Supplier Quality Manual Motorpal, a.s. CONTENT
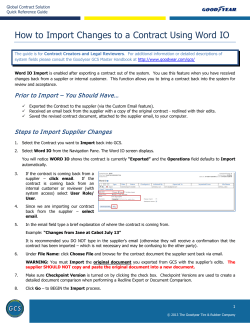
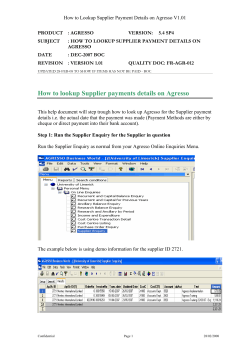
Supplier Quality Manual Motorpal, a.s. CONTENT 1. Motorpal, a.s. Supplier Quality Manual area of use 2. Effective range specification 3. Supplier’s responsibility 4. Quality system requirements 5. First samples requirements 6. Serial deliveries quality assurance 7. Change and deviation proceedings 8. Supplier Audit 9. Complaint procedure 10. Suppliers evaluation 11. Escalation process 12. Environment 13. Attachements : www.motorpal.cz Compiled by: David Vejslík Supplier quality dept. Signature: Date: Approved by: Ing.Karel Jiravský Quality vice-president Signature: 22.04.2014 Edition: 04/2014 Revision 2 Date: Effective: 22.04.2014 1.4.2011 Motorpal, a.s. Supplier Quality Manual 1. Motorpal, a.s. Supplier Quality Manual area of use Quality manual defines Motorpal, a.s. suppliers requirements and sets quality assuring procedures of purchased parts. Motorpal, a.s. expects intensive cooperation with suppliers aimed particularly on prevention and quality assurance during all process phases, especially in the phases of planning, product realisation and product delivery. Supplier alone is responsible for the quality assurance of purchased parts. This manual requirements are to be transfered on the sub-supplier in full extend. Motorpal, a.s. reserves the right to audit following of the rules and requirements of this Quality Manual. Aim is to build and develope supplier–customer relationships. 2. Effective range specification This Quality manual revision 2 is effective since 22.4.2014 and is mandatory for all Motorpal, a.s. suppliers. Current manual version is viable at www.motorpal.cz 3. Supplier’s responsibility Supplier guarantees that the supplied goods is without any defects and meets agreed reguirements, technical specifications and valid technical documentation. Supplier is fully responsible for materials and services of his subsuppliers. Warranty period of suplied goods is governed by the contract – general commercial terms (unless specified otherwise). 4. Quality system requirements Application of advanced quality planning and process approach are fundamental elements of quality assurance system. Supplier commits to plan, organize and realize his production process and quality assurance according to the Zero Defect strategy based on APQP methods (see attachement no.10). That leads to fullfilling all product quality requirements. Supplier is supposed to keep his quality management system updated according to latest ISO 9001 revision. Certification according to ISO/TS 16949 is a matter of agreement between supplier and Motorpal, a.s. Supplier is supposed to have a valid certification of evironmental management according to ISO 14001 and valid certification of Health and Safety management system according to OHSAS 18001. 5. First samples requirements Sampling including documentation is free of charge (unless specified otherwise in the order). All sampling documentation must be provided on Motorpal, a.s. forms. Supplier in cooperation with Supplier Quality Dept. is to specify sampling requirements on the PPAP form (see attachement no.11). Basic level: 05- Dimension inspection. 07 – Material inspection. 16 – Control plans. 21- Customer packaging requirements. All first samples must undergo mutual inspection of all dimensions and parameters stated on drawings including numerated positions marking. Supplier must properly identify the samples with label and number (see attachement no.6). Important: Samples must be labeled as SAMPLE (see attachement no.6) Supplier guarantees that Sample Inspection Report and samples meet requirements stated on the first page of the Sample Report. Sample Report must be submitted according to required level on the Motorpal, a.s. forms (on the page 2 (from 28) Motorpal, a.s. Supplier Quality Manual original MS Office Excel document). Forms can be downloaded on http://www.motorpal.cz/cz/kvalita/manual-kvalitypro-dodavatele Evaluated Sample Report will be sent back to supliers in electronic form after samples assesment in Motorpal, a.s. Samples are placed on Incoming Inspection Dept. in Motorpal, a.s. and in case of need (for example in case of nonconformity of serial delivery) are used as reference samples. Possible outcome of sampling: APPROVED – Motorpal, a.s. requirements has been met and supplier can supply the parts for test series. Sampling release does not free supplier from