two-way trip. The provider must use the transportation modifiers to indicate the place of origin and destination for each service. Multiple Destinations If the provider transports a member to multiple points in succession, the provider cannot bill for a trip between each point of the destination. The following examples explain this concept: • Example 1: A vehicle picks up a member at home and transports the member to the physician’s office. This is a one-way trip. • Example 2: A vehicle picks up a member from home and transports the member to the physician’s office. The provider leaves, and later the same vehicle picks up the member from the physician’s office and transports the member back to the member’s home. This is considered two one-way trips. • Example 3: A vehicle picks up the member from the physician’s office and transports the member to the laboratory for a blood draw, waits outside the laboratory for the member, and then transports the member home. This is a one-way trip, even though there was a stop along the way. A stop along the way is not considered a separate trip. • Example 4: A vehicle picks up Member A at the member’s home and begins to transport Member A to the dialysis center. Along the way, the vehicle stops to pick up Member B at a nursing home and transports Member A and Member B to the dialysis center. The stop at the nursing home is not considered a separate trip, and the transportation of Member A from home to the dialysis center is considered a one-way trip. Note: Table 8.110 includes information about the policy for multiple passengers. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-339 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Modifiers Use single-character modifiers for ambulance transportation in combination to report services to CMS. The first character indicates the transport’s place of origin, and the second character indicates the destination. Table 8.107 lists the modifiers used for ambulance transports. Table 8.107 – Modifiers – Ambulance Transport Modifier Description D Diagnostic or therapeutic site, other than P or H E Residential, domiciliary, or custodial facility (nursing home, not SNF) G Hospital-based dialysis facility (hospital or hospital-related) H Hospital I Site of transfer between types of ambulance (for example, airport or helicopter pad) J Non hospital-based dialysis facility N Skilled nursing facility (SNF) P Physician’s office (includes health maintenance organization [HMO] nonhospital facility, clinic, and so forth) R Residence S Scene of accident or acute event X Intermediate stop at physician’s office en route to the hospital (can only be used as a designation code in the second position of a modifier) Prior Authorization The IHCP requires PA for the following transportation services: • Trips exceeding 20 one-way trips per member, per rolling 12-month period, with certain exceptions as described in this billing guide • Trips of 50 miles or more one way, including all codes associated with the trip (wait time, parent or attendant, additional attendant, and mileage) • Interstate transportation or transportation services rendered by a provider located out-of-state in a nondesignated area • Train or bus services • Airline or air ambulance services With their PA requests, providers must include a brief description of the anticipated care and a description of the clinical circumstances necessitating the transportation. The appropriate MCO or CMO reviews the PA requests and sends copies of the decisions to the members and the rendering providers. Transportation providers may request authorization for members that exceed 20 one-way trips. Examples of situations that require frequent medical intervention include, but are not limited to, prenatal care, chemotherapy, and certain other therapy services. The IHCP does not approve additional trips for routine medical services. The IHCP may grant PA up to one year following the date of service. 8-340 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Twenty One-Way Trip Limitation and Exemptions The IHCP limits transportation to 20 one-way trips per member, per rolling 12-month period. Providers must request PA for members who exceed 20 one-way trips if the member requires frequent medical intervention. However, some services are exempt from the 20 one-way trip limitation. The following sections include information about those services. Emergency Transportation Services Emergency ambulance transportation is exempt from the 20 one-way trip limitation. Providers must indicate that the transportation was an emergency by using the Y indicator in field 24c on the CMS1500 or in the Emergency Indicator on the 837P. Hospital Admission or Discharge Transportation services for transporting a member to a hospital for admission or for transporting the member home following discharge from the hospital are exempt from the 20 one-way trip limitation. This includes interhospital transportation when the member is discharged from one hospital for the purpose of admission to another hospital. Providers must use the transportation modifiers to indicate the place of origin and destination for each service. Note: Transporting an IHCP member to or from a hospital for any reason unrelated to an admission or discharge is not exempt from the 20-trip limitation. Members on Renal Dialysis or Members Residing in Nursing Homes Members on renal dialysis and members residing in nursing homes are exempt from the 20 one-way trip limitation. Providers must file claims for members undergoing dialysis or members in nursing homes with one of the diagnosis codes listed in Table 8.108. Enter the diagnosis code on the CMS1500 or 837P, and place a 1 in field 24E of the CMS-1500 claim form or the Diagnosis Code Pointer on the 837P to indicate that the first diagnosis code applies. Note: The IHCP requires transportation providers to complete field 24E on the claim form only for claims being submitted for dialysis or nursing home patients. Failure to complete this field correctly may result in the IHCP denying the claim when the member meets the 20 one-way trip limitation. The aforementioned renal dialysis and nursing facility diagnosis codes must only be used when appropriate and medically necessary. These diagnosis codes should not be used to circumvent the prior authorization process required for trips exceeding the 20 one-way trip limitation. Table 8.108 – Diagnosis Codes for Transportation of Renal Dialysis Patients and Patients Residing in Nursing Homes Diagnosis Code Usage V56.0, V56.1, or V56.8 Patient undergoing renal dialysis V70.5 Patient residing in nursing facility Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-341 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Mileage The IHCP expects transportation providers to transport members along the shortest, most efficient route to and from a destination. All transportation providers must document mileage on the driver’s ticket using odometer readings or mapping software programs. The IHCP reimburses for mileage, in addition to the base rate, under the following circumstances: • The IHCP reimburses ambulance providers for loaded mileage for each mile of the trip regardless of the type or level of service being billed. • The IHCP reimburses CAS and NAS providers for loaded mileage when they transport a member more than 10 miles one way. • The IHCP does not reimburse taxi providers for mileage and does not require them to submit mileage with their claim. However, providers must document mileage on the driver’s ticket using odometer readings or mapping software, as outlined in the Documentation Requirements For Transportation Services section. • Although the IHCP automatically deducts the first 10 miles of a CAS or NAS trip from each oneway trip, CAS and NAS providers must bill for all mileage (including the first 10 miles) to ensure proper reimbursement. For trips less than 10 miles, the IHCP does not require the provider to bill mileage; however, if the provider does bill mileage, the IHCP processes the mileage as a denied line item. • For trips and associated mileage in excess of 50 miles one way, the IHCP requires PA. If the provider has not obtained PA, the IHCP denies reimbursement for mileage, the base rate, and any other transportation services related to the trip. Providers must bill for all transportation services provided to the same member on the same date of service on one claim form. • Providers must use procedure code A0425 and the appropriate U modifier for transportation services in conjunction with ALS, BLS, CAS, or NAS base rates to report mileage. Providers must not fragment mileage. Providers must submit mileage for round trips on one detail line using the appropriate code listed in Table 8.109. • IHCP made procedure code S0215 – Nonemergency transportation; mileage, per mile, nonreimbursable. Providers must bill the appropriate mileage code listed in Table 8.109. In addition, providers must not report procedure code S0215 with the codes listed in Table 8.109 to avoid IHCP reimbursing them incorrectly. Table 8.109 – Mileage Codes and Descriptions Code Description A0425 U1 ALS ground mileage, per statute mile A0425 U2 BLS ground mileage, per statute mile A0425 U3 CAS ground mileage, per statute mile A0425 U5 NAS ground mileage, per statute mile Mileage Units and Rounding Providers must bill the IHCP for whole units only. For partial mileage units, round to the nearest whole unit. For example, if the provider transports a member between 15.5 miles and 16.0 miles, the provider must bill 16 miles. If the provider transports the member between 15.0 and 15.4 miles, the provider must bill 15 miles. 8-342 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Multiple Passengers When providers transport two or more members simultaneously from the same county to the same vicinity for medical services, the IHCP reimburses for the second and subsequent member transported for medical services in a single CAS or NAS vehicle at one-half the base rate. The IHCP reimburses the full base code, mileage, and waiting time for the first member only. For example, providers should bill no mileage in conjunction with T2004 – Nonemergency transport; commercial carrier, multi-pass, individualized service provided to more than one patient in the same setting. The IHCP does not provide reimbursement for multiple passengers in ambulances or family member vehicles. The IHCP does not provide additional reimbursement for multiple passengers when the billing provider does not bill non-IHCP customers for these services. Table 8.110 shows the correct coding methods for multiple passengers. Table 8.110 – Coding Transportation for Multiple Passengers Type of Transportation First Member Second and Subsequent Members Commercial Ambulatory Services T2003 for base rate. A0425 U3 for mileage. T2007 U3 for waiting time, if applicable. T2004 for base rate. No reimbursement for mileage. No reimbursement for waiting time. Nonambulatory Services A0130 for base rate. A0425 U5 for mileage. T2007 U5 for waiting time, if applicable. A0130 TT for base rate. No reimbursement for mileage. No reimbursement for waiting time. Taxi, nonregulated, 0-5 miles A0100 UA (no mileage). A0100 UA TT (no mileage). Taxi, nonregulated, 6-10 miles A0100 UB (no mileage). A0100 UB TT (no mileage). Taxi, nonregulated, 11 or more miles A0100 UC (no mileage). A0100 UC TT (no mileage). Note: PA for a base code includes the base code and the multiple passenger code that corresponds to the approved base code. When last minute changes in scheduling modify the service from a single passenger to a multiple passenger, the provider must use the appropriate code. Accompanying Parent or Attendant When members younger than 18 years of age need an adult to accompany them to a medical service, the provider should bill the appropriate accompanying parent or attendant code. When adult members need an attendant to travel or stay with them for a medical service, the provider should bill the appropriate accompanying parent or attendant code. The following are guidelines for billing the accompanying parent or attendant codes: • Bill the procedure code for the base rate and the accompanying parent or attendant under the IHCP member’s identification number (RID). • The IHCP does not provide additional reimbursement for accompanying parent or attendant when the billing provider does not bill non-IHCP customers for like services. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-343 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions • The provider must maintain documentation on the driver’s ticket to support that the accompanying parent or attendant was transported with the IHCP member. This documentation must include the name, signature, and relation of the accompanying parent or attendant. Table 8.111 lists the base rates and the applicable accompanying parent or attendant code. The provider must bill the base code and the accompanying parent or attendant code using the member’s information. The IHCP does not apply procedure codes for accompanying parent or attendant to the member’s 20 one-way trip limitation. The IHCP requires prior authorization for an accompanying parent or attendant only when the trip exceeds 50 miles one way. Table 8.111 – Procedure Codes for Accompanying Parent or Attendant Type of Transportation Base Code Accompanying Parent/Attendant Commercial Ambulatory Services T2003 T2001 Nonambulatory Services A0130 A0130 TK Taxi, nonregulated, 0-5 miles A0100 UA A0100 UA TK Taxi, nonregulated, 6-10 miles A0100 UB A0100 UB TK Taxi, nonregulated, 11 or more miles A0100 UC A0100 UC TK Additional Attendant Transportation providers sometimes need an additional attendant to help load a member. In situations where the driver cannot load the member without help, such as when a wheelchair-bound member lives upstairs and the residence has no wheelchair ramp, the provider needs an additional attendant. This code is not subject to the 20-trip limit; however, if the trip exceeds 50 miles one way, the IHCP requires prior authorization for all procedure codes, including additional attendant codes. The additional attendant who assists must be an employee of the billing provider and is not required to remain for the trip. Providers must document the need for an additional attendant on the driver’s ticket. The IHCP may subject the documentation to postpayment review. The IHCP limits the number of additional attendants to a maximum of two extra units, although usually one attendant is sufficient. The IHCP limits reimbursement for an additional attendant to NAS or wheelchair van and ambulance transportation. For ambulance providers, the additional attendant is the third or fourth attendant, because the IHCP requires ambulances to have two attendants. The IHCP does not apply procedure codes A0424 – Extra ambulance attendant, ground (ALS or BLS) or air (rotary or fixed wing) and A0130 U6 – Nonemergency transportation; wheelchair van, additional attendant to the member’s 20 one-way trip limitation. The IHCP requires prior authorization for procedure codes A0424 and A0130 U6 when the trip exceeds 50 miles one way. Table 8.112 – Procedure Codes for an Additional Attendant Type of Transportation Nonambulatory or wheelchair van transportation 8-344 Procedure Code A0130 U6 Description Nonambulatory transportation; wheelchair van, U6 = additional attendant Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Type of Transportation Ambulance transportation (ALS and BLS) Procedure Code A0424 Description Extra ambulance attendant, ground (ALS or BLS) or air (fixed or rotary winged); (requires medical review) Waiting Time The IHCP reimburses for waiting time in excess of 30 minutes