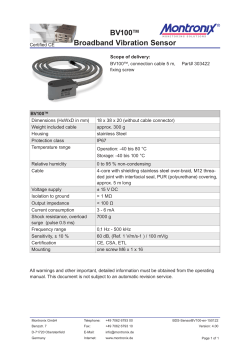
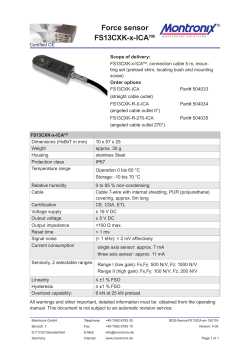
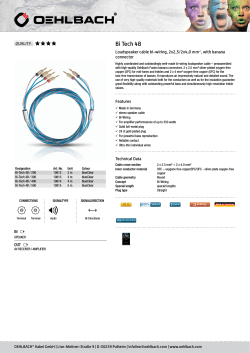
Document
07-May-15 Introduction to Internet What is Internet? Internet is a worldwide collection of networks that connects businesses, government agencies, educational institutions and more than one billion people who use the network every day. 1 07-May-15 “Online” what is it? When a computer is connected to a network such as a LAN, MAN, WAN or to the Internet then it is said to be “ONLINE”. Note: A computer can be online without being connected to the Internet Server (Host) - A computer that provides services and connections to other computers on a network Web Function of Web To create information and make it available for others to see on the Internet. Webpage Webpage is a document on the World Wide Web that can contain text, graphics, animation, audio and video. Website Website is a collection of related Web pages. 2 07-May-15 How can Internet use enhance daily life??? Distributed Data Processing 3 07-May-15 Network A NETWORK uses communication equipment to connect two or more computers and their resources Types: – PC based – LAN – shares data and resources among users in close proximity – WAN – shares data among users who are geographically distant Basic Components • Sending device • Communications link • Receiving device 4 07-May-15 Data Transmission • Digital lines – Sends data as distinct pulses – Need digital line • Analog lines – Sends a continuous electrical signal in the form of a wave – Conversion from digital to analog needed – Telephone lines, coaxial cables, microwave circuits Analog Transmission Alter the carrier wave • Amplitude – height of the wave is increased to represent 1 • Frequency – number of times wave repeats during a specific time interval can be increased to represent a 1 5 07-May-15 Modem • MOdulator + DEModulator • Modulate – Convert from digital to analog • Demodulate – Convert from analog to digital Modem Transmission process • Modulation – Computer digital signals converted to analog • Sent over analog phone line • Demodulation – Analog signal converted back to digital 6 07-May-15 Types of Modems • Direct-connect – External – Internal • PCMCIA – Personal Computer Memory Card International Association – Notebook and laptop computers DSL Digital Subscriber Line • Uses conventional telephone lines • Uses multiple frequencies to simulate many modems transmitting at once • No industry standard – Cost – Speed • Phone line shared between computer and voice 7 07-May-15 Cable Modem • Coaxial cables • Does not interfere with cable TV reception • Up to 10 million bps • Always on • Shared capacity • Security problem Bandwidth Data rate measured in bits (not bytes) per seconds – Kbps (Kilobits per seconds) • 125 chars/sec – Mbps (Megabits per seconds) • 1,250 chars/sec – Gbps (Gigabits per seconds) • 12,500 chars/sec 8 07-May-15 Connecting to the Internet • Requirement – A computer or PDA or cell phone – An account with an ISP (Internet Service Provider) – A modem (modulator/demodulator) for dial-up services or a NIC (Network Interface Card) for DSL/Cable services Home Network (Single Machine) Wall Jack DSL/Cable Modem USB/Ethernet Cable Laptop 9 07-May-15 Home Network (Multiple Machines) Wall Jack Hub/Switch/Router DSL/Cable Modem USB/Ethernet Cable Laptop Home Network (Multiple machines) Wall Jack Ethernet Cable DSL/Cable Modem Hub/Switch/Router 10 07-May-15 Home Wireless Network Wall Jack Ethernet Cable DSL/Cable Modem Hub/Switch/Router Connection Types • • • • • LAN WLAN Dial-up Services Broadband Services WAN 11 07-May-15 LAN (Local Area Network) • A network of computers that are in the same physical location, such as home or building • Usually connected using Ethernet – A standard on how computers communicate over a shared media (cable) Old: BNC connector for coaxial cable http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image:BNC_connector.jpg New: RJ45 for twisted pair cable http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image:Ethernet_RJ45_connector_p1160054.jpg LAN (Local Area Network) • Ethernet Standard – 10BaseT • 10Mbps (Mega bits per second) – 100BaseT • 100Mbps – 1000BaseT • 1000Mbps or 1Gbps 12 07-May-15 LAN (Local Area Network) • Question: Can 2 computers communicate by connecting each other using an Ethernet cable back-to-back? WLAN (Wireless LAN) • Wi-Fi (Wireless Fidelity) – A wireless technology that connects computers without cables • Access Point (AP) – A device (base station) that connects wireless devices together – Usually connected to a wired-network • ESSID (Extended Service Set ID) – A “name” for the AP, eg. Mobilenet • Hotspot – The area covered by wireless access points 13 07-May-15 WLAN (Wireless LAN) • Standard – 802.11b - 11Mbps – 802.11g - 54Mbps – 802.11a - 54Mbps 2.4G 5G • Security – WEP (Wired Equivalen Privacy) – WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) – To prevent wardriving Broadband Services • xDSL (Digital Subscriber Line) – A technology that provides digital data transmission over unused frequencies on traditional telephone lines – For example, ADSL (Asymmetric DSL): DL > UL – Speed • Downlink – 128Kbps - 4Mbps • Uplink – 64Kbps - 800Kbps – Need a DSL modem – Splitters are needed to separate the voice and data signal 14 07-May-15 Broadband Services • Cable – A technology that provides digital data transmission over cable TV infrastructure – Speed • Downlink –128Kbps - 3~5Mbps • Uplink –64Kbps - 128Kbps~1Mbps – Need a cable modem Broadband Services • Satellite – A technology that provide digital data transmission over satellites – Speed • Downlink –500Kbps - 1Mbps • Uplink –50Kbps - 100Kbps – Need a satellite dish 15 07-May-15 WAN (Wide Area Network) • A LAN spans a large geographic area, such as connections between cities • Usually connected using leased line – T1 (1.5Mbps) Telecommunication lines – T3 (45Mbps) – OC3 (155Mbps) Fiber optic lines – OC12 (622Mbps) – OC48 (2.4Gbps) Hub/Switch/Router • To connect multiple segments of networks into a larger one • Hub – A multiport repeater to enhance signal within the same LAN • Switch – Like hub but with intelligent – Better performance • Router – Forward packets from one LAN to another 16 07-May-15 Intranet vs. Internet • Intranet – A private network that is contained within an enterprise – Could be LANs and WANs • Internet – A public network of networks • Both use TCP/IP TCP/IP (cont) Application Layer Eg. WWW, FTP, IRC, Email, telnet, … Data Transport Layer Eg. TCP, UDP Segments Network Layer Eg. IP Packets Link Layer Eg. Ethernet, WiFi Frames Physical Layer Eg. Ethernet Cable, fiber-optics Bits 17 07-May-15 Packets • A small chunk of data transmitted over the Internet Jack Jill The Internet Thank You This PPT is downloaded from www.ec1107.weebly.com 18
© Copyright 2026