Jersey Milk An effective way of improving Cheddar cheese yield and profitability
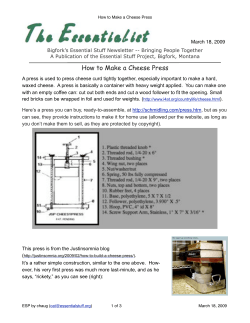
Jersey Milk An effective way of improving Cheddar cheese yield and profitability Constant Cheese Quality • • • • • Cheese composition fully met food quality standards Cheese fat increased in autumn, winter and spring (maximum increase 18%) Cheese moisture decreased in spring and summer (maximum decrease 8%) Cheese protein, salt or pH levels were not modified Cheese colour was yellower in a few batches of cheese, still overall no noticeable difference was found either by graders or instrumental colour analysis • Cheese texture was not affected by the inclusion of Jersey milk as determined both by instrumental analysis and grading • Cheese grading scores both at 3 & 8 months were not affected by the inclusion of Jersey milk and the cheese produced on a commercial scale was sold between 8 & 15 months • Consumers who tried mild Cheddar cheese made with up to 25% Jersey milk were not able to detect any differences “…up to 35% increase in cheese yield with no noticeable impact on quality, leading to a significant increase in manufacturing profitability” Financial Benefit • Profit was increased when Jersey milk was included. The higher cheese yield always outweighing the higher milk price • Cheese yield was the most important factor determining the level of additional profits while change in cheese price and milk price had a small impact, thus not putting the profitability by using Jersey milk at risk • Using high inclusion of Jersey milk reduces fluctuations in additional profit due to change in cheese yield up to 35% more yield Ease of Blending and Processing • The recommended blending amount is the highest possible level of Jersey milk due to the important increase in yield and profitability and the lack of detrimental effect on cheese quality • No change in processing was found to be necessary For more information contact: 01363 776623 [email protected] For more information: • Jersey Milk for Cheddar Cheese Production Project scientific articles J.H. Bland, C.C. Fagan & A.S. Grandison. Effect of blending Jersey and Holstein-Friesian milk on Cheddar Cheese Processing, Composition and Quality. Journal of Dairy Science. Under review. J.H. Bland, C.C. Fagan & A.S. Grandison. Estimation of the Financial Benefit of using Jersey milk at Different Inclusion Rate for Cheddar Cheese production using Partial Budgeting. Under review Reference (1) Capper, J. L.; Cady, R. A. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 165–176. (2) International Food Standards. Codex Alimentarius Standard for Cheddar cheese 263-1966 A-6- 1978, Rev.1-1999, Amended 2003 www.codexalimentarius.net/web/standard_list (accessed Apr 24, 2014). T he Jersey breed has a lower milk yield than Holstein-Friesians cows however, the milk has a higher fat, protein and casein content. In addition, this breed is well known for its increased longevity, higher fertility and lower feed and water requirements per unit of body weight. The Jersey Milk for Cheddar Cheese Project This study should remove any concerns about the effect which Jersey milk could have on Cheddar cheese texture or flavour – also demonstrating the Jersey milk attributes in a mature product. In addition to the beneficial effect on cheese yield, using Jersey milk was also shown to reduce the carbon footprint and environmental impact of Cheddar cheese production. An in-depth review of the compositional qualities of Jersey and Holstein milk was completed. This led to a better understanding of the effects of inclusion of Jersey milk into the standard milk supply to different levels on Cheddar cheese production, the process can be optimized, leading to benefits and financial gains to both cheese makers by increasing cheese yield and Jersey farmers by increasing milk demand. The project has been carried out by the University of Reading and sponsored by the following organisations: Pocock Memorial Trust Julie Bland, Reading University PhD student who completed the study UK Jerseys 40% Increase in Cheddar cheese yield Hilmar is one of the biggest producers of Cheddar cheese in the world, processing over 9.5 million litres of milk per day; and using 30% Jersey milk in their California site and 55% Jersey milk at their Texas site. 30% Effect of including Jersey milk in Holstein-Friesian milk on Cheddar cheese yield 24.5% 35% 17.5% 20% 14.0% 10.5% 10% 7.0% 3.5% 0% 0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60% 70% 80% The cheese making Percentage Jersey Milk process mirrored that of Lye Cross Farm by using non-standardized milk, starter cultures. 90% 100% Additional commercial trials were performed at Lye Cross Farm to ensure the result from the pilot scale conformed to what would be found commercially. All cheeses were analysed for yield, composition and sensory quality - the latter was evaluated by instrumental analysis of colour and texture, professional graders and sensory test using 280 consumers in total. Higher Cheddar Cheese Yield* • • • • Increased yield throughout the year (up to 35%) Constant increase throughout the year Increased fat recovery (up to 30%) Increased protein recovery (up to 13%) *Based on both pilot and commercial trial using unstandardized milk with an average Holstein-Friesian milk composition of 3.94% fat and 3.15% protein and Jersey milk composition of 5.43% fat and 3.74% protein. Additional profit (Pence per Litre of milk) Hilmar Cheese Company, an inspiration to the Jersey breed, worldwide. From the base research Cheddar cheese was produced using a wide range of inclusion rates of Jersey into HolsteinFriesian every month over a one year period in the University pilot plant. 12.00 10.00 Additional profit bought by the use of Jersey milk 3.89 8.00 4.92 6.00 3.94 4.00 2.00 9.84 2.95 1.97 0.98 0.00 0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60% 70% 80% 90% 100% Percentage Jersey Milk
© Copyright 2026