responsibility for delivered products quality. Requirements deviations that were undetected during sampling process can be the subject of claim or reclamation later. APPROVED UNDER CONDITIONS – Supplier can supply test serie according to approved documentation and Motorpal, a.s. order. Together with the test serie the plan of corrective actions for insufficiencies discovered during sampling must be submited for approval. In case the plan is not submited or realized the supplier is not allowed to supply untill all requirements are met. NOT APPROVED - Samples submited by supplier did not comfort to usage or funcion of Motorpal, a.s. products in key parameters. Incomplete reports and documentation will automatically lead to dissaprove the sampling. Supplier will be notified electronically and will be asked for new sampling. . 6. Serial deliveries quality assurance Commencement of serial deliveries follows obtaining of written or electronic Sampling Report approval. Due to assuring the serial deliveries quality supplier must constantly prove comformity of the product with the requirements by elaborating and recording the Preventive Quality Sheet. 6.1 Regulated documentation Supplier always has to produce according to valid regulated documentation. Supplier receives the regulated documentation from Motorpal, a.s. Purchase Dept. If the drawing is owned by the supplier it must be approved and filed by Motorpal, a.s. Supplier is not allowed to pass the drawings and technical documentation to the third party without written approval from Motorpal, a.s. Preventive Quality Sheet Preventive Quality Sheet is an instrument for bringing forward the customer’s requirements. Preventive Quality Sheet contains following basic tools: - FMEA – Failure mode and effects analysis - a method that helps to identify potential failure modes in advance. SPC – statistic process control MSA – measurement system analysis Cmk – machines capability Cpk – process capability Systematic transfer of all customer requirements (important dimensions etc.) For detailed guide to the Preventive Quality Sheet see attachement no.12 Control plan Supplier will introduce control plan for whole part and for process defining all methods used for measurements inspection and product testing (gauge type, measurement frequency, operations sequence etc.) – see attachement no.4. page 3 (from 28) Motorpal, a.s. Supplier Quality Manual Flowchart Supplier will introduce process flowchart clearly describing steps and sequence of production process. The flowchart must meet Motorpal, a.s. requirements and needs (it shall begin with incoming inspection and end with expedition, etc.). Packaging specification During the sampling process supplier will introduce a proposal of packaging method that will ensure to protect the part from corrosion and mechanical damage. In this proposal supplier will make provision for Motorpal, a.s. parts cleanness requirements. Supplier is obliged to use this (approved) packaging method during the whole course of deliveries. Technical change documentation (see attachement no.9). This document is an instrument for technical changes monitoring and it goes along with the product unless agreed otherwise. Inicial process study Inicial process study defines acceptable level of preliminary process capability for all significant signs. If no significant signs were defined customer reserves the right to request inicial process capability for another signs. Study can be performed using long-term data from similar or alike process with explicit agreement with customer. In case of process incapability supplier must identify, assess and if possible eliminate specific causes effects. Process incapability must be announced to customer and corrective actions plan must be introduced unless agreed otherwise. 6.2 Delivery documentation for incoming inspection: Failing to introduce following documents with each delivery batch may be a reason for refusing the batch. Material atest Supplier must introduce required material atest according ČSN EN 10204 as stated in the order. Atest 3.1 containing chemical composition and mechanical characteristics unless agreed otherwise. Atest 2.2 must contain chemical composition. Heat and surface treatment protocol Supplier is to introduce heat treatment process and quality documentation if he provides heat treatment (cementation, hardening, annealing, etc). In case of providing surface treatment the protocols must contain coat measurement (galvanizing, chromating etc) Dimensions measurement record (inspection results) Final inspection dimensions measurement record is introduced with each batch unless agreed otherwise (see attachement no.5). Dimensions measurement record must contain: • Measured dimensions (drawings @) • Visual control (corrosion, surface treatment, deburring) • Other dimensions (measurement range extension can be required during serial production due to claims, assembly problems, etc.) Delivery quality and completeness declaration Delivery quality and completeness declaration (see attachement no.7) is to be properly filled in by supplier. 