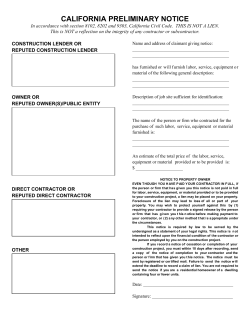
Message Security Troubleshooting Guide • Google Message Security • Google Message Discovery
Message Security Troubleshooting Guide • Google Message Security • Google Message Discovery Google, Inc. 1600 Ampitheatre Parkway Mountain View, CA 94043 www.google.com Part number: TSG_R613_01 05 Februrary 2007 © Copyright 2008 Postini, Inc. All rights reserved. © Copyright 2008 Google, Inc. All rights reserved. Google, the Google logo, Google Message Filtering, Google Message Security, Google Message Discovery, Postini, the Postini logo, Postini Perimeter Manager, Postini Threat Identification Network (PTIN), Postini Industry Heuristics, and PREEMPT are trademarks, registered trademarks, or service marks of Google, Inc. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners. Use of any Google solution is governed by the license agreement included in your original contract. Any intellectual property rights relating to the Google services are and shall remain the exclusive property of Google, Inc. and/or its subsidiaries( “Google”). You may not attempt to decipher, decompile, or develop source code for any Google product or service offering, or knowingly allow others to do so. Google documentation may not be sold, resold, licensed or sublicensed and may not be transferred without the prior written consent of Google. Your right to copy this manual is limited by copyright law. Making copies, adaptations, or compilation works, without prior written authorization of Google. is prohibited by law and constitutes a punishable violation of the law. No part of this manual may be reproduced in whole or in part without the express written consent of Google. Copyright © by Google, Inc. Postini, Inc. provides this publication “as is” without warranty of any either express or implied, including but not limited to the implied warranties of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose. Postini, Inc. may revise this publication from time to time without notice. Some jurisdictions do not allow disclaimer of express or implied warranties in certain transactions; therefore, this statement may not apply to you. GD Graphics Copyright Notice: Google uses GD graphics. Portions copyright 1994, 1995, 1996, 1997, 1998, 1999, 2000 by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory. Funded under Grant P41RR02188 by the National Institutes of Health. Portions copyright 1996, 1997, 1998, 1999, 2000 by Boutell.Com, Inc. Portions relating to GD2 format copyright 1999, 2000 Philip Warner. Portions relating to PNG copyright 1999, 2000 Greg Roelofs. Portions relating to libttf copyright 1999, 2000 John Ellson ([email protected]). Portions relating to JPEG copyright 2000, Doug Becker and copyright (C) 1994-1998, Thomas G. Lane. This software is based in part on the work of the Independent JPEG Group. Portions relating to WBMP copyright 2000 Maurice Szmurlo and Johan Van den Brande. Permission has been granted to copy, distribute and modify gd in any context without fee, including a commercial application, provided that this notice is present in user-accessible supporting documentation. This does not affect your ownership of the derived work itself, and the intent is to assure proper credit for the authors of gd, not to interfere with your productive use of gd. If you have questions, ask. “Derived works” includes all programs that utilize the library. Credit must be given in user-accessible documentation. 2 Message Security Troubleshooting Guide This software is provided “AS IS.” The copyright holders disclaim all warranties, either express or implied, including but not limited to implied warranties of merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose, with respect to this code and accompanying documentation. Although their code does not appear in gd 1.8.4, the authors wish to thank David Koblas, David Rowley, and Hutchison Avenue Software Corporation for their prior contributions. 3 Google Compliance Policies Notice: Google assumes no responsibility in connection with the Compliance Policies lexicon-filtering feature, including any failure to recognize credit card or social security numbers that do not follow an applicable pattern as established in Postini’s systems or any failure to encrypt a credit card or social security number. 4 Message Security Troubleshooting Guide Contents Chapter 1: Frequently Asked Questions 7 Activation 7 Administration Console 8 Approved/Blocked Senders Lists 10 Attachment Manager 13 Batch Commandline Interface 16 Connection Manager 22 Content Manager 22 Delivery Manager 23 Domain 26 Message Center 28 Message Recovery 30 MX Records and IP Addresses 33 Notifications and Alerts 36 Organizations 40 Outbound Servers 41 Reports 43 Spam 45 Spool Manager 49 Users, Aliases, Mailing Lists, and Administrators 51 Virus 55 Chapter 2: Mail Flow Troubleshooting Mail Flow 57 57 Contents 5 Frequently Asked Questions Chapter 1 Activation After registering, how do I get my password? After successfully completing your registration, you will receive the setup email within 1 to 2 business days. Use the information in this email to begin the process of configuring your service. Using the setup wizard, submit details about your account, including your domain name, administrator login address, and password. Once you have completed the wizard, you will receive your activation email, which includes the information you need to complete the final steps of the configuration process. For more information, see the Activation Step-by-Step Guide. If I have lost my activation key email, what do I do? First, check your spam folder to be sure the email was not quarantined. If you have lost your activation email, please contact Support. If you are a directly supported Postini Customer, please log in to the Postini Support Portal. Otherwise, contact your vendor, who can assist you. For more activation information, see the Activation Step-by-Step Guide. What are the next steps after getting my activation key? With your activation key, you are ready to complete the setup wizard. After setting up your initial account, switch your MX records to the email security service, test your service, and set up your organizations and users. For more information, see the Activation Step-by-Step Guide. Frequently Asked Questions 7 Administration Console If I forget my Administration Console login and password, what should I do? If you have forgotten your login, try your email address. If you have forgotten your password, enter an incorrect password in the login page. The next page has a Forgot Your Password link. Select this link and a temporary password will be mailed to you. To prevent easily-cracked passwords, the email security service has very strict guidelines for administrative passwords. An administrator password must a minimum of 6 characters (5 unique), no sequential letters or numbers, not resemble a dictionary word (as in cr@cker), and not be an email address. For more information about administrator password requirements, see Administrator Passwords. Why is the system not accepting my new password? If you are logging into the Administration Console for the first time, the system requires you change your initial password. If your new password does not meet the password guidelines, the system gives an error. To prevent easily-cracked passwords, the email security service has very strict guidelines for administrative passwords. An administrator password must a minimum of 6 characters (5 unique), no sequential letters or numbers, not resemble a dictionary word (as in cr@cker), and not be an email address. For more information about administrator password requirements, see Administrator Passwords. What does the “Service temporarily unavailable...” error message mean when I log into the Administration Console? Usually this message means the Administration Console is undergoing a scheduled maintenance update. These are usually planned for weekends or holidays and do not last for long periods of time. What do I do when I receive an error in red text when attempting to log in to the Administration Console? If the error is: We apologize for the inconvenience but the page that you are trying to reach has been moved. As a result, you will be required to log in again with your email address and password. 8 Message Security Troubleshooting Guide If you forgot your password, we suggest that you enter your correct email address and the password to your email account. If log in fails, click on the "Forgot your password?" link for specific instructions to retrieve your password. If you reached this page from a bookmark, a new bookmark will also need to be created after logging in. Thank you. This occurs when using Privately-Managed Password (PMP) authentication for all users, or only on Administrators when using POP authentication. The source of the issue is not having the User Access privilege for Account Settings. To correct this, log in to the Administration Console: 1. Select the organization containing affected users or the affected user: Go to Orgs and Users > Orgs and select the Organization containing the users. or Go to Orgs and Users > Users and select the affected user. 2. Select User Access in the Organization Settings or User Settings section of the page (as appropriate). 3. Select the Modify check box for Account Settings to enable the Account Settings privilege. How do I get another administrator account for a co-worker? You can create an sub-administrator account by creating a new authorization record for a registered user. For information about creating an account-level administrator, please contact Support. If you are a directly supported Postini Customer, please log in to the Postini Support Portal. Otherwise, contact your vendor, who can assist you. For more information about creating sub-administrators, see Create an Administrator. How can I add or delete another administrator at my account- level organization? To add or delete an account administrator, please contact Support. If you are a directly supported Postini Customer, please log in to the Postini Support Portal. Otherwise, contact your vendor, who can assist you. Frequently Asked Questions 9 Where is the “Add Email Config” link in my organization list? The ‘Add Email Config’ links are only next to Account organizations. In a typical organization hierarchy, email configs are sub-organizations of your Account organization. Approved/Blocked Senders Lists Who should I add to my Approved and Blocked Senders lists? Since adding an approved sender effectively allows traffic through filters, you should be cautious when deciding which addresses and domains to add to your Approved Senders list. Spammers can easily send emails which falsify the sender address to take advantage of any such configuration. For more information, see Deciding Which Approved Senders to Add. Note: Do not add your own domain to your Approved Senders list. With this configuration, all messages sent to your address or domain will be allowed through the filters regardless of the message’s spam-like nature. It is too easy for spammers to spoof. Is there a limit on how many users I can add to my Approved and Blocked Senders lists? The maximum number of characters is 4,000 characters for each list (organization approved senders, organization blocked senders, user approved senders, user blocked senders). If each address or domain is roughly 30 to 40 characters, each approved/blocked sender list can include approximately 100 to 130 addresses and domains. The maximum number of characters allowed for the approved mailing lists, which is available only through the Message Center, is 1,000 characters. 