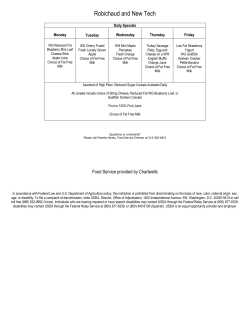
AfiLab The Tool for Ketosis – November 14, 2012
AfiLab The Tool for Ketosis OABP Meeting – November 14, 2012 Jeff Durkin, DVM Application Specialist afimilk USA [email protected] 360 610 1554 Ketosis and Negative Energy Balance • Very common in high producing herds • High losses • Sub clinical ketosis (SCK) >>> Clinical ketosis (CK) Ketosis and Production • Ketosis, leads to a gradual loss of appetite • Lowers milk production Peak, Persistency and Negative Energy Balance (NEB) 1st Lactations Cows* (8882 cows in 86 herds) peak persistency 90.0 84.3 84.8 89 70.0 60.0 50.0 88.5 88 89.2 87.5 87.6 40.0 30.0 87 86.5 Others NEB 1 % persistency = 304.0 lbs in 305 days * Oded Nir, 2010 Persistency (%) Peak (lbs/day) 80.0 89.5 Sub-Clinical Ketosis (SCK) - Losses • 100 herds average of 840 cows (range 265-2770) • 2785 cows tested • Cows with Sub-clinical ketosis: o Reduction of 14%-18% of conception rate o Less 453 kg/lactation (305 days) o Increase culling rate Nydam, 2011 Sub-Clinical Ketosis - Treatment • 4 herds - 1717 cow tested o Sub clinical ketosis definition BHBA=1.2-2 mmole/L o 43% of the cows with SCK (range 26.4-55.7%) o Propylene Glycol treatment – shorten time for recovery, decrease clinical ketosis and DA events, improve milk production and fertility Nydam, 2011 Negative Energy Balance by Days in Milk (DIM) % with fat/protein >1.4 Cows with NEB in milk tests 1st lact. 2nd lact. ≥3rd lact. 35.0% 30.0% 25.0% 20.0% 15.0% 10.0% 5.0% 0.0% 5 - 15 16 - 30 DIM Adapted from: Oded Nir 31 - 45 Clinical Ketosis Vs. Sub-Clinical Ketosis 2603 lactations of multiparous cows in 7 herds (1982-1984) From: Oded Nir Questions That Every Herdsman Must Ask • How do I find ketosis? • When do I check cows for ketosis? • What is the ketosis rate in my herd? The AfiLab Way…. • Fat:Protein ratio • Early detection • Continuous monitoring - every day all the day Milk fat Milk protein Fat:Protein Ratio • Correlation between metabolic diseases and milk components • Ketosis (NEB) – Fat/Protein Ratio (FPR)> 1.351.50 (Heuer et. al., 1999) Diagnosing Ketosis using AfiLab data • A field trial (395 cows sample) • The “gold standard”: Serum BHBA >1.4 mmol/l • Rate of ketosis 21.0% • Models: Model Fat/protein ratio Sensitivity Specificity Daily High 48.5% 80.7% Milking Low 80.9% 51.7% Daily List of “Ketotic” Cows (5 to 45 DIM) Cows high probability (80. 7%) of being “ketotic” Cows moderate probability (51.7%) of being “ketotic” Based on a study field preformed by Afimilk Applied Research Team. Shkulnik et al, 2009 Diurnal patterns of plasma BHBA (Beta-hydroxybutyrice acid) From: Meier et al., 2010 AfiLab – Negative Energy Balance Undetected Cows 300 X 0.3 Cows with NEB after calving Cows 90 X NEB Cow 0.5 X = 220 45 Undetected Cows = Lost Liters 1.6% Persistency Lost Undetected Cows Liters 90 NEB Cows Cows with NEB that will not be treated for Ketosis 45 9,900 = X $0.56 Liters ~ Per liter in Israel Profit of $5,500 per Year 14 9,900 $5,500 Per Year AfiLab – Early Treatment for NEB Cows 45 X Ketosis Cows 4,500 X Liters 100 Liter loss $0.56 Per liter in Israel = 4,500 Liters ~ $2,500 Per Year Profit of $2,500 per Year 15 AfiLab – Open Days Improvement 45 Untreated Cows 945 Days X X 21 = 945 Additional open Days days per cow $4 ~ $3,780 Per Day Per Year Profit of $3,780 per Year 16 AfiLab - Negative Energy Balance Profit 300 milking cow herd 17 Undetected Cow $5,500 Early Ketosis Treatment $2,500 Open Days $3,780 Per Year Profit $11,780 Afilab The Tool for Ketosis • Ketosis – high impact on dairy cows production and fertility • Fat:Protein ratio indication for ketosis • AFiLab – continuous monitoring • Expected benefit - 40$/cow/year What is wrong with cow 919? Milk Cow 919 have high fat:protein ration Milk Fat % So cow 919 is OK the AfiLab is wrong… A NEB in an Italian Herd (based on a Herd Health Report for the period 11/10-10/11) • 220 Holstein cows • The extended 305 days milk yield is 