7. Change and deviation proceedings 7.1. Deviation proceedings Supplier is not eligible to supply deliberately to Motorpal, a.s. any goods that doesn’t meet quality requirements given by mutualy agreed technical documentation and/or respective contract. In exceptional case when supllied good contains deviation from requirements and supplier can competently suppose that Motorpal, a.s. could under page 4 (from 28) Motorpal, a.s. Supplier Quality Manual specific circumstances utilize this goods supplier can (in advance before delivery) request deviation approval. Supplier requests Motorpal, a.s. Purchasing Dept. for deviation approval electronicaly or in writing on respective form (see attachement no.17). Approval/Denial decision is sent to supplier by the Purchasing Dept. executive in electronic form within 14 days from request introduction. Supplier must keep records about deviation validity end date. After validity of the deviation expires supplier must assure conformity with original specifications. Deliveries containing deviation must be properly labeled (see attachement no.8) 7.2. Change proceedings -Supplier iniciated change request Supplier requests Motorpal, a.s. Purchasing Dept. for change approval electronicaly or in writing on respective form. Filled 8D report is to be send along with the request. Approval/Denial decision is sent to supplier by the Purchasing Dept. executive in electronic form within 30 days from request introduction. Changes cannot be introduced into the process without Motorpal, a.s. written approval. Change reguest submission is required in the cases of: • Use of different construction or material from what was used in previous approved part or product • Production using new or modified tools or forms including tool replacement • Production after renovation or reseting of existing tools or machines. • Production using tools or machines moved to another place or in another facility. • Change arts, materials or services (heat treatment, surface treatment etc.) sub-supplier. • Production using tools that haven’t been used in serial production for longer than 12 month. • Product or process changes connected with product components made internally or by sub-supplier that can affect the assembly, shape, function, performance or durability of final product. -Motorpal, a.s. iniciated change Motorpal, a.s. reserves the right to change the design or technical specifications of the requested goods during the contract. Supplier will receive written announcement of technical change plan from Motorpal, a.s. Purchase Dept. Supplier will inform Motorpal, a.s. in response about goods quantity on stock and/or in process and about time needed to implement the requested change. These information including time plan suggestion for neccessary steps will be introduced to Motorpal, a.s. Purchase Dept. within 5 days unless agreed otherwise. After reviewing all questions regarding technical change Motorpal, a.s. can authorize the supplier to realize the technical change. Based on information from Motorpal, a.s. about releasing the change supplier is obliged to introduce detailed time plan for change implementation to Motorpal, a.s. Purchase Dept. and to report weekly about the progress. Supplier is not authorized to implement any change before obtaining information about technical change release from Motorpal, a.s. 8. Supplier Audit Supplier is obliged to enable Motorpal, a.s. to execute Supplier Audits. Motorpal, a.s. has a right to audit the suppliers facility in cases of product or process quality problems appearance. Supplier is to provide Motorpal, a.s. all necessary information and resources. Supplier has to enable Motorpal, a.s. and its customers the access to supplier’s (and its sub-supplier’s) stocks and production premises in order to parts, processes and documentation management quality assessment. Motorpal, a.s commits to announce the audit term in advance. Audit results are introduced to the supplier in the form of Audit Report. Supplier is obliged to propose and (after Motorpal, a.s. approval) realize corrective actions to eliminate insufficiencies discovered during audit in agreed schedule. 