10 Message Security Troubleshooting Guide Some tips are: • Remember it is not necessary to add your complete contact list to these lists. If you find messages from a particular good sender are getting quarantined, put that sender on your Approved Senders list. The same is true for blocking unwanted senders. • The list’s size includes address white spaces and commas. A comma has 2 characters: a space and a comma. Add these additional characters to get an accurate count of the list size. • If you run out of space and attempt to add another address, you will receive an error that is similar to: List length limit (4000) exceeded • To free up more space, delete addresses that are no longer used. • You may consider adding an address from a user’s list to the appropriate organization-level list to improve filtering for all users, while freeing up space for that particular user. • For batch commandline information, see “How do I edit my Sender Lists for all of my users?” on page 18. Why do I get a “too many addresses” error when I add addresses to my Approved and Blocked Senders lists? If you get this error, you need to edit the number of senders in your lists: “You currently have too many addresses in your list. Try deleting old addresses which are no longer used to free up more space and then try saving your address”, • The list size is 4000 characters for each approved/blocked sender list and 1000 characters for an approved mailing list. You may consider adding an address from an user's list to the appropriate organization list to improve filtering for your user population, while freeing up space for the user. • Remember the list’s size includes address white spaces and commas. A comma has 2 characters: a space and a comma. Add these additional characters to get an accurate count of the list size. • As the email security service regularly improves filtering, many addresses which were previously placed in a blocked sender list at one point may no longer be necessary. What should I do when I attempt to add or remove an entry from my approved or blocked sender list and I get an error? If you are attempting to add or remove a user from your Approved or Blocked Senders lists and you get this error, contact customer support. “A request could not be completed because of a system error. Try clicking “Back” on your browser and reload that page”. Frequently Asked Questions 11 To resolve this issue, please contact Support. If you are a directly supported Postini Customer, please log in to the Postini Support Portal. Otherwise, contact your vendor, who can assist you. Provide customer support the Org ID, System #, User ID, and which list the user is having an issue with (ex. approved, blocked, etc.,) Why does my Approved Senders list allow extra addresses? The approval mailing list looks for a substring in the list of recipients. For example, adding [email protected] to the user’s approved sender list automatically approves messages that include “al”, such as: [email protected] [email protected] [email protected] [email protected] Why is a domain or address added to my Approved or Blocked Senders list not working? Either the domain or user address: • Was not added before the message arrived. • Was not added to the user or organization containing the user. • Was added to multiple lists. Actions to take: 1. Compare the received date of the mail message to the last modification date/ time for the user: a. Go to Orgs and Users > Users b. Type in the user address and select Search c. Select Settings Summary d. Look at the Modified column, and compare the date & time to those in the email message. (This assumes the last user modification was to the Approved or Blocked Senders list.) 2. Look at the user Approved or Blocked Senders list: a. Select the user b. Select Sender Lists c. 12 Check all lists to see if the Approved or Blocked Senders list is listed Message Security Troubleshooting Guide 3. Look at the organization’s Approved or Blocked Senders list: a. Select ‘View Org-Level Sender Lists’ b. Check all lists to see if the Approved or Blocked Senders list is listed Note: When using a Quarantine Redirect for either Spam or Virus messages, the address or domain needs to be added to the user Approved or Blocked Senders list, and NOT the sender list for the quarantine redirect address. For more information, see Quarantine Redirect and Approved/Blocked Senders. Is it possible to get a list of user aliases and a list of my Approved and Blocked Senders for my organization? To get a full list: 1. If the setting is an organization, go to Orgs and Users > Orgs. If the setting is a user, go to Orgs and Users > Users. 2. Select the User or Org in question. 3. Select ‘Sender Lists’ or, if a user, ‘Aliases’. 4. Select the browser menu option “View -> Source”.Search for the first item displayed in the list. You will see something similar to: <option><an approved sender name></option> <option><a blocked sender name></option> or <option><an alias name></option> 5. Select all items within that set of option tags, and copy the entire list to a text editor. 6. Remove the <option> and </option> tags. 7. Save the text file. Attachment Manager What are the file size limits for attachments? For Attachment Manager, the message size filter’s maximum limit is 300 MB. The default is 200 MB. This policy applies to all traffic, including mail which is not filtered for spam and viruses. When an attachment exceeds the size limit, the message is bounced, and the sender receives the SMTP error message, 552 Message too large - psmtp. Frequently Asked Questions 13 How do I limit the file sizes of inbound attachments? Edit the Message Size filter. For more information, see Message Size Filter section of Create/Edit Attachment Manager Filters. Why are large attachments being bounced, even when Attachment Manager is turned off? The Message Size filter is always in effect, even if Attachment Manager is off. For more information, see Message Size Filter section of Create/Edit Attachment Manager Filters. Does Attachment Manager filter viruses? No, messages and attachments are scanned for viruses before they pass through the Attachment Manager filter. Any messages with viruses are disposed of before reaching the attachment filters. If I do not want messages from certain senders filtered, what do I do? You can allow Approved Senders for an organization to bypass Attachment Manager filters by selecting the Approved Senders check box on the Attachment Manager configuration page. To find the Attachment Manager configuration page: 1. Go to Orgs and Users > Orgs and select an organization that contains your users. 2. Select the Attachment Manager icon in the Inbound Services section of the page. How do I block just one file type, like a MP3 file? As an administrator, add the file extension to the Attachment Manager’s Custom File Types filter. For more information, see Custom File Types Filter section of the Create/Edit Attachment Manager Filters. 14 Message Security Troubleshooting Guide Can I block all incoming attachments but still allow the message through? No. The message and the attachment are treated as a single unit by the email security service. What happens if a message has several attachments, but only one triggers an attachment filter? If only one attachment triggers a filter, Attachment Manager performs the disposition of that filter on the entire message, including all of the other attachments. Why can I see a message in my user’s quarantine when it should have been redirected to an administrator’s quarantine, or blocked by Attachment Manager? The email message contained a virus, and your virus disposition is set to User Quarantine. Because virus scanning takes precedence over other filters, messages with viruses are disposed of according to your virus disposition. An alternative is to set your virus disposition to Delete. For more information, see the Configure Virus Settings for an Organization section in the Configure Inbound Virus Blocking chapter. What do I do when I get an attachment disposition conflict? If two or more attachments in the same message trigger a separate filter with different dispositions (except Ignore), Attachment Manager places the message in the designated quarantine for the Quarantine Redirect disposition. That way, the administrator can review the message and decide what to do with it. For example: • In this example, the executables and ‘mm’ files are set to bounce. • The compressed files are set to user quarantine. • When these configurations have a disposition conflict, the correct behavior is files with disposition conflict should be directed to the Quarantine Redirect account. A disposition conflict is: • When a message with an ‘exe’ file inside a zip file is filtered, it is being sent to the Quarantine Redirect account. • When a message with a ‘mm’ file inside a zip file is filtered, it is being sent to user quarantine. Frequently Asked Questions 15 For more information, see the Attachment Filter Dispositions section of the Create/Edit Attachment Manager Filters. Batch Commandline Interface How do I set up the Message Center for all of my users? To edit the Message Center at the organization-level, edit the Default User: • Locate the organization’s Default User template and Message Center access. And, if needed, enable the Message Center access. For more information, see Editing Your Message Center Access and Settings. • displayorg Sales The displayorg command’s output has the Default User name: default_user [email protected] • displayuser [email protected] The displayuser command’s output gives Message Center access. This displayuser output shows the access is disabled. weblocked 1 • • modifyuser pdefaultSales2jumboinc.com, weblocked=0 Set the Default User template’s spam filter settings. modifyuser [email protected], junkmail_filter=on, filter_bulk=moderate, filter_adult=moderately-aggressive, filter_bulk=moderate, filter_getrich=moderate, filter_offer =moderate, filter_racial=moderate How do I edit Message Center notifications for all of my users? To edit the organization-level Message Center user notification contacts: • Edit the company name and support contact information used in notification messages. For more information, see Editing Message Center General Notification Settings. modifyorg Sales company_name=Jumbo Inc, [email protected] • Edit the Message Center user notification settings. modifyorg Sales, disable_first_spam=0, at_notify_on=”Send to Redirect”, out_at_notify_on=”Send to Redirect”, spam_notify_on=on, virus_notify=1 16 Message Security Troubleshooting Guide How do I edit Quarantine Summary notifications for all of my users? To edit organization-level Quarantine Summary notifications: • Enable the Quarantine Summary links. For more information, see Editing Quarantine Summary Notifications. modifyorg Sales, quarantine_links=on, quarsum_links=on • Edit the general Quarantine Summary notification settings. modifyorg Sales, qsum_actionable= ”basic delivery”, qsum_enable=on, lang_locale=en_us.utf8 • Edit the Quarantine Summary redirect notification settings. modifyorg Sales, qtine_redir_ndr= [email protected], qtine_redir_out_atq = [email protected], qtine_redir_out_virus = [email protected], qtine_redir_spam = [email protected], qtine_redir_virus = [email protected] Frequently Asked Questions 17 How do I find and display all of my organizations, domains, and users? To list and display all of your organizations, domains, and users: • List all of your organizations starting at a top-level org and display each organization’s settings. For more information, see Listing the Organization Hierarchy. • listorgs ALL, targetOrg=Sales, childorgs=1 This examples has 3 organizations: orgname Sales ... orgname WestCoast ... orgname EUSales ... • displayorg Sales displayorg WestCoast displayorg EUSales • List all of your domains starting at a top-level org and display each domain’s settings. • listdomains ALL, targetOrg=Sales, childorgs=1 This example has 2 domains: domainname jumboinc.com domainname hugeIPS.com • displaydomain jumboinc.com displaydomain hugeISP.com • List all of your users (without the aliases) starting at a top-level org and display each user’s settings. • listusers ALL, targetOrg=Sales, aliases=0, childorgs=1 This example has 2 users: address [email protected] address [email protected] • display [email protected] display [email protected] How do I edit my Sender Lists for all of my users? To add users or domains to your Sender Lists: • 18 Edit the organization’s Approved Senders and Blocked Senders lists. Message Security Troubleshooting Guide For more information, see Adding Users and Domains to Sender Lists. • modifyorg Sales, approved_senders=”[email protected], [email protected]” • modifyorg Sales, blocked_senders=”[email protected]” How do I edit my message limit policies for all of my users? To edit the maximum size of attachments, the maximum number of messages per day, and for the message total each user has recieved: • Edit your organization’s message limit fields. For more information, see Editing Your Message Limit Policies. modifyorg Sales, max_message_size=250, outbound_max_message_size=250, default_message_limit=1000 • Edit the maximum number of messages allowed a user per day, and display the user’s present message count and whether the user has reached the allowed message limit. • modifyuser [email protected], message_limit=1000 • displayuser [email protected] This displayuser command’s output shows: message_count 16 message_limited 0 (no) Frequently Asked Questions 19 How do I edit my Message Archiving settings for all of my users? To display an organization’s archive settings, modify these settings, and disable the Message Center links: • Confirm your organization’s archive setting is enabled and display the archive settings. For more information, see Editing Message Archiving Settings. • displayorg Sales This command’s output shows: archive on • archive_settings display Sales This command’s output shows: Executed Without Incident Message Archiving Settings for Sales: Archive Enable on Mail Flow on Journaling off • Edit the organization’s archive settings and disable the Message Center Quarantine Summary subject links. • archive_settings modify archive_settings modify org=Jumbo ABC, archive_enable=on, mail_flow=on, journaling=on • modifyorg Sales, quarantine_links=0, quarsum_links=0 How can I get a list of all of my users’ aliases and primary addresses? To get all aliases for one user, list a user’s primary address and associated aliases throughout an org hierarchy, and get the user’s primary address from a user’s alias: • List all aliases for a user. For more information, see Listing User Aliases and Primary Addresses. listusers ALL, [email protected], targetOrg=100046262, childorgs=1, aliases=1 • List all primary addresses and associated aliases. listusers ALL, targetOrg=MyAccountOrg, childorgs=1, fields=PRIMARY_ADD|ADDRESS, aliases=1, sort=primary_add:nd • List a user address from an alias. listusers [email protected], targetOrg=200046262, childorgs=1, aliases=1, fields=ADDRESS|PRIMARY_ADD 20 Message Security Troubleshooting Guide How do I modify all users in a domain? To make changes to all users you will need to adjust the individual user records, as well as the default user (the template for new user creation). This is performed most efficiently by creating a batch file using the modifyuser command: 1. Go to Orgs and Users > Users and select your Account org from the Choose Org pull-down list. 2. Type in the “%” character and then the domain name and select Search. 