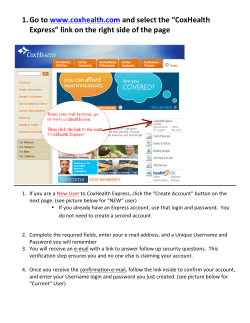
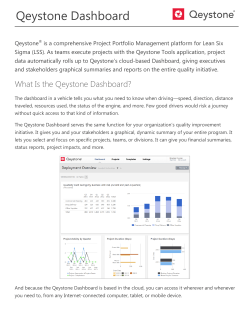
Administrating Concordance Evolution
Concordance Evolution Administrator's Guide Concordance® Evolution, version 3.3 • Security • Managing Licenses • Managing Users • System Management • Organizations • Folders • Matters • Datasets • Importing • Working with LAW PreDiscovery Cases • Binders • Review Sets • Tags • Productions • Exporting • Bulk Printing • Dataset Logs • Deduplication • Near-Deduplication • Knowledge Management • Searching - Admin • Search Settings • Reporting Concordance Evolution Administrator's Guide No part of this work may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying, recording, or by any information storage or retrieval system, without permission. While the information contained herein is believed to be accurate, this work is provided "as is," without warranty of any kind. The information contained in this work does not constitute, and is not intended as, legal advice. LexisNexis and the Knowledge Burst logo are registered trademarks of Reed Elsevier Properties Inc., used under license. Concordance is a registered trademark of LexisNexis a division of Reed Elsevier Inc. Other products or services may be trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective companies. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Concordance® Evolution Version: 3.3 Release Date: April 17, 2015 Contents 3 Table of Contents 8 Chapter 1 About Concordance Evolution Chapter 2 About the discovery process 10 Chapter 3 Concordance Evolution vs Concordance 14 Chapter 4 What's new in Concordance Evolution 18 Chapter 5 Administrating Concordance Evolution 22 ................................................................................................................................... 22 1 Navigating Concordance Evolution ................................................................................................................................... 26 2 Security .......................................................................................................................................................... 26 About Concordance Evolution security .......................................................................................................................................................... 27 About Security Policies .......................................................................................................................................................... 31 Creating user groups .......................................................................................................................................................... 33 Creating security roles .......................................................................................................................................................... 34 Customizing security policies .......................................................................................................................................................... 35 Assigning user group and roles ................................................................................................................................... 39 3 Managing Licenses .......................................................................................................................................................... 39 Importing Licenses .......................................................................................................................................................... 40 Assigning user licenses ................................................................................................................................... 41 4 Managing Users .......................................................................................................................................................... 41 Creating users .......................................................................................................................................................... 43 Importing users .......................................................................................................................................................... 44 Using Microsoft Active Directory Using Microsoft ......................................................................................................................................................... Active Directory 44 Adding Active ......................................................................................................................................................... Directory domains 45 Adding Active ......................................................................................................................................................... Directory servers 46 Deleting Active ......................................................................................................................................................... Directory domains 47 Deleting Active ......................................................................................................................................................... Directory servers 48 .......................................................................................................................................................... 49 Modifying users .......................................................................................................................................................... 51 Exporting users ................................................................................................................................... 52 5 System Management .......................................................................................................................................................... 52 Preference Management About preferences ......................................................................................................................................................... 52 Customizing ......................................................................................................................................................... admin preferences 57 .......................................................................................................................................................... 62 Server Management About server ......................................................................................................................................................... management 62 Maintaining......................................................................................................................................................... server services 62 .......................................................................................................................................................... 64 Printers Managing Printers ......................................................................................................................................................... 64 .......................................................................................................................................................... 64 Session Management Managing user ......................................................................................................................................................... sessions 64 .......................................................................................................................................................... 65 Job Management About jobs......................................................................................................................................................... 65 © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 4 Concordance Evolution View ing jobs ......................................................................................................................................................... 65 Reprocessing ......................................................................................................................................................... jobs 67 .......................................................................................................................................................... 73 Shares About shares ......................................................................................................................................................... 73 Creating shares ......................................................................................................................................................... 74 Modifying shares ......................................................................................................................................................... 75 .......................................................................................................................................................... 76 Notifications and Alerts About notifications ......................................................................................................................................................... and alerts 76 Creating notifications ......................................................................................................................................................... 77 View ing notifications ......................................................................................................................................................... 79 Deleting notifications ......................................................................................................................................................... 80 Creating search ......................................................................................................................................................... alerts 80 View ing search ......................................................................................................................................................... alerts 84 Editing search ......................................................................................................................................................... alerts 85 Deleting search ......................................................................................................................................................... alerts 85 .......................................................................................................................................................... 86 Audit Logs About audit......................................................................................................................................................... logs 86 View ing the ......................................................................................................................................................... system audit log 86 View ing the ......................................................................................................................................................... matter audit log 88 Exporting an ......................................................................................................................................................... audit log 89 Archiving system ......................................................................................................................................................... events 90 ................................................................................................................................... 91 6 Organizations .......................................................................................................................................................... 91 About organizations .......................................................................................................................................................... 91 Creating organizations .......................................................................................................................................................... 92 Managing organizations .......................................................................................................................................................... 92 Editing organizations .......................................................................................................................................................... 93 Deleting organizations ................................................................................................................................... 94 7 Folders About folders.......................................................................................................................................................... 94 .......................................................................................................................................................... 94 Creating folders .......................................................................................................................................................... 96 Editing folders .......................................................................................................................................................... 97 Deleting folders ................................................................................................................................... 98 8 Matters .......................................................................................................................................................... 98 About matters .......................................................................................................................................................... 99 Creating matters .......................................................................................................................................................... 100 Editing matters .......................................................................................................................................................... 101 Deleting matters .......................................................................................................................................................... 101 Managing Matters ................................................................................................................................... 103 9 Datasets .......................................................................................................................................................... 103 About datasets .......................................................................................................................................................... 105 Creating datasets .......................................................................................................................................................... 109 Editing datasets .......................................................................................................................................................... 110 Deleting datasets .......................................................................................................................................................... 111 About dataset fields 117 Adding fields.......................................................................................................................................................... to datasets .......................................................................................................................................................... 131 Editing dataset fields .......................................................................................................................................................... 133 Managing field-level security .......................................................................................................................................................... 135 Deleting fields from a dataset .......................................................................................................................................................... 135 Using CaseMap with Concordance Evolution .......................................................................................................................................................... 138 Using Equivio with Concordance Evolution ................................................................................................................................... 139 10 Importing .......................................................................................................................................................... 139 About importing files © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Contents 5 .......................................................................................................................................................... 139 About delimiter characters .......................................................................................................................................................... 141 Importing delimited text files .......................................................................................................................................................... 151 Importing LAW PreDiscovery cases .......................................................................................................................................................... 157 Importing subsequent data loads and overlays .......................................................................................................................................................... 164 Viewing dataset documents ................................................................................................................................... 164 11 Working with LAW PreDiscovery Cases .......................................................................................................................................................... 164 About LAW PreDiscovery and Concordance Evolution .......................................................................................................................................................... 166 Importing LAW PreDiscovery cases .......................................................................................................................................................... 171 Synchronizing data with LAW PreDiscovery ................................................................................................................................... 175 12 Binders .......................................................................................................................................................... 175 About binders .......................................................................................................................................................... 176 Creating binders .......................................................................................................................................................... 177 Managing binders ................................................................................................................................... 178 13 Review Sets 178 About review.......................................................................................................................................................... sets .......................................................................................................................................................... 179 Creating review sets .......................................................................................................................................................... 182 Assigning reviewers .......................................................................................................................................................... 183 Managing review sets .......................................................................................................................................................... 191 Exporting review sets .......................................................................................................................................................... 192 Deleting review sets ................................................................................................................................... 193 14 Tags About tags .......................................................................................................................................................... 193 .......................................................................................................................................................... 195 Creating tags .......................................................................................................................................................... 200 Managing tag security Editing tags .......................................................................................................................................................... 201 .......................................................................................................................................................... 204 Reordering tags Deleting tags.......................................................................................................................................................... 205 .......................................................................................................................................................... 206 Monitoring tags statistics ................................................................................................................................... 206 15 Productions .......................................................................................................................................................... 206 About productions .......................................................................................................................................................... 208 Creating production sets ................................................................................................................................... 217 16 Exporting .......................................................................................................................................................... 217 About exporting files .......................................................................................................................................................... 218 Exporting files .......................................................................................................................................................... 227 Synchronizing data with LAW PreDiscovery 231 17 Bulk................................................................................................................................... Printing .......................................................................................................................................................... 231 About bulk printing .......................................................................................................................................................... 232 Creating bulk print jobs ................................................................................................................................... 233 18 Dataset Logs .......................................................................................................................................................... 233 About dataset logs .......................................................................................................................................................... 234 Creating dataset logs ................................................................................................................................... 238 19 Deduplication .......................................................................................................................................................... 238 About deduplication .......................................................................................................................................................... 238 Creating deduplication jobs ................................................................................................................................... 240 20 Near-Deduplication .......................................................................................................................................................... 240 About Near-Deduplication .......................................................................................................................................................... 240 Creating near-deduplication jobs ................................................................................................................................... 242 21 Knowledge Management .......................................................................................................................................................... 242 Managing the knowledge base .......................................................................................................................................................... 243 Managing spelling variations © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 6 Concordance Evolution .......................................................................................................................................................... 246 Managing the thesaurus .......................................................................................................................................................... 250 Managing stop words .......................................................................................................................................................... 253 Managing reasons for redaction ................................................................................................................................... 257 22 Searching - Admin .......................................................................................................................................................... 257 Running admin dashboard searches ................................................................................................................................... 258 23 Search Settings .......................................................................................................................................................... 258 Defining dataset search settings .......................................................................................................................................................... 259 Managing saved search results .......................................................................................................................................................... 261 Managing Persistent Highlight ................................................................................................................................... 265 24 Reporting Audit Logs .......................................................................................................................................................... 265 About audit ......................................................................................................................................................... logs 265 View ing the ......................................................................................................................................................... system audit log 265 View ing the ......................................................................................................................................................... matter audit log 266 Exporting......................................................................................................................................................... an audit log 268 Archiving......................................................................................................................................................... system events 269 .......................................................................................................................................................... 269 Billing Reports Creating billing ......................................................................................................................................................... reports 269 .......................................................................................................................................................... 271 Matter reports View ing matter ......................................................................................................................................................... reports 271 Creating custom ......................................................................................................................................................... matter reports 274 Deleting matter ......................................................................................................................................................... reports 277 Exporting......................................................................................................................................................... matter reports 277 Chapter 6 Reference Information 280 ................................................................................................................................... 280 1 Unicode support ................................................................................................................................... 280 2 Glossary Index © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 287 Administrating Concordance Evolution User Guide About Concordance Evolution Chapter 1 8 Concordance Evolution About Concordance Evolution LexisNexis ® Concordance ® Evolution is a discovery enterprise solution that provides your team with a central location to manage all the electronically stored information that is generated. Concordance Evolution is designed to handle large-scale, complex litigation cases and helps your team search, review, organize, produce and share information during the discovery process. It offers the speed you demand with exceptional product management and support. You now can have the latest in modern discovery technology without the costly enterprise investment or overhead. Concordance® Ev olution features include: Scalable Microsoft® SQL Server back-end Concept searching from Vivisimo ® Velocity Integration with LAW PreDiscovery® Document family grouping Near-duplicates identification and comparisons Advanced searching Redactions and Annotation tools from IGC™ Brava! Find and redact Enhanced tagging File type icons in the Table view Privilege Log reason codes and descriptions LexisNexis now offers an electronic discovery and litigation document management solution that is a good fit for any size case. Use Concordance Evolution for large-scale litigation cases, while our established Concordance discovery review management software is well-suited for small- to mid-sized litigation cases. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution User Guide About the discovery process Chapter 2 10 Concordance Evolution About the discovery process Discovery has been around for a long time. In the past, it involved primarily paper documents that had to be searched through manually for privileged information or evidence. Today, discovery largely involves “electronically stored information” (ESI), which is simply data that exists in electronic format, stored in computers primarily as documents and e-mail. The question of how to search and review ESI for evidence comes down to two options: print it out and review it manually (slow and tedious) or put it into a database and review it on a computer (fast and effective). That’s where Concordance Evolution comes in—it’s an e-discovery review tool designed specifically for reviewing documents electronically, a process made faster and easier by its robust search and review features. Electronic discovery (e-discovery) starts with data being identified and collected. When all known discoverable data is collected, it needs to be “processed”. In this step, documents get scanned, electronic files get converted and/or extracted, and the process of data filtering is completed (which can reduce thousands of documents down to a few hundred). An administrator can then assign documents through reviewsets, where it gets reviewed and analyzed and, finally, produced for opposing counsel and/or the defense team. Discoverable Data Discoverable data is data that has been identified, preserved, and collected for a case that © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. About the discovery process 11 becomes (after many hours of review and analysis) the facts and issues that you either have to turn over to opposing counsel or use as evidence to defend a client. There are three types of discoverable data that Concordance Evolution works with: Paper documents Electronic documents E-mail Electronic Documents Concordance Evolution loads most electronic documents with ease, whether converted to tagged image file format (TIFF) or in their native form (created by popular software programs such as Microsoft® Word, Adobe ® Acrobat®, etc.). All electronic documents contain metadata that has been captured by the native application. However, additional metadata can still be added manually, if necessary. Native review can be done, using the Near Native view in Concordance Evolution. Near Native review has the following benefits: Review documents and images regardless of whether or not you have the native application An intuitive user interface for navigating and reviewing documents Advanced markup tools to review and annotate documents and images Find and Redact feature to redact only specific text within a document Original document format persisted E-mail Concordance Evolution makes it easy to import Microsoft® Outlook® e-mail messages (those with .PST file extensions). Other types of e-mail, such as those from Lotus Notes, must be converted before being loaded into Concordance Evolution. Paper Documents Even in this electronic age, people still use paper to write notes, capture diagrams, and so on. Additionally, letters, spreadsheets, reports and other documents created with computer programs are often printed out and the original electronic document lost or destroyed. In order for paper documents to be usable in Concordance, they must be scanned, to capture both text and an image (picture) of the document, and coded, to capture additional information such as author, document type, date created, and so on. This can be done using the scanning and optical character recognition (OCR) feature in a tool such as LAW PreDiscovery®. Scanning Paper is typically scanned into tagged image file format (TIFF) or portable document format (PDF). For each TIFF or PDF, you’ll have a corresponding file in the review tool, with matching document numbers. A TIFF can be a single page or multiple pages, just as a single document © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 12 Concordance Evolution can be one or several pages in length similar to a PDF file. So, not only will you be able to view the documents in Concordance Evolution, you’ll be able to read the text of the document also (as a result of optical character recognition software, such as LAW PreDiscovery®). Coding / Metadata Electronic documents contain additional information about them, referred to as metadata, which is data that is captured automatically by the software program, such as date created, author, and so on. This data is searchable and of great value to you during document review. However, because paper documents are scanned and lack this automatic coding, they must be coded manually (although there are now software tools that can help speed up this process). © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution User Guide Concordance Evolution vs Concordance Chapter 3 14 Concordance Evolution Concordance Evolution vs Concordance Specifications Concordance ® Concordance ® Evolution Case Size Small to midsize cases Large, complex or multi-district litigation cases Database Capacity Hundreds of registered databases, 12 megabytes of data per field and over 33 million records per database Hundreds of registered databases with software and network scalability to serve multiple reviewers and administrative tasks running concurrently Speed Dependent on firm, company, or agency's local computer and network environment Dependent on firm, company, or agency's local computer and network environment Installation Server or workstation Minimum of four servers (including SQL Server) Data Location Case data resides on firm, company Case data resides on firm, company or or agency internal network agency internal network Data Access Via firm, company or agency's internal network only. Via internal secure IP address No desktop installation required. Desktop installation required Data Security Upgrades Firm, company, or agency's network Firm, company, or agency's network security settings. security settings. Data resides behind the firewall of the organization. Data resides behind the firewall of the organization. Internal litigation/IT team installs. Initial setup and upgrades performed by Concordance Evolution Field Services team. Current subscription required. Internal litigation/IT team assumes responsibility after training. Current subscription required. Features Concordance ® Concordance ® Evolution Reviewer Search Alerts X Search Highlights in Native Viewer X Concept Search X Heavy Bulk Tagging X Multiple User Bulk Tagging X Tag Families and Threads X © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Concordance Evolution vs Concordance Features Concordance ® Concordance ® Evolution Find And Redact in Native Viewer X Undo and Redo Functions in Native Viewer X OCR On the Fly in Native Viewer X Global Replace X 15 X Administrator LAW PreDiscovery Integration ® X Security, Permissions, and Roles settings X Concordance Programming Language (CPL) X Unicode Support X Capture and Create Fields from .DAT file X Index and Reindex X Persistent Hit Highlighting X X X Tag Behavior settings X Run Parallel Jobs in the Background X Reporting X Binders & Review Sets X Native file conversion reprocessing X © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution User Guide What's new in Concordance Evolution Chapter 4 18 Concordance Evolution What's new in Concordance Evolution Concordance Evolution introduces the following features and product enhancements: Version 3.3 New Sticky Zoom and Sticky Rotate features for maintaining zoom and page rotation while navigating records during a review. For more information, see Adjusting document size. New server configuration option to remove blank pages when importing and converting files. For more information, see About importing files. Version 3.2 Concordance Evolution is now compatible with Microsoft® Windows® 8 and 8.1. New user interface for creating and exporting billing Reports from the System dashboard. For more information, see Creating billing reports. Improved performance when navigating between organizations, folders, matters, and datasets from the Admin dashboard. Version 3.1 Persistent Highlight Persistent Highlight for the Document Data view, when enabled, accesses a table of search terms assigned to a dataset and highlights those terms. For more information, see Using Persistent Highlight. Search History Search History is now retained after a user logs out of the system making it easy to rerun previous search queries when the user logs back in. For more information, see Viewing search history. Tags panel improvement Reviewers can set their preference for the Tags panel to be docked to the left or right side for reviewing documents. For more information, see Customizing personal preferences. Version 3.0 Improved reporting user interface Generate audit log reports for system and matter events using the new audit log reporting user interface. New matter charting features allow you to track user activity on a daily, weekly, monthly, and yearly basis. For more information, see About audit logs and Viewing matter reports. Unicode Support In Concordance Evolution version 3.0, the Unicode Standard is supported in Arabic, Chinese, English, Hebrew, Japanese, Korean, Russian, and other languages. For more information, see Unicode support. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. What's new in Concordance Evolution 19 Synchronize data with LAW PreDiscovery Once a LAW case is imported and reviewed, Concordance Evolution's synchronization feature uses the project.ini file to sync those changes back to the LAW PreDiscovery case for further processing. For more information, see About LAW PreDiscovery and Concordance Evolution or Synchronizing data with LAW PreDiscovery. Improved exporting options New auto-increment image file numbering, native file export, field naming for files, and recreating family grouping options. For more information, see Exporting files. Version 2.2.3 or earlier Built-in Near-Deduplication analysis Identify documents based on text percentage likeness allowing reviewers to compare differences and increase reviewing efficiency. For more information, see About NearDeduplication. Binder workflow for review organization Organize dataset review workflows using binders and review sets. For more information, see About Binders and About review sets. Automated tagging when checking in documents After a reviewer has finished a review, the reviewer has the option to select the Complete option and have Concordance Evolution automatically tag all the documents in the review set with the Reviewed tag. For more information, see About review sets. Import LAW PreDiscovery Cases Import LAW PreDiscovery cases without the use of a load file. Import field names and data, including Near Duplicate information. For more information, see Importing Law PreDiscovery Cases and About dataset fields. Improved production and load file export user interface New user interface for creating production sets and exporting load file from Concordance Evolution. For more information, see Creating production sets and Exporting to load files. Near-native conversion priority processing for import and production jobs When scheduling import and production jobs, the order the jobs are processed can be set to low, medium, or high priority allowing higher priority jobs to be processed first. For more information, see About importing files and Creating production sets. Recreate family groupings When exporting load files, the Recreate Family Group option uses a selected Family ID field to identify all the documents and corresponding attachments within a family group and export the family grouping information to the specified load file. For more information, see About exporting files © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 20 Concordance Evolution Share saved searches Create, save, and share search queries with other reviewers that are within the same Concordance Evolution organization. For more information, see Saving search queries. Auto assign user licenses Administrators can set the Auto Assign option so that when a user logs into Concordance Evolution for the first time, the system automatically validates the user and assigns the user a license. The license count is then automatically updated on the License Management dashboard. For more information, see Assigning user licenses. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution User Guide Administrating Concordance Evolution Chapter 5 22 Concordance Evolution Administrating Concordance Evolution Navigating Concordance Evolution The Concordance Evolution user interface consists of two main dashboards: Admin Review The dashboards available are dependent on the user group an individual is assigned. See, About Concordance Evolution security. The dashboards are accessible using the tabs at the top of the Concordance Evolution site. The Admin and Review tabs navigate to a dashboard specifically designed with the tools and information updates needed to perform administrative and review tasks. The Reports tab displays a list of reports that can be run for datasets or administrative needs. You can change the dashboard you want to use as your Home page by clicking the Preferences link on the Concordance Evolution bar. However, your Concordance Evolution permissions are set up by your system administrator and those permissions determine which dashboards you can view and access in Concordance Evolution. We recommend that you use the Concordance Evolution navigation tools to access different dashboards of the software as opposed to using your Internet browser's navigation tools, such as the Back button. Learn more about the Admin Dashboard: The Admin dashboard contains the tools you need to perform your administrative tasks quickly and efficiently. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 23 Most reviewers do not have access to the Admin dashboard unless permission has been granted by the system administrator. Admin Search bar The Admin Search bar is located on each page of the Admin dashboard. Use the Admin Search bar to locate information or areas of the application. See the Review dashboard for details on searching case/matter documents. Search results provide a navigation link that takes you to the applicable page in the Concordance Evolution. For example, if you type license in the Search field, the search results display a link to the License Management dashboard. For more information about searching, see Running Admin searches. System pane The System pane on the left side of the screen displays the hierarchical structure of organizations, folders, matters, and datasets. You can create multiple organizations, folders, matters, and datasets under the System folder, but there is only one System in Concordance Evolution. You can navigate to a specific organization, folder, matter, or dataset by clicking the corresponding organization, folder, matter, or dataset in the System pane. When you click an organization, folder, matter, or dataset, the dashboard for the selected organization, folder, matter, or dataset is displayed. The name of the element you select in the System pane displays above the dashboard toolbar. If you click System in the System pane, the © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 24 Concordance Evolution Admin dashboard is displayed. The System pane contains an Admin search field so you can locate a folder, matter, or dataset in the tree quickly. Your search term is highlighted in yellow so you can easily see it when scrolling within the pane. To show and hide the System pane, do one of the following: To hide the System pane, click the arrow button next to the pane. To show the System pane, click the green Arrow button on the left side of the dashboard. System information In the lower section of the Admin dashboard, the Concordance Evolution system status is displayed. The System status displays the following: Users displays the details of the number of reviewers (users) currently logged into the software and provides a link so that you can quickly email all logged in users from the Send Notifications dashboard. Click the User Management link to open the User Management dashboard and oversee all user accounts. Matters and Datasets displays the total number of datasets created in Concordance Evolution and the number of matters they are associated with. Click the Matters and Dataset link to open the Folders Matters and Datasets page where you can view a complete listing of all folders, matters, and datasets as well as the size of the datasets, the number of documents within it, and the percentage it has been reviewed to-date. Jobs provides a instant glance at the total number of scheduled and completed jobs today. Click the Jobs link to open the Job Management dashboard. The Job Management dashboard allows you to view job scheduling tasks, including the job type, job name, and scheduled run date and time. Servers displays current server(s) and services running within the Concordance Evolution environment. Learn more about the Review Dashboard: The Reviewer dashboard is the Home page for reviewers in Concordance Evolution. Here you will find the current status of your work assignments and it is where you can access review sets you are assigned. The Review dashboard task panes include: Review Binders pane The Review Binders pane displays a list of datasets and their associated binder(s) containing review sets that are assigned to for review. When you select a binder from the Review Binders pane, the Review Sets table is displayed in the center pane listing all the available review sets for the selected binder. Use the expand (+) and collapse (-) button to show/hide the binders and review sets. When a binder is selected, the Review Sets table displays in the center of the Review dashboard and lists the following information for each review set assigned to the selected binder: © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 25 Name - the name of the review set Due - the date review set is due to be completed Checked Out To - the name of the reviewer who has the review set checked out # Docs - the total number of documents within the review set Reviewed - the number of documents that are tagged as Reviewed. To view the tagged documents, click the number in the column. Not Reviewed - the number of documents that are tagged as Not Reviewed. To view the tagged documents, click the number in the column. Actions - contains three links for checking in/out the review set, checking the review set in as completed, or releasing the review set without checking the documents in so that another reviewer can view them. Messages The messages table displays any recent notifications you may have received. To view a message: 1. In the Notification column of the Messages table, click the message link for the message you want to view. The Notification Details dashboard opens and displays the message. 2. When finished, do one of the following: To open the Notification Management dashboard to see additional messages, on the Notification Details dashboard toolbar, click the Return to Notifications button. To return to the Review dashboard, click the Review tab. Quick Tools pane The Quick Tools pane contains links to quickly access areas of the application that you will use most: Search, Messages, and History. Search displays links to the Saved Searches, Saved Search Results, and Search Alerts dashboards. Messages links to the Notification Management dashboard that contains tabs for Notifications and Background Tasks. History links to the Search History dashboard that contains tabs for Search History, Saved Searches, Saved Search Results, and Search Alerts. Access review set documents: The Review Sets table in the center of the Review dashboard, displays the review sets assigned to the selected binder and contain the documents that are assigned to you for review. There can be more than one review set with a binder. A review set may contain various documents and files that are part of the case's overall record collection. For more information about review sets, see About review sets. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 26 Concordance Evolution Assignments are listed by Binder, then review set. Click a binder to view the current status of each review set assigned to the binder, including whether the review set is checked in or out, the user it was checked out to, the number of documents in the review set, and the number of documents reviewed and not reviewed. You can view the documents in a review set without checking them out or you can check out the documents. When a review set is checked out, it locks the review set so no other users can access the documents. If your Concordance Evolution system administrator set up the Binder with Secure Check Out Enabled option, when a review set is checked out it locks the review set so that others cannot check them out or view the documents. If the Secure Check Out Enabled option is not selected, when a review set is checked out the Reviewed and Not Reviewed tags for the review set are not available for other users. For more information about review sets, see About review sets. Navigate with links and breadcrumbs: Both the Admin and Review dashboards provide numerous links to help you navigate quickly within the application to perform your daily tasks. For the Admin dashboard, you can also follow the breadcrumb trail located at the top of each dashboard. Breadcrumbs can be referenced to help you locate where you are in the application, with the current dashboard displaying in black. Or you can click a breadcrumb link that is highlighted in blue to navigate to that particular application dashboard. Security About Concordance Evolution security Concordance Evolution manages security using security policy settings. Security policies provide the permission settings for field, tag, and function in Concordance Evolution. Security policies are defined per user group at the system, organization, folder, matter, and/or dataset level. An individual user's permissions are defined by the user group the user is assigned to. You cannot modify security policy settings at the individual user level. Field-level and tag-level security are based on the security policy settings for a user group at the dataset level, but field and tag security settings are defined at the individual field and tag levels within each dataset. For more information about field security, see Managing field security. For more information about tag security, see Managing tag security. When you modify security policy settings, the changes are applied the next time the user logs on to Concordance Evolution. The Active User check box on the Add User and Edit User dashboards and a current license determine whether a user can access Concordance Evolution. When the Active User check box is selected and the user is provided a license, the user can log on to Concordance Evolution. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 27 To set up user security in Concordance Evolution: 1. Create an Organization 2. Creating user groups 3. Create security roles, if needed 4. Assign security roles to user groups 5. Customize user group security policies, if needed 6. Create users and assign to user group(s) 7. Assign user licenses About Security Policies Security policies are used to approve and deny access to features within Concordance Evolution. Each policy within the system is enforced and automatically applied based on the default settings for the selected user role. Each policy can be set to Allowed or Deny by the Super Admin or the Concordance Evolution System Administrator. The following is a list of the default access security policy settings: Common Policies Policy Description Lim ited Review er Review er OrgReview er Lead Level Adm in Super/ System Adm in C anViewFolderMatter View folder, matters, and Dataset datasets C anViewReviewerda Enable/disable Reviewer shboard dashboard tab C an Manage NearNativeViewer Access the Near Native view, and associated image, including zoom features C anManageDocumen Access Document Data tDataViewer view C anViewSnippetView Access the Snippet view C anViewTableView Access the Table view C anViewThreadView View family & threads in the Near Native and Document data views C anSendToC aseMap Send document, documents and text to C aseMap from the © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 28 Concordance Evolution Policy Description Lim ited Review er Review er OrgReview er Lead Level Adm in Super/ System Adm in Lim ited Review er Review er OrgReview er Lead Level Adm in Super/ System Adm in Snippet, Table, Near Native and Document Data views C anPerformReviewe Run any simple or rSearch advanced search from the Reviewer dashboard C anManageGroupBy Access to GroupBy Fields features C anLaunchDualView Access to Dual view features for single and multiple browsers C anEmailDocuments Email documents C anPrintDocuments Print single or multiple documents C anViewField View and reorder fields C anSetC onceptSear ch Execute concept searches C anManageSystemFi View system fields from elds the Reviewer dashboard C anViewJobs View jobs C anViewNotification View and delete notifications Enhanced security policies Policy Description C anManageADDomai Add, edit, remove, and n view AD Domain C anManageAuditing View, clean up, and export the audit log on the Admin side C anManageBinder C reate, edit, and delete binders C anManageFolder C reate, edit, and delete folders C anManageMatter C reate, edit, and delete matters C anManageDataset C reate, edit, and delete dataset Full access to dataset for specific dataset © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution Policy Description C anManageTags C reate, edit, and delete tags C anManageImport View, create, edit, and cancel import (Load File, Edoc, DC B) jobs Lim ited Review er Review er OrgReview er Lead Level Adm in 29 Super/ System Adm in C reate and edit import templates C anManageExport C reate, view and cancel export job C reate an export template C anManageProductio View, create, and edit n productions and production templates C anManageBulkPrint Execute a bulk print job from the Admin side C anManagePrivilege Log View, create, and edit privilege log jobs C reate, use, delete and edit privilege log job templates C anManageDeduplic ation View, create and cancel deduplication job C anManageSystemS Edit system settings, set ettings password complexity and set system settings C anManageServers Add, edit, and remove servers Set Vivisimo settings and map printers C anManageJobs View jobs, job summary and Log files C anManageKnowled geBase C ustomize knowledge base, noise or stop words, reasons for redactions, spelling variations, and thesaurus Turn knowledge base on or off C anManageNotificati View and full access to on Notification, Alerts and Send Notification settings from the Admin dashboard C anManageUserGrou View user management © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 30 Concordance Evolution Policy Description p C anManageRolesAnd C reate, edit, and delete Policies custom roles and policies C anManageUser C reate, edit, export, import, and remove users Kill a user session C anManageReviewS ets C reate, edit, and delete review sets C anManageSystemR Run system audit log and eports billing report C anManageMatterRe Run all reports for ports assigned matters C anPerformMarkup Perform markups C anDeleteDocument Delete documents in the s reviewer interface C anManageC ommen View, create, edit, and ts delete document- and text-level comments C anForcePolicies Force polices C anEditField Edit field C anViewTags View tags C anManageTagSettin C reate and edit tags gs C anOverrideTag Override tags C anC hangeTagState C hange tag state (bulk, family & threads) C anDeleteTag Delete tags C anManagePreferen ces View and edit preferences C anManageAdminSe Perform admin search arch C anSetPreviewSize Set number of records can be viewed in Snippet View C anManageShares C reate, edit, and delete shares C anManageOrganiza C reate, edit, and delete tion an organization Org Admin ViewOnly View imports and server information © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Lim ited Review er Review er OrgReview er Lead Level Adm in Super/ System Adm in Administrating Concordance Evolution Policy Description Lim ited Review er Review er OrgReview er Lead Level Adm in 31 Super/ System Adm in Reviewer Lead View- View some application Only features C anViewRecentActivi Enable/disable viewing ty Recent Activity option C anViewAdmindashb Enable/disable Admin oard dashboard tab Creating user groups A user group contains a collection of users and security policies that are assigned to organizations. User groups allows you to use pre-defined security policy settings when you create a new user to help speed up the user creation process. For example, if you want to control access to datasets for reviewers, you can create a different user group or each case. You can also create user groups for your most commonly used roles, such as attorney, paralegal, and reviewer, and assign the user group each time you create a user ID. Users can belong to more than one user group and the security roles and policies can be set differently for each user or user group per organization, folder, matter, or dataset. There are two ways to add user groups to Concordance Evolution: Manually add user groups within Concordance Evolution. Microsoft® Active Directory® All users in an Active Directory domain are automatically added to the users list in Concordance Evolution when the Active Directory domain is added to Concordance Evolution. Updates to the users and user groups in the Active Directory domain, including user names and passwords, are automatically updated in Concordance Evolution. Active Directory users are not editable in Concordance Evolution, but you can assign Concordance Evolution security policies to the domain user groups in Concordance Evolution. For more information about adding Active Directory domains, see Adding Active Directory domains. When a user group is created within Concordance Evolution, it is called a local user group. When a user group is added to Concordance Evolution using Active Directory, is called an AD user group. To create a local user group: 1. Do one of the following: Point to the Admin tab, and then click User Groups. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard, click the Security button, and then click Roles. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 32 Concordance Evolution By default the Local User Group list is displayed. 2. On the User Group dashboard toolbar, click the Add a User Group button. 3. In the Name field, type the user group name. 4. (Optional) In the Description field, type the user group description. 5. To assign users to the user group, click the Assign button. 6. In the Choose User(s) dialog box, do one of the following: To add users from an Active Directory domain, select the Active Directory option (Default). To add users from a Local Directory, select the Local Directory option. 7. Select the check box next to the user(s) to include in the user group, and then click Save. If you have not created any users yet, you can add the users to the user group when you are creating the users on the Create User dashboard, or add the users to the user group on the Edit User dashboard after the users are added to Concordance Evolution. 8. From the Organization list, select an organization to assign the user group. 9. When finished, click Save to return to the User Group Management dashboard. The new user group is displayed in the Local User Groups list. After creating a user group, you can further assign a security role, users, and/or customize user group preferences. For more information about assigning security roles to user groups, see Assigning roles to user groups. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 33 Creating security roles In Concordance Evolution, a security role is a group of security policy settings. Security roles are assigned to user groups, and can be used as security profiles to define user groups by the jobs they perform. Concordance Evolution comes with some predefined system security roles that you can assign to user groups or use as templates for creating new custom user roles. On the Role Management dashboard, the predefined security roles are displayed in the System Roles list, and custom security roles are displayed in the Custom Roles list. Custom security roles are added using the Create Role dashboard. Security policies are assigned to security roles. When you assign a security role to a user group, the user group inherits the security policy settings for the security role. The following are the predefined Concordance Ev olution security roles: Org-level Admin - Full control of all functions within select sub-folders of the System folder. This role includes limited Admin rights to the Admin and Review tabs. Reviewer Lead - Limited rights to the System folder to Create Users and Edit User preferences; Limited rights to the Dataset level for View/Modify/Delete Reviewsets, Assign Reviewsets, Execute Dataset level jobs, and View/Modify/Delete Dataset settings. This role also includes limited rights to functions with the Admin and Review tabs, Reviewer - Full control of all functions within a Reviewset. Limited Reviewer - Limited rights to a Reviewset. System Security Roles cannot be changed. To create a custom security role: 1. Do one of the following: Point to the Admin tab, and then click Roles Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard, on the Admin dashboard toolbar click the Security button, and then click Roles. 2. On the Roles Management dashboard, click the Add Role button to open the Create Role dashboard. 3. In the Role Name field, type the security role name. 4. (Optional) In the Description field, type the security role description. When you are creating a security role you can assign a new set of security policies to a security role or copy the security policy settings of another security role to the new role, and then customize the security policy settings for the new role. 5. To define security policies for the role, do one of the following: To define a new set of security policies for the security role, select the Set New Policies option. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 34 Concordance Evolution To use the security policy settings from another role, select the Policies From option and then click the role containing the security policies settings you want to use for the security role. 6. Click the Continue button. Clicking Continue displays the Allowed Policies and the Denied Policies for the security role. When you click the Set New Policies option, by default, no security policies are applied to the security role. When you click the Policies From option, the security policy settings for the security role you selected from the Policies From list are displayed in the Allowed Policies and Denied Policies lists. 7. To view the security policies for a function, click the right arrow, , to expand a security policies list. To collapse a security policies list, click the down arrow, . 8. Do any of the following: To allow a security policy, expand the Denied Policies list and locate the security policy you want to add, and then click Allow. To deny a security policy, expand the Allowed Policies list and locate the security policy you want to remove, and then click Deny. The security policies you selected the Allow option for are displayed in the Policies list in the Allowed Policies box. The security policies you selected the Deny option for are displayed in the Policies list on the Denied Policies box. 9. When finished, click the Create button to return to the Roles Management dashboard. The new security role is displayed in the Custom Roles section of the Roles Management dashboard. Customizing security policies Custom security policy settings can be assigned to user groups at the system, organization, folder, matter, and/or dataset level. You can choose to customize the security policy settings at each individual level, or assign them at the parent level. When you apply custom security policy settings at the parent level, the settings are automatically inherited and applied at the child levels. If you want to lock security policy settings so that they cannot be edited by users, you can select the Forced check box for a policy on the Edit User Group Policy dashboard at the applicable level. When the Forced check box is selected, the security policy cannot be edited at the level you selected the check box, or at any of its child levels. If you select the Forced check box for a security policy at the parent level, and there is already a custom security policy setting for the policy at the child level for the user group, the parentlevel custom security policy setting takes precedence over the child-level setting for the user group. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 35 To customize security policies: 1. Do one of the following: Point to the Admin tab, and then click Roles. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard, click the Security button, and then click Roles. Both System and Custom Roles are list on the dashboard. System Roles cannot be changed. 2. Do any of the following: To allow a security policy, expand the Denied Policies list and locate the security policy you want to add, and then click Allow. To deny a security policy, expand the Allowed Policies list and locate the security policy you want to remove, and then click Deny. The security policies you selected the Allow option for are displayed in the Policies list in the Allowed Policies box. The security policies you selected the Deny option for are displayed in the Policies list on the Denied Policies box. 3. When finished, click the Save button. Assigning user group and roles After creating the user group and security roles, the user group can be assigned to an organization, folder, matter, and dataset level. When you assign a security role to a user group, the user group inherits the security policy settings of the security role. You can assign multiple roles or specific policies to a user group at the folder, matter, and dataset level. If a security role is applied at the parent level, then the security role and policy settings are automatically applied to the child levels. Security roles applied at the folder, matter, and dataset level can be further customized. Security Hierarchy (from top to bottom): System Organization (folders created under the System) Folder (folders created under an organization) Matter Folder (folders created under a matter) Dataset © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 36 Concordance Evolution To assign user groups and security roles at the organization level: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the organization to assign security roles to a user group. 3. On the organization's dashboard toolbar, click Grant Permissions. 4. In the Organization/Folders/Matters/Datasets section, click the organization checkbox. 5. Click the Assign Group button, and then in the Select User Group(s) dialog box, select the check box for each user group to assign to the organization, and then click the Save button. 6. In the User Groups for Selected Folder section in the Actions list, select the role from the list to apply to the user group. 