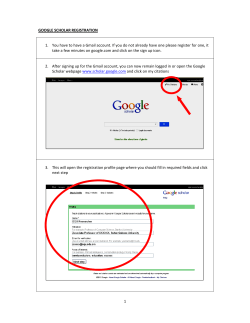
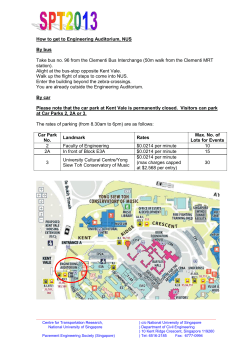
2014 IACSIT Singapore Conferences
2014 IACSIT Singapore Conferences 2014 IACSIT Singapore Conferences 2014 the 4th International Conference on Power and Energy Systems (ICPES 2014) International Conference on Mechanical Manufacturing and Control (ICMMC 2014) November 21-23, 2014 Singapore Quality Hotel A201 Balestier Road Singapore 329926 | Tel: (65)6355 9988 | Fax: (65) 6255 0998 Website: http://www.qualityhotel.com.sg/ Sponsored by 2 2014 IACSIT Singapore Conferences Welcome to IACSIT Conferences in Singapore during November 21-23, 2014 Dear Distinguished Delegates, Welcome to IACSIT Singapore Conferences which is co-sponsored by American Society for research. We’re confident that over the 3 days you’ll get theoretical grounding, practical knowledge, and personal contacts that will help you build long-term, profitable and sustainable communication among researchers and practitioners working in a wide variety of scientific areas with a common interest in Power and Energy Systems, and Mechanical Manufacturing and Control. After more than half a year’s preparation, we finally will have those conferences to be held in Singapore during November 21-23, 2014. For the conferences of ICPES2014 and ICMMC2014, we had received over 168 submissions, and 77 excellent papers were accepted and published finally. Congratulations for those papers. On behalf of IACSIT organization, I would like to thank all the authors as well as the Program Committee members and reviewers. Their high competence, their enthusiasm, their time and expertise knowledge, enabled us to prepare the high-quality final program and helped to make the conference become a successful event. Once again, thanks for coming to IACSIT conferences, we are dedicated to higher and better international conference experiences. We will sincerely listen to any suggestion and comment; we are looking forward to meeting you the next time. Yours Sincerely, Ms. Sophie Tsang Director of Conference Department II, IACSIT 3 2014 IACSIT Singapore Conferences ANNOUNCEMENT *ICPES 2014 conference papers were selected and published in Applied Mechanics and Materials Journal (ISSN: 1660-9336). *ICMMC 2014 conference papers were selected and published in Applied Mechanics and Materials Journal (ISSN: 1660-9336). *The best presentation will be selected from each session, announced and awarded a certificate at the end of each session. IACSIT Publication committee 4 2014 IACSIT Singapore Conferences Instructions for Oral Workshop Devices Provided by the Conference Organizer: Laptops (with MS-Office & Adobe Reader) Projectors & Screen Laser Sticks Materials Provided by the Presenters: PowerPoint or PDF files Duration of each Presentation (Tentatively): Regular Oral Session: about 15 Minutes Presentation including Q&A. Keynote Speech: 45 Minutes Presentation including Q&A. Author should copy his presentation file to conference laptop 10 minutes before his session. 5 2014 IACSIT Singapore Conferences Conference Schedule Day 1, Friday, November 21, 2014 – Onsite Registration Only Registration: Level 3 Foyer Arrival, Registration and Conference materials collection 09:30a.m.-12:00p.m. 14:00p.m.-17:00p.m **Certificate for Participant can be collected at the registration counter** Day 2, Saturday, November 22, 2014 – Presentation Day Simple Version: Quality Ballroom (3rd Floor) 08:30a.m.-12:05p.m. 08:30am-08:35am Opening Remarks Keynote Speech I: Prof. Michael Pecht, 08:35am-09:20am Center for Advanced Life Cycle Engineering (CALCE) A. James Clark School of Engineering, USA Keynote Speech II: Morning Prof. Nopbhorn Leeprechanon, IEEE-PES Thailand Chapter and Unit Head of Power System Planning and Energy Policy Research, Thammasat University, Thailand 09:20am-10:05am 10:05am-10:10am Plenary Photo 10:10am-10:20am Coffee Break 10:20am-12:05pm Quality Ballroom (3rd Floor) Emerald Room (2nd Floor) Session 1 Session 2 6 2014 IACSIT Singapore Conferences Lunch 12:00pm-13:00pm Afternoon --- Author’s Oral Presentation 13:00pm-19:00pm Quality Ballroom (3rd Floor) Emerald Room (2nd Floor) Session 3 Session 4 13:00pm-16:00pm Coffee break 16:00pm-16:10pm Session 5 16:10pm-19:00pm Dinner Session 6 19:00pm-20:00pm Full Schedule: Quality Ballroom (3rd Floor) Plenary Speech+ Plenary Photo 08:30a.m.-10:10a.m. 08:30am-08:35am Opening Remarks Keynote Speech I: Prof. Michael Pecht, 08:35am-09:20am Center for Advanced Life Cycle Engineering (CALCE) A. James Clark School of Engineering, USA Morning Keynote Speech II: Prof. Nopbhorn Leeprechanon, 09:20am-10:05am IEEE-PES Thailand Chapter and Unit Head of Power System Planning and Energy Policy Research, Thammasat University, Thailand 10:05am-10:10am Plenary Photo 7 2014 IACSIT Singapore Conferences 10:10am-10:20am Coffee Break Morning Session Authors’ Oral Presentation 10:20am-12:05pm Session 1(Quality Ballroom) 3rd Floor Session Chair: Dr. Romeo Marian, University of South Australia, Australia E15 Analysis of Smoothing Effect of Residential Electricity Demand Using Measured Data Toshihide Sato, Tomoko Iwata and Ryuji Matsuhashi The university of Tokyo, Japan Abstract—Community Energy Management System (CEMS) is remarkable system and has the attention currently. It is important that we estimate total residential electricity demand when we build CEMS. However, this estimate is difficult because the residential electricity consumption changes sharply. This change can become smaller by smoothing effect when some households are considered together. In this paper, we analyze and compare the smoothing effect of statics level with one of the level calculated using measured data. As a result, the smoothing effect of residential electricity demand is appeared to some degree. In addition, this effect is different due to season and time. we can estimate the 99% confidence demand intervals of households’ electricity demand in summer at 64% ~ 136% and that in winter at 74% ~ 126% at most widely when CEMS community has 65 households. E38 Index Terms—smoothing effect, residential sector, electricity demand, CEMS, standard error Economic Value of Grid-Scale Storage in Wholesale Electricity Markets Kyle Anderson and Abbas El Gamal Stanford University, USA Abstract—Grid-scale energy storage promises many benefits, such as shifting peak load and providing regulation service. Previous studies focused on either computing the intrinsic economic value of grid-scale storage under an ideal market model or computing the cash flow of storage providing peak load shifting. This paper presents a methodology for estimating the cash flow of an independently owned and operated storage unit pursuing a dual strategy of peak load shifting and regulation service. We estimate the present value (PV) of storage cash flow by solving a stochastic linear program that determines the optimal charging schedule based on future energy and regulation spot prices. We apply this methodology to two representative storage technologies using NEISO market data and show they currently offer modest returns 8 2014 IACSIT Singapore Conferences with the potential for substantially better returns as renewable penetration increases and storage cost decreases. E41 Index Terms—Energy Markets, Energy Storage, Regulation service, Ancillary service Optimal Placement of TCSC in Power Market Tran Phuong Nam, Dinh Thanh Viet, La van Ut and Le Dinh Hieu Hue Industrial College, Vietnam Abstract—Nowadays, the operation of power systems in the power market model has been researched and applied by many countries. At the same time, power systems operation becomes more important as the load demand increases all over the world. This change ensure the power system security as well as ensure the power market economy. Thyristor controlled series compensator (TCSC) devices can play very important role in power system congestion management. Due to high capital investment, it is necessary to locate these devices optimally in the power system. The scope of this paper is to decide optimal location of TCSC by congestion improvement and social welfare index. The effectiveness of proposed method is demonstrated on IEEE-39 bus test power system. E43 Index Terms—Power market; power system; TCSC; congestion; social welfare Optimal Location and Size of the DG’s in Distribution System for Time Varying Loads to Minimise the System Losses R. Shivarudraswamy Manipal Institute of Technology , Manipal University, India Abstract—This paper presents a methodology for optimal placement and sizing of distributed generators (DG) in distribution systems, in order to minimize the total system losses and to guarantee acceptable reliability level and voltage profile. The optimization process is solved by the genetic algorithms (GA) techniques for a 14 bus distribution systems with time varying load. E46 Index Terms—Distributed Generation, Distribution losses, Genetic algorithm, optimal location, Optimal size Effects of Dfig Wind Power Generation on Vietnam Power System Van-Tan Tran, Tsai-Hsiang Chen and Thanh-Luu Cao National Taiwan University of Science and Technology, Taiwan Abstract—This study shows steady state and dynamic analyses of doubly-fed induction generators (DFIGs) by mean of integrated comprehensive powerful software, PSS/E. The DFIG wind turbine model built in PSS/E version 32 was appliedto the simulation of a bulk power system in Soc Trang, Vietnam. The bulk power system was reducedto an equivalent power system before simulation was performed. The main purpose of this research is to observe, analyze and evaluate dynamic responses of the DFIG wind turbineto different disturbances such as a short circuit, loss of a generator and so on. The simulation results show that using uninterrupted operation and fast control of a DFIG converter, the DFIG wind turbines responded successfully to a symmetrical three-phase fault under the transient fault condition. Both voltage and frequency of the power system are critical important 9 2014 IACSIT Singapore Conferences factorsfor the assessment of influences of wind power on the intended power system transient behaviors and stability. Also controlling the pitch angle of DFIG wind turbines to obtain the expected power output is worthy of attention. E48 Index Terms—DFIG, wind turbine, dynamic simulation, transient stability Performance Modeling and Parametric Analysis of a Double Glazed Solar Oven Abdul Waheed Badar, Syed Ali Zaryab, Zain Ul Abedin and Muhammad Yasin Khan University of Sciences and Technology, Sector H-12, Islamabad, Pakistan Abstract—This paper investigates the thermal performance of a unique box type solar oven whose five sides are exposed to ambient and provisions are also provided to install the reflectors to enhance the intensity of incident solar radiation on the oven. Experiments were performed where temperatures attained inside the box cavity are recorded on different days and times of the day corresponding to various intensities of available solar radiation. A steady sate heat transfer numerical model of the solar oven without reflectors is also developed based on six individual thermal resistance networks which account for the heat losses through each flat-side of the oven box and a good agreement with the experimental data is achieved. A parametric study based on numerical calculations and experiments is then carried out to study the effects of various parameters on oven’s thermal performance, e.g. number of glazings, distance between glazings and box, type of absorber coating, etc. Higher box temperature is attained using double glazing than single glazing. As compared to black paint, selective surface coating results in significantly higher oven temperatures (up to 40 o C). Plate spacing of 20-30 mm is found to be optimum distance between oven box and glass covers. E53 Index Terms—Solar oven; oven box temperature; reflectors; overall heat transfer coefficient Application of Grid-level Battery Energy Storage System to Wind Power Fluctuation Smoothing Tsai-Hsiang Chen, Rih-Neng Liao, Chun-Yen Yang, and Yen-Hsun Chiang National Taiwan University of Science and Technology, Taiwan Abstract—Fluctuations in the output power of large-scale wind farms can have a considerable influence on power quality and stability, leading to the risk of grid frequency deviation, particularlyin isolated power system. Fluctuations in wind power can be smoothing through the inclusion of wind-storage system. In this system,wind turbines are connected with battery energy storage system (BESS).This paper proposes a novel operation control strategy, referred to as prediction-based control (PBC). The proposed strategy (which utilizes predicted changes in wind power generation) can effectively smooth the fluctuation in the output power of wind farms (WFs), based on the concept of confidence intervals. Furthermore, the rolling-wave planning and dynamic control of the BESS enhances its capacity. Finally, the proposed control strategy provides an avenue by which to examine the characteristics of large-scale WFs and BESS for better planning, design, and operations. Index Terms—grid-level battery energy storage system, wind farm, real-time 10 2014 IACSIT Singapore Conferences E57 control, prediction-based control, wind turbines, wind power fluctuation Comparative study of Parameter Estimation Methods for Solar Irradiation Forecasting Yashwant Kashyap, Ankit Bansal and Anil K Saoand Satyanarayan Patel India Institute of Technology Mandi, India Abstract—In this paper, autoregressive moving average (ARMA) has modeling for solar irradiation forecast by combining two types of parameter estimation methods, Forgetting Factor (FF) and Kalman Filter (KF). For this purpose, the geographical location of length, width and average height than 76.75 e, 31.75 N and 1130.3 meters were used. Parameter with regard to the mean absolute error (MAE), root mean square error (RMSE), mean square error (MSE) and R2 estimator is compared. The result shows that the KF consists of high convergence rate to solve complex problems. Index Terms—Solar irradiation, Autoregressive Moving Average, Forgetting Factor, Kalman Filter Morning Session Authors’ Oral Presentation 10:20am-12:05pm Session 2(Emerald Room) 2nd Floor Session Chair: E12 Voltage Standardization of DC Distribution System for DC Residential Buildings Rajeev Kumar Chauhan, Bharat Singh Rajpurohit and Robert Hebner Indian Institute of Technology Mandi, India Abstract—The renewable energy sources (RES) such as photovoltaic (PV) are basically