Patient Name
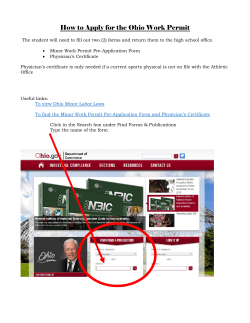
PAGE 1 of 14 SPECIMEN INFORMATION Patient Name ORDERED BY Ordering Physician Name The Cancer Center Primary Tumor Site: Upper lobe, lung Specimen Site: Upper lobe, lung Specimen Collected: XX/XX/2013 Specimen Received: XX/XX/2013 Initiation of Testing: XX/XX/2013 Completion of Testing: XX/XX/2013 Specimen Id: XYZ-123 1234 Main Street Dallas, TX 12345 (123) 456-7890 SE U AL Case Number: TN13-111111 Date Of Birth: XX/XX/1942 Sex: Female . PATIENT Agents Associated with Potential BENEFIT Potential Targets Associated with CLINICAL TRIALS FO R Agents Associated With Potential LACK OF BENEFIT .N O gemcitabine erlotinib N LY paclitaxel, docetaxel, nabpaclitaxel pemetrexed cMET T crizotinib TM ON NCCN COMPENDIUM MI-2013-10-10.0 C LI N IC Molecular Intelligence Summary cetuximab O trastuzumab, pertuzumab, ado-trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1) lapatinib TM PU R gefitinib PO OFF NCCN COMPENDIUM SE S irinotecan E fluorouracil, capecitabine R ST temozolomide, dacarbazine AT IV doxorubicin, liposomaldoxorubicin, epirubicin LU afatinib SA M PL E R EP O R T. IL Presence of T790M mutation in EGFR has been associated with higher likelihood of prolonged efficacy (PFS/OS) with afatinib than gefitinib or erlotinib (Katakami, et al. 2013). Recent data including AMP, CAP and NCCN guidelines support the continued use of EGFR TKIs in lung adenocarcinoma patients with EGFR activating mutations after the acquisition of a secondary mutation in EGFR-T790M that renders the kinase resistant to erlotinib or gefitinib. To overcome resistance, EGFR should continue to be targeted and discontinuation of EGFR TKIs may lead to further progression of the disease. (Lindeman, et al. 2013). Agents associated with potential benefit or lack of benefit, as indicated above, are based on biomarker results provided in this report, and are based on published medical evidence. This evidence may have been obtained from the studies performed in the cancer type present in the tested patient's sample or derived from another tumor type. The selection of any, all or none of the matched agents resides solely with the discretion of the treating physician. Decisions on patient care and treatment must be based on the independent medical judgment of the treating physician, taking into consideration all applicable information concerning the patient’s condition, such as patient and family history, physical examinations, information from other diagnostic tests, and patient preferences, in accordance with the applicable standard of care. Decisions regarding care and treatment should not be based on a single test such as this test or the information contained in this report. ** FINAL REPORT ** Patient: Patient Name TN13-111111 Physician: Physician Name 4610 South 44th Place / Phoenix, AZ 85040 / (888) 979-8669 / Fax: (866) 479-4925 / CLIA 03D1019490 / Zoran Gatalica, M.D., DSc, Medical Director Caris MPI, Inc. d/b/a Caris Life Sciences TN1014 PAGE 2 of 14 Clinical History . Per the submitted surgical pathology report (XYZ-123), the patient is a 71 year-old female with a history of adenocarcinoma. IC AL U SE Submitted Pathologic Diagnosis Lung, right upper lobe mass, wedge resection: Two separate foci of moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma with acinar and papillary patterns. The specimens consist of: SA M PL E R EP O R T. IL LU ST R AT IV E PU R PO SE S O N LY .N O T FO R C 1 (A) Paraffin Block - Client ID (XYZ-123), with the corresponding surgical pathology report labeled "XYZ-123". LI N Specimens Received (Gross Description) ** FINAL REPORT ** Patient: Patient Name TN13-111111 Physician: Physician Name 4610 South 44th Place / Phoenix, AZ 85040 / (888) 979-8669 / Fax: (866) 479-4925 / CLIA 03D1019490 / Zoran Gatalica, M.D., DSc, Medical Director Caris MPI, Inc. d/b/a Caris Life Sciences PAGE 3 of 14 Agents Associated with Potential BENEFIT cMET CISH Not Amplified 2.40 ✔ EGFR Next Gen SEQ Pathogenic L858R ✔ EGFR T790M Next Gen SEQ Pathogenic T790M KRAS Next Gen SEQ Wild Type PIK3CA Next Gen SEQ Wild Type PTEN IHC Positive 2+ 60% TS IHC Negative cetuximab EGFR IHC HScore Positive irinotecan TOPO1 IHC Positive Her2/Neu CISH PGP IHC ✝ Decreased Potential Benefit Data Reference Level* LI N C FO R .N O T ✔ ✔ . Lack of Potential Benefit IC Potential Benefit 2, 4 9, 11, 12, 13 5, 6, 7, 8 9, 10 2, 3 ✔ 1 ✔ 20, 21, 22 298 ✔ 24 2+ 30% ✔ 34, 35, 36 N LY ✔ S erlotinib, gefitinib Value SE Result U Method O Agents AL Test SE Clinical Association temozolomide, dacarbazine PO R PU E Negative 0+ 100% ✔ 37, 38 IHC Positive 2+ 20% ✔ 41, 42 IHC Negative 1+ 20% ✔ 43, 44 ✔ 39, 40 SA M PL E R EP O R T. MGMT IV AT 1.21 R IL TOP2A 1+ 7% Not Amplified LU doxorubicin, liposomaldoxorubicin, epirubicin ST fluorouracil, capecitabine, pemetrexed ** FINAL REPORT ** Patient: Patient Name TN13-111111 Physician: Physician Name 4610 South 44th Place / Phoenix, AZ 85040 / (888) 979-8669 / Fax: (866) 479-4925 / CLIA 03D1019490 / Zoran Gatalica, M.D., DSc, Medical Director Caris MPI, Inc. d/b/a Caris Life Sciences PAGE 4 of 14 Agents Associated with Potential BENEFIT Next Gen SEQ Pathogenic L858R EGFR T790M Next Gen SEQ Pathogenic T790M Decreased Potential Benefit Lack of Potential Benefit Data Reference Level* IC Potential Benefit SE EGFR ✝ Value U Result AL Method LI N ✔ ✔ C afatinib Test 50 50 FO R Agents . Clinical Association .N O T *The level of evidence for all references is assigned according to the Literature Level of Evidence Framework consistent with the US Preventive Services Task Force described further in the Appendix of this report. The data level of each biomarker-drug interaction is the average level of evidence based on the body of evidence, overall clinical utility, competing biomarker interactions and tumor type from which the evidence was gathered. LY = Greater level of evidence N = Intermediate level of evidence S O = Lower level of evidence SA M PL E R EP O R T. IL LU ST R AT IV E PU R PO SE ✝ Refer to Appendix for detailed Result and Value information for each biomarker, including appropriate cutoffs, unit of measure, etc. ** FINAL REPORT ** Patient: Patient Name TN13-111111 Physician: Physician Name 4610 South 44th Place / Phoenix, AZ 85040 / (888) 979-8669 / Fax: (866) 479-4925 / CLIA 03D1019490 / Zoran Gatalica, M.D., DSc, Medical Director Caris MPI, Inc. d/b/a Caris Life Sciences PAGE 5 of 14 Agents Associated with Potential LACK OF BENEFIT FISH Negative ROS1 FISH Negative RRM1 IHC Positive 2+ 50% PGP IHC Negative 0+ 100% SPARC Monoclonal IHC Negative 1+ 80% SPARC Polyclonal IHC Negative 1+ 25% TLE3 IHC Negative TUBB3 IHC Positive Her2/Neu CISH Not Amplified Her2/Neu IHC LI N 23 FO R C ✔ .N O T 30, 31 ✔ ✔ 32, 33 0+ 100% ✔ 28, 29 3+ 95% ✔ 25, 26, 27 1.21 ✔ 52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 59 Negative 0+ 100% ✔ 52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58 Not Amplified 1.21 ✔ 59, 60, 61, 62 Negative 0+ 100% ✔ 60, 61, 62 O N LY 32, 33 PU IV AT R CISH LU lapatinib ST Her2/Neu IHC R T. IL Her2/Neu 14, 15 16, 17, 18, 19 E trastuzumab, pertuzumab, adotrastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1) Data Reference Level* ✔ R paclitaxel, docetaxel, nabpaclitaxel Lack of Potential Benefit ✔ S gemcitabine Decreased