3. This performs a search across all of your organizations for user addresses using that domain, returning the first 15,000 users. 4. Select Download User/Settings. 5. Select and copy all of the lines that have email addresses on them. 6. Open a text editor (if using Microsoft Untapped, turn word-wrap off) and paste the text. Save the file using the file extension “.csv”. 7. Using a standard spreadsheet program, such as Microsoft Excel, open the .csv file saved in step 5. a. Delete all columns except the one containing the email addresses. b. Add a column to the left of the addresses column. c. Fill that column with the word: modifyuser d. In as many columns as necessary to the right of the addresses column, type in field=value pairs. e. Save the file again as a .csv file. 8. Load the file created in step 6 into a text editor and replace all occurrences of “modifyuser” with “modifyuser”. Save result as a .txt file. 9. You can now validate this file and upload it as a batch file. See “Introduction to Batch Processing” in the Batch Reference Guide for details on how to submit the batch command. How do I delete all users in a domain? Use the steps in the “How do I modify all users in a domain?” FAQ to create a batch file which uses the deleteuser batch command instead of the modifyuser command. Note: Default users cannot be deleted in this way. For more information, see Manage Default User Templates. Frequently Asked Questions 21 Connection Manager What is Manual Pass Through and how do I use it? Connection Manager detects servers that send a large amount of invalid mail spam, viruses, mail bombs or directory harvest attacks -- and blocks all mail from those senders. This prevents a load on your server and shuts down malicious senders. On rare occasions, Connection Manager can accidentally detect such an attack when the sender is legitimate. Examples are an opt-in mailing list or company newsletter may look like spam and get blocked, or another mail server might be deliberately set to redirect traffic to your primary mail server. If Connection Manager blocks all mail from an IP address you know is good, create a Manual Pass-Through to prevent Connection Manager from blocking a particular sending IP address. Also, do not set up a Pass Through for your contact lists, because this could create performance problems. Instead, set it up only if Connection Manager is blocking bulk mail that you know is valid. Note: Since messages are still filtered for spam and viruses, this is not the same as an approved senders list or white list. How do you locate the IP address of a server that has opened a long time-duration TCP/IP connection to your mail server? 1. From the Administration Console, go to the Organization pull-down list or the Show Hierarchy window, to select the appropriate email server config for the server that is being probed. 2. Select the Inbound Servers tab. The Connection Manager page appears. 3. Select the View Sender Specific Data link near the top right corner of the page. The IP you are looking for will have an extremely long ‘Avg. Duration’ time and possible ‘Msg. Size’of 0. Content Manager How do I use regular expressions in Content Manager rules? Regular expressions are a standard tool in many systems and scripting languages. For more information, see About Using Regular Expressions. 22 Message Security Troubleshooting Guide How do I catch messages that contain specific language characters? Set up a Content Manager rule that: • Looks for the language character set in the ‘font’ tag in the message header • Quarantine the message based on this criteria Note: If you need to quarantine all messages in this language, this rule will quarantine all messages with this character set. If your mail flow in this language includes good messages, this Content Manager rule is not as helpful. In this case, the rule creates a high percentage of false positives. When I create a content filter rule with a full file name for the value and a location of the ‘Entire Message’, why did the filter not capture messages that contain attachments with that file name? Content Manager does not scan the file name of attached files. Not all email programs include the names of attached files in the headers. If the file name does not appear in the headers, Content Manager will not capture the message. When I create filter rules, why does Content Manager capture messages that do not contain any of the words, phrases, or patterns in my rules? If the message contained a file attachment, the value you specified in the filter rule might appear in the attachment. In this case, the filter rule will not capture the message, unless you select Entire Message for the rule location. Delivery Manager What does “Graph Not Available” mean in the Inbound Servers Overview page? Activity graphs do not become available until the first mail is processed. In the meantime, the text "Graph Not Available" is displayed. After messages start being processed, the "Graph Not Available" display will appear during service updates and infrequently in the event that graphing processes are restarted. Note: Mail flow is best checked by examining your mail server logs and/or sending test email messages to your server from an external resource. Frequently Asked Questions 23 For additional information, see the “How do I read the Delivery Manager graphs?” FAQ. How do I read the Delivery Manager graphs? The Delivery Manager View page gives you a summary of connection and event activity for an email server config over the past 60 minutes and 60 seconds. The data displayed on this page is updated every few seconds but the page does not automatically refresh itself. Refresh the browser window to refresh the data. With access to Delivery Manager Message Traffic Graphs, it is easy to determine what traffic is following through the email security service. 1. In the Administration Console, select the appropriate email server from the pull-down list or the Show Hierarchy window. 2. Select the Inbound Servers tab, then the Delivery Manager link. The Message Traffic Graph appears. The graph will show whether or not traffic is flowing through the email security service: • Gray Bars -- Total attempted connections. Each gray bar represents one minute. • Dark Red Lines -- Failed connections • Light Green Lines -- Spooled connections • Any other color lines -- Delivered connections. See the legend on the graph for details about which line refers to which IP. Note: The Current Activity box in the upper right-hand corner of the Delivery Manager overview page also shows statistics for the current email server config. For more information, see the “What does “Graph Not Available” mean in the Inbound Servers Overview page?” FAQ. After changing my ISP, how do I change where the email security service delivers my mail? Edit your Delivery Manager’s Email Servers field in the Inbound Servers tab to update your email server’s hostname or IP address. For detailed information, see Setting up Delivery Manager. If I forward my mail, do I need to change the host name to reflect the change in IP address? No. Your mail is processed through the email security server before your mail server forwards the messages. 24 Message Security Troubleshooting Guide What should I do after moving my domain to a new mail server? For a new mail server or ISP, change the Delivery Manager’s email server address. For more information, see Setting Up Delivery Manager. Note: If the domain remains associated to the same user organization, the only change is the updating of the email config organization. If the domain is moved under a different email config, see Move a Domain. What happens if my connections goes over my connection limit? If you have several servers, make one a failover server. Otherwise, the sending server tries again to connect with your mail account. For more information about enabling a failover server event and related system alerts, see Events. Why are some of my Message Center emails delivered and others are not? There could be more than one cause: 1. Check your organization’s and your user’s Daily Message Limit. When exceeded, your incoming messages are bounced. For more information, see Set an Organization’s Message Limits. 2. The filters may have given a high spam score to the missing messages, and your Blatant Spam Blocking disposition is set to ‘black hole’. For more information, see Configure Spam Settings for an Organization. What does it mean if “Open Conn. = n/a” when a Conn. Limit is set through the Inbound Server’s Delivery Manager page? This means that the process which lists the number of simultaneous connections died. To request that this be reset, please contact Support. If you are a directly supported Postini Customer, please log in to the Postini Support Portal. Otherwise, contact your vendor, who can assist you. If no Conn. Limit is set, then the number of Open Conn. will not be listed. Frequently Asked Questions 25 Can I limit connections to my mail server so that my mail server does not go down due too much incoming mail? Yes, you can use Delivery Manager to impose connection limits. For detailed information on how to edit the Conn. Limit field, see the Conn. Limit field section in the “Setting up Delivery Manager” chapter. How do I remove persistent connections without rebooting? You can use Delivery Manager to impose connection limits. For more information about configuring the Conn. Limit field, see Setting up Delivery Manager. Domain How do I add another domain? Your service is initially set up for users in one domain. The domain resides in your initial user organization. To filter mail for a second domain, you must add the domain to one of your user organizations. For detailed information, see Add a Domain for Filtering. For more FAQ information, see the “When should I add a domain and when should I create a domain alias?” FAQ. When should I add a domain and when should I create a domain alias? If two or more of your domains share the same user lists, set up a domain alias. First add your users to the primary domain, and then set up domain aliases for the other domains. Creating domain aliases for duplicate user lists reduces your administrative maintenance load. You do not have to maintain duplicate lists and previous mail addresses are automatically forwarded. For example, if your company acquired another division, you would create a primary domain for the new division and you would make the old division’s domain an alias since they have the same user lists. For more FAQ information, see the “How do I add another domain?”, and “How do I add a domain alias?” FAQs. How do I add a domain alias? You can create domain aliases if the domains share the same user list. For detailed information, see Add a Domain Alias. For more FAQ information, see the “When should I add a domain and when should I create a domain alias?” FAQ. 26 Message Security Troubleshooting Guide How do I delete a domain? Before deleting a domain, make sure all users, user aliases, and domain aliases have been deleted. For more information, see Delete a Domain. What do I do when I get this error “Unable to add domain.”? For the errors “Unable to add domain 'domain.com'.” or “[email protected] clashes with an existing address or alias”, the domain is hosted by another email security service customer. Specifically, you get these errors when: • The new domain or user does not currently exist in any of your organizations, and the user address is not an alias to an existing registered user. • If the domain or user was previously hosted by another customer, the domain or user is still in the system under the other customer's hierarchy. In these cases, the system returns errors. The system will not allow domains or users which are not unique across all of the email security service production systems. Ask the former owner of the domain contact the DNS provider to remove the domain or remove the user from the email security service so you can update your hierarchy. How do I set up my mail to go to a new domain, and forward mail from my old domain? First add the new domain, and then make the old domain an alias to your new domain. For more information, see Add a Domain section of the “Add a Domain for Filtering” chapter. And for more information about domain aliases, see Domain Alias. Now that I have added a new domain and changed my MX records, how do I confirm that my mail server can accept messages from the email security service? If you have recently changed your MX records, you must wait for the propagation of these changes to be completed through out the Internet. After these updates are completed using the SMPT Message test. For more information, see the “How can I tell if the MX change worked” question in the Activation Step-by-Step Guide. And for more information about the SMTP Test, see SMTP Message Test. Frequently Asked Questions 27 Message Center What should I do if I forgot my password? If you forget your password, you can enter an incorrect password at the login page. A “Forgot Your Password link” appears that you can select to have a new temporary password mailed to you. For more information about Message Center passwords, see Set Message Center Passwords. Why do some logins fail even though my administrator login and password are correct? After a failed login, a 5 second delay occurs during which additional logins are not accepted by the system, even if login information is typed correctly. Wait a couple of seconds and try again. Why does my login fail? I get the error message: “Your authentication could not be verified.” Either the browser’s cookies are disabled, or the session has timed out. 1. Log out of the Message Center. 