Final Exam Review 2
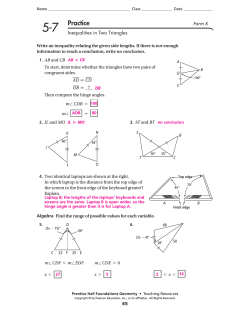
Fall Final Exam Practice 1 Name: ________________________ Period ______ 1 1. Given the function, f ( x) = A) x = 4 x , what is the value of x when f ( x) = 16 ? 4 B) x = -4 C) x = 64 1. _____ D) x = 8 2. Which diagram is a NOT a One to One Function? 2. _____ A) B) C) D) 3. If you have a rotational symmetry angle of 18°°, then your order is: A) 2 B) 5 C) 10 4. This shape has: A) Only Rotational Symmetry 3. _____ D) 20 B) Only Reflectional Symmetry 4. _____ C) Both Rotational & Reflectional Symmetries symmetry D) Neither 5. AB is rotated 87°° about point T. Which of the following statements is false? A) T = T’ B) AT = A’T C) AA’ = BB’ D) m∠ATA’ = 87° 5. _____ 6. If RO ,167° ( ∆ABC ) = ∆DEF then: A) m∠BOD = 167° B) m∠OAD = 167° C) m∠AOE = 167° D) m∠FOC = 167° 6. _____ Determine whether the following are (T)rue or (F)alse. 7. T ( x, y) − − − − > (3x, y + 2) is an isometric transformation. T or F 8. A rotational symmetry of order 2 means that the angle of the order is 90°°. 9. A rotation of 180°° reverses the orientation of the shape. 10. The isometric transformations are rotation, reflection, dilation and translation. T or F T or F T or F 11. Given coordinate rule, T ( x, y) − − − − > ( x + 2, y − 6) determine the pre-image of A’(-2,2)? 12. Given the shape, shade it so that it has reflectional symmetry. a) 1 line of symmetry b) 2 lines of symmetry c) Order 4 d) Order 4 2 13. ∆ABC is mapped by a single isometric transformation to ∆A’B’C. Name ALL of the isometric transformations that could have performed this? Explain why you chose the one(s) you did. 14. Determine whether the following are (T)rue or (F)alse. a) F (x,y) -------> (x + 3,y) is a translation of 3 units to the right. b) RO ,180 = Rx axis R y axis T or F T or F c) A composite transformation of a rotation followed by translation reverses the orientation of the shape. d) A double reflection over y = 3 followed by y = 4, translates all points up 2 units. e) R y = 11 R y = 6 = T< 0,10 > T or F T or F T or F 6 15. Perform the following on the grid. a) A D RM ,90° ( NOPQ) 4 C H b) RF ,180° ( ∆GHI ) 10 T〈 3,2〉 ( ∆JKL) M N B c) RAB (∆CDE ) d) 2 E G I O J 5 5 K F 2 Q P L 4 16. Determine the smallest positive angle of rotation that would perform the same rotation as the given one. a) R0,−50° = R0,_______ ° b) R0,400° = R0,_______ ° c) R0,−730° = R0,_______ ° 17. Use your rules to solve these. a) Rx axis A(5, 4) = A '(_______, _______) b) Ry axis Rx axis A(−5,1) = A ''(______, ______) c) Rx axis R y axis A(_______, _______) = A ''(4, −3) d) T〈−3,5〉 A(_______, _______) = A '(9, −3) e) T〈−2, −1〉 R y axis A(5,3) = A ''(_______, _______) f) Rx axis A( −1, 6) = A '(_______, _______) g) RO ,90 A(3, 2) = A '(_______, _______) h) RO ,90° A(_______, _______) = A '(8,3) 3 18. _____ 18. If two triangles are congruent, then: A) they have the same side lengths B) isometric transformation(s) map one onto the other C) they have the same angle D) all of the above are true 19. _____ 19. A student believes that he can prove these two triangles to be congruent using SSS because he knows that BD ≅ BD . What would be his reason for knowing this? C D B A) The triangles are congruent B) The Reflexive Property C) It can’t be SAS because no angle is given D) The Substitution Property E 20. To be able to prove that ∆ABD ≅ ∆CBD by HL, using the two given congruent corresponding sides, one piece of information is missing. Which of the following would be that piece of information? 