DC power sources. In the present scenario, the integration of RES to power distribution infrastructure necessitates the DC-AC converter. Moreover the DC loads in the buildings is ever increasing with the use of CFL, LED, refrigerator, TV, fan, air conditioner, laptop, and other electronics in workplaces and homes. This forced to introduce the internal or external AC-DC converter to tie the DC load to AC distribution infrastructure of existing power system. This is further adding losses and complexity. This AC-DC converter stage can be reduces up to a certain level by DC distribution system (DCDS). Secondly the multi voltage rating of RES and DC load insists to introduce DC-DC converter in DCDS infrastructure. This will further add losses and complexity. In this paper a standard voltage level DCDS is proposed to minimize the system losses, complexity. To verify the simulated results in terms of building load and converter losses, a DCDS equipped with different energy sources like solar panel (PV), public utility (PU) and battery bank (BB) is compared with ACDS. 11 2014 IACSIT Singapore Conferences E16 Index Terms—DC distribution system, DC appliances, voltage level, conversion losses, DC Microgrid. Transformer Differential Protection Using Process Bus According to IEC 61850-9-2 and Non-Conventional Instrument Transformers Gilberto Igarashi and Josemir Santos Escola Politécnica – Universidade de São Paulo, Brazil Abstract—Our aim is to show some impacts on the differential protection of power transformers when using Non-Conventional Instrument Transformers associated with the IEC 61850-9-2 process bus. Described herein are a model for simulating the samples in the process bus, a proposed algorithm for differential protection of power transformers adapted from conventional differential relays so that it works according to the IEC 61850-9-2 standard, and a response analysis of the protection algorithm with the loss of the time synchronization signal in the process bus. Suggestions on parameters to be followed for safer operation of the process bus in these circumstances are also offered. E40 Index Terms—IEC 61850-9-2, Non-Conventional Instrument Transformers, differential protection of power transformers Feasibility Analysis for the Application of Grid Connected Solar Photovoltaic Technologies in Food Manufacturing Plant Joy Dassgupta, Zeinab Haji Abolhasani, Romeo Marian University of South Australia Abstract—In Singapore, food manufacturing plants currently receive electricity from the national grid supply where the power generation is mainly based on fossil fuels. Singapore lacks land mass, and thus there are limited possible sources of renewable energy for the generation of electricity. Solar energy therefore, might be a buoyant source for the fulfilment of the country's energy requirements in the manufacturing sector. Moreover, solar energy technologies are environmentally friendly. This paper describes a feasibility study for the application of grid connected solar photovoltaic technologies in a food manufacturing plant. The study may help to discover opportunities for using solar energy to fulfil the electrical energy needs in food manufacturing facilities while contributing to an emission free environment. E59 Index Terms—Solar Photovoltaic (SPV) technology, Solar irradiation, Solar energy, Food manufacturing facilities Short-Term Wind Speed Forecasting with A Cascade Hybrid Method Sivanagaraja Tatinati and Kalyana C. Veluvolu Kyungpook National University, South Korea Abstract—In this paper, a hybrid method based on empirical mode decomposition (EMD), Autoregressive model (AR) and least-squares support vector machine (LS-SVM) is proposed for short term forecasting of wind speed (hourly forecasting). EMD has been employed to decompose the non-stationary wind speed time series into independent intrinsic functions (IMFs). Each IMF is then forecasted with a cascaded structure of AR model and LS-SVM. In the proposed cascade structure, AR model forecasts the IMFs and LS-SVM is employed to model the exogenous variables of AR model. The aggregate of the forecasted IMFs with the cascade 12 2014 IACSIT Singapore Conferences structure at an instant is the final forecasting of the wind speed at that instant. Forecasting results obtained with the proposed hybrid method show better performance compared to the existing hybrid methods. E60 Index Terms—Wind speed, Short term forecasting, EMD, AR, LS-SVM Day-ahead Electricity Price Forecasting Using Relevance Vector Machine Yubo Wang, K. C. Veluvolu Kyungpook National University, South Korea Abstract—The number of countries that have been switching from central regulated power distribution system to a competitive market scheme has been growing. All participants of that group require forecasted market price to gain an upper-hand in the biding and negotiation process. Due to the importance of day-ahead electricity market, it attracts a lot of research in developing price forecast algorithms. In this work, a RVM based day-ahead price forecast algorithm is proposed and tested on day-ahead price of the locational marginal pricing (LMP) obtained from the Pennsylvania-New Jersey-Maryland (PJM) market. The feature vector for RVM is constructed by using delay embedding theorem. The optimal embedding dimension and prediction horizon is identified. Simulation results show that RVM based algorithm is capable of capturing the daily and weekly pattern of day-ahead LMP. MC059 Index Terms—day-ahead electricity price, forecasting, relevance vector machine Direct Cladding from Molten Metals of Aluminum and Magnesium Alloys by using a Tandem Horizontal Twin Roll Caster Hideto HARADA, Shin-ichi NISHIDA, Mayumi SUZUKI, Hisaki WATARI, and Toshio HAGA Gunma University, Japan Abstract—This paper describes a direct cladding of magnesium and aluminum alloy by using a tandem horizontal twin roll caster which have three pairs of upper and lower rolls. Manufacturing conditions that is appropriate for fabricating the Al/Mg and A/Mg/Al cladded material have been investigated. Surface condition of the cladded cast strip was exmined. An electron probe micro analyzer was used to observe an interface between aluminum alloy and magnesium alloy. Tchikness of the mixed layer of aluminum and magnesium alloy was about fifiteen micrometers and the mechanism of the connection of both material was clarified. Microscopic observation as well as back scattered electron analysis to investigate into cladded mechanisms of the aluminum alloylayer and magnesium alloy. Average hardness was conducted by Vickers hardness test at aluminum layer, and the diffused layer between magnesium and aluminum alloys. It has been found that cladding Al/Mg alloy and A/Mg/Al is possible by the use of tandem twin roll caster. It also have been confirmed that Al3Mg2 and Al12Mg17 pahse precipitated at the interface of the alumium and the magnesium alloy during direct cladding from molten metals. MC201 Index Terms—Clad material, aluminum alloy, magnesium alloy, roll casting, rapid solidification Multiple Time Analysis of Weakly Coupled Non-linear Gyroscopic Systems Shailendra Kumar Mittal and Mittal Asha D. S. Kumar GANGAMAI COLLEGE OF ENGG., NAGAON, DHULE (M.S.) INDIA 13 2014 IACSIT Singapore Conferences Abstract—In this paper, transient and steady state behavior of Weakly Coupled Non-Linear Gyroscopic Systems response, amplitude and frequency of oscillation as well as stability properties have been studied in detail. The method adopted for analysis is based on multiple time perturbation approach. The present system is a coupled two degree of freedom system with dissipative terms as well as terms corresponding to weakly exchanges of energy due to nonlinear terms. E54 Index Terms—Synchronization, multiple time scaling, nonlinear coupled systems. Enhancement of Power Transfer Capability of Interconnected Power System using U.P.F.C Sandeep Sharma and Shelly Vadhera National Institute of Technology, Kurukshetra, Haryana, India Abstract—Unified power flow controller (UPFC) is the most effective FACTS device. UPFC is able to control the real and reactive power, voltage magnitude and phase angle. Along with these UPFC is also capable to maximize the power transfer capacity between the two interconnected power systems. This paper proposes use of phasor model of UPFC to maximize the power transfer capacity of interconnected power systems. The modeling is done in Matlab/Simulink using test system consisting of 20 bus system incorporating UPFC. The simulation results clearly shows that the model using UPFC has maximum value of power transfer as compared to the model without UPFC. MC015 Poster Presentation Index Terms—UPFC; Matlab/Simulink; Active power, Reactive power Nover Strategy for BLDC Motor Rotor Position Detection Cao Lingzhi and Yang Shenghao Zhengzhou University of Light Industry, China Abstract—The detection of rotor position plays an important role in the motor speed-adjustment system. By analyzing the back-EMF method and its improved methods, we know the amplitude of back-EMF is too small to be detected when the motor run at low speed. A new detection method of rotor position has been proposed in this paper. It detects the zero crossing point of line terminal voltage difference to acquire the rotor position signal after a 90 degrees mechanical angle delay. The amplitude of line terminal voltage difference is large in wide speed range, so the rotor position signal can be accurately acquired in most situations. Simulation results proved that the new method can obtain the rotor position signal exactly in both high and low speed. It meets the wide speed range of motor. Index Terms—Brushless dc motor, position sensorless, line terminal voltage difference Lunch 12:00pm-13:00pm 14 2014 IACSIT Singapore Conferences Afternoon Session Authors’ Oral Presentation 13:00pm-16:00pm Session 3(Quality Ballroom) 3rd Floor Session Chair: Prof. Shailendra Kumar Mittal, GANGAMAI COLLEGE OF ENGG., NAGAON, DHULE (M.S.) INDIA MC001 A Novel Tuning Algorithm for Fractional Order IMC Controllers for Time Delay Processes Cristina I. Muresan, Eva H. Dulf, and Roxana Both Technical University of Cluj-Napoca, Romania Abstract—This paper presents a novel tuning algorithm for fractional order IMC controllers for time delay processes. The tuning algorithm is based on computing the equivalent controller of the IMC structure and imposing frequency domain specifications for the resulting open loop system. A second order time delay process is used as a case study. An integer order IMC controller is designed, as well as a fractional order IMC controller. The simulation results show that the proposed fractional order IMC controller ensures an increased robustness to modeling uncertainties. MC016 Index Terms—fractional order controller, time delay processes, tuning algorithm, robustness Modal Analysis of Hummingbird Inspired MAV Flapping Wings David Kumar, Vemuri Shyam Kumar, Tigmanshu Goyal, P. M. Mohite and Sudhir Kamle Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur, India Abstract—Natural flyers are the best source of inspiration for making successful MAVs. Hummingbirds are known for their excellent flight characteristics such as long duration hovering, backward flying, high agility, etc. Giant hummingbird is chosen as the bio-inspiration for designing the wing. Wings are required to be light, strong, and fatigue resistant to be used for MAV applications. Carbon nanotubes (CNTs)/Polypropylene (PP) composite is chosen as the wing membrane material whereas carbon fiber (CF)/epoxy (E) composite is chosen for wing frame. Two types of wings are fabricated, one is CNTs/PP wing and another is CF/E frame with CNTs/PP membrane wing. Kinematics, structural dynamics, and aerodynamics are the main component of flapping flight studies. Modal analysis of fabricated wings is done using 3D visual image correlation (VIC-3D) and laser displacement sensor setup. In the end, the results of both type wings are compared with experimental results and a good correlation has been seen. The validation of results is done using Ansys. MC026 Index Terms—MAVs, Hummingbirds, CNTs, Polypropylene, Modal Analysis, Digital Image Correlation, Fast Fourier Transform Method Research of Rapid STL File Loading and Visualization 15 2014 IACSIT Singapore Conferences Kun Chen, Xiaodi Pan, and Jun Fang Wuhan University of Technology, China Abstract—STL file is the defacto industry standard in the field of rapid prototyping (RP) currently. The STL file loading and visualization effect greatly influences the subsequent processes of RP. Firstly, the feature of the STL file format is analyzed. On this basis, an algorithm for loading the STL file is proposed. The rapid loading and visualization of STL file in ASCII format is implemented in the VC++ 6.0 programing environment combined with the OpenGL graphics library. During the loading process, the redundant data in the STL file is eliminated by comparing and deleting the overlapped vertexes. As a result, the storage space is reduced and the processing efficiency is improved. Finally, experiments show the effect of rapid STL file loading and visualization. It provides a good basis for the subsequent processes of RP. MC033 Index Terms—STL file; rapid prototyping; VC++; OpenGL Web-based Conceptual Design Support System Dereje Engida Woldemichael and Fakhruldin Mohd Hashim Universiti Teknologi PETRONAS, Malaysia Abstract—Conceptual design is one of the most critical and important phase of design with least computer support. This paper presents an extension of a standalone conceptual design support tool developed previously by the authors on a web-based environment. The proposed framework is suitable for collaborative design which is performed by multiple participants, each potentially capable of proposing values for design issues and/or evaluating these choices. The framework uses design reuse philosophy which plays a major role in product development especially during the early concept generation phase supplementing the designer’s knowledge by providing stored knowledge outside the designer’s area of expertise. The reused design knowledge from existing product has an advantage of being tested for reliability in previous design and may inspire the designer to generate new concepts. Based on this philosophy, a web-based conceptual design support system (CDSS) has been developed and deployed on a local server which can be accessed on intranet network. The CDSS can be used either to