7. When finished, click the Apply Permissions button. The user group and assigned role are displayed in the Authorized Users table on the organization's dashboard. To edit permissions at the organization level: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the organization level to make changes to permissions. 3. On the organization's dashboard toolbar, click the Manage Permissions button. 4. Do any of the following: To change the permissions for an assigned group, click the Permissions link, make any necessary changes, and then click Save. To remove the permissions for an assigned group, click the Remove link, and then when prompted to confirm the deletion click OK. To add additional user group, click the Add Group button, and select the group(s) from the Select User Group(s) dialog box, and then click Save. 5. When finished, click the Back button to return to the organization's dashboard. To assign user groups and security roles at the folder level: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the folder to assign security roles to a user group. 3. On the folder's dashboard toolbar, click the Manage Permissions button. 4. To add a user group, click the Add Group button. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 37 5. In the Select User Group(s) dialog box, select the check box for each user group to assign to the folder. 6. To edit/assign security policies, for a user group, click the user group's Permissions link. 7. In the Permissions for User Group [user group name] section, do any of the following: To assign a role, click the Assign Roles button, in the Assign Roles dialog box, select the check box for each role you want to apply to the folder, and then click OK. To assign specific policies to a user group, click the Assign Policies button, in the Edit User Group Policy dialog box, select the Allow or Deny option for each policy, and then click OK. To lock a policy for all folders, matters and datasets under the selected folder, click the Assign Policies button, in the Edit User Group Policy dialog box, select the Forced check box for each policy you want to lock, and then click OK. 8. To export the permissions to a comma-separated (.csv) formatted file, click the Export button, and then when prompted do any of the following: Click Open to view the file, in the Download Complete dialog box, click Open to open the file in your default spreadsheet application. Click Save to save the file, in the Save As dialog box, navigate to where you want to save the file, and then in the File Name field, type the file name and click Save. 9. When finished, on the Folder Permissions toolbar, click the Save button. The user group and assigned role are displayed in the Authorized Users table on the organization's dashboard. To assign user groups and security roles at the matter level: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the matter to assign security roles to a user group. 3. On the matter's dashboard toolbar, click the Manage Permissions button. 4. To add a user group, click the Add Group button. 5. In the Select User Group(s) dialog box, select the check box for each user group to assign to the matter. 6. To edit/assign security policies, for a user group, click the user group's Permissions link. 7. In the Permissions for User Group [user group name] section, do any of the following: To assign a role, click the Assign Roles button, in the Assign Roles dialog box, select the check box for each role you want to apply to the folder, and then click OK. To assign specific policies to a user group, click the Assign Policies button, in the Edit User Group Policy dialog box, select the Allow or Deny option for each policy, and then click OK. To lock a policy for all folders, matters and datasets under the selected folder, click the Assign Policies button, in the Edit User Group Policy dialog box, select the Forced © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 38 Concordance Evolution check box for each policy you want to lock, and then click OK. 8. To export the permissions to a comma-separated (.csv) formatted file, click the Export button, and then when prompted do any of the following: Click Open to view the file, in the Download Complete dialog box, click Open to open the file in your default spreadsheet application. Click Save to save the file, in the Save As dialog box, navigate to where you want to save the file, and then in the File Name field, type the file name and click Save. 9. When finished, on the Matter Permissions toolbar, click the Save button. The user group and assigned role are displayed in the Authorized Users table on the organization's dashboard. To assign user groups and security roles at the dataset level: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the dataset to assign security roles to a user group. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Manage Permissions button. 4. To add a user group, click the Add Group button. 5. In the Select User Group(s) dialog box, select the check box for each user group to assign to the dataset. 6. To edit/assign security policies for a user group, click the user group's Permissions link. 7. In the Permissions for User Group [user group name] section, do any of the following: To assign a role, click the Assign Roles button, in the Assign Roles dialog box, select the check box for each role you want to apply to the dataset, and then click OK. To assign specific policies to a user group, click the Assign Policies button, in the Edit User Group Policy dialog box, select the Allow or Deny option for each policy, and then click OK. To lock a policy, click the Assign Policies button, in the Edit User Group Policy dialog box, select the Forced check box for each policy you want to lock, and then click OK. 8. To export the permissions to a comma-separated (.csv) formatted file, click the Export button, and then when prompted do any of the following: Click Open to view the file, in the Download Complete dialog box, click Open to open the file in your default spreadsheet application. Click Save to save the file, in the Save As dialog box, navigate to where you want to save the file, and then in the File Name field, type the file name and click Save. 8. When finished, on the Folder Permissions toolbar, click the Save button. The user group and assigned role are displayed in the Authorized Users table on the organization's dashboard. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 39 M anaging Licenses Importing Licenses Use the License Management dashboard to add, remove, and manage your Concordance Evolution licenses. Concordance Evolution comes with one System Admin license. Additional licenses may be purchased from Concordance Evolution Sales and added to Concordance Evolution. When the license seats are activated, the Concordance Evolution license count on the License Management dashboard is updated. Seats are valid during the date range specified and are listed in the order of expiration. If the Auto assign license is enabled, when valid users login for the first time, they are automatically given a license and the license count is updated. To add a new Concordance Evolution license key: 1. Contact Concordance Sales at [email protected] or phone at 1-800-4218398 to request a Concordance Evolution license. In the license request, please include the following: MAC address of the Server where the Director Service is running (possible the Application Server) Number of seats needed Length of time needed When your license request is approved, LexisNexis will send an e-mail containing the license key. 2. Once you receive the license keys, open Concordance Evolution. 3. Do one of the following: Point to the Admin tab, and then click Licensing. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard, click the Config button, and then click Licensing. 4. On License Management dashboard toolbar, click the Add License button. 5. In the Add New License dialog box, in the License Key field, copy and paste the license number from the email you received. 6. In the Description field, type a description for the license. 7. Click the Add button to activate this license. When the seats are activated, the license count is updated and the license key is added to the license key list on the License Management dashboard. Seats are valid during the © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 40 Concordance Evolution date range you specified in the e-mail. When you enter the license key, make sure that there are no extra spaces at the front or end of the entry, otherwise you will receive an error stating that it is a duplicate license and that you need to contact the sales department. To delete a license: 1. Do one of the following: Point to the Admin tab, and then click Licensing. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard, click the Config button, and then click Licensing. 2. On the License Management dashboard, from the list of licenses, click the Remove link for the license you want to remove. 3. When prompted, click Yes to delete the file. Assigning user licenses When the licenses are activated, the Concordance Evolution license count on the License Management dashboard is updated. Seats are valid during the date range specified. If the Auto Assign License is enabled in the System Configuration Service settings, when valid users login for the first time, they are automatically given a license and the license count is updated. For more information, see To assign users to licenses: 1. Do one of the following: Point to the Admin tab, and then click Licensing. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard, click the Config button, and then click Licensing. 2. On the License Management dashboard toolbar, from the list of licenses, click the Users link to assign a license. 3. On the Assign User(s) dashboard, click the Assign button. 4. Do one of the following: To add users from an Active Directory domain, select the Active Directory option. To add users from the local directory, select the Local Directory option. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 41 The list of users is automatically generated based on the option selected. 5. In the Select User(s) dialog box, select the check box for each user you want to assign a license. To quickly find a user, type the username in the filter field and then click Filter. To clear the filter field, click Reset. 6. When finished, click Save. Each user that is assigned to the selected license is displayed in the list of assigned users along with the number of seats available. 7. When finished, click the Save button. To remove users from licenses: 1. Do one of the following: Point to the Admin tab, and then click Licensing. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard, click the Config button, and then click Licensing. 2. On the License Management dashboard, from the list of licenses, click the Users link for the license you want to edit. 3. On the Assign User(s) dashboard, from the assigned users list, select the user(s) you want to remove, and then click the Unassign button. 4. When finished, click the Save button. M anaging Users Creating users There are three ways to add users to Concordance Evolution: Manually add users: Users can be added manually from the Add User(s) dashboard. Importing users: Users can be imported into Concordance Evolution from CSV (commaseparated values) files. For more information about importing users, see Importing users. Microsoft® Active Directory®: All users in an Active Directory domain are automatically added to the users list in Concordance Evolution when the Active Directory domain is added to Concordance Evolution. Updates to the users and user groups in the Active Directory domain, including user names and passwords, are automatically updated in Concordance Evolution. Active Directory users are not editable in Concordance Evolution, but you can assign Concordance Evolution security policies to the domain user groups in Concordance Evolution. For more information about adding Active Directory domains, see Adding Active Directory domains. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 42 Concordance Evolution When a user is created within Concordance Evolution manually or by import, it is called a local user. When a user is added to Concordance Evolution using Active Directory, it is called an AD user. To manually add local a user: 1. Do one of the following: Point to the Admin tab, and then click Users. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard, click the Security button, and then click Users. 2. On the Users dashboard toolbar, click the Add User button to open the Add User dashboard. 3. On the Details tab, in the User Name field, type the user's user name for logging on to Concordance Evolution. Concordance Evolution user names must be unique. The following special characters are not allowed in Concordance Evolution or Microsoft Active Directory user names: /\;:|=,+* ? <>@" 4. In the First Name field, type the user's first name. 5. In the Last Name field, type the user's last name. 6. In the Password and Retype Password fields, type the user's Concordance Evolution password. Passwords require the following: Does not contain the user name or user's full name Contains characters from three of the following five categories: o English uppercase characters (A through Z) o English lowercase characters (a through z) o Base 10 digits (0 through 9) o Non-alphabetic characters (for example, !, $, #, %) o A catch-all category of any Unicode character that does not fall under the previous four categories. This fifth category can be regionally specific. 7. To make sure the user changes their password after the account is setup, select the Change password on next login check box. 8. In the Email field, type the user's e-mail address. 9. Select the Active check box to activate the user. The Active User check box needs to be selected for the user to log on to Concordance Evolution. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 43 When you create a user, you can assign the user to a user group. A user group is a collection of users and pre-defined security policy settings you can use to help speed up the user creation process. You can assign a user to a user group on the Create User, Add User Group or Edit User Group dashboards. For more information about security policies, see Assigning roles to user groups. 10. For Privilege, the Super Admin check box is not selected by default. When the Super Admin check box is selected, all Concordance Evolution security policies, regardless of the user group the user is assigned to, are set to Allow for the user. Only users designated as a Super Admin can access the Super Admin check box for other users on the Create User and Edit User dashboard. It is best practice to create at least two super admin users. 11. To add the user to a user group, in the Membership section, click the Assign button. If the user is assigned the Super Admin access, the user does not have to be assigned to any user groups as they have full access to the Concordance Evolution environment. 12. In the Select User Group(s) dialog box, select the check box for each user group you want to assign the user, and then click Save. 13. (Optional) Click the Contact Information tab and fill out the users contact information. 14. When finished, click the Create button to save the user and add it to the list on the Users dashboard. After creating a user, you can customize the user's preferences at the bottom of the Edit User dashboard. For more information about user preferences, see Customizing admin preferences. Importing users If you have a large number of users to add to Concordance Evolution, you can quickly add them at one time by importing users from a comma-separated value (.csv) file into Concordance Evolution. Only local users can be imported into Concordance Evolution. The user import only supports CSV (comma-separated values) files. Active Directory users cannot be imported into Concordance Evolution, see Using Microsoft Active Directory The following special characters are not allowed in Concordance Evolution or Microsoft Active Directory user names: /\;:|=,+*?<>@" You can import user data for the following Concordance Evolution fields: © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 44 Concordance Evolution UserName FirstName LastName EmailID When you import users, Concordance Evolution assigns a generic password, [username]$1, to each user created during the import. To import users: 1. Do one of the following: Point to the Admin tab, and then click Users. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard, click the Security button, and then click Users. 2. On the Users dashboard toolbar, click the Import Users button, and then click Browse. 3. In the Choose File to Upload dialog box, navigate to and then click the .csv file you want to import, and then click Open. Clicking Open adds the file name and location to the Import Users box. 4. Click the Import button. The import results are displayed on the Import Results dashboard. 5. Click the Close button. The users' user name, first name, last name, and email address are added to Concordance Evolution, and the users are displayed in the Users list on the Users dashboard. 6. To activate, add additional information, and/or define preferences for an imported user, in the Users list, click the edit button next to the user's name to open the Edit User dashboard. 7. Make the applicable edits and then click the Update button to return to the Users dashboard. Using Microsoft Active Directory Using Microsoft Active Directory Microsoft® Active Directory® is most commonly used for external authentication. One of the benefits of using Active Directory is not just to implement user names and passwords, but to also take advantage of the organization features offered for managing users. When using Concordance Evolution with Microsoft® Active Directory® to authenticate users, a © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 45 two-fold verification takes place. The user is first authenticated with Active Directory. If the person is a valid user, they are then authenticated in Concordance Evolution and will have permissions based on the security policies applied to the user group to which the user is assigned in Concordance Evolution . Any users and user groups in an Active Directory domain are automatically added to the users list and user groups list in Concordance Evolution when the Active Directory domain is added to Concordance Evolution. Updates to the users and user groups in the Active Directory domain, including user names and passwords, are automatically updated in Concordance Evolution. Active Directory users and user groups are not editable in Concordance Evolution, but you can assign Concordance Evolution security policies to the domain user groups in Concordance Evolution. To use Active Directory for external authentication in Concordance Evolution: 1. Set up users and user groups in Active directory. 2. Add the Active Directory domain to Concordance Evolution. 3. Add the Active Directory server information for the domain. 4. Assign Concordance Evolution security policies to the applicable domain users groups. Adding Active Directory domains When you add an Active Directory domain to Concordance Evolution, any users and user groups in an Active Directory domain are automatically added to the users list and users groups list in Concordance Evolution. Updates to the users and user groups in the Active Directory domain, including user names and passwords, are automatically updated in Concordance Evolution. Active Directory users are not editable in Concordance Evolution, but you can assign Concordance Evolution security policies to the domain user groups in Concordance Evolution. An Active Directory domain cannot be added on the Add Active Directory Domain dashboard if a domain with the same name was previously deleted from Concordance Evolution. For more information, see Deleting Active Directory domains. To add an Active Directory domain: 1. Do one of the following: Point to the Admin tab, and then click AD Domains. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard, click the Security button, and then click AD Domains. 2. On the AD Domain Management dashboard, click the Add a domain link to open the Add Active Directory Domain dashboard. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 46 Concordance Evolution 3. In the Name field, type the Active Directory domain name. 4. (Optional) In the Description field, type the Active Directory description. 5. In the LDAP Root for User field, type the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) root for the Active Directory domain's users. The Add AD Server link is disabled when you add a domain to Concordance Evolution. After adding a domain, the Active Directory server information is added for the domain using the Add AD Server link on the Edit Active Directory Domain dashboard. For more information, see Adding Active Directory servers. 6. In the User Name field, type the domain administrator's user name. 7. In the Password field, type the domain administrator's password. 8. When finished, click the Add button to return to the AD Domain Management dashboard. The new domain is displayed in the domain list. Adding Active Directory servers When you are using Microsoft® Active Directory® for external authentication, you will need a Microsoft Active Directory compatible credentials server. The Active Directory user credentials are verified by the server. If a user name or password is not recognized by the domain controller, then the user is refused access by Concordance Evolution. If the user is verified by the domain controller, then the user is given access to Concordance Evolution. The security policies assigned to the user group associated with the user in Concordance Evolution, determine the features and functions the user can access within Concordance Evolution. If you enter an IP address and the server's IP address changes, Concordance Evolution will not be able to communicate with the credential server until the address is manually updated in Concordance Evolution. Firewall ports that need to be open for Active Directory include: 389 (LDAP), 636 (secure LDAP), and NetBIOS ports for the change password feature. To add an Active Directory server: 1. Do one of the following: Point to the Admin tab, and then click AD Domains. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard, click the Security button, and then click AD Domains. 2. On the AD Domain Management dashboard, from the Domain list, click the edit link for the domain you want to add the server. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 47 3. On the Edit Active Directory Domain dashboard, click the Add AD Server link to open the Add AD Server dashboard. 4. In the Host field, type the server's IP address. 5. In the Port field, type the applicable firewall port. make sure that the firewall port is open. 6. Click the Test Connection button to test the connection between the server and Concordance Evolution. If the connection is good, the Test Connection Success message is displayed below the Port field. 7. Click the Add button to return to the Edit Active Directory Domain dashboard. The new server is displayed in the Servers list. To add additional servers, click the Add AD Server link again, and repeat the steps for adding a server. 8. When finished, click the Update button to return to the Admin dashboard. Deleting Active Directory domains When an Active Directory domain is deleted from the Edit Active Directory Domain dashboard, the Active Directory domain is removed from the Active Directory domain list on the AD Domain Management dashboard, but remains in the system. An Active Directory domain cannot be added on the Add Active Directory Domain dashboard if a domain with the same name was previously deleted from Concordance Evolution. If an Active Directory domain needs to be permanently deleted from Concordance Evolution, the Active Directory domain needs to be deleted from the Edit Active Directory Domain dashboard, all Active Directory users that belong to the deleted domain need to be manually deleted, and the domain entry needs to be physically deleted from the database. Once done, an Active Directory domain can be added on the Add Active Directory Domain dashboard with the same name. To delete an Active Directory domain from the domain list: 1. Do one of the following: Point to the Admin tab, and then click AD Domains. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard, click the Security button, and then click AD Domains. 2. On the AD Domain Management dashboard, from the Domain list, locate the domain you want to delete, and then do one of the following: Click the delete link. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 48 Concordance Evolution Click the edit link, and then on the Edit Active Directory Domain toolbar, click the Delete button. 3. When prompted, click Yes to confirm the deletion. Clicking Yes deletes the Active Directory domain from the domain list on the AD Domain Management dashboard. Deleting Active Directory servers If you need to delete a Microsoft Active Directory server associated with an Active Directory domain in Concordance Evolution, you can delete the server from domain's server list in Concordance Evolution on the Edit AD Server dashboard. To delete an Active Directory server from a domain's server list: 1. Do one of the following: Point to the Admin tab, and then click AD Domains. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard, click the Security button, and then click AD Domains. 2. On the AD Domain Management dashboard, from the Domain list, click the edit link for the domain you want to add the server. 3. Servers list displays the servers currently associated with the domain. 4. From the Servers section, in the Host column, click the link for the server you want to delete. 5. Clicking the server link opens the Edit AD Server dashboard. 6. Click the Remove button. 7. When prompted, click Yes to confirm the deletion. Clicking Yes deletes the Active Directory server from the domain's server list on the Edit Active Directory Domain dashboard. 8. Click the Update button to save your changes to the domain and return to the AD Domain Management dashboard. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 49 Modifying users Only local users can be modified or deleted in Concordance Evolution. Active Directory users, including user passwords, cannot be modified or deleted in Concordance Evolution, but you can assign Concordance Evolution security policies to the domain user groups in Concordance Evolution. To modify a user: 1. Do one of the following: Point to the Admin tab, and then click Users. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard, click the Security button, and then click Users. 2. From the list of users on the Users dashboard, locate the user you want to modify, and then in the Actions column click the Edit link. 3. Make the applicable edits. The following special characters are not allowed in Concordance Evolution or Microsoft Active Directory user names: /\;:|=,+* ? <>@" 4. Click the Update button. When you modify a user, the changes are applied the next time the user logs on to Concordance Evolution. To change a user's password: 1. Do one of the following: Point to the Admin tab, and then click Users. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard, click the Security button, and then click Users. 2. From the list of users on the Users dashboard, locate the user you want to change the password for, and then in the Actions column click the Edit link. 3. In the Password and Re-Type Password fields, type the user's new Concordance Evolution password. 4. Click the Update button. When you modify a user's password, the changes are applied the next time the user logs on to Concordance Evolution. To activate or deactivate a user: © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 50 Concordance Evolution 1. Do one of the following: Point to the Admin tab, and then click Users. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard, click the Security button, and then click Users. 2. From the list of users on the Users dashboard, locate the user you want to change the status for, and then in the Actions column click the Edit link. 3. Do one of the following: To deactivate the user, clear the Active User check box. To activate the user, select the Active User check box. 4. Click the Update button. When you deactivate or activate a user, the changes are applied the next time the user logs on to Concordance Evolution. If you deactivate a user, the user will not be able to log on to Concordance Evolution. If you need to deactivate and log off a user that is currently logged on to Concordance Evolution, you can deactivate the user and then disconnect the user's session on the the User Session Management dashboard. For more information about disconnecting user sessions, see Managing user sessions. To delete a user: 1. Do one of the following: Point to the Admin tab, and then click Users. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard, click the Security button, and then click Users. 2. From the list of users on the Users dashboard, locate the user you want to delete, and then do one of the following: In the Actions column click the Edit link, and then click the Remove button. In the Actions column click the Delete link. 3. When prompted, click OK to confirm the deletion. If you delete a user that is currently logged on to Concordance Evolution, the user's session is immediately disconnected when the user is deleted. If a user is deleted and then recreated, the user's name is shown as a duplicate in the Filter performed by list of the Audit Log. To unlock a user: If a user is attempting to log on to Concordance Evolution, and they exceeds the number of © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 51 login attempts allowed by Concordance Evolution, the user's account is locked, and the Locked check box on the Edit User dashboard is selected by the system. To unlock a user: 1. Do one of the following: Point to the Admin tab, and then click Users. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard, click the Security button, and then click Users. 2. From the list of users on the Users dashboard, locate the user you want to change the status for, and then in the Actions column click the Edit link. 3. Click the Contact Information tab, and then clear the Locked check box. 4. When finished, click the Update button. Exporting users Both Active Directory users and local Concordance Evolution users can be exported from Concordance Evolution. When you click the Export Selected Users button on the User Management dashboard, the users are exported to a CSV (comma-separated values) file. The export exports user data from the following fields: UserName FirstName LastName DomainName (for Active Directory users only) EmailID To export users: 1. Do one of the following: Point to the Admin tab, and then click Users. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard, click the Security button, and then click Users. 2. On the Users, from the Show Users list, select Local Users or AD Users. Only local users or Active Directory users can be exported at one time. You cannot export both types of users for the same export. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 52 Concordance Evolution 3. In the Users list, select the check box for the each user to include in the export. 4. Click the Export Users button. 5. In the File Download dialog box, click Save. 6. In the Save As dialog box, navigate to where you want to save the .csv file. 7. In the File name field, type the file name. The Save as type field defaults to Microsoft Office Excel Comma Separated Value. Concordance Evolution only supports CSV files for importing users. If you are planning on importing the exported users list into Concordance Evolution, be sure to save the file as a CSV file. 8. Click Save to close the dialog box and return to the Users dashboard. System M anagement Preference Management About preferences There are two types of preference settings in Concordance Evolution: Admin preference settings are defined in the Admin dashboard. Admin preferences include password settings, number of items to display in lists, default view for search results, tag format settings, and so on. For more information, see Customizing admin preferences. Personal preference settings are defined on the My Preference dashboard. In Concordance Evolution the administrator can customize the default preference settings for users, user groups, folders, matters, but as long as a preference setting is not locked by the administrator, a user can customize the preference settings for themselves on the My Preference dashboard. For example, the administrator can define the default tag format settings, but allow users to customize the tag format preference settings for themselves on the My Preference dashboard. You can access the My Preference dashboard by clicking the Preferences link next to the Help link at the top of the page anywhere in the Admin, Review, and Report dashboards. For more information, see Customizing personal preferences. Preferences Available in Concordance Evolution © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 53 Concordance Evolution Preferences Function Name Description AD domains per page Default number of items per page for the AD Domain Management dashboard AD domains sort order Preference for sorting domains in ascending or descending order on AD Domain Management dashboard Audit items per page Default number of items per page for Audit Management dashboard Enable send document links to CaseMap Determines whether the Send Document Links to CaseMap feature is enabled AD Managem ent Audit Managem ent CaseMap For more information about CaseMap preferences, see Using CaseMap with Concordance Evolution. Maximum number of document links Maximum number of document links a user can export at one time to the CaseMap.cmbulk file in the Review dashboard Font color for comments Default font color for comment text Font name for comments Default font for comment text Font size for comments Default font size for comment text Sorting order for comments Default sorting for comments in ascending or descending order Document control number text How the DCN (document control number) field name is displayed in the Review dashboard Com m ents DCN Deduplication © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 54 Concordance Evolution Concordance Evolution Preferences Comparison method Default deduplication comparison method. Original Document or Fields Deduplication items per page Default number of items per page for the Deduplication dashboard Maximum email size in MB Maximum combined document size in megabytes (MB) allowed for sending an email Maximum number of documents to email Maximum number of documents allowed to be sent in an email Maximum number of documents to print Maximum number of documents allowed for a print job Default document viewer Default view for viewing documents in Review dashboard Document zoom level Zoom level for viewing documents Enable hit highlight in document data viewer Determines whether search hit highlighting is enabled in the Document Data view Enable hit highlight in near native viewer Determines whether search hit highlighting is enabled in the Near Native view Deliv ery Options Docum ent Viewer Em ail Conv ersation Threading Maximum Thread Depth to Display Maximum number of threads to show in the Thread view Export items per page Default number of items per page for export jobs on the Export dashboard Import items per page Default number of items per page for import jobs on the Import dashboard Export Im port Knowledge Management © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 55 Concordance Evolution Preferences Preview size Default setting in kilobytes (KB) for Preview Size field on Reviewer Search Settings dashboard Spelling variations sort order Preference for sorting spelling variations in ascending or descending order Stop words sort order Preference for sorting step words in ascending or descending order Thesaurus sort order Preference for sorting thesaurus entries in ascending or descending order Landing page Default page to be displayed when users log on to Concordance Evolution. Reviewer dashboard or Admin dashboard Notification items per page Default number of items per page for the Notifications tab on Notification Management dashboard Type of notification Preference for type of notification to send to users. Online, Email, or Both. Default view for explore documents Default view for selecting documents when you click the Go to document explorer link on Create Review Set dashboard Explore document items per page Default number of items per page for search results in Document Explorer Tag window Default location for the Tag pane when reviewing documents Saved Search items per page Default number of items per page for the Saved Searches tab on Saved Search dashboard Landing Page Notification Rev iew Set Sav ed Search Search Alert © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 56 Concordance Evolution Concordance Evolution Preferences Search alert items per page Default number of items per page for the Search Alerts tab on Search Alert dashboard Search history item count Maximum number of searches saved on the Search History tab for the current session Search history items per page Default number of items per page for the Search History tab on Search History dashboard Default view for search results Default view for viewing search results in Review dashboard Search results per page Default number of items per page for the Search Results dashboard Search History Search Results Session Managem ent Session management items per page Default number of items per page for the User Session Management dashboard Tag font Default font for tag text in Tags pane Tag font color Default font color for tag text in Tags pane Tag font size Default font size for tag text in Tags pane Tag highlight color Default highlight color for tagging. Default color setting for Tag Color field on Create a Tag and Edit Tag dashboards. Alert user to change password Number of days before user needs to change password that you want to alert user to change password Number of users per page Default number of items per page for the User Management dashboard Tagging User Managem ent © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 57 Concordance Evolution Preferences Password expiry in days Password expiration in days Sort order for user group management Preference for sorting users in ascending or descending order for User Group Management User list sort order Preference for sorting users in ascending or descending order Customizing admin preferences Some preferences are assigned by system, user group, or user at the system, organization, folder, or matter level. Preferences include password settings, number of items to display in lists, default view for search results, tag format settings, and so on. Preferences for the system, user groups, and users can all be defined on the Preference Management dashboard. You can also define user group admin preferences on the Edit User Group dashboard and user admin preferences on the Edit User dashboard. You can lock a preference setting at the system, organization, folder, or matter level for the entire system or a specific user group or user with the Force Down check box. When the Force Down check box is selected on the Preference Management dashboard, the preference setting is applied to the child levels and cannot be modified at any of the levels below the parent level and a lock icon, , is displayed next to the preference name. When the default preference setting has been changed, the preference text in the preference list is bolded. When a preference is currently set to the preference default setting, the preference text in the preference list is not bolded. In the Review dashboard, users can also define their personal preferences on the My Preference dashboard. For more information about defining user preferences in the Review dashboard, see Customizing personal preferences. Preference Precedence Information Preference precedence flows from System > User Group > User. However, you can customize the preferences in the User Group Preferences section of the Edit User Group dashboard, or the User Preferences section on the Edit User dashboard. Preference Parent/Child Hierarchy (from top to bottom): System User Group User © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 58 Concordance Evolution System Parent/Child Hierarchy (from top to bottom): System Organization created under the system Folder created under the organization Matter Folder created under a matter Dataset If you customize a user preference setting on the Edit User dashboard, the preference setting flows from User > User Group > System. The setting applies to the user at all levels (user group(s) the user is assigned to, dataset, folder/matter, folder, organization and system levels). If a user belongs to multiple user groups, the preferences of the user group with the highest priority, will take precedence over the other preference settings. If you customize a user group preference setting on the Edit User Group dashboard, the preference setting flows from the User Group > Users assigned to the User Group > System. The setting applies to the user group at all levels (users assigned to the user group, dataset, folder/matter, folder, and system). If a preference setting is customized for a user, and the same preference setting is customized for the user group the user is assigned to but the user and user group have a different value for the preference, the user preference setting takes precedence over the user group preference setting unless the preference setting is locked (the Force Down check box is selected) at the user group level. The preference setting for a function or page in the application will only apply to the user and/or user group, if the user and/or user group has access to the function or page. Otherwise, if the user does not have access, the preference setting does not affect anything. To customize preferences at the system level: 1. Do one of the following: Point to the Admin tab, and then click Preferences. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard, click the Config button, and then click Preferences. 2. On the Preference Management dashboard, click the Select System Preference option. 3. On the Preference Management dashboard, preferences are organized by Concordance Evolution function. To view the preferences for a function, click the right arrow, , next to the function to expand the preferences list. To close a preferences list, click the down arrow, , next to the function. You can also click the Expand All button or Collapse All button at the bottom of the dashboard to view all the preference lists. 6. To view a preference, in the Preference Name column click the preference's name link. Clicking the preference's name link opens the Edit Preference dashboard. Only the Value field and Force Down check box can be edited. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 59 7. In the Value field, modify the default setting to customize the preference setting. 8. If you want the preference setting to apply to all users and users groups, and all organizations, folders, matters, and datasets under the system, select the Force Down check box. When the Force Down check box is selected, the preference settings is only editable at the system level and is not editable at the child levels. 9. Click the Update button to save the preference setting. Any preference settings that you customize will be displayed in bold text in the preferences list. 10. When finished, click the System link in the breadcrumbs to return to the Admin dashboard. When modifying preference settings, the changes are applied the next time the user logs on to Concordance Evolution. To customize a preference at the organization level: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane, locate and click the organization to change preferences. 3. In the Assigned Users table of the organization's dashboard, click the link for the user group to edit. 4. In the User Group Preferences section, the preferences are organized by Concordance Evolution function. To view the preferences for a function, click the right arrow, , next to the function to expand the preferences list. To close a preferences list, click the down arrow, , next to the function. You can also click the Expand All button or Collapse All button at the bottom of the page to expand or collapse all the preference lists on the page. 5. To view a preference, click the preference's name link in the Preference Name column. Clicking the preference's name link opens the Edit Preference dashboard. Only the Value field and Force Down check box can be edited. 6. In the Value field, modify the default setting to customize the preference setting. 7. If you want the preference setting to apply to all users and users groups, and all folders, matters, and datasets under the folder, select the Force Down check box. When the Force Down check box is selected, the preference settings is only editable at the organization level, and is not editable at the child levels. 8. Click the Update button to save the preference setting. Any preference settings that you customize will be displayed in bold text in the preferences list on the Preference Management dashboard. 9. When finished, click the System link in the breadcrumbs to return to the Admin dashboard. When modifying preference settings, the changes are applied the next time the user logs on to Concordance Evolution. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 60 Concordance Evolution To customize a system preference at the folder level: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane, locate and click the folder to change preferences. 3. In the Assigned Users table of the folder's dashboard, click the link for the user group to edit. 4. In the User Group Preferences section, the preferences are organized by Concordance Evolution function. To view the preferences for a function, click the right arrow, , next to the function to expand the preferences list. To close a preferences list, click the down arrow, , next to the function. You can also click the Expand All button or Collapse All button at the bottom of the page to expand or collapse all the preference. 5. To view a preference, click the preference's name link in the Preference Name column. Clicking the preference's name link opens the Edit Preference dashboard. Only the Value field and Force Down check box can be edited. 6. In the Value field, modify the default setting to customize the preference setting. 7. If you want the preference setting to apply to all users and users groups, and all folders, matters, and datasets under the folder, select the Force Down check box. When the Force Down check box is selected, the preference settings is only editable at the folder level, and is not editable at the child levels. 8. Click the Save button to save the preference setting. Any preference settings that you customize will be displayed in bold text in the preferences list on the Preference Management dashboard. To customize a system preference at the matter level: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane, locate and click the matter to change preferences. 3. In the Assigned Users table of the matter's dashboard, click the link for the user group to edit. 4. In the User Group Preferences section, the preferences are organized by Concordance Evolution function. To view the preferences for a function, click the right arrow, , next to the function to expand the preferences list. To close a preferences list, click the down arrow, , next to the function. You can also click the Expand All button or Collapse All button at the bottom of the page to expand or collapse all the preference lists. 5. To view a preference, click the preference's name link in the Preference Name column. Clicking the preference's name link opens the Edit Preference dashboard. Only the Value field and Force Down check box can be edited. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 61 6. In the Value field, modify the default setting to customize the preference setting. 7. If you want the preference setting to apply to all users and users groups, and all datasets under the matter, select the Force Down check box. When the Force Down check box is selected, the preference settings is only editable at the folder level, and is not editable at the child levels. 8. Click the Save button to save the preference setting. Any preference settings that you customize will be displayed in bold text in the preferences list on the Preference Management dashboard. When modifying preference settings, the changes are applied the next time the user logs on to Concordance Evolution. To customize a user preference on the Edit User dashboard: 1. Do one of the following: Point to the Admin tab, and then click Users. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard, click the Security button, and then click Users. 2. From the list of users on the Users dashboard, locate the user you want to modify, and then in the Actions column click the Edit link. 3. On the Edit User dashboard in the User Preferences section, preferences are organized by Concordance Evolution function. To view the preferences for a function, click the right arrow, , next to the function to expand the preferences list. To close a preferences list, click the down arrow, , next to the function. You can also click the Expand All button or Collapse All button at the bottom of the page to expand or collapse all the preference lists on the page. 4. To view a preference, click the preference's name link in the Preference Name column. Clicking the preference's name link opens the Edit Preference dashboard. Only the Value field and Force Down check box can be edited on the Edit Preference dashboard. 5. In the Value field, modify the default setting to customize the preference setting. 6. If you want the preference setting to apply to the user at all levels under the system, select the Force Down check box. When the Force Down check box is selected, the preference settings is only editable for the user on the Edit User dashboard, and is not editable at the user group or system level. 7. Click the Update button to save the preference setting. Any preference settings that you customize will be displayed in bold text in the preferences list on the Preference Management dashboard. 8. When you are done customizing preferences, click the Update button to save the preference settings and return to the User Management dashboard. When modifying preference settings, the changes are applied the next time the user logs on to Concordance Evolution.. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 62 Concordance Evolution Server Management About server management In Concordance Evolution you can view the current server settings, add or remove servers, and set the default servers for the SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol), SQL Server, and search servers used by Concordance Evolution. You can also add the printers used by Concordance Evolution. There can only be one default server for each of the servers used by Concordance Evolution, so you can add multiple servers to the server list, but only one of each type of server can be the default server for the server type. Maintaining server services The Servers dashboard provides information about each server, the server's status, and services that are running on each server in the Concordance Evolution environment. All services are installed on all machines; however, most services are in a "stopped" state after installation. After the installation, the System Administrator must login to the Servers dashboard and start the appropriate services on each server. The following table provides a list of recommended services that should be running on each server: Server Services SQL Server (primary database) System Configuration Service UI Server (Web Services Server) System Configuration Service Vault Service Web Reviewer Service Web Admin Service Search Server (Velocity Server) System Configuration Service Application Server (Queue Server) Printer Service Search Service System Configuration Service Application Jobs Service System Jobs Service Imaging Job Processor Service Application Director Service © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution Conversion Server 63 System Configuration Service Imaging Queue Service Imaging Job Processor Service To add additional servers to the Concordance Evolution environment, you will need to run the Concordance Evolution Installation Wizard. To view server information: 1. Do one of the following: Point to the Admin tab, and then click Servers. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard, in the System Details pane, click the Servers link. 2. To access a list of services running on a particular server, in the Server column, click the server link. The Services dashboard for the selected server is displayed showing the services status. To start and stop services for a server: 1. Do one of the following: Point to the Admin tab, and then click Servers. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard, in the System Details pane, click the Servers link. 2. In the Server column, click the server link. 3. In the Action column, do one of the following: To start a service, click the Start link. To stop a service, click the Stop link. 4. When finished, click the Back button to return to the Servers dashboard. To modify server services configurations: 1. Do one of the following: Point to the Admin tab, and then click Servers. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard, in the System Details pane, click the Servers link. 2. In the Server column, click the server link. 3. In the Services column, select the services link to modify. 4. In Service Configuration dashboard, make any necessary changes for the available settings. Only the service settings for the selected server are available for modification. All other © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 64 Concordance Evolution settings appear shaded. 5. When finished, click the Save button. Printers Managing Printers The Manage Printers dashboard provides all the tools you need to add and remove network printers. to create print jobs, see About bulk printing. To add a printer: To edit printer settings: To remove a printer: Session Management Managing user sessions In Concordance Evolution, if a user does not respond to a broadcast message requesting users to exit the application or you have an emergent need for users to exit the application immediately, you can manually disconnect the user's session on the User Session Management dashboard. If you do not need to disconnect user sessions immediately, it is best practice to send a notification to the users you need to exit the application before manually disconnecting their session. This gives users time to save their work and exit the application on their own. For more information about sending notifications, see Creating notifications. When you disconnect a user session on the User Session Management dashboard, Concordance Evolution immediately logs off the selected users, performing a hard kill. Performing a hard kill does not guarantee that the users’ session data is saved. To disconnect a user session: © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 65 1. Do one of the following: Point to the Admin tab, and then click Sessions. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard, click the Config button, and then click Sessions. 2. On the Session Management dashboard, in the user list, select the check box for each user to log off. To log off all users currently logged on to Concordance Evolution, select the check box to the left of the User Name header to select all the users' check boxes. 3. In the Notification field, type the notification you want to send to the users you are logging off. 4. Click the Log Out button. 5. When prompted, click Yes to confirm the disconnect. When you click Yes, the selected users are logged off and the notification is displayed for the user. Job Management About jobs In Concordance Evolution, certain tasks, such as running imports, exports, print jobs, productions, or creating review sets are performed using jobs. The Job Management dashboard displays a list of jobs created in the system. The list includes each job’s name, type, status, hierarchy level, and the last run date and time. By default, jobs are processed in the order they were created if the Now option was selected when scheduling the job, or by the date and time the job is scheduled to run. Viewing jobs On the Job Management dashboard you can view the list of jobs created in the system. You can view a job's details and history on the Job Summary dashboard. If a job fails, you can open the Error Log to view additional information about the problems encountered. Jobs are also listed on the dashboard for each dataset in the Recent Jobs section at the bottom of the dashboard. For more information, see About dataset job logs © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 66 Concordance Evolution To view jobs: 1. Do one of the following: Point to the Admin tab, and then click Jobs. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard, click the Config button, and then click Jobs. The jobs list on the Manage Jobs dashboard includes each job’s type, dataset, created by, start date, end date, Near Native conversion status, and job status. 2. To refine the listed jobs, do any of the following: To display the results for a specified past number of days, from the Filter by Last Modified list, and then select the time frame. To display the results for a specific matter(s), from the Filter by Matter list, select the check box for each matter. To display the results for a specific dataset(s), from the Filter by Dataset list, select the check box for each dataset. 3. To view a job, do any of the following: To view the information about a specific job, in the Name column, click the job name link. To view the log file for a specific job, locate the job you want to view, and then in the Actions column, click the job log link. 3. Clicking the job name link opens the Job Summary dashboard for the selected job. The Job Summary dashboard displays the Job Name, Description, Status, when the job was run, and the Job History. To view an error log: 1. To view the Error Log, in the Job History table, locate the log you want to view and then click the Error Log link. 2. To export the job information, in the upper right corner, click the Export CSV. 3. In the File Download dialog box, do one of the following: Click Open to view the file, in the Download Complete dialog box, click Open to open the file in your default spreadsheet application. Click Save to save the file, in the Save As dialog box, navigate to where you want to save the file, and then in the File Name field, type the file name and click Save. 4. When finished, click the Close button to close the Log dialog box, and return to the Manage Jobs page. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 67 Reprocessing jobs Import and Production Jobs containing documents that did not complete the Near Native conversion successfully, can be reprocessed without having to re-import or reproduce the files. Reprocessing can be executed at the system level or the dataset level. If reprocessing at the system level, the Manage Jobs dashboard displays all the jobs for all the organizations. If reprocessing at the dataset level, only the jobs for the selected dataset are shown in the Recent Jobs section of the Dataset Managment dashboard. When a job contains files that did not complete the Near Native conversion, the reprocess files link is enabled in the Actions column. If a job has files that need reprocessing, when the link is clicked, the Manage Conversions dashboard is opened. The Manage Conversions dashboard displays a table of all image and native documents and their status. You can filter the table to display only the documents that need to be reprocessed. You can export a list of documents for a job to a CSV file, save it to your local machine, and then use the CSV file to reprocess the documents at a later time. Or if you have a list of document control numbers (.txt), you can use this list to reprocess only those documents in the file. The Manage Conversions dashboard toolbar also provides the ability to tag the documents that are reprocessed making it easier to find them later. The Manage Conversions dashboard table displays the following information: Column Description DCN Document Control Number Cross Ref ID (FieldName) Field data used for cross-referencing files to corresponding Native document. All Production, DCB import, eDoc and LAW PreDiscovery import display as N/A as the Cross Ref ID is not populated from the import jobs. Status Current processing status for the job: Completed or Failed CategoryReason Error reason for Failed jobs Last Modified Date record modified for reprocessing File Size (KB) Document file size MIME Type Document type for documents imported from Native file sets Document set Dataset name for Import jobs or redactable set for Production jobs File Path Location for imported file To reprocess files at the system level: 1. Do one of the following: Point to the Admin tab, and then click Jobs. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard, click the Config button, and then click Jobs. All the documents that were processed for the job are displayed in the Manage Conversions table. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 68 Concordance Evolution 2. To refine the list of documents, select any of the following from the filtering options: Filter By Last Modified Option Last Hour Today Yesterday Last Week Last Month Reason Dependent upon the Category - Reason section Size Empty (0 KB) Tiny (0 KB - 10 KB) Small (10 KB - 100 KB) Medium (100 KB - 1 MB) Large (1 MB - 16 MB) Huge (16 MB - 128 MB) Gigantic ( > 128 MB) The documents that meet the specified criteria are displayed in the Manage Conversions table. To reset the filter to their default state, click the Clear link to the right of the filter lists. By default only 5 documents are shown per page. To change the number of documents displayed, select the maximum number to display from the Items per page list. 3. To select the documents to reprocess, do any of the following: To select all the documents on the page, select the check box in the far left corner of the table. To select individual documents, select the check box for each document to reprocess. 4. To track the documents selected for reprocessing using a tag, on the Manage Conversions dashboard toolbar, click the Tag Selected button, select a tag from the list, and then click the Tag button. 5. When finished, on the Manage Conversions dashboard toolbar, click the Reprocess Selected button. 6. In the Reprocess Selected dialog box, review the Original Details section to ensure the job information is accurate. 7. In the Reprocessing Options section, set the Near Native Conversion Priority processing: Low Medium High © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 69 All production jobs that are assigned a priority are processed in order of first-in, firstprocessed. High priority jobs take precedence over Low and Medium priority. 9. In the Scheduling section of the Summary tab, select one of the following: To run the import job immediately, select the Run immediately option. To schedule the import to run at a later time, select the Run at a specified time option, and then type the date and time or click the Calendar button to select the date, and time you want to run the import. 10. When ready, click OK. To reprocess files at the dataset level: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the dataset that contains the files you want to reprocess. 3. In the Recent Jobs section, locate the job that contains the files for reprocessing. 4. In the Actions column, click the reprocess files link. 5. To refine the list of documents, select any of the following from the filtering options: Filter By Last Modified Option Last Hour Today Yesterday Last Week Last Month Reason Dependent upon the Category - Reason section Size Empty (0 KB) Tiny (0 KB - 10 KB) Small (10 KB - 100 KB) Medium (100 KB - 1 MB) Large (1 MB - 16 MB) Huge (16 MB - 128 MB) Gigantic ( > 128 MB) The documents that meet the specified criteria are displayed in the Manage Conversions table. To reset the filter to their default state, click the Clear link to the right of the filter lists. By default only 5 documents are shown per page. To change the number of documents displayed, select the maximum number to display from the Items per page list. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 70 Concordance Evolution 6. To select the documents to reprocess, do any of the following: To select all the documents on the page, select the check box in the far left corner of the table. To select individual documents, select the check box for each document to reprocess. 7. To track the documents selected for reprocessing using a tag, on the Manage Conversions dashboard toolbar, click the Tag Selected button, select a tag from the list, and then click the Tag button. 8. When finished, on the Manage Conversions dashboard toolbar, click the Reprocess Selected button. 9. In the Reprocess Selected dialog box, review the Original Details section to ensure the job information is accurate. 10. In the Reprocessing Options section, set the Near Native Conversion Priority processing: Low Medium High All production jobs that are assigned a priority are processed in order of first-in, firstprocessed. High priority jobs take precedence over Low and Medium priority. 11. In the Scheduling section of the Summary tab, select one of the following: To run the import job immediately, select the Run immediately option. To schedule the import to run at a later time, select the Run at a specified time option, and then type the date and time or click the Calendar button to select the date, and time you want to run the import. 12. When ready, click OK. To reprocess a document using an import list: 1. Do one of the following: Point to the Admin tab, and then click Jobs. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard, click the Config button, and then click Jobs. 2. On the Manage Jobs dashboard, in the Actions column, click the reprocess files link for the job to reprocess. All the documents that were processed for the job are displayed in the Manage Conversions table. 3. To refine the list of documents, select any of the following from the filtering options: Filter By Last Modified Option Last Hour Today © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 71 Yesterday Last Week Last Month Reason Dependent upon the Category - Reason section Size Empty (0 KB) Tiny (0 KB - 10 KB) Small (10 KB - 100 KB) Medium (100 KB - 1 MB) Large (1 MB - 16 MB) Huge (16 MB - 128 MB) Gigantic ( > 128 MB) The documents that meet the specified criteria are displayed in the Manage Conversions table. To reset the filter to their default state, click the Clear link to the right of the filter lists. By default only 5 documents are shown per page. To change the number of documents displayed, select the maximum number to display from the Items per page list. 4. Review the list of documents. 5. When finished, on the Manage Conversions dashboard toolbar, click the Reprocess File button. 6. In the Reprocess File dialog box, review the Original Details section to ensure the job information is accurate. 7. In the Reprocessing Options section, click the Browse button, locate the Exported Details (.csv) or Cross-Reference ID List (.txt) file, and then click OK. The header row of the Exported Details (.csv) file must contain all the required columns and the subsequent rows must have the required number of comma separators. The Cross-Reference ID list (.txt) file must be a plain text file and cannot contain comma separators. 8. To set the Near Native Conversion Priority processing, select one of the following options: Low Medium High All production jobs that are assigned a priority are processed in order of first-in, firstprocessed. High priority jobs take precedence over Low and Medium priority. 9. In the Scheduling section of the Summary tab, select one of the following: © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 72 Concordance Evolution To run the import job immediately, select the Run immediately option. To schedule the import to run at a later time, select the Run at a specified time option, and then type the date and time or click the Calendar button to select the date, and time you want to run the import. 10. When ready, click OK. To export a list of documents: 1. Do one of the following: Point to the Admin tab, and then click Jobs. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard, click the Config button, and then click Jobs. 2. On the Manage Jobs dashboard, in the Actions column, click the reprocess files link for the job to reprocess. All the documents that were processed for the job are displayed in the Manage Conversions table. 3. To refine the list of documents, select any of the following from the filtering options: Filter By Last Modified Option Last Hour Today Yesterday Last Week Last Month Reason Dependent upon the Category - Reason section Size Empty (0 KB) Tiny (0 KB - 10 KB) Small (10 KB - 100 KB) Medium (100 KB - 1 MB) Large (1 MB - 16 MB) Huge (16 MB - 128 MB) Gigantic ( > 128 MB) The documents that meet the specified criteria are displayed in the Manage Conversions table. To reset the filter to their default state, click the Clear link to the right of the filter lists. By default only 5 documents are shown per page. To change the number of documents displayed, select the maximum number to display from the Items per page list. 4. To select the documents to export, do any of the following: To select all the documents on the page, select the check box in the far left corner of © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 73 the table. To select individual documents, select the check box for each document you want to export. 5. When finished, on the Manage Conversions dashboard toolbar, click the Export Selected button. 6. When prompted, do one of the following: Open and view the Concordance Evolution ConversionLog.csv file. Save the Concordance Evolution ConversionLog.csv file to a specified location on the local computer. 