9. Complaint procedure Supplier will be notified in writting, by e-mail or fax or in urgent cases by phone when Motorpal, a.s discovers that purchased part, material or service does not meet defined specifications. Supplier is obliged to immediately perform page 5 (from 28) Motorpal, a.s. Supplier Quality Manual suitable corrective actions according to general purchase terms and is obliged to send filled 8D report (see attachement no.18). Unless agreed otherwise Motorpal, a.s. performs financial assessment of complaints monthly by submiting External Failure Record Summary which is sent electronicaly and in writing together with the claimed goods. Complaint procedure costs are contained in general purchase terms. 10. Suppliers evaluation Motorpal, a.s. Supplier Quality Dept. evaluates suppliers‘ ppm on the basis of their deliveries. „Zero ppm“ is the key quality indicator of each supplier. In case supplier discontinues fulfiling this key indicator he is (regardless on evaluation of other indicators) obliged to introduce effective corrective actions that will restore the process into agreed state. Suppliers evaluation is based on following indicators: • • • • • Zero ppm Delivering in time System certifications Price accommodation Communication 11. Escalation process After major deviations Motorpal, a.s. Supplier Quality Dept. will include supplier in escalation program „Critical suppliers“. Deescalation will be possible after proving sustainable effectiveness of implemented actions. Program contains four defined levels: Level 0: Supplier with problems Level 1: Suplier not succesful in problems solution Level 2: Supplier in need of assistance to secure deliveries capability. Warning Level 3: Supplier not suitable for Motorpal, a.s. quality. Evaluation In case of repeated incidence and/or not meeting Motorpal, a.s. requirements on improvement process, terms keeping or not reaching goals (rank „A“) following escalation principle is used: 1st escalation level: Suppliers process audit measures verification. Suppliers Development, Incoming Control and Purchase Logistics communicate with supplier on daily basis. Logistics and commercial representative is responsible on the supplier’s side. 2nd escalation level: Quality theme dialogue with competent specialised departments with management involvement. Head of Purchase Logistics, Global Sourcing referent and Head of Supliers Quality on side of Motorpal, a.s. – Head of Production, Suppliers Quality on supplier’s side. 3rd escalation level: Quality theme dialogue on the level of company management including top management. Possible rank shift to „D“ category. Purchase Manager, Quality Vicepresident, Production Vicepresident on Motorpal, a.s. side. Supplier’s side – management. page 6 (from 28) Motorpal, a.s. Supplier Quality Manual 12. Environment Supplier must assure that all materials and raw materials used in production chain meet all legal requirements as well as Motorpal, a.s. customers requirements especially concernig dangerous and forbidden materials regulations. We expect the suplier to follow ISO 14001 environmental management system standard as well as Health and Safety management OHSAS 18001 certification. Suppliers oblige during first sampling to insert material data into IMDS (International Material Data System www.mdsystem.com) and guarantee inserted data correctness. In case supplier is not able to secure this supplier is to provide all relevant data to Motorpal, a.s. to insert them to IMDS. page 7 (from 28) Motorpal, a.s. Supplier Quality Manual 13. Attachements These attachements are available on www.motorpal.cz Attachement Attachement Attachement Attachement Attachement Attachement Attachement Attachement Attachement Attachement Attachement Attachement Attachement Attachement Attachement Attachement no.1: SAMPLING – COVER SHEET no.2: SAMPLING - INSPECTION RESULTS no.3: SAMPLING - IMDS PROTOCOL no.4: CONTROL PLAN no.5: MEASUREMENTS PROTOCOL no.6: SAMPLES LABELING no.7: DELIVERY QUALITY AND COMPLETENESS DECLARATION no.8: DEVIATION IDENTIFICATION LABEL no.9: TECHNICAL CHANGES DOCUMENTATION no.10: APQP FORM no.11: PPAP FORM no.12: PREVENTIVE QUALITY SHEET no.13: FMEA COVER SHEET no.14: TIME PLAN no.15: DEVIATION