only when the provider parks the vehicle outside the medical service provider, awaiting the return of the member to the vehicle, and if the member is transported 50 miles or more one way. The provider must obtain PA for all codes associated with trips of 50 miles or more one way, including waiting time. The IHCP does not cover the first 30 minutes of waiting time; however, the provider must include the total waiting time or else the IHCP cannot pay the claim appropriately. For all procedure codes that providers use to bill waiting time, providers should use one unit of service for every 30 minutes of waiting time. When providers wait between 15 to 30 minutes, they should round up the partial 30-minute increments to the next unit. For example, if providers wait 45 minutes, they would bill the units of service as two, or 2.0. For partial 30-minute increments of less than 15 minutes, providers must round down. For example, if providers wait one hour and 10 minutes, providers must bill the units of service for waiting time as two, or 2.0. Providers must maintain documentation, including start and stop times, on the driver’s ticket to support the waiting time billed. Ambulance Transportation Services The IHCP covers emergency and nonemergency ALS and BLS ambulance transport services. The IHCP exempts emergency ambulance services from the 20 one-way trip limit and does not require PA. In addition, the IHCP exempts emergency ambulance services from the copayment requirement. To indicate that the service rendered was an emergency, providers must use the Y indicator in field 24c on the CMS-1500 or the Emergency Indicator on the 837P to bill emergency services. Remember that transportation must be the least expensive type of transportation available that meets the medical needs of the member. Note: The IHCP requires PA for air ambulance and interstate transportation services. In addition, the IHCP requires PA for any transportation services provided by a provider located in an out-of-state, nondesignated area. Level of Service Rendered Versus Level of Response Providers must bill all transportation services according to the level of service rendered and not according to the provider’s level of response or vehicle type. The IHCP provides reimbursement for emergency and nonemergency ambulance services; however, the IHCP covers ALS services only when the level of service is medically necessary and BLS services are not appropriate due to the medical conditions of the member being transported. Ambulance providers should refer to the Indiana EMSC definitions of ALS and BLS services listed in Title 836 of the IAC. Ambulance providers must bill the IHCP according to the level of service rendered. The following examples explain the level of service policy: • Example 1: ALS personnel and ambulance respond to a call. On arrival, the personnel find the member to need emergency medical transport but no ALS services. In this case, the provider must use the BLS emergency transport code. Subsequently, if no emergency is present, providers must use the nonemergency BLS ambulance transport code to transport the member. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-345 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions • Example 2: An ambulance responds to a call to transport a member to a scheduled appointment. Upon arrival, the ambulance personnel discover that a CAS service or wheelchair van can transport the member. The ambulance provider can either call for the appropriate vehicle or transport the patient in the ambulance. If the ambulance provider transports the member, the provider must bill the IHCP for the appropriate CAS or NAS transportation code(s). Table 8.113 includes a complete listing of ambulance transportation codes. The procedure codes listed in Tables 8.113 and 8.114 are valid for ambulance providers to bill for CAS or NAS level of service. The IHCP no longer reimburses for procedure codes A0426 U3, A0428 U3, A0426 U5, and A0428 U5. Ambulance providers must bill the most appropriate CAS or NAS code listed in Tables 8.113 and 8.114 if the level of service does not meet the EMSC definition of ALS or BLS services. The IHCP still permits ambulance providers to bill A0425 U1 or A0425 U2 to be reimbursed for mileage. Table 8.113 – Valid CAS Codes for Ambulance Providers Procedure Code Description T2003 Nonemergency transportation, encounter/trip T2007 U3 Transportation waiting time, air ambulance and nonemergency vehicle, one-half (1/2) hour increments; CAS Table 8.114 – Valid NAS Codes for Ambulance Providers Procedure Code Description A0130 Nonemergency transportation, wheelchair van base rate A0130 U6 Nonemergency transportation, wheelchair van base rate; additional attendant T2007 U5 Transportation waiting time, air ambulance and nonemergency vehicle, one-half (1/2) hour increments; NAS Note: Ambulance providers must bill procedure codes T2003 and T2007 U3 when the level of service rendered is that of a CAS provider. Ambulance providers must bill procedure codes A0130, A0130 U6, and T2007 U5 when the level of service rendered is that of a NAS or wheelchair van provider. The IHCP still permits ambulance providers to bill A0425 U1 or A0425 U2 to be reimbursed for mileage. Ambulance Mileage The IHCP reimburses for each mile of the trip only for loaded ambulance mileage. The provider’s documentation must contain mileage from mapping software or odometer readings indicating starting and ending trip mileage. Providers must use A0425 U1 – Ground mileage, per statute mile; ALS or A0425 U2 – Ground mileage, per statute mile; BLS to bill ambulance mileage. The IHCP uses U1 and U2 modifiers to differentiate between ALS and BLS mileage. The IHCP denies claims billed without the U1 or U2 modifier and requires providers to resubmit the claim with the appropriate modifier. Neonatal Ambulance Transportation The IHCP makes reimbursement available for specialized neonatal ambulance services especially equipped for interhospital transfers of high-risk or premature infants only when the member has been discharged from one hospital for admission to another hospital. Providers must use procedure code 8-346 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions A0225 – Ambulance service, neonatal transport, base rate, emergency transport, one way only for neonatal ambulance transport. Oxygen and Oxygen Supplies Providers must not bill procedure code A0422 – Ambulance (ALS or BLS) oxygen, and oxygen supplies, life sustaining situation with ALS codes A0426, A0427, and A0433. These base codes for ALS transport include the reimbursement for supplies and oxygen in an ALS situation. Providers can bill procedure code A0422 with BLS codes A0428 or A0429, if medically necessary. Emergency medical technicians (EMTs) and paramedics must document the medical necessity for oxygen use in the medical record maintained by the provider. Member Copayments The IHCP requires a copayment for transportation services. Providers should review 405 IAC 5-30-2 for complete copayment narratives. The IHCP determines the member’s copayment amount based on the reimbursement for the base rate or loading fee only. The IHCP does not require a copayment for an accompanying parent or attendant. Transportation providers may collect a copayment amount from the IHCP member equal to those listed in Table 8.115. Table 8.115 – Transportation Copayments Transportation Service Member Copayment Transportation services that pay $10.00 or less $0.50 each one way trip Transportation services that pay $10.01 to $50.00 $1.00 each one way trip Transportation services that pay $50.01 or more $2.00 each one way trip Exemptions to Copayments for Transportation Services The IHCP exempts the following services from the copayment requirement: • Emergency ambulance services • Services furnished to members younger than 18 years old • Services furnished to pregnant women • Services furnished to members who are in hospitals, NFs, ICFs/MR, or other medical institutions - This includes instances where a provider transports a member for the purpose of admission or discharge. • Transportation services provided under an MCO to its Hoosier Healthwise enrollees Federal Guidelines for Copayment Policy According to 42 CFR 447.15, providers may not deny services to any member due to the member’s inability to pay the copayment amount on the date of service. Pursuant to this federal requirement, this service guarantee does not apply to a member who is able to pay, nor does a member’s inability to pay eliminate his or her liability for the copayment. It is the member’s responsibility to inform the provider Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-347 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions that he or she cannot afford to pay the copayment on the date of service. The provider may bill the member for copayments not paid on the date of service. Package C Transportation Services Hoosier Healthwise Package C members are eligible to receive emergency ambulance services, subject to the prudent layperson definition of emergency in 407 IAC 1-1-6. The IHCP covers nonemergency ambulance transportation between medical facilities when ordered by the treating physician. Risk-Based Managed Care Hoosier Healthwise Services The MCO is responsible for transportation services for risk-based managed care (RBMC) members. Providers must contact the appropriate MCO for more information about transportation guidelines for RBMC members. Noncovered Transportation Services The IHCP does not reimburse for the following transportation services: • One-way trips exceeding 20 per member, per rolling 12-month period, except when the provider documents medically necessity for additional trips through the PA process • Trips of 50 miles or more one way, unless the provider obtains PA • First 30 minutes of waiting time for any type of conveyance, including ambulance • Nonemergency transportation provided by any of the following: - A volunteer with no vested or personal interest in the member - An interested individual or neighbor of the member - A caseworker or social worker • Ancillary, nonemergency transportation charges including, but not limited to, the following: - Parking fees - Tolls - Member meals or lodging - Escort meals or lodging • Disposable medical supplies, other than oxygen, provided by a transportation provider • Transfer of durable medical equipment, either from the member’s residence to place of storage, or from the place of storage to the member’s residence • Use of red lights and siren for an emergency ambulance call • All interhospital transportation services, except when the member has been discharged from one hospital for admission to another hospital • Delivery services for prescribed drugs, including transporting a member to or from a pharmacy to pick up a prescribed drug Documentation Requirements for Transportation Services Providers must support each claim with the following documentation on the driver’s ticket or run sheet: • 8-348 Complete date of service; including day, month, and year of service, such as 12/15/09 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions • Complete member name and address of pickup, including street address, city, county, state, and ZIP Code • Member identification number • Member signature, and if the member is unable to sign, the driver should document that “the patient was unable to sign” and list the reason for the inability • Waiting time; including the actual start and stop time of the waiting period, such as wait time from 1 p.m. to 3:20 p.m. • Complete service provider name and address, including street address, city, county, state, and ZIP Code Note: If the service provider’s name is abbreviated on the driver’s ticket, the provider must document the complete provider name or maintain a facility abbreviation listing. This helps to expedite the postpayment review process. • Name of the driver who provided transportation service • Vehicle odometer reading at the beginning and end of each trip or mileage from mapping software, including the date that the provider performed the transportation service and the specific starting and destination address - If the provider used mapping software, it must indicate the shortest route. Note: All providers, including taxi providers, must document mileage using either odometer readings or mapping software. Taxi providers must document the distance traveled to support the metered or zoned rate or mileage code billed. • Indication of a one-way or round trip • Indication of CAS or NAS transportation • Name and relationship of any accompanying parent or attendant to support the accompanying parent or attendant code billed, if applicable Note: When providers bill an attendant or parent as part of the transport, the parent or attendant must also sign the driver’s ticket. Providers are responsible to verify that they are transporting the member to or from a covered service. Providers are responsible to maintain documentation that supports each transport and/or service provided. Transportation providers put themselves at risk of recoupment of payment if they do not maintain the required documentation or cannot verify covered services. Registration Requirements Commercial or Common Ambulatory and Nonambulatory Providers • The IHCP requires all for profit-only CAS and NAS providers to certify annually through the Indiana Motor Carrier Services (MCS) and obtain a Motor Carrier Certification. • Providers must keep a copy of the certification for their records. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-349 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Taxi Providers • Providers must have documentation showing operating authority from a local governing body (city taxi or livery license), if applicable. • Providers must keep a copy of the documentation for their records. Ambulance • Providers must have an Emergency Medical Services (EMS) Commission certification. • Providers must keep a copy of the certification for their records. • Vehicles and staff that provide ambulance services must be certified by the EMS Commission to be eligible for reimbursement for transports involving either advanced life support or basic life support services. Providers who fail to maintain the EMS Commission certification on all vehicles involved in transporting members risk termination of the IHCP Provider Agreement. Bus • Providers must have an MCS certificate from the Indiana Department of Revenue. • Providers must keep a copy of the certification for their records. Family Member • Providers must have an authorization letter from the local Office of Family and Children (OFC) (contact caseworker). • Providers must keep a copy of the authorization letter for their records. Air Ambulance • Providers must have EMS Commission Air Ambulance certification. • Providers must keep a copy of the certification for their records. Chapter 4 of this manual includes detailed information about enrollment requirements and responsibilities. The IHCP may refer providers who fail to maintain the required registration documentation to the appropriate governing agencies. Transportation Code Sets The IHCP limits transportation providers to specific codes based on the provider specialty listed on the provider enrollment file. Tables 8.116 through 8.122 list the procedures codes allowed for each transportation provider specialty. Each table lists the national code(s), and the procedure code description for each provider specialty. Table 8.116 – CAS Provider Code Set 264 Commercial Ambulatory Service (CAS) Provider 8-350 HCPCS Code Description A0425 U3 Ground mileage, per statute mile; CAS T2003 Nonemergency transportation, encounter/trip (CAS) T2004 Nonemergency transportation, commercial carrier, multi-pass (CAS) T2001 Nonemergency transportation, patient attendant/escort (CAS) Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Table 8.116 – CAS Provider Code Set 264 Commercial Ambulatory Service (CAS) Provider HCPCS Code Description T2007 U3 Transportation waiting time, air ambulance and nonemergency vehicle, one-half hour increments; CAS Note: Providers must indicate the origin and destination modifiers with the base rate and mileage procedure codes. Nonambulatory Service Provider Note: For ambulatory members transported in a vehicle equipped to transport nonambulatory members, providers must bill according to the CAS level of service and rate, and not bill according to the vehicle type. The NAS provider code set and Table 8.116 list the CAS codes. Table 8.117 – NAS Provider Code Set 265 Nonambulatory Service (NAS) Provider HCPCS Code Description A0425 U5 Ground mileage, per statute mile; NAS A0130 Nonemergency transportation, wheelchair van base rate A0130 TK Nonemergency transportation, wheelchair van base rate; extra patient or passenger, nonambulance A0130 TT Nonemergency transportation, wheelchair van base rate; individualized service provided to more than one patient in same setting A0130 U6 Nonemergency transportation, wheelchair van base rate; additional attendant T2007 U5 Transportation waiting time, air ambulance and nonemergency vehicle, one-half hour increments; NAS A0425 U3 Ground mileage, per statute mile; CAS T2003 Nonemergency transportation, encounter/trip (CAS) T2004 Nonemergency transportation, commercial carrier, multi-pass (CAS) T2001 Nonemergency transportation, patient attendant/escort (CAS) T2007 U3 Transportation waiting time, air ambulance and nonemergency vehicle, one-half hour increments; CAS Note: For ambulatory members transported in a vehicle equipped to transport nonambulatory members, providers must bill according to the CAS level of service and rate, and not bill according to the vehicle type. The NAS provider code set and Table 8.116 include the CAS codes. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-351 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Ambulance (ALS and BLS) Provider Note: Providers must bill transportation according to the level of service rendered. Therefore, the Ambulance (ALS and BLS) provider code set and Table 8.118 list the CAS and NAS codes. Table 8.118 – Ambulance Provider Code Set 260 Ambulance (ALS and BLS) Provider HCPCS Code Description A0422 Ambulance (ALS and BLS) oxygen and oxygen supplies, life-sustaining situation A0425 U1 Ground mileage, per statute mile; ALS A0425 U2 Ground mileage, per statute mile; BLS A0420 U1 Ambulance waiting time ALS, one-half hour increments A0420 U2 Ambulance waiting time BLS, one-half hour increments A0426 Ambulance service, advanced life support, nonemergency transport, level 1 (ALS1) A0427 Ambulance service, advanced life support, emergency, level 1 (ALS1emergency) A0428 Ambulance service, basic life support, nonemergency transport (BLS) A0429 Ambulance service, basic life support, emergency transport, one way (BLSemergency) A0433 Advanced ALS (Level 2) A0225 Ambulance service, advanced life support, nonneonatal transport, base rate, emergency transport, one way A0999 Unlisted ambulance service (Manual price) A0424 Extra ambulance attendant, ground (ALS or BLS) or air (rotary and fixed wing) T2003 Nonemergency transport wheelchair van base rate (level 1) (ALS1); CAS A0130 Ambulance service, advanced life support, nonemergency transport, level 1 (ALS1); NAS T2003 Nonemergency transportation, encounter/trip (CAS) (NAS) A0130 Nonemergency transportation, wheelchair van base rate (NAS) T2007 U3 (Use this code for waiting time when the transport is a CAS level of service.) Transportation waiting time, air ambulance and nonemergency vehicle, onehalf hour increments; CAS A0130 U6 Nonemergency transportation, wheelchair van base rate; additional attendant T2007 U5 (Use this code for waiting time when the transport is a NAS level of service.) Transportation waiting time, air ambulance and nonemergency vehicle, onehalf hour increments; NAS 8-352 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Note: Providers must bill transportation according to the level of service rendered. Therefore, the Ambulance (ALS and BLS) provider code set and Table 8.116 list CAS and NAS codes. Air Ambulance Table 8.119 – Air Ambulance Code Set 261 Air Ambulance HCPCS Code Description Nonemergency transportation and air travel (private or commercial), intrastate or interstate Ambulance service, conventional air service transport, one way (fixed wing) Ambulance service, conventional air service, transport, one way (rotary wing) Ambulance service, conventional air service, transport, one way (rotary wing); if the member is pronounced dead after takeoff to point of pickup, but before the member is loaded Rotary wing air mileage, per statute mile Unlisted ambulance service A0140 A0430 A0431 A0431 QL A0436 A0999 Taxi Provider Table 8.120 – Taxi Code Set 263 Taxi Provider HCPCS Code Description A0100 UA A0100 UB A0100 UC A0100 TK UA A0100 TK UB A0100 TK UC A0100 TT UA A0100 TT UB A0100 TT UC A0100 U4 Taxi, rates nonregulated, 0-5 miles Taxi, rates nonregulated, 6-10 miles Taxi, rates nonregulated, 11 or more miles Taxi, rates nonregulated, 0-5 miles for accompanying parent/attendant Taxi, rates nonregulated, 6-10 miles for accompanying parent/attendant Taxi, rates nonregulated, 11 or more miles for accompanying parent/attendant Taxi, rates nonregulated, 0-5 miles for multiple passengers Taxi, rates nonregulated, 6-10 miles for multiple passengers Taxi, rates nonregulated, 11 or more miles for multiple passengers Nonemergency transportation; taxi, suburban territory Family Member Transportation Provider Table 8.121 – Family Member Transportation Provider Code Set 266 Family Member Provider HCPCS Code A0090 Description Nonemergency transportation, per mile – vehicle provided by individual (family member, self, neighbor) with vested interest Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-353 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Bus Provider Table 8.122 – Bus Provider Code Set 262 Bus Provider HCPCS Code A0110 Description Nonemergency transportation and bus, intrastate or interstate carrier Vaccines for Children The Indiana Immunization Program, ISDH, administers the federal Vaccines for Children (VFC) Program. Eligible Members The goal of the VFC Program is to help raise childhood immunization levels in the United States by supplying healthcare providers with free vaccine to administer to children 18 years old and under who meet one or more of the following criteria: • Enrolled in Medicaid* • Without health insurance • Identified by parent or guardian as American Indian or Alaskan native • Underinsured, for example, children with health insurance that does not cover immunizations - Underinsured patients who have health insurance that does not cover immunizations are eligible to receive VFC vaccines only at an FQHC or RHC. *Note: Through a special arrangement with the Indiana Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP or Hoosier Healthwise Package C), VFC vaccines are also available for immunizing children enrolled in Hoosier Healthwise Package C. Additional information about VFC vaccine administration follows in this section. Provider Enrollment in the VFC Program The Indiana Immunization Program, ISDH, handles VFC provider enrollment and education as well as VFC vaccine orders and distribution. To participate in the VFC Program, providers should complete the following steps: • Contact the ISDH and request VFC provider enrollment forms • Complete and mail the provider enrollment forms • Receive appropriate training and technical assistance • Order vaccines periodically, as needed, and maintain appropriate vaccine supply records 8-354 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Providers may contact the ISDH about the VFC at the following address: Indiana Immunization Program Indiana State Department of Health 2 North Meridian Street Indianapolis, IN 46204 Telephone: (317) 233-7704 or 1-800-701-0704 Fax: (317) 233-3719 Vaccines for Children Forms To screen patients for VFC eligibility, providers may use the Patient Eligibility Screening Record form, available from the ISDH. This form includes a box to indicate Hoosier Healthwise Package C eligible children, as well as a box to indicate Hoosier Healthwise Package A (Medicaid) eligible children. Providers may use this form or may incorporate it into existing clinical forms. Because different funding sources provide the free vaccines, the ISDH must separately track the number of doses administered to Package A (Medicaid) enrolled children from those administered to children enrolled in Hoosier Healthwise Package C. The Patient Eligibility Screening Record and the Vaccine Accountability Tally Sheet forms available from ISDH incorporate tracking for vaccines administered to children enrolled in Hoosier Healthwise Package A and Package C. Vaccine Storage The IHCP does not require providers to physically separate vaccine stock for children in the VFC Program from vaccine stock for Hoosier Healthwise Package C children. No additional storage rules are necessary. VFC Vaccine Coverage and Billing Procedures Currently, the VFC Program offers free vaccines against the following diseases: • Diphtheria • Hemophilus influenza type B • Hepatitis A • Hepatitis B • Human Papilloma virus • Influenza • Measles • Meningococcal disease • Mumps • Rubella • Pertussis • Pneumococcal disease • Polio • Rotavirus Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-355 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions • Tetanus • Varicella All Hoosier Healthwise members 18 years old or younger are eligible for the VFC Program. For vaccines available through the VFC Program and provided to members age 18 years old and younger, the IHCP limits reimbursement to the fee for vaccine administration only. IHCP providers may bill the IHCP up to $8 for administering VFC vaccine to any IHCP-eligible child age 18 years old or younger. IHCP reimbursement for VFC vaccine administration is the lesser of the provider’s submitted charge for VFC vaccine administration or $8. To address the need for immunizations and deal with potential shortage of available influenza vaccines, the IHCP is not limiting reimbursement for any influenza vaccines, regardless of their availability from the VFC Program. This policy, effective October 1, 2008, allows providers to obtain reimbursement for privately purchased influenza vaccines for eligible VFC members when VFC vaccines are not available and supplies are delayed. For administering a free VFC vaccine, providers should bill the appropriate CPT procedure code but not charge more than the $8 VFC vaccine administration fee. Do not bill the separate administration CPT code. When administering a privately purchased influenza vaccine, providers may bill for the cost and administration of the vaccine. The IHCP-allowable reimbursement is based on 105 percent of the wholesale ascquisition cost (WAC) of the vaccine. Providers may separately bill an appropriate CPT administration code (96372, 96373, 96374) in addition to the CPT vaccine procedure code. If an evaluation and management (E/M) service code is billed with the same date of service as an officeadministered immunization, do not bill the vaccine administration code separately. Reimbursement for administration is included in the E/M code allowed amount. Separate reimbursement is allowed when the administration of the drug is the only service billed by the practitioner. In addition, if more than one injection is given on the same date of service and no E/M code is billed, providers may bill for an administration fee for each injection using 96372, 96373, or 96374, as appropriate. Remember – bill no more than the $8 VFC administration fee for free VFC influenza vaccine; or bill the usual and customary rate for the influenza vaccine CPT plus the appropriate administration CPT for provider-purchased influenza vaccine when the immunization is provided without the E/M service. Providers must continue to submit claims to the appropriate delivery system (HP or the member’s managed care organization) for each member, regardless of the source of the vaccine stock. Claims are eligible for postpayment review, and providers must maintain documentation and invoices related to private stock when substituting for VFC vaccine. Rates for rural health clinics (RHCs) and Federally Qualified Health Centers (FQHCs) include payment for the vaccine and administration fee. Table 8.123 lists the procedure codes for vaccines available through the VFC Program. Providers should direct questions about the Medicaid fee-for-service reimbursement for VFC vaccines to Customer Assistance at (317) 655-3240 in the Indianapolis local area or 1-800-577-1278. In addition, providers can refer to http://www.in.gov/isdh/17203.htm with questions regarding vaccine availability and general program information. For members enrolled in an MCO, the provider should contact the MCO for answers to questions about the VFC vaccine administration and reimbursement. 8-356 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Table 8.123 – Procedure Codes – VFC-Available Vaccines Procedure Code Description 90633 Hepatitis A Vaccine, Pediatric/adolescent dosage (2 dose schedule), for intramuscular use per 720 unit single dose vial (effective 7/17/2006) 90634 Hepatitis A Vaccine, Pediatric/adolescent dosage (3 dose schedule) for intramuscular use per 360 unit single dose vial (effective 7/17/2006) 90647 Hemophilus influenza b vaccine (Hib), PRP-OMP conjugate (3 dose schedule), for intramuscular use 90648 Hemophilus influenza b vaccine (Hib), PRR-T conjugate (4 dose schedule), for intramuscular use 90649 Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) Vaccine for members 9 to 18 years of age 90650 Human Papilloma virus (HPV) vaccine, types 16, 18, bivalent, 3 dose schedule, for intramuscular use 90655 Influenza virus vaccine, split virus, preservative free, for children 6-35 months dosage, for intramuscular use 90656 Influenza virus vaccine, split virus, preservative free, for individuals 3 years and above, for intramuscular use 90657 Influenza virus vaccine, split virus, for children 6-35 months of age, for intramuscular use 90658 Influenza virus vaccine, split virus, for use in individuals 3 years of age and above, for intramuscular use 90660 Influenza virus vaccine, live, for intranasal use for members 2 to 49 years of age 90669 Pneumoccocal conjugate vaccine, polyvalent, for children under 5 years, for intramuscular use NOTE: Removed from VFC program March 2010. 