generate new concepts from the design repository (database) or from the designer which can be added to the repository through knowledge acquisition module for future design. MC035 Index Terms—Conceptual design, design support system, collaborative design, web-based system. Optimal State Feedback Controller Design for Vibration Attenuation in a Class of Image Transfer Belt Jie Yu and Hiroshi Yamaura Tokyo Institute of Technology, Japan Abstract—An optimal state feedback controller based on H2 norm is proposed for attenuating the belt vibration caused by loading disturbance in a class of image transfer belt which is widely applied in multi-color printers. Based on the simplified mechanical model of the image transfer belt unit, the presented controller acts on the actuating torque generated by a direct-current motor and optimizes the defined variables related to the quality of the original image formation. Simulation results responding to a periodic loading disturbance ascertain its efficacy with comparisons of the conventional speed 16 2014 IACSIT Singapore Conferences control. It is certified that the image transfer belt unit is successfully maintained in a satisfying condition with effective vibration attenuation under the proposed control architecture. MC036 Index Terms—Electrophotography, intermediate transfer belt, state feedback control, optimization, H2 control, multi-color printer Flow Control using Air-jet to Improve the Aerodynamic Performance of a Multi-element Airfoil Hassan Akbar, Jiao Yuqin, and Abu Bakar Northwestern Polytechnical University, China Abstract—This paper describes the application of active flow control for the NLR7301 supercritical airfoil/flap configuration at Re = 2.51x106. A parametric analysis is conducted to investigate the effects of jet parameters (jet direction, jet location and momentum coefficient) on the aerodynamic performance of a multi-element airfoil. The results indicate that flow separation is delayed and efficiency of jet can be improved with specific momentum coefficient (the best lift-drag ratio at Cμ=0.16) and jet angle (16°) when the jet is located near the separation point of the airfoil. MC041 Index Terms—Active flow control, steady blowing, jet momentum coefficient, jet slot, aerodynamic performance A Study on Influence of System Parameters on Servo Pneumatic System and Multi-response Optimization using Taguchi – Grey Methodology Saravanakumar D, Mohan B and Muthuramalingam T Anna University, India Abstract—Servo pneumatics is a mechatronic approach that enables accurate position control of pneumatic drives with high speed. Simulation model of the servo pneumatic system with fuzzy PD controller has been created in Matlab-Simulink software using nonlinear mathematical model of the system. The influence of supply pressure and size of the cylinder on the positioning accuracy and speed has been studied. It is observed that the supply pressure is the most influencing factor in positioning accuracy and speed compared to the size parameters of the cylinders. Further a multi-response optimization of the system parameters minimize settling time, overshoot and ITAE (Integral of time-weighed absolute error) values has been carried out using Taguchi based Grey relational analysis methodology. The optimal system characteristics have been observed when supply pressure is 0.2 MPa, diameter of the cylinder is 0.05 m and length of the cylinder is 0.15 m. MC043 Index Terms—Servo-pneumatic system, Multi-response optimization, Taguchi method, Grey relational analysis, Simulation. Tire Force Control Strategy for Semi Active Magnetorheological Damper Suspension System using Quarter Heavy Vehicle Model Syabillah Sulaiman, Pakharuddin Mohd. Samin, Hishamuddin Jamaluddin, Roslan Abd. Rahman and Saiful Anuar Abu Bakar Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Malaysia Abstract—This paper proposed semi active controller scheme for magnetorheological (MR) damper of a heavy vehicle suspension known as Tire Force Control (TFC). A reported algorithm in the literature to reduce tire force is Groundhook (GRD). Thus, the 17 2014 IACSIT Singapore Conferences objective of this paper is to investigate the effectiveness of the proposed TFC algorithm compared to GRD. These algorithms are applied to a quarter heavy vehicle models, where the objective of the proposed controller is to reduce unsprung force (tire force). The simulation model was developed and simulated using MATLAB Simulink software. The use of semi active MR damper using TFC is analytically studied. Ride test was conducted at three different speeds and three bump heights, and the simulation results of TFC and GRD are compared and analysed. The results showed that the proposed controller is able to reduced tire force significantly compared to GRD control strategy. E19 Index Terms—Heavy vehicle, Simulink, MR Damper, Tire Force Control, Semi active suspension A Systematic Approach for Optimal Design of SVC Controller to Reduce the Disturbances in Electric Arc Furnace using Genetic Algorithm Darioosh Noorzadeh and Mohammadali Abbasian Islamic Azad University- Isfahan(Khorasgan) Branch, Iran Abstract—Static reactive power compensator (SVC) as one of FACTS devices in parallel network in order to keep the range of voltage used is electric arc furnaces in industries like :steel and foundry widely used. At this moment the amplitude fluctuations of grill too reactive and active power , cause power quality problems in the network and production facilities , and other steel consumer and also provides distribution system disturbances resource. SVC , as a fast reactive power control equipment , play on important role in improving the voltage profile and the transient dynamics of the system as well as the adjustment and resolution of problems and conflicts arising from the nature of the arc . the collection process can be time consuming and a TCR reactive power in a closed loop control system to maintain constant , the control system is done by controlling the firing angle of thyristor. E33 Index Terms—SVC, Generator Dynamic Response, Reactive Power Control A Hybrid System Approach to Static Var Compensator Modeling and Control Ky-Suong The Nguyen, Hong Zhu, Thanh-Trung Han and Yuping Zhang University of Electronic Science and Technology of China Abstract—This paper proposes a hybrid model of Static var compensator (SVC) capturing the continuous and discrete behaviors of SVC in term of hybrid system and an approach to design a controller of SVC to maintain voltage of power system in normal range based on maximal controlled invariant set. The proposed SVC's model is representable complex interactions between continuous dynamics and discrete events of SVC. The proposed controller is able to ensure the power system working in safe set despite the change of the grid parameters. E34 Index Terms—Hybrid system, Static var compensator, power system Enhancement of PV Penetration with Centralized Control Method in Cimei Island Distribution System Chia-Hung Lin, Chao-Shun Chen, Cheng-Ting Hsu, Wei-Lin Hsieh, Yih-Der Lee, Sheng-Chang Cheng, Yung-Ruei Chang and Chin-Ying Ho Institute of Nuclear Energy Research, Atomic Energy Council. Taiwan(R.O.C.) Abstract—This paper discusses the use of centralized control method in an Intelligent 18 2014 IACSIT Singapore Conferences Energy Management System (iEMS) to prevent voltage violation after load transfer between distribution feeders with high PV penetration level. The proposed method comprises three control modes with different control algorithms for regulating both reactive and active power output of PV inverters in a distribution system with multiple PV installations. Before the execution of load transfer, the total reactive power compensation required at the critical Point of Common Coupling (PCC) is solved by the reactance of distribution feeder line segment to prevent system voltage violation. With the proposed control algorithms, the iEMS dispatches total reactive power compensation among PV systems according to the reactance of line segment and issues the control command to each PV inverter for adjustment of PV power generation so that the ancillary service of voltage support can be provided by all PV systems in a fairer manner. A practical Cimei island distribution feeder pair is selected for computer simulation to verify the effectiveness of the proposed control method after load transfer between two feeders. E51 Index Terms—Intelligent Energy Management System, Photovoltaic, Renewable Energy Management system Robust Backstepping Controller for Grid-Side Converter of Doubly Fed Induction Generator Enabling Low Voltage Ride Through Hyoung-Woo Kim, Cheol-Jin An, Sung-Mun Park and Joon Young Choi Pusan National University, South Korea Abstract—A robust backstepping controller with nonlinear damping is designed for grid-side converter of doubly fed induction generator in wind energy conversion systems in order to enable low-voltage ride-through (LVRT). The designed controller achieves the exponential ultimate boundedness of the systems errors with an arbitrarily fast decay rate and an arbitrarily small bound in the presence of grid faults. A desirable feature that distinguishes the proposed controller from other existing controllers is that the proposed controller is able to perform both the normal control operation and LVRT with a single reference input, and it is constructed only by static feedback of measured states. As a result, the control input becomes smooth and easy to implement without requiring of differentiation or switching operations. The exponential boundedness and performance of the designed controller are demonstrated by simulation using SimPowerSystems in Matlab and compared with a proportional-integral LVRT controllers. E102 Index Terms—Doubly Fed Induction Generator, Low Voltage Ride Through, Robust Backstepping Control, Wind Energy Conversion Systems The Impact of Distributed Generators Placements on The Reliability of Typical Industrial Power Distribution System Ibrahim M. Al-Yami Saudi Aramco, Saudi Aramco, Saudi Arabia Abstract—Electrical Distribution systems that are radially configured with one utility power source are inherently exposed to higher rates of outages and interruptions, due to failures of system components, including: transformers, breakers and switching devices. In addition, fault conditions can also be caused by weather, animals or human error. Historically in Saudi Arabia, many industrial and residential distribution networks suffered from these problems. Large-size, growing demand and cost — with the time requirements for enhancement projects — results in distributed generation (DG) — as 19 2014 IACSIT Singapore Conferences online or backup —playing a key role in the residential, commercial and industrial sectors of the power system. In this paper, the value of DG — installed as an online power source for typical industrial distribution network in Saudi Arabia — is quantified by reliability indices that include System Average Interruption Duration Index (SAIDI), Customer Average Interruption Duration Index (CAIDI) and Energy Not Supplied (ENS). The study outcomes will provide power system engineers with the reliability benefits of DG penetration and an approach to assessing its installations, based on different factors such as size and location. E303 Index Terms—Distributed Generation, Reliability Indices; SAIDI, CAIDI, ENS Using Indoor Environmental Sensors for Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring Thamir Alshehri Queensland University of Technology, Australia Abstract—There are a number of factors driving concerns about the energy usage within buildings. These range from system wide issues, such as greenhouse gas reduction and reducing peak load (to control distribution network capital investment), through to individual consumer issues, such as reducing overall power consumption, deciding when to replace appliances and equipment and maximising the advantages of differential tariffs where these are available. Non-intrusive load monitoring (NILM) is an inexpensive way to examine live electricity consumption. However, previous work has shown that “signatures” of power profiles of appliances and equipment by themselves are not sufficient to reliably distinguish amongst many smaller loads. Environmental sensors have been added to installations to improve the accuracy of recognition. Previous studies have also shown that only a small proportion of users take a long-term interest in monitoring energy usage. This identifies the need to capture as much of the necessary user input to configure a NILM system in the first days of installation. This paper will describe the approach we have used to combine environmental sensor data with the standard NILM appliance signatures to improve the recognition of usage patterns within domestic premises. This includes early profiling of appliances with occupant involvement and mapping of appliances, equipment and environmental sensors within the residence. The manner in which the system is structured to provide eventual autonomous support to users will also be covered. Index Terms—Non-intrusive load monitoring (NILM), Energy efficiency, Building automation, Smart meter, Environmental sensor Afternoon Session Authors’ Oral Presentation 13:00pm-16:00pm Session 4(Emerald Room) 2nd Floor Session Chair: Prof. Jahng Hyon Park, Hanyang University, Korea MC022 Acetylene Sensing Characteristics of SnO2 Nanowires 20 2014 IACSIT Singapore Conferences Wang Bing Shenzhen University, China Abstract—SnO2 nanowires have been fabricated using thermal evaporation of the mixed powders of SnO2 and active carbon with Au catalysts. The morphology and structure of the prepared nanowires are determined on the basis of field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM), energy-dispersive X-ray spectrometer (EDS), x-ray diffraction (XRD) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The comb-shape interdigitating electrode made by MEMS technology is used to auxiliary investigating the gas sensing performance of the synthesized SnO2 nanowires. The SnO2 nanowires have sensing response to acetylene concentration of 1000 ppm under operated temperature of 300℃. The gas sensing mechanism is attributed to the gas adsorption and desorption processes occurring on the surface of the gas sensing material. MC024 Index Terms—Nanowires, gas sensor, SnO2 Robust Stability Analysis of DC-DC Buck Converter Circuit using Gerschgorin Theorem Yogesh V. Hote INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY ROORKEE, India Abstract—Robust control analysis using Gerschgorin theorem is an important tool for the research of linear uncertain system which is expressed in state space form. The main purpose of this paper is to show how this technique can be applied for robust stability analysis of dc-dc converters. In this paper, robust stability analysis of dc-dc Buck converter is presented using Y. T. Juang and C. S. Shao criterion. This criterion is based on Gerschgorin theorem and similarity transformation. MC029 Index Terms—DC-DC buck converter, Gerschgorin theorem, interval systems and robust stability margin. Study on the Influence of Workrest Positions on the Deflection of Crankshaft of an Orbital Grinding System Joon Jang, Woo Chun Choi, Chang Rae Cho, and Soon Joo Cho Korea University, South Korea Abstract—In this study, the influence of workrest positions on the deflection of a crankshaft is investigated, in order to enhance the machining precision in orbital grinding. Crankshafts of 3m, 5m and 8m are selected, and three types of states (no machining, journal machining and pin machining) are studied. The model is simplified with stiffnesses applied to the stock instead of real contact between workrest and stock. As the workrests are positioned to the machining region, the deflection of the machined stock is reduced. Pin machining shows more stable result than journal machining. MC045 Index Terms—Orbital, Crankshaft, Workrest, Optimization, Precision, Structural Analysis Evaluation of Surface Finish of Electrical Discharge Machined AISI 304 Stainless Steel With Various Pulse Generators Muthuramalingam Thangaraj, Mohan B and Saravanakumar D 21 2014 IACSIT Singapore Conferences SRM University, India Abstract—The performance improvement in Electrical Discharge Machining process is a tedious one in materials and manufacturing processes especially in making of complex die and moulds. Due to non linear nature of this process, conventional pulse generators such as RC pulse generator and transistor pulse train generator cannot produce uniform energy distribution. Since RC pulse generator can produce smaller crater volume, it can make better surface finish than transistor pulse train generator crater size is influenced by the discharge current produced during the machining process. Due to its stochastic behavior, the discharge current is varied for every spark. The modified iso current pulse generator can produce uniform energy distribution with smaller crater size. In this study, EDM drilling experiments have been conducted on AISI 304 stainless steel with the RC pulse generator, Transistor pulse generator and iso energy pulse generator in electrical erosion process. The effects of these pulse generators on surface characterization have been evaluated and analyzed. From the evaluation results, it has been detected that the iso energy pulse generator has produced better surface structure than conventional pulse generators. MC049 Index Terms—Energy, Duration, MRR, Discharge, Surface. Lubrication for Moving Mechanical Systems used in Spacecraft Sathyan Krishnan Prince Mohammad Bin Fahd University, Saudi Arabia Abstract—Spacecraft, irrespective of their mission’s purpose, contain a number of moving mechanical assemblies such as control moment gyros, momentum/ reaction wheels, gyroscopes, scanners, solar array drives, etc. Most problems encountered with these moving systems are related to tribology and, specifically, lubrication. Lubrication problems result from the loss of lubricant from the working zone by evaporation, surface migration, etc. Therefore, to ensure long-term uninterrupted performance of these systems, an efficient lubricant replenishment system is essential. This article describes various lubricating methods and lubrication systems used for the successful operation of some of these systems for the entire mission periods. MC058 Index Terms—Space Tribology, Momentum wheels, Centrifugal lubricators, Lubrication. Decision Support for Choosing an Appropriate Simulation Method for Dynamic Material Flow Analysis Markus Philipp Roessler, Joshua Riemer, Maximilian Mueller, and Joachim Metternich Institute of Production Management, Technology and Machine Tools (PTW), Technische Universitaet Darmstadt, Germany Abstract—When improving industrial process chains in terms of productivity it is becoming more and more important to not only consider the static, but also the dynamic behavior of value streams. The effects of intended changes on production systems often are unknown and could underlie vast variations due to the planned outcome. In order to validate such changes before implementation, the use of material flow simulation is widely discussed in research and industrial practice. 22 2014 IACSIT Singapore Conferences Such optimization projects usually require the collaboration of production system and simulation experts. Through the increased dissemination of various simulation tools on the market as well as multiple simulation methods available (discrete event, agent based and system dynamics) the actual selection of a suitable simulation setting is a challenging task. To support such optimization teams in the selection of an appropriate simulation method a decision making approach based on comparative criteria is shown and discussed in this article, concluding with a case study. MC060 Index Terms—Material flow simulation, production system, decision support, discrete event simulation, agent based simulation, system dynamics. Extension of the Upper Extremity with Shoulder Movements Nobuaki Nakazawa and Toshikazu Matsui Gunma University, Japan Abstract—In this paper, we investigated characteristics of human's upper limb extension with shoulder movements when the grasped object was moved from one point to other point. In cases where the goal position is put in a farther place than the length of the extended arm, not only the velocity profile of the hand by extension exercise but also that of the shoulder by anteflexion exercise are bell-shaped. These two exercises are simultaneously performed, but the hand velocity becomes a peak earlier in comparison with the shoulder one. Reproducing the measured human data, the exercises of a three-link arm with shoulder or body movements are simulated and the characteristics of a human-likeness fusion are examined by shifting the start time of the shoulder movement. As an evaluation result, it was found that the relation between the velocity peak positions of the hand and shoulder remarkably influences on the human-likeness. MC061 Index Terms—Lasers, Radiation, Blast wave, Plasma Characteristic Feature of Dynamic Motion for Servo Press Machine Takanori Yamazaki and Akihiro Watanabe Tokyo Denki University, Japan Abstract—Servo press machine can enable us to high precision, but the dynamic behavior does not seem to be considered well. In order to improve the accuracy in manufacturing, it has been discussed effectiveness of reducing the elastic deformation of die structure on forming by mechanically compensating die structure which includes a servo die cushion system. MC303 Index Terms—Metal processing, Servo press, Die cushion, Force compensation Numerical Simulation of Radiation Losses in a Decaying Laser Spark using LBL Method Ankit Sharma, Ankit Bansal, Anil Kishan and Ratan Joarder Indian Institute of Technology Mandi, India Abstract—An investigation has been done to numerically simulate the radiation losses which occur due to laser energy deposition in a domain of interest. Although the fluid dynamic effects due to laser energy deposition has been studied by a number of researchers independently but the effect of radiation has either been neglected or has not been highlighted effectively. When laser energy is deposited in a domain, very high temperatures are reached. At such high temperature, the 23 2014 IACSIT Singapore Conferences diatomic air species may become highly dissociated and emission from the resulting two mono atomic species N and O cannot be neglected and is the major source of radiation loss. Accurate prediction of radiation losses, hence, become necessary to minimize the errors in heat transfer calculations. An Open Source CFD software Open Foam has been used to study the above effects. P1 radiation model along with radiation Line by Line code has been used to calculate the radiation losses. Radiation losses obtained are 20 times higher as compared to the past reported data. E01 Index Terms—Lasers, Radiation, Blast wave, Plasma Power Quality Compensation using Superconducting Magnetic Energy Storage Manikandan Mani and MahabubBasha A Erode Sengunthar Engineering College / Anna University Chennai, India Abstract—Power systems have been experiencing dramatic changes in electric power generation, transmission, distribution, and end-user facilities. Continuing electric load growth and higher power transfer in a largely interconnected network lead to complex and less secure power system operation. Superconducting magnetic energy storage (SMES) technology has been progressed actively in recent years. SMES technology has the potential to bring real power storage characteristic to protect consumers from the grid voltage fluctuations. This paper analyses the operation of the SMES for power conditioning in the event of voltage sag, and its design is based on simple PI control method to compensate voltage sags. Modeling and simulation of the proposed DVR is implemented in MATLAB/SIMULINK platform. The simulation results have proved t hat t he proposed desi gn m et hod gi ves reliable pow erfu l S MES controller. E06 Index Terms—P ower qual i t y, DVR , S ME S , Vol t age S a g Classification of Voltage Sag using Multi Resolution Analysis and Support Vector Machine Noraliza Hamzah, Hanim Ismail and ZuhainaZakaria Universiti Teknologi MARA, Shah Alam, Malaysia Abstract—Voltage sag disturbance can cause catastrophe failures to both utility and end users of electrical power. The causes of this disturbance include power system fault condition and induction motor starting. This paper presents a research to classify the causes of voltage sag by employing Multi Resolution Analysis (MRA) and Support Vector Machines (SVM). Voltage sag data are obtained from the implementation of various fault conditions and induction motor starting using PSCAD modeling and data generation. Multi Resolution Analysis (MRA) is developed as a representation of a signal with various levels of decomposition for the features extraction. The two features used are the minimum and maximum of voltage and the energy distribution of ten decomposition levels of the MRA. Those features are used as the input for classification using Support Vector Machines (SVM). In classification part, the Radial Basis Function (RBF) kernel of the SVM has been used. The result shows that the MRA and SVM can classify the source of voltage sag with promising accuracy. Index Terms—Power Quality, Voltage sag, Multi Resolution Analysis, Support Vector Machine 24 2014 IACSIT Singapore Conferences E11 Investigation of Cold Flow Properties of Waste Cooking Biodiesel Gaurav Dwivedi and Mahendra Pal Sharma Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee, India Abstract—Waste Cooking Biodiesel has high potential as a new and renewable energy source in the future, as a substitution fuel for diesel and can be used in existing diesel engine without modification. But the major quality issue associated with biodiesel to use it as engine fuel is its poor cold flow property. The poor cold flow property results in gum formation and crystallization of fuel particles which lead to solidification of fuel lines and filters and creates the fuel starvation which will ultimately lead to starting problem in engine. The objective of this study to investigate and improve the cold flow properties of Waste cooking biodiesel by blending and winterization. Blending was found to be more favourable for improvement in cold flow properties of biodiesel without any effect on yield. The result of experimental investigation shows that Cloud Point and Pour Point of Waste cooking biodiesel (WCB100) is improved from 14.5⁰C to 9⁰C and 13.7⁰C to 7.5⁰C respectively by three step winterization at the rate of 0.2⁰C at each step. The result also show that 20% ethanol blending lead to drastic improvement in cold flow properties of waste cooking biodiesel and makes it suitable to be used in cold climatic condition. E21 Index Terms—Biodiesel; Cloud Point; Pour Point; Blending; Ethanol Challenges Due to Operation of Turboshaft Engine with Synthetic Gas Nikola Davidović, Aiman Elmahmodi, Predrag Miloš and Ramadan Almadani University of Tripoli, Libya Abstract—Synthetic gas is nowadays co-product of processes such as waste gasification and various industry waste gases. The logic idea is to use these gases as energy and to prevent atmospheric pollution. Idea to use gases from waste as a fuel for gas-turbine generator that producing electric power is very attractive engineering research project, but also challenging. In this paper the necessary modifications of an existing turbo-shaft engine combustion chamber in order to be capable to operate with synthetic gas were presented. It was experimentally proven that, this type of combustion chamber and atomizer of the gas turbine generator are very suitable for application with synthetic gas or with dual liquid and gaseous fuel operation. Tests shown excellent behavior and practically identical thermodynamic efficiency. E31 Index Terms—airblast atomizer, combustion chamber, stochiometric ratio, synthetic gas Matlab/Simulink based Model of Non-ideal Zeta Converter Man Mohan Garg and Mukesh K Pathak Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee, India Abstract—There are various computer-aided softwares available to simulate dc-dc power converters using discrete semiconductor devices. In this paper, a simple approach is proposed to simulate a fourth order dc-dc zeta converter using Matlab/simulink. This approach avoids the use of discrete semiconductor devices, resulting in fast and efficient simulation model. The approachalso takesnon-idealities of zeta converter into account. The results obtained are exactly same as with discrete 25 2014 IACSIT Singapore Conferences semiconductor devices. Index Terms—Dc-dc converter, Modeling, Simulation, Zeta converter, Matlab/simulink Coffee Break 16:00pm-16:10pm Afternoon Session Authors’ Oral Presentation 16:10pm-19:00pm Session 5(Quality Ballroom) 3rd