2. Re-enable your cookies. 3. Log in again. Why does my login fail with an “Invalid log in...” message? If the error message is: Invalid log in or server error. Please try again. Forgot your password? Your password is the same as your email account password. Contact your email service provider for assistance. This happens when Message Center Access is disabled for a user. To enable Message Center Access: 1. Go to Orgs and Users > Users and select the user 2. Select User Access in the User Settings section of the page 28 Message Security Troubleshooting Guide 3. Set Message Center Access to Enable and select Save Note: If using POP Authentication, this error can also be caused by incorrect configuration of the Authentication Data string. For examples of Authentication Data configuration and testing information, see POP Authentication Configuration Examples. How do I change a password? An administrator can reset a user’s Message Center password. For detailed information, see Reset a User’s Password. How do I fix my Message Center access? A user’s Message Center access is managed under the User Access settings. For detailed information, see Enable/Disable Message Center Access. For Batch Commandline Interface information, see “How do I set up the Message Center for all of my users?” on page 16, and “How do I edit Message Center notifications for all of my users?” on page 16. Why is my Message Center slow or sometimes unavailable? There is either a network issue between your ISP and the data center server, or the data center is experiencing a high-volume or slow performance situation. The data center is designed to prioritize good email traffic over quarantined email in suboptimal conditions such as these. This ensures prompt delivery of valid email traffic regardless of Message Center availability. In event of such a slowdown, try logging in later the same day. Such issues rarely last a long length of time. Why does my Message Center put messages in a disabled quarantine category? The message was: • Of the category type, even though the category is off and not part of the filtering process. • Quarantined due to its Bulk Email rating. Frequently Asked Questions 29 Why can I not delete more than a 100,000 messages in the Message Center? If more than 100,000 messages are quarantined in Message Center for a user, the Delete All button on the Junk, Trash, and Delivered tabs is removed automatically. This helps prevent performance issues in the new Message Center. Message Recovery How do I set up email archiving? When setting up Message Recovery, the basic steps are: • Choose an archiving option • Optionally, configure your Outbound service • Optionally, set up your organization hierarchy • Turn on archiving • Optionally, set up journaling For more information, see About Setting Up Message Archiving. For batch commandline information, see “How do I edit my Message Archiving settings for all of my users?”. Why is my archive empty? The most likely reason for an empty archive is you have not yet activated your email security service. For details about activating your service, see the Activation Step-by-Step Guide. What are all the things I can do with my archive? After you log in to your archive, you can: 30 • Search for archived messages • View the content of archived messages and attachments • Print archived messages • Recover (export) archived messages to your Inbox Message Security Troubleshooting Guide How do I access my message archive? To access your archive, you'll need your user name and password for your email security service. When activating your service, you provided this user name (the email address you use to log in to your email account) and set your password. 1. Go to https://login.postini.com 2. Log in to your email security service. 3. Select System Administration. 4. Select the Orgs and Users > Orgs. 5. Select a user organization in your organization hierarchy. 6. On the Organization Management page, under Organization Settings, select Archiving. 7. On the Archive Settings page, select Message Archiving. How do I search for messages? To search for messages, you enter the search criteria on a search panel. For example, you can enter a date range, the email address of the sender or recipient, and text that appears in the message subject line or body. The more criteria you enter, the smaller the set of messages Message Recovery retrieves. For more information, see Search and Discovery Options. Who can search for messages in my archive? Initially, one user account has access to the archive. This account is the administrator account that you set up when activating your email security service. However, this administrator can grant the archive "search" privilege to other users who have accounts on your service, by creating an authorization record. For more information, see About Archive Privileges. How do I view messages in the archive? After you retrieve messages from the archive, Message Recovery presents the results as a list of message summaries. To view the content of a message in the list, click its subject link. Frequently Asked Questions 31 Why can I not find a specific message in the archive? If you can't find a specific message in the archive, the reason might be one of the following: • The date range on the search panel is incorrect. • There's a typographical error in the search text you entered. • The search text you entered includes only parts of words instead of complete words. • The message hasn't been archived yet—it may take 30-60 minutes for a message to appear in the archive. How do I recover (export) messages from the archive? In your search results list, do the following: 1. Select the check box for one or more messages. 2. In the Actions menu (at the upper-left side of the page, select Export Selected Messages. 3. In the dialog box that appears, select Email as attachments. Why does my archive contain duplicate messages? Message Archiving does not check for duplicate journaled messages received from your email server. In most cases, your email server journals only one copy of any message. For example, Microsoft Exchange Server journals only one copy any message that a user sends to multiple recipients or that multiple users receive. For details about duplicate message handling during the journaling process, refer to your email server’s documentation and support resources. Note: If you set up journaling on two or more email servers, multiple servers might journal a separate copy of the same message. In this case, Message Archiving would store multiple copies of the message. 32 Message Security Troubleshooting Guide MX Records and IP Addresses What are the IP addresses for the email security service? The following are the IP ranges for the email security service. Note, for system 20 customers, both sets of IP ranges are applicable. System IP Range CIDR Range IP/Subnet Mask Pair 5, 6, 7, 8, 20 64.18.0.0 64.18.15.255 64.18.0.0/20 64.18.0.0 mask 255.255.240.0 20, 200, 201 207.126.144.0 207.126.159.255 207.126.144.0/ 20 207.126.144.0 mask 255.255.240.0 For information on how to find your system number, see IP Range. What are DNS MX records? When your domain is registered, it is assigned several DNS records, which enable it to be located on the Internet. These include MX records, which direct the domain’s mail flow. Each MX record points to an email server that is configured to process mail for that domain. There is typically one record that points to a primary server, then additional records that point to one or more backup servers. For users to send and receive email, their domain's MX records must point to a server that can process their mail. To filter messages through the email security service, you must insert new records that instead point to the service’s servers. For more information, see the Activation Step-by-Step Guide’s How MX Records Work FAQ. How do I find the DNS information in the Administration Console? The DNS instructions can be found in your organization’s settings page. For additional information, see Changing MX Records for a Domain. What is the correct syntax for updating my MX records? The exact steps and syntax vary depending upon the domain host you use. For more information, see “What’s the format of a MX record?” question in the Activation Step-by-Step Guide’s How MX Records Work FAQ. Frequently Asked Questions 33 And for detailed examples of the more common domain hosts, see Changing MX Records for a Domain. Why is the priority of MX records important, anyway? Inserting the new MX records at a higher priority than your existing records directs mail flow to email security servers where it can get filtered, instead of sending it directly to your mail server where no filtering occurs. An MX record consists of three parts: the domain name, a priority, and an email host. The priority indicates which record gets looked at first when determining where to route a message sent to the domain. Normally, the primary server named in the record with the highest priority, is used. But if that server is not available, the next highest priority’s record is evaluated, which is typically a backup server. And so on. For more information, see “What’s the format of a MX record?” question in the Activation Step-by-Step Guide’s How MX Records Work FAQ. What if my domain’s MX records are not prioritized using a 1 through 4 numbering scheme? Priority is often indicated using the numbers 100-600, where 100 has the highest priority. But if your DNS service prioritizes them differently, for example using a 16 numbering scheme, or a 10-60 numbering scheme, that is OK, too. You can use any scheme, as long as the new entries are inserted at a higher priority than any existing entries. When inserting the email security service MX records, we recommend using a number scheme of 1 through 4. For more information, see “Why do I need four separate MX records?” question in the Activation Step-by-Step Guide’s How MX Records Work” FAQ. What is a TTL setting? When you change a domain’s MX records to point at a different server, the change does not take effect immediately. Instead, it has to propagate throughout the Internet. How long this takes can depend on the current TTL, or Time to Live setting. This is typically measured in seconds, so a TTL of 3600, for example, means it might take up to an hour for the changed to propagate. Shortening the TTL can make the change propagate more quickly. For more FAQ information, see the “About MX Record Propagation” information. For more information, see “What’s the format of a MX record?” question in the Activation Step-by-Step Guide’s “How MX Records Work” FAQ. 34 Message Security Troubleshooting Guide Will I lose mail when I change my MX records? No. While your MX record information is being propagated, your Inbox continues to get mail delivery. Once the MX record update is completed, temporarily, your Inbox has a mix of messages sent before the update and messages filtered by the email security service. For more MX record information, see the Activation Step-by-Step Guide’s “How MX Records Work” chapter. In addition, see the “How long does it take to change my MX records?” FAQ. How long does it take to change my MX records? It depends upon your domain host requirements. But usually the longest part of this process is the propagation of your MX record changes throughout the Internet. How long this takes depends on the current Time to Live setting (TTL). This is typically measured in seconds, so a TTL of 3600, for example, means it might take up to an hour for your MX record changes to propagate. When editing your MX records, it is good practice to change your MX record’s TTL field to 900 seconds (15 minutes). Remember this change takes the previous TTL time period before the 15 minute TTL is in effect. But, once the 15 minute TTL value is propagated, it is easy to make your MX record edits and run your system tests. Once your MX record edits are validated, you can change your TTL field to an optimal time period. While your MX record information is being propagated, your Inbox continues to get mail delivery. Once the MX record update is completed, your Inbox has a mix of messages sent before the update and messages filtered by the email security service. For additional MX record information, see the Activation Step-by-Step Guide’s How MX Records Work FAQ. About MX Record Propagation Your DNS provider manages the master copy of your MX records. When someone sends you mail, the Internet locates your address on your DNS server. In this process, the sending mail server keeps a copy of your email address just in case it needs to send you another message. Specifically, your MX record information is cached on the sending server