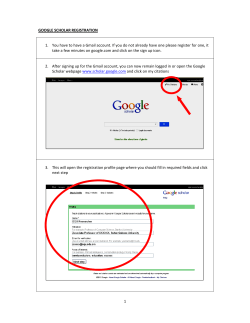
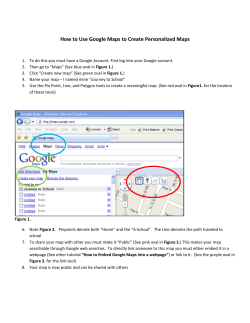
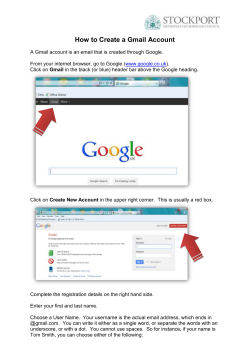
Click - ICNB 2014
Conference Schedule 2014 Barcelona Conferences Barcelona, Spain December 18-20, 2014 2014 3rd International Conference on Power Science and Engineering (ICPSE 2014) 2014 5th International Conference on Nanotechnology and Biosensors (ICNB 2014) 2014 International Conference on Mechanical Properties of Materials (ICMPM 2014) Conference Schedule This conference is made possible with the support of Thank you also to our sponsors 1 Conference Schedule Welcome to 2014 Barcelona Conferences The American Society for Research (ASR) and our host, IACSIT, welcome you to attend ICPSE2014, ICNB2014, and ICMPM2014 in beautiful and historic Barcelona! Each year, ASR endeavors to provide a perfect balance between professional and personal development. We hope that over the 2 days your work and that of your institution or company will be enhanced both by what you learn and those with whom you connect. Our field is enriched by the dialogue among colleagues from around the world which occurs during presentation sessions as well as informal conversations. We hope this is a memorable, valuable, and enjoyable experience! Table of Contents Items Welcome Table of Contents Announcement General Conference Information Instructions for Oral Workshop Conference Keynote Speakers Conference Schedule ICPSE2014 Sessions ICNB2014 Sessions ICMPM2014 Sessions Pages 2 2 3 4 4 5-6 7-8 9-12 16-22 35-39 45-51 22-29 39-45 13-16 30-34 51-53 53 54-60 Session 1 Session 3 Session 6 Session 8 Session 4 Session 7 Session 2 Session 5 Poster Presentation Hotel Information Upcoming Conferences 2 Conference Schedule ANNOUNCEMENT *ICPSE 2014 conference papers will be published in Applied Mechanics and Materials Journal (ISSN: 1660-9336). Indexed by Elsevier: SCOPUSwww.scopus.com and Ei Compendex (CPX) www.ei.org. Cambridge Scientific Abstracts (CSA)www.csa.com, Chemical Abstracts (CA) www.cas.org, Google and Google Scholar google.com, ISI (ISTP, CPCI, Web of Science) www.isinet.com, Institution of Electrical Engineers (IEE) www.iee.org, etc. *ICNB 2014 conference papers will be published in Applied Mechanics and Materials Journal (ISSN: 1660-9336). Indexed by Elsevier: SCOPUSwww.scopus.com and Ei Compendex (CPX) www.ei.org. Cambridge Scientific Abstracts (CSA)www.csa.com, Chemical Abstracts (CA) www.cas.org, Google and Google Scholar google.com, ISI (ISTP, CPCI, Web of Science) www.isinet.com, Institution of Electrical Engineers (IEE) www.iee.org, etc. *ICMPM 2014 conference papers will be published in Applied Mechanics and Materials Journal (ISSN: 1660-9336). Indexed by Elsevier: SCOPUSwww.scopus.com and Ei Compendex (CPX) www.ei.org. Cambridge Scientific Abstracts (CSA)www.csa.com, Chemical Abstracts (CA) www.cas.org, Google and Google Scholar google.com, ISI (ISTP, CPCI, Web of Science) www.isinet.com, Institution of Electrical Engineers (IEE) www.iee.org, etc. A best presentation will be selected from each session, announced and award a certificate at the end of session 3 Conference Schedule General Conference Information Take a look at 2014 Barcelona conferences offer you... •There are 8 sessions, on topics as Electrical materials and alloys materials, Civil Engineering Materials, Composites materials, Nanosensors and biochemical materials, Electrical Engineering and Electric Machines, Power Systems and Control Engineering, Electrical and electronic materials, Energy Engineering and Management. • Inspiring and thought-provoking keynote presentationsfrom Prof. Magnus Thor Jonsson and Prof. B.V. Reddy (see page 5-6 for details about the keynote speakers) • Plenty of opportunities to network and forge connections with your fellow attendees from across the globe,including Keynote Speech Session and Oral presentation Sessions. • Explorethe rich and colorful attraction in Barcelona. Instructions for Oral Workshop Devices Provided by the Conference Organizer: • Laptops (with MS-Office & Adobe Reader) • Projectors & Screen • Laser Sticks Materials Provided by the Presenters: • PowerPoint or PDF files Duration of each Presentation (Tentatively): • Regular Oral Session: about 15 Minutes Presentation