7. When ready, click OK. Shares About shares A share is a file repository for storing Concordance Evolution data files. Before a dataset can be created in Concordance Evolution, shares need to be added on the Shares dashboard at the organization level. When users are creating datasets, one or more shares are selected in the Share path on the Create Dataset dashboard. Multiple shares can be added to Concordance Evolution for a dataset to help improve performance and organization. Exam ple shares to set up: Exports to store exported files Extracted Files to store extracted archived files Import Sources to store files for import Privilege Logs to store log files Production Sets to store production files Related Topics Creating shares Modifying shares Creating datasets About productions © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 74 Concordance Evolution Creating shares Shares are added to Concordance Evolution at the organization level on the Shares dashboard. Once a share is added, it will be available for selection when creating a dataset in the in the Share path on the Create Dataset dashboard. Multiple shares can be used for a dataset to help improve production performance for a dataset. When a production set is created, the files are saved to the selected share(s). Exam ple shares to create: Exports to store exported files Extracted Files to store extracted archived files Import Sources to store files for import Privilege Logs to store log files Production Sets to store production files To add a share: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System tree, click the organization you want to add a share. 3. On the organization's toolbar, click Shares. 4. On the Shares toolbar, click the Add Shares button. 5. On the Add Share dashboard, in the Friendly Name field, type the share name. 6. In the Root Path field, enter the directory where you want to save dataset production files generated during productions. 7. Click the Test Path button to validate the directory entered in the Root Path field. Valid path is displayed next to the Test Path button for valid directories. Invalid path is displayed for invalid directories. 8. To update the available and used disk space values for the directory entered in the Root Path field, click the Refresh button. 9. When finished, click Save. Clicking Save closes the Add Share dashboard and adds the share to the Shares list on the Shares dashboard. The share is now available for selection in the Share path on the Create Dataset dashboard. Related Topics © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 75 About shares Modifying shares Creating datasets About productions Modifying shares Shares can be edited and deleted from the Edit Share dashboard. Shares can only be deleted if there are no files in the share directory. To modify a share: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System tree, click the organization you want to change a share. 3. On the organization's toolbar, click Shares. 4. Locate the share you want to modify in the list of shares and then click the edit link. 5. Make the applicable edits. 6. To update the available and used disk space values for the directory entered in the Root Path field, click the Refresh button. 7. Click Save. To delete a share: A share can only be deleted if there are no files in the manage share. 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System tree, click the organization you want to delete the share from. 3. On the organization's toolbar, click Shares. 4. Locate the share you want to delete in the list of shares and then do one of the following: Click the delete link. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 76 Concordance Evolution Click the edit link, and then on the Edit Share toolbar, click the Delete button. 5. When prompted, click OK to confirm the deletion. Clicking OK deletes the manage share from the Shares list. The share is also deleted from the shares list in the Share path for production field on the Create Dataset dashboard. Related Topics About manage shares Creating manage shares Creating datasets About productions Notifications and Alerts About notifications and alerts Notifications are messages sent by the system or administrator to Concordance Evolution users. They can be used to request users to log out of Concordance Evolution, to notify users when a job, such as an import or export job, is completed, or to share other information with users. There is also a notification called a search alert that can be set up to alert users when the search results for a saved search query change. Both administrators and users can create search alerts. The administrator can send notifications to all users currently logged on to Concordance Evolution, individual users, or all users in a user group. Search alerts are system generated notifications that are sent to the users selected when the search alert was created. For more information about search alerts, see Creating search alerts. Receiving Notifications The Notification Type preference under Notification on the Preference Management dashboard determines whether users receive notifications and search alerts online, by email, or both. If the Super Admin allows users to set this preference for themselves from the Admin or Review dashboards. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 77 If notifications and search alerts are sent using email, the notifications and search alerts are sent to the email address entered for the user on the Add User or Edit User dashboard in the Admin dashboard. For more information about preferences, see Customizing admin preferences. Viewing Notifications Users can view notifications sent to them on the Reviewer dashboard in the My Status box under My Messages and using the Notifications link in the Quick Tools pane. If the notification type preference for a user is set to Online or Both, when a notification is first sent, the message appears when the user accesses Concordance Evolution. For more information about viewing notifications, see Viewing notifications. Creating notifications Notifications can be created and sent from the Notifications and Alerts dashboard and the Send Notification dashboard in the Admin dashboard. Notifications can also be created on dashboards for specific tasks in Concordance Evolution, such as the Create Import Job dashboard, Create a Production Job (Settings) dashboard, and Create Deduplication Job dashboard. The Notification Type preference under Notification on the Preference Management dashboard determines whether users receive notifications online, by email, or both online and by email. If the administrator allows users to set this preference for themselves, users can set this preference on the My Preference dashboard in the Admin, Review, or Reports dashboard. Administrators and users can also create search alert notifications. In the Admin dashboard, Search alert notifications are created on the Create Alert dashboard. For more information, see Creating search alerts. For more information about viewing notifications in Concordance Evolution, see Viewing notifications. To create a notification on the Notifications and Alerts dashboard: 1. Do one of the following: Point to the Admin tab, and then click Notifications. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard, click the Messages button, and then click Notifications. 2. Click the Send New Notification button, and then do one of the following: To send the notification to specific users and/or user groups, click the Send to specific users/groups option, click the Assign button, select the check box for the user groups and/or individual users to which you want to send the notification, and then click Save. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 78 Concordance Evolution To send the notification to all users currently logged on to Concordance Evolution, click the Send to logged in users option. 3. In the Notification field, type the notification text. 4. When finished, click the Send button. When you create and send a notification from the Notifications and Alerts dashboard, the notification is sent after you click the Send button. To resend a notification: After a notification is created and sent, you can resend the notification if you need to from the Notification Details dashboard. For example, if a notification indicating users should be logged out of Concordance Evolution over the weekend for server maintenance was sent out on Monday, and you want to send the notification out again later in the week, you can resend the same notification. 1. Do one of the following: Point to the Admin tab, and then click Notifications. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard, click the Messages button, and then click Notifications. The five more recently sent notifications are displayed on the Notifications and Alerts dashboard. 2. Click the View All Notifications link to open the View All Notifications dashboard. 3. In the Notifications column, click the notification name link. Clicking the notification name link opens the notification on the Notification Details dashboard. 4. Click the Resend button. 5. To modify the notification recipients, in the Send Notification section, do one of the following: To send the notification to specific users and/or user groups, click the Send to specific users/groups option, click the Assign button, select the check box for the user groups and/or individual users to which you want to send the notification, and then click Save. To send the notification to all users currently logged on to Concordance Evolution, click the Send to logged in users option. 6. To modify the notification text, in the Notification field, edit the notification text. 7. When finished, click the Send button to send the notification and return to the Notifications and Alerts dashboard. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 79 Viewing notifications In the Admin dashboard you can view all notifications sent to all users on the View All Notifications dashboard. On the View All Notifications dashboard, you can organize the notifications by notification name, recipient, or date and time sent. You can view all notifications sent to you on the Notifications dashboard on the Notification Management dashboard. To view all notifications: 1. Do one of the following: Point to the Admin tab, and then click Notifications. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard, click the Messages button, and then click Notifications. The five most recently sent notifications are displayed on the Notifications and Alerts dashboard. 2. Click the View All Notifications link to open the View All Notifications dashboard. By default, the notifications are listed in order of date and time sent, from newest to oldest. 3. To view the details of a notification, click the notification name link in the Notifications column. Clicking the notification name link opens the notification on the Notification Details dashboard. The History section displays all the search alert run dates and times. If you only want to view the search alert runs where a change occurred in the query search results, select the Only show when change has occurred check box. By default, the Only show when change has occurred check box is not selected. 4. After reviewing the notification details, click Back to return to the View All Notifications dashboard. To view notifications sent to you: Do any of the following: From the Review dashboard, in the Quick Tools pane, under Messages, click the Notifications link. On the Admin dashboard, click the Messages button, and then click Notifications. In the upper right corner of Concordance Evolution, click the arrow next to your user name, and then click Notification. All notifications sent to you, including search alert notifications, are listed on the © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 80 Concordance Evolution Notifications tab. By default, the notifications are listed in order of date and time sent, from newest to oldest. Deleting notifications In the Admin dashboard you can delete notifications sent to all users on the View All Notifications dashboard. You can also delete notifications sent to you from the Notifications tab on the Notification Management dashboard. To delete notifications on the View All Notifications dashboard: 1. Do one of the following: Point to the Admin tab, and then click Notifications. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard, click the Messages button, and then click Notifications. 2. Click the View All Notifications link to open the View All Notifications dashboard. 3. Do any of the following: To select individual notifications, select the check boxes next to those you want to delete. To select all notifications, click the Select All link. To select all notifications on the current page, click the Select Page link. 4. Click the Delete button. 5. When prompted, click Yes to confirm the deletion. Creating search alerts Search alerts are set up to alert users when the search results for a saved search query change. Both administrators and users can create search alerts for generating search alert notifications. Administrators can create search alerts for themselves and other users on the Create Alert dashboard in the Admin dashboard. Users can create their own search alerts on the Create Alert dashboard in the Review dashboard. For more information about creating search alerts in the Review dashboard, see Creating © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 81 search alerts. To create a search alert in the Admin module: 1. Do one of the following: Point to the Admin tab, and then click Alerts. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard, click the Messages button, and then click Alerts. Clicking Alerts opens the View Alerts dashboard. 2. Click the New button to open the Create Alert dashboard. 3. In the Name field, type the search alert name. 4. Click the folder button, next to the Dataset field, navigate to and click the dataset associated with the search query. When you click the dataset, the dataset name is automatically added to the Dataset field. 5. Click the Assign button, below the Owner field, click the owner of the search alert, and then click Save. If you are creating the search alert for another user, click the user you are creating the search alert for. If you are creating the search alert for yourself, click your user name. The users in the Users list are organized by Local Directory and Active Directory. By default, the Local Directory users are displayed in the Users list. To view the Active Directory users, click the Active Directory option at the top of the Users list. 6. To send the search alert notification to specific users and/or user groups, click the Send to specific users/groups option, 7. Click the Assign button, below the Alert Recipients(s) field, select the check boxes next to the users you want to receive the search alert, and then click Save. The users in the Users list are organized by Local Directory and Active Directory. By default, the Local Directory users are displayed in the Users list. To view the Active Directory users, click the Active Directory option at the top of the Users list. 8. In the Search field, type the search query to use to generate the search alert. To add a search query to the Search field you can either type the search query in the field, add the query from your saved searches, or combine the search query you manually enter in the Search field with a saved search query. If you want to combine search queries, first type the search query in the Search field, and then add the query from your saved searches. To add a query from your saved searches: 1. On the Create Alert dashboard, click the My Saved Searches link under the Search field. Clicking the My Saved Searches link opens the My Saved Searches dialog box. If © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 82 Concordance Evolution you manually entered a search query in the Search field, the query is displayed in the Existing Search field. 2. Select the check box for the search query you want to use for the search alert. You can add multiple saved search queries to the search alert. 3. If you are combining search queries, click the Combine with Existing Search button. When you click the Combine with Existing Search button, the combined search query is displayed in the Existing Search field. If you need to undo the combination, click the Reset button. Clicking the Reset button resets the Existing Search field back to the original search query. 4. Click Save to add the search query to the Search field on the Create Alert dashboard. 9. To test the search query, click the Test Query button. Clicking the Test Query button runs the search query against the selected dataset and indicates the number of documents containing the search query. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 83 10. Schedule the search alert notification. To schedule a search alert: 1. On the Create Alert dashboard, click one of the following options to indicate when you want the search alert to run: Daily Hourly If you click the Hourly option, in the Hourly list click the hourly interval. For example, if you want the search alert to run every 2 hours, click 2Hours. Weekly If you click the Weekly option, in the Weekly list, click the day of the week you want the search alert to run. Monthly If you click the Monthly option, in the Monthly lists, click the month and day of the month you want the search alert to run. When you select any of these options, the Start Date field is automatically populated with the current date and time. 2. To change the start date and/or time, click the Calendar button to change the start date, and then click the Clock button to change the start time. 3. Click one of the following options to indicate how many times you want to run the search alert: No end date The search alert will run on an ongoing basis End After [#] Occurrence The search alert will only run the number of times you enter in this field End By [date and time] The search alert will only run until the date and time you specified. Click the Calendar button to add the end date, and then click the Clock button to add the end time. When you schedule a search alert, Concordance Evolution will run the search query associated with the search alert at the scheduled date and/or time. If there is a change in the number of documents returned for the search query, Concordance Evolution will automatically generate and send a search alert notification to the users selected in the Alert Recipient(s) field. The search alert notification will indicate the number of documents found for the search query. 11. Click the Create button. When you click the Create button, the search alert is added to the search alerts list on © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 84 Concordance Evolution the View Alerts dashboard in the Admin dashboard, and in the Review dashboard, the search alert is displayed for the owner of the search alert on the Search Alerts tab on the Search Alert dashboard. Viewing search alerts In the Admin dashboard you can view all existing search alerts on the View Alerts dashboard. On the View Alerts dashboard, you can organize the search alerts by search alert name, dataset, elapsed time, or next run date. In the Review dashboard, you can view your own search alerts on the Search Alerts tab on the Search Alert dashboard. If you are designated as a search alert's owner, the search alert is displayed for you in the Review dashboard. If you created a search alert for a user and are not designated as the search alert's owner, the search alert will not be displayed for you in the Review dashboard. Viewing a search alert is different from viewing a search alert notification. A search alert notification is generated from a search alert and is viewed like all other notifications in Concordance Evolution. For more information about viewing search alert notifications, see Viewing notifications. To view search alerts: 1. Do one of the following: Point to the Admin tab, and then click Alerts. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard, click the Messages button, and then click Alerts. Clicking Alerts opens the View Alerts dashboard. By default, the search alerts are listed from newest to oldest. 2. To view the details of a search alert, click the search alert name link in the Alert Name column. Clicking the search alert name link opens the search alert on the Alert Details dashboard. 3. After reviewing the notification details, click Done to return to the View Alerts dashboard. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 85 Editing search alerts Administrators can edit any search alert on the Edit Alert dashboard in the Admin dashboard, and search alert owners can edit their own search alerts on the Create Alert dashboard in the Review dashboard. For more information about editing search alerts in the Review dashboard, see Editing search alerts. To edit a search alert in the Admin module: 1. Do one of the following: Point to the Admin tab, and then click Alerts. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard, click the Messages button, and then click Alerts. Clicking Alerts opens the View Alerts dashboard. 2. In the Alert Name column, click the search alert name link you want to edit. Clicking the search alert name link opens the search alert on the Alert Details dashboard. 3. On the Alert Details toolbar, click the Edit button. Clicking the Edit button opens the Edit Alert dashboard. 4. Make the applicable edits, and then click the Done button to save your changes and return to the View Alerts dashboard. Deleting search alerts Administrators can delete any search alert on the View Alerts dashboard in the Admin dashboard, and search alert owners can delete their own search alerts in the Search Alerts on the Review dashboard. For more information about deleting search alerts in the Review dashboard, see Deleting search alerts. To delete a search alert: 1. Do one of the following: © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 86 Concordance Evolution Point to the Admin tab, and then click Alerts. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard, click the Messages button, and then click Alerts. Clicking Alerts opens the View Alerts dashboard. 2. In the Alert Name column, select the check box next to the search alert you want to delete. 4. Click the Remove button at the bottom of the page. 5. When prompted, click Yes to confirm the deletion. Clicking Yes permanently deletes the search alert from the system. Audit Logs About audit logs Audit Logs provide an account of events in Concordance Evolution both at the system and matter level. Events are records of user actions throughout the application, such as user access and data modification. The System Audit Log helps administrators track the system actions users performed during a session. The Matter Audit Log records the events of user's actions for a given matter such as searching, tagging and documents viewed. Related Topics Viewing the System Audit Log Viewing the Matter Audit Log Exporting Audit Logs Archiving System events Viewing the system audit log The System Audit Log is displayed on the Audit Management dashboard and provides a list of all events created in the system. The Audit Management dashboard displays the Event Date/ Time, Event Type, Event Name, Performed By, and Description. The System Audit Log displays information for each of the following event types: © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution Event type Description AD Domain An Active Directory Domain was added or modified Auditing An audit log was exported Folder A folder was created, deleted, or modified Licensing A seat license was added, removed, assigned or unassigned Login Logout A user session created, failed, or ended Matter A matter was created, deleted or modified Notifications A notification was sent Organization An organization was created, deleted, or modified Security A security role was created, deleted, or modified User A user was created, deleted, or modified User Group A user group was created, deleted, or modified 87 The events shown on the Audit Management page can be exported to a comma-separated (.csv) formatted file. For more information, see Exporting Audit Logs. To view events in the Audit Log: 1. Do one of the following: Point to the Admin tab, and then click System Audit Log. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard, and then on the Admin toolbar click the System Audit Log button. The Audit Management dashboard opens. By default, the Audit Management dashboard displays the 10 most recent events. To change the number of events displayed, in the lower right corner, from the Items Per Page list, select the number of events to display. 2. To refine the results, do any of the following: To view events by date, from the Filter By Last Modified list, select the days to display. To view events by type, from the Filter By Event Type list, select the check box for one or more event types to display. To view events by the user(s) who executed the event, from the Filter Performed By list, select the check box for one or more users to display. 3. To locate a specific event or events, type a value in the field below a column header and then press Enter to search for events that match the value specified. Only one value is allowed in each column header field. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 88 Concordance Evolution 4. To reset the event list back to the original list, do one of the following: Delete the field value and press Enter. Click the Clear link. Viewing the matter audit log The Matter Audit Log is displayed on the Audit Management dashboard and provides a list of all events created in the matter. The Audit Management dashboard displays the Event Date/Time, Event Type, Event Name, Performed By, and Description. The Matter Audit Log displays information for each of the following event types: Event type Description Binder A binder was created, deleted, or modified CaseMap A fact, document, link or text was sent to CaseMap Dataset A dataset was created, deleted or modified Document A document was viewed (Near Native or Document Data views), added, deleted, modified, downloaded, emailed, exported, produced tagged, untagged, or printed Markup A markup was created, deleted, or modified Review Set A review set was created, deleted, or modified Search A search was executed and saved search results were created, deleted, or modified Search Administration A search was executed using the quick search bar on the Admin dashboard Tagging A tag was created, deleted, modified, queried, or the tag was applied or removed The events shown on the Audit Management page can be exported to a comma-separated (.csv) formatted file. For more information, see Exporting Audit Logs. To view events in the Matter Audit Log: 1. In the System pane, locate and open the matter you want to view audit events. 2. On the Matter's dashboard toolbar, click the Audit Log button. The Audit Management dashboard opens. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 89 The Audit Management dashboard opens. By default, the Audit Management dashboard displays the 25 most recent events. To change the number of events shown in the table, in the lower right corner, from the Items Per Page list, select the number of events to display. 3. To refine the results, do any of the following: To view events by date, from the Filter By Last Modified list, select the days to display. To view events by type, from the Filter By Event Type list, select the check box for one or more event types to display. To view events by the user(s) who executed the event, from the Filter Performed By list, select the check box for one or more users to display. 4. To locate a specific event or events, type a value in the field below a column header and then press Enter to search for events that match the value specified. Only one value is allowed in each column header field. 5. To reset the event list back to the original list, do one of the following: Delete the field value and press Enter. Click the Clear link. Exporting an audit log The Audit Log can be exported to a comma-separated (.csv) formatted file. You can export the entire table of events or you can select specific events. To export audit log events: 1. To export the event of an audit log, do one of the following: To export the System Audit Log events, on the Admin dashboard, and then on the Admin toolbar click the System Audit Log button. To export the Matter Audit Log events, from the System pane, locate and open the matter to export events, and then on the matter's dashboard toolbar click the Audit Log button. 2. Do any of the following to refine the results: To view events by date, from the Filter By Last Modified list, select the number of days to display. To view events by type, from the Filter By Event Type list, select the check box for one or more event types to display. To view events by the user(s) who executed the event, from the Filter Performed By list, select the check box for one or more users to display. 3. From the results, do one of the following: To select all the events to export, select the check box in the upper left corner of the Events table or in the bottom left corner, click the Select All link. To one or more events to export, select the check box for each event. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 90 Concordance Evolution 4. On the Audit Management toolbar, click the Export Audit Log Events. 5. In the File Download dialog box, do one of the following: Click Open to view the file, in the Download Complete dialog box, click Open to open the file in your default spreadsheet application. Click Save to save the file, in the Save As dialog box, navigate to where you want to save the file, and then in the File Name field, type the file name and click Save. 6. In the Download Complete dialog box, click Open to view the file or click Close to close the dialog box. Archiving system events To prevent the server where the audit events are stored from getting bogged down with an endless amount of audit events, Concordance Evolution automatically archives the audit events and then deletes the events from the server. When Concordance Evolution servers are set up, the archive folder location and the maximum number of days to store system events on the server are specified. When the number of days is reached, Concordance Evolution exports the events as a comma-separated (.csv) formatted file and stores the file in the specified location. The exported .csv file is dated and saved using the following naming format: <Archive Date-Archive Time>_System_Audit_Log.csv For example, 20140325-09.33.38_EVMaster_SystemAuditLog.csv All archive audit file names are time stamped using Greenwich Mean Time (GMT). The default location on the SQL Server for the archive folder is: C:\ConcordanceEV \EV_AgentJobLogs\SystemAuditLogArchive and the default number of days is 90. These settings can be edited to meet your organization's needs. To edit the system audit archive settings: 1. From the Admin tab, click Servers. 2. Locate the SQL Server and click the server name link. 3. In the Services column, click the System Configuration Service link. 4. On the System Configuration Service tab, do any of the following: To change the number of days the audit events are stored on the server, in the System audit log archival days field, type the number of days. To change the location of the archive folder, in the System audit log archival location field, type the path for the archive folder. 5. When finished, on the Configure Services dashboard toolbar, click Save. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 91 Organizations About organizations In Concordance Evolution you can create organizations to help you manage your clients, cases, and case documents. Organizations form a hierarchy with a single top-level organization that contains a collection of folders, sub-folders matters and datasets below it. A single organization can be used to represent a client, such as Morrison Foerster. Folders can be used to represent the type of law practice, such as Family Law or Corporate Litigation. Matters can be used to represent the client case, such as Joe v Jane, and datasets created under matters can be used to organize the documents for the client case, such as Production_1. At the organization level, you can add folders and matters, apply advanced permissions and user groups, manage the organization's shares, and view an audit log of events for the matters assigned to the organization. To set Admin preferences for the organization, including password settings, number of items to display in lists, default view for search results, tag format settings, and so on, see About preferences and Customizing admin preferences. To assign security roles and policies to user groups at the organization level, see Assigning roles to user groups and Customizing user group security policies. Creating organizations Organizations can be added from the System pane or the Admin dashboard toolbar. To create an organization: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. Do one of the following: In the System pane on the left, right-click the System link, and then click Add Organization. On the Admin dashboard toolbar, click the Add Organization button. 3. In the Folder Name field, type the folder name. The organization name must be unique from other organizations. Organization names can include alphanumeric characters, and the following special characters: !@##$% ^&*()_-+ © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 92 Concordance Evolution 4. In the Folder Description field, type the folder description. 5. Click the Save button to add the organization and open the Organization's dashboard. Managing organizations From an organization's dashboard, you can directly edit or delete any folders, matters and datasets associated with the organization. You can make changes to advanced permissions and user groups for folders, manage the organization's shares, and view an audit log of events for the matters assigned to the organization. To set Admin preferences for the organization, including password settings, number of items to display in lists, default view for search results, tag format settings, and so on, see About preferences and Customizing admin preferences. To assign security roles and policies to user groups at the organization level, see Assigning roles to user groups and Customizing user group security policies. Before deleting an organization, all user groups associated with the organization must be deleted first. Editing organizations You can edit an organizations name, description, and permissions from the organization's dashboard. To edit an organization: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, locate and click the organization to edit. 3. To edit a organization's name or description, do one of the following: On the folder's dashboard toolbar, click the Edit button. From the Actions column of the organization list, click the edit link. 4. In the Edit Folder dialog box, make any necessary changes to the folder properties. 5. When finished, click Save. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 93 To edit the permissions for a folder: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, locate and click the organization to edit. 3. On the folder's dashboard toolbar, click the Manage Permissions button. The User Groups assigned to the folder are displayed. 4. To add a User Group, on the Folder Permissions toolbar, click the Add Group button, select the group(s) you want to add and then click Ok. 5. To change the permissions for a user group, click the Permissions link for the group you want to change. 6. Click the right arrow, change. , for the group to expand the role for the policies you want to 7. To change a policy, click the Allow or Deny link. 6. When finished, click Save. Deleting organizations You can delete organizations from the System pane and the organization's dashboard. If you are deleting a organization that contains other folders, matters, and/or datasets, you must archive or delete the folders, matters, and/or datasets under the organization before you can delete. To delete an organization from the System pane: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, locate and right-click the organization to delete, and then click Delete Folder. If you are deleting a folder containing other folders, matters, and/or datasets, you must archive or delete the folders, matters, and/or datasets under the folder before you can delete the folder. 3. When prompted, on the dashboard toolbar, click the Delete button to confirm the deletion. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 94 Concordance Evolution To delete a organization from the organization's dashboard: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, locate and click the organization to delete. 3. In the Actions column of the organization list, click the delete link. If you are deleting a folder containing other folders, matters, and/or datasets, you must archive or delete the folders, matters, and/or datasets under the folder before you can delete the folder. 4. When prompted, click Ok to confirm the deletion. Folders About folders In Concordance Evolution you can create organizations, folders, matters, and datasets to help you manage your clients, cases, and case documents. While you can create folders directly under the organization to represent clients, you can create additional folders under other folders and matters to help you further organize your clients and client cases. At the folder level, you can assign admin preferences. Admin preferences include password settings, number of items to display in lists, default view for search results, tag format settings, and so on. You can also assign security roles and policies to user groups at the folder level. For more information about preferences, see About preferences and Customizing admin preferences. For more information about assigning security roles and policies, see Assigning roles to user groups and Customizing user group security policies. Creating folders In the Admin dashboard, folders can be created from the System pane, the Organization dashboard, Folder dashboard, and Matter dashboard. To create a folder from the System pane: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, locate and right-click the organization, folder or matter link, and then click Create Folder. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 95 3. In the Create Folder dialog box, in the Folder Name field, type the folder name. The folder name must be unique from other folders at the same level. Folder names can include alphanumeric characters, and the following special characters: !@##$%^&*()_-+ 4. (Optional) In the Folder Description field, type the folder description. The Parent list defaults to the system, folder, or matter you selected. 5. To change the folder parent, click the folder button , next to the Parent list, click the organization, folder, or matter under which you want to create the folder, and then click OK. 6. When finished, click the Save button to add the folder and open the folder's dashboard. To create a folder from an organization dashboard: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, locate and click the organization you want to add a folder. 3. On the organization's dashboard toolbar, click the Add button, and then click Add Folder. 4. In the Create Folder dialog box, in the Folder Name field, type the folder name. The folder name must be unique from other folders at the same level. Folder names can include alphanumeric characters, and the following special characters: !@##$%^&*()_-+ 5. (Optional) In the Folder Description field, type the folder description. The Parent list defaults to the selected organization. 6. To change the folder parent, click the folder button , next to the Parent list, click the organization, folder, or matter under which you want to create the folder, and then click OK. 7. When finished, click the Save button to add the folder and open the folder's dashboard. To create a folder from a folder dashboard: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, locate and click the folder you want to add a folder. 3. On the folder's dashboard toolbar, click the Add button, and then click Add Folder. 4. In the Create Folder dialog box, in the Folder Name field, type the folder name. The folder name must be unique from other folders at the same level. Folder names can include alphanumeric characters, and the following special characters: !@##$%^&*()_-+ 5. (Optional) In the Folder Description field, type the folder description. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 96 Concordance Evolution The Parent list defaults to the selected organization. 6. To change the folder parent, click the folder button , next to the Parent list, click the organization, folder, or matter under which you want to create the folder, and then click OK. 1. When finished, click the Save button to add the folder and open the folder's dashboard. To create a folder from a matter dashboard: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, locate and click the matter you want to add a folder. 3. On the matter's dashboard toolbar, click the Add button, and then click Add Folder. 4. In the Folder Name field, type the folder name. The folder name must be unique from other folders at the same level. Folder names can include alphanumeric characters, and the following special characters: !@##$%^&*()_-+ 5. (Optional) In the Folder Description field, type the folder description. The Parent list defaults to the selected matter. 6. To change the folder parent, click the folder button , next to the Parent list, click the organization, folder, or matter under which you want to create the folder, and then click OK. 7. When finished, click the Save button to add the folder and open the folder's dashboard. Editing folders You can edit a folder's name, description, and permissions from the folder's dashboard. To edit a folder: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, locate and click the folder to edit. 3. To edit a folder's name or description, do one of the following: On the folder's dashboard toolbar, click the Edit button. From the Actions column of the folder list, click the edit link. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 97 4. In the Edit Folder dialog box, make any necessary changes to the folder properties. 5. When finished, click Save. To edit the permissions for a folder: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, locate and click the folder to edit. 3. On the folder's dashboard toolbar, click the Permissions button. The User Groups assigned to the folder are displayed. 4. To add a User Group, on the Folder Permissions toolbar, click the Add Group button, select the group(s) you want to add and then click Ok. 5. To change the permissions for a user group, click the Permissions link for the group you want to change. 6. Expand the role for the policies you want to change. 7. To change a policy, click the Allow or Deny link. 8. When finished, click Save. Deleting folders You can delete folders from the System pane and the Edit Folder dashboard. If you are deleting a folder that contains other folders, matters, and/or datasets, you must archive or delete the folders, matters, and/or datasets under the organization before you can delete. To delete a folder from the System pane: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, locate and right-click the folder you want to delete, and then click Delete Folder. If you are deleting a folder containing other folders, matters, and/or datasets, you must archive or delete the folders, matters, and/or datasets under the folder before you can delete the folder. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 98 Concordance Evolution Clicking the Delete button opens the Warning: Are you sure you want to delete this folder? message. 3. Click the Delete button. To delete a folder from the folder's dashboard: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, locate and click the folder you want to delete. 3. In the Actions column of the folder list, click the delete link. 4. When prompted, click OK to confirm the deletion. M atters About matters Matters created under client folders can be used to represent your client cases, and datasets created under matters can be used to organize the documents for your client cases. The matter dashboard displays the matter name, associated datasets and binders assigned to the matter, and a list of authorized user groups and users. Assigning matters to different Velocity search servers can improve the searching speed performance in the Review dashboard. Velocity search servers create a search collection for every matter created and assigned to the server, so assigning matters to multiple Velocity search servers can help spread the searching load across the different servers. Using the matter dashboard tools you can assign admin preferences, including password settings, number of items to display in lists, default view for search results, tag format settings, and security roles and policies to user groups. You can also view and access matter-level reports for tracking reviewer activity and a matter level audit log. For more information about preferences, see About preferences and Customizing admin preferences. For more information about assigning security roles and policies, see Assigning roles to user groups and Customizing user group security policies. For more information about matter-level reports and audit log, see Viewing matter reports and About audit logs. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 99 Creating matters In the Admin dashboard, matters can be created from the System pane and the Folder dashboard. You can only create a matter from a folder above a matter. You cannot create matters from a folder that is a child of a matter. To create a matter from the System pane: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, locate and right-click an organization or folder, and then click Create Matter. The folder cannot be a child of a matter. 3. On the Create Matter dashboard, in the Matter Name field, type the matter name. The matter name must be unique from other matters at the same level. Matter names can include alphanumeric characters, and the following special characters: !@##$% ^&*()_-+ 4. In the Description field, type the matter description. The default SQL Server database server for Concordance Evolution databases is displayed in the Database Server list. The default SQL Server database server is determined by the Is Default Server check box on the Add SQL Server and Edit SQL Server dashboards. You can add additional SQL Server database servers to Concordance Evolution on the Add SQL Server dashboard. 5. To point to a different SQL Server database server, in the Database Server list, click the database server you want to use for the matter and its dataset(s). The default search server is displayed in the Search Server list. The default search server is determined by the Is Default Server check box on the Add Search Server and Edit Search Server dashboards. You can add additional servers to Concordance Evolution on the Add Search Server dashboard. 6. To use a different search server for the matter and its dataset(s), in the Search Server list, click the search server you want to use for the matter and its dataset(s). Assigning matters to different Velocity search servers can improve the searching speed performance in the Review dashboard. Velocity search servers create a search collection for every matter created and assigned to the server, so assigning matters to multiple Velocity search servers can help spread the searching load across the different servers. 7. Click the Save button to add the matter and open the matter's dashboard. To create a matter from the Folder dashboard: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, locate and click the folder to create the matter. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 100 Concordance Evolution Clicking a folder in the System pane, opens the folder's dashboard. 3. From the folder's dashboard toolbar, click the Add button, and then click Add Matter. 4. On the Create Matter dashboard, in the Matter Name field, type the matter name. The matter name must be unique from other matters at the same level. Matter names can include alphanumeric characters, and the following special characters: !@##$% ^&*()_-+ 5. In the Description field, type the matter description. The default SQL Server database server for Concordance Evolution databases is displayed in the Database Server list. The default SQL Server database server is determined by the Is Default Server check box on the Add SQL Server and Edit SQL Server dashboards. You can add additional SQL Server database servers to Concordance Evolution on the Add SQL Server dashboard. 6. To point to a different SQL Server database server, in the Database Server list, click the database server you want to use for the matter and its dataset(s). The default search server is displayed in the Search Server list. The default search server is determined by the Is Default Server check box on the Add Search Server and Edit Search Server dashboards. You can add additional servers to Concordance Evolution on the Add Search Server dashboard. 7. To use a different search server for the matter and its dataset(s), in the Search Server list, click the search server you want to use for the matter and its dataset(s). 8. Click the Create button to add the matter and open the matter's dashboard. Editing matters You can edit a matter's name and description on the Edit Matter dashboard. If you want to change the security policy settings for a matter, see Customizing user group security policies. To edit a matter: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, locate and click the matter to edit. 3. Do one of the following: From the matter's dashboard toolbar, click the Config button, and then click Edit Matter. From the Actions column, click the edit link. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 101 4. On the Edit Matter dashboard, make the applicable changes. 5. When finished, click the Save button to save your changes and return to the matter's dashboard. Deleting matters You can delete matters from the Edit Matter dashboard. If you are deleting a matter containing folders and/or datasets, you must archive or delete the folders and/or datasets under the matter before you can delete the matter. To delete a matter: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, locate and click the matter you want to delete. 3. Do one of the following: From the matter's dashboard toolbar, click the Config button, click Edit Matter, and then click the Delete button. From the Actions column, click the delete link. If you are deleting a matter containing folders and/or datasets, you must archive or delete the folders and/or datasets under the matter before you can delete the matter. 4. When prompted, click OK to confirm the deletion. Managing Matters It is recommended that you plan a maintenance schedule for matters that are necessary for your organization or client needs. Typical m atter m aintenance includes: Backup - creates a backup of the matter and associated datasets, binders, and review sets Restore - restores the matter from a selected point in time Reindex - updates the matter's index and dictionary for searching The backup, restore, and reindex processes require all users to be logged out of the © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 102 Concordance Evolution matter before executing the process. If users are not logged out, when the Freeze check box is selected, all users for the selected matter will be kicked out of Concordance Evolution. Before performing a backup or restore process is executed, make sure that no other jobs are running for the matter. To backup a matter: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin ashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, locate and click the matter to edit. 3. Do one of the following: From the matter's dashboard toolbar, click the Config button, and then click Edit Matter. From the Actions column, click the edit link. 4. On the Edit Matter dashboard, select the Freeze check box, and then click Save. 5. From the matter's dashboard toolbar, click the Config button, and then click Backup. 6. When prompted, click OK to confirm the backup. 7. When prompted, click OK to confirm no other jobs are running for the matter and to proceed with the backup of the matter. 8. When the process is finished and you have received the notice that the backup job has completed successfully, do one of the following: From the matter's dashboard toolbar, click the Config button, and then click Edit Matter. From the Actions column, click the edit link. 9. On the Edit Matter dashboard, clear the Freeze check box, and then click Save. To restore a matter: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin ashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, locate and click the matter to edit. 3. Do one of the following: From the matter's dashboard toolbar, click the Config button, and then click Edit Matter. From the Actions column, click the edit link. 4. On the Edit Matter dashboard, select the Freeze check box, and then click Save. 5. From the matter's dashboard toolbar, click the Config button, and then click Backup. 6. When prompted, click OK to confirm the restore of the matter. 7. When prompted, click OK to confirm no other jobs are running for the matter and to proceed with the restore of the matter. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 103 8. When the process is finished and you have received the notice that the restore job has completed successfully, do one of the following: From the matter's dashboard toolbar, click the Config button, and then click Edit Matter. From the Actions column, click the edit link. 9. On the Edit Matter dashboard, clear the Freeze check box, and then click Save. To reindex a matter: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin ashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, locate and click the matter to edit. 3. Do one of the following: From the matter's dashboard toolbar, click the Config button, and then click Edit Matter. From the Actions column, click the edit link. 4. On the Edit Matter dashboard, select the Freeze check box, and then click Save. 5. From the matter's dashboard toolbar, click the Config button, and then click Reindex. 6. When prompted, click OK to confirm the reindex of the matter. 7. When the process is finished and you have received the notice that the reindex job has completed successfully, do one of the following: From the matter's dashboard toolbar, click the Config button, and then click Edit Matter. From the Actions column, click the edit link. 8. On the Edit Matter dashboard, clear the Freeze check box, and then click Save. Datasets About datasets When you import documents for a case into Concordance Evolution, documents are imported directly into the dataset(s) associated with the case. The Concordance Evolution dataset system fields are automatically added to a dataset when you create a dataset. After the dataset is created, you can add any custom fields, tag families, tag groups, and/or tags to the dataset that your organization wants to use. For more information about dataset fields and tags, see About dataset fields and About tags. At the dataset level, you can assign admin preferences. Admin preferences include number of items to display in lists, default view for search results, tag format settings, and so on. You can © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 104 Concordance Evolution also assign security roles and policies to user groups at the dataset level. For more information about preferences, see About preferences and Customizing admin preferences. For more information about assigning security roles and policies, see Assigning roles to user groups and Customizing user group security policies. Dataset Creation Process: 1. Create a dataset. 2. Add fields to the dataset. 3. Define field security for the dataset's fields. 4. Import documents into the dataset. 5. Verify the imported documents. 6. Create and assign document review sets. 7. Customize user group security at the dataset level. 8. Define the spelling variations. 9. Define the thesaurus. 10. Define the stop words. 11. Define the redaction reasons. 12. Define the dataset search settings. 13. Create tags for the dataset. 14. Define tag security. Dataset Checklist Checklist: Dataset Data Review Do you know how many documents or gigabytes (GB) of data have been received? Are your files converted to types that are recognized by Concordance Evolution? Do you understand Concordance Evolution dataset field structures and how it affects importing data? © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 105 Checklist: Dataset Review Load Files Have you reviewed the contents of the data volume you are about to load? Have you reviewed your data load file for acceptable delimiters and date formats? Do you have fields set in place for data that you are importing? Have you verified that the Bates number for the first record to be loaded does not overlap with the last Bates number used in the existing collection? If it does overlap, a correction should be requested from the source prior to loading. Did you receive an image load file along with your images? If not, you can create one. Did you adjust the directory path of your image load files, if need be? Have you reviewed how your OCR has been formatted, named and organized? Dataset Structure Did you create additional custom fields for the dataset? Case Review Have you reviewed case records to understand what types of files you are importing? Did you review case records to plan your dataset field structure? Do you understand the file and media requirements for print productions, especially for opposing counsel? Ongoing Maintenance Have you outlined maintenance processes and schedules that affect your new dataset? Creating datasets In the Admin dashboard, datasets can be created from the System pane and the Matter dashboard. You can also create a dataset from the Folder dashboard if you are creating the dataset from a folder under a matter. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 106 Concordance Evolution To create a dataset from the System pane: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, locate and right-click a matter or a folder under a matter, and then click Create Dataset. Clicking Create Dataset opens the Create Dataset dashboard. 3. In the Name field, type the dataset name. The dataset name must be unique from other datasets at the same level. Dataset names can include alphanumeric characters, and the following special characters: !@##$%^&*()_-+ 4. In the Description field, type the dataset description. 5. In the Location for extracted files field, type the path where you want files extracted from Concordance Evolution to be saved. 6. To validate the directory you entered, click the Test Path button. If the path is valid, the message Server location is valid is displayed next to the Test Path button. If the path is invalid, the message Invalid server location is displayed next to the Test Path button. 7. Select the Enable send to CaseMap check box to send document data from the dataset to CaseMap. For more information, see Using CaseMap with Concordance Evolution. 8. From the Near Duplication list to the view and compare documents with duplicate metadata content, select one of the following: Disabled - (Default) Near Deduplication comparison is not activated for the dataset External Load File - uses an external file to process near duplication data Near-Deduplication Job - uses Concordance Evolution's internal near-deduplication processing feature The DCN Field Name field defaults to DCN. The DCN Field Name field determines the name of the document control number (DCN) field automatically created for the dataset by Concordance Evolution. A document control number is a document-level number assigned to a document when it is imported into Concordance Evolution. The Document control number text preference value on the Edit Preference dashboard determines how the document control number label is displayed in the Review dashboard. For more information about preferences, see About preferences. When you import documents into a dataset, Concordance Evolution automatically assigns a unique document control number to each document. 9. To change the document control number field name, in the DCN Field Name field, edit the field name. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 107 10. In the DCN Prefix field, type document control number prefix. The document control number prefix can be up to 15 alphanumeric characters. The DCN Starting Number field defaults to 00000001. The DCN Starting Number field determines the starting number for the document control number and the length of the document control number. The leading zeros determine the length of the number. 11. To change the starting number or length of the document control number, in the DCN Starting Number field, edit the starting document control number and/or length. The document control number length can be up to 15 numeric characters. Once a dataset is created, you cannot edit the document control number prefix, starting number, or length. You can edit the document control number field name on the Edit Field dashboard. 12. Click the Create button to add the dataset and open the dataset's dashboard. Once you have created the dataset, you will need to add fields to the dataset. For more information, see Adding fields to datasets. To create a dataset from the Matter dashboard: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, locate and click the matter to create the dataset. Clicking a matter in the System pane opens the dashboard for the selected matter. 3. On the matter's dashboard toolbar, click the Add button, and then click Create Dataset. Clicking Create Dataset opens the Create Dataset dashboard. 4. In the Name field, type the dataset name. The dataset name must be unique from other datasets at the same level. Dataset names can include alphanumeric characters, and the following special characters: !@##$%^&*()_-+ 5. In the Description field, type the dataset description. 6. In the Location for extracted files field, type the path where you want files extracted from Concordance Evolution to be saved. 7. To validate the directory you entered, click the Test Path button. If the path is valid, the message Server location is valid is displayed next to the Test Path button. If the path is invalid, the message Invalid server location is displayed next to the Test Path button. 8. Select the Enable send to CaseMap check box to send document data from the dataset © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 108 Concordance Evolution to CaseMap. For more information, see Using CaseMap with Concordance Evolution. 7. From the Near Duplication list to the view and compare documents with duplicate metadata content, select one of the following: Disabled - (Default) Near Deduplication comparison is not activated for the dataset External Load File - uses an external file to process near duplication data Near-Deduplication Job - uses Concordance Evolution's internal near-deduplication processing feature The DCN Field Name field defaults to DCN. The DCN Field Name field determines the name of the document control number field automatically created for the dataset by Concordance Evolution. The Document control number text preference value on the Edit Preference dashboard determines how the document control number label is displayed in the Review dashboard. For more information about preferences, see About preferences. When you import documents into a dataset, Concordance Evolution automatically assigns a unique document control number to each document. 10. To change the document control number field name, in the DCN Field Name field, edit the field name. 11. In the DCN Prefix field, type document control number prefix. The document control number prefix can be up to 15 alphanumeric characters. The DCN Starting Number field defaults to 00000001. The DCN Starting Number field determines the starting number for the document control number and the length of the document control number. The leading zeros determine the length of the number. 12. To change the starting number or length of the document control number, in the DCN Starting Number field, edit the starting document control number and/or length. The document control number length can be up to 15 numeric characters. Once a dataset is created, you cannot edit the document control number prefix, starting number, or length. You can edit the document control number field name on the Edit Field dashboard. 13. Click the Create button to add the dataset and open the dataset's dashboard. Once you have created the dataset, you will need to add fields to the dataset. For more information, see Adding fields to datasets. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 109 Editing datasets You can edit a dataset's name, description, production share path(s), Send to CaseMap, and Enable Equivio settings on the Edit Dataset dashboard. You can also define the Redactable Document Set for the dataset. After importing the documents into the dataset, define the Redactable Document Set for the dataset on the Edit Dataset dashboard. The Redactable Document Set is the set of dataset documents reviewers can redact and markup in the Near Native view in the Review dashboard. Each dataset can only have one Redactable Document Set. A document set can be the images document set, native file document set, or produced documents document set. The native file document set is automatically created by Concordance Evolution and has the same name as the dataset. Image document sets are the image sets created for the dataset, and produced documents document sets are the production sets created for the dataset. It is best practice to use the native file document set as the Redactable Document Set for a dataset. The Options menu in the Near Native view determines which document set is displayed in the Near Native view. The Markup toolbar is only available in the Near Native view when the document set selected in the Redactable Document Set list on the Edit Dataset dashboard is selected in the Near Native view. When other document sets are selected, the Markup toolbar is disabled. If you need to edit dataset fields, dataset fields are edited on the Edit Field dashboard. For more information, see Editing dataset fields. If you want to change the security policy settings for a dataset, see Customizing user group security policies. To edit a dataset: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, locate and click the dataset you want to edit. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. In the Actions column, click the edit link for the dataset you want to change. Clicking the edit link opens the Edit Dataset dashboard. 4. Make the applicable edits. 7. To define the Redactable Document Set for the dataset, in the Redactable Document Set list, click the document set you want make available for reviewers to redact and mark up in the Near Native view of the Review dashboard. It is best practice to use the native file document set as the redactable document set for a dataset. The native file document set is automatically created by Concordance Evolution, and has the same name as the dataset. 8. To create a CaseMap link conversion file, click the Create CaseMap Link Conversion File © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 110 Concordance Evolution button. The Create CaseMap Link Conversion File button is only enabled for a dataset if documents from a Concordance DCB file have been imported into the dataset. For more information and step-by-step instructions for creating a CaseMap link conversion file, see Using CaseMap with Concordance Evolution. 9. When finished, click the Save button to return to the dataset's dashboard. Deleting datasets You can delete datasets from the Edit Dataset dashboard, but it is best practice to archive a dataset instead of deleting a dataset. Warning: When you delete a dataset, all documents, review sets, and other document information will be deleted from Concordance Evolution along with the dataset. To delete a dataset: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the dataset you want to delete to open the dataset's dashboard. 3. In the Dataset Tasks pane under Dataset Management, click Dataset Settings. 4. Click the Delete button. Clicking the Delete button opens the following message on the Remove Dataset Warning dashboard: You are about to delete a dataset from the system. It is recommended you archive the dataset instead of deleting it. All documents and associated workflow information will be lost upon deletion. Do you want to continue? 5. When prompted, click Yes to confirm the deletion. Clicking Yes opens the following message on the Delete Dataset Status dashboard: Dataset delete is in progress. Job has been queued to delete dataset. 6. Click OK to delete the dataset. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 111 About dataset fields Before you begin creating fields for a dataset, it is important to understand the types of data you will receive, and how that information can be categorized into the data format of Concordance Evolution dataset fields. Concordance Evolution Data Field Types Use the following table as a reference when you review your data. Concordance Evolution Data Field Types Data Type Capacity Notes Date 8 bytes Only valid dates Numeric 1-30 digits Currency, zero-filled, comma Text Variable (2 gigabytes (GB)) Alphanumeric, allows rich-text format. When you enter a zero for a text field's length, the field's maximum capacity is 2 gigabytes (GB) of data. Reason Code 1-100 characters Alphanumeric, allows rich-text format. A dataset can only have one reason code field. The reason code field is displayed in the Privilege Log panel in the Review dashboard, and is used by reviewers to indicate why a document was redacted for privilege. Document Description 1-100 characters Alphanumeric, allows rich-text format. A dataset can only have one document description field. The document description field is displayed in the Privilege Log panel in the Review dashboard, and is used by reviewers to add additional information about the document or why a document was redacted for privilege. Concordance Evolution System Fields The following fields are automatically created by Concordance Evolution when you create a dataset. These fields are considered system fields. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 112 Concordance Evolution Concordance Evolution System Fields Field Name Description Capacity DCN (Document Control Number) Field name, prefix, and length defined by user when creating a dataset. DCN field cannot be deleted. A dataset can only have one DCN field. The DCN number is unique per record. Prefix - 15 alphanumeric characters _EVPagesNatives Field populated during load file import with number of pages native documents from the Near Native conversion. _EVPagesImages Field populated during load file import with number of pages of converted images from the Near Native conversion. _EVDocumentModifiedDa te Last modified date of a document _EVDocumentFileType File type for imported file _EVFileExtension File extension for imported file _EVImportDescription Field populated during load file import. The default text is <Date(MM/DD/YYY)>_<Import type>_<Import job name>. This field can be edited during time of import. _EVFileSize File size of imported native file _EVLawDocId Used when importing LAW PreDiscovery cases. Matches the ID field within LAW PreDiscovery _EVRelationShipParentI D If a document is part of a family, this field displays the Parent documents _EVRelationShipDocumentID for all children documents. If the document is standalone, the field displays a 0 for the value. _EVRelationShipDocume ntID If a document is part of a family, this field displays the document relationship ID. Each document will have a unique number. _EVImportMessage During import if errors are encountered, an error message is displayed in the field. _EVMD5Hash MD5 hash value of native file during import © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Length - 15 numeric characters Administrating Concordance Evolution 113 Concordance Evolution System Fields Field Name Description Capacity _EVSHA1Hash SHA-1 hash value of native file during import _EVTitle Alphanumeric, allows rich-text format. A dataset can only have one Title field. The Title field is used as a hyperlink in the snippet view to open the document. The title field is required to map during import. If the field is not populated with valid data, "No title available" is displayed for the document in the Snippet view for a review set. 100 Characters Content Alphanumeric, allows rich-text format. A dataset can only have one Content field. The content field can store up to 2GB of data and can store all OCR content. 2 gigabytes (GB) System fields are automatically populated by Concordance Evolution. System fields cannot be edited or deleted, with the exception of the DCN field. You can change the field order of system fields on the Add Field to Dataset dashboard. For the DCN field, you can edit the DCN field's name on the Edit Field dashboard and manage security for the DCN field in the Field Security dialog box. About the DCN Field When you create a dataset, Concordance Evolution automatically creates the DCN (document control number) field. There can only be one DCN field in a dataset, and the field cannot be deleted from the dataset. The DCN Field Name field on the Create Dataset dashboard determines the name and numbering convention of the document control number field automatically created for the dataset by Concordance Evolution. The Document control number text preference value on the Edit Preference dashboard determines how the document control number label is displayed in the Review dashboard. For more information about preferences, see About preferences. Once you create the dataset, if you need to change the document control number field name, you can edit the name on the Edit Field dashboard. About the Content Field When you create a dataset, Concordance Evolution automatically creates the Content field. The Content field is an alphanumeric type field and allows rich-text format. A dataset can only have one content field. The content field stores up to 2GB of data and can store all OCR content. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 114 Concordance Evolution About the _EVTitle Field When you create a dataset, Concordance Evolution automatically creates the _EVTitle field. The _EVTitle field is an alphanumeric type field and allows rich-text format. A dataset can only have one _EVTitle field. The _EVTitle field is used for the dataset's document title field. If the document title field is not created with the Title field type, No title available is displayed for the document in the Snippet view of the Review dashboard. When you enter a zero for a title field's length, the field's maximum capacity is 2 gigabytes (GB) of data. Fields for Near-Duplicate mapping When comparing documents the following fields are necessary for mapping duplicate metadata content: Field Name Description ND_IsMaster The document is the master document. Within a family, the master document is the one with greatest overall similarity to all the other documents in the family. It has to be a nearduplicate of every other document in the family. ND_Sort The document's sort order ID. The Near-Duplicate utility sorts documents based on document similarity. The closer documents are to one another, the closer their sort order ID will be to each other. ND_FamilyID A unique ID for each near-duplicate document family. All documents within the same near-duplicate family will have the same ID in the ND_Family field. The ND_FamilyID value matches the master document's value, and is padded with zeros to eight digits. For example, if the master ID is 112, the ND_FamilyID value is 00000112. ND_Similarity The percentage of similarity between the document and its master document. Within a family, the master document is the one with the greatest overall similarity to all the other documents in the family. It has to be a near-duplicate of every other document in the family ND_ClusterID A unique ID for each near-duplicate document cluster. Documents in a cluster my be similar, but not as closely related as documents in the near-duplicate family, and some documents in a cluster may not be similar, but are connected by a chain of relationships between documents. ND_EquiSortAtt © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution Concordance Evolution fields Equivio fields LAW PreDiscovery fields ND_IsMaster Pivot ND_IsMaster ND_Sort Equisort ND_Sort ND_EquiSortAtt Equisortatt ND_FamilyID Equiset ND_ClusterID Dupsubset ND_Similarity Similarity 115 ND_FamilyID ND_Similarity Understanding Field Structure and Applying Properties Concordance Evolution does not have a pre-defined field structure. However, preliminary planning in how you construct fields and apply properties to each is essential. Concordance Ev olution’s field profile includes: No limit to number of fields per dataset No limit to length of dataset field names Field security is available for each user defined field and three of the system-created fields, _EVTitle, Content, and DCN. All other system-created fields are preset and not editable. For more information, see Managing field security. Concordance Evolution Field Properties Concordance Evolution Field Properties Field is hidden Field cannot be seen by users in the Review dashboard. Allow field sorting Field data can be sorted in ascending or descending order in the Table view. Allow group by Field will be available for selection in the Group By pane in the Review dashboard for sorting document data. By default, check box is selected for all field types except content fields. User writable field Field can be edited by users. If this check box is not selected, field is read-only in the Edit Document Data view. Enable send to CaseMap Field data is exported to CaseMap when the send to CaseMap feature is enabled for the dataset. For more information, see Using CaseMap with Concordance Evolution. Advance on data entry In the Edit Document Data view in the Review dashboard, cursor will automatically move to next field after user enters data in the field. No Default Date Value By default, this option is selected for all date fields. This option should be selected unless you want the field to automatically be © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 116 Concordance Evolution Concordance Evolution Field Properties populated with the document's import date or last edited date. (only available for date fields) Use Create Date Field is automatically populated with the date the document was imported. This date is populated from the ImportedDate field. (only available for date fields) Use Last Edit Date Field is automatically populated with the date the document was last edited in the Edit Document Data view. This date is populated from the DocumentModifiedDate field. (only available for date fields) Allow mixed case text Field allows both uppercase and lowercase text. (only available for text fields) Convert text to UPPERCASE All text entered in the field is automatically converted to uppercase. (only available for text fields) Convert text to lowercase All text entered in the field is automatically converted to lowercase. (only available for text fields) About Field Names in Concordance Evolution It is best practice not to use special characters and keywords used by the Vivisimo® Velocity® search engine in dataset field or tag names in Concordance Evolution. If you use them in the names, Velocity will use them as Velocity keywords and your document search results will return more data than expected. Special Characters and Keywords Used by Velocity / %field%: FOLLOWEDBY phrase \ .au greater-than quotes [ .ti greater-than-or-equal range ] [au] host regex ; [ti] image site : all intitle stem | AND inurl THRU = and language title * and+ less-than url ? ANDNOT less-than-or-equal weight < andnot link wildcard > any linktext wildchar @ author NEAR WITHIN © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution “ BEFORE not , category NOT & CONTAINING NOTCONTAINING () CONTENT NOTWITHIN (,) default-and-1 OR + domain or - equal OR0 ~ filetype OR1 117 WORDS Adding fields to datasets There are two ways to add fields to a dataset. You can manually add individual fields to a dataset or add fields from a field template. If you are going to be creating numerous datasets that will be using the same fields, in Concordance Evolution you can create a set of fields and save the fields to a template, which can be used to quickly add fields to new datasets. Once a field is created, you can assign field security in the Field Security dialog box. Field security can be applied to all fields except system-created fields, with the exception of the DCN system field. You can apply security to the DCN field. For more information about dataset fields, see About dataset fields. For more information about field security, see Managing field security. To manually create a date field: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, locate and click the dataset to add a date field. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Settings button, and then click Fields. 4. On the Field Settings dashboard, click the Add Field button. When creating fields, be aware that the order the fields are listed on the Field Setting Management dashboard is the order the fields are displayed in the Document Data view in the Review dashboard. By default, fields are listed in the order they are created. Once fields are created for a dataset, if you need to, you can rearrange the order of the fields. For more information, see Editing dataset fields. 5. In the Name field, type the field name. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 118 Concordance Evolution The field name must be unique from other fields in the dataset. The Name field only allows alphanumeric characters. It is best practice not to use special characters and keywords used by the Vivisimo® Velocity® search engine in dataset field or tag names in Concordance Evolution. If you use them in the names, Velocity will use them as Velocity keywords and your document search results will return more data than expected. For a list of the special characters and keywords used by Velocity, see the About Field Names in Concordance Evolution section in the "About dataset fields" topic. 6. In the Type list, click the Date field type. 7. In the Description field, type the field description. 8. In the Format list, click the date format you want to use for the field. There are three date formats: DDMMYYYY (default) MMDDYYYY YYYYMMDD For date fields, you do not need to fill out the Length and Decimal Places fields. It is best practice to use the same date format for all dataset date fields, and to have users enter dates in Concordance Evolution using the same date format you are using for the dataset date fields. 9. In the Default Date Value section, select one of the following: No Default Date Value — By default, this option is selected for all date fields. This option should be selected unless you want the field to automatically be populated with the document's import date or last edited date. Use Create Date — Field is automatically populated with the date the document was imported. This date is populated from the ImportedDate field. Use Last Edit Date — Field is automatically populated with the date the document was last edited in the Edit Document Data view. This date is populated from the DocumentModifiedDate field. 10. Select the check boxes for the property options that apply to the field: Hidden Allow field sorting Allow Group By User writeable field Enable send to CaseMap For more information about the field properties, see the Understanding Field Structure and Applying Properties section in the About dataset fields topic. 11. To create a pick list for the field, click the Pick List field, and enter the value(s) for the list. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 119 Pick lists (Authority Word Lists) are a list of words, numbers, and/or phrases that open in the Edit Document Data view when a user places their cursor in a field associated with a word list. Each value needs to be on a separate line in the list, so press ENTER after typing each value to add each value on a separate line. 12. Select the check boxes for the properties that apply to the pick list: Data entry must be from list — Users must select a value from the authority list in order to populate the field. Case sensitivity matching — Authority word list is case sensitive. For example, Milk and milk will be two different values in the list, they are not considered duplicate values. If a user enters a value in the field in the Edit Document Data view, and the value already exists in the authority word list but the case does not match, the value will be considered a new value. Allow user to add to the list — User can add values to the authority list by typing a new value in the field in the Edit Document Data view. When a users types a new value, the value is automatically added to the field's authority word list. Allow duplicate entries — User can add duplicate values to the field. If the Allow user to add to the list check box is selected along with the Allow duplicate entries check box, when a user enters a duplicate value, the duplicate value is saved to the authority word list. Single entry field — Field only allows users to enter or select one value for the field. If this check box is not selected, user can enter multiple values in the field in the Edit Document Data view. For more information, see To edit a field's pick list. 13. To make changes to the security settings for the field, in the Security section, select or clear the check boxes of the Can Read and Can Write columns for each group listed in the Group with Dataset Access column as needed. 14. When finished, click the Save button to save the field and return to the Field Settings Management dashboard. To manually create a numeric field: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, locate and click the dataset to add a numeric field. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Config button, and then click Fields. 4. On the Field Settings dashboard, click the Add Field button. When creating fields, be aware that the order the fields are listed on the Field Settings Management dashboard is the order the fields are displayed in the Document Data view in the Review dashboard. By default, fields are listed in the order they are created. Once fields are created for a dataset, if you need to, you can rearrange the order of the fields. For more information, see Editing dataset fields. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 120 Concordance Evolution 5. In the Name field, type the field name. The field name must be unique from other fields in the dataset. The Name field only allows alphanumeric characters. Special characters are not allowed. It is best practice not to use special characters and keywords used by the Vivisimo® Velocity® search engine in dataset field or tag names in Concordance Evolution. If you use them in the names, Velocity will use them as Velocity keywords and your document search results will return more data than expected. For a list of the special characters and keywords used by Velocity, see the About Field Names in Concordance Evolution section in the "About dataset fields" topic. 6. In the Type list, click the Numeric field type. 7. In the Description field, type the field description. 8. In the Format list, click the number format you want to use for the field. There are four number formats: Plain (default) Currency Comma ZeroFilled 9. In the Length field, type the maximum number of characters allowed for the field. For numeric fields, the Length field default value is 5. 10. In the Decimal field, type the number of decimal places to use for the field. The Decimal field defaults to 2. The decimal places are automatically applied to numbers added to a numeric field. For example, if the Decimal field is set to 2, and the user types 1050 in the numeric field in the Edit Document Data view, the system automatically changes the number to 10.50. 11. Select the check boxes for the property options that apply to the field: Hidden Allow field sorting Allow Group By Enable send to CaseMap User writeable field For more information about the field properties, see the Understanding Field Structure and Applying Properties section in the About dataset fields topic. 12. To create a pick list for the field, click within the Pick List field, and enter the value(s) for the list. Pick lists (Authority Word lists) are a list of words, numbers, and/or phrases that open in the Edit Document Data view when a user places their cursor in a field associated with a word list. Each value needs to be on a separate line in the list, so press ENTER after typing each © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 121 value to add each value on a separate line. 13. Select the check boxes for the properties that apply to the pick list: Data entry must be from list — Users must select a value from the authority list in order to populate the field. Case sensitivity matching — Authority word list is case sensitive. For example, Milk and milk will be two different values in the list, they are not considered duplicate values. If a user enters a value in the field in the Edit Document Data view, and the value already exists in the authority word list but the case does not match, the value will be considered a new value. Allow user to add to the list — User can add values to the authority list by typing a new value in the field in the Edit Document Data view. When a users types a new value, the value is automatically added to the field's authority word list. Allow duplicate entries — User can add duplicate values to the field. If the Allow user to add to the list check box is selected along with the Allow duplicate entries check box, when a user enters a duplicate value, the duplicate value is saved to the authority word list. Single entry field — Field only allows users to enter or select one value for the field. If this check box is not selected, user can enter multiple values in the field in the Edit Document Data view. For more information, see To edit a field's pick list. 14. To make changes to the security settings for the field, in the Security section, select or clear the check boxes of the Can Read and Can Write columns for each group listed in the Group with Dataset Access column as needed. 15. When finished, click the Save button to save the field and return to the Field Settings Management dashboard. To manually create a text field: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, locate and click the dataset to add a text field. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Config button, and then click Fields. 4. On the Field Settings dashboard, click the Add Field button. When you are creating fields, be aware that the order the fields are listed on the Field Settings Management dashboard is the order the fields are displayed in the Document Data view in the Review dashboard. By default, fields are listed in the order they are created. Once fields are created for a dataset, if you need to, you can rearrange the order of the fields. For more information, see Editing dataset fields. 5. In the Name field, type the field name. The field name must be unique from other fields in the dataset. The Name field only allows alphanumeric characters. Special characters are not allowed. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 122 Concordance Evolution It is best practice not to use special characters and keywords used by the Vivisimo® Velocity® search engine in dataset field or tag names in Concordance Evolution. If you use them in the names, Velocity will use them as Velocity keywords and your document search results will return more data than expected. For a list of the special characters and keywords used by Velocity, see the About Field Names in Concordance Evolution section in the "About dataset fields" topic. 6. In the Type list, click the Text field type. 7. In the Description field, type the field description. For text fields, you do not need to fill out the Format and Decimal Places fields. 8. In the Length field, type the maximum number of characters allowed for the field. For text fields, the Length field defaults to 10. If the field is user-writeable field, make sure that the field length is large enough to hold the data that will be imported into the field. 9. From the Casting list, select one of the following options: Allow mixed case text — Field allows both uppercase and lowercase text. Convert text to UPPERCASE — All text entered in the field is automatically converted to uppercase. Convert text to lowercase — All text entered in the field is automatically converted to lowercase. 10. Select the check boxes for the property options that apply to the field: Hidden Allow field sorting Allow Group By Enable send to CaseMap User writeable field For more information about the field properties, see the Understanding Field Structure and Applying Properties section in the About dataset fields topic. 11. To create a pick list for the field, click the Pick List field, and enter the value(s) for the list. Pick lists (Authority Word lists) are a list of words, numbers, and/or phrases that open in the Edit Document Data view when a user places their cursor in a field associated with a word list. Each value needs to be on a separate line in the list, so press ENTER after typing each value to add each value on a separate line. 12. Select the check boxes for the properties that apply to the pick list: Data entry must be from list — Users must select a value from the authority list in order to populate the field. Case sensitivity matching — Authority word list is case sensitive. For example, Milk and milk will be two different values in the list, they are not considered duplicate values. If a user enters a value in the field in the Edit Document Data view, and the value already exists in the authority word list but the case does not match, the value © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 123 will be considered a new value. Allow user to add to the list — User can add values to the authority list by typing a new value in the field in the Edit Document Data view. When a users types a new value, the value is automatically added to the field's authority word list. Allow duplicate entries — User can add duplicate values to the field. If the Allow user to add to the list check box is selected along with the Allow duplicate entries check box, when a user enters a duplicate value, the duplicate value is saved to the authority word list. Single entry field — Field only allows users to enter or select one value for the field. If this check box is not selected, user can enter multiple values in the field in the Edit Document Data view. For more information, see To edit a field's pick list. 13. To make changes to the security settings for the field, in the Security section, select or clear the check boxes of the Can Read and Can Write columns for each group listed in the Group with Dataset Access column as needed. 14. When finished, click the Save button to save the field and return to the Field Settings Management dashboard. To manually create a reason code field: A dataset can only have one reason code field. Once a reason code field is created for a dataset, the ReasonCode selection is no longer available in the Type list on the Add Field and Edit field dashboards. The reason code field is displayed on the Privilege Log panel in the Review dashboard, and is used by reviewers to indicate why a document was redacted for privilege. When you are creating a reason code field, you need to create an authority list containing the reasons a document can be redacted for privilege. On the Privilege Log panel in the Review dashboard, the Reason code field is displayed with the name Reason Code regardless of the name you enter for the field in the Add Field or Edit field dashboard, and the field is displayed as a list. If you do not create an authority list for the field, reviewers cannot populate the field for documents. 1. Click the Admin tab to open the . 2. In the System pane on the left, locate and click the dataset to add a reason code field. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Settings button, and then click Fields. 4. On the Field Settings dashboard, click the Add Field button. When you are creating fields, be aware that the order the fields are listed on the Field Settings Management dashboard is the order the fields are displayed in the Document Data view in the Review dashboard. By default, fields are listed in the order they are created. Once fields are created for a dataset, if you need to, you can rearrange the order of the fields. For more information, see Editing dataset fields. 5. In the Name field, type the field name. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 124 Concordance Evolution The field name must be unique from other fields in the dataset. The Name field only allows alphanumeric characters. Special characters are not allowed. It is best practice not to use special characters and keywords used by the Vivisimo® Velocity® search engine in dataset field or tag names in Concordance Evolution. If you use them in the names, Velocity will use them as Velocity keywords and your document search results will return more data than expected. For a list of the special characters and keywords used by Velocity, see the About Field Names in Concordance Evolution section in the "About dataset fields" topic. On the Privilege Log panel in the Review dashboard, the reason code field is displayed with the name Reason Code regardless of the name you enter for the field in the Add Field or Edit Field dashboard. 6. In the Type list, click the ReasonCode field type. Once a reason code field is created for a dataset, the ReasonCode selection is no longer available in the Type list on the Add Field and Edit field dashboards. 7. In the Description field, type the field description. For reason code fields, you do not need to fill out the Format, Length, and Decimal Places fields. 8. From the Casting list, select one of the following options for the text field: Allow mixed case text — Field allows both uppercase and lowercase text. Convert text to UPPERCASE — All text entered in the field is automatically converted to uppercase. Convert text to lowercase — All text entered in the field is automatically converted to lowercase. 9. Select the check boxes for the property options that apply to the field: Hidden Allow field sorting Allow Group By Enable send to CaseMap User writeable field For the reason code field, the Index field for group by check box is selected by default. If you do not want the field to be available for selection on the Group By pane in the Review dashboard, clear the check box. Also, the User writeable field check box should be selected for the reason code field to ensure users can select a reason code from the Review dashboard. For more information about the field properties, see the Understanding Field Structure and Applying Properties section in the About dataset fields topic. 10. To create a pick list for the field, click the in the Pick List field, and enter the value(s) for the list. Pick lists (Authority Word lists) are a list of words, numbers, and/or phrases that open in the Edit Document Data view when a user places their cursor in a field associated with a © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 125 word list. Each value needs to be on a separate line in the list, so press ENTER after typing each value to add each value on a separate line. 11. Select the check boxes for the properties that apply to the pick list: Data entry must be from list — Users must select a value from the authority list in order to populate the field. Case sensitivity matching — Authority word list is case sensitive. For example, Milk and milk will be two different values in the list, they are not considered duplicate values. If a user enters a value in the field in the Edit Document Data view, and the value already exists in the authority word list but the case does not match, the value will be considered a new value. Allow user to add to the list — User can add values to the authority list by typing a new value in the field in the Edit Document Data view. When a users types a new value, the value is automatically added to the field's authority word list. Allow duplicate entries — User can add duplicate values to the field. If the Allow user to add to the list check box is selected along with the Allow duplicate entries check box, when a user enters a duplicate value, the duplicate value is saved to the authority word list. Single entry field — Field only allows users to enter or select one value for the field. If this check box is not selected, user can enter multiple values in the field in the Edit Document Data view. For more information, see To edit a field's pick list. 12. To make changes to the security settings for the field, in the Security section, select or clear the check boxes of the Can Read and Can Write columns for each group listed in the Group with Dataset Access column as needed. 13. When finished, click the Save button to save the field and return to the Field Settings Management dashboard. To manually create a document description field: A dataset can only have one document description field. Once a document description field is created for a dataset, the Document Description selection is no longer available in the Type list on the Add Field and Edit field dashboards. The document description field is displayed on the Privilege Log panel below the Reason Code field in the Review dashboard, and is a text field used by reviewers to add additional information about the document or why a document was redacted for privilege. The name you enter for the document description field on the Add Field or Edit Field dashboard is displayed on the Privilege Log panel. 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, locate and click the dataset to add a document description field. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 126 Concordance Evolution 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Settings button, and then click Fields. 4. On the Field Settings dashboard, click the Add Field button. When you are creating fields, be aware that the order the fields are listed on the Field Settings Management dashboard is the order the fields are displayed in the Document Data view in the Review dashboard. By default, fields are listed in the order they are created. Once fields are created for a dataset, if you need to, you can rearrange the order of the fields. For more information, see Editing dataset fields. 5. In the Name field, type the field name. The field name must be unique from other fields in the dataset. The Name field only allows alphanumeric characters. Special characters are not allowed. It is best practice not to use special characters and keywords used by the Vivisimo® Velocity® search engine in dataset field or tag names in Concordance Evolution. If you use them in the names, Velocity will use them as Velocity keywords and your document search results will return more data than expected. For a list of the special characters and keywords used by Velocity, see the About Field Names in Concordance Evolution section in the "About dataset fields" topic. 6. In the Type list, click the Document Description field type. Once a document description field is created for a dataset, the Document Description selection is no longer available in the Type list on the Add Field and Edit field dashboards. 7. In the Description field, type the field description. 8. From the Casting list, select one of the following options for the text field: Allow mixed case text — Field allows both uppercase and lowercase text. Convert text to UPPERCASE — All text entered in the field is automatically converted to uppercase. Convert text to lowercase — All text entered in the field is automatically converted to lowercase. 9. Select the check boxes for the property options that apply to the field: Hidden Allow field sorting Allow Group By Enable send to CaseMap User writeable field For more information about the field properties, see the Understanding Field Structure and Applying Properties section in the About dataset fields topic. 10. To create a pick list for the field, click the in the Pick List field, and enter the value(s) for the list. Pick lists (Authority Word lists) are a list of words, numbers, and/or phrases that open in the Edit Document Data view when a user places their cursor in a field associated with a © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 127 word list. Each value needs to be on a separate line in the list, so press ENTER after typing each value to add each value on a separate line. 11. Select the check boxes for the properties that apply to the pick list: Data entry must be from list — Users must select a value from the authority list in order to populate the field. Case sensitivity matching — Authority word list is case sensitive. For example, Milk and milk will be two different values in the list, they are not considered duplicate values. If a user enters a value in the field in the Edit Document Data view, and the value already exists in the authority word list but the case does not match, the value will be considered a new value. Allow user to add to the list — User can add values to the authority list by typing a new value in the field in the Edit Document Data view. When a users types a new value, the value is automatically added to the field's authority word list. Allow duplicate entries — User can add duplicate values to the field. If the Allow user to add to the list check box is selected along with the Allow duplicate entries check box, when a user enters a duplicate value, the duplicate value is saved to the authority word list. Single entry field — Field only allows users to enter or select one value for the field. If this check box is not selected, user can enter multiple values in the field in the Edit Document Data view. For more information, see To edit a field's pick list. 12. To make changes to the security settings for the field, in the Security section, select or clear the check boxes of the Can Read and Can Write columns for each group listed in the Group with Dataset Access column as needed. 13. When finished, click the Save button to save the field and return to the Field Settings Management dashboard. To add a pick list to an existing field: Pick lists (Authority Word list) are lists of words, numbers, and/or phrases that open in the Edit Document Data view when a user places their cursor in a field associated with an authority word list. Pick list entries are always inserted at the current cursor location in the Edit Document Data view. An authority word list can contain anything, including zip codes, author's names, and complex chemical names. Any data entry task that is repetitive and prone to errors is a good candidate for an authority list. Selecting entries from the list lowers the number of errors introduced through data entry, and the number of keystrokes — thus saving labor and expense while improving accuracy. You can create an authority word list for date, numeric, and text fields. You cannot create authority word lists for the Document Control Number field or content fields. 1. On the Field Settings dashboard, click the edit link for the field to add a pick list. 2. In the Pick list field, type the pick list values. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 128 Concordance Evolution Each value needs to be on a separate line in the list, so press ENTER after typing each value to add each value on a separate line. 3. Select the check boxes for the properties that apply to the authority word list: Data entry must be from list — Users must select a value from the authority list in order to populate the field. Case sensitivity matching — Authority word list is case sensitive. For example, Milk and milk will be two different values in the list, they are not considered duplicate values. If a user enters a value in the field in the Edit Document Data view, and the value already exists in the authority word list but the case does not match, the value will be considered a new value. Allow user to add to the list — User can add values to the authority list by typing a new value in the field in the Edit Document Data view. When a users types a new value, the value is automatically added to the field's authority word list. Allow duplicate entries — User can add duplicate values to the field. If the Allow user to add to the list check box is selected along with the Allow duplicate entries check box, when a user enters a duplicate value, the duplicate value is saved to the authority word list. Single entry field — Field only allows users to enter or select one value for the field. If this check box is not selected, user can enter multiple values in the field in the Edit Document Data view. 4. Click Save to save the list values and return to the Field Settings Management dashboard. To add dataset fields from a template: Currently, Concordance Evolution comes with two predefined field templates: SystemTemplateForOpticon for documents imported from a Concordance Image files (.dir), and SystemTemplateForEmail/Edocs for documents imported from email and electronic documents. 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, locate and click the dataset to add a fields. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Settings button, and then click Fields. Clicking Fields opens the Field Settings dashboard. A list of templates, if available, are displayed in the Templates list when you click the Templates button on the Field Setting Management toolbar. If there are existing fields in the dataset, and any of the field names and types match the names and types of fields in the field template you are importing into the dataset, the fields from the template overlay the existing fields. 4. From the Templates list, click the template you want to import into the dataset. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 129 5. Click the Add Fields button to add the fields to the dataset. When you are creating fields, be aware that the order the fields are listed on the Add Fields To Dataset dashboard is the order the fields are displayed in the Document Data view in the Review dashboard. By default, fields are listed in the order they are created. Once fields are created for a dataset, if you need to, you can rearrange the order of the fields. For more information, see Editing dataset fields. 6. Once you have finished adding the fields to the dataset, click the Done button to save the fields and field settings. To create a dataset field template: If you are going to be creating numerous datasets that will be using the same fields, in Concordance Evolution you can create a set of fields and save the fields to a template, which can be used to quickly add fields to new datasets. You can save dataset fields to an existing custom field template or create a new custom field template. If you want to save the fields to an existing field template, see To save fields to an existing field template in this topic. When you save dataset fields to a field template, the fields, field settings, and field order are saved to the template. System-created fields are not saved to dataset field templates. 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, locate and click the dataset create a field template. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Settings button, and then click Fields. 4. On the Field Settings Management dashboard, add the dataset fields you want to save to the field template. 5. Once you have finished adding the fields, on the Field Settings Management dashboard toolbar, click the Templates button. 6. In the Save Current fields as Template box, type the name of the field template. Field template names must be unique from other custom field templates. The template name field only allows alphanumeric characters. Special characters are not allowed. 6. When finished, click Save. Once the fields are saved to the field template, the The fields have been successfully saved to template message is displayed on the Field Settings Management dashboard. To save fields to an existing field template: © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 130 Concordance Evolution You can save dataset fields to an existing custom field template or create a new custom field template. If you are adding fields to an existing field template, you can only add the fields to a custom field template. Fields cannot be added to the pre-defined field templates: SystemTemplateForOpticon and SystemTemplateForEmail/Edocs. If you want to save the fields to a new field template, see To create a dataset field template in this topic. When you save dataset fields to a field template, the fields, field settings, and field order are saved to the template. System-created fields are not saved to dataset field templates. 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, locate and click the dataset to save fields. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Settings button, and then click Fields. 4. On the Field Settings Management dashboard, add the dataset fields you want to save to the existing field template. 5. Once you have finished adding the fields, on the Field Settings Management dashboard toolbar, click the Templates button. 6. Click the Save Current fields as Template box, and then select the existing field template. 6. Click Save. Once the fields are saved to the field template, the The fields have been successfully saved to template message is displayed on the Field Settings Management dashboard. To create field definitions for CaseMap Creating field definitions for CaseMap is optional and can be done for any dataset which has the Enable send to CaseMap check box selected for any of the dataset's fields. Field definitions are created for CaseMap by clicking the Export Definitions button on the Field Settings Management dashboard toolbar. Clicking the Export Definitions button generates an XML file that contains the Concordance Evolution dataset's field definitions for the fields that have the Enable send to CaseMap check box selected. Once the file is created, you can open the XML file in CaseMap to map the Concordance Evolution fields in the XML file to the corresponding fields in CaseMap. For more information about using CaseMap with Concordance Evolution and step-by-step instructions for creating the casemap.cmbulk XML file, see Using CaseMap with Concordance Evolution. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 131 Editing dataset fields When you create a dataset, Concordance Evolution automatically creates the DCN (document control number), Content, and Title fields and some system fields. System fields cannot be edited, with the exception of the DCN, Content, and Title fields. You can only change the field order of system fields on the Field Settings Management dashboard. For the DCN field, you can edit the DCN field's name on the Edit Field dashboard and manage security for the DCN field in the Field Security dialog box. For the rest of the fields created in a dataset, you can edit all the field properties and settings. If you need to modify a field's security settings, see Managing field security. You can also edit a dataset's field order. The order dataset fields are listed on the Add Fields To Dataset dashboard is the order the fields are displayed in the Document Data view in the Review dashboard. By default, fields are listed in the order they are created. To edit a field: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, locate and click the dataset you want to add a field. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Settings button, and then click Fields. 4. On the Field Settings dashboard, in the Action column, click the Edit link. Clicking the Edit link in the Actions column opens the Edit field dashboard. 5. Make the applicable edits. Warning: If you are changing a field's type, and there is existing data in the field, changing the field type can impact the existing data. Here are the impacts for each conversion: Text to Numeric: Non-numeric values in the field will be lost Text to Date: Non-numeric values will be lost, along with the length of the numeric information Numeric to Date: Some numeric decimal and field length settings may be lost Numeric to Text: Decimal information may be lost Date to Numeric: Date format information will be lost Date to Text: Field values are retained Any type to Date: All field values will be lost unless the field is associated with an authority list containing date values You cannot change a content, reason code, document description, title, or container field's field type to another field type, and you cannot change other field's field types to the content, reason code, document description, title, or container field type. 6. If you want to modify or add a pick list for the field, in the Pick List field, type the new © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 132 Concordance Evolution value(s). For more information, see To edit a field's pick list. 7. Click the Save button to save your changes and return to the Field Settings Management dashboard. To edit a field's pick list: A Pick list (Authority Word lists) are lists of words, numbers, and/or phrases that open in the Edit Document Data view when a user places their cursor in a field associated with an authority word list. Authority list entries are always inserted at the current cursor location in the Edit Document Data view. An authority list can contain anything, including zip codes, author's names, and complex chemical names. Any data entry task that is repetitive and prone to errors is a good candidate for an authority list. Selecting entries from the list lowers the number of errors introduced through data entry, and the number of keystrokes — thus saving labor and expense while improving accuracy. You can create an authority word list for date, numeric, and text fields. You cannot create authority word lists for the DCN field, system, or content fields. 1. On the Add Field or Edit Field dashboard, in the Pick List field, edit, delete, or add additional authority word list values. Each value needs to be on a separate line in the list, so press the ENTER key after typing each value to add each value on a separate line. 2. Select the check boxes for the properties that apply to the authority word list: Data entry must be from list — Users must select a value from the authority list in order to populate the field. Case sensitivity matching — A word list is case sensitive. For example, Milk and milk will be two different values in the list, they are not considered duplicate values. If a user enters a value in the field in the Edit Document Data view, and the value already exists in the authority word list but the case does not match, the value will be considered a new value. Allow user to add to the list — User can add values to the authority list by typing a new value in the field in the Edit Document Data view. When a users types a new value, the value is automatically added to the field's authority word list. Allow duplicate entries — User can add duplicate values to the field. If the Allow user to add to the list check box is selected along with the Allow duplicate entries check box, when a user enters a duplicate value, the duplicate value is saved to the authority word list. Single entry field — Field only allows users to enter or select one value for the field. If this check box is not selected, user can enter multiple values in the field in the Edit Document Data view. 3. Click Save to save the list values and return to the Field Settings Management dashboard. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 133 To change a dataset's field order: When you are creating fields, be aware that the order the fields are listed on the Add Fields To Dataset dashboard is the order the fields are displayed in the Document Data view in the Review dashboard. By default, fields are listed in the order they are created. Once fields are created for a dataset, if you need to, you can rearrange the order of the fields. 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, locate and click the dataset you want to edit. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Settings button, and then click Fields. 4. On the Field Settings dashboard toolbar, click the Reorder Fields button. 5. In the Reorder Fields dialog box, to move a single field, do any of the following: To move a field up in the field list, click the up arrow button or drag the field up to the desired position. To move a field down in the field list, click the down arrow button or drag the field down to the desired position. 6. To move multiple fields at one time, do any of the following: To move consecutive fields, press SHIFT, click the first field, click the last field you want to move, and then drag the fields to the desired position. To move non-consecutive fields, press CTRL, click the fields you want to move, and then drag the fields to the desired position. 7. When finished, click Save. Managing field-level security In Concordance Evolution you can add field-level security to individual fields in a dataset on the Add Field or Edit Field dashboards . Field-level security allows you to assign read and/or write access for each field in a dataset. By default, each field allows read and write access. The read and write security settings determine whether a field is read-only, editable, or not displayed in the Document Data and Edit Document Data views in the Review dashboard for users in a user group. You can add field security to all fields in a dataset except for the system-created fields, with the exception of the DCN field. The DCN field is a system field, but you can add field security to the field. Field security can be added to fields after the fields have been added to a dataset. You cannot add field security to a field while you are adding the field to the dataset on the Add Field dashboard. You can only access the Field Security dialog box from the Edit Field dashboard. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 134 Concordance Evolution Field-level security is assigned by user group. To assign field-level security to a user group, the user group must have security policies allowing the user group access to the dataset assigned to the user group on the Dataset Security dashboard for the dataset. For more information about assigning user groups and security policies to datasets, see Assigning roles to user groups and Customizing user group security policies. If no user groups have access to a dataset, the following message is displayed in the Field Security dialog box: To manage security for a dataset field: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, locate and click the dataset you want to edit security. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Settings button, and then click Fields. 4. On the Field Settings dashboard, located the field you want edit. 5. In the Actions column, click the Edit link for the field you want to edit security settings. You cannot manage security for the system-created fields, with the exception of the DCN, Content, and Title fields. 6. In the Security section, make any of the following changes: To make a field read-only for users in the user group in the Document Data and Edit Document Data views, make sure that the Can Read check box is selected, and clear the Can Write check box. To allow users in the user group to view the field in the Document Data and Edit © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 135 Document Data views, and edit the field in the Edit Document Data view, select the Can Read and Can Write check box. To prevent users in the user group from viewing and editing the field in the Document Data and Edit Document Data view, clear the Can Read and Can Write check boxes. 7. When finished, on the Edit Field toolbar, click the Save button to return to the Field Settings Management dashboard. Deleting fields from a dataset You can delete fields from a dataset on the Edit Field dashboard. If the field is already populated with values, the field values will be deleted from the dataset along with the field. To delete a field from a dataset: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, locate and click the dataset you want to remove a field. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Settings button, and then click Fields. 4. On the Field Settings dashboard, locate the field you want to delete. 5. In the Action column, and then click the Delete link. 6. When prompted, click OK to confirm the deletion. Using CaseMap with Concordance Evolution The Send to CaseMap feature in Concordance Evolution allows you to send a fact, a document, or multiple documents to CaseMap. Selected document text will display in CaseMap's Facts spreadsheet as a new Fact record. Selected documents sent to CaseMap display in the Objects - Documents spreadsheet. All tags, tag groups, and tag folders associated with a document are also included in the export. All fact and document records in CaseMap will link directly back to the document or selected text in Concordance Evolution. If you need to send updated fact text from the same document, the associated Fact record in CaseMap will be updated. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 136 Concordance Evolution For more information about sending data to CaseMap from the Review dashboard, see Sending documents to CaseMap. Before users can send data to CaseMap from the Review dashboard, the Send to CaseMap feature needs to be enabled for the dataset, dataset fields, and users in the Admin dashboard. Process for Using CaseMap with Concordance Evolution: In order to use the Send to CaseMap feature in Concordance Evolution, certain actions need to be performed in the Admin and Review dashboards. The following steps define how to enable and use the Send to CaseMap feature in Concordance Evolution. 1. Allow Can Send to CaseMap policy. Make sure that the Can Send to CaseMap security policy is set to Allow. The Can Send to CaseMap security policy is located under Document Data Viewer on the Security dashboard. For more information about defining security policies, see Customizing user group security policies. 2. Activate the Enable send document links to CaseMap preference. To activate the Enable send document links to CaseMap preference for the system, an organization, a folder, matter, dataset, user, or user group, in the Value field on the Edit preference dashboard in the Admin dashboard, click the True option. By default, the Value field is set to False. For more information about setting system folder, matter, dataset, user, or user group preferences, see Customizing admin preferences. If you are enabling the Enable send document link to CaseMap preference for yourself, in the Set Preference For Enable send document links to CaseMap field on the My Preference dashboard, click the True option. By default, the Set Preference For Enable send document links to CaseMap field is set to False. For more information about setting personal preferences, see Customizing personal preferences. When the Enable send document links to CaseMap preference is set to True, in the Admin dashboard, the Save Definitions button on the Add Fields to Dataset dashboard in the CaseMap Field Definitions box is enabled, and the Create CaseMap Link Conversion File button at the bottom of the Edit Dataset dashboard is enabled for a dataset after documents are imported into the dataset from a Concordance DCB file. In the Review dashboard, the Send to CaseMap button, , is enabled. 3. Define the Maximum number of document links preference. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 137 Define the Maximum number of document links preference to determine the maximum number of document links allowed per export to CaseMap. By default, the Maximum number of documents links preference is set to 100 documents. To modify the Maximum number of document links preference for the system, a user, or user group, in the Value field on the Edit preference dashboard, type the maximum number of links allowed per export to CaseMap. By default, the Value field is set to 100. If you are modifying the Maximum number of document links preference for yourself, in the Set Preference For Maximum number of document links field on the My Preference dashboard, type the maximum number of links allowed per export to CaseMap. By default, the Set Preference For Maximum number of document links field is set to 100. Click Save to save your changes. 4. Enable the Send to CaseMap feature for a dataset. To enable the Send to CaseMap feature for a dataset, on the Create Dataset or Edit Dataset dashboard in the Admin dashboard, select the Enable send to CaseMap check box for the dataset containing the documents and/or document text you want to export to CaseMap, and then click Save to save your changes. 5. Enable the Send to CaseMap feature for dataset fields. To enable the Send to CaseMap feature for dataset fields, on the Add Field or Edit Field dashboard in the Admin dashboard, select the Enable send to CaseMap check box for the dataset fields containing the data you want to export to CaseMap, and then click Save to save your changes. In Concordance Evolution, fact text can only be exported from the Content type field in Concordance Evolution to CaseMap. If you are going to be sending facts to CaseMap from Concordance Evolution, make sure that the Enable send to CaseMap check box is selected for the dataset's content field. 6. Create field definitions XML file for CaseMap (Optional). This step is optional and can be done for any dataset which has the Enable send to CaseMap check box selected for any of the dataset's fields. The field definitions XML file contains the Concordance Evolution dataset's field definitions for the fields that have the Enable send to CaseMap check box selected. This step will generate the casemap.cmbulk XML file. Once the file is created, you can open the casemap.cmbulk XML file in CaseMap to map the Concordance Evolution fields in the XML file to the corresponding fields in CaseMap. The casemap.cmbulk XML file is generated from the Add Fields to Dataset dashboard by clicking the Save Definitions button. The Save Definitions button is enabled on the Add Fields to Dataset dashboard once the Enable send document link to CaseMap preference is set to True. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 138 Concordance Evolution To create the field definitions XML file for CaseMap: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the dataset containing the fields you want to map to CaseMap. Before you create the casemap.cmbulk XML file, make sure that the Enable send to CaseMap check box selected on the Add Field or Edit Field dashboard for each field you want to map to CaseMap. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Config button, and then click Fields. 4. Click the Export Definitions button to open the File Download dialog box. 5. Click Save to open the Save As dialog box. 6. Browse to where to want to save the casemap.cmbulk file. 7. To rename the file, in the File name field, rename the file. 8. Make sure that .cmbulk Document is selected in the Save as type field, and then click Save. 9. In the Download complete dialog box, click the Open button to open the Bulk 'Send to CaseMap' Wizard and map the Concordance Evolution fields to the CaseMap fields, or click the Close button to close Download complete dialog box. Refer to the CaseMap documentation for how to use the Send to CaseMap wizards. 8. Create a review set containing the documents you want to send to CaseMap. For more information, see Creating review sets. 9. Send documents and/or facts to CaseMap. You can send individual documents and facts to CaseMap from the Document Data view, and you can send multiple documents from the Snippet, Thread, and Table views in the Review dashboard. For more information, see Sending documents to CaseMap. Using Equivio with Concordance Evolution Equivio® is an optional companion product for Concordance E-mail and Attachments databases. In Concordance, Equivio highlights the textual differences between two e-mail documents. Equivio helps you identify and skip redundant text during document reviews in Concordance, allowing you to focus on the unique text in each e-mail message. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 139 See, About deduplication. Importing About importing files Once you have created a Concordance Evolution organization, folder, matter, dataset and set up the dataset fields, you can populate the dataset by importing the following types of files from the corresponding Share location: Load files (delimited text files) Importing Law PreDiscovery Cases Files are imported into Concordance Evolution by creating import jobs. You can import files into a Concordance Evolution dataset from the dataset's dashboard. The priority for import jobs can be set as low, medium, or high. High priority jobs are processed first, based on the order in which they were setup. Low priority import jobs are processed after high and medium level priority processes. Concordance Evolution has the ability to remove blank pages when importing and converting Microsoft Word or Excel files. This option is set on the Server Management dashboard. For more information about enabling this option, please contact your Concordance Evolution System Administrator or Field Service Engineer. If the file has already been converted with blank pages and is produced, the blank pages will not be removed. Concordance Evolution does not support importing or exporting of live redactions to or from a traditional Concordance 10.x databases and Concordance Image 5.x imagebases. If you want to view redactions from a traditional Concordance 10.x databases and Concordance Image 5.x imagebases in Concordance Evolution, you will need to produce the applicable documents and burn the redactions and redlines onto the produced TIFF files in Concordance Image, and then import the produced TIFF files into Concordance Evolution. The redactions and redlines will not be editable in Concordance Evolution since they will be part of the TIFF files. About delimiter characters The following four columns represent the available delimiter characters. For each delimiter, the displayed symbol is on the left and the decimal equivalent is in parenthesis on the right. If the source program you are importing from uses a different font, it can change the symbolic representation of the delimiters. If this happens, match the delimiter characters with the decimal equivalents instead of relying on the displayed symbol. Using the decimal equivalents © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 140 Concordance Evolution will always result in a correct delimiter match. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 141 Importing delimited text files You can import documents and files into a dataset from the Dataset dashboard. Documents and files are imported into Concordance Evolution by creating import jobs. With the Load File Import, you can import load files (delimited text files) into Concordance Evolution. Load files or delimited text files typically have extensions ending in .dat, .csv, or .txt. Each file contains record metadata, but some may also include document text. Files can be received from a client, data processing vendor, or third party. As an administrator, when receiving data, you should always review all files on the disk, prior to loading the data. Opening and reviewing the delimited text files helps you ensure the file has the proper formats for Concordance Evolution. There are two ways to import delimited text files into Concordance Evolution. You can manually create an import job or you can create an import job using an import template. If you are going to be creating numerous import jobs for a dataset, you can create an import job and save the import settings to an import template, which can be used to quickly create new import jobs for the dataset. When rev iewing your data load files, always check for the following: Field names – each line of metadata is one record, check each header column to verify data Delimiters – unique characters that appear in the delimited text file and do not exist in your actual data Date format – date fields are an 8-character maximum with slashes. If dates include slashes, you can import any format. If slashes are not used, then you must use the universal date format of YYYYMMDD or the mm-dd-yyyy date format with dashes. Carriage return – a final carriage return ensures that the last record will load into the database. Concordance Delimiters Comma Field break indicator, default is ? (ASCII 20), customizable, avoid characters in data Quote Keeps text together, default is þ (ACSII 254) and is only required around fields that have text and spaces, customizable, avoid characters in data New Line Manual line break and text wraps within a field, default is ® (ASCII 174), customizable, avoid characters in data New Record Starts a new record, final carriage return loads the last record, cannot be changed, industry standard Delimiters are customizable for an organization's internal database design, but many organizations ask vendors to use Concordance default delimiters. If your case records contain the registered trademark symbol, you may want to consider changing the ® to another symbol in the load file. To review and edit delimited text files: © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 142 Concordance Evolution Before importing a delimited text file into a Concordance Evolution, review the delimited text file, and make any necessary corrections. 1. Open the delimited text file in any text editor program. Delimited text files can be opened with any text editor program, such as Microsoft® Notepad. We recommend using an advanced text editor program like TextPad ® or UltraEdit®. Below is an example of a delimited text file opened in UltraEdit: 2. Review the delimited text file for the following elements: File Type: The file must be a text-based format with an extension of .dat, .csv, .txt, .rtf, or any normal text file extension. Field Names: If there is not a header row containing field names, open the associated file for the first record and match the data in the record to the data in the file. Delimiters: Note the delimiters used in the file. Concordance Evolution can handle any standard text delimiters. Date Format: Note the date format used in the file. Concordance Evolution can load dates containing slashes in any order with either 2- or 4-digit years, with a maximum of 8 digits. The only date formats Concordance Evolution can load without slashes is the universal date format of YYYYMMDD and the mm-dd-yyyy date format with dashes. 3. Make the necessary edits, if applicable. 4. Save a copy of the file. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 143 To import delimited text files: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the dataset you want to import documents and files. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset dashboard toolbar, Import / Export button, and then click Import Load File. 4. Define the Job Details 1. In the Job Name field, type the import job name. 2. (Optional) In the Description field, type the import job description. 3. (Optional) To load a saved job settings, from the Template list, select the template to load and then click Next. 5. Define the Job Settings 1. For the Import File field, do one of the following: Enter the directory, including the load file name, for the delimited text files you want to import. Click the Browse button and locate the file you want to import. 2. The first time you import delimited text files into a dataset that does not contain any documents, only the Append option is available for selection in the Import Options section. If you are importing additional delimited text files into a dataset or importing a delimited text file into a dataset that already contains documents, see Importing subsequent data loads and overlays for more information. 3. When finished, click Next . 6. Define the File Formatting settings Documents are likely to contain text delimiters — commas, quotes, and carriage returns — that may confuse other programs, when reading the delimited text file. To avoid this problem, Concordance Evolution allows you to specify the characters recognized as the comma, quote, and newline delimiters in delimited text files. If you are exporting and importing documents within the Concordance Evolution system, then you will not need to change these default values. Change them only if you need to match the delimiters in the load file. 1. Verify the default delimiter settings for the load file: Delimiter Set list defaults to ConcordanceDefault delimiters. Column (comma) list defaults to ¶(20). The Column (comma) delimiter is a field delimiter that separates one field from the other. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 144 Concordance Evolution Quote list defaults to Þ(254). The Quote delimiter is a text qualifier delimiter that encloses text to differentiate it from field delimiters which may appear in the data. Newline defaults to ®(174). The Newline delimiter is a substitute carriage return. Some programs use this character to designate multi-level fields or fields-withinfields. Concordance Evolution replaces all carriage returns or carriage return linefeed combinations with the newline code within the data of a field. The record itself is still terminated with a real carriage return and a line feed. The delimiters available from the Column (comma), Quote, and Newline fields may appear as square symbols or may not be displayed. How the lists are displayed depends on the computer's language environment. The delimiters listed in the About delimiter characters topic use the Tahoma font, which displays the characters regardless of the language environment. All of the characters listed in the delimiter character list can be selected as the delimiter, even if the symbols they represent do not appear in the Column (comma), Quote, and Newline fields. To see the list of available delimiter characters, see About delimiter characters. Delimiters are customizable for an organization's internal database design, but many organizations ask vendors to use Concordance Evolution default delimiters. If your case records contain the registered trademark symbol, you may want to consider changing the ® to another symbol in the load file. 2. In the Date Format list, click the date format used in the delimited text file. The Date Format field defaults to the universal date format, yyyymmdd. 