so that your DNS server is not overwhelmed with Internet requests. How long does a sending mail server keep a copy of your address? As long as the copied MX record’s Time to LIve field (TTL) is current, the sending mail server continues to send messages to your address. When this server has new mail for you and your TTL has expired, the sending mail server goes back to your DNS server for updated MX record information. This means that it will take your updated MX record a full TTL time period to propagate changes to all of the various mail servers sending you messages. Frequently Asked Questions 35 For more MX record information, see the Activation Step-by-Step Guide’s How MX Records Work FAQ. For additional information about TTL, see the “What is a TTL setting?” FAQ. What should I do if the MX record test fails after just changing my MX records? If your MX Record Test failed, the test’s error message gives you troubleshooting information. For more information about the error message, see Error Messages and Next Steps in the “MX Record Test” chapter. What do I do if my mail is not being delivered? There are several things that can impact your mail flow: 1. Confirm your Delivery Manager configuration is correct. For information, see Verifying Email Flow. 2. Make sure your MX records are pointing to the correct system cluster. For finding your system cluster, see IP Range. For more MX record information see the Activation Step-by-Step Guide’s How MX Records Work FAQ. 3. Follow the troubleshooting mail flow instructions in Why am I not getting any mail at all?. Notifications and Alerts Do I need to verify a notification address? Yes, as good practice, you need to verify these addresses. The email security service does not validate the notification address. But if the receiving mail server has been configured to check the validity of the sending address that could cause your notifications to fail. What should I do when my notifications fail to be delivered? Some suggestions are: 36 • Check to see if your mail server has had any recent filter changes. • Check to see if any of your mail server’s spoofing filters are blocking the notifications. Message Security Troubleshooting Guide In addition, see the “Why do my customer notifications get bounced?” FAQ. Why do my customer notifications get bounced? Your template does not include the Date, To, From, and Subject headers listed in the default templates. The template headers are used when generating your notifications. Since the headers are common to all email messages, their absence causes your mail server to reject your notifications. For more information, see Default Notifications with Tokens. I am not getting spooling notifications (alerts). How do I fix this? Edit your Spool Manager alerts configuration on the Inbound Servers area of the Administration Console. For more information, see Setting Up Alerts. Can I set up spam notifications to a single user and not the organization? No. Notifications are configured organization-wide. The only user specific notification you can change is the ‘Notice Address.’ If you are managing this user’s service, you, the system administrator, can specify your address as the destination for this user’s notifications. For more information about disabling and redirecting notifications, see Disabling and Redirecting Notifications. Can my users change the frequency of their own spam summary notification? No. Notifications are configured organization-wide. The only user specific notification you can change is the Notice Address. For more information, see Configuring Notifications for an Organization. Why are my new users getting welcome notifications? I did not check the ‘Welcome users upon creation’ option. Unchecking the ‘Welcome users upon creation’ box means a welcome message is not sent immediately to the new user. This does not disable the ‘Welcome New User’ notification which, if enabled, the user receives in 24 hours. For more information, see the Welcome New User section of the Configuring Notifications for an Organization. Frequently Asked Questions 37 How does a user get access to the Message Center after receiving a quarantine summary? The Quarantine Summary links to the Message Center for each individual message. For more information, see Accessing Messages from the Quarantine Summary section in About Quarantine Summary. Why am I not getting my quarantine summaries? There could be several reasons. Some examples are: 1. Your mail account has not received new spam so there is nothing to quarantine. 2. Your Quarantine Summaries are being redirected. For more information about Enabling Quarantine Redirect, see Disabling and Redirecting Notifications. Can my group’s quarantine summaries be sent to one person instead of everyone? Yes. You can redirect your organization’s quarantine summaries, ‘My First Spam’, or the ‘New Spam’ notifications to a specific user. An exception is in the situation where a user has some unread quarantined messages before you configured the Redirect. For more information about Enabling Quarantine Redirect, see Disabling and Redirecting Notifications. Can we configure the email security service to send out the quarantine summary twice a day (morning and evening) to users. No. The minimum alert time frame is one day. From talking to a wide range of customers, we found the optimal spam notification intervals are between three to seven days. Fewer than every three days is considered a nuisance by some users and more than seven days does not leave enough notice to review quarantined messages before the system automatically expires your messages (two weeks from the time of receipt). For more information, see the Spam section in Configuring the Quarantine Summary. Is it possible to disable quarantine summary notifications for individual users? Yes. Configure your user’s Notification Address. For more information, see Configuring Notification Addresses in Disabling and Redirecting Notifications. 38 Message Security Troubleshooting Guide How do I change the quarantine summary’s sender email address and name? The Quarantine Summary Sender is your organization’s ‘Support Contact’ which can be edited in the organization’s General Settings page. For more information, see Organization General Settings. For information about the corresponding batch commandline steps, see “How do I edit Quarantine Summary notifications for all of my users?” on page 17. For my quarantine summary, how can I change the name of the company appearing in my notification’s ‘From’ header? The notifications use the value of the ‘Customer Name’ field which is specified per organization. If you are customizing notifications, this field corresponds to the token, <-isp->. To change the name in the ‘From’ field of the notifications: 1. In the Administration Console, go to the Orgs and Users > Orgs. 2. Choose the organization from the Choose Org pull-down list, or select the name of an organization in the organization list. 3. In the Organization Management page, scroll to the Organization Settings section and select General Settings. 4. Change the Customer Name field and select Save. 5. To change the email address as well, change the Support Contact settings, see Default Notifications with Tokens. For Batch Commandline Interface information, see “How do I edit Message Center notifications for all of my users?” on page 16, and “How do I edit Quarantine Summary notifications for all of my users?” on page 17. When building customer quarantine summary notifications, why are header fields such as Date, To, From, and Subject put into the body of the mail message? This happens when the field which contains the custom notification has an extra line break. This line break can between two fields or above the first field in the text input field which contains notification text. According to the SMTP RFC 2821, section 2.1, there is a <CRLF> (Carriage Return, Line Feed) character right at the beginning of a new line between the headers & the body of a message. Remove the extra <CRLF> to resolve the issue: 1. In the Administration Console, go to the Orgs and Users > Orgs. 2. Choose the organization from the Choose Org pull-down list, or select the name of the organization in the organization list. Frequently Asked Questions 39 3. In the Organization Management page, scroll to the Organization Settings section and select the Notifications icon. 4. Select the name of the affected notification. 5. Look for a line break at the top of the notification template. or between two of the header lines near the top of the template. 6. Remove the line break and select the Save Text button. For more information, see About Customizing User Notifications. What happens if I have more quarantined messages than can be displayed at one time in my Quarantine Summary? I am using Quarantine Redirect to quarantine all of my users’ spam and virus in a single administrator’s quarantine. If you have too many users are in the org to conveniently manage all their diverted messages from a single Quarantine, divide the users into sub-orgs underneath the original org. Then assign each org a separate Quarantine Redirect address. For more information, see Manage Quarantined Messages. Organizations When do I need to add more organizations? Initially, your service is set up with one user organization. This is sufficient if all of your users require the same filtering, services, and administrators. If your business requires a different organization hierarchy strategy, see Plan Your Organization Hierarchy. For additional information, see the “How do I add a new organization?” FAQ. How do I add a new organization? Go to the parent organization’s Management page and add a New Org. For more information, see Create an Organization. For additional information, see the “When do I need to add more organizations?” FAQ. 40 Message Security Troubleshooting Guide How do I delete an organization? Deletion of a large, complex organization, can be done after these steps are completed: 1. Confirm you have full administrative authorization privileges for this organization and any related organizations. 2. Clear any quarantine summary redirect addresses. 3. For email config organizations, clear the spool allocations. 4. Clear any references to users and domains residing outside of the organization. Clear any of the organization’s users or domains referenced by other outside organizations. For example clear your support contact, Attachment Manager, and Content Manager redirect addresses. 5. Delete users and related aliases. This includes any default users. 6. Delete domains and related aliases. 7. Delete sub-organizations. 8. Once these steps are completed, locate the organization in the Organizations page, and select Delete Org. For more information, see Delete an Organization. Can I create a new email config with the same settings as my other email config organizations? Email config organizations can be configured with similar settings. But each email config organization must be set up individually. For more information, see Creating an Email Config. Outbound Servers What is reinjection? Reinjection is necessary to avoid unexpected mail loss for a message sent to multiple recipients. Reinjection is the process of queueing a message back to the customer’s server when it cannot be delivered due to conflicting SMTP errors after DATA. For more information, see Set Up Reinjection in the Outbound Services Configuration Guide. In addition, see the “What happens if reinjection fails?” FAQ. Frequently Asked Questions 41 What happens if reinjection fails? If reinjection fails, the message is deferred to all recipients. This means that any recipient who did receive the message during the original transmission receives duplicates of that message. Some mail servers may compensate for these duplicates. In addition, see the “What is reinjection?” FAQ. What is a smarthost? A smarthost is a common term for a server that accepts outbound mail and passes it on to the recipient. For more information, see Set Up Smarthost in the Outbound Services Configuration Guide. Why does my compliance footer not show up? The messages were associated with an organization that does not have the compliance footer configured. For more information on how a message is associated with an organization, see Configuring Outbound Servers. How can I use one IP range for outbound servers for multiple server configurations? Break up the IP range into smaller ranges and associate those ranges with the appropriate email config. For more information, see About IP Ranges and Security. How do I remove an Outbound IP Range? Edit the outbound email server’s IP range found on the Outbound Servers page in the Administration Console. For more information, see Deleting an Outbound Servers Entry section in Setting Up Outbound Filtering. What is this error? “A reinjection host is required.” You get this error either: • 42 The reinjection functionality is not enabled. Message Security Troubleshooting Guide For more information, see Set Up Reinjection in the Outbound Services Configuration Guide. • When removing an Outbound Email Server by deleting all entries under Accepted IP Range and Reinjection Host. To fix follow these steps: 1. In the Administration Console, choose the appropriate email config organization and select the Outbound Servers tab. 2. Select the Outbound IP range to be removed by selecting on the IP range under the gray Status bar. 3. Delete the entries under Accepted IP Range. 