including 3 Minutes of Q&A • Keynote Speech: 40 Minutes of Presentation including 5 Minutes of Q&A 4 Conference Schedule Conference Keynote Speakers Prof. Magnus Thor Jonsson, University of Iceland, Iceland Magnus Thor Jonsson is a Professor of Mechanical Engineering at the School of Engineering and Science, University of Iceland, located in Reykjavik, Iceland. He received his MSc. degree in Mechanical Engineering from the University of Iceland, Department of Industrial Engineering in 1982 and his PhD in Mechanical Engineering from the Mechanical Department at the Technical University of Norway in Trondheim in 1987. His major field of study was model based design using nonlinear FEM models. His main research interest is in the field of model based optimization for geothermal power plants. He has published a number of reviewed research papers and led a number of funded research projects in the areas of thermal and structural modeling of geothermal wells and optimization of steam gathering systems for geothermal power plants. Prof. Jonsson has worked as the Department Head of the Mechanical Engineering Department and has been the chairman of the Engineering Research Institute, University of Iceland, chairman of Continuing Education, and the chairman of CAD, CAM and CAE Association in Iceland. He has also been the chairman of the Machine Group of Icelandic Standards. He has been a board member of many steering committees at the University of Iceland and at Icelandic associations such as the Icelandic Society of Engineers and the IT&T User Forum. 5 Conference Schedule Prof. B.V. Reddy, University of Ontario Institute of Technology (UOIT), Canada Bale Viswanadha Reddy (B.V. Reddy) is a Professor in Department of Mechanical Engineering in Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science, University of Ontario Institute of Technology (UOIT), Oshawa, Ontario, Canada. Prior to this Dr. Reddy also worked as an Associate Professor in Mechanical Engineering Department, University of New Brunswick (UNB), Fredericton, Canada. Dr. Reddy received his MTech and PhD degrees in Mechanical Engineering from IIT, Kharagpur, India. Dr. Reddy research interests are in the area of advanced and sustainable energy systems, exergy analysis, energy management, heat transfer, waste heat recovery and alternative energy sources. Dr. Reddy has led funded research projects in the area of combustion, energy systems, energy efficiency improvement and biofuels. Dr. Reddy has published 175 papers in refereed journals and refereed conference proceedings. He is also involved in the organization of many international conferences as a conference chair, track chair, organizing committee member, advisory committee member etc. He has also chaired technical sessions in international conferences and has delivered keynote and invited presentations in various international conferences. Dr. Reddy also contributed book chapters along with his research collaborators in thermodynamics and energy systems area. Dr. Reddy has also received best professor award for teaching excellence five times both in India (VIT, Vellore) and in Canada (UNB, Fredericton; UOIT, Oshawa). 6 Conference Schedule Conference Schedule Day 1, Thursday, December 18, 2014– Onsite Registration Only Registration: Hall 09:30am-12:00pm 14:00pm-17:00pm Arrival, Registration and Conferencematerials collection **Certificate for Participation can be collected at the registration counter** Day 2, Friday, December 19, 2014 Simple Version: SALON TERRAZA 08:30a.m.-12:05p.m. 08:30am-08:35am Opening Remarks Keynote Speech I: Prof. Magnus Thor Jonsson, 08:35am-09:20am University of Iceland, Iceland Keynote Speech II: Morning Prof. B.V. Reddy, 09:20am-10:05am University of Ontario Institute of Technology (UOIT), Canada 10:05am-10:10am Plenary Photo 10:10am-10:20am Coffee Break 10:20am-12:05pm SALON TERRAZA SALON TERRAZA C Session 1 Session 2 Lunch 12:00pm-13:00pm 7 Conference Schedule Afternoon --- Author’s Oral Presentation 13:00pm-19:00pm 13:00pm-16:00pm SALON TERRAZA A SALON TERRAZA B SALON TERRAZA C Session 3 Session 4 Session 5 Coffee break 16:00pm-16:10pm 16:10pm-19:00pm Session 6 pp. 9-12 Session 7 Session 8 Session 1 /10:20-12:05 Energy Engineering