Potential Benefit ✔ SE crizotinib Potential Benefit SE ALK ✝ Value U Result AL Method IC Test PO Agents . Clinical Association R EP O *The level of evidence for all references is assigned according to the Literature Level of Evidence Framework consistent with the US Preventive Services Task Force described further in the Appendix of this report. The data level of each biomarker-drug interaction is the average level of evidence based on the body of evidence, overall clinical utility, competing biomarker interactions and tumor type from which the evidence was gathered. M PL E = Greater level of evidence = Intermediate level of evidence SA = Lower level of evidence ✝ Refer to Appendix for detailed Result and Value information for each biomarker, including appropriate cutoffs, unit of measure, etc. ** FINAL REPORT ** Patient: Patient Name TN13-111111 Physician: Physician Name 4610 South 44th Place / Phoenix, AZ 85040 / (888) 979-8669 / Fax: (866) 479-4925 / CLIA 03D1019490 / Zoran Gatalica, M.D., DSc, Medical Director Caris MPI, Inc. d/b/a Caris Life Sciences PAGE 6 of 14 Agents Associated with INDETERMINATE BENEFIT Wild Type RET Next Gen SEQ Wild Type PIK3CA Next Gen SEQ Wild Type 45, 46 47, 48, 49 51 ✔ 63, 64, 65 LY everolimus, temsirolimus ✔ O vandetanib SE Next Gen SEQ ✔ Data Reference Level* U PDGFRA imatinib Lack of Potential Benefit AL Wild Type Decreased Potential Benefit IC Next Gen SEQ Potential Benefit LI N c-KIT ✝ Value C Result FO R Method T Test .N Agents . Clinical Association SE S O N *The level of evidence for all references is assigned according to the Literature Level of Evidence Framework consistent with the US Preventive Services Task Force described further in the Appendix of this report. The data level of each biomarker-drug interaction is the average level of evidence based on the body of evidence, overall clinical utility, competing biomarker interactions and tumor type from which the evidence was gathered. PO = Greater level of evidence R = Intermediate level of evidence PU = Lower level of evidence SA M PL E R EP O R T. IL LU ST R AT IV E ✝ Refer to Appendix for detailed Result and Value information for each biomarker, including appropriate cutoffs, unit of measure, etc. ** FINAL REPORT ** Patient: Patient Name TN13-111111 Physician: Physician Name 4610 South 44th Place / Phoenix, AZ 85040 / (888) 979-8669 / Fax: (866) 479-4925 / CLIA 03D1019490 / Zoran Gatalica, M.D., DSc, Medical Director Caris MPI, Inc. d/b/a Caris Life Sciences PAGE 7 of 14 SE . Expanded Mutational Analysis by Next Generation Sequencing Frequency (%) Exon EGFR L858R 74 21 Result IC Alteration Pathogenic LI N Gene AL U Genes Tested With Alterations C Interpretation: A pathogenic mutation was detected in EGFR O N LY .N O T FO R EGFR or epidermal growth factor receptor, is a transmembrane receptor tyrosine kinase belonging to the ErbB family of receptors. Upon ligand binding, the activated receptor triggers a series of intracellular pathways (Ras/MAPK, PI3K/Akt, JAK-STAT) that result in cell proliferation, migration and adhesion. Dysregulation of EGFR through mutation leads to ligand-independent activation and constitutive kinase activity, which results in uncontrolled growth and proliferation of many human cancers. EGFR mutations have been observed in 20-25% of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), 10% of endometrial and peritoneal cancers. Somatic gain-of-function EGFR mutations, including in-frame deletions in exon 19 or point mutations in exon 21, confer sensitivity to first- and second-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), whereas the secondary mutation, T790M in exon 20, confers reduced response. New agents and novel combination therapies are being explored (www.clinicaltrials.gov) for primary treatment of EGFR-mutated patients, as well as for patients that have progressed, including second-generation TKIs such as icotinib (NCT01665417) or combination therapies that include afatinib (NCT01647711) for NSCLC. T790M 23 SE EGFR S Germline mutations and polymorphisms of EGFR have been associated with familial lung adenocarcinomas. 