Floor Session Chair: Prof. Hisaki Watari, Gunma University, Japan MC003 Sensitivity Analysis of Material Constitutive Model Parameters in Numerical Simulation of the Orthogonal Turning Process Vijay Sekar K. S. and Pradeep Kumar M SSN College of Engineering, India Abstract—Numerical simulations in machining processes are dependent on the flow stress input data. The flow stress is computed from empirical models which depend on number of material parameters, the values of which are derived from various mathematical optimization techniques. The derived flow stress parameters vary based on the nature of techniques used and the flow stress testing procedure utilized. This results in variations in the numerical simulation results when working with different models. In this work, the Johnson Cook flow stress model is tested for its sensitivity towards the finite element (FE) results. Orthogonal turning is conducted with AA 6082 (T6) aluminium alloy and the process is simulated in Deform 2D. The flow stress computed from the Johnson Cook model is input to the FE code and the cutting force and chip thickness recorded. The FE results are input to the Minitab statistical code and an optimization process conducted based on the orthogonal arrays concept. The comparative study reveals the sensitivity of the five parameters of the material model towards the cutting force and chip thickness. MC008 Index Terms—Flow Stress, Optimization, Finite Element Simulation, Orthogonal Machining, Sensitivity Application of Multiobjective Optimization in Structural Design Padmanabh Limaye and Amit Pingle 26 2014 IACSIT Singapore Conferences John Deere India Pvt. Ltd., India Abstract—Present work discusses the application of Multi-Objective Optimization (MOO) in simulation based engineering design. The design objectives are maximizing the fundamental frequency, minimizing maximum stress and total mass of a structural assembly. Design variables are the 17 part thicknesses. Unconstrained MOO is performed for mass-frequency and mass-stress objectives to obtain ‘Pareto optimal curves using Genetic Algorithm (GA). The results are further improved by local search using Adaptive Response Surface Method (ARSM) and Sequential Quadratic Programming Method (SQP). The necessary condition of optimality is verified using generalized Karush Kuhn Tucker (KKT) conditions. Sub-differentials are used where objective function is non-differentiable. Authors show how MOO helps to gain insight into the problem and understand the underlying design principles. For given design specifications, effect of considering additional design parameters is also studied depending on shape of the Pareto curve, to achieve efficient design. MC009 Index Terms—Engineering, optimization, multiobjective, optimality Determination of Optimum Parameter Levels for Quality Characteristics in Conventional Drilling of Thick Polymeric Composites Balasubramanian Ramesh, A. Elayaperumal and S. Satishkumar Anna University, India Abstract—Since literature on the machinability of non laminated composites is scarce, an investigation was extended away to study the machinability of thick non laminated Glass Fiber Reinforced Plastic (GFRP) composites and to compare the above with machinability of thick laminated composites. The composites with high fiber weight fraction were drilled with a special geometry coated carbide drill (Ratio drill). Taguchi’s orthogonal array and analysis of variance (ANOVA) were used to examine the influence of process parameters (feed and spindle speed) on quality characteristics (thrust force and torque). The optimum degree of process parameters towards aperture quality was obtained. MC010 Index Terms—Polymer-matrix composites (PMCs), Compression molding, Pultrusion, Drilling, Taguchi, MINITAB. Design and Kinematic Analysis of Gull Inspired Flapping Wing Model Tigmanshu Goyal, David Kumar, Vemuri Shyam Kumar, P. M. Mohite and Sudhir Kamle Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur, India Abstract—A flapping wing mimicking the Black Headed Gull was developed and tested for its kinematics. All the individual joints in the gull wing, namely the shoulder, elbow and wrist joint were mimicked with their corresponding functionalities. The shoulder joint is designed to control the flapping frequency, flapping amplitude, flapping plane and the speed of the upstroke-downstroke. Similarly, the elbow and wrist joints control the upstroke span reduction and twisting of the wing, respectively. Geometry, inertia, mass and frequency data of the gull were used to model the wing. A control input program was designed for the independent control of all the 6 joints (3 per wing). The motion of the manufactured 27 2014 IACSIT Singapore Conferences wing system was verified using LASER Displacement Sensor. MC012 Index Terms—Bio mimicking, Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV), Laser Displacement Sensor, Flapping Wing, Kinematics. Kinematics Optimization of A 3-SPS Parallel Redundant Motion Mechanism using Conformal Geometric Algebra Jahng Hyon Park, Jeseok Kim, and Jinhan Jeong Hanyang University, Korea Abstract—In this paper, an actuation mechanism for high-speed aiming of a target is proposed. The mechanism is a 3DOF-SPS (spherical-prismatic-spherical) parallel manipulator and can be used for a missile defense system with a fast reaction time. This type of parallel mechanism has high rigidity against external disturbances and accordingly high stiffness and precision. The target aiming requires 2 degrees of freedom and this 3 DOF mechanism has one redundancy. For fast manipulation of the proposed mechanism, the redundancy can be exploited and an optimal solution can be found out of the infinite number of inverse kinematic solutions. For finding a near time-optimal solution, a cost function is formulated considering displacement of each parallel link and an optimization technique is used for solution of the inverse kinematic problem. MC013 Index Terms—3-SPS parallel redundant motion mechanism, conformal geometric algebra, and inverse kinematics Frictional Contact Stress Analysis of Spur Gear by Using Finite Element Method Muhammad Farhan, Saravanan Karuppanan and Santosh Patil UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI PETRONAS, MALAYSIA Abstract—Spur gear is used to transfer rotary motion between parallel shafts. The simplicity in its design is one of the advantages of the spur gear. However higher frictional force that is accumulated on the gear teeth will influence the spur gear performance. Many previous papers elaborated more about the contact stress in the spur gear but few of them gave the details on how friction affects the gear teeth. In this paper, contact stress of spur gear has been evaluated with and without friction. There is an insufficient frictional effect data in the gear and thus should be regarded as an important research parameter. In this work, Hertz theory, AGMA standard and finite element method (FEM) have been employed. The frictionless contact stress result has been validated with both the theoretical methods with minimum deviation. Frictional coefficient range of 0.0 to 0.3 was selected and the corresponding contact stress is directly proportional to the friction coefficient. The work also involves the variation of face width of the gear set under the influence of friction. The contact stress of spur gear was found to be inversely proportional to face width. MC023 Index Terms—Spur Gear, Contact Stress, Finite Element Analysis, Friction Buckling Optimization of Composite Shells by Utilizing Finite Element Analysis, Neural Networks and Genetic Algorithm Hossein Amirabadi and Mehdi Mostofi Abadeh Branch, Islamic Azad University, Iran Abstract—The main goal in this investigation is optimization of two, four, eight and 28 2014 IACSIT Singapore Conferences twelve layer shells in order to identify optimized fiber angle in different layers aiming maximizing critical load. In order to identify critical load parameter, a hybrid approach including Finite Element Method (FEM) and Neural Networks (NN) is employed. To achieve the above results, required data for NN is supplied by FEM and the appropriate network is trained. For optimization of obtained function, Genetic Algorithm (GA) is utilized. In this case, GA is also employed over and over in order to obtain the effect of different parameters. Furthermore, existence of several close optimized points and interactions among layers, critical load and fiber angle are discussed. MC042 Index Terms—Composite shells, buckling, optimization, neural network, genetic algorithm. Effect of Lanthanum Addition on Fluidity of Complex Al-11Si-Cu-Mg Cast Alloy Rosli Bin Ahmad and M.B.A. Asmael Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia, Malaysia Abstract—This research was to determine the effect of rare earth metal (REM) on the fluidity of eutectic Al-11Si-Cu-Mg cast alloy. The rare earth metal used here is Lanthanum to produce Al-11Si-Cu-Mg-0.1La, Al-11Si-Cu-Mg-0.5La and Al-11Si-Cu-Mg-1.0La alloys. The fluidity was measured by permanent spiral mold, pre-heated at 450oC. The microstructure was characterized by optical microscope. The fluidity of complex Al-11Si-Cu-Mg eutectic alloy decreased with the increase of La addition. The 1.0 % of La addition led to refinement of silica particles, which reduced the fluidity length by 25%. MC047 Index Terms—Aluminium alloy, Lanthanum, Fluidity Multi-Response Optimization of Wire -EDM Process Parameters of Titanium Alloy Using Taguchi Method and Grey Relational Analysis Ramamurthy Annamalai, Sivaramakrishnan R, Venugopal S, Muthuramalingam T Anna University, India Abstract—It is very important and complexity to find the optimum values of wire EDM process parameters and contribution of each parameter to attain the better performance characteristics. In this study, an attempt has been made to optimize those parameters while machining the titanium alloy. Since the process involves more one than one response parameter, it is essential to carry out the multi-response optimization methodology .The experiments have been conducted with different levels of input factors such as pulse on time ,pulse off time and wire tension based on Taguchi L9 orthogonal table. Wire EDM optimal process parameter has been identified using grey relational analysis and significant parameter has been determined by analysis of variance. Experimental results have indicated that the multi-response characteristic such material removal rate and surface roughness can be improved effectively through grey relational analysis. MC048 Index Terms—WEDM, titanium, grey relational analysis. Effect of Cerium Addition and Cooling Rate on Microstructure of ADC12 Eutectic Cast Alloy Rosli Bin Ahmad and M.B.A. Asmael Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia, Malaysia 29 2014 IACSIT Singapore Conferences Abstract—This research was to determine the effect of Cerium and cooling rate on the microstructure of eutectic Al-11Si-Cu-Mg cast alloy. The Cerium was added to produce Al-11Si-Cu-Mg-1.5Ce alloys. The microstructure was characterized by optical microscope. The Si structure was modified with the increase of the cooling rate, where smaller area was achieved. Ce formed rich intermetallic phase, such as Al-Si-Ce. MC054 Index Terms—Aluminum alloy, cerium, cooling rate Growth of Anodized Layer and Cerium Sealing on Al7xxx/SiC Composite Badrul Munir, Vika Rizkia, Johny W. Soedarsono, Bambang Suharno, Andi Rustandi Department of Metallurgy and Materials Engineering Universitas Indonesia, Indonesia Abstract—Anodizing process conducted in Al7xxx/SiC produced non-uniform thickness of porous anodic film with cavities, micro-pores and micro-cracks. Cerium sealing was chosen as a post treatment to remedy the poor anodic film by providing a composite layer in order to further enhance the corrosion resistance in aggressive environment. In this study, anodizing process was conducted in H2SO4 solution at current density values of 15, 20, and 25 mA/cm2 at room temperature, 0oC and -25oC for 30 minutes. Subsequently, electroless sealing was conducted in CeCl3.6H2O + H2O2 solution at room temperature and pH 9 for 30 minutes. Integrated protection composed of anodizing at 0oC and cerium sealing process in surface of anodic oxide layer. These spherical deposits covered the entire surface of anodic oxide layer in accordance with the morphology of the oxide layer. Otherwise, almost no cerium deposit formed on the surface of the oxide layer by conducted integrated protection at room temperature and -25oC. The integrated process conducted at anodizing temperature of 0oC presented a highest protection degree. The cerium protective layer which leads to the decreasing of corrosion rate and current density up to 99,99% or four orders magnifications than that of bare composite. E305 Index Terms—Aluminum Matrix Composite, anodizing, cerium sealing, corrosion Preparation and Characterization of Nickel and Copper Oxide/Hydroxide Films on Stainless Steels Substrates for Use As Cathodes In Alkaline Water Electrolysi Paulo S. D. de Brito, David P. Cardoso and Luiz F. Rodrigues Instituto Politécnico de Portalegre, Portugal Abstract—The production high purity hydrogen by water electrolysis based renewable sources as a mean to store energy, has gained some attention in the last years due to the high specific energy of hydrogen, the potentially neutral carbon and zero emission of the usage of H2 as fuel. However, it remains certainly necessary to develop efficient and lower cost electrolyzers. Such a situation requires the search for and the development of inexpensive and stable electrode materials, showing low polarization to hydrogen evolution reduction (HER). In this work copper and nickel oxides were studied for use as electrodes for the reduction of hydrogen in alkaline water electrolysis. The nickel and copper oxide composites coatings were deposited 30 2014 IACSIT Singapore Conferences electrochemically as oxides/hydroxides on a stainless steel (SS) electrode and characterized using electrochemical methods such as cyclic voltammetry (CV), cathodic polarization and Tafel slops. The HER was studied using as electrolytic cathodes unmodified AISI 304 stainless steel (SS), nickel coated stainless steel (SS/Ni), copper coated stainless steel (SS/Cu), and nickel (under layer) and copper (top layer) coated stainless steel (SS/Ni/Cu) in 5 M KOH solution. It was found that, the SS/Ni/Cu electrode presents good electrocatalytic activity and stability toward the HER, compared to the SS electrodes modified by single nickel oxide layer. This behavior seems be explained by the synergistic interaction of Ni and Cu with Fe present in the stainless steel. Index Terms—Hydrogen evolution reaction, alkaline water electrolysis, nickel modified electrodes, Ni-Cu modified electrodes Afternoon Session Authors’ Oral Presentation 16:10pm-19:00pm Session 6(Emerald Room) 2nd Floor Session Chair: Associate Prof. R. Shivarudraswamy, Manipal Institute of Technology, Manipal University, India MC011 Particle Swarm Optimization based Empirical Correlation for Prediction of Hydrate Formation in Deep-water Pipeline Aijaz Abbasi and Fakhruldin M Hashim Universiti Teknologi PETRONAS, Malaysia Abstract—Since formation of hydrate in deep water pipeline could cause problems such as decreasing hydrocarbon production and increasing operational cost and time, this work offers to ascertain when and where hydrate will form with respect to change in pressure and temperature in deep water gas pipeline. The pressure is relatively high in deep water pipeline, and it is entirely possible to meet the hydrate formation conditions and pose a significant operational and security challenge. The study aims to develop a correlation that will help in finding hydrate formation pressure and temperature conditions of gas mixture flowing in deep water pipeline. The correlation is based on gas hydrates formation temperature with and without concentration of inhibitors. On the basis of existing published experimental data from the work by ‘E. Dendy Sloan’ and ‘Riki Kabayashi’, a new correlation will be developed using Particle Swarm Optimization. This research provides an effective coefficients for predicting hydrate formation Pressure / Temperature conditions for deep water gas pipeline. 