and Management Venue: SALON TERRAZA pp. 16-22 ICPSE2014 Time Table Session 3 / 13:00-16:00 Electrical Engineering and Electric Machines Venue: SALON TERRAZA A pp. 35-39 Session 6/ 16:10-19:00 Power Systems and Control Engineering Venue: SALON TERRAZA A pp. 45-51 Session 8/ 16:10-19:00 Electrical and electronic materials Venue: SALON TERRAZA C ICNB 2014 Time Table pp. 22-29 pp. 39-45 Session 4/ 13:00-16:00 Composites materials Venue: SALON TERRAZA B Session 7/ 16:10-19:00 Nanosensors and biochemical materials Venue: SALON TERRAZA B ICMPM 2014 pp. Time Table Session 2/10:20-12:05 13-16 pp. 30-34 Civil Engineering Materials Venue: SALON TERRAZA C Session 5/13:00-16:00 Electrical materials and alloys materials Venue: SALON TERRAZA C 8 Conference Schedule Full Schedule: SALON TERRAZA Plenary Speech+ Plenary Photo 08:30a.m.-10:10a.m. 08:30am-08:35am Opening Remarks Keynote Speech I: 08:35am-09:20am Prof. Magnus Thor Jonsson, University of Iceland, Iceland Morning Keynote Speech II: 09:20am-10:05am Prof. B.V. Reddy, University of Ontario Institute Technology (UOIT), Canada 10:05am-10:10am Plenary Photo 10:10am-10:20am Coffee Break of Morning Session Authors’ Oral Presentation 10:20am-12:05pm Session 1(SALON TERRAZA) ICPSE2014-Energy Engineering and Management Session Chair:Prof.Mohammed Aounallah, University of Sciences and Technology Mohamed Boudiaf of Oran USTO-MB, Algeria 9 Conference Schedule SE23 Experimental Study of Temperature Variation of a Solar Air Collector Tassoult Houda, Haddad Brahim and Sellami Rabah Unité de Développement des Equipements Solaires, UDES/Centre Développement des Energies Renouvelables, CDER, Algeria de Abstract—Solar energy which is free and abundant in most parts of the world has proven to be an economical source of energy in many applications. The energy that the earth receives from the sun is so enormous and so lasting that the total energy consumed annually by the entire world is supplied in as short a time as half an hour. The sun is a clean and renewable energy source, which produces neither green-house effect gas nor toxic waste through its utilization. The development of solar air collectors has seen its growth during the oil crisis. These sensors are generally used in space heating, particularly in the field of drying food products. Our experimental work is the study of the variation of the temperature of a solar air between the absorber and the working window with natural convection and for drying of food products. The measured temperatures of the absorber and the air at the outlet of the sensor have been used to find the temperature profile. This study will be useful for a new design of a photovoltaic-thermal hybrid solar panel in order to improve the electrical performance extrairant heat at the absorber. SE34 Index Terms—Component / solar air collector / solar drying / air distribution / thermal effect. Energy Efficiency in Small and Medium Enterprises: Lessons Learned in 280 Energy Audits across Europe Fabio Morea, Johannes Fresner, Christina Krenn, Juan Aranda Uson, Fabio Tomasi AREA Science Park, Italy Abstract—This paper investigates the main factors influencing an energy auditing procedure, leading to the adoption of energy efficiency measures by small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), providing suggestions both for enterprises and energy policy makers. Our analysis is based on a sample of 280 SMEs from 7 European countries which participated in an international project devoted to industrial energy efficiency. Lessons learned during the energy audits are summarized in 8 key findings: (1) Energy Audits are a valuable activity for SMEs, yet (2) not a viable option for consultancy on a commercial basis. The main difficulties in carrying out an energy audit are (3) lack of data on energy consumption, (4) information barriers and (5) other soft factors such as expectations and previous experience. Economic factors (6) are significant barriers to energy efficiency. Among the energy efficiency measures (7) behaviour and control are key factors. Finally (8) an appropriate method for energy auditing is a key to success. SE46 Index Terms—Energy Conservation, Industrial Energy Efficiency, Energy Audit, Small and Medium-sized