APPROVAL REQUEST no.16: 8D-REPORT page 8 (from 28) Motorpal, a.s. Supplier Quality Manual Attachement no.1 page 9 (from 28) Motorpal, a.s. Supplier Quality Manual Attachement no.2 page 10 (from 28) Motorpal, a.s. Supplier Quality Manual Attachement no.3 page 11 (from 28) Motorpal, a.s. Supplier Quality Manual Attachement no.4 page 12 (from 28) Motorpal, a.s. Supplier Quality Manual Attachement no.5 page 13 (from 28) Motorpal, a.s. Supplier Quality Manual Attachement no.6 Attachement no.7 Attachement no.8 page 14 (from 28) Motorpal, a.s. Supplier Quality Manual Attachement no.9 page 15 (from 28) Motorpal, a.s. Supplier Quality Manual Attachement no.10 page 16 (from 28) Motorpal, a.s. Supplier Quality Manual Attachement no.11 page 17 (from 28) Motorpal, a.s. Supplier Quality Manual Attachement no.12 page 18 (from 28) Motorpal, a.s. Supplier Quality Manual Attachement no.13 Attachement no.14 page 19 (from 28) Motorpal, a.s. Supplier Quality Manual Attachement no.15 page 20 (from 28) Motorpal, a.s. Supplier Quality Manual Comments on Preventive Quality Sheet 1) Other samples: Offer sample - „Sample for visualization and offer assessment“ Mounting sample - „Sample for mounting experiments“ Development sample - „Sample for development status control“ Note No.1: There is an option to define special development samples for certain development steps Note No.2: Also „design samples“, „prototype“ Test samples - „Samples for function tests and reliability tests“ 2) A-samples - „functional": A-sample in priciple confirms technical functionality (design confirmation). It can be used as an information for customer and it can be used for preliminary tests. Note 1: Dimensions do not necessarily have to correspond with drawings. Note 2: There can still be limits of meeting customer requirements and RB specifications, for example by working voltage, working temperature, appearence or dimensions. A - samples are not suitable for long-term tests. Note 3: Definitive materials are used only partly. Production takes place in sample department (special production) or it is only adjusted existing product. 3) B-sample - „test": B - sample basically confirms technical functionality and can be used for first tests (also by customer) on the vehicle and can be set to test state. It serves for product requirements verification (also for first long-term tests). Note 1: Connecting and stopping dimensions match serial production. Note 2: All customers requirements may not be fulfilled yet. Note 3: B-sample is large made of final materials. Production uses test or subsidiary tools. 4) C-sample - „for release": C - samples meet customer and RB specifications. Customer testing enables "technical release" product releasing internaly closes development phase. Note 1: C samples are produced with serial tools (if possible) and with manufacturing process close to serial Note 2: Final material are used, suppliers are specified. Note 3: Product corresponds to the drawings 5) D-samples „pre-serial": These samples are in addition labeled with sample report number (see attachement 1,2,3). Approved sample report is a basis for seriál production release. Note 1: All parts of first samples must be produced using serial tools and serial processes and assembled and inspected under serial conditions. 6) Use for series: Product is release for serial production by Motorpal, a.s. Supplier Quality Dept. 7) Process FMEA: Motorpal, a.s. defines deadline for Process FMEA submision and subsequently cempletes point 16 in Preventive Quality Sheet - importance of failure consequences. 8) Parts criticality levels: Used critical marks to be defined here (symbol + specification) 9) Parts, Functionality, critical parameters information page 21 (from 28) Motorpal, a.s. Supplier Quality Manual critical (important) product functions description 10) Final product: Final product description. 11) Important parameters: Here are specified important paremeters according to actual drawing. 