20 Pathogenic PU R PO Interpretation: Presence of the T790M mutation has been associated with acquired resistance to EGFR-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitors, therefore erlotinib and gefitinib are potentially of minimal benefit for this patient. However, recent data including NCCN guidelines support the continued use of EGFR TKIs in lung adenocarcinoma patients with EGFR activating mutations after the acquisition of a secondary mutation in EGFR-T790M that renders the kinase resistant to erlotinib and gefitinib. To overcome resistance, EGFR should continue to be targeted and discontinuation of EGFR TKIs may lead to further progression of the disease. A second generation EGFR TKI may also be considered. R T. IL LU ST R AT IV E EGFR or epidermal growth factor receptor, is a transmembrane receptor tyrosine kinase belonging to the ErbB family of receptors. Upon ligand binding, the activated receptor triggers a series of intracellular pathways (Ras/MAPK, PI3K/Akt, JAK-STAT) that result in cell proliferation, migration and adhesion. Dysregulation of EGFR through mutation leads to ligand-independent activation and constitutive kinase activity, which results in uncontrolled growth and proliferation of many human cancers. EGFR mutations have been observed in 20-25% of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), 10% of endometrial and peritoneal cancers. Somatic gain-of-function EGFR mutations, including in-frame deletions in exon 19 or point mutations in exon 21, confer sensitivity to first- and second-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), whereas the secondary mutation, T790M in exon 20, confers reduced response. New agents and novel combination therapies are being explored (www.clinicaltrials.gov) for primary treatment of EGFR-mutated patients, as well as for patients that have progressed, including second-generation TKIs such as icotinib (NCT01665417) or combination therapies that include afatinib (NCT01647711) for NSCLC. SA M PL E R EP O Germline mutations and polymorphisms of EGFR have been associated with familial lung adenocarcinomas. ** FINAL REPORT ** Patient: Patient Name TN13-111111 Physician: Physician Name 4610 South 44th Place / Phoenix, AZ 85040 / (888) 979-8669 / Fax: (866) 479-4925 / CLIA 03D1019490 / Zoran Gatalica, M.D., DSc, Medical Director Caris MPI, Inc. d/b/a Caris Life Sciences PAGE 8 of 14 Genes Tested With Alterations Alteration Frequency (%) Exon Result TP53 Y236H 14 7 Presumed Pathogenic U SE . Gene IC AL Interpretation: A TP53 mutation was detected in this sample. This mutation has been reported previously for several tumor types in limited publications. Despite these reports, The clinical significance of this mutation is not fully known and therefore is classified as Presumed Pathogenic. .N O T FO R C LI N TP53, or p53, plays a central role in modulating response to cellular stress through transcriptional regulation of genes involved in cellcycle arrest, DNA repair, apoptosis, and senescence. Inactivation of the p53 pathway is essential for the formation of the majority of human tumors. Mutation in p53 (TP53) remains one of the most commonly described