4. Leave the entries under Reinjection Host. 5. Select the Submit button. This will successfully remove both the IP range and associated Reinjection Host. Why do I see an error message, “Can’t find account level org above mail hosts.”? There is a problem with your account’s organization hierarchy. Contact Support. If you are a direct Postini Customer, log into the Postini Support Portal. Otherwise, contact your vendor, who can assist you. Reports Since I am just getting started, what are the most useful reports? When you are first setting up, we recommend: • Inbound Traffic by Domain Report -- Gives detailed inbound information including the total number of messages received or blocked. For more information, see Traffic by Domain Report. • Outbound Traffic Activity Log -- Gives detailed data for outgoing messages during the past 20 minutes. Frequently Asked Questions 43 For more information, see Outbound Reports. Why does my report data seem out of date? Your report data is based on data from the previous day. The report shown is the latest report available. Generally reports for the previous day are available around noon (or earlier) Pacific Time the next day. The exact time of availability fluctuates with quantity of traffic processed. Why does a domain show up in an organization report when the domain is not located in that organization? There is at least one address in that domain which is aliased to a primary user record in the selected organization. For example: • The user, [email protected], and the domain, domain.com, are registered in the organization “Corporate”. • The user, [email protected], has an alias, [email protected]. • The domain, domain.net, is registered in another organization, “Internal”. Quarantined messages for [email protected] count as statistics for the Message Center of [email protected], and therefore count towards domain.com. How can statistics on falsely quarantined emails be determined? An organization's ‘Spam by Account’ report shows totals on the number of messages delivered from each user's Message Center. The totals include both falsely quarantined e-mails, and junk e-mails which the user wants delivered. 1. Select the Reports tab. 2. Select Spam by Account report. 3. Look at the “Delivered from Quarantine” column. 4. Optionally, select the ‘Download link’ in the upper right-hand corner of the report window. This report shows all statistics for the organization beneath the selected organization. 44 Message Security Troubleshooting Guide What is the difference between Messages and Account Messages in my reports? The Messages number includes all messages passing through the system that are accepted by your mail server. The Account Messages (Acct Msgs) only counts messages sent to registered accounts and aliases. Any discrepancies are accounts which the receiving mail server returns a 550 user unknown error, or accounts which an administrator has specifically chosen not to add to the email security service. What is the difference between Blocked Senders and Blocked Servers in the Spam Reports? Blocked Senders are messages quarantined because the specific sender address was listed in either a user-level or org-level Blocked Senders list. Blocked Servers are messages quarantined because the message’s domain was listed in a Blocked Senders list as a domain, not a specific user address. Why is Content Manager appearing on the Reports tab? I do not have inbound Content Manager configured. Probably, you have outbound Content Manager configured. Inbound Content Manager is included with outbound Content Manager, so configuring outbound Content Manager causes inbound Content Manager to appear on the Reports tab. This applies to inbound and outbound Attachment Manager configurations as well. Spam Do I need to filter for specific types of spam? In general, the Blatant Spam Blocking, which deletes most obvious spam, and the Spam Disposition, which determines how spam messages are managed for your organization, are the most efficient spam configurations. For more information, see Configure Spam Settings for an Organization. When filtering for specific types of words, phrases, or text patterns, use the Content Manager Filters. These filters scan your messages and then take action on messages that contain these specific text. To use the Content Manager, you must first configure it for your organizations, create your custom filters, and set up your compliance policies. Frequently Asked Questions 45 For more information, see About Content Manager. Why are these spam messages not being filtered? If too much spam is getting through: 1. First confirm that the message was not filtered. Search the message headers for X-pstn-levels header.If this header is present, the message was filtered for spam and the header shows the filter scores. For more information about this filter, see X-pstn_levels Header. 2. Confirm the user is registered to the email security service by searching for the user in your organization hierarchy. If the user is not registered and NonAccount Bouncing is disabled, unfiltered mail is being delivered to this user. The best practice recommendation is to add this user to the service since this is the most common reason for getting unfiltered spam messages. 3. Confirm the user’s Filtering Status is enabled on the user’s Spam Filtering page. 4. Disable the Spam Filters ‘Modify’ setting for your organization-level User Access page to prevent new users from turning the Spam Filtering setting off. For more information, see Control What Users Can View and Modify. 5. Confirm the user’s Bulk Email and other filters on the Spam Filtering page are set high enough.For more information, see Fine-Tune Spam Filters. 6. If the message was sent to a distribution list or mailing list, confirm the list is registered with the email security service as a user or user alias. 7. If the message was directly accepted by your mail server, it bypassed the email protection service. Some of your mail server’s MX records are not mapped to the email protection service. For more MX record information see the Activation Step-by-Step Guide’s How MX Records Work FAQ. 8. If your email server is configured to deliver intranet mail locally, messages exchanged amongst users on the same server are not processed by the email protection service. 9. Confirm the sender and the sender’s domain are not in the org-level and userlevel Approved Senders lists. Senders on these lists are delivered regardless of spam-like content. For more information, see Editing Approved/Blocked Senders for Organizations. 10. Confirm users have not added their own address or domain in a user-level Approved Recipients list. If so, all spam addressed to the user is delivered unfiltered. 11. Confirm the spam did not have sufficient spam characteristics to trigger filtering. Check the message header for the spam score. For more information, see Interpreting Header Tags. 46 Message Security Troubleshooting Guide Why am I suddenly getting all of this spam? If your filtering was working fine and then suddenly you get a lot of spam through the filter with messages containing GOOD RECIP in the message’s X-pstn header, check your approved sender lists. • If the user has added his/her own e-mail address or domain to his/her approved mailing list configuration, all messages sent to that user or the user's domain will be allowed through regardless of how spam-like nature of the message. The administrator can remove this configuration using the Administration Console. For more information, see Editing Approved/Blocked Senders and Mailing Lists for Users. • Depending on the User Access configuration, a user can remove this configuration using Message Center. For more information, see Editing Approved/Blocked Senders Using Message Center. • For more detailed spam troubleshooting, see the “Why are these spam messages not being filtered?” FAQ. Why do obvious spam messages occasionally get through the filters? Spammers commonly forge the sender address from popular domains in attempts to bypass filtering. These may be approved senders you added, or approved senders which were pre-populated for your organization. You may wish to modify the Approved Sender lists for your organizations to remove these approved senders. For more detailed spam troubleshooting, see the “Why are these spam messages not being filtered?” FAQ. How do I prevent good messages from getting filtered out as spam? (false positives) On rare occasions, legitimate messages can be falsely quarantined as spam (often called false positives). Or conversely, messages might get past the filters and reach user’s Inboxes. Some common reasons for false positives include: • Filter levels are too aggressive. Frequently Asked Questions 47 The message might have characteristics that make it look like spam, such as disclaimers, URLs, dollar signs, multiple exclamation points, and little or no body content apart from a link, image, or file attachment. The more such characteristics it has, the more likely it will be caught, depending on your filter levels. Special Offer filter -- In particular, aggressive category filters can falsely tag valid messages as spam. Try lowering category settings, beginning with the Special Offer filter. Businesses tend to receive legitimate email containing commercial content, so false positives in this category are more likely. Bulk Email filter -- An aggressive Bulk Email filter can falsely tag valid emails, too, but should do so less often than a category filter. • A listserv or news group server sent the message. Mailing lists share many characteristics of spam. If the sender address is always the same, for example, [email protected], add it to the userlevel Approved Recipients list. • The message was sent by an automated email service and appeared “spoofed.” This might include a message from a group reservation or auction site. Add these addresses to your org-level Approved Senders list. • The sender appears on the org-level or user-level Blocked Senders list. Remove it from this list. • If messages are being received from a particular sender that are regularly being falsely quarantined, the sender's email address or domain can be added to the user's or organization's Approved Senders list to ensure that future messages are not quarantined. • Examining the spam score in a message’s header can also provide clues to why it was identified as spam. For more information, see About Header Tags. For more information about how to achieve the most effective spam filtering, see Enable/Adjust Spam Filters. Can I filter messages for unregistered users? It depends on how you have configured your organizations: • An unrecognized user can be automatically added to your organization and then filtered for spam • The unrecognized user’s message can be bounced and not filtered • Deliver the unrecognized user’s message without filtering or adding the user to the email security service For more information, see Handle Mail to Unrecognized Addresses. 48 Message Security Troubleshooting Guide Why do messages from a blocked domain keep getting through? There could be several reasons: 1. System misconfiguration -- The domain on the org-level Blocked Senders list and, at the user-level, there is an Approved Sender with the domain. 2. Port 25 -- Messages are flowing directly to your mail server via port 25. Set up your email server or firewall to only accept email from the email security service’s IP ranges. For information, see Setting Up Secure Mail Delivery. 3. User or mailing list is unregistered -- A user address or mailing list is unregistered with the email security service. For more information, see User Validation. What does this error mean, "ERROR 550 xf071772.xxx"? My mail is bouncing when sent to email security service. Your Inbound mail is bouncing with the error code "ERROR 550 xf071772.xxx" where the xxx are three numbers. The email security service has determined that this message matched the characteristics of an existing Spam outbreak. If you see this error, please contact Support. If you are a directly supported Postini Customer, please log in to the Postini Support Portal. Otherwise, contact your vendor, who can assist you. When Submitting a Message to Support The message must include the message headers for analysis, so you must send message as an email attachment: 1. Send messages as attachments to support. 