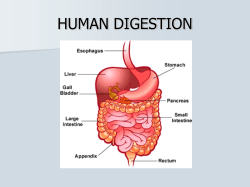
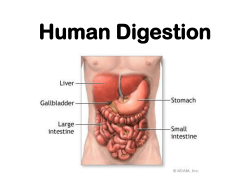
Terms: 1. Peritoneum- a transparent membrane that lines the
Terms: 1. Peritoneum- a transparent membrane that lines the abdominal cavity in mammals and covers most of the organs. 2. Peritoneal cavity- 3. Omenta- 4. Mesentery- 5. Ligaments- The cavity within the abdomen, inside of which are the internal organs. a double layer of peritoneum that links the stomach to other intra-abdominal organs. The lining that connects the intestine to the back of the abdominal wall; contains the arteries and veins that supply the intestines. Fibrous, slightly elastic band of tissue which holds organs in place. Structures: 1. parietal peritoneum- Transparent membrane that lines the abdominal cavity. 2. visceral peritoneum- Transparent membrane that covers most of the organs of the abdominal cavity. 3. greater omentum- Attached to the lower border (greater curvature) of the stomach and folded around the coiled small intestine, it supplies protection and insulation. 4. spleen- 5. lesser omentum- 6. mesentery proper- 7. mesocolon- 8. colon- 9. cecum- beginning of the large intestine; it is connected to the lower part of the small intestine, called the ileum. 10. ascending colon- part of the colon on the right side of the abdomen. Ascends (goes up) from the cecum to the 11. transverse colon- part of the colon that extends across the abdomen from right to left. 12. descending colon- 13. rectum- 14. small intestine- 15. duodenum- 16. ileum- Organ lying between the stomach and diaphragm that stores red blood cells and filters blood. Membrane attached to the superior or medial border (lesser curvature) of the stomach. broad, fan-shaped fold of peritoneum which connects the folds of the small intestine with the posterior wall of the abdomen. mesentery that holds the lower colon the back abdominal wall. Another name for the large intestine. It extracts moisture from food residues before they are excreted. transverse colon. the part of the large intestine that descends from the transverse colon to the sigmoid colon. lower end of the large intestine, leading to the anus. Organ where most digestion occurs; includes the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. The first part of the small intestine (the part food enters immediately after it leaves the stomach). The part of the small intestine that is near the large intestine. 17. jejunum- 18. umbilical ligament- 19. urinary bladder- 20. uterus- the female reproductive organ that nourishes the fetus until birth. 21. ovary- One of a pair of reproductive glands in women. The ovaries produce the ovum or female egg, which is middle section of the small intestine between the duodenum and ileum. the attachment of the urinary bladder to the ventral body wall. a membranous sac for temporary storage of urine. transferred through the fallopian tube for fertilization by the sperm. The ovary also produces both the hormones estrogen and progesterone. 22. pancreas- 23. kidneys- bean-shaped organs in the back part of the abdominal cavity that form and excrete Long gland that lies behind the stomach; manufactures insulin and digestive enzymes. urine, regulate fluid and electrolyte balance, and act as endocrine glands. 24. Renal cortex- 25. Renal pelvis- Outer functional region of the kidney. Inner sinus of the kidney which receives urine and drains it out through the ureter to the urinary bladder. 26. Renal papilla- 27. Renal medulla- 28. adrenal glands- 29. gall bladder- 30. stomach- a saclike enlargement of the alimentary canal, forming an organ for storing, diluting, Tips of the renal pyramids. Inner reddish-brown region of the kidney which contain the renal pyramids. This gland is found above each kidney, and secretes important steroid hormones and produces adrenaline (epinephrine) and noradrenaline. the membranous sac, in which the bile, is stored up, as secreted by the liver. and digesting food. 31. greater curvature- 32. lesser curvature- 33. cardiac portion- 34. body of stomach- 35. fundus- 36. esophagus- 37. ureter- 38. liver- lower border of the stomach. the superior or medial border (lesser curvature) of the stomach. the valve or region between the distal end of the esophagus and the stomach. The central or main portion of the stomach. The bottom or base of the stomach, farthest from the opening. The muscular tube through which food passes from the throat to the stomach. Tube that carries urine from the kidney to the bladder. largest organ in the body; performs important functions such as making bile, changing food into energy, and cleaning alcohol and poisons from the blood. Arteries: 1. Abdominal aorta- Section of the aorta running through the abdomen between the diaphragm and the iliac arteries. Gives off arteries that branch and supply organs of the abdomen with oxygen-rich blood. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Superior mesenteric- Supplies the pancreas and small intestines with oxygen-rich blood. Gastric- Supplies the stomach with oxygen-rich blood. Inferior mesenteric- Supplies the transverse and descending colon with oxygen-rich blood. Renal- Supplies the kidneys with oxygen-rich blood. Internal iliac- Branch to supply the gluteal muscles, medial side of each thigh, urinary bladder, uterus and other structures with oxygen-rich blood. 7. External iliac- 8. Adrenolumbar (suprarenal)- Supply the adrenal glands with oxygen-rich blood. Iliolumbar- Supply spinal cord and muscles and skin of the lower back region with oxygen-rich blood. Hepatic- Supplies the liver and gall bladder with oxygen-rich blood. Splenic- Supplies the spleen with oxygen-rich blood. 9. 10. 11. Extend through the pelvis and enter the thighs to become the femoral arteries, supplying muscles of the legs with oxygen-rich blood. Veins 1. Gastric- Transports deoxygenated blood from the stomach back to the heart. 2. Inferior Vena Cava- Transports deoxygenated blood from the legs and abdomen back to the heart. 3. Hepatic- Transports deoxygenated blood from the liver back to the heart. 4. Renal- Transports deoxygenated blood from the kidneys back to the heart. 5. Adrenolumbar (suprarenal)- Transports deoxygenated blood from the adrenal glands back to the heart. 6. Iliolumbar- Transports deoxygenated blood from the spinal cord, and muscles and skin of the lower back region back to the heart. 7. Internal iliac- 8. External iliac- Transports deoxygenated blood from the gluteal muscles, medial side of each thigh, urinary bladder, uterus and other structures back to the heart. Are continuous with the femoral veins and receive deoxygenated blood from the lower extremities and inferior part of the anterior abdominal wall. Common iliac- Formed by the union of internal and external iliac veins, and join with the inferior vena cava. 10. Hepatic portal- Formed by the union of the superior mesenteric and splenic veins. 11. Inferior mesenteric- Transports deoxygenated blood from the large intestine back to the heart. 12. Superior mesenteric- Transports deoxygenated blood from the small intestine and superior portion of the large 9. intestine back to the heart. 13. Splenic- Transports deoxygenated blood from the spleen back to the heart.
© Copyright 2026