genetic events in human neoplasia, estimated to occur in 30-50% of all cancers with the highest mutation rates occurring in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and colorectal cancer. Generally, presence of a disruptive p53 mutation is associated with a poor prognosis in all types of cancers, and diminished sensitivity to radiation and chemotherapy. In addition, various clinical trials (on www.clinicaltrials.gov) investigating agents which target p53's downstream or upstream effectors may have clinical utility depending on the p53 status. For p53 mutated patients, Chk1 inhibitors in advanced cancer (NCT01115790) and Wee1 inhibitors in ovarian cancer (NCT01164995, NCT01357161) are being investigated. For p53 wildtype patients with sarcoma, mdm2 inhibitors (NCT01605526) are being investigated. S O N LY Germline p53 mutations are associated with the Li-Fraumeni syndrome (LFS) which may lead to early-onset of several forms of cancer currently known to occur in the syndrome, including sarcomas of the bone and soft tissues, carcinomas of the breast and adrenal cortex (hereditary adrenocortical carcinoma), brain tumors and acute leukemias. PO APC CSF1R FGFR2 IDH1 MPL ATM CTNNB1 FLT3 JAK2 NOTCH1 BRAF ERBB2 GNA11 PTEN RET Electronic Signature SA M PL E R EP O R T. IL LU ST R AT IV E ALK cMET FGFR1 HRAS PIK3CA R AKT1 KRAS GNAQ PDGFRA MLH1 VHL PU ABL1 c-KIT GNAS KDR NRAS SMO SE Genes Tested Without Alterations ** FINAL REPORT ** Patient: Patient Name TN13-111111 Physician: Physician Name 4610 South 44th Place / Phoenix, AZ 85040 / (888) 979-8669 / Fax: (866) 479-4925 / CLIA 03D1019490 / Zoran Gatalica, M.D., DSc, Medical Director Caris MPI, Inc. d/b/a Caris Life Sciences PAGE 9 of 14 TM Clinical Trials Connector Locations AL, AZ, CA, CO, FL, GA, IL, IN, LA, MA, MN, MO, NV, NC, OH, OR, PA, WA . Drug(s) SE Potential Target Phase U Title 2 cMET onartuzumab NCT01496742 A Study of Onartuzumab (MetMAb) in Combination With Bevacizumab (Avastin) Plus Platinum And Paclitaxel or With Pemetrexed Plus Platinum in Patients With Non-Squamous Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer 2 cMET onartuzumab NCT01395758 Erlotinib Plus ARQ 197 Versus Single Agent Chemotherapy in Locally Advanced or Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer 2 cMET NCT01121575 A Study Of Combined C- MET Inhibitor And PAN-HER Inhibitor (PF-02341066 And PF-00299804) In Patients With Non- Small Cell Lung Cancer 1 NCT01014936 First-in-Man, Dose-escalation Trial of C-met Kinase Inhibitor EMD 1214063 in Subjects With Advanced Solid Tumors LI N IC NCT01519804 A Study of Onartuzumab (MetMAb) Versus Placebo in Combination With Paclitaxel Plus Platinum in Patients With Squamous NonSmall Cell Lung Cancer AL Protocol T FO R C AL, AZ, CA, CO, FL, GA, IL, IN, LA, NV, NY, NC, OH, OR, PA, WA CA, CO, DC, FL, IL, KS, MD, MA, PA, SC, TX cMET crizotinib CO, MD, MA cMET EMD 1214063 SE S O N LY .N O ARQ 197 TX SA M PL E R EP O R T. IL LU ST R AT IV E PU R PO 1 ** FINAL REPORT ** Patient: Patient Name TN13-111111 Physician: Physician Name 4610 South 44th Place / Phoenix, AZ 85040 / (888) 979-8669 / Fax: (866) 479-4925 / CLIA 03D1019490 / Zoran Gatalica, M.D., DSc, Medical Director Caris MPI, Inc. d/b/a Caris Life Sciences To view the rest of the report, contact a Molecular Intelligence representative today. (888) 979-8669 [email protected] ** FINAL REPORT ** Patient: Patient Report TN13-111111 Physician: Ordering Physician Name 4610 South 44th Place / Phoenix, AZ 85040 / (888) 979-8669 / Fax: (866) 479-4925 / CLIA 03D1019490 / Zoran Gatalica, M.D., DSc, Medical Director Caris MPI, Inc. d/b/a Caris Life Sciences
© Copyright 2026