12) Critical characteristics: S = Characteristics important in term of safety G = Characteristics important in term of legal regulations SG = Characteristics important in term of safety and legal regulations K = Important characteristic of product or process that is crucial for customer or inner process satisfaction OS = Characteristic important for operating personell safety C = Special characters requiered by customer and marked additionally in relevant documents (ISO/TS 16949) 13) Special characteristics status: Following critical characteristics are possible: Fu = functionally critical Fe = production critical Mo = Assembly critical 14) Customer mounting dimensions: Parameter directly connected to customer's important parameters (threads, surfaces,…) 15) Process FMEA: Possible risks analysis that identifies points of possible failures origination, quality improvement It is necessary to be particular about: Failure effects importance S (Severity) - (point 16) O (Occurrence) - (point 17) Failure appearence probability Failure detection probability D (Detection) - (point 18) Actions in stated sequence. Costs / demand factors, terms and goal must by considered in the choice of appropriate actions. Responsible department and implementation term is defined for each action. Customers requirements (stated in contract) about actions in FMEA that vary from FMEA methodic standards are taken into consideration here. Process FMEA actions specification criteria Failure risk assessment: S x O. Goal of Product FMEA is reaching S x O < 36. Values higher than 36 indicate that process is not optimally designed. - Deviation S x O < 36 must be reasoned in FMEA cover sheet (see attachement no.15). Assessment of failures that may not be discovered: O x D. Goal of Process FMEA is to O x D <15. Higher values indicates that defective products may get to the customer. Note: - Deviations O x D <15 must be reasoned in FMEA cover sheet (see attachement no.15). 16) Severity of failure effects S (Severity) Evaluation in 1-10 scale. Our products must be without severe defects. High risks as safety risks (S = 10) or not observing legal regulations (S = 9) must be lowered. System changes as failure detecting by detection device, diagnostics, function backup efffect or warning/alarm can lower the severity to S < 9. General assessment Failure with the very high severity affecting safety evaluation 10 Criteria related to application method Uawares blocked motor, uncontrolled increasing or falling of engine rpm, torsional moment increase insufficient torsional moment flamable mixture on hot motor parts, strong page 22 (from 28) Motorpal, a.s. Supplier Quality Manual Failure with the very high severity partly affecting safety and/or braching legal regulations High severity failure, basic functions failure, uncontrolable engine stop 9 Severe failure, heavily limited engine function, imediate need of repair 7 Significant failure, important service and comfortance systems failuire, not imediate need of repair Heavier failure, limitation of important service and comfort systems function Mild failure, minor limitation of service and comfort system (noticable by any operator) 6 Insignificant failure, customer lightly limited, noticable by qualified operator Customer unable to notice any insufficiencies, failure can be detected only by specialised personel with diagnostic equipment No failure effects 3 8 5 4 2 1 temperature rise in catalyzer, uncontrolable device function. Engine failure during ride, engine fails to stop, diesel particulate filter cloth, fuel in environment, Sudden power drop by >20 %, noice, legal regulations branch (branch of emissions regulations, vehicle or operator safety threating failure. Engine fails to start, sudden power drop by >15 %, engine jamming, impossibility of components assembly by customer. Unstable engine idling (engine jerking), retarded start, impossibility to start the engine under freezing point, threat to other engine components functions (as insuficient turbo pressure) >10 % power loss, problematic engine start process, smell – excess components temperature, (as contact resistance on temperature sensor connector) increase of fuel consumption, amount of emissions, driver physical stress, noice level (without legal regulation branch), (for expample temperature sensor failure) Visual defect – non-readable marking, rumpled bolts, starting corrosion, shot engine power fluctulation Minor idle engine speed increase, minor engine power changes, minor emissions increase, minor noice increase Unnoticable minor effects, detectable only by technical means (as slight temperature increase on control unit) No failure effects 17) Failure appearance probability O (Occurrence) Evaluation in 1-10 scale Basic rule: Final goal is to reach O = 1. According to assessments tables, process is sutable when O ≤ 2. Process is thought of being stable when O < 3. Process FMEA is in faulty mode when O > 4. Further preventive actions must be defined. General assessment criteria Possible failure extend * ppm * cpk *** Assessment points Very high. It is almost certain that failure/cause occurs often. 