2. You can also collect mail messages into a compressed file format (zip, gzip, etc) and attach the compressed file to your email. Spool Manager How do I manage my spooling configuration in the Administration Console? Select an email config organization. In the Inbound Servers tab at the top of the Administration Console, select Spool Mgr. And go to the Edit page. For detailed information, see Configuring the Spool Manager. Frequently Asked Questions 49 How do I change my spooling allocation? If you are the account administrator, you can allocate your total spool storage across all or some of your email config organizations. When you add or delete an email config, or purchase additional spool storage, you must adjust the spool allocation. For detailed information, see Allocating Spool. How do I unspool my mail? Unspooling can be controlled either automatically or manually. Also, you should configure your Unspooling Connection Rate in order to optimize and protect your mail servers from the volume of delivered messages. For more information, see Configuring the Spool Manager. Can I view my spooled emails? No. Spooled messages can not be viewed. How do I get spooling alerts? I am not getting them. When your service is activated, alerts are not configured. It is vital that you set up your alerts for each email config so that you will receive proactive notification when an urgent server event occurs. Edit your Spool Manager alerts configuration on the Inbound Servers area of the Administration Console. For more information, see Alerts and Events for Spool Manager. Another important point about alerts, is to send your Delivery Manager and Spool Manager alerts to mobile devices and not your email security service mail address. For more information, see Setting Up Alerts. Note: Confirm your spooling alerts configuration does not use your domain. If the alert is sent to your domain during a spooling event, you will not receive it since the alert message is being spooled. What happens to my mail during the 15 minute spooling delay period? Your mail is not lost during this time period. The sending mail server defers your mail, and sends the message later. 50 Message Security Troubleshooting Guide Why has my mail not automatically unspooled? My mail server connection is now working and I still have spooled mail. • Either your Unspooling Control is configured to manual. The unspooling process must be manually initiated (even after your mail servers are reestablished). For more information, see the Unspooling Control section of Configuring the Spool Manager. • Alternately, your Unspooling Control is configured to automatic, and your server has not been available for three successive minutes. Why is my email being spooled even though my mail server is running? You have an intermittent or slow network connection. And this is interpreted by the Spool Manager as a failed mail connection. Increase your spool delay period. For more information, see the Spool Delay field in Configuring the Spool Manager. Users, Aliases, Mailing Lists, and Administrators How do I add a user? Go to the Orgs and Users > Users tab and select Add/Delete/Move Users link. For detailed information, see Add/Delete/Move Users. How do I create a user alias? Locate the user to whom you want to add an alias. In that user’s Alias settings page, enter the alias. For more information, see Manage User Aliases. In addition, see the “How do I add a user?”, “How do I protect internal distribution or mailing lists from spam and viruses?”, and “How do I add an administrator?” FAQs. How do I protect internal distribution or mailing lists from spam and viruses? Add each list to the email security service, either as a user, or aliased to a user. See Protect Your Mailing and Distribution Lists. In addition, see the “How do I create a user alias?”, “How do I add a user?”, and “How do I add an administrator?” FAQs. Frequently Asked Questions 51 How do I stop mail from external mailing lists being falsely filtered as spam? Edit the user’s Approved Recipients list (under Sender Lists), or the user can do this at the Message Center. See Approved and Blocked Sender Lists. How do I add an administrator? Before creating an administrator: • If the user does not already exist, create a user. An administrator must be a registered user before becoming an administrator. • Determine the type of administrator you want to create. For example, some administrators only monitor organizations and others edit user settings. These administrators need different privileges. • Decide where in your account hierarchy to place the administrator’s authorization record. • Create the administrator and, if necessary, customize the authorization record. For more information, see Create Administrators and Manage Authorization Records. In addition, see the “How do I add a user?”, “How do I protect internal distribution or mailing lists from spam and viruses?” , and “How do I create a user alias?” FAQs. Who are these guys? I have unknown users in my organization and they are not provisional users. But I can see these users in my spam/account report. Probably your organization is configured to automatically add users using SmartCreate. For more information, see Add Users Automatically to an Org. Can I change my Default Users? The Default User is a useful template for settings across all user configurations. Do not edit or delete the account-level Default User. If a lower level Default User is not longer assigned to any organization and is not longer needed, you can delete this template. For more information, see Manage Default User Template. 52 Message Security Troubleshooting Guide How do I switch my user’s authentication methods? Changing authentication methods can not be done by an administrator. To change authentication methods, please contact Support. If you are a directly supported Postini Customer, please log in to the Postini Support Portal. Otherwise, contact your vendor, who can assist you. How do I authenticate specific users using different methods? Each organization can only use one authentication method. 1. Create a new organization for each authentication method. For more information, see Create an Organization. 2. To change the authentication method for each new organization, please contact Support. If you are a directly supported Postini Customer, please log in to the Postini Support Portal. Otherwise, contact your vendor, who can assist you. 3. Move users and add users to the appropriate organization. For more information, see Add/Delete/Move Users. How do I block all traffic to an address? The service will pass traffic through if there is no associated user account. To block all traffic to an address, create a user account for the address, and set the user’s Daily Message Limit to 0. After creating the user: 1. Go to Orgs and Users > Users. 2. Type in the user’s address and select Search. 3. Select the user address, and select Message Limits in the Inbound Services section. 4. Scroll down to the bottom of the page and set the Daily Message Limit field to 0 (zero). 5. Select Save. What does this error message mean? “Mail limit exceeded” Either the user-level or the organization-level has a Daily Message Limit setting that has been reached. An immediate change to the limit does not restore mail flow to the user until the next day. Frequently Asked Questions 53 To edit the existing Daily Message Limit: 1. Go to Orgs and Users > Users. 2. Type the user address into the Find User field and select Search. (You may need to use the Choose Org pull-down menu to select the org containing the user.) 3. Select the user’s address. 4. Select Message Limits in the Inbound Services section of the page. 5. If the limit is not listed, it is imposed on the organization which contains the user, so select “View Org-Level Message Limits.” 6. Configure the limit. How do I view a list of my user aliases? You can see a list of users and aliases through the Administration Console: 1. Go to Orgs and Users > Users. 2. Select “aliases” and select Search. 3. You will see a list of all users and their aliases in your org structure. 4. To narrow this search, you can enter special criteria into the “Find User” text box. You can also see a list of aliases in the Usage Details. You must be logged in as an administrator on the account-level organization to do so. 1. Go to Orgs and Users and select the account-level organization in the list of orgs. 2. In the Organization Management page, scroll down to Organization Settings and select Usage Details. 3. On the Monthly Usage Details page, go to “Alternate Addresses”. 54 Message Security Troubleshooting Guide You will see a list of alias addresses, sorted by organization. This information is compiled monthly, so recent changes will not be included in this report. Virus Why was this virus apparently delivered despite virus blocking? 1. Confirm your inbound virus blocking is configured correctly. It is especially important to confirm the organization’s Non-Account Virus Blocking feature and the Default User’s Virus Blocking field are enabled. For more information, see Configure Inbound Virus Blocking. 2. Often the user or mailing list receiving the message is not registered in the email security service. Check the headers of the virus email to determine the recipient and to see whether the message was sent directly to and was accepted by your mail server, bypassing the email security service. a. Search the message headers for X-pstnvirus header. If this header is present, the message went to a registered recipient and was filtered for a virus. For more information, see X-pstnvirus Header. b. Confirm all of your user addresses and mailing lists are registered with the email security service. Messages to unregistered users and mailing lists are delivered unfiltered. For more information, see Search for Users. Why does Virus Blocking seem to be blocking legitimate messages? Virus Blocking either quarantines or blocks all fragmented messages, since fragmented messages cannot be properly scanned. Message fragmenting is not used widely since most mail messages can be sent within the SMTP standard using the common networking technologies and processing power of today’s computers. For more information on Virus Fragment Blocking, see Configure Virus Settings for an Organization. Frequently Asked Questions 55 Mail Flow Troubleshooting Chapter 2 Mail Flow Why am I not getting any mail at all? Follow these steps to find out why you can’t receive mail from any outside sender. Stages of Mail Flow Before you begin troubleshooting mail flow, be sure you understand how messages normally flow from a sender to your server through the message security service. Then you can find out at what stage the failure is occurring. This graph shows the normal steps of mail flow: 1. The sender connects to the email security service and sends the message. 2. The email security service filters the message for spam, viruses, content and attachments. 3. The email security service sends the message to the recipient server. 4. The recipient server delivers mail to the user. Mail Flow Troubleshooting 57 First Steps of Troubleshooting These steps describe how to begin troubleshooting a mail flow problem. 1. Send a test message from an outside address (such as your personal Gmail account) to confirm that outside mail isn’t flowing. If the problem is only happening for a single sender, see “Why am I not getting mail from one sender?” on page 63. 2. View the Delivery Manager Graphs. a. Log in to the Administration Console. b. Select your email config organization. Usually, this will have “Email Config” in the organization title. c. Click the Inbound Servers tab. d. Click the Delivery Manager link near the top of the page. See the sections below for instructions on how to interpret Delivery Manager graphs. Interpret Delivery Manager Graphs: No Mail Activity If the Delivery Manager graph shows no activity, or very little activity, this indicates that the problem is happening before the message security service filters mail. The graph may look like this: 58 Message Security Troubleshooting Guide The graph may instead look like this: Here are the most common causes for no activity in the Delivery Manager graphs, and the steps to resolve them: • Routing Problems There may be other routing problems. To find out more about what’s happening, run the SMTP Message Test: “Test mail flow through the data center.” For instructions, see SMTP Message Test. • Incorrect MX records If your MX records are set improperly for this domain, mail will never reach the message security service. Run the MX records test. For instructions, see MX Record Test. If there is a problem with your MX records, switch your MX records so they route mail to the message security service properly. • Domain not added to the email security service Check that your domain is registered. If you have changed your MX records without adding your domain, this may cause problems. See Add a Domain for Filtering. Interpret Delivery Manager Graphs: Messages Blocked If the delivery manager graph shows a red line, this indicates that messages are being blocked. (The sidebar will also show no successful connections and many failed connections.) Mail Flow Troubleshooting 59 The graph will look like this: Here are the most common causes for blocked messages in the Delivery Manager graphs, and the steps to resolve them: • Delivery Errors Your server may be returning errors when the message security service tries to deliver mail. Run SMTP Message Test “Test an email from the data center directly to your mail host”. See SMTP Message Test. If you see problems, contact your mail server vendor or administrator to resolve these problems. • Incorrect Delivery Information The message security service may be trying to deliver to the wrong location. If this is the case, update your Delivery Manager settings. See Setting up Delivery Manager. Interpret Delivery Manager Graphs: Messages Spooled If the delivery manager graph shows a green line, this indicates that messages are being spooled. (You can also click the Spool Mgr link near the top of the page to find out if spooling is happening.) 