20. _____ B C A) Base angles of an isosceles are congruent B) BD ≅ BD C) BD bisect ∠ABC D) ∠ADB is a right angle D A 21. Quadrilateral FHJK is congruent Quadrilateral MNPO. Complete the following congruent statements. b) NP ≅ ______ a) ∠J ≅ ∠ ______ c) ∠M ≅ ∠ ______ d) KF ≅ ______ B 22. Which triangle congruence criteria will determine congruence for given diagram? E C A) SSS B) SAS C) ASA D) AAS A E) HL D 22. _____ Choose whether they are (T)rue or (F)alse. 23. Given ∆ABC & ∆RTS and ∠A ≅ ∠R, ∠B ≅ ∠T, ∠C ≅ ∠S then ∆ABC ≅ ∆RTS. T or F 24. Determine the following for any point P. k a) R_________ R_________ ( P ) would result in a rotation of 82°. b) R_________ R_________ ( P ) would result in a rotation of -174°. c) R_________ R_________ ( P ) would result in a rotation of 256°. l m 87° 41° A E 25. Three of the four items listed can be used to establish congruence by ASA. Determine which one is NOT needed to prove ∆BCA ≅ ∆DCE by ASA? A) ∠DCE AND ∠BCA are vertical ∠’s B) AB ≅ ED C) C is the midpoint of AE D) ∠A ≅ ∠E B C D 24. ________ A 26. If isosceles ∆ABC has a base angle, ∠B, with a measure of 45°°, then ∆ABC is A) an acute ∆ B) a right ∆ C) an obtuse ∆ D) a scalene ∆ 25. ________ 4 27. Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of all rectangles? A) Consecutive angles are supplementary B) Opposite angles are congruent C) Diagonals bisect each other D) Diagonals are perpendicular 26. ________ 28. Which of the following group of quadrilaterals have diagonals that are perpendicular? A) Rhombus, Square B) Rhombus, Parallelogram, Square C) Rectangle, Square D) Rectangle, Rhombus, Square 27. ________ Determine whether the following are (T)rue or (F)alse. 29. ∆ABC has m∠ ∠C = 71°° and m∠ ∠B = 71°°, then AB ≅ AC . T or F 30. A rhombus has four congruent angles. T or F 31. Consecutive sides are congruent in a rectangle. T or F 32. What are the missing measures in Parallelogram SRQP? m∠9 = 66˚ m∠2 = 14˚ m∠1 = 16˚ Q 3 m∠6 = ________ 9 m∠10 = ________ m∠11 = ________ m∠3 = ________ 33) GIVEN: CB || ED & CA ≅ DA PROVE: BA ≅ EA STATEMENT REASON 1 6 T 10 2 P 5 4 11 8 7 S R 5 34. Solve for the unknown values. a) x = ___________ b) x = ___________ c) x = ___________ 9x - 11 5x + 25 7x + 15 d) x = ________ e) x = ________ 126° x f) x = ________ 41° 89° g) x = ________ x 165° x h) x = ________ 35° i) x = ________ x x 32° 53° x Solutions 1. C 2. B 3. D 4. C 5. C 6. D 7. F 8. F 9. F 10. F 11. No, Different Sizes 12. 13. Translation or Rotation 14a. T 14b. T 14c. F 14d. T 14e. T 15a-d. 16a. 310 16b. 40 16c. 350 17a. (5,-4) 17b. (5, -1) 17c. (-4, 3) 17d. (12,8) 17e. (-7, 2) 17f. (-1, -6) 17g. (-2,3) 17h. (3, -8) 18. D 19. B 20. D 21a. P 21b. HJ 21c. F 21d. OH 22. C 23. F 24a. k,m 24b. k,l 24c. l,m 25. B 26. B 27. D 28. A 29. T 30. F 31. F 32a. 14 32b. 114 32c. 66 32d. 100 33. 34a. 23 34b. 13 34c. 11 34d. 36 34e. 76 34f. 76 34g. 74 34h. 74 34i. 60 x x
© Copyright 2026