90670 Pneumococcal conjugate vaccine, 13 valent, for intramuscular use 90700 Diphtheria, tetanus toxoids, and acellular pertussis vaccine (DTaP), for use in individuals younger than 7 years, for intramuscular use 90702 Diphtheria and tetanus toxoids (DTP) absorbed for use in individuals younger than 7 years, for intramuscular use 90707 Measles, mumps, and rubella virus vaccine (MMR), live, for subcutaneous use 90713 Poliovirus vaccine, inactivated, (IPV), for subcutaneous or intramuscular use 90715 Tetanus, diphtheria toxoids and acellular pertussis vaccine(Tdap) for use in individuals 7 years or older, for intramuscular use (Boostrix and Adacel) 90716 Varicella virus vaccine, live, for subcutaneous use 90718 Tetanus and diphtheria toxoids (Td) absorbed for use in individuals 7 years old or older, for intramuscular use 90721 Diphtheria, tetanus toxoids, and acellular pertussis vaccine and Hemophilus influenza B vaccine (DtaP-Hib), for intramuscular use Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-357 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Procedure Code Description 90723 Diphtheria, tetanus toxoids, acellular pertussis vaccine, Hepatitis B, and poliovirus vaccine, inactivated (DtaP-HepB-IPV), for intramuscular use 90734 Meningococcal conjugate vaccine, Serogroups A, C, Y, 4-135, IM 90744 Hepatitis B vaccine, pediatric/adolescent dosage (three-dose schedule), for intramuscular use 90748 Hepatitis B and Hemophilus influenza b vaccine (HepB-Hib), for intramuscular use Reporting Individual Cases of Varicella (Chickenpox) As of December 12, 2008, all primary cases of varicella (chickenpox) are reportable to the local health department under 410 IAC 1-2.3-47. Healthcare providers should report all individual cases of chickenpox to the local health department within 72 hours for investigation by department staff. Cases of varicella should be reported to the local health department using the Report of Confidential Communicable Diseases Form available at http://www.in.gov/isdh/files/43823.pdf. The complete revised Communicable Disease Control Rule is available at http://www.in.gov/legislative/iac/T04100/A00010.PDF?\. VFC and HealthWatch If a HealthWatch provider chooses not to participate in the VFC Program, the provider must document the IHCP-enrolled patient’s immunization history. If a Care Select PMP chooses not to participate in the VFC Program, the PMP must have a procedure in place, such as a Memorandum of Collaboration (MOC), to ensure that children are adequately and appropriately immunized. Provider-Purchased Vaccine To address an initial shortage of available meningococcal vaccines under VFC, the IHCP does not limit reimbursement for MCV4 or Menactra vaccine, regardless of availability from the VFC program. This allows providers to obtain reimbursement for using privately purchased meningococcal vaccine if they cannot obtain VFC vaccine. When administering privately purchased meningococcal vaccine, providers may bill for the cost of the vaccine plus its administration, and the IHCP-allowable reimbursement includes payment for both. Note: If a provider administers a free VFC vaccine, the provider should bill the appropriate meningococcal vaccine procedure code but must not charge more than the $8 VFC vaccine administration fee and not bill the separate administration CPT code. Use CPT code 90734 – Meningococcal conjugate vaccine, serogroups A, C, Y and W-135 (tetravalent), for intramuscular use. One unit of 90734 equals 0.5ml of the vaccine. Administration Fee For vaccines that are part of the VFC program and are received free by the provider as part of VF C program, the provider may bill the appropriate CPT vaccine procedure code and the lesser of the usual and customary administration fee or $8. A separate CPT administration code should not be billed for a VFC-administered vaccine. 8-358 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions For vaccines that are typically part of the VFC program but have been purchased or supplied out of private stock, providers may bill for both the vaccine and its administration (using CPT code 96372, 96373, or 96374). However, if an evaluation and management (E/M) service code is billed with the same date of service as an office-administered immunization, providers should not bill the vaccine administration code separately. Reimbursement for the administration is included in the E/M codeallowed amount. Separate reimbursement is allowed only when the administration of the drug is the only service billed by the practitioner. For vaccines that are not part of the VFC program, providers may bill for both the vaccine and its administration (using CPT code 96372, 96373, or 96374). However, if an E/M service code is billed with the same date of service as an office-administered immunization, providers should not bill the vaccine administration code separately. Reimbursement for the administration is included in the E/M code-allowed amount. Separate reimbursement is allowed when the administration of the drug is the only service billed by the practitioner. In addition, if more than one vaccine is administered on the same date of service and no E/M code is billed, providers may bill an administration fee for each injection. The Indiana Medicaid maximum fee information may be found on the http://provider.indianamedicaid.com/ihcp/Publications/MaxFee/fee_schedule.asp Web site. Be aware of the member’s primary medical provider assignment, managed care delivery system assignment, and third-party liability resource(s). RHCs and FQHCs Note: RHC- and FQHC-specific encounter rates already include payment for immunizations. When providers submit RHC and FQHC claims to track encounters – claims that the IHCP denies – providers should bill no more than the $8 VFC administration fee for use of VFC influenza vaccine or bill the usual and customary rate for the influenza vaccine CPT plus the administration CPT 90782 for use of provider-purchased meningococcal vaccine. Third Party Liability For vaccines administered to VFC-eligible children, providers can bill directly to the appropriate delivery system (HP or the MCO) when the primary diagnosis is V20.2. Providers need not bill these vaccines to the primary insurance company prior to billing the IHCP. Providers should not experience TPL claim denials for children enrolled in Hoosier Healthwise Package C. If providers obtain information that identifies a primary insurance for children enrolled in Hoosier Healthwise Package C, they should contact the HP TPL Unit at (317) 488-5046 in the Indianapolis local area or 1-800-4574510. Package C The VFC Program is for uninsured children. Although the IHCP considers Hoosier Healthwise Package C an insurance program, the OMPP, the Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP), and the ISDH have worked together to open the VFC Program to children in all the Hoosier Healthwise benefit packages, including Hoosier Healthwise Package C. The Vaccine Accountability Tally Sheet contains an additional column for reporting vaccines administered to children enrolled in Hoosier Healthwise Package C. This allows for accurate tracking of the amount of vaccine used for children in each group. Providers must check the appropriate column on the Patient Eligibility Screening Record and the Vaccine Accountability Tally Sheet. Providers no Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-359 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions longer need to submit the Vaccine Accountability Tally Sheet when ordering vaccines. Instead, providers should submit the form to the ISDH monthly, by the 10th of the month following the month in which the provider administered the vaccines. This change standardizes the reporting period for all providers. Providers who use the Children and Hoosiers Immunization Registry Program (CHIRP) immunization registry do not have to submit the Doses Administered Form (Vaccine Accountability Tally Sheet) to the ISDH. The ISDH generates Doses Administered Reports from CHIRP on the 10th of each month. Send forms to the following address: Indiana Immunization Program Indiana State Department of Health 2 North Meridian Street Indianapolis, IN 46204 The telephone numbers are as follows: (317) 233-7704 or 1-800-701-0704 Children and Hoosiers Immunization Registry Program The ISDH has a statewide, Internet-based immunization registry that contains immunization data for Children and Hoosiers Immunization Registry Program (CHIRP) members. Enrolled users can request View-Only Access to see whether a patient is present in the database and obtain that person’s data, or users can request Full-Access, which includes entry of immunization data into the database directly from an office or clinic, or through an export file from the healthcare provider’s billing vendor. Scientific Technologies Corporation (STC) is the vendor for ISDH development of CHIRP. The ISDH’s goal is to enroll other public facilities – such as community health centers, physicians in private practice, and hospitals, including emergency and clinics – and to expand to schools, Headstart centers, and childcare facilities. Physicians already enrolled as VFC providers were contacted by the ISDH to provide CHIRP information and enrollment packs for consideration. A 2003 change in state law allows for including patient immunization data in CHIRP without specific patient consent and affords provider liability protection for good-faith participation in CHIRP. Patients who choose not to participate can “opt out” by signing a form designed for that purpose. CHIRP has built-in algorithms to recommend the appropriate immunization schedule for each person. It maintains a vaccine inventory and reports vaccine usage. The system also provides reminder or recall capabilities to contact parents through printed mailing labels for postcards and letters. In addition, CHIRP can generate a variety of reports to help a healthcare provider assess the vaccine coverage rates for a practice. It also produces electronic reports for managed care plans and Health Plan Employer Data and Information Set (HEDIS) assessments. Continued development and implementation of CHIRP will ensure that a sustainable system exists to monitor the percent of children who are adequately immunized and to assist in the attainment of the national goal of 90 percent or more of 2-year-old children being appropriately immunized. Obtain more information about CHIRP from the CHIRP Web site at https://chirp.isdh.state.in.us or by calling the ISDH at 1-888-227-4439. 8-360 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Medical Review Team Billing Procedures This section provides billing and claim processing guidelines for Medical Review Team (MRT) providers. MRT claims use IHCP claim processing billing procedures, although there may be minor differences, as follows: • Providers must submit MRT claims via a paper CMS-1500 claim form, Web interChange, or the 837P transaction within one year of the date of service. Providers must properly identify and itemize all services rendered. • Claims that providers submit on paper should be submitted on standard CMS-approved paper CMS-1500 claim forms. For information on purchasing CMS-1500 claim forms, refer to http://www.cms.hhs.gov/ElectronicBillingEDITrans/16_1500.asp. • All providers must be valid participants in the MRT program. • Providers should submit paper CMS-1500 claim forms to the following address: HP CMS-1500 Claims P.O. Box 7269 Indianapolis, IN 46207-7269 • Providers submitting claims via Web interChange must meet the technical requirements for Web interChange access, and have a valid Web interChange account and password. Providers should allow five business days to process each new Web account. Providers that currently have a Web interChange account and password do not need an additional account and password to submit claims for MRT. • New providers wanting to use the 837P transaction must complete, submit, and obtain prior approval of their vendor’s software, trading partner ID, logon ID, and password. Providers should allow one week to process vendor and account information. Providers may obtain instructions for account setup by obtaining a copy of the Companion Guide – 837 Professional Claims and Encounters Transaction from the IHCP Web site at http://provider.indianamedicaid.com. Note: Providers that are currently transmitting claims using the 837P transaction are not required to submit a second application. • Providers cannot submit MRT claims for payment with a claim for Medicaid or services for any other IHCP program. Providers must submit MRT claims with the unique MRT member identification number. • MRT claims are subject to all edits and audits not excluded by MRT program requirements. • Providers can bill for partial units of service. • MRT financial information is available in the electronic 835 RA transaction. • MRT claims processing information is reflected on the 276/277 Claim Status Request and Response Transactions. Providers can inquire on the claims status request and response using Web interChange. • At no time will an applicant bear financial responsibility for an MRT claim if the services were requested by the MRT or county caseworker. MRT claims are paid even if the disability application is denied. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-361 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions MRT Reimbursement for Transportation The MRT program reimburses for transportation services in cases of financial hardship when no transportation is available for medically necessary examinations or tests; however, the provider must contact the MRT to obtain approval prior to rendering the service. Only the following codes will be authorized and billed for most trips: • T2003 SE – Nonemergency transportation, encounter, trip; $10 each way, regardless of vehicle type • T2007SE – Transportation waiting time, air ambulance and nonemergency vehicles, one-half hour increments; $4.50 • A0425 SE – Ground mileage, per statute mile; $1.25 Note: These codes are different from transportation codes used in the IHCP. For billing purposes, a trip is defined as the act of transporting a member from the initial point of pickup to the drop-off point at the final destination. Transportation providers are expected to transport the member along the shortest and most efficient route to and from the destination. MRT Procedure Codes The following tables provide information to help providers select the procedure code that best describes the services rendered. When providers have questions about procedure codes used for billing MRT services or the RBRVS/Maximum Fee Schedule, or when they require clarification about a specific code, they should follow the appropriate avenue of resolution listed in Chapter 1 of this manual. The complete fee schedule is available on the IHCP Web site at http://provider.indianamedicaid.com. Table 8.124 – MRT CPT® Procedure Codes and Fee Schedule Procedure Code 8-362 Modifier Procedure Code Description Modifier Description 36415 Collection of venous blood by venipuncture 70210 Radiologic examination, sinuses, paranasal; less than three views 70220 Radiologic examination, sinuses, paranasal; complete, minimum of three views 70250 Radiologic examination, skull; less than 4 views 70260 Radiologic examination skull; minimum of 4 views 71010 Radiologic examination, chest; single view, frontal 71020 Radiologic examination, chest; two views, frontal and lateral 71100 Radiologic examination, ribs, unilateral; two views Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Procedure Code Modifier Procedure Code Description 71250 Computed tomography, thorax; without contrast material 71260 Computerized tomography, thorax; with contrast material(s) 72040 Radiologic examination, spine, cervical; two or three views 72050 Radiologic examination, spine, cervical; minimum of four views 72052 Radiologic examination, spine, cervical; complete, including oblique and flexion and/or extension studies 72069 Radiologic examination, spine, thoracolumbar, standing (scoliosis) 72070 Radiologic examination, spine; thoracic; two views 72072 Radiologic examination, spine; thoracic; three views 72074 Radiologic examination, spine; thoracic; minimum of four views 72080 Radiologic examination, spine; thoracolumbar; two views 72100 Radiologic examination, spine, lumbosacral; two or three views 72110 Radiologic examination, spine, lumbosacral; minimum of four views 72114 Radiologic examination, spine, lumbosacral; complete, including bending views 72170 Radiologic examination, pelvis; one or two views 72200 Radiologic examination, sacroiliac joints; less than three