3. In the File Encoding Type list, select the Unicode™ type file encoding used for the delimited text file: ANSI (Default) UTF-8 UTF-16 4. If the delimited text file contains a header row, select the File contains header row check box. By default, the File contains header row check box is not selected. If the delimited text file does not contain a header row, make sure that the File contains header row check box is not selected. 5. Click the Load Data button. When you click the Load Data button a preview of the contents of the delimited text file is displayed below the Load Data button. 6. When finished, click Next. 7. Define the Image import settings © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 145 When you are importing delimited text files into Concordance Evolution, you can also import the images associated with the delimited text files. 1. To import image files, select the Import Images check box. 2. In the Image Type list, click the format of the images to import. All (Default) TIFF PDF JPG 3. To specify the .LOG or .OPT file for the images associated with the records you are importing, do one of the following: Click the Browse button, in the Select File dialog box, locate and select the .LOG or .OPT file for the images and then click OK. In the Path to .LOG or .OPT file field, type the directory, including the .LOG or .OPT file name for the images. 4. To add a substitution to part of the file path, first enter the directory for the .LOG or .OPT file, then click the File Path Substitution button. Clicking the File Path Substitution button opens the File Path Substitution dialog box. In the Replace this field, enter the portion of the file path directory you want to replace, and in the With this field, enter what you want to replace the portion of the file path directory with. Click the Display New Path button to generate and view the new path. Click the Save button to save the substitution. 5. When you are importing images, you can create a new image set for the images, or add the images to an existing image set in Concordance Evolution. To specify the imageset, do any of the following: To create a new image set, click the New Imageset option and type the name of the new image set. To add the images to an existing image set, click the Existing Imageset option, and in the image set list, click the image set name. 6. When finished, click Next. 8. Define the Text/OCR settings. 1. To import Text/OCR files, select the Import Text/OCR check box. 2. Do any of the following: Select the Load File field with body content (choose first field if more than one) option, and then select the field in the delimited text file that contains the content. Import extracts content from one or more fields in the delimited text file. When you select the Load File field with body content (choose first field if more than one) option, in the field list, select the field you want to extract content. If you are extracting from multiple delimited text file fields, click the first field you want to extract content. For example, if you have two content fields, OCR1 and OCR2, and you click the OCR1 field, and Concordance Evolution will automatically extract the content from © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 146 Concordance Evolution the OCR2 field after it has finished extracting the content from the OCR1 field. Select the Load File field with text file location option, select the field from the list. If you want to add a substitution to part of the file path, click the File Path Substitution button. Clicking the File Path Substitution button opens the File Path Substitution dialog box. In the Replace this field, enter the portion of the file path directory you want to replace, and in the With this field, enter what you want to replace the portion of the file path directory with. Click the Display New Path button to generate and view the new path. Click the Save button to save the substitution. Select the Text file location option, click the Browse button, locate and select the top-level folder that contains the text files you want to import, and then from the Matching field list select the field name that contains the document text. Select the Text file located at .LOG or .OPT file location option, click the Browse button, and then locate and select the .LOG or .OPT file containing the content you want to import. If you want to add a substitution to part of the file path, first enter the directory for the .LOG or .OPT file, then click the File Path Substitution button. Clicking the File Path Substitution button opens the File Path Substitution dialog box. In the Replace this field, enter the portion of the file path directory you want to replace, and in the With this field, enter what you want to replace the portion of the file path directory with. Click the Display New Path button to generate and view the new path. Click the Save button to save the substitution. 3. For Select field to import text, leave the default Content field selected. If the text is not imported into the Content field (default), the text is not displayed in the Snippet view. However, the field data is available for searching and can be included in binders. 4. When finished, click Next. 9. Define the native file import settings. When you are importing delimited text files into Concordance Evolution, you can also import the native files associated with the delimited text files. 1. To include native files, click the Import Native check box. 2. Select the field in the delimited text file that contains the name and path of the native files associated with each record. If you want to add a substitution to part of the native file path, first select the applicable field, then click the File Path Substitution button. Clicking the File Path Substitution button opens the File Path Substitution dialog box. In the Replace this field, enter the portion of the file path directory you want to replace, and in the With this field, enter what you want to replace the portion of the file path directory with. Click the Display New Path button to generate and view the new path. Click the © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 147 Save button to save the substitution. 3. When finished, click Next. 10. Define the Family & Threads settings. 1. To include document family group relationships in the import, select the Family Group and Parent to Child Mapping check box. 2. From the Document Id or Beginning Bates Field list, click the field in the delimited text file that contains the document ID or beginning Bates number. If the field you selected contains values that are a range, select the Field is a range check box. 3. From the Parent ID or Beginning Attachment Field list, click the field in the delimited text file that contains the parent document ID or beginning attachment number. If the field you selected contains values that are a range, select the Field is a range check box. 4. To add e-mail threading, select the Include the conversations check box, and select the field in the delimited text file that contains the conversation index. 5. When finished, click Next. 11. Define the Field Mapping settings The Field Mapping section allows you to specify which delimited text file source data is stored in which dataset field. The dataset's field names are listed in the Destination Field column, and the available source field names are listed in the Source Field column. By default the Automatically Map fields with same name check box is selected above the Field Mapping section. When the check box is selected, Concordance Evolution automatically maps any dataset field names that exactly match the available source field names. 1. To manually map the fields, clear the Automatically Map fields with same name check box. 2. In the Source Field lists, click the delimited text file source field that corresponds to each dataset field. 3. When finished, click Next. 12. Define the job options. 1. In the Import Description section, the _EVImportDescription field is automatically © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 148 Concordance Evolution populated with during the import. The default text is <Date(MM/DD/YYY)>_<Import type>_<Import job name>. This field can be edited if needed. 2. .In the Cross Reference Field list, select a field from the delimited text file to use to find documents that did not import properly. 3. If you want Concordance Evolution to automatically generate and send a notification to users when the import job is completed, select the Send Notification when this job completes check box 4. Click the Assign button, in the Choose User(s) & User Group(s) dialog box select the recipients, and then click Save. 5. In the Message field, type the notification message. 6. To set the Near Native Conversion Priority processing, select one of the following options: Low Medium High All jobs that are assigned a priority are processed the order of first in first processed. High priority jobs take precedence over Low and Medium priority jobs. 6. To save the job settings as a template for another time, select the Save Job as Template check box, and select one of the following: Select New Template to save the settings as a new template. Select Overwrite Existing Template to replace the settings of an existing template. 7. Type a template name in the text box, and then click the Save button. 8. When finished, click Next. For more information about notifications, see About notifications and alerts. 13. On the Summary tab, review the import settings you defined. If you need to change any of the settings, click the import setting tab on the left, and make the applicable edits. 14. In the Scheduling section of the Summary tab, select one of the following: To run the import job immediately, select the Run immediately option. To schedule the import to run at a later time, select the Run at a specified time option, and then type the date and time or click the Calendar button to select the © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 149 date, and time you want to run the import. 15. When ready, click Finish. The import job is then created and displayed in the import job list on the Import dashboard. Once the import job is complete, the Status column will display Completed for the import job. After importing the documents into the dataset, define the redactable document set for the dataset on the Edit Dataset dashboard. The redactable document set is the set of documents reviewers can redact and mark up in the Near Native view. A document set can be the images document set, native file document set, or produced documents document set. For more information, see Editing datasets. To create an import job using a template: Import job templates retain all the load file import job settings except for the import job name, description and schedule settings. When you create a load file import job using an import template you will need to enter the import job name and description, and schedule the import job. And if you want to change any of the import template settings for the import job, you will need to make those changes. Import templates can only be used for datasets created under the same matter, and can only be used for the same type of import from which the import template was originally created. 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the dataset for which you want to import documents. 3. On the dataset dashboard toolbar, click the Import / Export button, and then click Import Load File. 4. In the Job Name field, type the import job name. 5. In the Description field, type the import job description. 6. From the Template list, click the import template to use for the current import job. The only load file import settings not included in the load file import template are the import job name, description, and schedule settings. When you create an import job using a load file import template you will need enter the import job name and description, and schedule the import job. If you want to change any of the import template settings for the import job, you will need to make those changes. 7. On the Summary tab, review the import settings you defined. If you need to change any of the settings, click the import setting tab on the left, and make the applicable edits. 8. In the Scheduling section of the Summary tab, select one of the following: To run the import job immediately, select the Run immediately option. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 150 Concordance Evolution To schedule the import to run at a later time, select the Run at a specified time option, and then type the date and time or click the Calendar button to select the date, and time you want to run the import. 9. When ready, click Finish. The import job is then created and displayed in the import job list on the Import dashboard. Once the import job is complete, the Status column will display Completed for the import job. After importing the documents into the dataset, define the redactable document set for the dataset on the Edit Dataset dashboard. The redactable document set is the set of dataset documents reviewers can redact and mark up in the Near Native view in the Review dashboard. A document set can be the images document set, native file document set, or produced documents document set. For more information, see Editing datasets. To create a new import template: If you are going to be creating numerous import jobs that will be using the same or similar import settings, in Concordance Evolution you can create an import job and save its settings to an import template. Load file import templates retain all the load file import job settings except for the import job name, description and schedule settings. When you are creating an import job and select an import template, the import settings from the import template are automatically defined for the new import job. Import templates can only be used for datasets created under the same matter, and can only be used for the same type of import from which the import template was originally created. 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the dataset for which you want to create a Load File import template. 3. On the dataset dashboard toolbar, click the Import / Export button, and then click Import Load File. 4. In the Job Name field, type the import job name. 5. In the Description field, type the import job description. 6. Click Next. 7. Define all the import settings. 8. On the Job Options tab, click the Save Job as Template checkbox. 9. Click the New Template option and type the new import template name. Import template names must be unique. 10. Click the Save button to save the import template. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 151 Load file import templates retain all the import job settings except for the import job name, description and schedule settings. 11. When finished, click Next. 12. In the Summary section, review the import settings you defined. If you need to change any of the settings, click the individual import section links in the Summary section, and make the applicable edits. To save import settings to an existing import template: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the dataset for which you want to modify a Load File Import template. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset dashboard toolbar, click the Import / Export button, and then click Import Load File. 4. In the Import Job Name field, type the import job name. 5. In the Import Job Description field, type the import job description, and then click Next. 6. Define all the import settings. 7. On the Job Options tab, click the Save Job as Template button at the bottom of the page. 8. Click the Overwrite Existing Template option and then select the existing template to overwrite. 9. Click the Save button to save the import template. Load file import template retain all the import job settings except for the import job name, description and schedule settings. 10. When finished, click Next. 11. In the Summary section, review the import settings you defined. If you need to change any of the settings, click the individual import section links in the Summary section, and make the applicable edits. Importing LAW PreDiscovery cases With the LAW PreDiscovery Import command, you can import LAW PreDiscovery case documents without using a load file. The LAW PreDiscovery project.ini file is the link between Concordance Evolution and the LAW PreDiscovery Server. Once Concordance Evolution is connected to a LAW PreDiscovery SQL server and the project.ini file is loaded, the case files are available to import into a dataset for tracking and review. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 152 Concordance Evolution Before im porting a LAW PreDiscov ery case, keep the following in m ind: Concordance Evolution only supports importing for LAW PreDiscovery SQL cases. Only one LAW PreDiscovery case can be assigned to a dataset. Do not import the same LAW PreDiscovery case into multiple datasets at the same time. The LAW PreDiscovery project.ini file must be in one of the registered shares for the organization. The following fields are mapped automatically when importing LAW PreDiscovery cases: LAW PreDiscovery fields Concordance Evolution DocumentID _EVLawDocId AttachPID _EVRelationShipParentID ID _EVRelationShipDocumentID To load a LAW PreDiscovery case into Concordance Evolution: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane, locate and click the dataset you want to add a LAW PreDiscovery case. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Settings button, and then click LAW PreDiscovery Case. 4. On the LAW PreDiscovery Cases dashboard toolbar, click the Add LAW PreDiscovery Case button. 5. Click the Browse button, and then locate and select the project.ini file for the case you want to load. 6. When finished, click OK. 7. Click the Test Connection button to validate the path entered in the field. 8. When finished, click the Save button. The LAW PreDiscovery case files are now available for importing. To import a LAW PreDiscovery case: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the dataset to import LAW PreDiscovery case files. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset dashboard toolbar, click the Import / Export button, and then click Import LAW PreDiscovery Case. The Create Import Job dashboard opens. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 153 4. Define the Job Details 1. In the Job Name field, type the import job name. 2. (Optional) In the Description field, type the import job description. 3. (Optional) To load an existing job template, from the Template list, select the template you want to load, and then click Next. 5. Define the Job Settings Only the cases that are loaded into the selected organization are available. 1. In the Import Options section, select one of the following for importing Images and Natives. Append New - imports any new images and native files into the dataset. Replace Matching - imports and replaces only those files that contain the same unique identifier. Append and Replace Matching - adds new images and native files and replaces any files that contain the same unique identifier. 2. In the Document Selection section, to select documents for import, do one of the following: Select All Documents to import all the case documents. Select Specific Tags, and then select the tag(s) to filter the selected case documents for importing. 3. When finished, click Next. 6. Define the Content settings 1. To import a set of images, select the Import Images check box, and then select one of the following: To create a new imageset for the imported image files, click the New Imageset option, and then type the name of the new imageset. To add the images to an existing image set, click the Existing Imageset option, and then in the imageset list click the name of the imageset to import. 2. To set the text import precedence for extracted, printed, or OCR text, select the Import Text/OCR check box, and then in the Text Import Order field, select a text option and using the arrows, rearrange the text import order as needed. 3. For documents that contain redacted text, from the Select field to import text list, click the field you want to place redacted text. If the redacted text is not imported into the Content field (default), the text is not displayed in the Snippet view. However, the field data is available for searching and can be included in binders. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 154 Concordance Evolution 4. To import native files, select the Import Natives check box. 5. In the Family & Threads section, do any of the following: To import the family group information from the case files, select the Create Family Groups check box. To import the conversation index from the case files, select the Create Threads check box. 6. When finished, click Next. 7. Define the field mapping The Field Mapping section allows you to map the LAW PreDiscovery case field data to fields in Concordance Evolution where the data will be stored. Concordance Evolution automatically reads the LAW PreDiscovery case field names and field types and creates the same field name and type for the dataset. Dataset field names can be renamed after import as needed. Boolean tag fields from LAW PreDiscovery will not appear in the Field Mapping table. Do not change the field name for near-deduplication fields as this will cause an error when writing the data to the fields and the document will not appear in the Near Duplicate view. The following table defines the conversions for the LAW PreDiscovery field type to Concordance Evolution field type: LAW Concordance PreDiscover Evolution y Description Text Text Default text field Auto increment Text Default text field Date Date Date field matching the same date format as in LAW PreDiscovery List Text (Authority List) Default text field. The information will populate the Authority list in Concordance Evolution Memo Text Default text field Numeric Number Default numeric field 1. To select case fields for mapping, do any of the following: To select all the case fields on the current page, click the check box in the title row of the table. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 155 To select all the case fields available, use the paging at the bottom of the field list, and then select the check box in the title row of the table for each page. To select individual case fields, click the check box for the fields to map. By default only 10 fields are shown per page. To change the number of fields displayed, select the maximum number of fields to display from the Items per page list. 2. For each field selected, in the Dataset Field column, do any of the following: To map a case field to different dataset field, select the field name from the list. To rename any of the selected fields, select the dataset field name, and then type a new name for the field. 3. When finished, click Next. 8. Define the tag mapping Tag Mapping allows you to map LAW PreDiscovery case tags to tags in Concordance Evolution. Concordance Evolution automatically reads the LAW PreDiscovery case tag names and creates the same tag name and type for the dataset. Selected Tag names can be renamed as needed. When a LAW PreDiscovery case tag is selected for import, the tag is applied to the associated documents in Concordance Evolution. If the LAW PreDiscovery case tag is renamed, the new tag name is applied to the associated documents. 1. To map case tags, in the Tag Mapping table, do any of the following: To select all the LAW PreDiscovery tag fields on the current page, click the check box in the title row of the table. To select all the LAW PreDiscovery tag fields available, use the paging at the bottom of the Tag Mapping table, and then select the check box in the title row of the table for each page. To select individual LAW PreDiscovery tag fields, click the check box for the tags to map. By default only 10 Tag fields are shown per page. To change the number displayed, select the number from the Items per page list. 2. For each tag selected, in the Tag column, do any of the following: To map a case tag to a different tag, select the tag name from the list. To rename any of the selected tag names, in the Tag column, select the current tag name, and then type a new name for the tag. 3. When finished, click Next 9. Define the job options 1. For the Import Description section, in the _EVImportDescription field type the © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 156 Concordance Evolution information you want to store in the dataset field regarding the import. By default the field displays the date the import job was created, the job type, and the job name. 2. To send a notification to specific users when the production set job is completed, select the Send a notification when this job completes check box. 3. Click the Assign button, select the users to send the notification, and then click Save. The selected users are displayed in the Recipients field. 4. In the Message field, type the notification message. 5. To set the Near Native Conversion Priority processing, select one of the following options: Low Medium High All jobs that are assigned a priority are processed the order of first in first processed. High priority jobs take precedence over Low and Medium priority jobs. 6. To save the job settings as a template for another time, select the Save Job as Template check box, and select one of the following: Select New to save the settings as a new template. Select Overwrite Existing to replace the settings of an existing template. 6. Type a template name in the text box, and then click the Save button. 7. When finished, click Next. For more information about notifications, see About notifications and alerts. 10. On the Summary tab, review the import settings. If you need to change any of the settings, click the import setting tab on the left, and make the applicable edits. 11. In the Scheduling section, select one of the following options: To run the import job now, select Run immediately. To schedule the import to run at a later time, select Run at a specified time, and then type the date and time or click the Calendar button to select the date, and time you want to run the import. 12. When ready, click Finish. The import job is then created and displayed in the import job list on the Import dashboard. Once the import job is complete, the Status column for the import job will display Completed. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 157 Related Topics About LAW PreDiscovery cases Synchronizing data with LAW PreDiscovery Importing subsequent data loads and overlays Typically, all data for a specific case is not processed or received at the same time. Subsequent loads of data may arrive on an ongoing basis. You may receive delimited text files to replace existing data or need to load more data into existing records. When you import additional delimited text files into a dataset, you can append the documents to the dataset after the last record in the dataset or overlay the existing documents in the dataset. The overlay option compares the data between a single field in the load file and dataset to determine if documents match each other. When documents match each other, the import loads the data from the delimited text files into the matching existing dataset documents. When you use the overlay option for a log file import you can choose whether documents that do not match are appended to the dataset or not imported into the dataset. You can also choose whether tags are deleted from or retained on the existing documents that match documents being imported. To import subsequent data loads using the Append option: If you are going to append the documents you are importing, the import process is the same process as a standard load file import, just make sure that the Append option is selected in the Job Settings tab on the Create Import Job dashboard. For more information, see Importing delimited text files. To import subsequent data loads using the Overlay option: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the dataset you want to import documents. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset dashboard toolbar, click the Import / Export button, and then click Import Load File. The Create Import Job dashboard opens. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 158 Concordance Evolution 4. Define the Job Details 1. In the Job Name field, type the import job name. 2. (Optional) In the Description field, type the import job description. The Destination Dataset list defaults to the currently selected dataset. 3. (Optional) To load a saved template, from the Template list, select the template to load, then click Next. 5. Define the Job Settings 1. For the Import File field, do one of the following: Enter the directory, including the load file name, for the delimited text files you want to import. Click the Browse button and locate the file you want to import. 2. In the Import Options section, select one of the following: To append the records to the end of the dataset, select the Append option. To overlay the existing records, select the Overlay option. 3. If the Overlay option is selected, specify the following: For Images and Natives, select Replace matching records and append new records or Replace matching records only. For Tag Options, select Retain all tags on affected records or Remove all tags on affected records. 4. When finished, click Next . 6. Define the File Formatting settings Documents are likely to contain text delimiters — commas, quotes, and carriage returns — that may confuse other programs, when reading the delimited text file. To avoid this problem, Concordance Evolution allows you to specify the characters recognized as the comma, quote, and newline delimiters in delimited text files. If you are exporting and importing documents within the Concordance Evolution system, then you will not need to change these default values. Change them only if you are using these characters in the text of your documents. 1. Verify the default delimiter settings for the load file: Delimiter Set list defaults to ConcordanceDefault Column (comma) list defaults to ¶(20). The Column (comma) delimiter is a field delimiter that separates one field from the other. Quote list defaults to Þ(254). The Quote delimiter is a text qualifier delimiter that encloses text to differentiate it from field delimiters which may appear in the data. Newline defaults to ®(174). The Newline delimiter is a substitute carriage return. Some programs use this character to designate multi-level fields or fields-withinfields. Concordance Evolution replaces all carriage returns or carriage return linefeed combinations with the newline code within the data of a field. The record © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 159 itself is still terminated with a real carriage return and a line feed. The delimiters available from the Column (comma), Quote, and Newline fields may appear as square symbols or may not be displayed. How the lists are displayed depends on the computer's language environment. The delimiters listed in the About delimiter characters topic use the Tahoma font, which displays the characters regardless of the language environment. All of the characters listed in the delimiter character list can be selected as the delimiter, even if the symbols they represent do not appear in the Column (comma), Quote, and Newline fields. To see the list of available delimiter characters, see About delimiter characters. Delimiters are customizable for an organization's internal database design, but many organizations ask vendors to use Concordance Evolution default delimiters. If your case records contain the registered trademark symbol, you may want to consider changing the ® to another symbol. 2. In the Date format list, click the date format used in the delimited text file. The Date format field defaults to the universal date format, yyyymmdd. 3. In the File Encoding Type list, select one of the following Unicode™ type file encoding used for the delimited text file: ANSI (Default) UTF-8 UTF-16 4. If the delimited text file contains a header row, select the File contains header row check box. By default, the File contains header row check box is not selected. If the delimited text file does not contain a header row, make sure that the File contains header row check box is not selected. 5. Click the Load Data button. When you click the Load Data button a preview of the contents of the delimited text file is displayed below the Load Data button. 6. When finished, click Next. 7. Define the Image import settings When you are importing delimited text files into Concordance Evolution, you can also import the images associated with the delimited text files. 1. To import image files, select the Import Images check box. 2. In the Type of images to import list, click the type of images to import. All (Default) © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 160 Concordance Evolution TIFF PDF JPG 3. To specify the .LOG or .OPT file for the images associated with the records you are importing, do one of the following: Click the Browse button, in the Select File dialog box, locate and select the .LOG or .OPT file for the images and then click OK. In the Path to .LOG or .OPT file field, type the directory, including the .LOG or .OPT file name for the images. 4. If you want to add a substitution to part of the file path, first enter the directory for the .LOG or .OPT file, then click the File Path Substitution button. Clicking the File Path Substitution button opens the File Path Substitution dialog box. In the Replace this field, enter the portion of the file path directory you want to replace, and in the With this field, enter what you want to replace the portion of the file path directory with. Click the Display New Path button to generate and view the new path. Click the Save button to save the substitution. When you are importing images, you can create a new image set for the images, or add the images to an existing image set in Concordance Evolution. 5. To specify the image set, do any of the following: To create a new image set, click the New Imageset option and type the name of the new image set. To add the images to an existing image set, click the Existing Imageset option, and in the image set list, click the image set name. 6. When finished, click Next. 8.Define the Text/OCR settings. 1. To import Text/OCR files, select the Import Text/OCR check box. 2. Do any of the following: Select the Load File field with body content (choose first field if more than one) option, and then select the field in the delimited text file that contains the name and path of the text or OCR file containing the content. Import extracts content from one or more fields in the delimited text file. When you select the Load File field with body content (choose first field if more than one) option, in the field list, select the field you want to extract content. If you are extracting from multiple delimited text file fields, click the first field you want to extract content. For example, if you have two content fields, OCR1 and OCR2, and you click the OCR1 field, and Concordance Evolution will automatically extract the content from the OCR2 field after it has finished extracting the content from the OCR1 field. Select the Load File field with text file location option, select the field from the list. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 161 If you want to add a substitution to part of the file path, first enter the directory for the .LOG or .OPT file, then click the File Path Substitution button. Clicking the File Path Substitution button opens the File Path Substitution dialog box. In the Replace this field, enter the portion of the file path directory you want to replace, and in the With this field, enter what you want to replace the portion of the file path directory with. Click the Display New Path button to generate and view the new path. Click the Save button to save the substitution. Select the Text file location option, click the Browse button, locate and select the top-level folder that contains the text files you want to import, and then from the Matching field list, select the field name in the load file that contains the document text. Select the Text file located at .LOG or .OPT file location option, click the Browse button, and then locate and select the .LOG or .OPT file containing the content you want to import. If you want to add a substitution to part of the file path, first enter the directory for the .LOG or .OPT file, then click the File Path Substitution button. Clicking the File Path Substitution button opens the File Path Substitution dialog box. In the Replace this field, enter the portion of the file path directory you want to replace, and in the With this field, enter what you want to replace the portion of the file path directory with. Click the Display New Path button to generate and view the new path. Click the Save button to save the substitution. 3. To import the text into a specific Concordance Evolution field, from the Select field to import text list, click the field name. If the text is not imported into the Content field (default), the text is not displayed in the Snippet view. However, the field data is available for searching and can be included in binders. 4. When finished, click Next. 9.Define the native file import settings. When you are importing delimited text files into Concordance Evolution, you can also import the native files associated with the delimited text files. 1. To import native files, click the Import Native check box. 2. Select the field in the delimited text file that contains the name and path of the native files associated with each record. If you want to add a substitution to part of the native file path, first select the applicable field, then click the File Path Substitution button. Clicking the File Path Substitution button opens the File Path Substitution dialog box. In the Replace this field, enter the portion of the file path directory you want to replace, and in the With this field, enter what you want to replace the portion of the file path directory with. Click the Display New Path button to generate and view the new path. Click the Save button to save the substitution. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 162 Concordance Evolution 3. When finished, click Next. 10.Define the Family & Threads settings. 1. To include e-mail threading and document family group relationships in the import, select the Family group and parent to child mapping check box. 2. From the Document ID or Beginning Bates Field list, click the field in the delimited text file that contains the document ID or beginning Bates number. If the field you selected contains values that are a range, select the This Field is a range check box. 3. From the Parent ID or Beginning Attachment Field list, click the field in the delimited text file that contains the parent document ID or beginning attachment number. If the field you selected contains values that are a range, select the Field is a range check box. 4. To add e-mail threading, select the Include conversations check box, and then from the Load file field with conversation index list, select the field in the delimited text file that contains the conversation index data. 5. When finished, click Next. 11.Define the Field Mapping settings The Field Mapping section allows you to specify which delimited text file source data is stored to which dataset field. The dataset's field names are listed in the Destination Field column, and the available source field names are listed in the Source Field column. By default the Automatically map fields with same name check box is selected above the Field Mapping section. When the check box is selected, Concordance Evolution automatically maps any dataset field names that exactly match the available source field names. 1. To manually map the fields, clear the Automatically map fields with same name check box. 2. In the Source Field liss, click the delimited text file source field that corresponds to each dataset field. 3. In the Select unique field to match column, select one field as the key field for matching the documents from the load file to the dataset. 4. When finished, click Next. 12.Define the job options settings. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 163 1. From the Cross Reference Field list, select the field to use as a cross reference for any load file import errors. 2. If you want Concordance Evolution to automatically generate and send a notification to users when the import job is completed, select the Send Notification when this job completes check box 3. Click the Assign button, in the Choose User(s) & User Group(s) dialog box select the recipients, and then click Save. 4. In the Message field, type the notification message. 5. To set the Near Native Conversion Priority processing, select one of the following options: Low Medium High All production jobs that are assigned a priority are processing the order of first in first processed. High priority jobs take precedence over Low and Medium priority. 6. To save the job settings as a template for another time, select the Save Job as Template check box, and select one of the following: Select New to save the settings as a new template. Select Overwrite Existing Template to replace the settings of an existing template. 7. Type a template name in the text box, and then click the Save button. 8. When finished, click Next. For more information about notifications, see About notifications and alerts. 13. On the Summary tab, review the import settings you defined. If you need to change any of the settings, click the individual import section tabs on the left, and make the applicable edits. 14. In the Scheduling section of the Summary tab, select one of the following: To run the import job immediately, select the Run immediately option. To schedule the import to run at a later time, select the Run at a specified time option, and then type the date and time or click the Calendar button to select the date, and time you want to run the import. 15. When ready, click Finish. The import job is then created and displayed in the import job list on the Import dashboard. Once the import job is complete, the Status column will display Completed for the import job. After importing the documents into the dataset, define the redactable document set for the dataset on the Edit Dataset dashboard. The redactable document set is the set of © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 164 Concordance Evolution dataset documents reviewers can redact and mark up in the Near Native view in the Review dashboard. A document set can be the images document set, native file document set, or produced documents document set. For more information, see Editing datasets. Viewing dataset documents After importing documents into a dataset, you can quickly view the documents associated with a dataset in the Snippet view of the Review dashboard to verify that the documents and associated information imported correctly. To view dataset documents: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the dataset to view documents. 3. On the dataset dashboard toolbar, click the View Documents button. The Snippet tab of the Review dashboard opens to display the documents associated the current dataset. 4. When finished viewing the documents, click Cancel. Working with LAW PreDiscovery Cases About LAW PreDiscovery and Concordance Evolution LAW PreDiscovery converts electronic and paper documents for review and production. Concordance Evolution has the ability to populate an empty dataset with tags, fields and files directly from LAW PreDiscovery. Utilizing the LAW PreDiscovery case project.ini file as a link to the data in the LAW PreDiscovery SQL server, Concordance Evolution can import the files for review, including fields and tags. Once the review process is completed, if images have redactions, the Concordance Evolution administrator can execute a production run in Concordance Evolution to create images with headers, footers, and redactions. The files are now ready to be synchronized with the LAW PreDiscovery case. The synchronization writes the updated data back to LAW PreDiscovery and places the new images in the LAW PreDiscovery $Image Archive\EVImages\Job# folder. The documents, images, and tags are now accessible by LAW PreDiscovery to take advantage of its processing power to generate a set of endorsed, numbered TIFF files for electronic production or blow-back. The following diagram depicts the LAW PreDiscovery/Concordance Evolution workflow: © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 165 © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 166 Concordance Evolution Related Topics Importing LAW PreDiscovery cases Synchronizing data with LAW PreDiscovery Importing LAW PreDiscovery cases With the LAW PreDiscovery Import command, you can import LAW PreDiscovery case documents without using a load file. The LAW PreDiscovery project.ini file is the link between Concordance Evolution and the LAW PreDiscovery Server. Once Concordance Evolution is connected to a LAW PreDiscovery SQL server and the project.ini file is loaded, the case files are available to import into a dataset for tracking and review. Before im porting a LAW PreDiscov ery case, keep the following in m ind: Concordance Evolution only supports importing for LAW PreDiscovery SQL cases. Only one LAW PreDiscovery case can be assigned to a dataset. Do not import the same LAW PreDiscovery case into multiple datasets at the same time. The LAW PreDiscovery project.ini file must be in one of the registered shares for the organization. The following fields are mapped automatically when importing LAW PreDiscovery cases: LAW PreDiscovery fields Concordance Evolution DocumentID _EVLawDocId AttachPID _EVRelationShipParentID ID _EVRelationShipDocumentID To load a LAW PreDiscovery case into Concordance Evolution: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane, locate and click the dataset you want to add a LAW PreDiscovery case. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Settings button, and then click LAW PreDiscovery Case. 4. On the LAW PreDiscovery Cases dashboard toolbar, click the Add LAW PreDiscovery Case button. 5. Click the Browse button, and then locate and select the project.ini file for the case you want to load. 6. When finished, click OK. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 167 7. Click the Test Connection button to validate the path entered in the field. 8. When finished, click the Save button. The LAW PreDiscovery case files are now available for importing. To import a LAW PreDiscovery case: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the dataset to import LAW PreDiscovery case files. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset dashboard toolbar, click the Import / Export button, and then click Import LAW PreDiscovery Case. The Create Import Job dashboard opens. 4. Define the Job Details 1. In the Job Name field, type the import job name. 2. (Optional) In the Description field, type the import job description. 3. (Optional) To load an existing job template, from the Template list, select the template you want to load, and then click Next. 5. Define the Job Settings Only the cases that are loaded into the selected organization are available. 1. In the Import Options section, select one of the following for importing Images and Natives. Append New - imports any new images and native files into the dataset. Replace Matching - imports and replaces only those files that contain the same unique identifier. Append and Replace Matching - adds new images and native files and replaces any files that contain the same unique identifier. 2. In the Document Selection section, to select documents for import, do one of the following: Select All Documents to import all the case documents. Select Specific Tags, and then select the tag(s) to filter the selected case documents for importing. 3. When finished, click Next. 6. Define the Content settings © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 168 Concordance Evolution 1. To import a set of images, select the Import Images check box, and then select one of the following: To create a new imageset for the imported image files, click the New Imageset option, and then type the name of the new imageset. To add the images to an existing image set, click the Existing Imageset option, and then in the imageset list click the name of the imageset to import. 2. To set the text import precedence for extracted, printed, or OCR text, select the Import Text/OCR check box, and then in the Text Import Order field, select a text option and using the arrows, rearrange the text import order as needed. 3. For documents that contain redacted text, from the Select field to import text list, click the field you want to place redacted text. If the redacted text is not imported into the Content field (default), the text is not displayed in the Snippet view. However, the field data is available for searching and can be included in binders. 4. To import native files, select the Import Natives check box. 5. In the Family & Threads section, do any of the following: To import the family group information from the case files, select the Create Family Groups check box. To import the conversation index from the case files, select the Create Threads check box. 6. When finished, click Next. 7. Define the field mapping The Field Mapping section allows you to map the LAW PreDiscovery case field data to fields in Concordance Evolution where the data will be stored. Concordance Evolution automatically reads the LAW PreDiscovery case field names and field types and creates the same field name and type for the dataset. Dataset field names can be renamed after import as needed. Boolean tag fields from LAW PreDiscovery will not appear in the Field Mapping table. Do not change the field name for near-deduplication fields as this will cause an error when writing the data to the fields and the document will not appear in the Near Duplicate view. The following table defines the conversions for the LAW PreDiscovery field type to Concordance Evolution field type: © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution LAW Concordance PreDiscover Evolution y Description Text Text Default text field Auto increment Text Default text field Date Date Date field matching the same date format as in LAW PreDiscovery List Text (Authority List) Default text field. The information will populate the Authority list in Concordance Evolution Memo Text Default text field Numeric Number Default numeric field 169 1. To select case fields for mapping, do any of the following: To select all the case fields on the current page, click the check box in the title row of the table. To select all the case fields available, use the paging at the bottom of the field list, and then select the check box in the title row of the table for each page. To select individual case fields, click the check box for the fields to map. By default only 10 fields are shown per page. To change the number of fields displayed, select the maximum number of fields to display from the Items per page list. 2. For each field selected, in the Dataset Field column, do any of the following: To map a case field to different dataset field, select the field name from the list. To rename any of the selected fields, select the dataset field name, and then type a new name for the field. 3. When finished, click Next. 8. Define the tag mapping Tag Mapping allows you to map LAW PreDiscovery case tags to tags in Concordance Evolution. Concordance Evolution automatically reads the LAW PreDiscovery case tag names and creates the same tag name and type for the dataset. Selected Tag names can be renamed as needed. When a LAW PreDiscovery case tag is selected for import, the tag is applied to the associated documents in Concordance Evolution. If the LAW PreDiscovery case tag is renamed, the new tag name is applied to the associated documents. 1. To map case tags, in the Tag Mapping table, do any of the following: To select all the LAW PreDiscovery tag fields on the current page, click the check box in the title row of the table. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 170 Concordance Evolution To select all the LAW PreDiscovery tag fields available, use the paging at the bottom of the Tag Mapping table, and then select the check box in the title row of the table for each page. To select individual LAW PreDiscovery tag fields, click the check box for the tags to map. By default only 10 Tag fields are shown per page. To change the number displayed, select the number from the Items per page list. 2. For each tag selected, in the Tag column, do any of the following: To map a case tag to a different tag, select the tag name from the list. To rename any of the selected tag names, in the Tag column, select the current tag name, and then type a new name for the tag. 3. When finished, click Next 9. Define the job options 1. For the Import Description section, in the _EVImportDescription field type the information you want to store in the dataset field regarding the import. By default the field displays the date the import job was created, the job type, and the job name. 2. To send a notification to specific users when the production set job is completed, select the Send a notification when this job completes check box. 3. Click the Assign button, select the users to send the notification, and then click Save. The selected users are displayed in the Recipients field. 4. In the Message field, type the notification message. 5. To set the Near Native Conversion Priority processing, select one of the following options: Low Medium High All jobs that are assigned a priority are processed the order of first in first processed. High priority jobs take precedence over Low and Medium priority jobs. 6. To save the job settings as a template for another time, select the Save Job as Template check box, and select one of the following: Select New to save the settings as a new template. Select Overwrite Existing to replace the settings of an existing template. 6. Type a template name in the text box, and then click the Save button. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 171 7. When finished, click Next. For more information about notifications, see About notifications and alerts. 10. On the Summary tab, review the import settings. If you need to change any of the settings, click the import setting tab on the left, and make the applicable edits. 11. In the Scheduling section, select one of the following options: To run the import job now, select Run immediately. To schedule the import to run at a later time, select Run at a specified time, and then type the date and time or click the Calendar button to select the date, and time you want to run the import. 12. When ready, click Finish. The import job is then created and displayed in the import job list on the Import dashboard. Once the import job is complete, the Status column for the import job will display Completed. Related Topics About LAW PreDiscovery cases Synchronizing data with LAW PreDiscovery Synchronizing data with LAW PreDiscovery After reviewing LAW PreDiscovery case records in Concordance Evolution, you can write the information back to the LAW PreDiscovery server for further processing. As a best practice, make sure that the case file is not open in LAW PreDiscovery before executing the synchronization job. To write data back to a LAW PreDiscovery case: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the dataset you want to export. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 172 Concordance Evolution 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Import / Export button, and then click LAW PreDiscovery Sync. 4. Define the Job Details 1. In the Job Name field, type the synchronization job name.. 2. (Optional) In the Description field, type the export job description. 3. (Optional) To load a saved job template, from the Template list, select the template to load, then click Next. 5. Define the Job settings: 1. In the Sync Tag Name field, type a tag name to tag all records for the job in the LAW PreDiscovery case. All synchronized documents are tagged automatically with the Sync Tag Name. 2. In the Select Documents for Sync, do one of the following: To send all the documents in the dataset, click the All documents option. To send only the documents from the results from a saved query, click the Saved Query option, and then select a saved query from the list to execute the query and pull the documents. To send only the documents that are tagged with a specific tag, click the Tag option, and then select a tag from the list. To send only the documents from the results of a query, click the Query option, and then type the query in the field. 3. When finished, click Next. 4. When prompted, click OK to confirm the number of documents. 6. Define the Markup settings: 1. To update the images associated with the selected documents, click the Images check box, and then do one the following. To send only the images from the results of a save query, click the Saved Query option, and then select a saved query from the list. To send only the image that are tagged with a specific tag, click the Tag option, and then select a tag from the list. To send only the images from the results of a query, click the Query option, and then type a query in the field. Images produced will be from the Redactable Set that is assigned to the dataset and the images must meet both query criteria specified in the job. If the image does not meet both query criteria, the image is excluded from the synchronization job process. 2. In the Color section, select one of the following: To convert the documents to shades of gray, select Black and White. To produce the image in color (4-bit -16 colors), select Color. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 173 Concordance Evolution creates single page images to place into LAW PreDiscovery. 3. To burn markups onto the images, select the Include Burn Markups check box, and then select the check box for each markup to burn onto the images. 4. When finished, click Next. The synchronization job will create a new folder, EVImage, within the case $Image Archive folder. All synchronization jobs will have it's own folder. Each job folder will consist of volume folders each containing a maximum 50 documents with no page limits. For example, $Image Archive\EVImage\Job<JobID>\0001 etc. 7. Define the Field mappings: The Field Mapping section allows you to map the field data in Concordance Evolution to the case fields in LAW PreDiscovery for updating and processing. The default Concordance Evolution fields are mapped to the default corresponding LAW PreDiscovery field. The data in the selected Concordance Evolution field will overwrite the data in the corresponding LAW PreDiscovery field. For new fields, the conversion from Concordance Evolution to LAW PreDiscovery is as follows: Concordance Evolution Field Type LAW PreDiscovery Field Type Text Memo Date Date Numeric Numeric The following fields cannot be synchronized: Begdoc#, Enddoc#, Attachmt, Batesrng, BegAttach, EndAttach, EDFolder, EdFolderID, EdSession, EdSessionID, EdSource, EDSourceID, ID, PgCount, ParentID, TimeZoneProc, TimeZoneID, and CustodianID. 1. To select fields for mapping, do any of the following: To select all the fields, select the check box at the top of the of the Field Mapping table. To select individual fields, select the check box next to the field to map. 2. To change the field mappings for the selected fields, in the LAW PreDiscovery Fields column, do any of the following: To map to an existing field, click the arrow next to the LAW PreDiscovery field, and then select the field name. To map to a new field, click the field to highlight the current field name, type a new field name, and the press Enter. 3. When finished, click Next. 4. When prompted, click OK to confirm the number of documents to be imaged. 8. Define the Tags mapping: © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 174 Concordance Evolution Tag Mapping allows you to select which Concordance Evolution tags are written back to LAW PreDiscovery. LAW PreDiscovery automatically reads the Concordance Evolution tag names and updates the mapped tag for the corresponding document in the database. Selected Tag names can be renamed as needed. If the LAW PreDiscovery tag is renamed, the new tag name is applied to the associated documents. 1. To write tag information back to LAW PreDiscovery, do any of the following: To select all the tags, select the check box at the top of the Tag Mapping table. To select one or more tags, in the Concordance Evolution Tag column, select the check box next to the tag name. 2. In the LAW PreDiscovery Tag column, do any of the following: To map to an existing tag, click the arrow next to the LAW PreDiscovery tag, and then select a tag name. To map to a new tag, click the field to highlight the current tag name, type a new tag name, and the press Enter. When sending Concordance Evolution tags to LAW PreDiscovery the tags are converted to Tag (Boolean) type fields. All Concordance Evolution folders, structure, and rules will be lost. 3. When finished, click Next. 9. Define the Job Options 1. To generate and send a notification to users when the export job is completed, in the Notifications box, select the Send Notification check box. 2. For the Recipients, click the Assign button, and select the check box for the user groups and/or individual users to which you want to send the notification, and then click OK. 3. In the Message field, type the notification message. 4. To set the Near Native Conversion Priority processing, select one of the following options: Low Medium High All jobs that are assigned a priority are processed the order of first in first processed. High priority jobs take precedence over Low and Medium priority jobs. 5. To save the job settings as a template for use at a later time, select the Save Job as Template check box, and then do one of the following: Click New, in the template field type the name of the template, and then click Save. Click Overwrite Existing, from the list select a saved template, and then click Save. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 175 6. When finished, click Next. 10. On the Summary tab, review the synchronization settings you defined. If you need to change any of the settings, click the individual import section tabs on the left, and make the applicable edits. 11. In the Scheduling section of the Summary tab, select one of the following: To run the synchronization job immediately, select the Run immediately option. To schedule the synchronization to run at a later time, select the Run at a specified time option, and then type the date and time or click the Calendar button to select the date, and time you want to run the import. 12. When ready, click Finish. After the job is complete, make sure to view the job log or job reprocessing log to locate documents that did not synchronize with LAW PreDiscovery. Related Topics About LAW PreDiscovery cases Importing LAW PreDiscovery cases Viewing jobs Reprocessing jobs Binders About binders Once the data is imported into a dataset you can use Binders to organize the data for reviews. In Concordance Evolution, binders are used as containers to organize and track review set documents for different review stages. For example, Review_First_Pass and Review_Second_Pass. Each binder within a dataset may contain multiple review sets The following table shows how a single dataset can be structured to distribute documents among multiple binders and review sets. A single document may be assigned within multiple binders; however, the document can only be assigned to one review set within a single binder. For example, document DCN0000126 appears in three binders, but only one review set per binder. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 176 Concordance Evolution When organizing binders and rev iew sets, keep the following in m ind: A single dataset may contain one or more binders A single binder may contain one or more review sets A single document can only be assigned to one review set within a binder; however, the document can be included in multiple binders within a dataset. Binders provide the ability to restrict review sets to near-native, image, and/or production sets Secure check in/check out option can be setup for review sets within a binder Binders are traceable with specific reviewed/not reviewed tags Each binder can be setup to appear only on the Review dashboard for the user group(s) assigned to the binder. Related Topics Creating Binders Managing Binders Creating binders After creating a dataset and importing the documents, you can create one or more binders to organize review sets and documents. Each binder may contain multiple review sets and a single document may only be assigned to one review set within a binder. To create a binder: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the dataset to which you want to add a review set. 3. On the dataset dashboard toolbar, click the Create Binder button. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 177 4. In the Binder Name field, type a name for the binder. 5. (Optional) In the Description field, type a description for the binder. 6. To give users permission to check the documents in and out securely, make sure that the Secure Check Out Enabled check box is selected. If your Concordance Evolution system administrator set up the Binder with Secure Check Out Enabled option, when a review set is checked out it locks the review set so that others cannot check them out or view the documents. If the Secure Check Out Enabled option is not selected, when a review set is checked out the Reviewed and Not Reviewed tags for the review set are not available for other users. 7. To select the documents to include in the binder, in the Enable Document & Image Sets section, do any of the following: To select all the documents and image sets assigned to the dataset, select the All Sets option. To include a selected set of documents and image sets, select the Specific Sets option, and then select the check box for each set to include from the dataset. 8. When finished, click Save. Managing binders The Binder Management dashboard provides the tools for managing permissions, review sets, and assigning user groups and user access for reviewing in the Review dashboard. For more information about review sets, see Creating review sets. Once a binder is created, the binder is available from the Review dashboard for the assigned reviewers. Binder access is managed by user groups. If multiple binders exist for a dataset, you may need to limit which user group(s) can view a binder and its review sets. For example, three binders are assigned to Dataset0001; however, user group A only needs to view one of the binders. Using policies, you can deny user group A access to the other two binders. When the reviewers associated with user group A open Concordance Evolution, only one binder is displayed on the Review dashboard. Assigning users to a binder: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, locate and open the dataset with the binder and review sets you want to assign users. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Manage Permissions button. 4. On the Datasets Permissions dashboard toolbar, click the Add Group button. 5. In the Select User Group(s) dialog box, select the User Group to grant access to the binder and review set, and then click Save. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 178 Concordance Evolution 6. In the Actions column, click the Permissions link. 7. In the Permissions for User Group section, click the Assign Roles button. 8. Click the check box next to the role name for each user group to assign to the dataset, and then click OK. 9. When finished, click the Save button to save the role(s) 10. On the Dataset Permissions dashboard toolbar, click the Back button. The user group is added to the Authorized Users table. Editing a binder: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the dataset that contains the binder you want to edit. 3. On the dataset dashboard, in the Review Binders table, click the Edit link for the binder you want to edit. 4. Make any necessary changes, and then click Save. Deleting a binder: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the dataset that contains the binder you want to delete. 3. On the dataset dashboard, in the Review Binders table, click the Delete link for the binder you want to edit. 4. When prompted to confirm the deletion, in the Delete Binder dialog box, type the name of the binder, and then click Yes. Review Sets About review sets Review sets in Concordance Evolution are used to organize review documents in a dataset. Review sets are associated with a binder and a single binder may contain multiple review sets. A single review set may contain all documents in the dataset or selected documents. Dataset documents are not visible to a reviewer in the Review dashboard until documents are added to a review set and the user is assigned to the review set. A Concordance Evolution System Admin can grant read-only access to any user that is not assigned to a review set to view those documents. Unlike other jobs in Concordance Evolution, you do not schedule review set jobs. Once you create the review set job, the job runs immediately. Once the job is completed, you will receive a notification and the review set information is displayed on the Binder Management © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 179 dashboard. For more information about creating a review sets, see Creating review sets. Review sets can be split into additional review sets and the review set(s) are added to the binder the original review set was created in. Additional documents can be added to a review set. For more information, see Managing review sets. Related Topics Creating review sets Assigning reviewers Managing review sets About Binders Creating review sets Once a binder is created, review sets can be created from the document or image sets assigned to the binder on the Binder Management dashboard. Unlike other jobs in Concordance Evolution, you do not schedule review set jobs to run immediately or at a later time. Once you create the review set, the job runs immediately. To create a review set: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the binder name for the dataset you want to add a review set. The Binder Management dashboard is displayed. 