Enterprises; energy efficiency barriers; Linear Regression. Wide Spread Exploitations of Bioenergy: Are the Ways towards Sustainable Energy? Md. Mizanur Rahman, Jukka V. Paatero, and Risto Lahdelma 10 Conference Schedule Aalto University, Finland Abstract—The recoverable proven reserves of fossil fuel sources are projected to be exhausted by the end of this century. In response to the exhaustion of fossil resources, there is a serious need to find alternative fuel sources. Bioenergy is one of the potential candidates to counteract the fossil-fuel depletion challenge. Despite bioenergy sources appear to be renewable and net-zero GHG emitter, bioenergy undergoes competition with food, feed and other crucial applications. Since earth’s eco system has a limited capacity of land and water resources, overuse of these resources in bioenergy production could cause adverse social and environmental impacts. This paper summarizes the key sustainability issues involve in bioenergy chain, and examine the potential role of bioenergy in dealing with these sustainability issues. We found that bioenergy can be a sustainable source of energy provided that it has maintained irrationality in using of natural resources and several limits. In contrary, bioenergy would provoke further social and environmental problems if the sustainability issues are not given proper consideration. SE57 Index Terms—Sustainability, bioenergy, soil erosion, biodiversity, emission. Energy Losses Decrease in Oil Transportation Based on Plant-Wide Technology Dmitrii Starikov, Evgeny Rybakov and Evgeny Gromakov National Research Tomsk Polytechnic University, Russian Federation Abstract—Energy losses minimization with Plant-wide technology usage is described in the article. Main consumer in oil transport is founded and described to decrease losses during regulation. Obtained results during research show possibility of power losses in oil transport system and appearance of synergetic effect. SE68 Index Terms—Pressure control, Plant-wide, bypass valve, pipeline, energy efficiency. A Study on the Development of Cooling Water Pump with Closed Construction for Electric Vehicle Joohan Kim and Youngkyoun Kim Korea Electronics Technology Institute (KETI), South Korea Abstract—It is used electric drive water pump for efficient thermal emission in electric vehiclecooling system. Electric vehicle is managing thermal emission of drive motor, inverter and highpower devices efficiently. There is difference with mode that cool heat that is occurred in engine ofconventional vehicles. Therefore, need correct cooling water pump in electric vehicle property. Thispaper deals with a high efficiency design of cooling water pump for electric vehicle, especiallybrushless DC (BLDC) motor and impeller for cooling water. We achieved impeller flow analysisabout high efficiency and low commutation torque ripple motor design. We have used the 2D FiniteElement Method for calculating the characteristics of brushless DC (BLDC) motor, computing fluidmechanics (CFD) as numerical analysis for impeller design. We confirmed generating power of 32w,in the case of approving voltage of 13.5 V this experiment. In this load point, input current is about 2.6A, motor efficiency was evaluated about 78 %. We confirmed static pressure of 0.59 Bar and flow rateof 16LPM, wad evaluated about 59.3% of 11 Conference Schedule pump impeller efficiency. SE304 Index Terms—Cooling pump, Impeller, CFD, BLDC motor, Static pressure, Efficiency Evaluation of the Use of a Solar Source for Air Conditioning for Home in Algeria Nor REBAH University of Souk Ahras, Algeria Abstract—Today's global environmental problems, such as global warming, destruction of the ozone layer, degradation of air quality and their implications for human health have become a major concern for the environment, residential areas as well as our living conditions. Numerous research studies were devoted to address these topics due to their crucial importance. The purpose of this study is to develop and improve the bioclimatic architecture of residential housing according to the Algerian energy policy. We have calculated the reduction of housing energy consumption for air conditioning and hot water by replacing the