UNIT B: âBody Worksâ
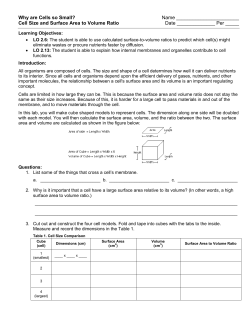
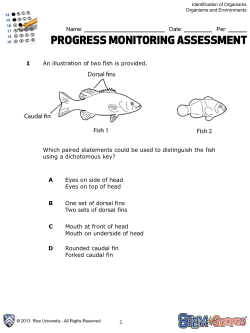
Final Exam Study Guide 6th Name: ________________________ Per:_____ Unit A: “Studying People Scientifically” Circle or highlight the correct answer(s) 1. A well planned experiment : *includes a small/medium/large sample size *includes two/multiple/no trials *can/cannot be reproduced by others to get similar results * respects/disrespects/does not use human and animal subjects 2. Qualitative data includes exact measurements/colors/shapes/textures. 3. Quantitative data includes exact measurements/colors/numbers/textures 4. A suggested solution to a problem or question based on fact is a hypothesis/conclusion/trade-off UNIT B: “Body Works” Fill in the blanks 5. Name 3 things blood transports through your body. 1) ______________________ 2) _____________________ 3) _______________ 6. During digestion, what is the effect of mechanical breakdown on the speed of chemical breakdown? (Hint: think of our Alka-Seltzer lab with vinegar!) Mechanical digestion ________________ the speed of chemical digestion. 7. You have just eaten lunch. What path does food take through your digestive system? mouth ___________ ___________ small intestine ____________ 8. You are walking down the street when you decide to run. After running for a few minutes, what will happen to the speed of your pulse? The speed of my pulse is likely to have ______________. 9. Name 3 wastes produced by your body. 1)___________________, 2)__________________, 3)_________________ 10. You stop exercising regularly for 6 months. What is most likely to happen to your resting pulse (compared to your resting pulse 6 months ago)? Because I stopped exercising, my resting pulse will probably ____________. 11. Describe how the human body is organized, from the smallest to largest structure? Organelle Cell __________ __________ __________ _________ 12. You have a headache and decide to take some medicine. What would be trade-off of taking medicine to treat your headache? A trade-off of taking medicine is that I might experience ______________, such as stomach pain or nausea. UNIT C: “Micro-Life” True or False – Circle true if the statement is true. If the statement is false, write a statement with the correct answer on the line. 13. The following microbes in order from smallest to largest are: bacteria, virus, protist. True/False__________________________________________________________ 14. Bacteria can be found only in dirt and soil True/False__________________________________________________________ 15. Infectious diseases cannot be caused by genes; they are caused by microbes. True/False__________________________________________________________ 16. Three basic functions that a cell performs are respiration, taking in nutrients, and producing wastes. True/False__________________________________________________________ 17. Cancer, diabetes, and asthma are all examples of infectious diseases. True/False__________________________________________________________ 18. When you use a microscope, you should always carry it with 2 hands and turn off the light when you are finished using it. True/False__________________________________________________________ 19. Quarantine is sometimes used to prevent the spread of an infectious disease. A trade-off of using quarantine is that people with a disease get to keep their freedom. True/False__________________________________________________________ 20. The “Germ Theory of Disease” is the idea that infectious diseases are caused by genes. True/False__________________________________________________________ 21. Substances pass in and out of a cell through the ribosomes. True/False__________________________________________________________ 22. All cells look the same and perform the same function. The shape of a cell is not related to its function. True/False__________________________________________________________ 23. One of the most effective ways you can prevent the spread of infectious disease is to wash your hands. True/False__________________________________________________________ 24. Antibiotics can be used to kill only living mibrobes (bacteria and protists); it cannot kill viruses. True/False__________________________________________________________ 25. According to the graph above, the number of people infected with this disease over time decreased. True/False__________________________________________________________ UNIT D: “Our Genes” Matching: Write the letter of the correct answer in the blank. Question Answer Choices 26. ____ The father of Genetics is a. recessive 27. ____ Where are genes located? 28. ____ The gene that always shows itself is called ** Albinism (albino) is a recessive trait. Both parents are heterozygous (Aa) for the trait. If you are heterozygous (Aa), you will not show the trait. Complete the punnett square and then answer questions 29-31. b. similar c. on chromosomes, in DNA, in the nucleus of the cell d. some plants, bacteria, and yeast e. Gregor Mendel 29. ____ How many offsprings are dominant? 30. ____ How many offspring are recessive? f. dominant 31. ____ What are the chances the offspring will be albino? g. three 32. ____ Offspring of sexual reproduction will look ____ to the parents. h. all/one 33. ____ Traits can be determined by genes or by the 34. ____ Offspring of asexual reproduction get ___ of their genetic material from ___ parent. 35. ____ Name 3 organisms that reproduce asexually. i. dogs, some plants, humans j. twenty-five percent or one out of four k. half/each 36. ____ Name 3 organisms that reproduce sexually. 37. ____ Offspring of sexual reproduction get ____ of their genetic material from _____ parents. 38. ____ Name 2 trade-offs in choosing to have genetic testing. Use this pedigree chart to answer questions 39 and 40. Individuals with the trait are shown with shading. 