31 2014 IACSIT Singapore Conferences MC014 Index Terms—Hydrate formation temperature / pressure, empirical correlation models and Particle Swarm Optimization. Performance Improvement using Simulation and Line Balancing; Application in Departure Terminal at Airport Dimas Novrisal, Nadia Hamani, Abderrahman Elmhamedi and Tresna Priyatna Soemardi University of Indonesia & University Paris 8, Indonesia Abstract—Evaluation of service at the airport is important for the passenger satisfaction. Based on the evaluation results, the management of the airport can decide what can be done to improve the system. In this research, we have evaluated and improved the performance of the departure terminal system at Soekarno-Hatta International Airport using simulation and line balancing methods. There are several steps in the research: evaluating the performance of existing system using simulation method: optimizing the system using line balancing and simulation methods: and analysing the results of the optimization process. The results show that the performance of the optimization process can decrease passenger processing and waiting time. We conclude that line balancing and simulation methods can be utilized to optimize the system of the departure terminal at the airport. MC044 Index Terms—Performance, Simulation, Line Balancing Understanding the Usefulness of Supply Chain Technology in Malaysian Textile and Apparel Industry Lee Khai Loon, Mohamad Ghozali Hassan, Zulkifli Mohamed Udin Universiti Utara Malaysia, Malaysia Abstract—Through the rapid innovation of technology and increasing affordability, it was transformed from a means of convenience to indispensable tools for work, socialization, entertainment, and learning. Given the relevance of the topic, the purpose of this study was aimed to explore the usefulness of supply chain technology (SCT) adoption in Malaysian textile and apparel (T&A) industry. The nature of this industry is characterized as a huge dynamic flow of physical, information, and financial. Undoubtedly, to handle the delicate nature of this business, the position of SCT has increased not only in the manufacturing sector, but also in smooth movement of upstream and downstream of the supply chain. Thus, the understanding and practicing of SCT adoption has become a crucial prerequisite for keeping competitive in the global race. Even though technology is widely implemented and studied in many industries and countries by researchers, but the study of adoption of SCT in Malaysian T&A industry is insufficient. In view of the significance given to Third Industrial Master Plan by the government Malaysia, it is necessary to recognize the stimulus of SCT adoptions. The results suggest and highlight the extent of SCT adoption and the benefits perceived by T&A companies from SCTs. This study believed that SCT adoption could be beneficial to both internal and external supply chains. The result of this study could be used as a precursor to support future researchers in further investigation on this extent. MC046 Index Terms—Usefulness, supply chain technology adoption, Malaysian textile and apparel industry. Quantifying the Bullwhip Effect in a Supply Chain: The Impact of Demand 32 2014 IACSIT Singapore Conferences Correlation between Two Market Groups for the MA(1) Time Series Kittiwat Sirikasemsuk King Mongkut’s Institute of Technology Ladkrabang, Thailand Abstract—The phenomenon in which the variation of upstream members' orders is amplified than the variation of downstream members' demands in the supply chain is called the bullwhip effect (BWEF). Most of existing research studies did not realize the demand dependency of market demands. Thus, this research focused on the study of the influence of the demand correlation coefficient between two market groups on the BWEF. The incoming demand processes are assumed the separate first-order moving average, [MA(1)] demand patterns. The scope of the supply chain structure used in this research is composed of one manufacturer and two distribution centers. The general result reveals that the coefficient of correlation is one of several factors affecting the BWEF. MC050 Index Terms—supply chain, bullwhip effect, first-order moving average model, demand correlation, order-up-to policy, decentralized warehouse Development on Smart Data Collection and Management in Workshop based on the Internet of Things Sheng Leng, Cuihua Chao, Fanglin Zou, and Zhi Nie Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, China Abstract—Considering the requirement of tracking the real-time production process and operation data such as the execution information, the quality of parts, the states of machines etc., a solution which applying the Radio Frequency Identification(RFID) and two-dimension Code into smart data collection system integrated with Manufacturing Execution System(MES) was presented. This paper introduces the smart data collection system for improving the workshop management level in the perspective of illustrating the software design and implementation. The first contribution from this paper is a framework of smart data collection system is proposed, which is generic and helpful for MES construction. The second is the agent and interface middleware is reported to enable the real-time intercommunication with other models. Thirdly, a real-life application case describes how the system to enhance a workshop management, which can be referenced by other companies when initiate and implement the RFID solutions to improve their manufacturing ability and production efficiency. MC302 Index Terms—Data collection, RFID, Two-dimension Code, Data tracing Data Mining of Dispatching Rules of Composite Materials Production based on Decision Tree Wenhua Ye, Sheng Leng, Jian Li Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, China Abstract—Data mining is an effective method to extract the unknown, valuable combination rules of scheduling from a great deal of production data. In this paper, aimed at composite materials production scheduling that is characterized by reentrance and capacity constraints, a method of extracting scheduling priority rules by C4.5 decision tree algorithm is studied. The principle of extracting scheduling rules with C4.5 algorithm is proposed, the application process of the approach is 33 2014 IACSIT Singapore Conferences introduced, an example is given, the results of the example indicate that the rules extracted by the proposed algorithm can guide scheduling effectively. E22 Index Terms—data mining, priority rule, decision tree, C4.5 algorithm Ecology and water supply based multi-objective optimal dispatch model and its case study in Yangtze basin Xuemin Wang, Jianzhong Zhou and Chao Wang Huazhong University of Science & Technology, China Abstract—The cascade reservoir dispatching based on the ecology and water supply is a new topic in recent years. This paper present the Ecology and Water-supply Based Multi-objective Optimal Dispatch Model (EWSB-MODM) with three objectives: ecological benefit, water supply benefit and power generation benefit. Then, by using the Monthly Frequency Computation method and considering the ecological factors (includes the breeding of Chinese sturgeon and the four major Chinese carps, preventing saltwater intrusion, avoiding dissolved gas supersaturation and the water level control of the Dongting and Poyang Lake), this paper defines the suitable ecological flow for the Three Gorges Cascade (TGC), which is taken as the ecological benefit criterion. Meanwhile, with a view to the situation of water demands and the local water shortage risks appearing in the upper and middle reaches of the Yangtze River, the water requirement is determined, and it is converted into the water supply rate as the criterion of the water supply benefits. Finally, this paper imports the multi-objective differential evolution algorithm (MODE) to solving the engineering case of the Three Gorges cascade. Results show that the model and method proposed in this paper can gain non inferior solution set which is uniform distributed and meets the ecological and water supply benefits, providing a scientific basis for reservoir schedulers to make the reasonable decision. E23 Index Terms—the Three Gorges Cascade, ecology, water supply, power generation, multi-objective optimal dispatch The ecological optimization dispatch of the Three Gorges reservoir considering aquatic organism protection Chao Wang, Jianzhong Zhou and Xuemin Wang Huazhong University of Science & Technology, China Abstract—This paper focus on the ecological optimization operation problem of the Three Gorges reservoir in flood recession. In this season, the primary goal of the reservoir is impounding to get the maximum economic benefit. As people increasing concern about their environment, impact of the reservoir operation to the aquatic habitat at the downstream area becomes an increasing important factor. The conflict between economic benefit and habitat conservation makes the dispatch a multi-objective problem. In this paper, stored energy at the end of dispatch period is proposed to be the economic objective and the weighted usable area (WUA) of the habitat is used to represent the environmental demand. The multi-objective differential evolution (MODE) and a particular constraint handling strategy proposed in this paper are used to solve this problem. Simulation results show that the proposed constraint handling strategy improves the performance of MODE in solving this problem. More importantly, the Pareto optimal front of different operating condition shows that the conflict between economic benefit and 34 2014 IACSIT Singapore Conferences environmental benefit is sharp, especially in low flow years. The degree of conflict relates to the value of average inflow. So it is necessary to consider the habitat conservation while operating. And this work provides a support to aquatic organism protection and ecological operation of the Three Gorges reservoir. E39 Index Terms—ecological optimization dispatch, aquatic organism protection, the Three Gorges reservoir, multi-objective optimization Analysis of Earthing System Cabinet of Telekom Malaysia David Caulker and Annuar Ramli TM R&D SDN BHD, CYBERJAYA, SEPANG, SELANGOR, MALAYSIA Abstract—This paper investigated the impact on the earthing systems of cabinets of Telekom Malaysia(TM) when subjected to dangerous voltages due to current injection from remote sources. TM have received numerous cases regarding the failures of their cabinets due to power related issues (PRI) as well as lightning. These failures may have occurred partly due to the existing earthing systems installations. This research aims to determine earthing impedance of 5 ohms or less of TM cabinets with respect to local soil conditions. Low impedance earthing is not easy to realize mainly due to the local soil resistivity, layering and structures. To achieve a low impedance of below 5 ohms as per Telekom Malaysia’s requirement, three types of earthing electrodes were modelled and simulated using CDEGS computer simulation software. Results have demonstrated that the existing earthing system of 3 rods practice by TM is sufficient for areas of resistivity less than 500Ω-m. Combination of rectangular and vertical rods for resistivity of 500Ω-m above is the preferred choice of earthing. Analysis and discussions presented in this study can be used as a guide for TM for their cabinet installations. Results also highlighted that achieving less than 5Ω does not constitute a safe earthing system. Other parameters have to be taken into account before ascertain which type of earthing to be used in a specific location of a TM installation. E42 Index Terms—Soil Resistivity, Earthing Impedance, Earth Potential Rise, Touch Voltage, Earthing Energy Efficiency in residential Buildings with well-established Energy Management Systems Jie Zheng and Frithjof Clauss Technical University Darmstadt Energy Center, Germany Abstract—A rational exploitation and efficient utilization of energy over a wide field of production and life is the main direction and object of modern society development, in order to keep its sustainability for today and future. With the rapid economic growth and strong competition among all the countries worldwide, the excessive thirst for energy has become more serious than ever before. Therefore, a series of efforts had to be made to keep the stability and sustainability of the global energy market. To achieve a Green and growth path, German government has made the decision to direct its energy supply towards sustainable energy, particularly renewable energy resource, and has also developed a comprehensive and effective