system which is based on fossil fuels (oil and gas) by the newly proposed architecture which is based on renewable solar energy. This is being conducted for three different sites within Algeria. We carried out an explorative economic comparison of the two systems. Based on experimental results, the proposed system proved to be able to cover more than 55% of the total electricity needs for air conditioning. Therefore, this shows the potency of reducing the electricity utility bill up to a half with much better expected results for southern regions of Algeria. SE310 Index Terms—Energy buildings consumption, Solar heating System, Energy simulation of building, economic comparison, Algerian regulation. Experimental Studies on a Pendulor Wave Energy Extractor in a Wave Channel Sumesh Narayan, Ashneel Deo, Niranjwan Chettiar and Jai Goundar The University of the South Pacific, Fiji Abstract—A Pendulor wave energy convertor was tested in a two-dimensional Wave Channel, whichproduced sinusoidal waves, to study its performance at different wave frequencies (varied from 0.5Hz to 1.0 Hz) and four different mean water depths of 240 mm, 260 mm, 280 mm and 290 mm. Thewave parameters such as wave height and the wave frequencies were measured for the available wavechannel. It was found that the wave height increases while the wavelength decreases with increasingwave frequency and water depth. The relationship of pendulor paddle swing angle, rotational speed,torque and output power against wave frequency were obtained and discussed in this paper. It isfound that the output power is more when the paddle moves in the direction of wave propagation,compared to the backstroke when the paddle is moving against the direction of wave propagation. Index Terms—Wave energy, Pendulor, Wave frequency, Water Depth. 12 Conference Schedule Morning Session Authors’ Oral Presentation 10:20am-12:05pm Session 2(SALON TERRAZA C) ICMPM 2014-Civil Engineering Materials Session Chair:Dr. Charles E. Lord, University of Sheffield, United Kingdom PM001 Mechanical properties of high-strength steel obtained using DIC for specimens with a hole Michaela Štamborská, Miroslav Kvíčala, Monika Losertová VŠB – Technical university of Ostrava, Czech Republic Abstract—This article is aimed at determining the mechanical properties of high-strength steel obtained by digital image correlation for specimens with a hole in different rolling direction. This geometry generates a heterogeneous strain field which was measured during the test using a digital image correlation system. The advantage of using a heterogeneous strain field in the identification procedure is that a complex state of stress-strain can be analyzed at the same time and much more information can be obtained in a single test. On the other hand, the stress field cannot be directly computed from the test and a suitable identification procedure must be developed. Here, the virtual fields method (VFM) adapted for large strains and plasticity was used to identify the hardening behaviour and the anisotropy of the material. The values obtained with the VFM were compared with the results from a standard identification made using uniaxial tensile tests. PM002 Index Terms—specimen with a hole, digital image correlation, virtual fields method Sintered SiO2 modulus of rupture optimization by means of artificial neural networks Miroslav Kvíčala, Michaela Štamborská VŠB – Technical university of Ostrava, Czech Republic Abstract—This article discusses the use of artificial neural networks for solving industrial non-trivial problem, which is undoubtedly modulus of rupture optimization in case of sintered ceramics based on amorphous SiO2. Melting crucibles made from high purity silica are commonly used for production of high purity silicon ingots that are used in photovoltaic industry. Optimal modulus of rupture is very important variable that is related to the reliability and crucible usage value. Index Terms—modulus of rupture, neural networks, optimization, silica, sintering 13 Conference Schedule PM003 A Computational Chemistry Approach for Investigation of Low Friction Mechanisms based on FEP Film with Functionalized SiO2 Nanoparticles Yusuke Morita, Marleen De Weser and Gerhard