views 72202 Radiologic examination, sacroiliac joints; three or more views 72220 Radiologic examination, sacrum and coccyx; minimum of two views 73020 Radiologic examination, shoulder; one view 73030 Radiologic examination, shoulder; complete, minimum of two views 73060 Radiologic examination, humerus; minimum of two views 73070 Radiologic examination, elbow; two views Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Modifier Description 8-363 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Procedure Code 8-364 Modifier Procedure Code Description Modifier Description 73080 Radiologic examination, elbow, complete; minimum of three views 73090 Radiologic examination, forearm; two views 73100 Radiologic examination, wrist; two views 73110 Radiologic examination, wrist; complete, minimum of three views 73120 Radiologic examination, hand; two views 73130 Radiologic examination, hand; minimum of three views 73500 Radiologic examination, hip; unilateral, one view 73510 Radiologic examination, hip; complete, minimum of two views 73520 Radiologic examination, hips, bilateral; minimum of two views of each hip, including anteroposterior view of pelvis 73550 Radiologic examination, femur; two views 73560 Radiologic examination, knee; one or two views 73562 Radiologic examination, knee; three views 73564 Radiologic examination, knee; complete, four or more views 73565 Radiologic examination, knee; both knees, standing, anteroposterior 73590 Radiologic examination, tibia and fibula; two views 73600 Radiologic examination, ankle; two views 73610 Radiologic examination, ankle; complete, minimum of three views 73620 Radiologic examination, foot; two views 73630 Radiologic examination, foot; complete, minimum of three views 74000 Radiologic examination, abdomen; single anteroposterior view 74020 Radiologic examination, abdomen; complete, including decubitus and/or erect views 74022 Radiologic examination, abdomen; complete acute abdomen series, including supine, erect, and/or decubitus views; single view chest 80048 Basic metabolic panel 80053 Comprehensive metabolic panel Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Procedure Code Modifier Procedure Code Description 80061 Lipid profile 80076 Hepatic function panel 80100 Drug screen, qualitative; multiple drug classes, chromatographic method; each procedure 80164 Dircpylacetic acid (valproic acid) 82150 Amylase 82465 Cholesterol, serum or whole blood; total 82565 Creatinine; blood 82575 Creatinine; clearance 82947 Glucose; quantitative, blood (except reagent strip) 83036 Hemoglobin; glycosylated (AIC) 83690 Lipase 83718 Lipoprotein, direct measurement; high density cholesterol (HDL cholesterol) 84436 Thyroxine, total 84443 Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) 84450 Transferase; aspartate amino (AST) (SGOT) 84460 Transferase; alanine amino (ALT) (SGPT) 84478 Triglycerides 84479 Thyroid hormone (T3 or T4) uptake or thyroid hormone binding ratio (THBR) 84550 Uric acid; blood 85018 Blood count; hemoglobin (Hgb) 85025 Blood count; complete (CBC), automated (Hgb, Hct, RBC, WBC, and platelet count) and automated differential WBC count 85651 Sedimentation rate, erythrocyte; nonautomated 85652 Sedimentation rate, erythrocyte; automated, Westergren test 86361 T cells; absolute CD4 count 86430 Rheumatoid factor; qualitative 86707 Hepatitis Be antibody (HBeAB) 86708 Hepatitis A antibody (HAAB); total 86803 Hepatitis C antibody Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Modifier Description 8-365 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Procedure Code 8-366 Modifier Procedure Code Description Modifier Description 90801 SE Psychiatric diagnostic interview examination State and/or federally funded programs/ service 92002 SE New: Ophthalmological services: medical examination and evaluation with initiation of diagnostic and treatment program; intermediate, new patient State and/or federally funded programs/ services 92012 SE Established: Ophthalmological services: medical examination and evaluation, with initiation or continuation of diagnostic and treatment program; intermediate, established patient State and/or federally funded programs/ services 92015 Determination of refractive state 92083 Visual field extended examination (e.g., Goldmann visual fields with at least 3 isopters plotted and static determination within the central 30 degrees, or quantitative, automated threshold perimetry, Octopus programs G-1, 32 or 42, Humphrey visual field analyzer full threshold programs 30-2, 24-2, or 30/60-2) 92551 Screening test; pure tone, air only 92552 Pure tone audiometry (threshold); air only 92553 Pure tone audiometry (threshold); air and bone 92557 Comprehensive audiometry threshold evaluation and speech recognition (92553 and 92556 combined) 93000 Electrocardiogram, routine ECG with at least 12 leads; with interpretation and report 93010 Electrocardiogram, routine ECG with at least 12 leads; interpretation and report only 94010 Spirometry, including graphic record, total and timed vital capacity, expiratory flow rate measurement(s) with or without maximal voluntary ventilation 94060 Bronchodilation responsiveness, spirometry as in 94010, pre- and post-bronchodilator administration 95816 Electroencephalogram (EEG); including recording awake and drowsy 95819 Electroencephalogram (EEG); including recording awake and asleep 95860 Needle electromyography; one extremity with or without related paraspinal areas Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Procedure Code Modifier Procedure Code Description 95861 Needle electromyography; two extremities with or without related paraspinal areas 95863 Three extremities with or without related paraspinal areas 95864 Four extremities with or without related paraspinal areas 95900 Nerve conduction, amplitude and latency/velocity study; each nerve, motor, without F-wave study 95903 Nerve conduction, amplitude and latency/velocity study; each nerve, motor, with F-wave study 95904 Sensory Modifier Description 96100 SE Psychological testing – includes psychodiagnostic assessment of personality, psychopathology, emotionality, intellectual abilities, such as Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale – Revised (WAIS R), Rorschach, Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory (MMPI) – with interpretation and report, per hour State and/or federally funded programs/ services 96101 SE Psychological testing (includes psychodiagnostic assessment of emotionality, intellectual abilities, personality and psychopathology, such as MMPI, Rorschach, WAIS) per hour of the psychologist’s or physician’s time, both face-to-face time with the patient and time interpreting test results and preparing the report State and/or federally funded programs/ services 99080 Special reports as insurance forms, more than the information conveyed in the usual medical communications or standard reporting form 99199 Unlisted special service, procedure or report 99244 Office consultation for a new or established patient 99245 Office consultation for a new or established patient 99274 Confirmatory consultation for a new or established patient 99275 Confirmatory consultation for a new or established patient 99450 Basic life and/or disability examination Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-367 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Procedure Code A0425 Modifier SE Procedure Code Description Modifier Description SE – State and/or federally funded programs/service Ground mileage, per statute mile S9981 Medical records copying fee, administrative T1023 Screening to determine the appropriateness of consideration of an individual for participation in a specified program, project or treatment protocol, per encounter T2003 SE Nonemergency transportation; encounter/trip State and/or federally funded programs/services T2007 SE Transportation waiting time, air ambulance and nonemergency vehicle, one-half hour increments State and/or federally funded programs/ services Pre-Admission Screening and Resident Review Billing Procedures This section provides billing and claim processing guidelines for Pre-Admission Screening and Resident Review (PASRR) providers. PASRR claims use normal claim processing billing procedures and payment logic, although there may be minor differences. For Provider Enrollment, new Diagnostic and Evaluation (D&E) Teams and CMHCs are only approved to conduct PASRR Level II assessments through contractual arrangements with the Division of Disability, Rehabilitative Services (DDRS), and the Division of Mental Health and Addiction (DMHA). The OMPP refers the names of new entities to the HP Provider Enrollment Unit for further enrollment processing. PASRR providers that are currently enrolled as IHCP providers do not need to re-enroll. The current IHCP provider ID number that has been assigned for Medicaid or other nonwaiver IHCP programs will be the provider’s PASRR provider ID number. If a current provider ID does not exist, the provider must enroll as a PASRR provider. To enroll as a PASRR provider and to obtain a valid provider ID to submit PASRR claims, providers should visit the IHCP Web site at http://provider.indianamedicaid.com to obtain and complete enrollment applications. Providers should submit completed applications to the following address: HP Provider Enrollment P.O. Box 7263 Indianapolis, IN 46207-7263 PASRR applicants or members may be dually eligible in the IHCP. When providers submit claims for PASRR, the provider must use the PASRR member ID that consists of 800 and the applicant’s Social Security number, or the applicant’s PASRR identification number (for example, 800999999999). At no time shall a member bear financial responsibility for a PASRR Level II assessment. 8-368 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions PASRR claims must be submitted via a paper CMS-1500 claim form, Web interChange, or the 837P transaction within one year of the date of service. The provider must properly identify and itemize all services rendered. Providers should submit paper claims on standard CMS-approved paper CMS-1500 claim forms to the following address: HP CMS-1500 Claims P.O. Box 7269 Indianapolis, IN 46207-7269 Providers submitting claims using the Web interChange must meet the technical requirements for Web interChange access, and have a valid Web interChange account and password. Providers should allow five business days to process each new Web account. Providers that currently have a Web interChange account and password do not need an additional account and password. New providers wanting to use the 837P transaction must complete, submit, and obtain prior approval of their vendor’s software, trading partner ID, logon ID, and password. Providers should allow one week to process vendor and account information. Providers may obtain instructions for account setup by obtaining a copy of the Companion Guide – 837 Professional Claims and Encounters Transaction on the IHCP Web site at http://provider.indianamedicaid.com. Providers who currently send claims using the 837P transaction are not required to make a second application. Providers must submit a claim for each service instance. Services cannot be combined with other nonPASRR service types, even if the services are rendered on the same day or same visit. For example, a claim for PASRR services cannot be combined with a claim for Medicaid services. PASRR claims are subject to all edits and audits not excluded by PASRR program requirements. If a claim encounters an edit or audit for missing or invalid information, the claim suspends or denies. Provider reimbursement for rendered services is determined by the procedure codes, modifiers, and associated maximum (max) fee rate. Procedure codes, modifiers, and max fee rates must accompany all PASRR claim submissions. Providers are responsible for entering billable charges per the published procedure code and max fee rate. Procedure codes and modifiers must accompany all claim submissions. IndianaAIM will capture as many as four modifiers for all PASRR claims with MI or MR segments. If the procedure code or applicable modifier is missing or invalid, edits will deny or suspend claims. Providers may void or replace PASRR claims. PASRR financial information is available on the 835 RA transaction. PASRR claims processing information is reflected on the 276/277 Claim Status Request Response Transactions. Providers can inquire on the claims status request and response using Web interChange. Table 8.125 lists the procedure codes and modifiers for PASRR. Table 8.125 – Procedure Codes for PASRR Procedure Code T2011 U1 UA Code Description Level II PAS-MR Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Procedure Code and Modifiers T2011: Preadmission Screening and Resident Review (PASRR) Level II Evaluation, per Evaluation U1: PAS (Preadmission Screening) UA: Mental Retardation / Developmental Disability 8-369 Chapter 8 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Section 4: CMS-1500 and 837P Transaction Billing Instructions Procedure Code Code Description Procedure Code and Modifiers T2011 U1 UA H1 Level II PAS-MR Psych Exam T2011: Preadmission Screening and Resident Review (PASRR) Level II Evaluation, per Evaluation U1: PAS (Preadmission Screening) UA: Mental Retardation / Developmental Disability HI: Integrated Mental Health and Mental Retardation / Developmental Disabilities Program T2011 U2 UA Level II RR-MR T2011: Preadmission Screening and Resident Review (PASRR) Level II Evaluation, per Evaluation U2: RR (Resident Review) UA: Mental Retardation / Developmental Disability T2011 U2 UA H1 Level II RR-MR Psych Exam T2011: Preadmission Screening and Resident Review (PASRR) Level II Evaluation, per Evaluation U2: RR (Resident Review) UA: Mental Retardation / Developmental Disability HI: Integrated Mental Health and Mental Retardation / Developmental Disabilities Program T2011 U1 UB Level II PAS-MI Initial T2011: Preadmission Screening and Resident Review (PASRR) Level II Evaluation, per Evaluation U1: PAS (Preadmission Screening) UB: Mental Illness T2011 U1 UB TS Level II PAS-MI Initial Update T2011: Preadmission Screening and Resident Review (PASRR) Level II Evaluation, per Evaluation U1: PAS (Preadmission Screening) UB: Mental Illness TS: Follow-up service T2011 U2 UB Level II RR-MI T2011: Preadmission Screening and Resident Review (PASRR) Level II Evaluation, per Evaluation U2: RR (Resident Review) UB: Mental Illness Notes: 1. U1, U2, UA, and UB modifiers would be assigned by the Medicaid Program. 2. HI and TS modifiers are existing national modifiers. 8-370 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 5: Dental Claim Form Billing Instructions Introduction The Indiana Health Coverage Programs (IHCP) accepts only the American Dental Association (ADA) 2006 Dental Claim Form for paper claim submissions, which this section refers to as the ADA 2006 claim form or Dental Claim Form. The 837 Health Care Claim: Dental Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) transaction is the HIPAA-compliant electronic dental transaction. This section refers to this transaction as the 837 Dental or 837D transaction. HP does not supply dental claim forms, and they are not available on the IHCP Web site. Providers can obtain dental claim forms from several sources, including the American Dental Association at 1-800-947-4746. The IHCP returns claims submitted on any other claim form to the provider. Providers Using the Dental Claim Form The following types of providers use the Dental Claim Form or the 837D transaction to bill services to the IHCP: • Endodontists • General dentistry providers • Orthodontists • Oral surgeons • Pediatric dentists • Periodontists • Prosthodontists ADA 2006 Paper Claim Form Changes and Requirements This section provides a brief overview of the requirements for completion of the ADA 2006 claim form. The ADA 2006 claim form replaced the ADA 1999, Version 2000 claim form on March 1, 2008. The instructions outlined in this manual are effective for the new ADA 2006 paper claim submissions starting April 15, 2007. All ADA 2006 paper claims received on and after March 1, 2008, must meet the new ADA 2006 claim form requirements. Noncompliant paper claims submitted for processing are returned to the provider. During the transition period of April 1, 2007, to March 1, 2008, the IHCP accepted the old and the new claim forms. As of March 1, 2008, providers are required to report their National Provider Identifier (NPI) to the IHCP and may include their IHCP Legacy Provider Identifier (LPI) on the paper claim form. After March 1, 2008, only the NPI is required to process claims. For more instructions about NPI requirements, see the National Provider Identifier and One-to-One Match section. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-371 Chapter 8 Section 5: Dental Claim Form Billing Instructions Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Rendering NPI Required All dental group providers must use their rendering and billing provider NPIs on the new ADA 2006 dental claim form. To expedite claims, providers should follow the claim form completion guidelines as listed in Table 8.126 when submitting claims. Date of Service Definition All claims must reflect a date of service. The date of service is the date the specific services were actually supplied, dispensed, or rendered to the patient. For example, when rendering services for space maintainers or dentures, the date of service must reflect the date the appliance or denture is delivered to the patient. This requirement is applicable to all IHCP-covered services. ADA 2006 Dental Claim Form Fields This section includes instructions for completing the dental claim form. Table 8.126 describes each field of the ADA 2006 Dental Claim Form. The field chart uses bold to indicate fields that are required or required, if applicable. The instructions describe each field, or data element, by referring to the number found in the left corner of each box on the dental claim form. Several fields are not numbered. These fields are listed as unlabeled. The narrative sequence moves from left to right, top to bottom, across the claim form. Note: Each claim form must have all required fields completed, including a total dollar amount. Providers can list only one procedure code per service line. If the number of service lines exceeds the number of service lines allowed on the form, providers must complete an additional claim form. All dental providers are required to include dental rendering provider NPI. This requirement is for claims received on or after April 15, 2007. This requirement includes submission of noncheck- and check-related adjustments submitted by paper or replacements that are performed on Web interChange. If the claim or adjustment submitted does not include the appropriate rendering provider NPI, the claim will be denied. In the event that your claim or adjustment request was denied, your claim or adjustment request must be resubmitted with the necessary corrections. In the event that a mass adjustment (claims that begin with region 56) is initiated by HP for erroneously denied claims and the claim was originally paid based on a date of receipt prior to April 15, 2007, and the claim suspends for a rendering NPI edit, the claim will be forced. If the mass adjustment is processed and the original date of receipt is after April 15, 2007, the claim will be denied appropriately. Providers who have administrator access in Web interChange can view their provider profiles to access a list of the rendering providers linked to the group. Providers can contact the Provider Enrollment Helpline at 1-877-707-5750 to discuss any updates that need to be made to the provider group information. Description of Fields on the ADA 2006 Dental Claim Form This section explains completion of the ADA 2006 claim form. Some information is required to complete the claim form, while other information is optional. All dental providers must use their rendering and group NPI numbers. When two or more dentists are rendering services for a member, the providers must use separate claims to expedite claims processing. Providers should follow the guidelines in Table 8.126 when submitting claims. 8-372 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 5: Dental Claim Form Billing Instructions The ADA 2006 Claim Form Field Descriptions table uses bold type to indicate if a field is Required or Required, if applicable. Optional and Not applicable information is displayed in normal type. Specific instructions applicable to a particular provider type are noted as well. The instructions describe each form locator by referring to the number found in the left corner of each box on the ADA 2006 claim form. These boxes contain the data elements. Figure 8.3 – American Dental Association (ADA) 2006 Dental Claim Form Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-373 Chapter 8 Section 5: Dental Claim Form Billing Instructions Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Table 8.126 – ADA 2006 Dental Claim Form Field Descriptions Form Field Narrative Description/Explanation 1 Type of Transaction (mark all applicable boxes) – Mark the box stating, Dentist’s statement of actual services and/or EPSDT. Optional. 2 Predetermination/Preauthorization Number – Prior Authorization #: If it is an emergency situation, include the word Emergency in this field. Required if applicable. 3 INSURANCE COMPANY/DENTAL BENEFIT PLAN INFORMATION – Company Plan Name, Address, City, State, ZIP Code – Enter primary insurance information with name and address, ZIP Code+4. Optional. Only required if member has other insurance. This field is not to be used for Indiana Medicaid information. 4 OTHER DENTAL OR MEDICAL COVERAGE? – Mark yes or no. Optional. 5 OTHER SUBSCRIBER NAME – If another insurance is available and the policyholder is other than the member indicated in field 20, provide the policyholder’s name. Optional. 6 DATE OF BIRTH: MM/DD/CCYY – If another insurance is available and the policyholder is other than the member indicated in field 20, provide the policyholder’s birth date in MMDDCCYY format. Optional. 7 GENDER – M, F – Mark the appropriate box. Optional. 8 POLICYHOLDER/SUBSCRIBER ID (SSN OR ID#) – Required, if applicable. 9 PLAN/GROUP NUMBER – Required, if applicable. 10 PATIENT’S RELATIONSHIP TO PERSON NAMED IN #5 – Required, if applicable. 11 OTHER INSURANCE COMPANY/DENTAL BENEFIT PLAN NAME, ADDRESS, CITY, STATE, ZIP CODE – Required, if applicable. 12 POLICYHOLDER/SUBSCRIBER INFORMATION (FOR INSURANCE COMPANY NAMED IN #3) – Enter the member’s last name, first name, and middle initial as found on the member’s IHCP identification card. Required for field 12 or field 20. 13 DATE OF BIRTH (MM/DD/CCYY) – Optional. 14 GENDER – Optional. 15 POLICYHOLDER/SUBSCRIBER ID (SSN OR ID#) – This field accommodates the 12 numeric characters. Required for either field 15 or field 23. 16 PLAN/GROUP NUMBER – Required, if applicable. 17 EMPLOYER NAME – Required, if applicable. PATIENT INFORMATION 18 RELATIONSHIP TO POLICYHOLDER/SUBSCRIBER IN #12 ABOVE – Enter an ‘X’ in the appropriate box. Optional. 19 STUDENT STATUS – Optional. 20 PATIENT NAME (LAST, FIRST, MIDDLE INITIAL, SUFFIX), ADDRESS, CITY, STATE, ZIP CODE – Enter the member’s last name, first name, and middle initial as found on the member’s IHCP identification card. Required for field 12 or field 20. 21 DATE OF BIRTH – Optional. 22 GENDER – Optional. 8-374 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Form Field Chapter 8 Section 5: Dental Claim Form Billing Instructions Narrative Description/Explanation 23 PATIENT ID/ACCOUNT # (ASSIGNED BY DENTIST) – Enter the IHCP member’s identification (RID) number. This field accommodates the 12 numeric characters. Required for field 15 or field 23. 24 PROCEDURE DATE – Enter the date the service was rendered in MM/DD/CCYY format. Required. Date of service is the date the specific services were actually supplied, dispensed, or rendered to the patient. For example, this date will reflect the date the denture or space maintainer is delivered to the patient. 25 AREA OF ORAL CAVITY – Optional. 26 TOOTH SYSTEM – Optional. 27 TOOTH NUMBER(S) OR LETTER(S) – Enter the tooth number or letter for the service rendered. Required for any procedure performed on an individual tooth. Required, if applicable. 28 TOOTH SURFACE – Enter the tooth surface for the service rendered. Required, if applicable. 29 PROCEDURE CODE – Enter the appropriate ADA Current Dental Terminology (CDT) procedure code. Required. 30 DESCRIPTION – Optional. 31 FEE – Enter the amount charged for the procedure code. Eight digits are allowed, including two decimal places. Required. 32 OTHER – Not used. 33 TOTAL FEE – Enter the total of all the individual service line charges. Eight digits are allowed, including two decimal places. Required. 34 MISSING TEETH INFORMATION – (PLACE AN ‘X’ ON EACH MISSING TOOTH) Mark the diagram as directed. Optional. 35 REMARKS – Enter only the amount paid by prior payer. All commercial payments are required in this field. Required, if applicable. 36 AUTHORIZATIONS – PATIENT/GUARDIAN SIGNATURE AND DATE – Optional. 37 AUTHORIZATIONS – SUBSCRIBER SIGNATURE AND DATE – Optional. ANCILLARY CLAIM/TREATMENT INFORMATION 38 PLACE OF TREATMENT – Indicate the type of facility where treatment was rendered by marking an ‘X’ in the appropriate box. Required. 39 NUMBER OF ENCLOSURES (00 TO 99) – Not applicable. 40 IS TREATMENT FOR ORTHODONTICS? – If Yes is marked, provide the additional information requested. Optional. 41 DATE APPLIANCE PLACED (MM/DD/CCYY) – Enter date. Optional. 42 MONTHS OF TREATMENT REMAINING – Optional. 43 REPLACEMENT OF PROSTHESIS? – If Yes is marked, provide the additional information requested. Optional. 44 DATE PRIOR PLACEMENT (MM/DD/CCYY) – Enter date. Optional. 45 TREATMENT RESULTING FROM – Mark the appropriate box. Required, if applicable. 46 DATE OF ACCIDENT (MM/DD/CCYY) – Enter date. Required, if applicable. 47 AUTO ACCIDENT STATE – Enter state of accident. Required, if applicable. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-375 Chapter 8 Section 5: Dental Claim Form Billing Instructions Form Field Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Narrative Description/Explanation BILLING DENTIST OR DENTAL ENTITY 48 NAME, ADDRESS, CITY, STATE, ZIP CODE – Enter the billing provider office location name, address, city, state, and nine-digit ZIP Code +4. Required. 49 NPI – Enter the 10-digit numeric NPI of the billing or group provider. Required. 50 LICENSE NUMBER – Leave field blank. Effective October 1, 2009, healthcare providers will no longer enter the LPI in this field. 51 SSN OR TIN – Optional. 52 PHONE NUMBER – Optional. 52A ADDITIONAL PROVIDER ID – Enter the taxonomy code for the billing provider NPI. Required if needed to establish one-to-one NPI/LPI match if the provider has multiple locations. TREATING DENTIST AND TREATMENT LOCATION INFORMATION 53 TREATING DENTIST AND TREATMENT LOCATION INFORMATION – SIGNED (TREATING DENTIST) – An authorized person, someone designated by the provider, or the dentist must sign and date the claim. A signature stamp is acceptable; however, a typed signature is not acceptable. Required, unless the Signature on File form has been completed and is included in the provider enrollment file. DATE – Provide the date the claim was submitted in a MMDDYYYY format. Required. Note: If two or more physicians perform services on the same patient on the same date of service, these services must be filed on separate claims. 54 NPI – Enter the rendering provider NPI. Required. 55 LICENSE NUMBER – Optional. 56 ADDRESS, CITY, STATE, ZIP CODE – Enter rendering provider address. Optional. 56A PROVIDER SPECIALTY CODE – Enter the rendering provider taxonomy code for the NPI. Required if needed to establish a one-to-one NPI/LPI match if the provider has multiple locations. 57 PHONE NUMBER – Optional. 58 ADDITIONAL PROVIDER ID – Leave field blank. Effective October 1, 2009, healthcare providers will no longer enter the LPI in this field. 837D Electronic Transaction Providers must use the standard 837D format to submit electronic institutional claims. These standards are published in the 837D Implementation Guides (IGs). An addendum to most IGs has been published and must be used to properly implement each transaction. The IGs are available for download through the Washington Publishing Company Web site at http://wpc-edi.com. Companion Guides The IHCP has developed technical companion guides to assist application developers during the implementation process. Information contained in the IHCP Companion Guides is intended only to supplement the adopted IGs, and provide guidance and clarification as it applies to the IHCP. The Companion Guides are never intended to modify, contradict, or reinterpret the rules established by the 8-376 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 5: Dental Claim Form Billing Instructions IGs. The Companion Guides are located on the IHCP Web site at http://provider.indianamedicaid.com in the EDI Solutions section. Some data elements that providers submit may not be used in processing the 837I or 837P transaction; however, those data elements may be returned in other transactions, such as the 277 Claim Status Request and Response or the 835 Remittance Advice transactions. These data elements are necessary for processing, and failure to add these data elements may result in claim suspension or claim denial. Billing Procedures Current Dental Terminology Procedure Codes The IHCP end-dated in IndianaAIM all IHCP dental codes not listed as Current Dental Terminology (CDT) procedure codes. As updates to the CDT occur, the IHCP notifies providers of the changes through the Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS) updates in IHCP provider bulletins, newsletters, and banner page articles. Dental Extractions The following billing requirements and reimbursement policies apply to tooth extractions. The IHCP allows only one tooth number per service line for dental extractions. A provider submitting a claim for D7140 – Extraction, erupted tooth or exposed root (elevation and/or forceps removal) must indicate the tooth number for each tooth extracted on a separate service line in field 27 on the ADA 2006 Dental Claim Form. The IHCP pays 100 percent of the maximum allowed amount or the billed amount, whichever is less, for the initial extraction. This dental service is not applied toward the IHCP member’s $600 Dental Cap services. For multiple extractions within the same quadrant on the same date of service, the IHCP pays 90 percent of the maximum allowed amount for procedure code D7140 or the billed amount, whichever is less. Package E Billing With the assistance of the Dental Advisory Panel (DAP), the IHCP created a table of the CDT codes that are allowed for reimbursement of emergency services provided to Package E members. These codes are shown in Table 8.127. The listing of a code in Table 8.127 does not eliminate the need for providers to document the emergency medical condition that required treatment. The Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act of 1990 (OBRA) defines an emergency medical condition as follows: A medical condition of sufficient severity (including severe pain) that the absence of medical attention could result in placing the member’s health in serious jeopardy, serious impairment of bodily functions, or serious dysfunction of an organ or part. Radiographs must be billed only when the member presents with symptoms that warrant the diagnostic service. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-377 Chapter 8 Section 5: Dental Claim Form Billing Instructions Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Table 8.127 – CDT Codes Allowed for Package E Members CDT Code Description D0140 Limited oral evaluation – problem focused D0210 Intraoral – complete series (including bitewings) D0220 Intraoral – periapical – first film D0230 Intraoral – periapical – each additional film D0240 Intraoral – occlusal film D0270 Bitewing – single film D0272 Bitewings – two films D0273 Bitewings – three films D0274 Bitewings – four films D0330 Panoramic film D7111 Extraction, coronal remnants – deciduous tooth D7140 Extraction, erupted tooth or exposed root D7210 Surgical removal of erupted tooth requiring elevation of mucoperiosteal flap and removal of bone and/or section of tooth D7220 Removal of impacted tooth – soft tissue D7230 Removal of impacted tooth – partially bony D7240 Removal of impacted tooth – completely bony D7241 Removal of impacted tooth – completely bony, with unusual surgical complications D7250 Surgical removal of residual tooth roots (cutting procedure) D7260 Oroantral fistula closure D7261 Primary closure of sinus perforation D7270 Tooth reimplantation and/or stabilization of accidentally evulsed or displaced tooth D7280 Surgical access of unerupted tooth (impacted tooth not intended for extraction) D7282 Mobilization of erupted or malpositioned tooth to aid eruption D7285 Biopsy of oral tissue – hard D7286 Biopsy of oral tissue – soft D7288 Brush biopsy – transepithelial sample collection D7510 Incision and drainage of abscess – intraoral soft tissue D7511 Incision and drainage of abscess – intraoral soft tissue – complicated (includes drainage of multiple fascial spaces) D7520 Incision and drainage of abscess – extraoral soft tissue D7521 Incision and drainage of abscess – extraoral soft tissue – complicated (includes drainage of multiple fascial spaces) D7560 Maxillary sinusotomy for removal of tooth fragment or foreign body D7610 Maxilla – open reduction (simple fracture) D7620 Maxilla – closed reduction (simple fracture) D7630 Mandible – open reduction (simple fracture) 8-378 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual CDT Code Chapter 8 Section 5: Dental Claim Form Billing Instructions Description D7640 Mandible – closed reduction (simple fracture) D7650 Malar and/or zygomatic arch – open reduction (simple fracture) D7660 Malar and/or zygomatic arch – closed reduction (simple fracture) D7670 Alveolus – closed reduction, may include stabilization of teeth (simple fracture) D7671 Alveolus – open reduction, may include stabilization of teeth (simple fracture) D7680 Facial bones – complicated reduction with fixation and multiple surgical approaches (simple fracture) D7710 Mandible Maxilla – open reduction (compound fracture) D7720 Mandible Maxilla – closed reduction (compound fracture) D7730 Mandible – open reduction (compound fracture) D7740 Mandible – closed reduction (compound fracture) D7750 Malar and/or zygomatic arch – open reduction (compound fracture) D7760 Malar and/or zygomatic arch – closed reduction (compound fracture) D7770 Alveolus – open reduction, may include stabilization of teeth (compound fracture) D7771 Alveolus – closed reduction, may include stabilization of teeth (compound fracture) D7780 Facial bones – complicated reduction with fixation and multiple surgical approaches (compound fracture) D7910 Suture of small wounds up to 5cm (excludes surgical incisions) D7911 Complicated suture – up to 5cm (excludes surgical incisions) D7912 Complicated suture – greater than 5cm (excludes surgical incisions) D7999 Unspecified oral surgery procedure – by report D9220 General anesthesia – first 30 minutes. (Covered only if medically necessary. Only covered in the office setting for members less than 21 years of age. Only covered for members 21 years of age and older in the hospital (inpatient or outpatient) or ASC setting.) D9221 General anesthesia – each additional 15 minutes. (See D9220.) D9230 Analgesia, anioxlysis, inhalation of nitrous oxide. (Covered only for members 20 years of age and younger and limited to one unit per visit.) D9241 Intravenous conscious sedation/analgesia – first 30 minutes. (Covered for oral surgical procedures only.) D9242 Intravenous conscious sedation/analgesia – each additional 15 minutes. (Covered for oral surgical procedures only.) D9248 Nonintravenous conscious sedation D9920 Behavior management Attachments In the past, the IHCP allowed attachments only with paper claim submissions. However, HIPAA allows attachments to be submitted with paper and electronic claims. Attachment control numbers (ACNs) are only for electronic claim submission. Providers must submit attachments for electronic claims by mail for processing. Providers must use the attachment transmission code BM (by mail) Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-379 Chapter 8 Section 5: Dental Claim Form Billing Instructions Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual – when submitting all attachments for electronic claims. Providers must submit all attachments at the same time. Each time a claim that has attachments is submitted electronically, the ACN must be a unique number. Providers must mail the attachment and cover sheet to the IHCP at the following address: HP P.O. Box 7259 Indianapolis, IN 46207 If HP does not receive an attachment within 45 days of claim submission, the IHCP automatically denies the claim. If HP receives an incorrect attachment, the IHCP automatically denies the claim. Attachment Control Number Attachments must contain an ACN. This code identifies each attachment. The ACN allows the IHCP to match the attachment to the submitted claim and must be written at the top of each page of the attachment. The provider must create the ACN, which can be numbers, letters, or a combination of letters and numbers. ACNs can be up to 30 characters in length. The numbers must be unique to each attachment for each claim. The provider must indicate the number of pages on the Claims Attachment Cover Sheet (not including the cover sheet) and on each page of a multiple-page document. The Claims Attachment Cover Sheet is available on the Forms page of the IHCP Web site at http://provider.indianamedicaid.com/general-provider-services/forms.aspx. Report Type Code For processing, providers must also use the Report Type Code indicating the type of attachment that they are sending. Report Type Codes are as follows: • B4 – Referral Form – Used by Surveillance and Utilization Review (SUR) for the Right Choices Program • DA – Dental Models – Used by SUR and submitted only upon request • DG – Diagnostic Report – Used by prior authorization (PA) and SUR • EB – Explanation of Benefits – Used by Third Party Liability (TPL), Resolutions, and SUR • OB – Operative Note – Used by PA, Resolutions, Medical Policy, and SUR • P6 – Periodontal Charts – Used for specific periodontal procedures • RR – Radiology Reports – Used by PA, Medical Policy, and SUR • RB – Radiology Films – Used by PA and SUR • OZ – Support Data for Claim – The following are uses for progress notes: - Invoices (Manual Pricing) - Durable Medical Equipment delivery tickets - Transportation run tickets - Sterilization/Hysterectomy consent forms - Spend-down Form 8A - Past filing limit documentation - PA request/response copies - Environmental modification service requests - Consultation reports 8-380 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 5: Dental Claim Form Billing Instructions Return to Provider Letter Providers receive a return to provider (RTP) letter when the number of attachments behind the attachment cover letter does not match the number the provider listed on the Claims Attachment Cover Sheet. HP matches the attachments received with the parent claim electronically. When providers correctly submit attachments with all numbers matching, Claim Support, Resolutions, and the appropriate MCO or CMO processes the claim. When an ACN that is not unique is submitted on a claim, an error message prompts the provider to change the ACN; the claim cannot be submitted without a unique ACN. Paper Claims with Attachments HIPAA implementation did not change the process for paper claim attachments. Providers should continue to follow current procedures for submitting paper claims with attachments as outlined in Chapter 10 of this manual. Managed Care Considerations Hoosier Healthwise risk-based managed care (RBMC) is the delivery system for the mandatory managed care program for parents and children who receive Temporary Assistance for Needy Families (TANF) and for children and pregnant women at or just above the federal poverty limit. Care Select enrolls most aged, blind, and disabled Medicaid enrollees. Care Select excludes enrollees with a nursing facility or waiver Level of Care, or those who have spend-down. The IHCP pays dental claims for Hoosier Healthwise and Care Select members the same way it pays traditional IHCP fee-for-service (FFS) claims. Providers must submit dental claims to HP for payment. Providers do not need primary medical provider (PMP) authorization or program authorization for members to access dental services, except for dental surgery provided in an inpatient, outpatient, or ambulatory surgical center (ASC) setting. Note: For RBMC members, contact the appropriate MCO for instructions regarding surgery. MCO contact information can be found in Chapter 1. Care Select Dental claims using the CDT codes for services provided to Care Select members do not require certification from the PMP. However, for services rendered in an inpatient, outpatient, or ASC setting to a Care Select member, the provider must have the services authorized by the PMP; the anesthesiologist’s services also must be authorized by the PMP. For claims billed on the CMS-1500 or UB-04 claim form for Care Select members, providers must have the claim authorized by the PMP to be reimbursed. Providers can submit these claims to HP for payment. Risk-Based Managed Care In RBMC, the State contracts with managed care organizations (MCOs) to provide covered services, including dental services provided in an inpatient, outpatient, or ASC setting to enrolled IHCP members. The MCOs prefer prenotification by dentists using other service providers for delivery of dental services. The IHCP carves out dental provider services billed on a dental claim form from RBMC and MCO services. Providers must submit dental claims incurred by RBMC members to HP for adjudication. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-381 Chapter 8 Section 5: Dental Claim Form Billing Instructions Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual When providers perform dental services in an inpatient, outpatient, or ASC setting, they bill their services with the Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS) codes on a CMS-1500 claim form. The IHCP does not carve out ancillary services, such as anesthesia, and providers must bill these services to the MCO. Services Associated with Dental Services for Hoosier Healthwise RBMC Networks For dental services that providers submit with CDT codes included in the IHCP Dental Fee Schedule and bill on a dental claim form (paper or electronically), the IHCP carves out these services from Hoosier Healthwise RBMC managed care. Providers must submit claims for these services to HP. Providers can find a copy of the Dental Fee Schedule on the IHCP Web site at http://provider.indianamedicaid.com. Information on how to obtain a paper copy of the fee schedule is presented in the Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System Codes section. Dental services, which are performed by the following dental specialists and billed on the ADA 2006 or the 837 Health Care Claim: Dental (837D) electronic transaction, are carved out or excluded from the responsibility of Hoosier Healthwise RBMC: • Endodontists • General Dentistry Practitioners • Oral Surgeons • Orthodontists • Pediatric Dentists • Periodontists • Mobile Dentists • Prosthodontists • Dental Clinics All dental services billed using CDT procedure codes must be submitted to HP using the ADA 2006 claim form or the 837D transaction. Prior to dental services being provided in an inpatient or outpatient hospital setting or an ASC for an RBMC member, the dental providers must first contact the member’s MCO before rendering services to determine whether PA is required. When the provider obtains MCO authorization and provides services, the services must then be billed as follows: • Dental-related facility charges must be billed on a UB-04 claim form. • Dental services provided in an inpatient, outpatient, or ASC setting can be billed with CDT codes on a dental claim form. These services are carved out of RBMC, and must be billed to HP using the ADA 2006 claim form or the 837D transaction. • All other associated professional services, such as oral surgery, radiology, and anesthesia, as well as ancillary services related to the dental services, must be billed to the MCO on the CMS-1500 claim form or the 837P transaction, along with appropriate authorization information. Note: If a member is enrolled in Care Select, the PMP must authorize services rendered in an inpatient, outpatient, or ASC setting for providers to receive reimbursement. The MCOs and CMOs are responsible for determining which services require PA for their members. The MCOs’ and CMOs’ decisions to authorize, modify, or deny a given request are based on medical 8-382 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 5: Dental Claim Form Billing Instructions necessity, reasonableness, and other criteria. A provider must make requests for reviews and appeals by contacting the appropriate MCO and CMO. Member Eligibility Verification and Billing for Dental Services As in the traditional FFS IHCP, providers must verify eligibility at the time a member makes an appointment and again prior to rendering the service on the day the appointment is scheduled. Providers can verify eligibility through the Automated Voice Response (AVR) system, Omni swipe card device (Omni), and the Web interChange. These methods are the same whether the member is in Hoosier Healthwise, Care Select, or the Traditional Medicaid network. Dental Cap The IHCP places a $600 cap on dental services per calendar year, per member, for members 21 years of age and older. This includes members who reach 21 years of age during the year and new members who are 21 years of age or older on the date the member is eligible for dental services. The $600 cap includes services provided on or after the date a member reaches 21 years old. Dental services provided in a hospital do not apply to the cap. If the provider does not indicate the place of service on the claim form, the IHCP assumes the service was delivered in a dental office. If services were rendered in a hospital, providers should indicate a hospital place of service in field 38 of the ADA 2006 claim form. Table 8.128 identifies codes for services included in the $600 dental cap when provided in a dentist’s office. Table 8.128 – CDT Codes Included in the $600 Dental Cap CDT Code Description D0120 Periodic oral evaluation D0140 Limited oral evaluation – problem focused D0145 Oral evaluation for a patient under 3 years of age and counseling with primary caregiver D0150 Comprehensive oral evaluation D0160 Detailed and extensive oral evaluation – problem focused, by report D0170 Reevaluation – limited, problem focused (established patient; not postoperative visit) D0210 Intraoral – complete series (including bitewings) D0220 Intraoral – periapical – first film D0230 Intraoral – periapical – each additional film D0240 Intraoral – occlusal film D0250 Extraoral – first film D0260 Extraoral – each additional film D0270 Bitewing – single film D0272 Bitewings – two films D0274 Bitewings – four films D0290 Posterior-anterior or lateral skull and facial bone survey film Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-383 Chapter 8 Section 5: Dental Claim Form Billing Instructions CDT Code 8-384 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Description D0310 Sialography D0330 Panoramic film D0340 Cephalometric film D1110 Prophylaxis-adult D2140 Amalgam – one surface, permanent D2150 Amalgam – two surfaces, permanent D2160 Amalgam – three surfaces, permanent D2161 Amalgam – four or more surfaces, permanent D2330 Resin-based composite – one surface, anterior D2331 Resin-based composite – two surfaces, anterior D2332 Resin-based composite – three surfaces, anterior D2335 Resin-based composite – four or more surfaces or involving incisal angle (anterior) D2390 Resin-based composite crown, anterior D2391 Resin-based composite crown, one surface – posterior D2392 Resin-based composite crown, two surfaces – posterior D2393 Resin-based composite crown, three surfaces – posterior D2394 Resin-based composite crown, four or more surfaces – posterior D2910 Recement inlay D2920 Recement crown D2930 Prefabricated stainless steel crown – primary tooth D2931 Prefabricated stainless steel crown – permanent tooth D2940 Sedative filling D2951 Pin retention – per tooth, in addition to restoration D2980 Crown repair, by report D3220 Therapeutic pulpotomy (excluding final restoration) removal of pulp coronal to the dentinocemental junction and application of medicament D3222 Partial pulpotomy for apexogenesis – permanent tooth with incomplete root development D3230 Pulpal therapy (resorbable filling) – anterior, primary tooth (excluding final restoration) D3240 Pulpal therapy (resorbable filling) – posterior, primary tooth (excluding final restoration) D4210 Gingivectomy or gingivoplasty – per quadrant D4211 Gingivectomy or gingivoplasty – per tooth D4240 Gingival flap procedure, including root planing – per quadrant D4241 Gingival flap procedure, including root planing – one to three contiguous teeth or bounded teeth spaces per quadrant D4355 Full-mouth debridement to enable comprehensive periodontal evaluation and diagnosis D5110 Complete denture – maxillary Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual CDT Code Chapter 8 Section 5: Dental Claim Form Billing Instructions Description D5120 Complete denture – mandibular D5130 Immediate denture – maxillary D5140 Immediate denture – mandibular D5211 Upper partial – resin base (including any conventional clasps, rests, and teeth) D5212 Lower partial – resin base (including any conventional clasps, rests, and teeth) D5213 Maxillary partial denture – cast metal framework with resin denture bases (including any conventional clasps, rests, and teeth) D5214 Mandibular partial denture – cast metal framework with resin denture bases (including any conventional clasps, rests, and teeth) D5225 Maxillary partial denture – flexible base (including any clasps, rests, and teeth) D5226 Mandibular partial denture – flexible base (including any clasps, rests, and teeth) D5510 Repair broken complete denture base D5520 Replace missing or broken teeth – complete denture (each tooth) D5610 Repair resin denture base D5620 Repair cast framework D5630 D5640 D5650 D5660 D5730 D5731 D5740 D5741 D5750 D5751 D5760 D5761 D9220 D9221 Repair or replace broken clasp Replace broken teeth – per tooth Add tooth to existing partial denture Add clasp to existing partial denture Reline complete maxillary denture (chairside) Reline lower complete mandibular denture (chairside) Reline maxillary partial denture (chairside) Reline mandibular partial denture (chairside) Reline complete maxillary denture (laboratory) Reline complete mandibular denture (laboratory) Reline maxillary partial denture (laboratory) Reline mandibular partial denture (laboratory) General anesthesia – first 30 minutes General anesthesia – each additional 15 minutes D9230 Analgesia D9248 Nonintravenous conscious sedation The dental cap applies only to the IHCP paid dental services provided in a dental office. The dental cap excludes dental services for root planing and scaling, intravenous sedation provided in conjunction with oral surgery, and osseous surgery. Providers can bill the usual and customary charge to the member for any services provided after the member has exhausted the cap. However, if the IHCP partially pays for a service because of the cap limit, the provider can bill the member only for the difference between what the IHCP would have reimbursed to the provider and what the IHCP actually paid. The situation must meet the following guidelines for an IHCP provider to hold a member responsible for payment: • The service rendered must be determined to be noncovered by the IHCP. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-385 Chapter 8 Section 5: Dental Claim Form Billing Instructions Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual • The member has exceeded the program limitations for a particular service. • The member must understand before receiving the service that the IHCP does not cover the service and that the member is responsible for the charges associated with the service. • The provider must maintain documentation that the member voluntarily chose to receive the service knowing that the IHCP does not cover the service. In summary, a provider can bill a member only when the above criteria are fully met. A consent form is not acceptable unless it identifies the specific procedure being performed, and the member signs the consent before receiving the service. If the consent form uses written statements, the statement must not contain language such as, “If an IHCP service is not covered...” Note: The IHCP does not require a written statement. However, before providers can bill members, providers must demonstrate that they informed the members that the IHCP does not cover the service and the member voluntarily chose to receive the service knowing the IHCP would not cover it. Providers must verify member eligibility prior to delivering services. The Eligibility Verification System (EVS) for the AVR and Web interChange confirms if a member has reached the dental cap. Audit 6236 – Dental services are limited to $600 per member 21 years of age and older identifies whether a member has met his or her cap. To inquire about eligibility via AVR, providers must use the billing number for the dental office. Note: Federally Qualified Health Center (FQHC) and rural health clinic (RHC) providers must utilize the rendering NPI of the dentist, not the billing NPI, to access benefit limitation information via EVS. To verify how much of the dental cap the IHCP has paid, providers can call the Customer Assistance Unit at (317) 655-3240 in the Indianapolis area, or 1-800-577-1278. The dental cap met amount is also given when providers use any of the EVS options. Dentists should remember that the information provided by Customer Assistance and EVS reflects only services paid up to the time of the inquiry. Note: The IHCP does not reserve services for a provider or guarantee payment of services even with prior authorization. Dental Service Limitations This section presents the more commonly used dental services and service limitations. Orthodontics The IHCP covers orthodontic procedures only for members younger than 21 years old. The Office of Medicaid Policy and Planning (OMPP) requires PA for all orthodontic services. Providers must submit prior authorization requests on the IHCP Medical Prior Authorization Form, not on the IHCP Prior Authorization Dental Request Form. Providers can access this form through the IHCP Web site at http://provider.indianamedicaid.com/general-provider-services/forms.aspx. A member of a recognized craniofacial anomalies team, such as a member of the American Cleft Palate-Craniofacial Association, must diagnose the IHCP member. A licensed practitioner who minimally accepts routine craniofacial patients for orthodontic services, such as patients with cleft lip 8-386 Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Chapter 8 Section 5: Dental Claim Form Billing Instructions and palate, must treat the member. Braces are a primary example of the type of procedure code that is not covered as a reimbursed service through the IHCP unless the member has a recognized diagnosis, such as a craniofacial abnormality, cleft lip and palate, or a malocclusion diagnosis, and has been diagnosed through a prior authorization from a recognized craniofacial anomalies team member or a member of the American Cleft Palate-Craniofacial Association. The IHCP covers orthodontic services for patients with documentation of one or more of the diagnoses for craniofacial and malocclusion. Cleft palate and craniofacial specialists helped develop the criteria. A signed statement from the practitioner, who is a member of a hospital-based craniofacial team, certifies the correct craniofacial diagnosis and malocclusion. The diagnosis must include information descriptive of facial and soft tissue, skeletal, dental/occlusal, functional, and applicable medical or other conditions. The provider must submit a step-wise treatment plan with the treatment phase and length of treatment specified. The PA lasts for the time period of the length of treatment specified. The IHCP expects that most patients who meet the criteria require comprehensive orthodontic treatment. The IHCP reviews prior authorization requests for limited or interceptive orthodontic treatment (procedure codes D8010 through D8060) on a case-by-case basis. PA requests for removable or fixed appliance therapy (procedure codes D8210 or D8220) must show that the patient meets the criteria and has a harmful habit in need of correction. The IHCP denies prior authorization requests for any member who does not meet the criteria. Providers must maintain documentation for orthodontic services in the patient’s dental or medical record, as required by 405 IAC 1-5-1, Medical records; contents and retention. This rule states, “Medicaid records must be of sufficient quality to fully disclose and document the extent of services provided to individuals receiving assistance under the provisions of the Indiana Medicaid program. All providers participating in the Indiana Medicaid program shall maintain, for a period of seven years from the date Medicaid services are provided, such medical and/or other records, including X-rays, as are necessary to fully disclose and document the extent of the services. A copy of the claim form that has been submitted by the provider for reimbursement is not sufficient documentation, in and of itself, to comply with this requirement. Providers must maintain records which are independent of claims for reimbursement.” The IHCP does not cover procedure codes D8680, Orthodontic retention – removal of appliances, construction and placement of retainer(s), D8691 – Repair of orthodontic appliance, and D8692 – Replacement of lost or broken retainer. The IHCP includes these services in the reimbursement for orthodontic treatment and does not separately reimburse for them. The IHCP will cover D8693 – Rebounding or recementing; and/or repair, as required, of fixed retainers as of January 1, 2007. The IHCP expects most patients who meet the criteria for orthodontic services to require comprehensive orthodontic treatment, which providers must bill using procedure codes D8070, D8080, or D8090, as listed in the Current Dental Terminology Users Manual. The IHCP considers appliances and retainers as included in the fee for the comprehensive treatment, and providers cannot separately bill for them when rendering comprehensive treatment. Because the comprehensive treatment codes have a manual-pricing indicator, the IHCP calculates reimbursement based on 90 percent of the billed amount. The IHCP advises practitioners to carefully consider the appropriate amount to bill for the service and advises them to bill their usual and customary charge for the service rendered. The IHCP expects patients to continue treatment with the same practitioner for the period of treatment time that is prior authorized. In the unlikely event that the patient must discontinue treatment with one practitioner and begin treatment with another practitioner, the practitioner continuing the treatment must submit a new PA request. The first practitioner must refund part of the reimbursement to the IHCP. Library Reference Number: PRPR10004 Revision Date: August 26, 2010 Version: 10.0 8-387 Chapter 8 Section 5: Dental Claim Form Billing Instructions Indiana Health Coverage Programs Provider Manual Generally, one-third of the reimbursement is for the evaluation and treatment plan, and two-thirds of the reimbursement is for the actual treatment. Based upon the time remaining in the treatment rendered by a new practitioner, the first practitioner must prorate the amount to be refunded to the program. Prophylaxis 405 IAC 5-14-6 states that prophylaxis for noninstitutionalized members from 12 months of age up to their 21st birthday is limited to one unit every six months, or two units per rolling calendar year. Refer to Chapter 2 of this manual for a description of a rolling calendar year. However, federal law requires providers to supply all medically necessary services for children under 21 years old, even if the service is not covered under the State plan. The IHCP covers prophylaxis for children younger than 12 months old when the service is medically necessary. The IHCP limits prophylaxis for adult members ages 13 or older to one unit every six months for institutionalized members, and one unit every 12 months for noninstitutionalized members 21 years old and older. If the provider supplies an adult prophylaxis, the provider can bill code D1110 once every six months for member ages 13 years old up to 21 years old, and every 12 months after the member turns 21 years old. Providers use code D1120 to bill for child prophylaxis up to age 13, and providers can bill for this once every six months. Note: For residents of a nursing home or a group home, the IHCP will pay for prophylaxis only once every six months. Oral exams and routine cleanings for residents of state-operated group homes are included in the per diem when performed at the group home. When the member is discharged from a state-operated group home, this dental benefit is one every 12 months. Effective January 1, 2008, providers billing procedure codes D1120 – prophylaxis – child and D1203 – total application of fluoride excluding prophylaxis – child for the same member, on the same date of service will be reimbursed a bundled rate. Providers billing procedure codes D1110 – prophylaxis – adult and D1204 – total application of fluoride excluding prophylaxis – adult for the same member, on the same date of service will be reimbursed a bundled rate. Two audits – 6247 and 6248 – will be applied to the claim when the services are bundled. According to Indiana Administrative Code (IAC) 405 IAC 5-14-4, reimbursement is available for one topical application of fluoride only for patients who are 12 months of age or older, but who are younger than 21 years of age. Providers must bill D1203 for this service with D1120 when fluoride and prophylaxis are provided on the same date of service for members 1 to 12 years of age. Providers must bill D1204 for this service with D1110 for members 13–20 years of age. Topical fluoride is noncovered for
© Copyright 2026