1/10 1/20 100.000 50.000 - ** - ** 10 9 High. Failure/cause occurs repeatedly. Inaccurate process. 1/50 1/100 20.000 10.000 - ** - ** 8 7 Moderate. Failure/cause occurs occasionally. Comparable with process. 1/20 1/1.000 1/2.000 5.000 1.000 500 0,94 1,10 1,17 6 5 4 Minnor. Rare occur of failure/cause. Competent process. 1/15.000 1/150.000 ≤1/1.500.000 67 6,7 ≤0,67 1,33 1,50 ≤1,67 3 2 Unlikely. Improbable occur of failure/cause. * After product life cycle **no point 1 ***during Process FMEA 18) Failure detection probability D (Detection) Assessment in 1-10 scale This criteria serve for disclosure of failure detection probability in process. Analysis should be considered only in combination with another activities as process effectiveness – detection failure (diagnostic function, SPC,…) , Probability of defect parts leak (see point no.15 OxD factor evaluation) page 23 (from 28) Motorpal, a.s. Supplier Quality Manual DETECTION PROBABILITY CRITERIA DETECTION METHODS SPREAD Cannot detect or is not checked EVALUATION 10 Almost impossible Absolute certainty of non-detection Very remote Controls will probably not detect Remote Controls have poor chance of detection Very low Controls have poor chance of detection Low Controls may detect Moderate Controls may detect Moderately high Controls have a good chance to detect High Controls have a good chance to detect Very high Controls almost certain to detect Error detection in-station, SPC – measurement, automatic measurement 2 Controls certain to detect Discrepant parts cannot be made because item has been error proofed by progress/product design. 1 Almost certain Control is achieved with indirect or random checks only. Control is achieved with visual inspection only. Control is achieved with double visual inspection only Control is achieved with SPC (Statistical Process Control). Calibre control of first piece after setting. Control is based on variable gauging after parts have left the station, OR Go/No Go gauging performed on 100% of the parts after parts have left the station. Error Detection in subsequent operations, OR gauging performed on set-up and firstpiece check. Error detection in-station, error detection in subsequent operations by multiple layers of acceptance. 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 19) Risk factor- RPN: RPN- risk priority number. RPN exposure is counted as product of three values (S,O,D) based on Process FMEA. If RPN≥100 points supplier must always submit corrective actions for approval (unless stated otherwise by customer). Severity of failure effects Failure appearence probability Failure appearence probability S (Severity) O (Occurrence) D (Detection) - (point 16) - (point 17) - (point 18) S x O x D = RPN (max.125) Result higher than 100 indicates unstable process. 20) Comments: Comments on "Important parameters" column can be added here (for example A-A section; A view; RPZ or control plan/testing instruments etc.). Also another necessary quality assurance supplier actions os machining tests, SPC, material and structural analysis, etc. 21) Control plans / measuring instruments: page 24 (from 28) Motorpal, a.s. Supplier Quality Manual Supplier will submit part control plan that defines all control methods used for product measurement and testing control (measuring device type, control frequency, operations sequence, …) see attachement 4. 22) Machine capability: Machine capability - Cm/Cmk Performing machine capability is based on customer requirement. Customer defines required sample volume for machine capability calculation. Unless stated otherwise, machine capability is usually measured on 50 ok successive samples without intervention into machine. Machine is capable if Cmk ≥ 1,67. Rarely due to measurements costs required amount for Cmk can be 35pcs. Machine is capable if Cmk from 35pcs ≥ 2,0. 23) Process capability: Process capability Ppk ≥1,33 Preliminary process capability Cpk ≥ 1,67 Schopnost procesu se provádí na základě požadavku zákazníka. Předběžná způsobilost procesu Cpk = krátkodobé zkoumání (méně než 30 výrobních dní, minimálně 100 naměřených výsledků z min. 25 podskupin) umožňující včasné získání informací o účinnosti (nového nebo modifikovaného) procesu. Postup: Zkoumání by se mělo zakládat na co největším počtu měřených hodnot. Aby bylo získáno dostatečné množství informací pro rozhodování, musí být k dispozici výsledky alespoň 25 výběrů tak, aby bylo celkem naměřeno 100 hodnot (při jednom výběru nutno odebrat 3 - 5 dílů vyráběných ve sledu za sebou, doporučuje se odebrat 5 dílů za sebou). Období pro zkoumání předběžné způsobilosti procesu nesmí přesáhnout 30 dnů.Trvalá (průběžná) způsobilost procesu Ppk = dlouhodobé zkoumání (minimálně 20 výrobních dní, min. 25 podskupin, minimálně 100 naměřených výsledků) umožňující získání informací o účinnosti procesu za delší časové období. 