3. On the Binder Management toolbar, click the Create Review Sets button. 4. In the Reviewset Name field, type a name for the review set. The review set name must be unique for the dataset. 5. (Optional) In the Description field, type a description for the review set. 6. In the Start Date field, enter the start date for reviewing the documents in the review set. You can type the start date or click the calendar button and then click the start date. The Start Date field defaults to today's date. 7. In the End Date field, enter the end date for completing the review of the documents in © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 180 Concordance Evolution the review set. You can type the end date or click the calendar button to click the end date. The End Date field defaults to tomorrow's date. 8. In the Select documents section, select one of the following: All Dataset Documents (default) 1. Click the All Dataset Documents option. 2. Click the Retrieve Documents button. When you click the Retrieve Documents button, a message appears at the top of the dashboard indicating the number of documents available in the dataset that are not currently part of the review set. 3. To manually select a subset of all the retrieved documents to include in the review set, click the Document Explorer button. When you click the Document Explorer button, all documents retrieved are displayed in the Snippet view. By default, all the documents retrieved are selected in the Snippet or Table view. To select only a subset of the documents, remove the check mark for the documents you do not want to include in the review set. 4. When finished, click the Done button. When you click the Done button, you are returned to the Add Documents to Reviewset dashboard. Only the selected documents are now ready to be added to the review set. Filter by Tag The Filter by Tag option locates all the documents in the dataset that have been assigned a specific tag(s) you select. 1. Click the Filter by Tag option. When you click the Tag option, the tag list for the dataset is displayed. 2. Click the tag(s) you want to use to locate documents. To select multiple tags, use SHIFT+click or CTRL+click. 3. Click the Retrieve Documents button. When you click the Retrieve Documents button, a message appears at the top of the dashboard indicating the number of documents available in the dataset that are not currently part of the review set. 3. To manually select a subset of all the retrieved documents to include in the review set, click the Document Explorer button. When you click the Document Explorer button, all documents retrieved are displayed in the Snippet view. By default, all the documents retrieved are selected © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 181 in the Snippet or Table view. To select only a subset of the documents, remove the check mark for the documents you do not want to include in the review set. 4. When finished, click the Done button. When you click the Done button, you are returned to the Add Documents to Reviewset dashboard. Only the selected documents are now ready to be added to the review set. Filter by Saved Query The Query option locates all the documents in the dataset that match the search query you enter. 1. Click the Filter by Saved Query option. 2. Select the saved search query you want to use to locate documents. 3. Click the Retrieve Documents button. When you click the Retrieve Documents button, the a message appears at the top of the dashboard indicating the number of documents available in the dataset that are not currently part of the review set. 4. To manually select a subset of all the retrieved documents to include in the review set, click the Document Explorer button. When you click the Document Explorer button, all documents retrieved are displayed in the Snippet view. By default, all the documents retrieved are selected in the Snippet or Table view. To select only a subset of the documents, remove the check mark for the documents you do not want to include in the review set. 5. When finished, click the Done button. When you click the Done button, you are returned to the Add Documents to Reviewset dashboard. Only the selected documents are now ready to be added to the review set. Query The Query option locates all the documents in the dataset that match the search query you enter. 1. Click the Query option. 2. In the Query field type the search query to locate documents. 3. Click the Retrieve Documents button. When you click the Retrieve Documents button, the a message appears at the top of the dashboard indicating the number of documents available in the dataset that are not currently part of the review set. 4. To manually select a subset of all the retrieved documents to include in the review set, click the Document Explorer button. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 182 Concordance Evolution When you click the Document Explorer button, all documents retrieved are displayed in the Snippet view. By default, all the documents retrieved are selected in the Snippet or Table view. To select only a subset of the documents, remove the check mark for the documents you do not want to include in the review set. 5. When finished, click the Done button. When you click the Done button, you are returned to the Add Documents to Reviewset dashboard. Only the selected documents are now ready to be added to the review set. In Concordance Evolution you can divide the documents within a review set into multiple review sets. When you create multiple review sets using this option, when the review sets are created, each of the review sets will have the same name with a number appended to each review set name to make the names unique, and the review set description, start date, and due date will be the same for each of the review sets. 9. To divide the documents into multiple review sets, select any of the following options: To create one reviewset, click Single Reviewset. To divide the documents into multiple reviewset, click Reviewsets and type the number of review sets you want. To divide the reviewset by a specific number of documents, click the Doc(s) per Reviewset, and then type the number of documents you want in each reviewset. By default, the following rules are selected for the review set: Keep families and threads together if there are documents in the review set that belong to a document family group or the same e-mail thread, those documents are kept together in the review set. Keep duplicates together if there are duplicate documents and/or e-mail messages in the review set, the duplicate documents or e-mail messages are kept together in the review set. 10. If you do not want a review set rule to apply to the review set(s), clear the check box for the rule. Once the review set rules are defined and saved for the review set, they cannot be modified. 11. When finished, click the Save button to create the review set job. Clicking the Confirm button opens the Binder Management dashboard. Once the review set job has finished running, the review set(s) will be displayed in the review sets table on the Binder Management dashboard, and you can assign users to the review set on the Edit Review Set dashboard. Assigning reviewers After creating a review set, reviewers are generally assigned to a review set at the binder level © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 183 as part of a user group. You can assign a single user at the review set level when the Secure Checkout option is enabled for the binder. However, if the reviewer is part of a user group that has been denied access to the binder, the user will not have access to the review set. For more information about assigning users to review sets, see Managing Binders. To assign users to a review set: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the binder name for the dataset to which you want to assign users to a review set. The Binder Management dashboard is displayed. 3. In the Review Sets table, in the Action column, click the Edit link for the review set you want to assign users. 4. On the Edit Review Set dashboard, next to the Assigned Users field, click the Assign button. 5. In the Choose User(s) dialog box, select the user to assign to the review set, and then click Save. 6. When finished, click the Save button. Managing review sets Once a review set is created, you can edit the review set's name, description, user assignment, and due date. You can also add additional documents to the review set or remove individual documents, or split a review set into more than one set. After a review set is created, you cannot edit the review set's start date or review set rules. To edit a review set: Review sets can be edited on the Edit Reviewset dashboard. You can edit the review set's name, description, user assignments, and due date. You cannot edit the review set's start date or review set rules. 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the binder name under the dataset that contains the review set to edit. The Binder Management dashboard is displayed. 3. In the Review Sets table, from the Action column, click the Edit link for the review set to edit. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 184 Concordance Evolution 4. Make any necessary changes. 5. To edit the users list, do any of the following: To add additional users, click the Assign button, in the Choose User(s) dialog box, select the check box next to user(s) and/or group(s) you want to assign to the review set, and then click Save. To remove a user, in the Assigned Users field, select the name you want to remove, and then click the Unassign button. 6. When finished, click the Save button. When you click the Save button, your changes are saved and the Binder Management dashboard opens. To add additional documents to a review set: Once a review set is created, you can add additional documents from the dataset to the review set on the Add Documents to Reviewset dashboard. 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the binder name for the dataset to add documents to a review set. The Binder Management dashboard opens. 3. In the Review Sets table, in the Action column, to open the Add Documents to Reviewset dashboard, do one of the following: Click the Edit link, and then click the Add Docs button. Click the Add link. The Add Documents to Reviewset dashboard opens. 4. To add additional documents from the current dataset to the review set, in the Select documents section, select one of the following: All Dataset Documents (default) 1. Click the All Dataset Documents option. 2. Click the Retrieve Documents button. When you click the Retrieve Documents button, a message appears at the top of the dashboard indicating the number of documents available in the dataset that are not currently part of the review set. 3. To manually select a subset of all the retrieved documents to add to the review set, click the Document Explorer button. When you click the Document Explorer button, all documents retrieved are displayed in the Snippet view. By default, all the documents retrieved are selected © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 185 in the Snippet or Table view. To select only a subset of the documents, remove the check mark for the documents you do not want to include in the review set. 4. When finished, click the Done button. When you click the Done button, you are returned to the Add Documents to Reviewset dashboard. Only the selected documents are now ready to be added to the review set. Filter by Tag The Filter by Tag option locates all the documents in the dataset that have been assigned a specific tag(s) you select. 1. Click the Filter by Tag option. When you click the Tag option, the tag list for the dataset is displayed. 2. Click the tag(s) you want to use to locate documents. To select multiple tags, use SHIFT+click or CTRL+click. 3. Click the Retrieve Documents button. When you click the Retrieve Documents button, a message appears at the top of the dashboard indicating the number of documents available in the dataset that are not currently part of the review set. 3. To manually select a subset of all the retrieved documents to add to the review set, click the Document Explorer button. When you click the Document Explorer button, all documents retrieved are displayed in the Snippet view. By default, all the documents retrieved are selected in the Snippet or Table view. To select only a subset of the documents, remove the check mark for the documents you do not want to include in the review set. 4. When finished, click the Done button. When you click the Done button, you are returned to the Add Documents to Reviewset dashboard. Only the selected documents are now ready to be added to the review set. Filter by Saved Query The Query option locates all the documents in the dataset that match the search query you enter. 1. Click the Filter by Saved Query option. 2. Select the saved search query you want to use to locate documents. 3. Click the Retrieve Documents button. When you click the Retrieve Documents button, a message appears at the top of the dashboard indicating the number of documents available in the dataset that © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 186 Concordance Evolution are not currently part of the review set. 3. To manually select a subset of all the retrieved documents to add to the review set, click the Document Explorer button. When you click the Document Explorer button, all documents retrieved are displayed in the Snippet view. By default, all the documents retrieved are selected in the Snippet or Table view. To select only a subset of the documents, remove the check mark for the documents you do not want to include in the review set. 4. When finished, click the Done button. When you click the Done button, you are returned to the Add Documents to Reviewset dashboard. Only the selected documents are now ready to be added to the review set. Query The Query option locates all the documents in the dataset that match the search query you enter. 1. Click the Query option. 2. In the Query field type the search query to locate documents. 3. Click the Retrieve Documents button. When you click the Retrieve Documents button, the a message appears at the top of the dashboard indicating the number of documents available in the dataset that are not currently part of the review set. 4. To manually select a subset of all the retrieved documents to add to the review set, click the Document Explorer button. When you click the Document Explorer button, all documents retrieved are displayed in the Snippet view. By default, all the documents retrieved are selected in the Snippet or Table view. To select only a subset of the documents, remove the check mark for the documents you do not want to include in the review set. 5. When finished, click the Done button. When you click the Done button, you are returned to the Add Documents to Reviewset dashboard. Only the selected documents are now ready to be added to the review set. The selected documents are displayed at the top of the page. The Assigned Users field on the Add Documents to Reviewset dashboard determines which users will receive a notification about the change to the review set. When you add users, the users will receive a notification about the changes to the review set. It does not mean the users are assigned to the review set. 8. To notify additional users about the additional documents being added to the review set, click the Assign button. 9. Select or clear the check box next to the user(s) and/or group(s) to which you want to © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 187 send the notification, and then click Save. The user list is updated with the changes. 11. On the Add Documents to Reviewset dashboard toolbar, click the Save button. When you click the Save button, the documents you selected are added to the review set and the Binder Management dashboard opens. To view the updated review set, you will need to refresh the Binder Management dashboard by navigating away from and back to the dashboard. To split a review set into multiple review sets: Once a review set has been created, you can split the review set into additional review sets on the Split Reviewset dashboard. When you split a review set into new review sets, the original review set is archived, and any documents in the review set that you did not select to add to the new review sets are released from the review set. The original review set's name, description, start date, due date, review set rules settings, and user assignments are automatically applied to the new review sets. Any tags, comments, edits, redactions, and markups made to the documents in the original review set are retained in the documents when the review set is split. 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, locate and click the binder containing the review set you want to split. Clicking the binder opens the Binder Management dashboard. 3. In the Actions column of Review Sets table, click the Split link for the review set to split. Clicking the Split link opens the Split Review Set dashboard. 4. To select the documents in the review set to divide into a new review set(s), do one of the following: All documents(default) The All documents option selects all the documents in the review set. To select all review set documents: 1. Click the All documents option. 2. Click the Retrieve Documents button. When you click the Retrieve Documents button, the a message appears at the top of the dashboard indicating the number of documents available in the dataset that are not currently part of the review set. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 188 Concordance Evolution 3. To manually select a subset of all the retrieved documents to add to the review set, click the Document Explorer button. When you click the Document Explorer button, all documents retrieved are displayed in the Snippet view. By default, all the documents retrieved are selected in the Snippet or Table view. To select only a subset of the documents, remove the check mark for the documents you do not want to include in the review set. 4. When finished, click the Done button. When you click the Done button, you are returned to the Add Documents to Reviewset dashboard. Only the selected documents are now ready to be added to the review set. The Document Explorer button is used to view all documents in the dataset in the Review dashboard, including documents already included in a review set. When you click the Document Explorer button, you will navigate away from the Split Review Set dashboard without saving the review set you are creating. For more information, see Viewing all documents in a dataset. Filter by Tag The Tag option locates documents in the review set that have been assigned the tag(s) you select. To locate review set documents from a tag: 1. Click the Filter by Tag option. When you click the Filter by Tag option, the dataset tag list is displayed. 2. Click the tag(s) you want to use to locate documents. To select multiple tags, use CTRL+SHIFT or CTRL+click. 3. Click the Retrieve Documents button. When you click the Retrieve Documents button, the a message appears at the top of the dashboard indicating the number of documents available in the dataset that are not currently part of the review set. 4. To manually select a subset of all the retrieved documents to add to the review set, click the Document Explorer button. When you click the Document Explorer button, all documents retrieved are displayed in the Snippet view. By default, all the documents retrieved are selected in the Snippet or Table view. To select only a subset of the documents, remove the check mark for the documents you do not want to include in the review set. 5. When finished, click the Done button. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 189 When you click the Done button, you are returned to the Add Documents to Reviewset dashboard. Only the selected documents are now ready to be added to the review set. The Document Explorer button is used to view all documents in the dataset in the Review dashboard, including documents already mapped to a review set. When you click the Document Explorer button, you will navigate away from the Split Review Set dashboard without saving the review set you are creating. For more information, see Viewing all documents in a dataset. Filter by Saved Query The Filter by Save Query option locates only those documents in the review set that match the selected saved query. To locate review set documents from a saved search query: 1. Click the Filter by Saved Query option. 2. Click the saved search query to use to locate the documents. 3. Click the Retrieve Documents button. When you click the Retrieve Documents button, a message appears at the top of the dashboard indicating the number of documents available in the dataset that are not currently part of the review set. 4. To manually select a subset of all the retrieved documents to add to the review set, click the Document Explorer button. When you click the Document Explorer button, all documents retrieved are displayed in the Snippet view. By default, all the documents retrieved are selected in the Snippet or Table view. To select only a subset of the documents, remove the check mark for the documents you do not want to include in the review set. 5. When finished, click the Done button. When you click the Done button, you are returned to the Add Documents to Reviewset dashboard. Only the selected documents are now ready to be added to the review set. The Document Explorer button is used to view all documents in the dataset in the Review dashboard, including documents already mapped to a review set. When you click the Document Explorer button, you will navigate away from the Split Review Set dashboard without saving the review set you are creating. For more information, see Viewing all documents in a dataset. Query © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 190 Concordance Evolution The Query option locates only those documents in the review set that match the search query you enter. To locate review set documents from a search query: 1. Click the Query option. 2. Type the search query in the Query field or click the Saved Searches link and then click the saved search query you want to use to locate documents. 3. Click the Retrieve Documents button. When you click the Retrieve Documents button, a message appears at the top of the dashboard indicating the number of documents available in the dataset that are not currently part of the review set. 4. To manually select a subset of all the retrieved documents to add to the review set, click the Document Explorer button. When you click the Document Explorer button, all documents retrieved are displayed in the Snippet view. By default, all the documents retrieved are selected in the Snippet or Table view. To select only a subset of the documents, remove the check mark for the documents you do not want to include in the review set. 5. When finished, click the Done button. When you click the Done button, you are returned to the Add Documents to Reviewset dashboard. Only the selected documents are now ready to be added to the review set. The Document Explorer button is used to view all documents in the dataset in the Review dashboard, including documents already mapped to a review set. When you click the Document Explorer button, you will navigate away from the Split Review Set dashboard without saving the review set you are creating. For more information, see Viewing all documents in a dataset. When you split a review set, when the new review sets are created, each of the review sets will have the same name as the original review set with a number added to the end of each review set name to make the names unique, and the new review sets will have the same review set description, start date, due date, review set rules settings, and user assignments as the original review set. 5. In the Split the documents into section, indicate how you want to divide the documents into the review sets. To divide the documents by number of review sets, click the Reviewsets option, and type the number of review sets to create. To divide the documents by number of documents per review set, click the Doc(s) per Reviewset option and type the number of documents to put into each new review set. The documents you selected in the review set are evenly distributed between each of © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 191 the new review sets. The Assigned Users field determines which users receive a notification about the change to the review set. The Assigned Users field defaults to the users currently assigned to the original review set. When you split a review set, the users assigned to the original review set are automatically assigned to the new review sets. When you add additional users to the Assigned Users field the new users will also receive a notification about the changes to the review set. It does not mean the users are assigned to the new review sets. 6. To notify additional users about the changes to the review set, click the Assign button. 7. Select the check box next to the user(s) and/or group(s) to send the notification. If you want to remove a users or user groups from the list, clear the check box next to the user(s) and/or group(s) you want to remove from the review set. 8. When finished, click Save. Clicking Save updates the user list in the Assigned Users field. 9. When finished, on the Split Reviewset dashboard toolbar, click the Save button. When you click the Save button, the review set is split into the new review sets and the Binder Management dashboard opens. The original review set is archived, and any documents in the original review set that were not added to the new review sets are released from the original review set. To view the newly created review set(s), you will need to refresh the Binder Management dashboard by navigating away from and back to the Binder Management dashboard. Exporting review sets After creating a review set, you can export the following information for a review set(s) to a comma-separated formatted (.csv) file: Review set name Review set due date User who has the review set checked out Number of Documents Number of documents tagged as Reviewed Number of document tagged as Not Reviewed To export a review set report: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 192 Concordance Evolution 2. In the System pane on the left, locate and click the Binder that contains the review set information you want to export. 3. In the Review Sets table, do any of the following: To export a single review set, select the check box for the review set to export. To export multiple review sets, select the check box for each review set export. To export all the review sets, select the check box in the upper left corner. 4. On the Binder Management dashboard toolbar, click the Export Review Sets button. 5. In the File Download dialog box, do one of the following: Click Open to view the file, in the Download Complete dialog box, click Open to open the file in your default spreadsheet application. Click Save to save the file, in the Save As dialog box, navigate to where you want to save the file, and then in the File Name field, type the file name and click Save. 6. In the Download Complete dialog box, click Open to view the file or click Close to close the dialog box. Deleting review sets Before deleting a review set, make sure that no one is reviewing the documents. To delete a review set: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, locate and click the Binder that contains the reviewset you want to remove. 3. In the Review Sets table, do any of the following: To delete a single review set, in the Actions column, click the Delete link for the review set. To delete multiple review sets, select the check box for each review set, and then on the Binder Management dashboard toolbar, click the Delete Review Sets button. To delete all the review sets, select the check box in the upper left corner, and then on the Binder Management dashboard toolbar, click the Delete Review Sets button. 4. When prompted to confirm the deletion, click Yes. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 193 Tags About tags Tagging records is a critical step in the discovery process. It is your organization’s way of essentially putting color-coded flags on your documents to categorize them by privilege, review status, or other criteria during document review. Typically a Concordance Evolution administrator or Litigation Support Manager works with a lead attorney to build a set of tags for case review that include standard naming conventions and adhere to internal guidelines for a case review. These tags are often organized into folder structures that indicate phases of review, case topics, or are designated by reviewer. Once tagging conventions are determined, as the administrator you will most likely be setting up these tags and folders after you build the dataset so the review team can be begin searching and tagging immediately. If you are working with a team of administrators, we recommend that only one or two people be in charge of tag management, especially when making new ones and deleting unnecessary tags. This prevents duplication of efforts and helps to keep tag structures uncluttered for all reviewers working in the dataset. Tag Hierarchy In Concordance Evolution, for each dataset you can create: Tag folders Tag folders are used to organize tag groups and tags. Tag folders can only be created under other tag folders. Tag folders cannot be created under tag groups or tags. Tag groups Tag groups are similar to tag folders, in that they are used to organize tags groups and tags, but unlike tag folders, a tag group is also a tag that can be applied to documents or document text. It is essentially a parent tag that you can create child tags under. Tag groups can only be created under tag folders or other tag groups. Tag groups cannot be created under tags. Document-level and text-level tags A tag can only be a document-level tag or a text-level tag. One tag cannot be used as both a document and text-level tag. Tags can only be created under tag folders and tag groups. Tags cannot be created under other tags. Tag Group Families Tag group families are system created tags that can be added to each dataset. Currently, there is one tag group family that is installed with Concordance Evolution: Review Status When you add the Review Status tag group family to a dataset, the Not Reviewed and Reviewed tags are automatically added to the dataset. These tags are used to indicate whether a document has been reviewed. Concordance Evolution uses these two tags to track the review progress for documents in the dataset and its review sets. You can edit a tag group family tag's name, shortcut key, and behavior properties, but you © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 194 Concordance Evolution cannot modify the tag's type or scope, or move the tag under a tag folder or tag group on the Edit Tag dashboard. Tag Security In Concordance Evolution you can add tag-level security to individual tags in a dataset in the Tag Security dialog box. Tag security determines whether users in a user group can create, view, delete, edit, and/or change the state of a tag. For more information about tag security, see Managing tag security. Public versus Personal Tags Public tag folders, tag groups, and tags are available to all users that have access to the dataset and are available for selection from the Tags pane in the Review dashboard, unless tag security limits a user's access to the them. Public tag folders, groups, and tags can be created by the administrator on the Add Tag dashboard, and by users in the Tags pane in the Review dashboard. Personal tag folders, tag groups, and tags are only available to the user that created them and Concordance Evolution administrators. Other users cannot view the personal tag folders, tag groups, and tags in the Tags pane in the Review dashboard. Personal tag folders, tag groups, and tags are created by users in the Tags pane in the Review dashboard. The administrator can view all personal tag folders, tag groups, and tags, and can convert them from personal to public on the Edit Tag dashboard. To distinguish between personal and public tags in the Review dashboard, a is displayed next to personal tag folders, tag groups, and tags in the Tags pane in the Review dashboard. Tag Names It is best practice not to use special characters and keywords used by the Vivisimo® Velocity® search engine in dataset field or tag names in Concordance Evolution. If you use them in the names, Velocity will use them as Velocity keywords and your document search results will return more data than expected. Special Characters and Keywords Used by Velocity / ' FOLLOWEDBY phrase \ .au greater-than quotes [ .ti greater-than-or-equal range ] [au] host regex © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution ; [ti] image site : all intitle stem | AND inurl THRU = and language title * and+ less-than url ? ANDNOT less-than-or-equal weight < andnot link wildcard > any linktext wildchar @ author NEAR WITHIN “ BEFORE not WORDS , category NOT %field%: & CONTAINING NOTCONTAINING () CONTENT NOTWITHIN (,) default-and-1 OR + domain or - equal OR0 ~ filetype OR1 195 Creating tags There are two ways to add tag folders, tag groups, and tags to a dataset. You can manually add them individually to a dataset or add them from a saved template. If you are going to be creating numerous datasets that will be using the same tags and tag structure, in Concordance Evolution you can create a set of tag folders, tag groups and tags and save the them to a template. Once a template is created, it can be used to quickly add the tag structure to new datasets. When creating a tag structure, you specify the properties and security settings for each tag folder, tag group, or tag properties. For more information, see Managing tag security and Editing tags. For more information about tags, see About tags. To create a tag folder: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 196 Concordance Evolution 2. In the System pane on the left, click the dataset you want to add a tag group. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Config button, and then click Tags. 4. On the Tags dashboard toolbar, click the Add Tag button. 5. In the Name field, type the tag folder name. It is best practice not to use special characters and keywords used by the Vivisimo® Velocity® search engine in dataset field or tag names in Concordance Evolution. If you use them in the names, Velocity will use them as Velocity keywords and your document search results will return more data than expected. For a list of the special characters and keywords used by Velocity, see the Tag Names section in the "About tags" topic. 6. In the Tag Type list, click Tag Folder. 7. From the Scope list, do one of the following: Select Document to set the tag group as a document-level tag group. Select Text to set the tag group as a text-level tag group. 8. In the Behaviors section, select any of the following options: Dynamic — additional tag folders, tag groups, and/or tags can be created under the tag folder. Fixed — no additional tag folders, tag groups, and/or tags can be created under the tag folder. 9. When finished, click Save to add the tag group and return to the Tags dashboard. The tag folder is displayed in the tag list. If you created the tag folder under another tag folder, on the Tags dashboard, an arrow, , is displayed next to the parent tag folder name. To view the tag folder you created, click the parent tag folder name link to expand the tag subfolder list. To create a tag group:: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the dataset you want to add a tag group. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Config button, and then click Tags. 4. On the Tags dashboard toolbar, click the Add Tag button. 5. In the Name field, type the tag group name. 6. From the Type list, click Tag Group. 7. From the Scope list, do one of the following: © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 197 Select Document to set the tag group as a document-level tag group. Select Text to set the tag group as a text-level tag group. 8. In the Behaviors section, select any of the following options: Unique — only one tag group of this tag type can exist for the dataset. Exclusive — only one tag in the tag group may be used. Locked — no user can edit the tag or tag group unless they has the Tag Override policy set to Allow. Child Updates Parent — if any child tag of the tag group is selected then the parent tag group is selected. Clear Parent to Clear group — if the parent tag group is cleared, then all of its children are cleared. Dynamic — additional tag folders, tag groups, and/or tags can be created under the tag folder. Fixed — no additional tag folders, tag groups, and/or tags can be created under the tag folder. Cannot be deleted — the tag or tag group cannot be deleted unless the user has the Tag Override policy set to Allow. 9. In the Security section, for each admin org group, select or clear the check boxes for the security settings for users in the user group: To hide a tag group or tag, clear the Can View Tag check box. When you clear the Can View Tag check box, all the other check boxes are automatically cleared. To make a tag group or tag read-only for users in the user group in the Tags pane in the Review dashboard, make sure that the Can View Tag check box is selected, and clear the Can Change Tag State and Can Delete Tag check boxes. To only allow users in the user group to apply or remove the tag group or tag, make sure that the Can View Tag and Can Change Tag State check boxes are selected, and clear the Can Delete Tag check box. 10. When finished, click Save to add the tag group and return to the Tags Summary dashboard. The Not Reviewed and Reviewed tags are automatically added to the dataset and are displayed in the tag list. In the Tags panel in the Review dashboard, a circle, instead of a check box, is displayed next to tags in a tag group family. A check box is displayed next to all other tag groups, folders and tags in the Tags panel in the Review dashboard. To create a tag: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the dataset you want to add a tag group. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Config button, and then click Tags. 4. On the Tags dashboard toolbar, click the Add Tag button. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 198 Concordance Evolution 5. In the Tag Name field, type the tag name. It is best practice not to use special characters and keywords used by the Vivisimo® Velocity® search engine in dataset field or tag names in Concordance Evolution. If you use them in the names, Velocity will use them as Velocity keywords and your document search results will return more data than expected. For a list of the special characters and keywords used by Velocity, see the Tag Names section in the "About tags" topic. 5. In the Tag Type list, click Tag. 6. From the Scope list, do one of the following: Select Document to set the tag group as a document-level tag group. Select Text to set the tag group as a text-level tag group. 7. To create a shortcut key for the tag, in the Shortcut Keys list, click the shortcut key you want to use for the tag. When you create a shortcut key for a tag, users can add and remove the tag on documents or text using the shortcut key. The shortcut key you select in the Shortcut Keys list will be displayed next to the tag name in the Tags pane in the Review dashboard. You can only assign one shortcut key to one tag. Once a shortcut key is assigned to a tag, the shortcut key is no longer available for selection in the Shortcut Keys list. If you remove a shortcut key from a tag by clicking (none) in the Shortcut Keys list on the Edit Tag dashboard, once you remove the shortcut key from the tag, the shortcut becomes available again in the Shortcut Keys list on the Create a Tag and Edit tag dashboards. 8. In the Behaviors section, select any of the following options: Locked — no user can edit the tag or tag group unless they has the Tag Override policy set to Allow. Cannot be deleted — the tag or tag group cannot be deleted unless the user has the Tag Override policy set to Allow. Tag applies to all duplicates Tag always applies to entire family group Tag always applies to entire thread 9. In the Security section, for each admin org group, select or clear the check boxes for the security settings for users in the user group: To hide a tag group or tag, clear the Can View Tag check box. When you clear the Can View Tag check box, all the other check boxes are automatically cleared. To make a tag group or tag read-only for users in the user group in the Tags pane in the Review dashboard, make sure that the Can View Tag check box is selected, and clear the Can Change Tag State and Can Delete Tag check boxes. To only allow users in the user group to apply or remove the tag group or tag, make sure that the Can View Tag and Can Change Tag State check boxes are selected, and clear the Can Delete Tag check box. 10. When finished, click the Save button to add the tag and return to the Tags dashboard. The tag is displayed in the tag list. If you created the tag under a tag folder or tag group, on the Tags dashboard, an arrow, , is displayed next to the parent tag folder © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 199 or tag group name. To view the tag you created, click the parent tag folder or tag group name link to expand the tag list. To save a Tags template You can save tag groups, tag folders, and/or tags to an existing tag template or create a new tag template. When you save tag groups, tag folders, and/or tags to a tag template, the tag groups, tag folders, and/or tags and their settings are saved to the template. 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the dataset you want to add a tag group. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Config button, and then click Tags. 4. On the Tags dashboard toolbar, click the Templates button to display the Tags Templates menu. 5. In the Save current tags as template field, do one of the following: To create a new template, type the template name in the field, and then click Save. To overwrite an existing template, click the arrow in the field, select the template you want to overwrite, and then click Save. 6. When prompted to confirm the template action, click OK. To create tags for a dataset from a template 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the dataset you want to add a tag group. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Config button, and then click Tags. 4. On the Tags dashboard toolbar, click the Templates button to display the Tags Templates menu. 4. In the tag template list, click the template you want to import into the dataset. 5. Click the Load link to add the tag groups, tag folders and/or tags from the template to the dataset. 6. When prompted to confirm loading the tags from the selected template, click OK. The tag folders, tag groups, and/or tags from the template are displayed in the tag list. To modify the tag folder, tag group, or tag properties or security settings, see Editing tags and Managing tag security. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 200 Concordance Evolution Managing tag security In Concordance Evolution you can add tag-level security to individual tags in a dataset when you create a tag group, folder or tag. Tag security determines whether users in a user group can create, view, delete, edit, and/or change the state of a tag. By default, each tag allows users to create, view, delete, edit, and/or change the state of a tag. The tag security settings determine whether users in a user group can create, view, delete, edit, and/or change the state of a tag in the Tags pane in the Review dashboard. Tag Security is set when you create the tag group, tag folder, or tag on the Edit Tag dashboard. You can add tag security to all public tags groups and tags in a dataset, including tags from tag families. However, tag security cannot be added to public tag folders or any personal tag groups, tag folder, or tags. Tag-level security is assigned by user group. To assign tag-level security to a user group, the user group must have security policies allowing the user group access to the dataset assigned to the user group on the Dataset Permissions dashboard for the dataset. For more information about assigning user groups and security policies to datasets, see Assigning roles to user groups and Customizing user group security policies. To manage security for a tag group or tag: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the dataset you want to edit the security settings for the tag group or tag. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Config button, and then click Tags. 4. In the Actions column of the Tags table, click the edit link for the tag group or tag you want to edit. 5. In the Security section, clear the check boxes for the tag group or tag security settings you want to disallow for users in the user group. To hide a tag group or tag, clear the Can View Tag check box. When you clear the Can © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 201 View Tag check box, all the other check boxes are automatically cleared. To make a tag group or tag read-only for users in the user group in the Tags pane in the Review dashboard, make sure that the Can View Tag check box is selected, and clear the Can Change Tag State and Can Delete Tag check boxes. To only allow users in the user group to apply or remove the tag group or tag, make sure that the Can View Tag and Can Change Tag State check boxes are selected, and clear the Can Delete Tag check box. 6. When finished, click the Save button to save the tag group or tag security settings and return to Tags dashboard. Editing tags You can only edit public tag folders, tags groups, and tags. You cannot edit or assign security to private tag folders, tag groups, or tags. Once a public tag folder is created, you can edit the folder's name and parent, and define the folder properties on the Edit Tag Folder dashboard. Once a public tag group or tag is created, can edit the tag or tag group's name and parent, edit the tag shortcut, define the tag group or tag properties, and assign tag security on the Edit Tag Group or Edit Tag dashboard. If you want to change the security policy settings for a public tag group or tag, see Managing tag security. Also, if a user has created a personal tag folder, tag group, or tag that you want to make available to all dataset users, you can convert the personal tag folder, tag group, or tag to a public folder, tag group, or tag on the Edit Folder, Edit Tag Group, and Edit Tag dashboards. To edit a tag: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the dataset you want to add a tag group. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Config button, and then click Tags. 4. In the Actions column of the Tags table, click the edit link for the tag folder you want to edit. 5. In the Edit Tag dashboard, make the applicable edits. 6. To modify the tag properties, in the Behaviors section, select or clear the check boxes for the properties you want to apply to the tag. Locked — no user can edit the tag or tag group unless they has the Tag Override policy set to Allow. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 202 Concordance Evolution Cannot be deleted — the tag or tag group cannot be deleted unless the user has the Tag Override policy set to Allow. Tag applies to all duplicates Tag always applies to entire family group Tag always applies to entire thread 7. To modify the security settings for the tag group, in the Security section, for each admin org group, select or clear the check boxes for the security settings you want to allow or disallow for users in the user group: To hide a tag, clear the Can View Tag check box. When you clear the Can View Tag check box, all the other check boxes are automatically cleared. To make a tag read-only for users in the user group in the Tags pane in the Review dashboard, make sure that the Can View Tag check box is selected, and clear the Can Change Tag State and Can Delete Tag check boxes. To only allow users in the user group to apply or remove the tag, make sure that the Can View Tag and Can Change Tag State check boxes are selected, and clear the Can Delete Tag check box. 8. When finished, click the Save button to add the tag and return to the Tags dashboard. To edit a tag folder: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the dataset you want to add a tag group. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Config button, and then click Tags. 4. In the Actions column of the Tags table, click the edit link for the tag folder you want to edit. 5. In the Edit Tag dashboard, make the applicable edits. 6. To modify the tag folder properties, in the Behaviors section, select or clear the check boxes for the properties you want to apply to the tag folder: Dynamic — additional tag folders, tag groups, and/or tags can be created under the tag folder. Fixed — no additional tag folders, tag groups, and/or tags can be created under the tag folder. 7. To modify the security settings for the tag folder, in the Security section, for each admin org group, select or clear the check boxes for the security settings you want to allow or disallow for users in the user group: To hide a tag folder or tag, clear the Can View Tag check box. When you clear the Can View Tag check box, all the other check boxes are automatically cleared. To make a tag folder or tag read-only for users in the user group in the Tags pane in the Review dashboard, make sure that the Can View Tag check box is selected, and clear the Can Change Tag State and Can Delete Tag check boxes. To only allow users in the user group to apply or remove the tag folder or tag, make © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 203 sure that the Can View Tag and Can Change Tag State check boxes are selected, and clear the Can Delete Tag check box. 8. When finished, click the Save button to save your changes and return to the Tags dashboard. To edit a tag group: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the dataset you want to add a tag group. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Config button, and then click Tags. 4. In the Actions column of the Tags table, click the edit link for the tag group you want to edit. 5. In the Edit Tag dashboard, make the applicable edits. 6. To modify the tag group properties, in the Behaviors section, select or clear the check boxes for the properties you want to apply to the tag group: Unique — only one tag group of this tag type can exist for the dataset. Exclusive — only one tag in the tag group may be used. Locked — no user can edit the tag or tag group unless they has the Tag Override policy set to Allow. Child Updates Parent — if any child tag of the tag group is selected then the parent tag group is selected. Clear Parent to Clear group — if the parent tag group is cleared, then all of its children are cleared. Dynamic — additional tag folders, tag groups, and/or tags can be created under the tag folder. Fixed — no additional tag folders, tag groups, and/or tags can be created under the tag folder. 7. To modify the security settings for the tag group, in the Security section, for each admin org group, select or clear the check boxes for the security settings you want to allow or disallow for users in the user group: To hide a tag group, clear the Can View Tag check box. When you clear the Can View Tag check box, all the other check boxes are automatically cleared. To make a tag group read-only for users in the user group in the Tags pane in the Review dashboard, make sure that the Can View Tag check box is selected, and clear the Can Change Tag State and Can Delete Tag check boxes. To only allow users in the user group to apply or remove the tag group, make sure that the Can View Tag and Can Change Tag State check boxes are selected, and clear the Can Delete Tag check box. 8. When finished, click the Save button to save your changes and return to the Tags dashboard. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 204 Concordance Evolution To make a personal tag group, tag folder, or tag public: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the dataset you want to view tags. 3. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 4. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Config button, and then click Tags. 5. In the Actions column of the Tags table, click the edit link for the private tag group, tag folder, or tag you want to convert to public. 6. On the Edit Tag dashboard toolbar, click the Convert To Public Tag button. 7. Make the applicable edits. 8. To modify the tag group, folder, or tag properties, in the Behaviors section, select or clear the check boxes for the properties you want to apply. 9. To modify the security settings for the tag group, folder, or tag, in the Security section, for each admin org group, select or clear the check boxes for the security settings you want to allow or disallow for users in the user group: To hide a tag group, folder, or tag, clear the Can View Tag check box. When you clear the Can View Tag check box, all the other check boxes are automatically cleared. To make a tag group, folder, or tag read-only for users in the user group in the Tags pane in the Review dashboard, make sure that the Can View Tag check box is selected, and clear the Can Change Tag State and Can Delete Tag check boxes. To only allow users in the user group to apply or remove the tag group, folder, or tag, make sure that the Can View Tag and Can Change Tag State check boxes are selected, and clear the Can Delete Tag check box. 10. When finished, click the Save button to save your changes and return to the Tags dashboard. Reordering tags When reordering tags in the Tags table, keep the following in mind: You cannot move a tag assigned to a tag group or tag folder into another tag group or tag folder. You cannot move tag folders within a tag group into another tag group When moving a tag group or tag folder, the entire contents tag group, tag folder are moved to the new structure location © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 205 To reorder tags in the Tags table 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the dataset you want to add a tag group. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Config button, and then click Tags. 4. On the Tags dashboard toolbar, click the Reorder Tags button. 5. In the Reorder Tags dialog box, drag the tag, tag folder, or tag group to the desired position in the structure. The Tags dashboard will automatically refresh and display the new tag structure in the Tags table. Deleting tags If you have the proper permissions are enabled, you can delete both public and private tag folders, tag groups and tags. Otherwise, you can only delete public tag folders, tags groups, and tags. You cannot delete private tag folders, tag groups, or tags. If you want to delete personal tag folders, tag groups, or tags, you will first need to convert them from personal to public, and then delete them. For more information about converting personal tag folders, tags groups, and tags from personal to public, see Editing tags. When you delete tag groups or tags that are currently assigned to documents, the tag group or tags and their documents assignments will be deleted. If you delete a tag folder containing other tag folders, tag groups, and/or tags, the contents of the tag folder will automatically be deleted when you delete the tag folder. The same is true for tag groups. If you delete a tag group, if the tag group contains other tags groups and/or tags, they will automatically be deleted when you delete the tag group. Please be aware that deleting the Review Status tag group family from a dataset also removes the review status for the documents in the dataset. To delete a tag folder, tag group or tag: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the dataset containing the tag group, tag folder, or tag you want to delete. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Config button, and then click Tags. 4. In the Tags table, locate the tag folder, tag group, or tag you want to delete. 5. In the Actions column, click the delete link. 6. When prompted to confirm the delete, click OK to delete the tag folder and any tag © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 206 Concordance Evolution folders, tag groups, and/or tags in the tag folder, and their document assignments. Monitoring tags statistics The Tag Statistics panel to the right of the dataset dashboard allows you to monitor tags applied to the documents within the dataset. This is useful when monitoring an individual's review progress. The Tag Statistics panel shows the number of tags applied by tag name or by user for a single dataset. The Overview tab displays each tag, and the number of times the tag has been applied to a document. The User tab displays a list of users and the number of times they have tagged a document. To review tag statistics: 1. In the System pane, locate and open the dataset dashboard for the tag statistics you want to view. 2. In the Tags Statistics panel, do any of the following: Click the Overview tab to display the name of the tag, and how many times the tag was applied to a document. Click the Users tab to display each reviewer, the total number of tags they applied, and the name of the tag and how many times it was applied by the reviewer Productions About productions Once a document collection review is completed, documents typically need to be produced to opposing parties, this is known as a production. Concordance Evolution administrators prepare the electronic production using the production tools, based on queries or tagged sets of documents that are identified for production during the review phase. Managing Rolling Productions Due to the ever-increasing size of electronic productions, litigation support staff are often faced with the task of handling and tracking large volumes of data that are incoming and outgoing during the life cycle of an e-discovery project. As a best practice, we recommend establishing an organized tracking method to ensure that all data is properly handled and © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 207 nothing is missed. Examples of Data Handled during E-discovery: Here are some examples of data that can be handled during a large e-discovery: Data coming from clients that need to be processed. This could include paper documents, electronic files, e-mail files, images, metadata load files, and graphic files. Data produced from opposing parties to be loaded into a review tool, such as Concordance, for review by attorneys, paralegals, experts or investigators. Data going out to vendors for processing, scanning, coding, or printing. Data to be processed in-house using an e-discovery processing software, such as LAW PreDiscovery. Data such as exhibits, graphics, and presentations being prepared for trial to be loaded into trial presentation software. Data being copied or produced to other parties for review such as co-counsel and experts. Data being produced to opposing parties. Data that is to be archived from the network to disk or hard drive storage. Data that requires special handling, such as compliance with destruction or preservation orders. When handling forensically collected data, be sure to follow appropriate legal procedures for preservation, handling, and chain of custody to avoid spoliation issues. Tracking Data There are many ways that data can be tracked using database software tools specifically designed to help facilitate data tracking for e-discovery, such as Concordance Evolution, Concordance, Microsoft® Access ®, or Microsoft® Excel®. CDs, DVDs, and external hard drives are typically labeled using some sort of uniform numbering system so that it is possible to track all incoming and outgoing volumes. Production volumes are also usually numbered in a series for record-keeping purposes. It is also important to keep track of production Bates number series to avoid accidental production of documents with overlapping Bates numbers. Archiving Data Establishing a uniform system for archiving data that must be preserved, but is no longer being actively used is also important. Maintaining a uniform archival tracking system makes it easier to locate data in the event that it must be recovered from storage and uploaded to the network at a later date. We also recommend that you become familiar with your organization's backup, retrieval, and data retention policies so that you are prepared in the event that you need to recover data on short notice. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 208 Concordance Evolution Production Elements Numbering Documents As part of the production process, a new set of images are generated for documents that need to be produced. A Bates number series is then applied to all pages of all documents included in the production, with the option of “burning” or “fusing” the numbers to the image during the process. This number series usually differs from that of your internal collection. You can then track what has actually been produced and your Bates number series for the production is sequential with no gaps in the numbering. Fusing Annotations Redactions or other markups can be “burned” or “fused” to the images during production so that they cannot be altered. Confidentiality headers or footers can also be fused to the images during production. Bates numbers and/or document production numbers (DPN) are usually cross-referenced to those in the original review collection. If the Concordance Evolution administrator included fields for Bates numbers and/or document production numbers in your dataset, these numbers are then written to the Bates number and/or document production number fields during the production process. Later when you look at your internal document collection, you are able to see the Bates and/or document production number for any documents that were produced. Creating production sets Images or PDF files are produced in Concordance Evolution by creating a production set job. There are two ways to create production set jobs in Concordance Evolution. You can manually create a job or you can create a production set job using a previously saved production template. Production templates are best used to append documents to an existing production set for numbering continuity. When a production job is complete, the produced files are saved to the directory you specified for extracted files. Th Job Status column of the Create Production Set dashboard is also updated to Complete. After a production set is complete, you can use the file to create a production database DCB and load files using the Export features in Concordance Evolution. For more information, see About exporting files. The traditional Concordance DCB files generated by Concordance Evolution are compatible with Concordance 10.x or later. Concordance Evolution does not support importing or exporting of live redactions to or from traditional Concordance 10.x databases and Concordance Image 5.x imagebases. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 209 If you want to retain redactions and markups applied in Concordance Evolution when you export documents to a DCB file, you will need to produce the applicable documents and burn the redactions and markups onto the produced images in Concordance Evolution. The produced files can then be exported to a DCB file. The redactions and markups will not be editable in Concordance since they will be part of the produced files. Production jobs provide the following options for producing images: Burning markups onto images Creating Bates and/or document production numbers Applying header and footer information Selecting type of image files to create Excluding documents from productions Creating placeholders for excluded documents To create a production set: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane, locate and click the dataset to produce. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Processing button, and then click Create Production Set. The Create Production Job dashboard opens. 4. Define the job details: 1. In the Job Name field, type the production set name. 2. (Optional) In the Description field, type a description for the production set. 3. To use a saved production settings template, from the Template list, click a saved template. Dataset production templates are exclusive to the dataset for which the template was created. 4. When finished, click Next. 5. Define the job settings: 1. In the Production Set Name field, type a name for the production set. The Production Set Name is used as the folder name for the produced documents and for the name in the Near Native viewer. 2. To specify the location for the production files, click the Browse button, and then navigate to the location to store the produced documents. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 210 Concordance Evolution 3. In the Increment Folder Name field, type the starting incremental value. Zero fill the starting number to determine the desired number width. For example: 4. In the Maximum Number of Documents in a Folder field, type the maximum number of production documents to include in a folder. The contents of the folder can be copied to a CD or DVD for distribution. If you plan to copy the production files to a CD or DVD, make sure that you know the the recording capacity of the CD or DVD prior to setting the Maximum Number of Documents value. This ensures that the entire contents of the folder can be copied without running out of disk space. After a folder fills to the maximum size, a new folder is created and, if requested, will continue sequentially. Production files will not be split across folders. 5. Click the Preview Path button to view the full path for the initial folder. 6. In the Select Documents from Production Set, select one of the following options to locate the documents to produce: All documents The All documents in Production Set option locates all documents in the selected image set or dataset. 1. Click the All documents option. Saved Query The Saved Query option, executes a saved query to locate documents in the image set or dataset that match the saved search query. 1. Click the Saved Query option. 2. In the Saved Query list, click the saved search query to locate documents. Tag The Tag option locates documents in the image set or dataset that have been assigned the tag. 1. Click the Tag option. 2. In the Tag list, click the tag to use to locate the documents. Query © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 211 The Query option, executes a typed query, and then locates the documents in the image set or dataset that match the query. 1. Click the Query option. An empty query field is opened below the options. 2. In the query field, type the query to use to locate documents. 7. When finished, click Next. 8. When prompted, click OK to verify the number of documents found. 7. Define the markup settings: The Markups tab determines the document markups that are burned onto the production set images. 1. To include markups in the production, click the Burn Markups check box. 2. To select markups to burn onto the produced file, do one of the following: To select all the markups, click the Select All check box. To select individual markups, click the check box for the markup. 3. To exclude a markup, clear the markup's check box. 4. When finished, click Next. 8. Define the output settings: The Output tab determines the file type and color settings for the produced documents. 1. In the Image Type list, do one of the following: Click PDF (Default) Click TIFF, and then in the Color list, click the color setting to use for the produced TIFF images. 2. To produce a single page for each page of a document, select the Create one image per page check box. 3. To produce files with the text removed from under a redaction, select the Create scrubbed text file(s) check box. 4. When finished, click Next. 9. Define the numbering settings: The Production Set Numbering determines whether Bates numbers and/or document production numbers (DPN) are created for the produced images. The Bates numbers are used for page-level numbering and are usually stamped onto produced images. The © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 212 Concordance Evolution document production numbers are used for document-level numbering that can be referenced for native productions and the Privilege Log. The Field Name - Prefix and Field Value - Prefix must be unique for both the Bates Numbering and Document Production Numbering sections. 1. To create Bates numbers for the produced files, click the Use Bates Numbering check box. 2. In the Field Name - prefix field, type the field name to create for storing the Bates number. The Begin, End, and Range fields can be modified as needed. These fields are appended to the Bates name for each field. The Preview section displays how the field names will appear in Concordance Evolution. For example, Bates_Begin, Bates_End, and Bates_Range. 3. In the Field Value - prefix field, type the numbering prefix to use for the Bates numbering. The Bates number prefix can be up to 15 alphabetic characters. 4. In the Starting Number field, type the starting Bates number. Make sure to use leading zeros to set the length of the number. For example, if you type 0000000001, the starting number is 1 and the number length will be 10 digits long. The Bates number length can be up to 15 numeric characters. 5. To create document production numbers for the produced files, select the Document Production Numbering check box. 6. In the Field Name field, type the field name to create to store the production numbers. 7. In the Field Value - prefix field, type the prefix to use for the document production numbering. The document production number prefix can be up to 15 alphabetic characters. 8. In the Starting Number field, type the starting number and length of the document production number. Make sure to use leading zeros to set the length of the number. For example, if you type 0000000001, the starting number is 1 and the number length will be 10 digits long. The document production number length can be up to 15 numeric characters. 9. When finished, click Next. 10. Define the document placeholders. The Document Placeholder Page Options box determines whether to exclude some documents from the production set and create a placeholder for excluded documents in the production. If you do not need to exclude any documents, this step can be skipped. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 213 1. To exclude documents from the production set and insert placeholder pages for the documents, click the Insert placeholder page for excluded documents check box. 2. To include field content on the placeholder page, from the field list select the field(s), and then click the To Right arrow to move the field(s) to the selected fields list. The maximum number of fields to include on the placeholder page is 5. If the field content is greater than 245 characters, the content shown on the placeholder page will be truncated. Also, if the field content does not have any spaces and contains more than 45 characters, then the content shown on the placeholder page will be truncated. 3. To change the order the field content will appear on the page, select the field and then using the up or down arrow, move the field to the desired position. 4. To add additional text to the placeholder page, click the Placeholder Text check box, and then type the text in the field. The Placeholder Text may contain up to a maximum of 1000 characters and will appear after the field content. 5. To specify documents to exclude and replace with placeholder page, select one of the following: Saved Query The Saved Query option locates documents in the image set or dataset that match the saved search query. 1. Click the Saved Query option. 2. In the Saved Query list, click the search query name to use to locate documents. Tag The Tag option locates documents in the dataset that have been assigned the tag. 1. Click the Tag option. When you click the Tag option, the dataset tag list is displayed. 2. Click the tag to use to locate documents. Query The Query option locates documents in the dataset that match a search query. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 214 Concordance Evolution 1. Click the Query option. 2. In the Query field, type the search query. 5. When finished, click Next. 6. When prompted, click OK to verify the number of documents found. 11. Define the header and footer settings. The Header/Footer tab determines what headers and/or footers are burned onto the produced images. Headers can be burned onto images in the upper left corner, at the center of the top of the document, and/or the upper right corner of the document. Footers can be burned onto images in the lower left corner, at the center of the bottom of the document, and/or the bottom right corner of the document. 1. To include headers and footers, click the Header/Footer check box. Each header and footer defaults to Text with the Auto-Increment check box selected. 2. For each Header and/or Footer, from the Select Field list select any of the following: Field name — the contents of the field are burned onto the produced files. Text — If you select Text, type the text, Prefix, and Starting Number to burn onto the files. When the Auto Increment check box is selected, the number will be incremented for each page. Date & Time — Date and time the image was produced Date — Date the image was produced Time —Time the image was produced Page Number — The page number is auto-generated for the produced files. 3. To exclude any header or footer text from the produced images, in the applicable header or footer list, click None. 4. When finished, click Next. 12. Define the job options settings: 1. To send a notification to specific users when the production set job is completed, select the Send a notification when this job completes check box. 2. Click the Assign button, select the users to send the notification, and then click Save. The selected users are displayed in the Recipients field. 3. In the Message field, type the notification message. 4. To set the Near Native Conversion Priority processing, select one of the following options: © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 215 Low Medium High All production jobs that are assigned a priority are processed in order of first-in, firstprocessed. High priority jobs take precedence over Low and Medium priority. 5. To save the job settings as a template for another time, select the Save Job as Template check box, and select one of the following: Select New to save the settings as a new template. Select Overwrite Existing to replace the settings of an existing template. 6. Type a template name in the text box, and then click the Save button. 7. When finished, click Next. 13. On the Summary tab, review the production settings you defined. If you need to change any of the settings, click the individual production settings tab on the left, and make the applicable edits. 14. In the Scheduling section of the Summary tab, select one of the following: To run the production job immediately, select the Run immediately option. To schedule the production to run at a later time, select the Run at a specified time option, and then type the date and time or click the Calendar button to select the date, and time you want to run the job. 15. When ready, click Finish. The production job is then created and displayed in the production job list on the Create Production Job dashboard. Once the production job is complete, the Status column will display Completed for the associated job. To create a production set job using a template: Production job templates retain all production settings with the exception of the Job Name, selected documents for production, and the placeholder setting for excluded documents. Production set templates can be used for any dataset within the same Matter. When you select a Template to use, the production set settings are automatically loaded for each tab of the Production Job. 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the dataset to produce. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 216 Concordance Evolution Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Processing button, and then click Create Production Set. The Create Production Job dashboard opens. 4. In the Production Set Name field, type the production set name. 5. (Optional) In the Production Set Description field, type the production set description. 6. In the Template list, click the production set template you want to use. 7. When finished, click the Next button. 8. Review each production setting and make any necessary changes. To create a new production job template: Production set templates retain all production settings with the exception of the Job Name, selected documents for production, and the placeholder setting for excluded documents. Production set templates can be used for any dataset within the same Matter. When you select a Template to use, the production set settings are automatically loaded for each tab of the Production Job. You can save production settings to an existing template or create a new template. If you want to save the production set settings to an existing production template, see To save production job settings to an existing template in this topic. 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the dataset to create a production template. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Processing button, and then click Create Production Set. The Create Production Job dashboard opens. 4. In the Production Set Name field, type the production set name. 5. (Optional) In the Production Set Description field, type the production set description. 7. Define the production settings. 8. On the Job Options tab, in the Template section, click the Save Job as Template check box. 9. Select the New option, type a name for the template in the field, and then click the Save button. Once the production set template is saved, the Template created successfully message is displayed at the top of the page. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 217 To save production job settings to an existing template: You can save production job settings to an existing production job template or create a new template. If you want to save the production set settings as a new template, see To create a new production job template in this topic. 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the dataset to save production settings. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Processing button, and then click Create Production Set. The Create Production Job dashboard opens. 4. In the Production Set Name field, type the production set name. 5. (Optional) In the Production Set Description field, type the production set description. 6. Define the production settings. 7. On the Job Options tab, in the Template section, click the Save Job as Template check box. 8. Select the Overwrite Existing option, type a template name in the text box, and then click the Save button. Once the production set template is saved, the Template created successfully message is displayed at the top of the page. Exporting About exporting files Dataset documents are exported from Concordance Evolution by creating export jobs. You can access the dataset export feature from the Dataset dashboard. When exporting dataset documents, you will also be able to include native, image, and text files with the export, as well as recreate family groupings based a family ID field that identifies all the related attachments. Productions sets can also be exported as DAT load files. Concordance Evolution does not support importing or exporting of live redactions to or © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 218 Concordance Evolution from traditional Concordance 10.x databases and Concordance Image 5.x imagebases. If you want to retain redactions and markups applied in Concordance Evolution when you export documents to a DCB file, you will need to produce the applicable documents and burn the redactions and markups onto the produced files in Concordance Evolution, and then export the produced files to a DCB file. The redactions and markups will not be editable in Concordance since they will be part of the actual files. Related Topics Exporting to load files Synching cases with LAW PreDiscovery Exporting files Concordance Evolution datasets can be exported as a .DAT load file. The export job provides the tools needed to include native, image, and text files with the export, as well as recreate family groups. When exporting native, image, and text files, additional options are available for naming the files using a selected dataset field, excluding date and numeric fields. Choosing a field for one file type does not limit the selections for the others; meaning, the same field can be used for native, image, and text files. If a field is blank for the native, image, or text file, the file will not export and an error is recorded in the job log. For more information about job logs, see About jobs. When exporting image files, the Auto-increment file name on selected field option automatically increments the numbering of the file names. Below is a sample image set and the export results detailing how the files are named using the BegDoc field both with and without the Auto-increment file name on selected field option selected: Sample Image Set Document ID # of Pages BegDoc 0001 4 ABC001 0002 5 ABC005 0003 1 ABC010 0004 3 ABC011 © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 219 Export Results Document ID Name image file incrementally Option selected Name image file incrementally Option not selected 0001 ABC001 ABC001_001 0001 ABC002 ABC001_002 0001 ABC003 ABC001_003 0001 ABC004 ABC001_004 0002 ABC005 ABC005_001 0002 ABC006 ABC005_002 0002 ABC007 ABC005_003 0002 ABC008 ABC005_004 0002 ABC009 ABC005_005 0003 ABC010 ABC010_001 0004 ABC011 ABC011_001 0004 ABC012 ABC011_002 0004 ABC013 ABC011_003 When exporting single page images with overlapping field name numbers, the newest document with the same name will overwrite the older document. Data is exported from Concordance Evolution by creating export jobs. The export job processes the selected files and saves them to the location specified. If you are going to be creating numerous export jobs that will be using the same or similar export settings, you can create an export job and save it as a template. Export templates retain all export job settings except the export job name, document selection, and export job schedule. To export a dataset to a load file: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the dataset you want to export. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 220 Concordance Evolution Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Import / Export button, and then click Export Load File. The Create Export Job dashboard opens. 4. Define the Job Details 1. In the Job Name field, type the export job name. 2. (Optional) In the Description field, type the export job description. 3. (Optional) To load a saved job template, from the Template list, select the template to load, then click Next. 5. Define the Job settings 1. For the Export File Name field, do one of the following: Enter the directory, including the file name, for the load files to export. Click the Browse button, locate the folder to store the exported load files, in the File Name field type a file name for the exported files, and then click OK. 2. In the Select Documents for export, do any of the following: Click All documents to include all the documents in the dataset. Click Filter by Saved Query, and then select a saved query from the list to execute the query, and include only the documents from the results of the query. Click Filter by Tag, and then select a tag from the list to include only the documents that are tagged with the selected tag. 3. When finished, click Next. 4. When prompted to confirm the number of documents to export, click OK. 6. Define the Images Settings 1. To include images with the export, click the Include Images check box. 2. Do any of the following: Click the Production Set option to export the images and documents associated with a dataset's production set, and then select the production set from the list. Click the Image set option to export the images and documents associated with the dataset's image set, and then click the image set from the list. 2. From the Field for image file names from dataset list, select the field name to use for naming the exported image files. 3. To automatically increment numbering for the exported image files, click the Autoincrement file name on selected field check box. 4. When finished, click Next. 7. Define the Files settings © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 221 1. To include native files in the export, select the Include native files check box. 2. In the Field Name for native path field, type the field name to create for the native file path in the load file. 3. From the Field for native files name from dataset list, select the field that contains the name for the native files. 4. To select only the native files that are tagged with a specific tag, click the Include native for tagged documents only check box, and then do one of the following: To select a public tag, click the Public Tags option, and then select a tag from the tag list. To select a private tag, click the Private Tags option, and then select a tag from the tag list. When selecting the Include native for tagged documents only option, if a document is tagged and not part of the export selection, the native file will not be exported. Or, if the document is part of the export selection but not tagged, the native file will not be exported. 5. To include text files in the export, select the Include text files check box, and do one of the following: Click the Use OPT file for text file name option to use the name of the .opt file for the text file name. Click the Use Field in load file for text file name option, in the Field name for text file name field, type the field name for the path to the location of the text files, and then from the Field for text files name from dataset list, select the field that contains the name for the text file. 6. To export text, from the Select field to export from list, select the field name that contains the text that you want to export. By default the Content field is selected. 7. To set Text Priority for Scrubbed and Extracted text, from the Option 1 list, select the text with the highest priority, and then from the Option 2 list, select the text with the lowest priority. 8. When finished, click Next. 8. Define the Tags settings Keep the following in m ind when exporting a tag list: Tag folders and structures will not be exported Tag rules will not be exported Personal tags will be converted to public tags Hidden tags will be visible 1. To export tags assigned to the documents in the dataset, select the Include Tags (will create tags in the load file) check box. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 222 Concordance Evolution 2. In the New Tag Field Name field, type the new field name you want the export to create in the load file for the exported tags. 3. From the Tag Separator Delimiter list, select the delimiter you want to use to separate the exported tags in the load file. The default value is ;(Semicolon). The Tags to Export list displays all the dataset's public tags. To display personal tags, select the Show personal tags check box below the displayed tag list. 4. In the Tags to Export list, select the check box next to the tags you want to export. 5. When finished, click Next. 9. Define the Formatting settings When exporting within the Concordance Evolution system you will not need to change these default values. Change them only if you are using these characters in the text of your documents. 1. Verify the default delimiter settings for the load file: Delimiter Set list defaults to ConcordanceDefault Column (comma) list defaults to (20). The Column (comma) delimiter is a field delimiter that separates one field from the other. Quote list defaults to Þ(254). The Quote delimiter is a text qualifier delimiter that encloses text to differentiate it from field delimiters which may appear in the data. Newline defaults to ®(174). The Newline delimiter is a substitute carriage return. Some programs use this character to designate multi-level fields or fields-withinfields. Concordance Evolution replaces all carriage returns or carriage return linefeed combinations with the newline code within the data of a field. The record itself is still terminated with a real carriage return and a line feed. The delimiters available from the Column (comma), Quote, and Newline fields may appear as square symbols or may not be displayed. How the lists are displayed depends on the computer's language environment. The delimiters listed in the About delimiter characters topic use the Tahoma font, which displays the characters regardless of the language environment. All of the characters listed in the delimiter character list can be selected as the delimiter, even if the symbols they represent do not appear in the Column (comma), Quote, and Newline fields. To see the list of available delimiter characters, see About delimiter characters. Delimiters are customizable for an organization's internal database design, but many organizations ask vendors to use Concordance Evolution default delimiters. If your case records contain the registered trademark symbol, you may want to consider changing the ® to another symbol in the load file. 2. In the Date format list, click the date format to be used in the delimited text file. The Date format field defaults to yyyy/mm/dd. 3. In the File Encoding Type section, select any of the following: © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 223 Allow Unicode™ to permit Unicode type file encoding in the delimited text file. Decode to ANSI to remove Unicode type file encoding in the delimited text file. 10. Define the Fields settings The Fields tab allows you to recreate family groupings during an export. The Recreate Family group option provides the ability to select a field that determines the beginning and ending numbering for the exported data. You also can specify which dataset source fields are written to which field name in the delimited text file. The dataset's source field names are listed in the DataSet Field column, and the available load file field names are listed in the Load File Field column. The default names can be changed as needed. 1. To recreate family groups based on production numbers or other fields in the export job, click the Recreate Family group check box. 2. In the Family ID section, do the following: From the Beg Number list, select the field to use to create the family group beginning number. From the End Number field, select the field to use to create the family group ending number. The End Number field is optional and should only be used with page number fields. The End Number field is not needed when a document level number field, such as DOCID, is used for the beginning number. 3. To create fields for any attachments, from the Attachment Field list, do one of the following: To create beginning and ending attachment fields, click Beg Attach and End attach. To create a single attachment range field, click Attachment range. 4. In the Select fields to map section, to specify the order the fields are listed in the delimited text file, click the Reorder Fields button. 5. In the Reorder Fields dialog box, select the field(s) you want to move, and then click the Up or Down arrow. 6. When finished, click Save. 7. To manually map the fields, clear the Select All check box. 8. In the Load File Field, type the name of the field you want the data written to in the delimited text file. 9. When finished, click Next. 11. Define the Output Settings By default, the Use relative path check box is selected. 1. Do one of the following: © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 224 Concordance Evolution To assign a relative path to the exported files, click the Use relative path check box. To assign the actual file path to the exported files, clear the Use relative path check box. By default, the Use volume folders and Create separate folders for image, native, and text files check boxes are selected. The Use volume folders check box determines whether the exported files are organized into volume folders during the export. 2. Do one of the following: To create volume folders, click the Use volume folders check box. To not create volume folders, clear the Use volume folders check box. 3. In the Base folder name for volumes field, type the volume folder name you want the export to create. Default is Vol. 4. To create separate folders for image, native, and text files, make sure that the Create separate folders in the volume folder for image, native, and text files check box is selected. If you do not want the export to create separate folders, clear the Create separate folders in the volume folder for image, native, and text files check box. 5. In the Base folder name for image files field, type the image folder name you want the export to create. Default is images. 6. In the Base folder name for native files field, type the native folder name you want the export to create. Default is natives. 7. In the Base folder name for text files field, type the text folder name you want the export to create. Default is text. The Increment volume folder names check box determines whether all files are exported to one volume folder or whether you want to allow a maximum number of files or volume size for volume folders, and if the maximum number of files or volume is exceeded, to have the export create incremental volume folders for the exported files. By default, the Increment volume folder names check box is selected. When the check box is selected, the export will create incremental volume folders when needed. For example, if the base folder name is VOL, the volume folder limit is 500, the volume folder numbering format is 001, and the number of exported files is exporting 1500, the export will create three folders, VOL001, VOL002, and VOL003 with 500 files in each of the folders. 8. To increment the volume folder names, select the Increment volume folder names check box and type the numbering format you want the export to use for incrementing volume folders. Default is 001. 9. In the Maximum number of files in a folder field, type the maximum number of files allowed in each volume folder. Default is 500. 10. To set a maximum volume size for volume folders, select the Maximum volume size check box, type the maximum volume size, and then click the volume size measurement. Default is 800 MB. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 225 You can select MB (megabytes), GB (gigabytes), or TB (terabytes) for the volume size measurement. If you have a maximum number of files allowed and a maximum volume size defined for volume folders, the export job will create incremental volume folders when either the maximum number of files or maximum volume size is reached. 11. When finished, click Next. 12. Define the Job Settings 1. To generate and send a notification to users when the export job is completed, in the Notifications box, select the Send Notification check box. 2. For the Recipients, click the Assign button, and select the check box for the user groups and/or individual users to which you want to send the notification, and then click OK. 3. In the Message field, type the notification message. 4. To save the job settings as a template for use at a later time, select the Save Job as Template check box, and then do one of the following: Click New, type the name of the template in the template field, and then click Save. Click Overwrite Existing, select a saved template from the list, and then click Save. 5. When finished, click Next. 13. On the Summary tab, review the export settings you defined. If you need to change any of the settings, click the individual import section tabs on the left, and make the applicable edits. 14. In the Scheduling section of the Summary tab, select one of the following: To run the export job immediately, select the Run immediately option. To schedule the export to run at a later time, select the Run at a specified time option, and then type the date and time or click the Calendar button to select date and time you want to run the export. 15. When ready, click Finish. To create a load file export job using a template: Export templates retain all export job settings except the export job name, document selection, and export job schedule. You can change any of the export template settings as needed prior to running the job. Export templates can only be used for the same type of export from which the template was originally created. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 226 Concordance Evolution 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the dataset you want to create an export template. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Import / Export button, and then click Export Load File. The Create Export Job for Dataset dashboard opens. 4. On the Job Details tab, in the Job Name field, type the export job name. 5. (Optional) In the Description field, type the export job description. 6. To load a job template, from the Template list, select the template settings you want to load, then click Next. 7. For each of the Export Job tabs review the settings and make any necessary changes. 8. On the Summary tab, review the export settings you defined. If you need to change any of the settings, click the individual export section tabs on the left, and make the applicable edits. 9. In the Scheduling section of the Summary tab, select one of the following: To run the export job immediately, select the Run immediately option. To schedule the export to run at a later time, select the Run at a specified time option, and then type the date and time or click the Calendar button to select the date and time you want to run the export. 11. When ready, click Finish. To create a new or overwrite an export template: Export templates retain all export job settings except the export job name, document selection, and export job schedule. You can change any of the export template settings as needed prior to running the job. Export templates can only be used for the same type of export from which the template was originally created. For example, if the template was created from a DCB export, you can only use the export template for other DCB exports. You can also save export settings to an existing export template or create a new export template. 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the dataset to use to create an export template. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Import / Export button, and then click Export Load File. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 227 The Create Export Job for Dataset dashboard opens. 4. On the Job Details tab, in the Job Name field, type the export job name. 5. (Optional) In the Description field, type the export job description. 6. Click Next. 7. For each of the Export Job tabs, review the settings and make any necessary changes. 8. On the Job Options tab, in the Template section, click the Save Job as Template checkbox. 9. Do one of the following, and then click the Save button: Click New, type the name for the template in the template field. Click Overwrite Existing, select a saved template from the list to overwrite. 10. When finished, click Next. 11. On the Summary tab, review the export settings you defined. If you need to change any of the settings, click the individual export section tabs on the left, and make the applicable edits. 13. In the Scheduling section of the Summary tab, select one of the following: To run the export job immediately, select the Run immediately option. To schedule the export to run at a later time, select the Run at a specified time option, and then type the date and time or click the Calendar button to select the date and time you want to run the export. 14. When ready, click Finish. Synchronizing data with LAW PreDiscovery After reviewing LAW PreDiscovery case records in Concordance Evolution, you can write the information back to the LAW PreDiscovery server for further processing. As a best practice, make sure that the case file is not open in LAW PreDiscovery before executing the synchronization job. To write data back to a LAW PreDiscovery case: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the dataset you want to export. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 228 Concordance Evolution 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Import / Export button, and then click LAW PreDiscovery Sync. 4. Define the Job Details 1. In the Job Name field, type the synchronization job name.. 2. (Optional) In the Description field, type the export job description. 3. (Optional) To load a saved job template, from the Template list, select the template to load, then click Next. 5. Define the Job settings: 1. In the Sync Tag Name field, type a tag name to tag all records for the job in the LAW PreDiscovery case. All synchronized documents are tagged automatically with the Sync Tag Name. 2. In the Select Documents for Sync, do one of the following: To send all the documents in the dataset, click the All documents option. To send only the documents from the results from a saved query, click the Saved Query option, and then select a saved query from the list to execute the query and pull the documents. To send only the documents that are tagged with a specific tag, click the Tag option, and then select a tag from the list. To send only the documents from the results of a query, click the Query option, and then type the query in the field. 3. When finished, click Next. 4. When prompted, click OK to confirm the number of documents. 6. Define the Markup settings: 1. To update the images associated with the selected documents, click the Images check box, and then do one the following. To send only the images from the results of a save query, click the Saved Query option, and then select a saved query from the list. To send only the image that are tagged with a specific tag, click the Tag option, and then select a tag from the list. To send only the images from the results of a query, click the Query option, and then type a query in the field. Images produced will be from the Redactable Set that is assigned to the dataset and the images must meet both query criteria specified in the job. If the image does not meet both query criteria, the image is excluded from the synchronization job process. 2. In the Color section, select one of the following: To convert the documents to shades of gray, select Black and White. To produce the image in color (4-bit -16 colors), select Color. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 229 Concordance Evolution creates single page images to place into LAW PreDiscovery. 3. To burn markups onto the images, select the Include Burn Markups check box, and then select the check box for each markup to burn onto the images. 4. When finished, click Next. The synchronization job will create a new folder, EVImage, within the case $Image Archive folder. All synchronization jobs will have it's own folder. Each job folder will consist of volume folders each containing a maximum 50 documents with no page limits. For example, $Image Archive\EVImage\Job<JobID>\0001 etc. 7. Define the Field mappings: The Field Mapping section allows you to map the field data in Concordance Evolution to the case fields in LAW PreDiscovery for updating and processing. The default Concordance Evolution fields are mapped to the default corresponding LAW PreDiscovery field. The data in the selected Concordance Evolution field will overwrite the data in the corresponding LAW PreDiscovery field. For new fields, the conversion from Concordance Evolution to LAW PreDiscovery is as follows: Concordance Evolution Field Type LAW PreDiscovery Field Type Text Memo Date Date Numeric Numeric The following fields cannot be synchronized: Begdoc#, Enddoc#, Attachmt, Batesrng, BegAttach, EndAttach, EDFolder, EdFolderID, EdSession, EdSessionID, EdSource, EDSourceID, ID, PgCount, ParentID, TimeZoneProc, TimeZoneID, and CustodianID. 1. To select fields for mapping, do any of the following: To select all the fields, select the check box at the top of the of the Field Mapping table. To select individual fields, select the check box next to the field to map. 2. To change the field mappings for the selected fields, in the LAW PreDiscovery Fields column, do any of the following: To map to an existing field, click the arrow next to the LAW PreDiscovery field, and then select the field name. To map to a new field, click the field to highlight the current field name, type a new field name, and the press Enter. 3. When finished, click Next. 4. When prompted, click OK to confirm the number of documents to be imaged. 8. Define the Tags mapping: © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 230 Concordance Evolution Tag Mapping allows you to select which Concordance Evolution tags are written back to LAW PreDiscovery. LAW PreDiscovery automatically reads the Concordance Evolution tag names and updates the mapped tag for the corresponding document in the database. Selected Tag names can be renamed as needed. If the LAW PreDiscovery tag is renamed, the new tag name is applied to the associated documents. 1. To write tag information back to LAW PreDiscovery, do any of the following: To select all the tags, select the check box at the top of the Tag Mapping table. To select one or more tags, in the Concordance Evolution Tag column, select the check box next to the tag name. 2. In the LAW PreDiscovery Tag column, do any of the following: To map to an existing tag, click the arrow next to the LAW PreDiscovery tag, and then select a tag name. To map to a new tag, click the field to highlight the current tag name, type a new tag name, and the press Enter. When sending Concordance Evolution tags to LAW PreDiscovery the tags are converted to Tag (Boolean) type fields. All Concordance Evolution folders, structure, and rules will be lost. 3. When finished, click Next. 9. Define the Job Options 1. To generate and send a notification to users when the export job is completed, in the Notifications box, select the Send Notification check box. 2. For the Recipients, click the Assign button, and select the check box for the user groups and/or individual users to which you want to send the notification, and then click OK. 3. In the Message field, type the notification message. 4. To set the Near Native Conversion Priority processing, select one of the following options: Low Medium High All jobs that are assigned a priority are processed the order of first in first processed. High priority jobs take precedence over Low and Medium priority jobs. 5. To save the job settings as a template for use at a later time, select the Save Job as Template check box, and then do one of the following: Click New, in the template field type the name of the template, and then click Save. Click Overwrite Existing, from the list select a saved template, and then click Save. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 231 6. When finished, click Next. 10. On the Summary tab, review the synchronization settings you defined. If you need to change any of the settings, click the individual import section tabs on the left, and make the applicable edits. 11. In the Scheduling section of the Summary tab, select one of the following: To run the synchronization job immediately, select the Run immediately option. To schedule the synchronization to run at a later time, select the Run at a specified time option, and then type the date and time or click the Calendar button to select the date, and time you want to run the import. 12. When ready, click Finish. After the job is complete, make sure to view the job log or job reprocessing log to locate documents that did not synchronize with LAW PreDiscovery. Related Topics About LAW PreDiscovery cases Importing LAW PreDiscovery cases Viewing jobs Reprocessing jobs Bulk Printing About bulk printing The Bulk Print feature in Concordance Evolution is used to print documents from a production set, image set or native set by creating a bulk print job. Documents within the production set, image set, or native set can be added to bulk print jobs by search, query, or tag. Individual or multiple documents in a dataset can be printed directly from the Review dashboard by selecting the check boxes next to the documents they want to print in the Snippet or Table view and clicking the print button. Before any documents can be printed using the Bulk Print feature, the applicable printer services must be running. For more information, see . Maintaining server services © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 232 Concordance Evolution Creating bulk print jobs Bulk print jobs can be created for any dataset documents in a production set, image set, or native set. After determining the type of set the documents will be printed from, you can narrow down the document selection within the set by search query or tag. When printing docum ents, keep the following in m ind: When printing documents that have been reviewed and redacted, any redaction placed on the document will print transparent, revealing the text underneath. If you want to print redactions as opaque, you must produce the documents in Concordance Evolution, then print the produced document. Printing documents that contain markups to Adobe PDF using the File > Print option, does not permanently burn the markups in the document. If you want markups burned in, you must produce the documents in Concordance Evolution, then print the produced document. To print a set of documents: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, locate and click the dataset you want to print. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Processing button, and then click Create Bulk Print Job. The Create Print Job for Dataset dashboard opens. 4. In the Bulk Print Job Name field, type the name of the bulk print job. 5. (Optional) In the Bulk Print Job Description field, type the description for the bulk print job. 6. For the Select file output folder, click the Browse button, locate the folder to print the files, and then click OK. 7. From the Select Field for Naming Files, click the field to use to name the print files. 8. From the Select Printer list, click the printer to use to print the files. 9. In the Select Images to Print section, do any of the following: Click Production Set to print a selected set of produced documents, and then in the Production Set list, click the production set containing the documents you want to print. Click Image Set to print a selected set of images, and then in the Image Set list, click the image set containing the documents you want to print. Click Native Set to print the documents directly from the dataset's document native set. 10. In the Select Documents from [set type] for Bulk Print section, click one of the following: Click the All Documents option. Click the Saved Search option, and then from the list, click the query to use to locate the documents to print. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 233 Click the Tag option, and then from the list, click the tag to use to locate the documents to print. 11. Click the Retrieve Documents button. 12. To schedule the bulk print job, do any of the following: Click the Now option to run the bulk print job immediately. Click the Schedule option to schedule the bulk print job to run at a specific date and time. You can then type the date and time or click the Calendar button to select the date, and select the time you want to run the bulk print job. 13. When finished, on dashboard toolbar, click the Print button to run the job when scheduled. After clicking the Print button, the bulk print job is created and displayed in the bulk print job list on the Bulk Print dashboard. Once the bulk print job is completed, Completed will be displayed for the bulk print job in the Status column. When the bulk print job runs, Concordance Evolution creates a log that contains the following information: Job Name Timestamp of the print job How many documents successfully printed. How many documents failed. List of DCNs, with the error codes and descriptions. Dataset Logs About dataset logs Depending on the fields you choose, you can use the Create Job command to create any of the following job logs (.csv file) for a dataset: Privilege Log - a list of all documents that have associated privilege tags and/or reasons and descriptions applied during review. Chain of Custody - a list of documents containing a MD5 hash value when the documents were imported, along with any selected tag(s) and/or field value. Cross-Reference - a list of tags and fields to compare documents Related Topics Adding fields to datasets Tagging individual documents © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 234 Concordance Evolution Tagging multiple documents Applying privilege reasons Creating privilege logs Creating dataset logs There are two ways to generate a job log in Concordance Evolution. You can manually create a log job or you can create a job log using a job log profile. If you are going to be creating numerous log jobs for a dataset, you can create a log job and save the settings to a profile, which can be used to quickly create new log jobs for the dataset. To create a Log job: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, locate and click the dataset to create a job log. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Processing button, and then click Create Log. The Create Job Log for Dataset dashboard opens. 4. In the Log Job Name field, type the name for the log job. 5. In the Log Job Description field, type a description for the log job. 6. Click Next. 7. In the Path to Log Folder field, do one of the following: Type the directory and file where you want to save the log file. Click the Browse button and navigate to the location you want to save the log file. 9. In the File Name field, type the name for the file, and then click OK. 10. In the Select Documents from [dataset name] for Log section, select the documents you want to create a log for by clicking one of the following options: Saved Query The Saved Query option locates documents in the dataset that match the saved search query. 1. Click the Saved query option. 2. In the Saved query list, click the saved search query you want to use to locate © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 235 documents. 3. To locate and add all documents in the query to the log, click the Retrieve Documents button. When you click the Retrieve Documents button, the documents are added to the log job and the message [number of documents] Documents Found as Result is displayed next to the Retrieve Documents button. Tag The Tag option locates documents in the dataset that have been assigned the selected tag. 1. Click the Tag option. 2. In the Tag list, click the tag you want to use to locate the documents. 3. To locate and add all documents assigned the selected tag to the log job, click the Retrieve Documents button. When you click the Retrieve Documents button, the documents are added to the log job and the message [number of documents] Documents Found as Result is displayed next to the Retrieve Documents button. 11. Click Next. 12. In the Log Field Selection list, select the check box for the fields to include in the log. To select all fields, select the check box at the top of the Log Field Selection list. 13. Make sure that the fields you selected have a corresponding field name in the Log Field column. You can edit the field name displayed on the log by editing a field name in the Log Field column. 14. Click Next. 15. To include tags in the log, in the Select tags for Log section, do any of the following: To include a list of personal tag, click the Show personal tags list. To select individual tags, click the check box for the tag. To select all tags, click the Select all link. 16. In the Select Reason for redaction list, select the check box for each redaction reason to include on the log. To select all fields, select the check box at the top of the Select Reason for redaction list. 17. Click Next. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 236 Concordance Evolution 18. In the Summary box, verify the selections made for the log job. 19. To make changes, click the Change Log Options link to start over, or click the links in the Summary box for the individual option. 20. Click the Test Paths button to validate the log path entered in the Path to Log Folder field. 21. To run the job, do one of the following: Click the Run Now button to run the log job immediately. Click the Schedule button to schedule the log job to run at a specific date and time. Clicking the Schedule button opens the Scheduling section. You can type the date and time or click the Calendar button to select the date, and select the time you want to run the log job. After clicking the Run Now or Save button in the Scheduling section, the log job is created and displayed in the log list on the Log dashboard. Once the job is completed, Completed will be displayed in the Status column. To save job log settings to a profile: To create a job log from a saved profile: Log profiles retain all log field selection and field name settings. When you create a job log using a log profile you will need to enter the job log name, and all log settings except the field selections and field names. And if you want to change any of the log field selection and field name settings for the job log, you will need to make those changes. 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, locate and click the dataset to load log profile settings. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Processing button, and then click Create Log. The Create Job Log for Dataset dashboard opens. 4. Clicking Create job log opens the Create job log dashboard. 5. In the job log Name field, type the name for the job log. 6. In the job log Description field, type a description for the job log. 7. In the Log Profile list, click the log profile you want to use for the job log. 8. Click Next. 9. In the Path to Log Folder field, enter the directory where you want to save the log. 10. In the Select Documents from [dataset name] for Log section, select the documents to © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 237 create a log for by clicking one of the following options: Saved Query The Saved Query option locates documents in the dataset that match the saved search query. To add documents in the dataset from a search query: 1. Click the Saved query option. 2. In the Saved query list, click the saved search query you want to use to locate documents. 3. To locate and add all documents in the query to the job log, click the Retrieve Documents button. When you click the Retrieve Documents button, the documents are added to the job log and the message [number of documents] Documents Found as Result is displayed next to the Retrieve Documents button. Tag The Tag option locates documents in the dataset that have been assigned the selected tag. To add documents in the dataset from a tag: 1. Click the Tag option. 2. In the Tag list, click the tag you want to use to locate the documents. 3. To locate and add all documents assigned the selected tag to the job log, click the Retrieve Documents button. When you click the Retrieve Documents button, the documents are added to the job log and the message [number of documents] Documents Found as Result is displayed next to the Retrieve Documents button. 11. In the Log Field Selection list, make any necessary changes, and then click Next. 12. In the Select tags for log section, make any necessary changes. 13. In the Select Reason for redaction list, select the check box for each redaction reason to include on the log. To select all the redaction reasons, select the check box at the top of the Select Reason for redaction list. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 238 Concordance Evolution 14. Click Next. 15. In the Summary box, verify the selections made for the job log. 16. If you need to make changes, click the Change Log Options link to start over, or click the links in the Summary box for the individual option. 17. Click the Test Paths button to validate the log path entered in the Path to Log Folder field. 18. To run the job, do one of the following: Click the Run Now button to run the job log immediately. Click the Schedule button to schedule the job log to run at a specific date and time. Clicking the Schedule button opens the Scheduling section. You can type the date and time or click the Calendar button to select the date, and select the time you want to run the job log. After clicking the Run Now or Save button in the Scheduling section, the job log is created and displayed in the log list on the Log dashboard. Once the job is completed, Completed will be displayed for the job log in the Status column. Deduplication About deduplication The Deduplication command in Concordance Evolution compares the documents in a dataset to determine if the dataset contains duplicate documents. Deduplication compares the unique fingerprint for each file, based on the contents of that file. These fingerprints are known as hash tables, and are also used in cryptography and security applications. Concordance Evolution then compares the hash tables for all the documents in the selected dataset. If any document hash values match up, those files are considered to be duplicates of each other. To compare and identify duplicate documents, a deduplication job is created and run against a dataset. When a Deduplication job is created, you have the option of deleting any duplicate documents or grouping and then tagging the duplicate document without deleting them from the dataset. Creating deduplication jobs Deduplication jobs can be created for any dataset containing documents. When you are creating a deduplication job you can determine how duplicate documents are identified in the dataset and what to do with the duplicate documents that are found. After each deduplication job runs a log file is created for the job and can be accessed from the Deduplication dashboard by clicking the Log link in the Log column. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 239 To deduplicate within a dataset: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane, locate and click the dataset to create a deduplication job. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset dashboard toolbar, click the Processing button, and then click Create Deduplication Job. Clicking the Create Deduplication Job opens the Create Duplication Job dashboard. 4. In the Job Name field, type a name for the deduplication job. 5. (Optional) In the Job Description field, type a description for the deduplication job. The Dataset list defaults to the currently selected dataset. The Compare By list defaults to Original Document. The original document is defined as the first document that Concordance Evolution finds in the selected dataset. 6. In the Algorithm list, click SHA1 (default) or MD5. The algorithm is used for creating hash tables for each file. The algorithm is used to search for duplicates within the selected dataset. 7. In Action section, select how you want duplicates to be handled by Concordance Evolution. Delete duplicates - duplicate documents found within the dataset will be deleted. Group duplicate documents - duplicate documents found within the dataset are grouped together and marked without being deleted from the dataset. 8. To schedule a time for the deduplication job to run, do one of the following: Click the Now option if you want to run the deduplication job immediately. Click the Schedule option to schedule the deduplication job to run at a specific date and time. You can then type the date and time or click the Calendar button to select the date, and select the time you want to run the deduplication job. 9. To request Concordance Evolution to generate and send a notification to users when the import job is completed, select the Yes option, type the notification message, and do one of the following: To send the notification to all users currently logged on to Concordance Evolution, click the Send to all Logged in users option. To send the notification to specific users and/or user groups, click the Send to specific users/groups option, click the Assign button, select the check box for the user groups and/or individual users to which you want to send the notification, and then click OK. For more information about notifications, see About notifications and alerts. 10. When finished, click the Create button. After clicking the Create button, the deduplication job is created and displayed in the deduplication job list on the Deduplication dashboard. Once the deduplication job is completed, Completed will be displayed in the Status column. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 240 Concordance Evolution Near-Deduplication About Near-Deduplication In near duplication, a family is a collection of one or more near-duplicate documents. The NearDeduplication feature in Concordance Evolution compares the text of documents within a selected dataset to determine the percentage of likeness between documents. The process then assigns a master document to each family. The master document is the document most representative of the document family. Within a family, the master document is the one with the greatest overall similarity to all the other documents in the family. It has to be a nearduplicate of every other document in the family. The Family Threshold setting in the NearDuplicate Analysis utility determines the percentage of similarity between the master document and the documents within its document family. A document cluster contains documents more loosely related to each other than a document family. The documents in a cluster contain similar content. How similarly the documents are related is determined by the Cluster Threshold setting. Documents assigned to a document cluster will have a percentage of similarity at or above the current Cluster Threshold setting in the Near-Duplicate Analysis utility. Documents which have no direct relationship to each other might still belong to the same cluster, as long as there is some chain of relationships at or above the Cluster Threshold setting that connects them. There is no limit on how long this chain can be, so two documents in the same cluster may be very distant cousins with no apparent similarity. After running the Near-Duplicate Analysis utility, six near-duplicate fields are automatically populated with the applicable near-duplicate data for the case's documents: ND_Sort ND_EquiSortAtt ND_FamilyID ND_ClusterID ND_Similarity ND_IsMaster Do not change the field name for near-deduplication fields as this will cause an error when writing the data to the fields and the document will not appear in the Near Duplicate view. Creating near-deduplication jobs Near-Deduplication jobs can be created for any dataset containing documents with text. After each Near-Deduplication job runs a log file is created for the job and can be accessed from the Jobs dashboard and clicking the Log link in the Log column. The Near-Deduplication job is for datasets in which near deduplication has not been loaded from an external load file, the dataset does not contain any near deduplication data, or the data needs to be updated (overwritten). © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 241 Create Near-Deduplication Job dialog box Executing a Near-Deduplication job on an existing dataset will overwrite any previous data stored in the associated near-deduplication fields. Do not change the field name for near-deduplication fields as this will cause an error when writing the data to the fields and the document will not appear in the Near Duplicate view. To create a near-deduplication job: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, locate and click the dataset to create a deduplication job. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 242 Concordance Evolution 3. To make sure the dataset can run the Near-Deduplication process, in the Actions column, click the Edit link for the dataset. 4. From the Near Deduplication list, select Near-Deduplication Job, and then click Save. 5. On the dataset dashboard toolbar, click the Processing button, and then click Create Near-Deduplication Job. The Create Near-Deduplication Job dialog box opens. 6. In the Options section, do the following: For the Cluster Threshold, move the slider to adjust the similarity threshold. For the Family Threshold, move the slider to adjust the family threshold. The Cluster Threshold setting determines the minimum similarity to be considered when assigning clusters of related documents. The Family Threshold setting determines the minimum similarity to be considered when assigning documents to near-duplicate families. By default, the Cluster Threshold is set to 70 and the Family Threshold is set to 85. Once you run the Near-Duplicate Analysis utility, the utility retains the last cluster and family threshold settings. Moving the slider to the right increases the threshold, and moving the slider to the left decreases the threshold. 7. In the Scheduling section, select one of the following: To run the production job immediately, select the Run immediately option. To schedule the production to run at a later time, select the Run at a specified time option, and then type the date and time or click the Calendar button to select the date, and time you want to run the job. 8. In the Notifications section, to send a notification to specific users when the neardeduplication job is completed, select the Send a notification when this job completes check box. 9. Click the Assign button, select the users to send the notification, and then click Save. The selected users are displayed in the Recipients field. 10. In the Message field, type the notification message. 11. When finished, click Ok. Knowledge M anagement Managing the knowledge base In Concordance Evolution, each dataset has its own knowledge base, which is used to support searching and applying redactions in the Review dashboard. Administrators can customize the following knowledge base lists for a dataset: Spelling Variations - can be used to apply spelling variations to a search word. When the © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 243 word is searched on, results will include documents containing the spelling variations that were added to the spelling variations list. Thesaurus - is used to add synonyms to a search word. When the word is searched on, results will include documents containing the synonyms that were added to the thesaurus list. Stop Words - are used to omit words from the searching index. Stop words are the most common words in the English language (and, the, but, etc.). Stop words are not words that are generally searched for by reviewers. Eliminating stop words from the index ensures that searches run much faster and efficiently. Reason for Redaction - is used to add redaction reason which will be available to reviewers while applying redactions in the Near Native view. The Customize Knowledge Base section on Search Settings dashboard determines which knowledge base features are used by the dataset. By default, each of the above knowledge base features are enabled for a dataset. For more information about the other search settings on the Search Setting dashboard, see Defining dataset search settings. Related Topics Defining dataset search settings Managing spelling variations Managing stop words Managing reasons for redaction Managing spelling variations When executing a search, if the Spelling Variations feature is enabled and the search term has a spelling variation associated with it in the Spelling variations list, the search engine looks for the search term and its associated spelling variations, and returns both the search term and its spelling variations in the results. For example, if a name in the case documents has different variations, such as Ken, Kenneth, and Kenny, you can add each of the variations to the Spelling Variations list, and if someone searches on any version of Ken, the search engine will include all versions of Ken in the search results. Administrators can add, edit, or delete spelling variations and can import and export a spelling variations list to and from a .csv file. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 244 Concordance Evolution To add spelling variations: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, locate and click the dataset to add a spelling variation. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Settings button, and then click Search Settings. 4. On the Search Settings toolbar, click the Knowledge Management button, and then click Spelling Variations. Clicking Spelling Variations opens the Spelling Variations dashboard. 5. Click the Add a word button to open the Add Spelling Variations dashboard. 6. In the Original Word field, type the original search term you want to add spelling variations. 7. In the Add one variation per line box, type each of the spelling variations for the search term you entered in the Original Word field. When adding multiple spelling variations, make sure that there is only one spelling variation per line. 8. On the dashboard toolbar, click the Add Word button. The original word and its spelling variations are added to the Spelling Variations list on the Spelling Variations dashboard. 9. When finished, click the Close button. To import a spelling variation list: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, locate and click the dataset to import a list of spelling variations. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Settings button, and then click Search Settings. 4. On the Search Settings toolbar, click the Knowledge Management button, and then click Spelling Variations. Clicking Spelling Variations opens the Spelling Variations dashboard. 5. In the Import Spelling Variations box, click the Browse button. 6. In the Choose File to Upload dialog box, navigate to and select the .csv file containing © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 245 the spelling variations to import, and then click Open. Clicking Open adds the file name and location to the Import Spelling Variations box. 7. Click the Import button. Clicking the Import button imports the spelling variations and adds the spelling variations to the Spelling Variations list on the Spelling Variations dashboard. 8. When finished, click the Close button. To export a spelling variation list: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, locate and click the dataset to export the spelling variations. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar,click the Settings button, and then click Search Settings. 4. On the Search Settings toolbar, click the Knowledge Management button, and then click Spelling Variations. Clicking Spelling Variations opens the Spelling Variations dashboard. 5. To export a list of spelling variations, from the list of spelling variation words, do one of the following: Click the check box for each spelling variation you want to export. Click the Select All link to export all the spelling variations in the list. 6. In the Export Spelling Variations section, click the Export button. 7. In the File Download dialog box, click Save. 8. In the Save As dialog box, navigate to where you want to save the .csv file. 9. In the File name field, type the file name. The Save as type field defaults to Microsoft Office Excel Comma Separated Value. 10. Click Save. 11. In the Download complete dialog box, click Open to view the .csv file or click Close to close the dialog box. 12. When finished, click the Close button To edit a spelling variation: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 246 Concordance Evolution 2. In the System pane on the left, click the dataset containing the spelling variation to edit. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar,click the Settings button, and then click Search Settings. 4. On the Search Settings toolbar, click the Knowledge Management button, and then click Spelling Variations. Clicking Spelling Variations opens the Spelling Variations dashboard. 5. In the Spelling Variations table, from the Words column, click the word link for the word you want to edit. 6. In the Edit Spelling Variations dashboard, make the applicable edits. 7. When finished, click the Update button. Clicking the Update button saves your edits, and closes the Edit Spelling Variations dashboard. To delete a spelling variation: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the dataset containing the spelling variation to edit. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar,click the Settings button, and then click Search Settings. 4. On the Search Settings toolbar, click the Knowledge Management button, and then click Spelling Variations. Clicking Spelling Variations opens the Spelling Variations dashboard. 5. In the Spelling Variation table, click the word link for the word you want to delete. 6. On the Edit Spelling Variations dashboard toolbar, click the Remove button. 7. When prompted to confirm the deletion, click OK. Managing the thesaurus If the Thesaurus feature is enabled, when a search runs, if the search term is associated with thesaurus words (synonyms) in the Thesaurus list, the search engine looks for the term and its associated thesaurus words, and returns both the term and its thesaurus words in the results. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 247 For example, if a word in the case documents contains other words with the same meaning, such as dog, hound, puppy, or canine, you can add each of the words to the Thesaurus list, and if someone searches on any version of dog, the search engine will include all words associated with dog in the search results. Administrators can add, edit, or delete thesaurus words and can import and export a thesaurus word list to and from a .csv file. To add a word to the thesaurus: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the dataset to add a thesaurus word. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Settings button, and then click Search Settings. 4. On the Search Settings toolbar, click the Knowledge Management button, and then click Thesaurus. Clicking Thesaurus opens the Thesaurus dashboard. 5. Click the Add a word link to open the Add Word to Thesaurus dashboard. 6. In the Original Word field, type the original search term you want to add synonyms to. 7. In the Add one synonym per line box, type each of the synonyms for the search term you entered in the Original Word field. When adding multiple synonyms, make sure that there is only one synonym per line. 8. On the dashboard toolbar, click the Add Word button. The original word and its synonyms are added to the Thesaurus list on the Thesaurus dashboard. Synonyms are listed by the search term entered in the Original Word field on the Add Word to Thesaurus dashboard. 9. Click the Close button to return to the dataset's dashboard. To import a thesaurus list: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the dataset to import a list of thesaurus words. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Settings button, and then click Search Settings. 4. On the Search Settings toolbar, click the Knowledge Management button, and then click Thesaurus. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 248 Concordance Evolution Clicking Thesaurus opens the Thesaurus dashboard. 5. In the Import Thesaurus section, click the Browse button. 6. In the Choose File to Upload dialog box, navigate to and select the thesaurus list's .csv file you want to import, and then click Open. Clicking Open adds the file name and location to the Import Thesaurus field. 7. Click the Import button. Clicking the Import button imports the thesaurus list and adds the thesaurus words and their synonyms to the Thesaurus list on the Thesaurus dashboard. 8. Click the Close button to return to the dataset's dashboard. To export a thesaurus list: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the dataset to export a list of thesaurus words. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Settings button, and then click Search Settings. 4. On the Search Settings toolbar, click the Knowledge Management button, and then click Thesaurus. Clicking Thesaurus opens the Thesaurus dashboard. 5. In the Thesaurus table, select the check box next to the words you want to export. To select all thesaurus words, select the check box at the top of the Thesaurus list. 6. In the Export Thesaurus section, click the Export button. 7. In the File Download dialog box, click Save. 8. In the Save As dialog box, navigate to where you want to save the .csv file. 9. In the File name field, type the file name. The Save as type field defaults to Microsoft Office Excel Comma Separated Value. 10. Click Save. 11. In the Download complete dialog box, click Open to view the .csv file or click Close to close the dialog box. 12. When finished, click the Close button To edit a word in the thesaurus: © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 249 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the dataset to edit thesaurus words. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Settings button, and then click Search Settings. 4. On the Search Settings toolbar, click the Knowledge Management button, and then click Thesaurus. Clicking Thesaurus opens the Thesaurus dashboard. 