10,981 kg • All cows are checked routinely for ketosis 5 to 12 days postpartum % pregnancy to 1st AI with NEB 30.0 21.1 % open >150 DIM without NEB 25.7 38.6 16.7 16.0 0.0 First Second lactation with NEB without NEB 53.6 41.3 41.6 38.9 ≥Third 0.0 First Second lactation A cow with a fat/protein ratio >1.4 in the milk tests carried out 5 to 35 DIM was defined to be in a state of a NEB Next 3 slides based on: Oded Nir ≥Third A NEB in an Italian Herd (based on a Herd Health Report for the period 11/10-10/11) Comparing the milk test results to the cows diagnosed with ketosis Number of cows with fat/protein ratio >1.4 in the first milk test with no diagnosis of ketosis high fat/protein & ketosis low fat/protein, no ketosis 21 124 low fat/protein & ketosis 24 high fat/protein, no ketosis 45 • Ketosis rate – 42% (90/214) • 45 cows detected out of 90 cases (50%) Total annual financial loss is estimated at US$ 11,685 US$ 61.4/cow in the herd • Why so many cows are missed? • The answer lies in the profile of the NEB in this herd: a late ketosis! Cows in negative energy balance by lactation first second third or more % with fat/protein >1.4 60.0% 40.0% 20.0% 0.0% 15 - 5 30 - 16 Days in Milk 45 - 31 • What can he do more? o Improve the feeding in the transition period? He tried! o Use feed additives? He tried! o Check all cows for ketosis everyday? Not practical?!! Afilab Now let’s talk about feeding …. Thank you AfiLab – Real Time Milk Analyzer • Daily milk component measurement device Fat Protein Lactose • Quality Control Alerts On line blood detection, alerting and stop milking (Panel lock) On Going Development SCC non labeled (clean) detection of four levels: I. Less than 200K II. 200-400K III. 400-800K IV. More than 800 Technological Discipline Optical characteristics of light scattering off matter Multivariate analysis of absorbance Spectrum of milk in near infra-red AfiLab Concept Automated coupling of the “lab” to each stall in real time • Free flow • Continuously measures milk components during milking • Provides daily milk analysis for animal health and performance • Easy maintenance • Part of the regular cleaning system in the milking parlor • Clean Measurement – No use of reagents needed • Affordable for every milking point Multiple Sampling VS. Single Periodic Sampling Real Life %Fat %6 XiRefL Afilab XiA Estimation… XP Periodic lab samplings Periodic lab samplings 5% %5 30 32 Days Day-to-day Variation for Individual Cows • During a week’s time, is milk fat % for a given cow better determined using 14 measures (each milking) by AfiLab or 2 consecutive measures (1 day) by an Infra-red lab? o 30 Holstein Cows averaging 40.7 kg/d of milk o Milk sampled for 14 consecutive milkings (7 days) o Milk composition analyzed by AFI-lab DHIA lab using Bentley NIR equipment (FL) o Milk sample collection began the day after recalibration of AFI University of Florida (Staples et al., 2011) Daily Variation in Milk Fat % Across 7 Days of Sampling (DHIA Lab) for Cow 15891 3.80% 7-day Mean of 3.11% 2.75% 2.51% From: Staples et al., 2011 Day-to-day Variation for Individual Cows Results: Using 2x milking data, 39.7% (73/184) of daily measures of milk fat% by DHIA were more than 0.2 percentage units from the weekly average (i.e. 3 of 7 days) Conclusion: When AfiLab is accurate, AfiLab measures averaged across 14 milkings can be a more reliable tool for measure of weekly milk fat % than NIR when milk samples are collected at two consecutive milkings University of Florida (Staples et al., 2011) Milk Quality Mastitis Alert - Lactose • Sub-clinical mastitis detection and improve clinical mastitis detection 15-20% of milking cows are infected Early treatment improve milk production • Concept: Lactose sharply drops during clinical events Some bacteria (sub-clinical) decrease lactose level Clinical mastitis Milk Quality – Blood Milk Quality – Milk Separation High Prot % Low fat % Blood, SCC Good Quality Milk
© Copyright 2026