39. ____ By studying the diagram above, you will see the trait skips a generation. You can conclude that the trait is 40. ____The gene that gets covered by another gene is called l. you may not be able to get insurance, and you may have to restrict your activity m. one n. recessive o. environment UNIT E: “ECOLOGY” Fill in the missing information (Vocabulary Term, Definition, or Picture) # Vocabulary Term Definition Picture/Example A species that is introduced into an ecosystem and has a negative impact on it. Nile Perch, Zebra Mussels 41. 42. A forest ecosystem can support 1 bear, 47 deer, 78 rabbits, and 98 species of plants. Carrying capacity 43. Decomposers Organisms that get food by breaking down dead organisms and waste material. They add nutrients to the soil. 44. Predator And Prey and 45. Organisms that get food/energy from eating other living things. 46. The number of ladybugs living in my garden. Population The number of fox in a forest. 47. Process by which plants make their own food. Carbon Dioxide + Water Energy glucose + oxygen 48. Food Chain A way of showing the food relationships among a small group of organisms. It starts with a producer. 49. Food Web 50. The original source of energy for all ecosystems on Earth. 51. Living and non-living things in an environment, together with their interactions. 52. Producer Plants, algae and plankton UNIT F: “Evolution” Answer Each Question 53. Define “Diversity of species”: ______________________________________________ 54. Name 5 things that could cause the extinction of a species: 1. 4. 2. 5. 3. Mark each statement as either TRUE or FALSE. 55. Millions of species of organisms live on Earth. 56. Organisms have evolved only over the last few hundred years. 57. Many species that have lived on Earth no longer exist. 58. Species that are endangered have a high risk of becoming extinct. ________ ________ ________ ________ 59. Which of these are fossils? (Circle Yes or No) Footprint Yes / No Tooth Yes / No Bones Yes / No Rock Yes / No Use the stratographic column below to answer questions 60-61 ‹— Plants ‹— Fish ‹— Shells 60. What evidence does the diagram above show? ________________________ 61. Based on evidence in the diagram above, the organism that lived most recently is the ____________________________. 62. Name the organism that has survived the longest on our planet. _____________________ 63. Name two observations can you make about fossilized footprints? 1) __________________________ 2)______________________________ 64. List organisms from youngest to oldest. (fish, bird, bacteria, mammals) 65. Name 2 scientists that contributed to the evolutionary theory. 1. ___________________ 2. ________________ 66. According to geological evidence, the earth is ____________ years old. Use the following paragraph to answer 67-70: A population of birds eats the green moths that live in a pine forest. Every so often, the green moths have a brown offspring. The brown moths are usually seen more quickly by the birds and eaten sooner. 67. The fact that the brown moths are easier to see and are less likely to survive as a result is known as ____________________ selection. Mark each “True” or “False.” 68. The brown moths are probably a result of a mutation. _______ 69. The brown moths increase the variation within the moth population. _______ 70. Why do the green moths survive in the forest? _______________________ ______________________________________________________________ 71. Mutations are always/sometimes/never helpful. 72. Charles Darwin developed his theories based on his work with _________________ on the ________________ Islands. 73. Bringing an extinct species back to life is not yet possible. Still, some people would like to see it happen because the species could be a source of new information. What is a trade-off of such a decision? _________________________________________________________. 74. Over long periods of time, some species have become extinct, while new species have descended from earlier species. These changes over time are known as ________________. 75. A woman lifts weights and exercises until she is very muscular. She works out with the hope that her children will also be very strong. What is wrong with her thinking? _______________________________________________________________________ 76. Variation is the result of randomly occurring _________________________ (changes in DNA that change the traits of organisms). Mark each “True” or “False.” 77. The more similar the DNA, the less closely related the organisms. ______ 78. The more similar the DNA, the more closely related the organisms. ______ 79. The more different the DNA, the more closely related the organisms. ____ 80. Where are we located in the Universe or what is our “address” in the Universe? Planet: __________ System __________ Galaxy __________ (aka Cosmos) Give 3 descriptions of each of the 5 classes of chordates in the Animal Kingdom. 81. Fish ______________________________________________________ 82. Amphibians _________________________________________________ 83. Reptiles ___________________________________________________ 84. Birds _____________________________________________________ 85. Mammals __________________________________________________ 86. You enter your science classroom and notice some supplies and equipment set up on your table. You should ___________________________________. If a new student joins our class, name 4 lab safety rules that we must maintain in our labs to be safe. 87. _________________________________________________________ 88. _________________________________________________________ 89. _________________________________________________________ 90. _________________________________________________________ For 91-100, name the contribution that the scientist made (What did he/she do that contributed to our understanding of the world?) # 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 Scientist Dr. Joseph Goldberger Louis Pasteur Alexander Fleming Robert Hooke Anton van Leeuwenhoek Florence Nightingale Gregor Mendel Antoine Marfan Carl Linnaeus Charles Darwin Contribution
© Copyright 2026