Digestive system and Nutrition
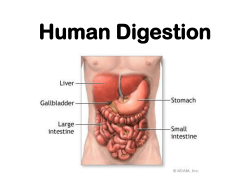
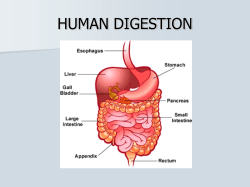
Digestive system and Nutrition WHAT IS DIGESTION? ! HOW DOES YOUR BODY ABSORB NUTRIENTS? ! WHAT DO WE KNOW ABOUT THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM? ! -the digestive system functions to break down the macromolecules found in your diet into usable forms for the body ! -products of digestion are used for energy, building blocks, and as enzymes and/or coenzymes Secretion Site of production Function saliva mouth contributes to starch digestion via salivary amylase; lubricates the inside of the mouth to assist in swallowing mucus mouth, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine protects the cells lining the innermost portion of the digestive tract; lubricates food as it travels through the digestive tract enzymes mouth, stomach, small intestine, and pancreas promote digestion of food masses into particles small enough for absorption into the bloodstream acid stomach promotes digestion of protein bile liver (stored in gall bladder) suspends fat in water, using bile salts, cholesterol, and lecithin to aid digestion of fats in small intestine bicarbonate pancreas and small intestine neutralizes stomach acid when it reaches the small intestine hormones stomach, small intestine, and stimulate production and/or release of acid, pancreas enzymes, bile, and bicarbonate; help to regulate peristalsis Anatomy of the digestive system: Alimentary Canal Accessory Digestive Organs ingests teeth digests tongue absorbs large digestive glands defecates liver gallbladder pancreas Alimentary Canal (GI tract) mouth: mechanical breakdown of food, begins chemical pharynx: connects mouth with the esophagus esophagus: peristalsis pushes food to the stomach stomach: secretes acids and enzymes to begin digestion of proteins small intestine: mixes food with bile and pancreatic fluid, main site of nutrient absorption large intestine: absorbs water and electrolytes to form feces Rectum:regulates emission of feces Anus: exit vent Accessory organs: salivary glands: secrete saliva which contains enzymes that initiate breakdown of carbs ! Liver: produces bile which emulsifies fats ! Gallbladder: Stores bile and secretes it into the the small intestine ! Pancreas: Produces and secretes pancreatic fluids into the small intestine Layers of the alimentary canal Lumen: the cavity (not a layer) Inner-most layer is the mucosal layer(secretes mucous and absorbs nutrients from ingested material) ! submucosa: blood vessels, glands, vessels move nutrients to other parts of the body. Muscular layer: contracts and releases to move food Serosa: outer covering, secretes fluid to keep layer moist and lubricated so all organs slide freely against each other. Mouth (pg 404) Uvula Epiglottis oral cavity tongue Nasal cavity pharynx Soft and Hard Palate Hyoid Lingual Frenulum Naso, oro, laryngo Salivary glands Pharynx and Esophagus (pg410) Read about swallowing mechanism straight collapsible tube about 25 cm long passageway for food Movement is caused by Peristalsis Stomach pyloric sphincter Gastric secretions Food and acids= Chyme Stomach Stomach is for digestion Only chemicals absorbed by the stomach are aspirin and alcohol Contains pepsin: a protein digesting enzyme Hydrochloric acid: activates pepsin, prevents microbial growth Mucous prevents acid from digesting stomach lining ! Pancreas Pancreatic juice: proteolytic enzymes lipase Liver Can weigh 3 lbs -role in carbohydrate metabolism by maintaining normal glucose levels in the blood. -oxidizes fatty acids -protein metabolism -makes urea -converts amino acids to other amino acids -stores vitamin A, D and B12, Iron, glycogen -destroys damaged red blood cells -Main function pertaining to digestion is Bile production 4 Lobes ! Right, Left, Quadrate, caudate What is Bile? water, bile salts, bile pigments, cholesterol, electrolytes So what is bile? a bitter greenish-brown alkaline fluid that aids digestion and is secreted by the liver and stored in the gallbladder Gallbladder -Pear shaped sac near the liver -stores bile and concentrates bile -Gallstones are cholesterol that have precipitated out of solution. SOOOO The Liver, Gallbladder and Pancreas all secrete enzymes, and fluids to aid in the breakdown of ingested food. But each has its own important function Liver: Makes bile, oxidizes fatty acids, Gallbladder: stores bile Pancreas:pancreatic juices, proteolytic enzymes -Chyme is pushed into the duodenum of the small intestine where most digestion occurs. ! -Moves on to the jejunum then the ileum where absorption occurs. 90% absorption takes place in the small intestine. ! -accessory organs secrete juices to aid in digestion ! - villi are finger-like structures that create greater surface area Lacteal: lymphatic capillary that absorbs fat, eventually empties into the bloodstream Large intestine Main functions: water absorption, houses bacteria, produces feces. xray swallowing crash course 2 min video on digestion bozeman Science
© Copyright 2026