24) Measurement instruments capability: Measurement system analysis; Measuring instruments capability is evaluated by two basic procedures. 1, Measuring instrument potential / Measuring instrument capability - Cg/Cgk ≥1,33; Measuring instrument potential (cg) – value representing influence of measurement reproductibility, that means rate of 15% of process width (6σ - equate probability 99,73% of normal data distribution) or 15% of tolerance field (T) width and widht of variability (reproducibility) of measuring instrument (6sm - equate probability 99,73% of normal data distribution). Measuring instrument capability (cgk) – value representing of influence of measuring instrument accurancy and reproducibility. Compared to potential it can in adition record shift of median outside the etalon value. 2, Total measuring instrument variance – R&R ≤10 % Measuring system is reproducable if different operator using same measuring instrument reach identical or very similar results. Measuring system is repeatable if repeated measurement of same part gives same results. 25) SPC - regulated process: Regulated measurement process that process data obtained by measuring of monitored quality parameter (data in numeral form). Regulated process is automatically applied on significat/critical characteristics. If Preliminary process capability Cpk is ≥ 1,33 supplier is required to use SPC – regulated process. If Preliminary process capability Cpk is lower then 1,33 supplier is required to submit corrective actions. 26) Process control/regulation: page 25 (from 28) Motorpal, a.s. Supplier Quality Manual Describe the process regulation or inspection method here (for example x/s, x/R, lower value, colection card) 27) Dokumentace Cpk : Cpk from supplier is required here and it is to be revised and recorded monthly. 28) Batch definition A = material batch B = heat treatment batch C = production batch D = lead off batch All yellow colored fields are filled in by supplier, white fields by customer! Cross-hatched fields will be filled in additionally by customer in case of uding in seriál production. page 26 (from 28) Motorpal, a.s. Supplier Quality Manual Attachement no.16 : page 27 (from 28) Motorpal, a.s. Supplier Quality Manual 8D report description 8D-Report search for problem definiton and understanding. It asks why the process works outside the target range and gives suitable corrective action. 8D-Report is devided into 8 steps. 1) Team assembly If a single person cannot solve the problem quickly than put together small gruop of people with good knowledge of product/process. Share the roles in the team (leader, members). Record the team members and identify their goals, roles and responsibilities. 2) Problem description Describe the problem entirely, not only its symptoms. Its recommended to ask questions (who, what, where, how, how many, why,…) 3) Short-term actions Implement, audit and record actions leading to isolation of problem from customer until permanent corrective action is implemented. For example sorting the N.OK parts by customers (assembly, stocks, incoming inspection). Or immediate replacement of N.OK parts with OK parts (if you have any). 4) Analysis of reasons Goal is to identify all possible causes of problem occurance. Use Ishikawa chart (fish-bone chart) and identify possible problem causes. Record the most probable causes. 5) Actions for elimination Identify possible actions that should eliminate main causes of the problem. Assess the costs and supposed effectiveness and choose the most suitable ones. 6) Effectiveness of introduced actions Define, apply and monitor the permanent corrective action that will eliminate the problem. 7) Preventive actions Goal of this phase is to prevent reoccurence of the solved problem by both technical and system means, for example by changes in FMEA and control plan of this product and of all alike products with risk of same problem occurance. 8) Evaluation Evaluation of introduced actions and 8D-Report closing. page 28 (from 28)
© Copyright 2026