energy concept on the basis of scientific studies. Not only in trade and industry as well transport sector, more concepts and ideas on energy saving or efficient use have been emphasized and optimized in domestic fields which are interested by 35 2014 IACSIT Singapore Conferences everyone’s daily life because an enormous energy and resource saving potential is supposed to be exploited. It is repeatedly stressed that energy efficiency is the most cost-effective pillar supporting Germany’s energy turnaround which could be achieved not only depending on continuous technical innovation and research, more important on a complete set of energy management systems and a healthy energy economics mechanism as well as energy policies. This paper is to present the advanced experiences of energy efficiency with its existing sophisticated energy management systems in Germany depending on the authors’ theoretical research and practical work, especially how energy efficiency has been enhanced in residential fields and which can be made more widespread as well what shall be moved forward further. Comprehensive information exchange and potential coordination are proposed to go further in the field of energy efficiency for a smart, sustainable and clean growth. E304 Index Terms—Efficiency, Resource Management, Systematized Energy Management, Smart Metering, Renewable Energy, Climate, Energy Package Application of Explosive Production Managing System based on Internet of Things XU Qin Jiujiang University, Jiangxi, China Abstract—With the high cost of deployment and maintenance of existing device in the explosive production, it is necessary to establish the digital managing system to real-time transmit producing data. The monitoring system of explosive production based on Internet of Things (IoT) technology is established. For the reliability and safety of initiating device and production and personnel management, the new scheme implements the technical application of the IoT and the explosive production managing system. The design of the self-adaptive network is key part of the managing system of explosive production, with self-organization and self-recovery mechanisms for the wireless sensor networks and the wireless location technology used in production safety. And the system can include the technology of terminal nodes and the technical details of the data acquisition and transmission effects. The system works in the simulation experiment and analysis test. The experimental results show the network architecture has good performance. The system can change the existing information and data transmission, thus achieving the goal of real-time monitoring. The professional information platform is established to manage the entire process to reduce the pressure of social and public safety on the supervision the explosive production. E307 Index Terms—Explosive producing managing system; Internet of Things; Self-adaptive network structure Security of Supply and Generation Reserve Management Delegation under extremely High Load Curtailment Cost Enrique B. Cedeno Nanjing Tech University, China Abstract—Power failures in a number of electric systems worldwide emphasize the importance of security of electric supply. Security of supply involves long term resource adequacy and medium to short term generation reserve management. Generation reserve requirements are usually determined using empirical rules 36 2014 IACSIT Singapore Conferences considering the demand as a deterministic quantity. Ignoring randomness could lead to suboptimal decisions. The research presented here differs from that prevailing in the literature by considering the demand as a random variable following a doubly truncated normal distribution this has the advantage of allowing considering day to day and seasonal variations. In this paper two new mathematical models are presented to determine generation reserve requirements for a market in which the regulator imposes an extremely high load curtailment cost in any unmet demand and delegates the role of buying generation reserves on the generators in a secondary market. These models are helpful tools to study analytically or by numerical simulation the interactions between the two markets. A potential scope for application of the proposed models is presented for the Colombian electric market. Index Terms—security of supply, generation reserves, random demand, deregulated power sector, Colombian electric market Dinner 19:00pm-20:00pm Day 3,Sunday, November 23, 2014 – One Day Tour The End Conference Venue Quality Hotel 37 2014 IACSIT Singapore Conferences A201 Balestier Road Singapore 329926 | Tel: (65)6355 9988 | Fax: (65) 6255 0998 Website: http://www.qualityhotel.com.sg/ About Keynote Speakers Michael Pecht, Chair Professor and Director Center for Advanced Life Cycle Engineering (CALCE) A. James Clark School of Engineering, USA Prof Michael Pecht is a world renowned expert in strategic planning, supply chain management, design, test, IP and risk assessment of electronic products and systems. In 2013, he was awarded the University of Wisconsin-Madison’s College of Engineering Distinguished Achievement Award. In 2011, he received the University of Maryland’s Innovation Award for his new concepts in risk management. In 2010, he received the IEEE Exceptional Technical Achievement Award for his innovations in the area of prognostics and systems health management. In 2008, he was awarded the highest reliability honor, the IEEE Reliability Society’s Lifetime Achievement Award. Prof Pecht has an MS in Electrical Engineering and an MS and PhD in Engineering Mechanics from the University of Wisconsin at Madison. He is a Professional Engineer, an IEEE Fellow, an ASME Fellow, an SAE Fellow and an IMAPS Fellow. He has previously received the European Micro and Nano-Reliability Award for outstanding contributions to reliability research, 3M Research Award for electronics packaging, and the IMAPS William D. Ashman Memorial Achievement Award for his contributions in electronics analysis. He is the editor-in-chief of IEEE Access, and served as chief editor of the IEEE Transactions on Reliability for nine years, chief editor for Microelectronics Reliability for sixteen years, an associate editor for the IEEE Transactions on Components and Packaging Technology, and on the advisory board of IEEE Spectrum. He is the founder and Director 38 2014 IACSIT Singapore Conferences of CALCE (Center for Advanced Life Cycle Engineering) at the University of Maryland, which is funded by over 150 of the world’s leading electronics companies at more than US$6M/year. The CALCE Center received the NSF Innovation Award in 2009, as well as the National Defense Industrial Association award (2009) for demonstrating outstanding achievement in the practical application of Systems Engineering principles, promotion of robust systems engineering principles throughout the organization, and effective systems engineering process development. He is currently a Chair Professor in Mechanical Engineering and a Professor in Applied Mathematics at the University of Maryland. He has written more than twenty books on product reliability, development, use and supply chain management. He has also written a series of books of the electronics industry in China, Korea, Japan and India. He consults for 22 international companies. He has written over 700 technical articles and has 5 patents. Prof. Nopbhorn Leeprechanon President of Faculty Senate of Thammasat University, Thailand Dr. Nopbhorn Leeprechanon obtained his Bachelor (Honors) and Master of Engineering specialized in Electrical Power Engineering from the King Mongkut's Institute of Technology Ladkrabang, Bangkok, Thailand, and received his Ph.D. in Power System Economics and Policy from the Royal Melbourne Institute of Technology (RMIT University), Victoria, Australia. He later obtained another Master of Art in Politics and Government from Thammasat University, Bangkok Thailand. Dr.Leeprechanon is currently with the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Thammasat University. He has been an active researcher in the area of electrical power system operations and planning, power system economics and energy policy for almost 2 decades and has published/presented over 30 articles in both national and international level related to his research interests in four continents. Dr.Leeprechanon had experiences in engineering industries, business and higher education sectors. He had worked in the field of power engineering and associated industries including NS, WIC, BICC, ABB for several years before joining Thammasat University in 1996. He is currently an Honorable Advisor of the Standing Committee for Energy, Senate of the Kingdom of Thailand, Executive Committee of the IEEE Power & Energy Society (PES) Thailand Chapter, His research interests are Renewable Energy Optimization Modeling, Smart Grid Technology, Electricity Economics, Tariffs, Restructuring and Reforming of State Enterprise and Public Utilities. He also plays a key role in driving a Smart Grid policy in Thailand. His managerial 39 2014 IACSIT Singapore Conferences experiences include President of the Faculty Senate, Thammasat University (2007-2013), Secretary General of the Thai Association of Governing Board of Universities and Colleges (2012-2013), President of Council of University's Faculty Senate of Thailand (2010-2011), Deputy Dean of Engineering, Thammasat University (2003-2005). Dr. Leeprechanon is a Senior Member of IACSIT. Welcome to American Society for (www.asr.org) Upcoming Conferences: DATE NAME Research PAPER WILL BE PUBLISHED BY Applied Mechanics and Materials Journal (ISSN: 1660-9336) ICPSE 2014 2014 3rd International Conference on Power Science and Engineering http://www.icpse.org/ Dec 18-20, 2014 Barcelona, Spain ICNB 2014 2014 5th International Conference on Nanotechnology and Biosensors http://www.icnb.org/ ICMPM 2014 2014 International Conference on Mechanical Properties of Materials(ICMPM 2014) http://www.icmpm.org/ 40 Indexed by Elsevier: SCOPUS www.scopus.com and Ei Compendex (CPX) www.ei.org. Cambridge Scientific Abstracts (CSA) www.csa.com, Chemical Abstracts (CA) www.cas.org, Google and Google Scholar google.com, ISI (ISTP, CPCI, Web of Science) www.isinet.com, Institution of Electrical Engineers (IEE) www.iee.org, etc. Applied Mechanics and Materials Journal (ISSN: 1660-9336) Indexed by Elsevier: SCOPUS www.scopus.com and Ei Compendex (CPX) www.ei.org. Cambridge Scientific Abstracts (CSA) www.csa.com, Chemical Abstracts (CA) www.cas.org, Google and Google Scholar google.com, ISI (ISTP, CPCI, Web of Science) www.isinet.com, Institution of Electrical Engineers (IEE) www.iee.org, etc. Applied Mechanics and Materials Journal (ISSN: 1660-9336) Indexed by Elsevier: SCOPUS www.scopus.com and Ei Compendex (CPX) www.ei.org. Cambridge Scientific Abstracts (CSA) www.csa.com, Chemical Abstracts (CA) www.cas.org, Google and Google Scholar google.com, ISI (ISTP, CPCI, Web of Science) www.isinet.com, Institution of Electrical Engineers (IEE) www.iee.org, etc. 2014 IACSIT Singapore Conferences All accepted papers will be published in one of the indexed Journals after being selected. Journal of Computers (JCP, ISSN: 1796-203X, 20 Papers) ICCNE 2014 2014 International Conference on Communications and Network Engineering http://www.iccne.org/ Journal of Software (JSW, ISSN: 1796-217X, 20 Papers) International Journal of Future Computer and Communication (IJFCC, ISSN: 2010-3751, 30 Papers) International Journal of Computer and Communication Engineering (IJCCE, ISSN: 2010-3743, 30 Papers) ICOAI2014 2014 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence http://www.icoai.org/ Dec 22-24, 2014 Barcelona, Spain Journal of Advances in Computer Networks (JACN, ISSN: 1793-8244, 20 Papers) International Journal of Machine Learning and Computing (IJMLC ISSN: 2010-3700) Abstracting/ Indexing: Engineering & Technology Digital Library, Google Scholar, Crossref, ProQuest, Electronic Journals Library, DOAJ and EI (INSPEC, IET). All accepted papers will be published in one of the indexed Journals after being selected. Journal of Computers (JCP, ISSN: 1796-203X, 20 Papers) Journal of Software (JSW, ISSN: 1796-217X, 20 Papers) Journal of Communications (JCM, ISSN: ISSN: 1796-2021, 20 papers) ICCSIT 2014 International Journal of Future Computer and Communication (IJFCC, ISSN: 2010-3751, 30 Papers) 2014 7th International Conference on Computer Science and Information Technology International Journal of Computer Theory and Engineering (IJCTE, ISSN: 1793-8201, 30 Papers) http://www.iccsit.org/ International Journal of Computer and Electrical Engineering (IJCEE, ISSN: 1793-8163, 30 Papers) International Journal of Information and Electronics Engineering (IJIEE, ISSN: 2010-3719, 20 Papers) International Journal of Information and Education Technology (IJIET, ISSN: 2010-3689, 20 Papers) Journal of Advances in Computer Networks (JACN, ISSN: 1793-8244, 20 Papers) Lecture Notes on Software Engineering (LNSE, ISSN: 2301-3559, Papers) 41 2014 IACSIT Singapore Conferences ICSST 2015 2015 the 4th International Conference on Security Science and Technology http://www.icsst.org/ Jan 15-16, 2015 Portsmouth, UK ICNCS 2015 2015 the 4th International Conference on Network and Computer Science http://www.icncs.org/ ICK 2015 2015 International Conference on Knowledge All accepted papers will be published in the volume of International Journal of Engineering and Technology (IJET) (ISSN; 1793-8244 (Online Version); 1793-8236 (Print Version)) All accepted papers will be published in the volume of International Journal of Future Computer and Communication (IJFCC) (ISSN: 2010-3751) Abstracting/ Indexing: Google Scholar, Engineering & Technology Digital Library, and Crossref, DOAJ, Electronic Journals Library, EI (INSPEC, IET). All accepted papers will be published in the volume of International Journal of Knowledge Engineering (IJKE) http://www.ick.org/ All accepted papers of ICMM 2015 will be published by Applied Mechanics and Materials Journal (ISSN: 1660-9336). ICMM 2015 2015 6th International Conference on Mechatronics and Manufacturing http://www.icmm.org/ Feb 12-13, 2015 Busan, South Korea ICAEE 2015 2015 the 2nd International Conference on Advances in Electronics Engineering http://www.icaee.org/ ICAPM 2015 2015 5th International Conference on Applied Physics and Mathematics http://www.icapm.org/ Mar19-20, 2015 Florence, Italy ICMLC 2015 2015 7th International Conference on Machine Learning and Computing http://www.icmlc.org/ 42 Indexed by Elsevier: SCOPUS www.scopus.com and Ei Compendex (CPX) www.ei.org. Cambridge Scientific Abstracts (CSA)www.csa.com, Chemical Abstracts (CA) www.cas.org, Google and Google Scholar google.com, ISI (ISTP, CPCI, Web of Science) www.isinet.com, Institution of Electrical Engineers (IEE) www.iee.org, etc. All accepted papers of ICAEE 2015 will be published by International Journal of Information and Electronics Engineering (IJIEE) (ISSN: 2010-3719) Indexed by Google Scholar, Electronic Journals Library,Engineering & Technology Digital Library,Crossref and ProQuest, DOAJ, Ei (INSPEC, IET). All accepted papers of ICAPM 2015 will be published by International Journal of Applied Physics and Mathematics (IJAPM) (ISSN: 2010-362X) Indexed by EI (INSPEC, IET),Chemical Abstracts Services (CAS), DOAJ,Electronic Journals Library, Engineering & Technology Digital Library, Nanowerk Database, Crossref, Google Scholar and ProQuest. All accepted papers of ICMLC 2015 will be published by International Journal of Machine Learning and Computing (IJMLC) (ISSN: 2010-3700) Indexed by Engineering & Technology Digital Library, Google Scholar, Crossref, ProQuest, Electronic Journals Library, DOAJ and EI (INSPEC, IET). 