Schottner Toyota Motor Europe, Belgium Abstract—To improve the fuel efficiency of automobile internal combustion engines, we investigated the fundamental mechanism of friction reduction within engine moving parts. A new coating was designed by introducing SiO2 nanoparticles in FEP film. The SiO2 nanoparticles were functionalized with hydrophobic fluoroalkyl units on their surface to create additional low friction property. Universal Surface Tester friction measurements revealed a significant reduction of the friction coefficient with increasing number of hydrophobic fluoroalkyl units for SiO2 surface functionalization. To clarify the friction reduction mechanisms by the functionalization of SiO2 nanoparticles, a quantum chemical calculation was carried out. The result indicates that an attractive force occurs between nanoparticle Si atoms and polymer F atoms, while by adding fluoroalkyl units on the SiO2 nanoparticle surface, this force changes to repulsive. By performing a molecular dynamics simulation of a shear model between FEP film and SiO2 nanoparticles, we observed a decrease of friction force with increasing fluoroalkyl units which lead smooth rolling motion of nanoparticles, thus confirming the repulsive effect of nanoparticle functionalization. We conclude that fluoroalkyl units on the SiO2 surface play an important role in creating a repulsive force between nanoparticle and FEP film which lead to low friction coefficienty. PM017 Index Terms—friction reduction, SiO2 nanoparticle, functionalization, molecular dynamics, quantum chemical calculation Effect of martensite morphology and Mn partitioning on mechanical properties of low carbon dual phase steels Manoranjan Kumar Manoj, V Pancholi and S K Nath National Institute of Technology, Raipur, India Abstract—Dual phase (DP) steels have been developed from normalized plain low carbon steel containing 0.14wt % carbon. Intercritical austenitisation (ICA) treatment was carried out at 740oC, 760oC, 780oC and 800oC followed by water quenching. Duration of ICA treatment was varied from 1 to 15 minutes. Different martensite volume fractions (MVFs) ranging from 17.3% to 63.7% have been found in these DP steels. Two different morphologies of martensite have been obtained in these DP steels. First one is networking of martesnite along prior austenite grain boundaries and secondly, formation of islands of martensite primarily at triple junction of grain boundaries. Further, during ICA treatment, alloying element (Mn) redistributed itself between ferrite and austenite depending upon ICA temperature and time. Networking of martensite has been found to increase strength considerably and hardness marginally but decreased ductility. On the other hand, it has been found that Mn present as solid solution provide better mechanical properties compared to accumulation at grain boundaries. Index Terms—Dual phase steel; Martensite morphology; Hardness; Ductility; Manganese Partitioning 14 Conference Schedule PM023 Quantitative Evaluation of Voids in Lead Free Solder Joints Sabuj Mallik, Jude Njoku and Gabriel Takyi University of Greenwich, United Kingdom Abstract—Voiding in solder joints poses a serious reliability concern for electronic products. The aim of this research was to quantify the void formation in lead-free solder joints through X-ray inspections. Experiments were designed to investigate how void formation is affected by solder bump size and shape, differences in reflow time and temperature, and differences in solder paste formulation. Four different lead-free solder paste samples were used to produce solder bumps on a number of test boards, using surface mount reflow soldering process. Using an advanced X-ray inspection system void percentages were measured for three different size and shape solder bumps. Results indicate that the voiding in solder joint is strongly influenced by solder bump size and shape, with voids found to have increased when bump size decreased. A longer soaking period during reflow stage has negatively affected solder voids. Voiding was also accelerated with smaller solder particles in solder paste. PM024 Index Terms—Voiding, Soldering, X-ray, Lead Free Solder Paste. A Phenomenological Predictive Model for