60 Message Security Troubleshooting Guide The graph will look like this: This usually indicates that messages were blocked and spooling is storing messages so that no mail data will be lost. Here are the most common causes for spooled messages in the Delivery Manager graphs, and the steps to resolve them: • Delivery Errors Your server may be returning errors when the message security service tries to deliver mail. Run SMTP Message Test “Test an email from the data center directly to your mail host”. See SMTP Message Test. If you see problems, contact your mail server vendor or administrator to resolve these problems. • Incorrect Delivery Information The message security service may be trying to deliver to the wrong location. If this is the case, update your Delivery Manager settings. See Setting up Delivery Manager. • Spool Manager If there are no delivery errors, Spool Manager may be set to spool all mail. Check to see if Manual Spooling is enabled. After you have resolved other issues, start unspooling. See Configuring the Spool Manager for more information. Interpret Delivery Manager Graphs: Messages Accepted If the Delivery Manager graph shows a blue line, this indicates that messages are being delivered successfully. If there is a problem, it is happening after your server received the message. This is also how the Delivery Manager graph will look when mail is being delivered successfully. Mail Flow Troubleshooting 61 The graph will look like this: Here are the most common causes for problems with mail flow when you see accepted messages in the Delivery Manager graphs, and the steps to resolve them: • Internal Routing Your mail gateway (or mail server) may be accepting messages initially, then losing messages during internal routing. Send a test to see what happens when mail is sent directly to your mail server. Run an SMTP Message Test with the “Test an email from the data center directly to your mail host” to find out what might be happening. See SMTP Message Test. After this, troubleshoot your mail server’s internal routing. • Messages Quarantine It may be that most mail is being delivered successfully but some mail messages are being filtered. Check your user’s quarantine to see if the messages are there. See Manage Quarantined Messages for more information about how to view and modify quarantines. • After Troubleshooting After you’ve followed these steps, send another message from an outside server (such as your personal Gmail address) to confirm that the problem has been resolved. Contact Support If the problem continues after these troubleshooting steps, please contact Support. If you are a directly supported Postini Customer, please log in to the Postini Support Portal. Otherwise, contact your vendor, who can assist you. 62 Message Security Troubleshooting Guide Why am I not getting mail from one sender? Follow these steps to find out why you can’t receive mail from a single sender. Common Causes If a single sender is unable to send you mail, here are some common causes: • Sender mail server: The problem may be happening on the sender’s side, either due to mail server issues, network issues, or DNS issues. • Connection Manager blocking: Sometimes the message identifies a sender as the source of an email attack and blocks mail. You can set up a passthrough to prevent this from happening. • Filter Settings: You may have a filter set up to block mail from the sender. You can usually identify what’s causing this by looking at the error message. • Recipient mail server: Your own server may be rejecting the message. The message security service passes any errors generated by your server back to the sending server, so you can usually identify what’s happening by looking at the error message. First Steps of Troubleshooting Begin troubleshooting by collecting information about what’s happening. 1. Confirm that the problem is only happening for one sender. Send a test message to your mail server from an outside mail account such as your personal Gmail account. If the problem is happening for multiple senders, see “Why am I not getting any mail at all?” on page 57 for troubleshooting steps. 2. Contact the sender directly and collect the following information • The error message the sender gets when trying to send mail. • The IP address of the sending server. 3. If the sender doesn’t know their IP address, you can collect this information through other emails. • If the sender has sent messages successfully in the past, look at an old message from the sender and review the full headers for the IP information. • Otherwise, ask the sender to send mail to a third-party email address, such as your personal Gmail account. Look at the headers to get the sending server’s IP address. To see the full headers in Gmail, click the blue triangle on the upper right of the message and select “Show Original” from the pull-down menu. Mail Flow Troubleshooting 63 The IP address will be listed in a line that begins with the word “Received:”. There will probably be several lines that start with “Received:” so use the one that is “from source” or from the sending server’s domain. For instance, if you’re looking at a message sent by someone at jumboinc.com, you might see the following header: Received: from source ([172.220.209.220]) by exprod8mx216.postini.com ([64.18.7.10]) with SMTP; Mon, 28 Jan 2008 10:48:00 PST The IP address for jumboinc.com would then be 172.220.209.220. Interpret Error Messages Once you have the error message the sender’s seeing, you can use this information to find out what’s wrong and resolve the problem. No error message If the sender doesn’t get any error message at all, there are a few possible causes: • The sending server is blocked by Connection Manager. If this happens, find the sender’s IP address and add a pass through. See Pass Throughs: Preventing Attack Blocking. • A Content Manager rule is blackholing the message. Check your Content Manager rules in the Administration Console. See Create or Edit a Content Manager Filter. • An Attachment Manager rule is blackholing the message. Check your Attachment Manager rules in the Administration Console. See Create / Edit Attachment Manager Filters. • The sending server is unable to send mail out. Ask the sender to troubleshoot their outgoing mail to find out what’s happening. Error messages from another source First, check that the error message came from the message security service. Error messages generated by the message security service will end with the text “-psmtp”. If an error message doesn’t end with “-psmtp” or uses a different format than the error messages below, the message was generated by another server. If this happens, there are two possibilities: • The message was generated by the sender. • The message was generated by your recipient servers. The message security service passes any error it receives from your server back to the sending server. If you see a message from another source, verify whether the problem is happening with the sender or the recipient, then contact the vendor or administrator of that mail server. 64 Message Security Troubleshooting Guide Message security service error messages If the message did come from the email security service, consult the following table. Error Message Possible Causes Action to Take 550 552 553 554 571 Connection Manager Set Up A Pass Through. See Pass Throughs: Preventing Attack Blocking. 550 no such user Non-Account Bouncing Add the recipient’s email address in the Administration Console. See Add / Delete / Move Users. 571 message refused Blatant Spam Blocking If this is valid mail, add the sender as an Approved Sender in the Administration Console. See Editing Approved / Blocked Senders for Organizations. 582 This message violates our email policy Content Manager Check your Content Manager filters. See Create or Edit a Content Manager Filter. 582 The file attached violates our email policy Attachment Manager Check Attachment Manager settings. See Create / Edit Attachment Manager Filters. 582 (Custom error message) Attachment Manager or Connection Manager This is a custom message, set by an administrator using either Attachment Manager or Connection manager. Check both to see what rules are being triggered. See Create / Edit Attachment Manager Filters and Create or Edit a Content Manager Filter. 571 Virus Blocked Virus Blocking The sender’s mail server is infected. Ask the sender to run antivirus diagnostics. 451 STARTTLS is required for this sender TLS Change your TLS settings to accept mail from the sender. See Set Up Inbound TLS. mailbox unavailable storage allocation exceeded mailbox name not allowed transaction failed spam source blocked If you do not want to change your TLS settings, ask the sender to install TLS on their mail server. After Troubleshooting After you’ve followed these steps, ask the sender to send another message to confirm that the problem has been resolved. Contact Support If the problem continues after these troubleshooting steps, please contact Support. If you are a directly supported Postini Customer, please log in to the Postini Support Portal. Otherwise, contact your vendor, who can assist you. Mail Flow Troubleshooting 65 66 Message Security Troubleshooting Guide Index A activation activation key 7 password 7 Administration Console account-level administrator 9 create an administrator 9 email config 10 login error 8 password 8 service unavailable 8 Approved/Blocked Senders add/remove error 11 address not working 12 batch modified lists 18 extra addresses 12 limit 10 list of senders 13 too many addresses error 11 who to add to these lists 10 Attachment Manager block attachments 15 block file types 14 bounced attachments 14 disposition conflict 15 file size 13 filter senders 14 limit file sizes 14 multi attachment filtering 15 quarantined messages 15 viruses 14 B Batch Message Center notifications 16 Quarantine Summary notifications 17 batch delete all users in a domain 21 display all orgs, domains, and users 18 edit Sender Lists 18 list user aliases and primary addresses 20 modify domains 21 modify Message Archiving settings 20 modify message limits 19 C Connection Manager IP address 22 Manual Pass Through 22 Content Manager captured messages not in the rules 23 full file name content rule 23 language characters 23 regular expressions 22 D Delivery Manager connection limit 25 forwarded mail 24 graph not available 23 limit connections 26 mail delivery 25 new ISP 24 new mail server 25 Open Conn setting 25 reading graphs 24 removing persistent connections 26 Domain add a domain 26 add a domain alias 26 confirm domain changes 27 delete a domain 27 forward mail from old domains 27 modify all users 21 unable to add a domain 27 when to add a domain or alias 26 M Mail flow Why am I not getting any mail at all? 57 Why am I not getting mail from one sender? 63 Message Archiving batch modified user settings 20 Message Center batch notifications 16 Index 67 change a password 29 deleting more than 100,000 messages 30 disabled quarantine categories 29 login failure 28 Message Center access 29 password 28 slow or unavailable 29 Message Recovery access archive 31 archive features 30 DNS information page 33 duplicate messages 32 empty archive 30 export or recover messages 32 MX record priority 34 MX record syntax 33 MX records overview 33 search 31 search for specific message 32 set up 30 TTL 34 view messages 31 who can search 31 MX Records how long to change a MX record 35 IP addresses 33 loosing mail 35 MX record propagation 35 MX record test 36 no mail delivery 36 N Notifications batch Message Center 16 batch Quarantine Summary 17 change Quarantine Summary sender’s name 39 changing Quarantine Summary From header 39 disable Quarantine Summaries 38 fixing spool alerts 37 frequency of spam notifications 37 Message Center access 38 no Quarantine Summaries 38 notifications bounced 37 notifications not delivered 36 Quarantine Summaries to one person 38 Quarantine Summary header fields in messages 39 send out Quarantine Summaries 38 spam notifications 37 too many Quarantine Summary messages 40 validate addresses 36 welcome notifications 37 O Organizations adding an org 40 deleting an org 41 email config settings 41 when to add other orgs 40 Outbound Servers Can’t find account level org error 43 68 Release 6.12 compliance footer does not display 42 IP range 42 reinjection 41 reinjection error 42 reinjection fails 42 remove IP ranges 42 smarthhost 42 R Reports Blocked Senders and Blocked Servers 45 Content Manager on Reports tab 45 domains from other orgs in reports 44 falsely quarantined mail statistics 44 Messages and Act Msgs 45 old data 44 useful reports 43 S Spam ERROR 550 xf071772.xxx 49 false positive messages 47 filter for specific spam 45 messages from blocked domains 49 suddenly getting spam 47 unfiltered messages 46, 47 unregistered user messages 48 Spool Manager add user alias 51 change allocation 50 configuration 49 mail during spooling delay 50 mail not automatically unspooled 51 spooling alerts 50 spooling when mail server is running 51 unspool mail 50 view spooled mail 50 U Users add an administrator 52 add users 51 authentication methods 53 automatically added users 52 batch list of aliases and primary addresses 20 batch modify message limits 19 block all traffic to an address 53 change Default User 52 delete all users in a domain 21 distribution or mailin lists 51 keep mailing lists filtered as spam 52 Mail limit exceeded error 53 modify all users in a domain 21 switch authentication methods 53 user alias list 54 V Virus blocking legitimate messages 55 virus getting through 55
© Copyright 2026