2014 IACSIT Singapore Conferences ICEIT 2015 2015 4th International Conference on Educational and Information Technology http://www.iceit.org/ ICICN 2015 2015 3rd International Conference on Information and Computer Networks http://www.icicn.org/ ICFD 2015 2015 International Conference on Fluid Dynamics http://www.icfd.org/ April 6-7, 2015 Orlando, USA ICCEB 2015 2015 4th International Conference on Computer Engineering and Bioinformatics http://www.icceb.org/ ICTLE 2015 2015 4th International Conference on Traffic and Logistic Engineering http://www.ictle.org/ 43 All accepted papers of ICEIT 2015 will be published by Journal of Information and Education Technology (IJIET). (ISSN: 2010-3689) Indexed by EI (INSPEC, IET),Cabell's Directories, DOAJ, Electronic Journals Library, Engineering & Technology Digital Library, EBSCO, Google Scholar, Crossref and ProQuest. All accepted papers of ICICN 2015 will be published by Journal of Advances in Computer Networks (ISSN: 1793-8244) Indexed by Engineering & Technology Digital Library, EBSCO, DOAJ, Electronic Journals Library, Ulrich's Periodicals Directory, International Computer Science Digital Library (ICSDL), ProQuest, and Google Scholar. All accepted papers of ICFD 2015 will be published by Applied Mechanics and Materials Journal (ISSN: 1660-9336) Indexed by Elsevier: SCOPUS www.scopus.com and Ei Compendex (CPX) www.ei.org. Cambridge Scientific Abstracts (CSA)www.csa.com, Chemical Abstracts (CA) www.cas.org, Google and Google Scholar google.com, ISI (ISTP, CPCI, Web of Science) www.isinet.com, Institution of Electrical Engineers (IEE) www.iee.org, etc. All accepted papers of ICCEB 2015 will be published by International Journal of Engineering and Technology (IJET) (ISSN: 1793-8236). Indexed by Chemical Abstracts Services (CAS), DOAJ, Engineering & Technology Digital Library, Google Scholar, Ulrich Periodicals Directory, Crossref, ProQuest, Electronic Journals Library, Index Copernicus, EI (INSPEC, IET). All accepted papers of ICTLE 2015 will be published by Journal of Traffic and Logistics Engineering (JTLE) (ISSN: 2301-3680) Indexed by Ulrich's Periodicals Directory, Google Scholar, EBSCO, Engineering & Technology Digital Library and Electronic Journals Digital Library. 2014 IACSIT Singapore Conferences All accepted papers of ICCIT 2015 will be published in the one of the following Journal with ISSN. Journal of Software (JSW, ISSN 1796-217X) ICCIT 2015 2015 International Conference on Computer and Information Technology http://www.iccit.org/ International Journal of Computer Theory and Engineering (IJCTE) (ISSN: 1793-8201) Indexed by Index Copernicus, Electronic Journals Library, EBSCO, Engineering & Technology Digital Library, Google Scholar, Ulrich's Periodicals Directory, Crossref, ProQuest, WorldCat, and EI (INSPEC, IET), Cabell's Directories. International Journal of Computer and Electrical Engineering (IJCEE) (ISSN: 1793-8163) Indexed by Ulrich's Periodicals Directory, Google Scholar, EBSCO, Engineering & Technology Digital Library, Crossref, ProQuest, EI (INSPEC, IET), and Electronic Journals Library Lecture Notes on Information Theory (ISSN: 2301-3788) Indexed by EI(INSPEC, IET), Ulrich's Periodicals Directory, Google Scholar, EBSCO, Engineering & Technology Digital Library and etc. All accepted papers of ICEEE 2015 will be published in the one of the following Journal with ISSN. Applied Mechanics and Materials Journal (ISSN: 1660-9336) Indexed by Elsevier: SCOPUS www.scopus.com and Ei Compendex (CPX) www.ei.org. Cambridge Scientific Abstracts (CSA)www.csa.com, Chemical Abstracts (CA) www.cas.org, Google and Google Scholar google.com, ISI (ISTP, CPCI, Web of Science) www.isinet.com, Institution of Electrical Engineers (IEE) www.iee.org, etc. April 28-29, 2015 Ankara, Turkey ICEEE 2015 2015 2nd International Conference on Electrical and Electronics Engineering http://www.iceee.org/ International Journal of Electronics and Electrical Engineering (ISSN: 2301-380X) Indexed by Ulrich's Periodicals Directory, Google Scholar, EBSCO, Engineering & Technology Digital Library, etc. Journal of Automation and Control Engineering (ISSN: 2301-3702) Indexed by EI (INSPEC, IET), Ulrich's Periodicals Directory, Google Scholar, EBSCO, Engineering & Technology Digital Library and etc. International Journal of Electrical Energy (ISSN: 2301-3656) Indexed by EI(INSPEC, IET), Ulrich's Periodicals Directory, Google Scholar, EBSCO, Engineering & Technology Digital Library and etc. 44 2014 IACSIT Singapore Conferences All accepted papers of IOAC 2015 will be published by Applied Mechanics and Materials Journal (ISSN: 1660-9336) ICOAC 2015 2015 International Conference on Automatic Control http://www.icoac.org/ ICMMT 2015 2015 6th International Conference on Material and Manufacturing Technology http://www.icmml.org/ May 9-10, 2015 Bali, Indonesia ICRE 2015 2015 International Conference on Reliability Engineering http://www.icre.org/ Indexed by Elsevier: SCOPUS www.scopus.com and Ei Compendex (CPX) www.ei.org. Cambridge Scientific Abstracts (CSA)www.csa.com, Chemical Abstracts (CA) www.cas.org, Google and Google Scholar google.com, ISI (ISTP, CPCI, Web of Science) www.isinet.com, Institution of Electrical Engineers (IEE) www.iee.org, etc. All accepted papers of ICMML 2015 will be published by Advanced Materials Research (ISSN: 1022-6680). Indexed by Elsevier: SCOPUSwww.scopus.com and Ei Compendex (CPX) www.ei.org/. Cambridge Scientific Abstracts (CSA) www.csa.com, Chemical Abstracts (CA) www.cas.org, Google and Google Scholar google.com, ISI (ISTP, CPCI, Web of Science) www.isinet.com , Institution of Electrical Engineers (IEE)www.iee.org , etc All accepted papers of ICRE 2015 will be published in the one of the following Journal with ISSN. Advanced Materials Research (ISSN: 1022-6680). Indexed by Elsevier: SCOPUSwww.scopus.com and Ei Compendex (CPX) www.ei.org/. Cambridge Scientific Abstracts (CSA) www.csa.com, Chemical Abstracts (CA) www.cas.org, Google and Google Scholar google.com, ISI (ISTP, CPCI, Web of Science) www.isinet.com , Institution of Electrical Engineers (IEE)www.iee.org , etc Journal of Engineering and Technology (IJET) (ISSN: 1793-8236). Indexed by Chemical Abstracts Services (CAS), DOAJ, Engineering & Technology Digital Library, Google Scholar, Ulrich Periodicals Directory, Crossref, ProQuest, Electronic Journals Library, Index Copernicus, EI (INSPEC, IET). All accepted papers of ICLB 2015 will be published by Advanced Materials Research (ISSN: 1022-6680). ICLB 2015 2015 International Conference on Lithium Batteries http://www.iclb.org/ 45 Indexed by Elsevier: SCOPUSwww.scopus.com and Ei Compendex (CPX) www.ei.org/. Cambridge Scientific Abstracts (CSA) www.csa.com, Chemical Abstracts (CA) www.cas.org, Google and Google Scholar google.com, ISI (ISTP, CPCI, Web of Science) www.isinet.com , Institution of Electrical Engineers (IEE)www.iee.org , etc 2014 IACSIT Singapore Conferences All accepted papers of ICCSN 2015 will be published in the one of the following Journal with ISSN. WIT Transactions on Information and Communication Technologies (ISSN: 1743-3517) ICCSN 2015 2015 the 7th International Conference on Communication Software and Networks http://www.iccsn.org/ Indexed by EI Compendex, Scopus and ISI. Journal of Communications (JCM) (ISSN: 1796-2021; DOI: 10.12720/jcm) Indexed by EI Compendex; SCOPUS; ULRICH's Periodicals Directory; Google Scholar; INSPEC; etc. All accepted papers of ICIIP 2015 will be published in the one of the following Journal with ISSN. WIT Transactions on Information and Communication Technologies (ISSN: 1743-3517) June 6-7, 2015 Chengdu, China ICIIP 2015 2015 the 4th International Conference on Intelligent Information Processing http://www.iciip.org/ Indexed by EI Compendex, Scopus and ISI. Journal of Industrial and Intelligent Information (ISSN: 2301-3745; DOI: 10.12720/jiii) Indexed by EI(INSPEC, IET), Google Scholar, EBSCO, Engineering & Technology Digital Library and etc. All accepted papers of ICWOC 2015 will be published in the one of the following Journal with ISSN. WIT Transactions on Information and Communication Technologies (ISSN: 1743-3517) ICWOC 2015 2015 the 4th International Conference on Wireless and Optical Communications http://www.icwoc.org/ ICDDM 2015 The 2015 4th International Conference on Database and Data Mining http://www.icddm.org/ July 2-3, 2015 Chicago, USA ICKD 2015 The 2015 4th International Conference on Knowledge Discovery http://www.ickd.org/ ICOIP 2015 The 2015 4th International Conference on Optoelectronics and Image Processing http://www.icoip.org/ 46 Indexed by EI Compendex, Scopus and ISI. International Journal of Future Computer and Communication (ISSN: 2010-3751; DOI: 10.7763/IJFCC) Indexed by Google Scholar, Engineering & Technology Digital Library, and Crossref,DOAJ, Electronic Journals Library, EI (INSPEC, IET). All accepted papers of ICDDM 2015 will be published by WIT Transactions on Information and Communication Technologies (ISSN: 1743-3517) Indexed by EI Compendex, Scopus and ISI. All accepted papers of ICKD 2015 will be published by International Journal of Computer Theory and Engineering (IJCTE)(ISSN: 1793-8201) Indexed by Electronic Journals Library, EBSCO, Engineering & Technology Digital Library, Google Scholar, INSPEC, Ulrich's Periodicals Directory, Crossref, ProQuest, WorldCat, and EI(INSPEC, IET). All accepted papers of ICDDM 2015 will be published by WIT Transactions on Information and Communication Technologies (ISSN: 1743-3517) Indexed by EI Compendex, Scopus and ISI. 2014 IACSIT Singapore Conferences All accepted papers of ICROM 2015 will be published by Applied Mechanics and Materials (ISSN: 1660-9336) ICROM 2015 2015 2nd International Conference on Robotics and Mechatronics http://www.icrom.org/ ICAME 2015 2015 the 4th International Conference on Advances in Mechanics Engineering http://www.icame.org/ July 20-21, 2015, Madrid, Spain Indexed by Elsevier: SCOPUSwww.scopus.com and Ei Compendex (CPX) www.ei.org/. Cambridge Scientific Abstracts (CSA) www.csa.com, Chemical Abstracts (CA) www.cas.org, Google and Google Scholar google.com, ISI (ISTP, CPCI, Web of Science) www.isinet.com , Institution of Electrical Engineers (IEE)www.iee.org , etc All accepted papers of ICROM 2015 will be published by Applied Mechanics and Materials (ISSN: 1660-9336) Indexed by Elsevier: SCOPUSwww.scopus.com and Ei Compendex (CPX) www.ei.org/. Cambridge Scientific Abstracts (CSA) www.csa.com, Chemical Abstracts (CA) www.cas.org, Google and Google Scholar google.com, ISI (ISTP, CPCI, Web of Science) www.isinet.com , Institution of Electrical Engineers (IEE)www.iee.org , etc Submitted conference papers will be reviewed by technical committees of the Conference. All accepted papers will be published in one of the following Journals. International Journal of Electronics and Electrical Engineering(IJEEE) (ISSN: 2301-380X) ICCSS 2015 2015 5th International Conference on Circuits, System and Simulation http://www.iccss.org/ included in Ulrich's Periodicals Directory, Google Scholar, EBSCO, Engineering & Technology Digital Library and Electronic Journals Digital Library. International Journal of Information and Electronics Engineering(IJIEE) (ISSN: 2010-3719) included in Google Scholar, Electronic Journals Library, Engineering & Technology Digital Library, Crossref and ProQuest, DOAJ, Ei (INSPEC, IET). 47 2014 IACSIT Singapore Conferences All accepted papers will be published in one of the indexed Journals after being selected. International Journal of Computer Theory and Engineering (IJCTE) (ISSN: 1793-8201) DOI: 10.7763/IJCTE Editor-in-Chief: Prof. Wael Badawy ICCCD 2015 2015 the 5th International Conference on Computer and Communication Devices http://www.icccd.org/ Abstracting/Indexing: Index Copernicus, Electronic Journals Library, EBSCO, Engineering & Technology Digital Library, Google Scholar, Ulrich's Periodicals Directory, Crossref, ProQuest, WorldCat, and EI (INSPEC, IET), Cabell's Directories. International Journal of Computer and Communication Engineering (IJCCE)(ISSN: 2010-3743) DOI: 10.7763/IJCCE Editor-in-Chief: Dr. Maode Ma Aug 22-23, 2015 New Taipei, Taiwan Abstracting/ Indexing: EI (INSPEC, IET), Google Scholar, Engineering & Technology Digital Library, ProQuest, and Crossref, Electronic Journals Library All accepted papers will be published in one of the indexed Journals after being selected. ICOSP 2015 2015 International Conference on Signal Processing http://www.icosp.org/ ICRAS 2015 2015 5th International Conference on Robotics and Automation Sciences WIT Transactions on Information and Communication Technologies (ISSN: 1743-3517) Indexed by EI Compendex, Scopus and ISI. International Journal of Signal Processing Systems (IJSPS) (ISSN: 2315-4535) Indexing: Ulrich's Periodicals Directory, Google Scholar, EBSCO, Engineering & Technology Digital Library, etc. The ICRAS 2015 proceedings will be published by IEEE and all the papers will be archived in the IEEE Xplore and indexed by Ei Compendex and ISI. http://www.icras.org/ Note ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ 48 2014 IACSIT Singapore Conferences ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ 49 2014 IACSIT Singapore Conferences ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ 50
© Copyright 2026