Thermo-Mechanical Fatigue of Notched Type 304 Stainless Steel Justin Karl, Andrew Copeland, Amy Besio University of Central Florida, USA Abstract—The behavior of parts subjected to simultaneous thermal and mechanical fatigue loads is an area of research that carries great significance in the power generation, petrochemical, and aerospace industries. Machinery with expensive components undergo varying applications of force while exposed to variable temperature working fluids. An example case is found in steam turbines, which subject stainless steel blades to cyclic loads from rotation as well as the passing of heated gases. Accurate service life prediction is especially challenging due to the thermo-mechanical loading being present on the complex geometric profile of the blades. This research puts forth a method for determining crack initiation lifetimes in variably-notched type 304 austenitic stainless steel specimens subjected to differing fatigue and thermo-mechanical fatigue conditions. A base analytical model and genetic algorithm were used to develop phenomenology-informed predictions that fall within a factor of two of the actual crack initiation times. PM206 Index Terms—Stainless steel, fatigue, thermo-mechanical, LCF, creep, mechanics, prediction, notch, stress concentration, modeling, behavior. Nanofibrous filters for respirators Vysloužilová Lucie,Seidl Martin, Hrůza Jakub, Bobek Jiří, Lukáš David, Lenfeld Petr Technical University of Liberec, Czech Republic Abstract—This article deals with a development of new filtration materials for respirators. Contemporary used filters with charged microfibers are not sufficiently stable in all conditions and not efficient for all types of particles and that is the 15 Conference Schedule reason why the requirement for new generation of filtration materials is rising up. The research was focused on the development of nanofibrous filters that have a great precondition to be used as filters for respirators. The filtering material was designed as a multilayer sandwich consisting of spundbound, meltblown and nanofibrous layers. For the evaluation of final properties and filtering performances different 3D structures were also created. PM309 Index Terms—Filtration, nanofibers, respirators. An Experimental Study on the Usage of Poisson’s Ratio as a Damage Index Cagatay Yılmaz,Cagdas Akalın, Esat Selim Kocaman, and Mehmet Yıldız Sabanci University, Turkey Abstract—Damage accumulation in uni-directional glass fiber reinforced epoxy matrix composite manufactured with a stacking sequence of [90/0/0]s using vacuum infusion method is investigated by monitoring the change in Poisson’s ratio during quasi-static tension and quasi static cyclic tension test. During the tests, axial and transversal strains are recorded by utilizing extensometer and a strain gauge to compare the response of sensor types for the evolution of Poisson’s ratio. Index Terms—Poisson’s ratio; glass fiber; polymeric composites. Lunch 12:00pm-13:00pm Afternoon Session Authors’ Oral Presentation 13:00pm-16:00pm Session 3(SALON TERRAZA A) ICPSE2014-Electrical Engineering and Electric Machines Session Chair:Prof. Eduardo Vega-Fuentes, University of Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Spain SE04 Experimental Measurements of Pressure Losses in the Inter-Turbine Duct of a Gas Turbine Cleopatra Florentina Cuciumita, OLARU Daniel, VILAG Valeriu Alexandru, PORUMBEL Ionut, RIZNYK Sergiy and KHOMYLYEV Sergiy COMOTI Romanian Research and Development Institute for Gas Turbines, Romania Abstract—The paper presents the total pressure experimental measurements carried out at the Romanian Research and Development Institute for Gas Turbines COMOTI in 16 Conference Schedule order to determine the total pressure losses in the Inter - Turbine Duct of a two spools gas turbine, as a function of the gas turbine operating regime (mass flow rate) and rotational speed. The Inter - Turbine Duct experimental assembly has been designed, manufactured and tested at COMOTI. The total pressures were measured as a function of the pre-swirling angle, which simulates the influence of the high pressure turbine rotational speed located upstream of the Inter turbine duct in the real gas turbine, as