5. In the Thesaurus table, in the Words column, click the thesaurus word link. Clicking the thesaurus word link opens the Edit Synonyms dashboard. 6. Make the applicable edits. 7. Click the Update button. Clicking the Update button saves your edits, and closes the Edit Synonyms dashboard. 8. Click the Close button to return to the dataset's dashboard. To delete a word from the thesaurus: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the dataset delete a thesaurus word. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Settings button, and then click Search Settings. 4. On the Search Settings toolbar, click the Knowledge Management button, and then click Thesaurus. Clicking Thesaurus opens the Thesaurus dashboard. 5. In the Thesaurus table, click the word link for the word you want to delete, and then click the Remove button. 6. When prompted, click Yes to confirm the deletion. The word is deleted from the Thesaurus table. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 250 Concordance Evolution Managing stop words Stop words are the most common words in the English language (and, the, but, etc.). Stop words are not words that are generally searched for by reviewers. Stop words in the Stop Words list are automatically excluded from the search index and search queries, ensuring that searches run much faster and efficiently. Reviewers may request adding a specific word that is common to the case review documentation and needs to be avoided during searches. Administrators can add, edit, or delete stop words and can export the stop words list to a .csv file. The Stop Words list cannot contain any keywords used by the Vivisimo® Velocity® search engine. For a list of Velocity keywords, see About dataset fields. Commonly used stop words The following table contains a list of words commonly added to the stop words list for a dataset: Commonly Used Stop Words AN AND* AND/OR ANY* ARE AREN'T AS BE BEEN BEING BUT BY DO DOES DOESN'T FOR HAD HAS HAVE HAVING HE HE'LL HE'S HER HERE HERSELF HIM HIMSELF HIS IF INSTEAD IS ISN ISN'T IT IT'S ITS ITSELF LET LET'S LL MAYBE ME MERELY MR MRS MUCH MUST MY MYSELF NONE NOR NOT* NOTHING OF OFF OFTEN OKAY © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. PUT RE SAME SHE SHE'LL SO THAN THAT THAT'S THATS THE THEIR THEM THEMSELVES THEN THERE THERE'S THEREABOUTS THEREAFTER THEREFOR THEREFORE THEREOF THERETO THESE THEY THEY'D THEY'LL THEY'RE THIS WASN'T WE WE'D WE'LL WE'RE WE'VE WERE WEREN'T WHAT WHAT'S WHATEVER WHATSOEVER WHEN WHENEVER WHERE WHEREAS WHEREBY WHEREUPON WHETHER WHO WHOEVER WHOM WHOSE WITH WON'T WOULD WOULDN'T YET YOU Administrating Concordance Evolution HOWEVER I'D I'LL I'M I'VE I.E. OTHER OTHERS OUR PER PERHAPS PROBABLY THOSE THOUGH TO TOO VE WAS 251 YOU'D YOU'LL YOU'RE YOU'VE YOUR YOURS YOURSELF * Keyword used by Velocity To add a stop word: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the dataset for which you want to add stop word(s). Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Settings button, and then click Search Settings. 4. On the Search Settings toolbar, click the Knowledge Management button, and then click Stop Words. Clicking Stop Words opens the Stop Words dashboard. 5. In the Add Stop Words section, type the words you want to omit from the searching index. When adding multiple stop words, make sure that there is only one stop word per line. You can also copy and paste words into the Add Stop Words box. For example, you can copy the stop words from the .csv file of an exported stop words list and paste the words into the Add Stop Words box to quickly create a stop words list. 6. Click the Add Stop Words button. The new stop word(s) now display in the dataset's Stop Words table, and the new stop words will be excluded from the dataset's search index. 7. Click the Close button to return to the dataset's dashboard. To edit a stop word: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the dataset to edit the stop words list. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 252 Concordance Evolution 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Settings button, and then click Search Settings. 4. On the Search Settings toolbar, click the Knowledge Management button, and then click Stop Words. Clicking Stop Words opens the Stop Words dashboard. 5. In the Stop Words table, in the Stop Words column, click the stop word link. Clicking the stop word link opens the Edit Stop Word dialog box. 6. Edit the stop word. 7. Click the Update button. Clicking the Update button saves your edits, and closes the Edit Stop Word dialog box. 8. Click the Close button to return to the dataset's dashboard. To export a stop word list: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the dataset to export the stop words list. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Settings button, and then click Search Settings. 4. On the Search Settings toolbar, click the Knowledge Management button, and then click Stop Words. Clicking Stop Words opens the Stop Words dashboard. 5. In the Stop Words table, to select words to export, do any of the following: To select individual stop words, click the check box next to the stop word. To select all the stop words in the table, click the Select All link at the bottom of the table. 6. In the Export Stop Words section, click the Export button. 7. In the File Download dialog box, click Save. 8. In the Save As dialog box, navigate to where you want to save the exported file. 9. In the File name field, type the file name. The Save as type field defaults to Microsoft Office Excel Comma Separated Value. 10. Click Save. 11. In the Download complete dialog box, click Open to view the .csv file or click Close to close the dialog box. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 253 12. When finished, click the Close button To delete a stop word: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the dataset to delete stop words. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Settings button, and then click Search Settings. 4. On the Search Settings toolbar, click the Knowledge Management button, and then click Stop Words. Clicking Stop Words opens the Stop Words dashboard. 5. In the Stop Words table, select the check box for the stop word(s) you want to delete. 6. On the dashboard toolbar, click the Remove button. 7. When prompted, click Yes to confirm the deletion. The stop words are deleted from the dataset's Stop Words list. If documents in the dataset contain the deleted stop words, the deleted stop words will now be included in the dataset's search index. 8. Click the Close button to return to the dataset's dashboard. Managing reasons for redaction Administrators can create pre-defined redaction reasons so that when reviewers apply redactions to documents in the Near Native view, the reviewers can select one of the predefined reasons from the Enter Reason dialog box. Administrators can add, edit, or delete the redaction reasons, as well as import and export a .csv formatted file containing a list of redaction reasons. To add a reason for redaction: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the dataset for which you want to add redaction reasons. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 254 Concordance Evolution 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Settings button, and then click Search Settings. 4. On the Search Settings toolbar, click the Knowledge Management button, and then click Redaction Reasons. Clicking Redaction Reasons opens the Reasons for Redaction dashboard. 5. Click the Add a Reason for Redaction link to open the Add Reasons for Redaction dashboard. 6. In the Reason for Redaction field, type the redaction reason. 7. (Optional) In the Description field, type the redaction reason description. 8. Click the Add Reason button. The reason for redaction is added to the Reasons for Redaction table on the Reasons for Redaction dashboard. By default, the Add a reason for each redaction check box is selected. When the check box is selected, each time a reviewer applies a redaction in the Near Native view, the reviewer is required to assign a reason for redaction to the redaction. To make assigning a reason for redaction to redactions mandatory for reviewers, clear the Add a reason for each redaction check box. 9. To reorder the redaction reasons, in the Up/Down column, click the up or down arrow for a selected redaction reason. 10. When finished, click the Close button. To import a reasons for redaction list: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the dataset to import a list of redaction reasons. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Settings button, and then click Search Settings. 4. On the Search Settings toolbar, click the Knowledge Management button, and then click Redaction Reasons. Clicking Redaction Reasons opens the Reasons for Redaction dashboard. 5. In the Import a Reason for Redaction section, click the Browse button. 6. In the Choose File to Upload dialog box, navigate to and select the reason for redaction list's .csv file you want to import, and then click Open. Clicking Open adds the file name and location to the Import a Reason for Redaction field. 7. Click the Import button. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 255 Clicking the Import button imports the reason for redaction list and adds the redaction reasons to the Reasons for Redaction table on the Reasons for Redaction dashboard. 8. When finished, click the Close button. To export a reasons for redaction list: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the dataset to export a list of redaction reasons. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Settings button, and then click Search Settings. 4. On the Search Settings toolbar, click the Knowledge Management button, and then click Redaction Reasons. Clicking Redaction Reasons opens the Reasons for Redaction dashboard. 5. In the Reasons for Redaction table, to select redaction reasons for export, do one of the following: To select individual redaction reasons, click the check box next to the redaction reasons to export. To select all redaction reasons, click the Select All link at the bottom of the redaction reasons table. 6. In the Export a Reason for Redaction section, click the Export button. 7. In the File Download dialog box, click Save. 8. In the Save As dialog box, navigate to where you want to save the .csv file. 9. In the File name field, type the file name. The Save as type field defaults to Microsoft Office Excel Comma Separated Value. 10. Click Save. 11. In the Download complete dialog box, click Open to view the .csv file or click Close to close the dialog box. 12. When finished, click the Close button To edit a reason for redaction: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the dataset containing the redaction reason to edit. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 256 Concordance Evolution 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Settings button, and then click Search Settings. 4. On the Search Settings toolbar, click the Knowledge Management button, and then click Redaction Reasons. Clicking Redaction Reasons opens the Reasons for Redaction dashboard. 5. In the Reasons for Redaction table, click the redaction reason link in the Reason column. Clicking the redaction reason link opens the Edit Reason for Redaction dashboard. 6. Make the applicable edits. 7. Click the Update Reason button. Clicking the Update Reason button saves your edits, and closes the Edit Reason for Redaction dashboard. 8. When finished, click the Close button. To delete a reason for redaction: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the dataset containing the redaction reasons to delete. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Settings button, and then click Search Settings. 4. On the Search Settings toolbar, click the Knowledge Management button, and then click Redaction Reasons. Clicking Redaction Reasons opens the Reasons for Redaction dashboard. 5. In the Reasons for Redaction table, select the redaction reason link you want to delete. 6. On the Edit Reason for Redaction dashboard toolbar, click the Remove button. 7. When prompted, click Yes to confirm the deletion. The stop words are deleted from the dataset's Stop Words list. If documents in the dataset contain the deleted stop words, the deleted stop words will now be included in the dataset's search index. 8. When finished, click the Close button. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 257 Searching - Admin Running admin dashboard searches There are two ways to search in the Admin dashboard. You can search the System pane for a specific folder, matter, or dataset using the search field in the System pane, or the Admin Search bar in the Admin dashboard to search the entire system or specific categories in the Admin dashboard. To search using the System pane: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane search field, type your search term. 3. Click the Find button. 4. The search term is highlighted in yellow in the system. To search using the Admin Search bar: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the Admin Search bar, type your search term, click the magnifying glass button, , and then select the check box next to the search category you want to search. By default, all the category check boxes are selected. To search the entire system, click the Select All check box. 3. Click the Search button. The search results are displayed on the Search Result dashboard. Results are organized by category. To view the search results in a category, click the right arrow, , next to the category. To close the search results in a category, click the down arrow, , next to the category. 4. To view a specific item on the Search Result dashboard, click the item's name link in the Name column. 5. To view a user in the User Names category, click the user name link in the Login Id column. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 258 Concordance Evolution Search Settings Defining dataset search settings The Search Settings dashboard in the Admin dashboard is used to define the document search settings for a dataset in the Review dashboard. The search settings are defined for each dataset, and determine whether concept searching is enabled in the Review dashboard, the amount of data previewed for search results in the Snippet view, and whether the Concordance Evolution thesaurus, dictionary, stop words, and/or reasons for redaction are used for searching and applying redactions in the Review dashboard. By default concept searching, the thesaurus, stop words, spelling variations, and the reasons for redaction are all enabled for searching and applying redactions in the Review dashboard. To define a dataset's search settings for the Review dashboard: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, click the dataset you want to add a tag group. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Settings button, and then click Search Settings. Clicking Search Settings opens the Search Settings dashboard. 4. In the Concept Searching section, to enable or disable concept searching in the Review dashboard, select or clear the Allow Concept Searching check box. By default the Allow Concept Search check box is selected in the Concept Searching section. When the check box is selected, concept searching is enabled for the dataset in the Review dashboard, and the Concept Searching check box is displayed in the Quick Search bar in the Review dashboard. When you clear the Allow Concept Searching check box, concept searching is disabled for the dataset in the Review dashboard, and the Concept Searching check box is removed from the Quick Search bar in the Review dashboard. 5. In the Preview Size field, type the number of kilobytes (KB) to display for each document listed in the Snippet view of the Review dashboard. The Preview Size field defaults to 50 kilobytes. 6. In the Customize Knowledge Base section, enable or disable the features you want include or exclude from searches in the Review dashboard. You can use the Concordance Evolution thesaurus, stop words, spelling variations, and reasons for redaction for searching and applying redactions in the Review dashboard. By default, all the options are selected, the features are enabled and used for searches in the Review dashboard. When you clear the check boxes, the features are disabled and are not used for searches in the Review dashboard. For more information about the knowledge base settings, see Managing the knowledge base. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 259 7. When finished, click Save to save the dataset's search settings. To manage the knowledge base settings for a dataset: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System pane on the left, locate and click the dataset you want to add a field. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Settings button, and then click Search Settings. 4. On the Search Settings dashboard toolbar, click the Knowledge Management button, and then click Spelling Variations. By default, the Thesaurus, Stop Words, Spelling Variations, and Reasons for Redaction check boxes are selected in the Customize Knowledge Base box for each dataset. When a check box is selected, the feature is enabled for the dataset. When a check box is not selected, the feature is disabled for the dataset. 5. In the Customize Knowledge Base box, verify the knowledge base settings. 6. Select the check boxes for the knowledge base features you want to be enabled for the dataset. 7. Clear the check boxes for the knowledge base features you want to be disabled for the dataset. When the Thesaurus and Spelling Variations check boxes are selected, reviewer search results will include the spelling variations and synonyms defined by the administrator in the knowledge base. When the Reason for Redaction check box is selected, reviewers will be able to add redaction reasons while applying redactions in the Near Native view. When the Stop Words check box is selected, the stop words in the stop words list are automatically excluded from search queries when running searches in the dataset. 8. Click Save. Clicking Save applies the knowledge base settings to the dataset in the current session. Managing saved search results You can view the saved search results on the Manage Saved Search Results dashboard, which displays the search result number, search results name, search query, Binder:Review Set name, number of documents, the date and time the search was saved, and the user who saved the search. Search results do not display until the background task is completed. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 260 Concordance Evolution When you save, compare, or export search results, the process can run as a background task while you continue working. When the compare or export process completes, you will receive a notification with a link to open the .csv file. When you delete a saved search result, it is deleted from the list on the Saved Search Results tab. Any .csv files that were made to compare the results and were saved within the dataset directory location are also deleted. Any .csv files that are saved outside the dataset directory location will not be deleted. To view saved search results: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System Tree pane on the left, click the dataset you want to add a tag group. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Settings button, and then click Saved Search Results. The Manage Saved Search Results dashboard is displayed. To compare search results from a previous query: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System Tree pane on the left, click the dataset to run the compare option. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Settings button, and then click Saved Search Results. 4. In the Manage Saved Search Results table, locate the query you want to compare, and then click the Compare link. 5. Click the Run in Background button to continue working while the process completes. The search query is rerun on the dataset or review set. Clicking the Run in Background button helps ensure that the process saves properly, especially for search results with a large number of documents. You will receive a notification when the process completes. The notification will contain a link so you open the exported .csv file. 6. Open the exported .csv file. To compare the data to a previous saved search result, the data must first be exported to a .csv file. When you rerun the query, results from both searches are saved in the same spreadsheet for comparison. To export search results: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 261 2. In the System Tree pane on the left, click the dataset to export the search results. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Settings button, and then click Saved Search Results. 4. In the Manage Saved Search Results table, locate the search results you want to export, and then click the Export link. 5. In the File Download dialog box, click Save. 6. In the Save As dialog box, type a name for the search results file in the File name field. 7. Navigate to the directory folder where you want to save the file, then click Save. 8. When finished in the Download Complete dialog box, click Close. To delete saved search results: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. In the System Tree pane on the left, click the dataset to export the search results. Clicking the dataset opens the dataset's dashboard. 3. On the dataset's dashboard toolbar, click the Settings button, and then click Saved Search Results. 4. In the Managed Saved Search Results table, locate the search results you want to delete, and then click the Remove button. 5. When prompted, click Yes. The search results listing is now deleted from the Manage Saved Search Results table. Managing Persistent Highlight Persistent Highlight terms can be added and deleted from the list. To save time, a list of terms from a text (.txt) or comma-separated value (.csv) formatted file can be imported and the terms are automatically assigned a color. You can also export selected terms to a comma-separated value (.csv) formatted file. If you do not have permission to edit the Persistent Highlight terms, contact your Concordance Evolution administrator to make changes. Keep the following in m ind when adding highlight term s: Terms are limited to 150 characters Terms may not contain boolean operators (i.e., AND, OR, NOT) © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 262 Concordance Evolution Terms may not contain special characters (i.e., &,%:;) Terms cannot be Concordance Evolution stop words Terms in an import list may only contain one term per line Persistent Highlight is not available for production or image sets. To add a Persistent Highlight term: 1. From the System pane, locate and open the dataset you want to add Persistent Highlight terms. 2. On the Dataset Management dashboard toolbar, click the Settings button, and then click Persistent Highlight. The Persistent Highlight Management dashboard is displayed. 3. On the Persistent Highlight Management dashboard, click the Add a Highlight Term button. 4. In the Term field, type the term. 5. From the Color list select the color to highlight the term when viewing documents, and then click Save. The term is added to the Highlight Term table. To filter the list of terms shown in the table: 1. From the System pane, locate and open the dataset you want to filter Persistent Highlight terms. 2. On the Dataset Management dashboard toolbar, click the Settings button, and then click Persistent Highlight. The Persistent Highlight Management dashboard is displayed. 3. On the Persistent Highlight Management dashboard, in the Highlight Term column, click the Filter button . 4. To filter by one set criteria, do the following, and then click Filter: From the items with value that list, select the comparison command. Type the term in the field to filter on. 5. To filter by multiple criteria, do the following, and then click Filter: From the items with value that list, select the comparison command, and then type the term in the field to filter on. From the boolean list, select a boolean operator, and then type the term in the field to filter on. 6. To clear the filter(s), click the Filter button , and then click Clear. To enable or disable a Persistent Highlight term: © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 263 1. From the System pane, locate and open the dataset you want to add Persistent Highlight terms. 2. On the Dataset Management dashboard toolbar, click the Settings button, and then click Persistent Highlight. The Persistent Highlight Management dashboard is displayed. 3. On the Persistent Highlight Management dashboard, do one of the following: For the term you want to enable, and then in the Actions column, click the Enable link. For the term you want to enable, and then in the Actions column, click the Disable link. To edit a Persistent Highlight term: 1. From the System pane, locate and open the dataset you want to add Persistent Highlight terms. 2. On the Dataset Management dashboard toolbar, click the Settings button, and then click Persistent Highlight. The Persistent Highlight Management dashboard is displayed. 3. On the Persistent Highlight Management dashboard, in the Actions column, click the Edit link. 4. In the Edit Highlight Term dialog box, make the necessary changes, and then click the Save button. To delete a Persistent Highlight term: 1. From the System pane, locate and open the dataset you want to add Persistent Highlight terms. 2. On the Dataset Management dashboard toolbar, click the Settings button, and then click Persistent Highlight. The Persistent Highlight Management dashboard is displayed. 3. On the Persistent Highlight Management dashboard, do one of the following: Locate the term you want to delete, and then in the Actions column, click the Delete link. Click the check box for the term you want to delete, and then at the top of the table, click the Delete button. 4. In the Term field, type the term. 5. From the Color list select the color to highlight the term when viewing documents, and then click Save. The term is added to the Highlight Term table. To import a list of Persistent Highlight terms: © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 264 Concordance Evolution When importing a list, if any imported terms do not meet the term criteria described above, the term's status will be set to false until the term is edited. 1. From the System pane, locate and open the dataset you want to import a list of Persistent Highlight terms. 2. On the Dataset Management dashboard toolbar, click the Settings button, and then click Persistent Highlight. The Persistent Highlight Management dashboard is displayed. 3. In the Import List of Highlight Terms section, click the Browse button. 4. Locate and click the list file that contains the terms you want to import, and then click Open. 5. When ready, click the Import button. The terms are added to the list of Persistent Highlight terms and automatically assigned a color. To export a list of Persistent Highlight terms: 1. From the System pane, locate and open the dataset you want to export a list of Persistent Highlight terms. 2. On the Dataset Management dashboard toolbar, click the Settings button, and then click Persistent Highlight. The Persistent Highlight Management dashboard is displayed. 3. In the Highlight Term table, do one of the following: To export specific Highlight Terms, select the check box for each term you want to export. To export all the Highlight Terms listed on the current page of terms, click the check box at the top of the column. To export all the Highlight Terms on all pages, click the Select All button. 4. In the Export List of Highlight Terms section, click the Export button. 5. Locate and click the list file that contains the terms you want to import, and then click Open. 6. When prompted, save the file to your local directory. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 265 Reporting Audit Logs About audit logs Audit Logs provide an account of events in Concordance Evolution both at the system and matter level. Events are records of user actions throughout the application, such as user access and data modification. The System Audit Log helps administrators track the system actions users performed during a session. The Matter Audit Log records the events of user's actions for a given matter such as searching, tagging and documents viewed. Related Topics Viewing the System Audit Log Viewing the Matter Audit Log Exporting Audit Logs Archiving System events Viewing the system audit log The System Audit Log is displayed on the Audit Management dashboard and provides a list of all events created in the system. The Audit Management dashboard displays the Event Date/ Time, Event Type, Event Name, Performed By, and Description. The System Audit Log displays information for each of the following event types: Event type Description AD Domain An Active Directory Domain was added or modified Auditing An audit log was exported Folder A folder was created, deleted, or modified Licensing A seat license was added, removed, assigned or unassigned Login Logout A user session created, failed, or ended Matter A matter was created, deleted or modified Notifications A notification was sent Organization An organization was created, deleted, or modified Security A security role was created, deleted, or © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 266 Concordance Evolution modified User A user was created, deleted, or modified User Group A user group was created, deleted, or modified The events shown on the Audit Management page can be exported to a comma-separated (.csv) formatted file. For more information, see Exporting Audit Logs. To view events in the Audit Log: 1. Do one of the following: Point to the Admin tab, and then click System Audit Log. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard, and then on the Admin toolbar click the System Audit Log button. The Audit Management dashboard opens. By default, the Audit Management dashboard displays the 10 most recent events. To change the number of events displayed, in the lower right corner, from the Items Per Page list, select the number of events to display. 2. To refine the results, do any of the following: To view events by date, from the Filter By Last Modified list, select the days to display. To view events by type, from the Filter By Event Type list, select the check box for one or more event types to display. To view events by the user(s) who executed the event, from the Filter Performed By list, select the check box for one or more users to display. 3. To locate a specific event or events, type a value in the field below a column header and then press Enter to search for events that match the value specified. Only one value is allowed in each column header field. 4. To reset the event list back to the original list, do one of the following: Delete the field value and press Enter. Click the Clear link. Viewing the matter audit log The Matter Audit Log is displayed on the Audit Management dashboard and provides a list of all events created in the matter. The Audit Management dashboard displays the Event Date/Time, Event Type, Event Name, Performed By, and Description. The Matter Audit Log displays information for each of the following event types: © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution Event type Description Binder A binder was created, deleted, or modified CaseMap A fact, document, link or text was sent to CaseMap Dataset A dataset was created, deleted or modified Document A document was viewed (Near Native or Document Data views), added, deleted, modified, downloaded, emailed, exported, produced tagged, untagged, or printed Markup A markup was created, deleted, or modified Review Set A review set was created, deleted, or modified Search A search was executed and saved search results were created, deleted, or modified Search Administration A search was executed using the quick search bar on the Admin dashboard Tagging A tag was created, deleted, modified, queried, or the tag was applied or removed 267 The events shown on the Audit Management page can be exported to a comma-separated (.csv) formatted file. For more information, see Exporting Audit Logs. To view events in the Matter Audit Log: 1. In the System pane, locate and open the matter you want to view audit events. 2. On the Matter's dashboard toolbar, click the Audit Log button. The Audit Management dashboard opens. The Audit Management dashboard opens. By default, the Audit Management dashboard displays the 25 most recent events. To change the number of events shown in the table, in the lower right corner, from the Items Per Page list, select the number of events to display. 3. To refine the results, do any of the following: To view events by date, from the Filter By Last Modified list, select the days to display. To view events by type, from the Filter By Event Type list, select the check box for one or more event types to display. To view events by the user(s) who executed the event, from the Filter Performed By list, select the check box for one or more users to display. 4. To locate a specific event or events, type a value in the field below a column header and then press Enter to search for events that match the value specified. Only one value is allowed in each column header field. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 268 Concordance Evolution 5. To reset the event list back to the original list, do one of the following: Delete the field value and press Enter. Click the Clear link. Exporting an audit log The Audit Log can be exported to a comma-separated (.csv) formatted file. You can export the entire table of events or you can select specific events. To export audit log events: 1. To export the event of an audit log, do one of the following: To export the System Audit Log events, on the Admin dashboard, and then on the Admin toolbar click the System Audit Log button. To export the Matter Audit Log events, from the System pane, locate and open the matter to export events, and then on the matter's dashboard toolbar click the Audit Log button. 2. Do any of the following to refine the results: To view events by date, from the Filter By Last Modified list, select the number of days to display. To view events by type, from the Filter By Event Type list, select the check box for one or more event types to display. To view events by the user(s) who executed the event, from the Filter Performed By list, select the check box for one or more users to display. 3. From the results, do one of the following: To select all the events to export, select the check box in the upper left corner of the Events table or in the bottom left corner, click the Select All link. To one or more events to export, select the check box for each event. 4. On the Audit Management toolbar, click the Export Audit Log Events. 5. In the File Download dialog box, do one of the following: Click Open to view the file, in the Download Complete dialog box, click Open to open the file in your default spreadsheet application. Click Save to save the file, in the Save As dialog box, navigate to where you want to save the file, and then in the File Name field, type the file name and click Save. 6. In the Download Complete dialog box, click Open to view the file or click Close to close the dialog box. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 269 Archiving system events To prevent the server where the audit events are stored from getting bogged down with an endless amount of audit events, Concordance Evolution automatically archives the audit events and then deletes the events from the server. When Concordance Evolution servers are set up, the archive folder location and the maximum number of days to store system events on the server are specified. When the number of days is reached, Concordance Evolution exports the events as a comma-separated (.csv) formatted file and stores the file in the specified location. The exported .csv file is dated and saved using the following naming format: <Archive Date-Archive Time>_System_Audit_Log.csv For example, 20140325-09.33.38_EVMaster_SystemAuditLog.csv All archive audit file names are time stamped using Greenwich Mean Time (GMT). The default location on the SQL Server for the archive folder is: C:\ConcordanceEV \EV_AgentJobLogs\SystemAuditLogArchive and the default number of days is 90. These settings can be edited to meet your organization's needs. To edit the system audit archive settings: 1. From the Admin tab, click Servers. 2. Locate the SQL Server and click the server name link. 3. In the Services column, click the System Configuration Service link. 4. On the System Configuration Service tab, do any of the following: To change the number of days the audit events are stored on the server, in the System audit log archival days field, type the number of days. To change the location of the archive folder, in the System audit log archival location field, type the path for the archive folder. 5. When finished, on the Configure Services dashboard toolbar, click Save. Billing Reports Creating billing reports The billing report provides information regarding the file count size for native documents and image sets for each matter in an organization. To generate a billing report: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard. 2. On the System toolbar, click the Billing Report button. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 270 Concordance Evolution The Billing Report dialog box is displayed. 3. To change the number of items shown in the table, in the Items Per Page list, select the number of items to display. 4. To export a billing report, do any of the following: To export a report for a single matter, click the check box for the matter. To export a report for multiple matters, click the check box for each matter you want to include in the report. To export a report for all the matters in the system, click the Select All button. At any time you can use the Clear All button to clear the matter selections. However, please be aware that this also clears all Filter settings as well. 4. When finished, click Export. 5. When prompted that the billing report job is completed, click the Please click here to download billing report link. 6. In the File Download dialog box, do one of the following: Click Open to view the file, in the Download Complete dialog box, click Open to open the file in your default spreadsheet application. Click Save to save the file, in the Save As dialog box, navigate to where you want to save the file, and then in the File Name field, type the file name and click Save. 7. In the Download Complete dialog box, click Open to view the file or click Close to close the dialog box. The exported billing report contains the following information: Organization Matter name Users Count of Native Files Size of Native Files (MB) Count of Images Size of Images (MB) Total Size of Native + Images (MB) Database Size (MB) Total Size of Matter (MB) The report can also be accessed from the Notification Management dashboard, see Viewing notifications. To filter the list of matters and organizations: 1. Click the Admin tab to open the Admin dashboard, and then on the System toolbar click the Billing Report button. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 271 The Billing Report dialog box is displayed. 2. In the Billing Report dialog box, do one of the following: In the Matter column, click the Filter button . In the Organization column, click the Filter button . 3. To filter by a single term, from the items with value that list, select the comparison command, and then type the term in the field. 4. To filter by multiple terms, from the items with value that list, select the comparison command, type the first term in the field, select a boolean operator to use to combine the search terms, and then type the second term in the field. 5. When ready click Filter. 6. To clear the filter(s), in the Matter or Organization column click the Filter button then click Clear. , and Matter reports Viewing matter reports Concordance Evolution provides matter-level reports for tracking reviewer activity such as document comments, document edits, markups applied, tags applied, and documents viewed. When a matter dashboard is opened, the default matter report is displayed at the bottom of the page. Concordance Evolution ships with the following system reports: System Report Description Events Document Comments Displays the number of comments for all active users for the current date Comment Created Document Edits Displays the number of documents that were Document Modified changed/edited in the matter per user for the current date Markup Displays a line chart with the number of markups applied to documents per user in the matter for the current date Productivity Displays a bar type chart for the listed events Comment Created, for all active users for the current date Document Modified, Markup Created, Document Tagged, Document Viewed Document Data, Document Viewed Near Native Tag Displays the tag name and the number of times the tag was applied Markup Created Document Tagged © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 272 Concordance Evolution View Documents Displays the number of documents viewed in the Near Native or Document Data views Document Viewed Document Data, Document Viewed Near Native System matter reports cannot be overwritten. However, a system matter report can be used as a template and saved under a different report name. To view a matter report: 1. In the System pane, locate and open the matter to view reports. 2. In the Reports section, the default report is displayed. 3. To change between reports, select the report from the report list. 4. To view more details, click the View Report button. The Matter Reports dashboard opens. To change the chart display: You can use the matter report tools to adjust the information displayed on the chart. System matter reports can be adjusted to display the information that fits your needs; however, the system reports cannot be overwritten. To save the changes, you need to save the report using a different report name. 1. In the System pane, locate and open the matter to view reports. 2. In the Reports section, from the Reports list, select the report to show. 3. To open the Matter Reports dashboard, click the View Report button. 4. To show/hide the matter chart or grid, from the Display list, click Chart or Grid. A check mark next to the option indicates the display is activated. 5. To display a bar or line chart, from the Display list, click Bar or Line. A check mark next to the option indicates the current active chart option. 6. To show/hide the chart legend, from the Display list, click Legend. A check mark next to the option indicates the legend is displayed above the chart. 7. To show/hide the chart labels, from the Display list, click Labels. A check mark next to the option indicates the labels are shown in the chart. To change the display filters: © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 273 You can use the matter report tools to adjust the information displayed on the Matter Reports dashboard. 1. In the System pane, locate and open the matter to view reports. 2. In the Reports section, click the View Report button. The matter reports dashboard opens. You can use one of the system reports as a template and then save the changes under a new report name. 3. To change the reporting dates, from the Date Range list do any of the following: Click Custom and then specify the from and to dates in the date fields to display the data for dates that fall between the specified dates. Click Today (default) to display only the events from the current date. Click Yesterday, to display the data for the previous day's events. Click Last 7 Days to display the data for the previous seven days from the date the report is executed. Click Last 30 Days to display the data for the previous 30 days from the date the report is executed. Click Last 60 Days to display the data for the previous 60 days from the date the report is executed. Click Last 90 Days to display the data for the previous 90 days from the date the report is executed. 4. To specify the scale values, from the Group By list do any of the following: Click User to show the data for all users for the datasets within the matter for the date(s) specified. Click Hourly to show the data for the hour of the day for the date(s) specified. Click Hour of Day to show the data for every hour of the day for the date(s) specified. Click Daily (Default) to show the data for each day for the date(s) specified. Click Day of Week to show the data for each day of the week for the date(s) specified. Click Weekly to show the data for the week Sunday thru Saturday of the date(s) specified. Click Monthly to show the data for the month of the date(s) specified. Click Month of Year to show the data for each month of the date(s) specified. Click Quarterly to show the data for the monthly quarter of the date(s) specified. Click Yearly to show the data for the yearly totals of the date(s) specified. The Group By options display the scale values displayed for the X-axis of the Bar and Line chart and the first column of the Grid table. 5. To specify the variables, from the Summarize By list select one of the following: Click User to summarize the variables by user(s) assigned to the matter for the date(s) specified. Click Event to summarize the variables by event(s) that occurred in the matter for the date(s) specified. Click Tag Name to summarize the variables by tag name(s) applied to the matter for the date(s) specified. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 274 Concordance Evolution The Summarize By option defines the list of variables shown in the legend and the column names of the Grid table. 6. To specify additional filters, click the More Filters link. 7. To add or remove an event(s), do any of the following: If events are listed, click any event, and then click an event from the list. If no events are listed, click the Select... link, and then click an event from the list. To remove an event, click the (X) next to the event name. Available Events Events Document Viewed Document Data Document Created Document Viewed Near Native Document Deleted Document Modified Document Downloaded Document Tagged Document Emailed Markup Created Document Printed Document link Sent to CaseMap Document Untagged Send One or More Documents Markup Deleted Fact Sent To CaseMap Tag Created Comment Deleted Tag Deleted 8. To add or remove a specific matter user(s), do any of the following: To add a user, click the Select... link, and then select the user(s) to include in the report. To remove a user, click the (X) next to the user name. 9. To add or remove a specific matter tag(s), do any of the following: To add a tag, click the Select... link, and then select the tag(s) to include in the report. To remove a tag, click the (X) next to the tag name. Creating custom matter reports The Matter Reports dashboard provides several tools for creating and saving customized matter reports. Custom matter reports can be saved as Public or Private. Public reports are available to any user that has access to the matter's dashboard and can be edited or deleted. You can use the default Concordance Evolution matter reports as a basis for creating a custom report, however, you cannot overwrite any of the default Concordance Evolution system matter reports. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 275 To create a custom matter report: 1. In the System pane, locate and open the matter to view reports. 2. In the Reports section, click the View Report button. The matter reports dashboard opens. You can use one of the system reports as a template and then save the changes under a new report name. 3. To define the type of report to create, from the Display list, do the following: Click Chart to display the graph. Click Grid to display the grid table below the graph. Click Bar or Line to display a bar or line type graph. Click Legend to show/hide the chart legend. Click Labels to show/hide the chart labels. A check mark next to the option indicates the selected options. 4. To specify the report dates, from the Date Range list do any of the following: Click Custom and then specify the from and to dates in the date fields to display the data for dates that fall between the specified dates. Click Today (default) to display only the events from the current date. Click Yesterday, to display the data for the previous day's events. Click Last 7 Days to display the data for the previous seven days from the date the report is executed. Click Last 30 Days to display the data for the previous 30 days from the date the report is executed. Click Last 60 Days to display the data for the previous 60 days from the date the report is executed. Click Last 90 Days to display the data for the previous 90 days from the date the report is executed. 5. To change the scale values, from the Group By list do any of the following: Click User to show the data for all users for the datasets within the matter for the date(s) specified. Click Hourly to show the data for the hour of the day for the date(s) specified. Click Hour of Day to show the data for every hour of the day for the date(s) specified. Click Daily (Default) to show the data for each day for the date(s) specified. Click Day of Week to show the data for each day of the week for the date(s) specified. Click Weekly to show the data for the week Sunday thru Saturday of the date(s) specified. Click Monthly to show the data for the month of the date(s) specified. Click Month of Year to show the data for each month of the date(s) specified. Click Quarterly to show the data for the monthly quarter of the date(s) specified. Click Yearly to show the data for the yearly totals of the date(s) specified. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 276 Concordance Evolution The Group By options display the scale values displayed for the X-axis of the Bar and Line chart and the first column of the Grid table. 6. To change the variables, from the Summarize By list select one of the following: Click User to summarize the variables by user(s) assigned to the matter for the date(s) specified. Click Event to summarize the variables by event(s) that occurred in the matter for the date(s) specified. Click Tag Name to summarize the variables by tag name(s) applied to the matter for the date(s) specified. The Summarize By option defines the list of variables shown in the legend and the column names of the Grid table. 7. To add or remove an event(s), do any of the following: If events are listed, click any event, and then click an event from the list. If no events are listed, click the Select... link, and then click an event from the list. To remove an event, click the (X) next to the event name. Available Events Events Document Viewed Document Data Document Created Document Viewed Near Native Document Deleted Document Modified Document Downloaded Document Tagged Document Emailed Markup Created Document Printed Document link Sent to CaseMap Document Untagged Send One or More Documents Markup Deleted Fact Sent To CaseMap Tag Created Comment Deleted Tag Deleted 8. To add or remove a specific matter user(s), do any of the following: To add a user, click the Select... link, and then select the user(s) to include in the report. To remove a user, click the (X) next to the user name. 9. To add or remove a specific matter tag(s), do any of the following: To add a tag, click the Select... link, and then select the tag(s) to include in the report. To remove a tag, click the (X) next to the tag name. 10. When finished, on the report's dashboard toolbar, point to the Save button, and then do any of the following: To save the report as new, select the New option. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution 277 To replace the report settings for an existing report, select the Overwrite option. To save the report so that only you can view it, select the Private check box. To save the report so that other users can view it, clear the Private check box. If you are using a system report as template, the Overwrite option is not available and the report must be saved using a new report name. 11. Type the report name in the field, and then click Save. 12. When prompted that the report was saved successfully, click the close button (X) to close the dialog box. 13. To set the report as the default report to appear on the matter's dashboard, on the report's dashboard toolbar, click the Set as Default button. The report automatically display on the matter's dashboard each time the dashboard is opened. The report name appears in the report list with a red asterisk (*) next to the report name indicating it is the default report. Deleting matter reports All custom matter reports can be deleted. System reports cannot be deleted. To delete a matter report: 1. In the System pane, locate and open the matter to view reports. 2. In the Reports section, click the View Report button. 3. On the dashboard toolbar, select the report to delete from the reports list, and then click the Delete button. 4. When prompted, click Yes to confirm the deletion. Exporting matter reports Concordance Evolution matter reports can be exported to a comma-separated (.csv) formatted file and saved for later use. Matter reports export as a comma-separated (.csv) formatted files for Internet Explorer 10 or later and as a text (.txt) formatted file for Internet Explorer 9, Chrome, Firefox, and Safari. The Export feature is not compatible for Internet Explorer 8 or earlier. To export a matter report: © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 278 Concordance Evolution 1. In the System pane, locate and open the matter to view reports. 2. In the Reports section, click the View Report button. 3. On the dashboard toolbar, select the report to export from the reports list. The report is displayed in the dashboard. 4. Make any necessary changes. 5. When finished, on the dashboard toolbar, click the Export button. The data from the report is displayed in a new browser window. 6. In the Save HTML Document dialog box, navigate to the location to save the file, type a name for the file, and then click Save. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Administrating Concordance Evolution User Guide Reference Information Chapter 6 280 Concordance Evolution Reference Information Unicode support The Unicode Standard provides a consistent way to digitally represent the characters used in the written languages of the world. As an accepted universal standard in the computer industry, the Unicode Standard assigns each character a unique numeric value and name. This encoding standard provides a uniform basis for processing, storing, searching, and exchanging text data in any language. Concordance Evolution supports importing load and LAW PreDiscovery case files, viewing, exporting, producing, and searching Unicode. However, the application itself cannot be localized. Searching Unicode is shown only for the space bounded occurrences of the search expression. Unicode searches cannot be used in conjunction with concept, spelling variation or the thesaurus. Glossary A - L (Alert - LAW PreDiscovery) Alert There is a notification called a search alert that can be set up to alert users when the search results for a saved search query change. Both administrators and users can create search alerts. Search alerts are system generated notifications that are sent to the users selected when the search alert was created. Bates Numbering Documents in litigation collections are assigned a unique sequential number on each page of every document. These numbers are referred to as Bates numbers (named after the Bates automatic numbering machine) and are used to identify a document or page. In Concordance, these numbers are often referred to as BEGNO (beginning number) and ENDNO (ending number). Brava IGC Brava! Enterprise and IGC Redact-It Enterprise are used to provide Concordance Evolution with a near native viewer in order to view, annotate and redact multiple file formats in a single interface. Concept Search © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Reference Information 281 When a search query is run, the system finds synonyms and similar concepts to return additional results. When the concept search check box is not selected, Concordance Evolution will not return the additional synonyms and concepts. Content Field The content field can store all OCR content. A dataset can only have one content field. The content can store rich-text, alphanumeric characters and stores up to 2 GB. Database Server This server is the primary SQL server for storing configuration data, metadata and work product. It also acts as the reporting infrastructure back-end. Dataset Datasets created under matters can be used to organize the documents for your client cases. DCN (Document Control Number) The DCN field is a system created field that stores a dataset’s document control number. The administrator can define the prefix and length at the time of dataset creation. The DCN field cannot be deleted. A dataset can only have one DCN field. Delimited file A digital file that has a text qualifier, a delimiter, and a line separator to structure data uniformly. Deponent A person who testifies under oath, especially in writing. Deposition The memorialized minutes of an interview between a member of the legal profession and a litigant or witness. Document In Concordance Evolution, a document record is a record associated with a logical combination of pages. With paper, this term refers to collections of pages. With electronic files, this term refers to a digital file. Document Data View Document Data view displays the entire contents of the document. This view is similar to © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 282 Concordance Evolution the traditional Concordance Browse view. Electronic Data Discovery (EDD) or E-Discovery The process of collecting electronic files. Folder Folders created under the system can be used to represent your clients. Folders store matters and datasets. Group By The Group By panel is a great tool for gaining an item count for a specific field, organizing documents by field type, narrowing search results off a reduced set of records, and performing quick quality assurance checks. The Group By panel is similar to the Tally feature in traditional Concordance. Jobs In Concordance Evolution, certain tasks, such as running imports, exports, print jobs, and productions, or creating review sets, are performed using jobs. LAW PreDiscovery LAW PreDiscovery® software offers you and your litigation teams the power to produce and organize paper and electronic files with a dynamic imaging and electronic discovery processing application. With LAW PreDiscovery, pre-reviewing and culling non-responsive e-discovery and scanned documents before reviewing and processing helps you eliminate unnecessary costs and reduce time. M - Z (Markups - Web Server(IIS)) Markups Subjective text, notes, or symbols placed on a graphical image by a reviewer, which represent subjective information about the image. Matter Matters created under client folders can be used to represent your client cases. Matters are used to store datasets. Metadata Properties associated with a document that might or might not be contained within the body of the document, including the author, the creation date, and last modified date. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Reference Information 283 Microsoft SQL Server Microsoft SQL Server is a relational model database server produced by Microsoft. Multi-page TIFF A specific type of Tagged Image File Format (TIFF) image file in which many pages are combined into a single .TIF file. Native File An original electronic document. For example, Microsoft® Word document, Excel® document, Adobe ® PDF document, etc. Native View Native view allows you to view documents in the source software program. Near Native View The Near Native viewer allows you to view and redact electronic files, emails, and attachments without the need to have the software program installed. The viewer maintains the formatting of the files so that you can see them as they were originally created. The Near Native viewer is supported by Brava from Informative Graphics. Notifications Notifications are messages sent by the system or administrator to Concordance Evolution users. They can be used to request users to log out of Concordance Evolution, to notify users when a job, such as an import or export job, is completed, or to share other information with users. The administrator can send notifications to all users currently logged on to Concordance Evolution, individual users, or all users in a user group. Optical Character Recognition (OCR) An electronic process where the text in paper documents or digital files is extracted and prepared for eventual loading into a full-text information retrieval system. Personal Tag Folders/Groups/Tags Personal tag folders, tag groups, and tags are only available to the user that created them and Concordance Evolution administrators. Other users cannot view the personal tag folders, tag groups, and tags in the Tags pane in the Review dashboard. Production A process where you “produce” a copy of your images and files based on a current Concordance Evolution query, which can be renamed and renumbered to fit your needs. Productions are often run for internal case review and to provide opposing counsel with © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 284 Concordance Evolution records in preparation for trial. Public Tag Folders/Groups/Tags Public tag folders, tag groups, and tags are available to all users that have access to the dataset and are available for selection on the Tags pane in the Review dashboard, unless tag security limits a user's access to the folder, group, or tag. Redaction A blocked section of text intended to prevent others from viewing sensitive information in a document. REST API The REST API will allow clients to write scripts in standard web scripting languages like VBScript, JavaScript, Python, C#, and others. REST (Representational State Transfer) is a style of web software architecture. Review Sets Review sets are used to organize documents in a dataset for review. Review sets can be created by query, tag, or by locating all unassigned documents in a dataset. Review sets can then be divided by different logic and then assigned to an individual user or a group of users. Search Server This server provides the search engine infrastructure for providing real-time clustered results. Security Roles Security roles are used as security profiles that are assigned to user groups. Single-page TIFF A specific type of Tagged Image File Format (TIFF) image file in which many individual pages are separated into individual files. For example, a 40-page document could be represented as 40 individual .TIF files. SMTP Server The SMTP server is the server that will be used for generating and sending the system notification emails for Concordance Evolution. Snippet View © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Reference Information 285 Snippet view provides a brief look at the initial content of the document (about the first 96 words), so you can quickly assess the contents without opening the full document in Preview, Native, Near Native, or Document Data views. Spelling Variations Concordance Evolution provides a default list of common spelling variations, which can be modified for each dataset. When you run a search, any spelling variations for a particular word will also be located depending on how the search query is written. Stop Words Stop words are a list of words that include the most common words in the English language (and, the, but, etc.). Stop words are not words you would generally want to search for and their elimination from a dataset index ensures that searches are run faster and efficiently. Table View Table view provides a list of records in your review set. This view is similar to the Table View in traditional Concordance. Tag A descriptive marker in Concordance Evolution that can be used to categorize a document or a section of text within a document. Thesaurus Concordance Evolution includes a global thesaurus that helps process advanced, full-text query searches for synonyms. Search results will include synonyms found in the global thesaurus or synonyms added to the thesaurus for this dataset. User Groups User groups act as user role templates and allow you to use pre-defined security policy settings when you create a new user to help speed up the user creation process. Vivisimo Velocity Concordance Evolution utilizes Vivisimo's Velocity search platform, which also provides concept and clustering technology. Web Server The Web server provides all access for Web-based clients to communicate with the product. Web Server (IIS) © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 286 Concordance Evolution Internet Information Services (IIS) - A Web server application and set of feature extension dashboards created by Microsoft for use with Microsoft Windows. © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Index Index -Aactivating, users 49 Active Directory AD user groups 31 AD users 41 adding domains 45 adding servers 46 deleting domains 47 deleting servers 48 using 44 adding, fields 117 alerts 76 about (Admin) 76 deleting search alerts (Admin) 85 editing search alerts (Admin) 85 viewing search alerts (Admin) 84 Audit Log about 86, 265 archive, events 90, 269 export 89, 268 system 86, 88, 265, 266 authority word lists adding to fields 117 -Bbilling creating reports 269 binders about 175 creating 176 managing 177 bulk printing about 231 creating jobs 232 image sets 232 native files 232 productions 232 -CConcordance Evolution © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. about 8 navigating 22 security 26 what's new 18 creating billing reports 269 binders 176 datasets 105 folders 94 matter reports 274 matters 99 near-deduplicatin jobs notifications 77 production sets 208 review sets 179 search alerts (Admin) tags (Admin) 195 240 80 -Ddata exporting files 218 exporting, about 217 datasets 103 about 103 about dataset fields 111 adding fields to datasets 117 binders, about 175 creating 105 creating binders 176 defining search settings 258 deleting 110 deleting dataset fields 135 editing 109 editing dataset fields 131 manage shares 73 managing binders 177 managing field security 133 viewing documents 164 deactivating, users 49 deduplication about 238 creating jobs 238 deleting dataset fields 135 datasets 110 folders 97 matter reports 277 287 288 Concordance Evolution deleting matters 101 notifications (Admin) 80 review sets 192 search alerts (Admin) 85 tags (Admin) 205 users 49 delimiter characters 139 discovery process 10 documents about importing 139 viewing documents 164 domains adding AD domains 45 deleting AD domains 47 -Eediting dataset fields 131 datasets 109 folders 96 matters 100 search alerts (Admin) 85 tags (Admin) 201 users 49 exporting about 217 audit logs 89, 268 exporting dataset files 218 matter reports 277 search results (Admin) 259 users 51 -Ffields about dataset fields 111 adding authority lists 117 adding to datasets 117 deleting dataset fields 135 editing dataset fields 131 managing field security 133 folders 94 about 94 creating 94 deleting 97 editing 96 -Gglossary 280 -Iimage sets printing bulk 232 importing 139 about 139 about delimiter characters 139 delimited text files 141 LAW PreDiscovery Cases 151, 166 subsequent data loads and overlays 157 users 43 -Jjobs about 65 near-deduplication 240 reprocessing Near Native files viewing 65 67 -Kknowledge base 242 -LLAW PreDiscovery importing case files 151, 166 synchronizing case files 171, 227 load files exporting files 218 importing 141 -Mmanage shares about 73 creating 74 deleting 75 modifying 75 © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Index managing binders 177 datasets 177 matters 101 matters about 98 creating 99 creating reports 274 deleting 101 deleting reports 277 editing 100 exporting audit log 89, 268 exporting reports 277 managing 101 viewing reports 271 -Nnative files, printing bulk 232 navigating Concordance Evolution 22 Near Native jobs 67 reprocessing 67 near-deduplication about 240 creating jobs 240 notifications 76 about (Admin) 76 creating 77 deleting (Admin) 80 viewing (Admin) 79 -Oorganizing, data overlays 157 175 -Ppasswords changing user passwords preferences about 52 customizing (Admin) 57 printers 62 printing bulk 231 privilege logs about 233 creating 234 productions 206 about 206 bulk printing 232 creating production sets manage shares 73 -Rreasons for redaction about 242 adding 253 deleting 253 editing 253 exporting 253 importing 253 redactions importing 139 reports audit log, matter 88, 266 billing, creating 269 exporting, audit log 89, 268 matter level, creating 274 matter level, deleting 277 matter level, exporting 277 matter level, viewing 271 system level viewing 86, 265 reprocessing Near Native files 67 review sets 178 about 178 assigning users 177 creating 179 deleting 192 managing 183 managing, binders 177 roles assigning to user groups 35 creating security roles 33 49 © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 208 -Ssearch server searching 62 289 290 Concordance Evolution searching about alerts (Admin) 76 comparing results (Admin) 259 creating search alerts (Admin) 80 defining search settings (Admin) 258 deleting search alerts (Admin) 85 editing search alerts (Admin) 85 exporting results (Admin) 259 managing results (Admin) 259 running admin searches 257 viewing search alerts (Admin) 84 security about 26 assigning roles to user groups 35 assigning user group policies 35 binder policies 177 creating security roles 33 customizing user group security 34 managing field security 133 managing tag security 200 servers adding AD servers 46 deleting AD servers 48 management 62 printers 62 search server 62 SMTP 62 SQL Server 62 SMTP 62 spelling variations about 242 adding 243 deleting 243 editing 243 exporting 243 importing 243 SQL Server 62 stop words about 242 adding 250 deleting 250 editing 250 exporting 250 synchronizing, LAW PreDiscovery cases 171, 227 system archive, events 90, 269 exporting audit log 89, 268 -Ttags 193 about 193 creating (Admin) 195 deleting (Admin) 205 editing (Admin) 201 managing tag security 200 thesaurus about 242 adding words 246 deleting words 246 editing words 246 exporting 246 importing 246 -Uunlocking users 49 user groups Active Directory 31 assigning policies 35 assigning roles 35 assigning to Binders 177 creating 31 customizing security 34 users activating 49 Active Directory 41 creating 41 deactivating 49 deleting 49 exporting 51 importing 43 managing user sessions 64 modifying 49 unlocking 49 -Vviewing audit log, matter 88, 266 audit log, system 86, 265 dataset documents 164 jobs 65 matter reports 271 © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. Index viewing notifications (Admin) search alerts (Admin) 79 84 -Wwhat's new, Concordance Evolution word lists adding to fields 117 © 2015 LexisNexis. All rights reserved. 18 291
© Copyright 2026