well as for three operational regimes, without the pre-swirlers modules. The results indicate that the total pressure loss along the Inter - Turbine Duct is of maximum 0.9 %. The lowest overall total pressure loss occurs at 0ºpre-swirling angle, around 0.8%, while along the ITD struts, the lowest pressure loss is obtained for a 15ºpre-swirling, below 0.1%. The influence of the operating regime on the total pressure loss was found to be linearly, the pressure loss increasing with the reduced mass flow rate, between 1% and 1.9% overall, and between about 0.1% and 0.4 % along the struts. SE10 Index Terms—Gas turbine, pressure losses, inter-turbine duct, measurements. Link Power Level Improvements in an Amplified 8-Channel CWDM System with in-line HybridEDFA-SOA Amplifier Khadijah Ismail, P. S. Menon, Sahbudin Shaari, Abang Annuar Ehsan, Norhana Arsad, and A.Ashrif A. Bakar Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia Abstract—The link power improvement in a coarse wavelength division multiplexing (CWDM) system which is transmitted using a hybrid erbium-doped fiber amplifier (EDFA) and semiconductor optical amplifier (SOA) scheme as in-line amplifiers, is discussed. The network is designed for amplifying 8 CWDM channels ranging from 1471 nm to 1611 nm. The hybrid amplifiers’ gain measurement is obtained from experimental work with gain peak at 22 dB which is observed at 1531 nm. The amplifiers also caused power increment of 5.06 dB in the transmission link before the signal is split individually at the receiving end. Based on the higher gain peaks and power spectrum at 1531 nm and 1551 nm wavelengths, the proposed amplified link would be useful for the transmission of video applications. SE29 Index Terms—In-line, EDFA-SOA, 8 channel CWDM. Literature Study on Condition of Tertiary Bushing of Interbus Transformer and Alternative Protection Scheme Joko Muslim, Buyung S. Munir, Didik F. Dakhlan, Satyagraha A. K. and Arrester C.S. Rahayu PLN INDONESIA, Indonesia Abstract—Transformer bushing plays important role in the reliability of power system, especially the bushing of interbus transformer which interconnected between two different voltage levels thus enable the power interchange between these two voltage systems. Failure in the bushings, either in the primary or secondary or tertiary windings of a 500/150/66 kV interbus transformer will instantly lead to the power interruption and outage in the consumer sides. Normally, interbus transformers are constructed of three windings with the primary and secondary winding are connected in wye and the tertiary is connected delta. The primary and the secondary windings are loaded, and sometimes tertiary winding is loaded, but mostly not loaded. The main purpose of the tertiary 17 Conference Schedule winding is to provide the isolating system due to the unbalance from the other two windings. The windings of interbus transformer and the power system is linked via a bushing. Improper operating voltage of power system above the nominal voltage of the bushing tends to reduce the operating cycle of bushings. The displacement of absolute reference of voltage from phase to phase voltage thus will raise the operating voltage applied to the bushing which exceeds the nominal voltage of bushings. Theoretically, applying operating voltage of 1.571 x U0 to the tertiary bushing continuously is likely to reduce the life time of bushing to approximately 2.5 years. Online monitoring techniques to observe the diagnostic parameters of bushing could be occupied to monitor the changes in the bushings which due to the degradation of insulation quality. Literature study focusing on the ideal condition of a bushing against the real loading cycle of bushing in operation also considered to estimate the bushing insulation degradation mechanism. This study put more efforts in analyzing the bushing condition as the function of loading pattern and the applied voltage experienced by the bushing. Several measurement data of bushing online monitoring are attached as well to describe the occurrences inside the bushing. At the end of this study, options on the protection scheme are described with either directly earthed or floating analysis. SE30 Index Terms—Tertiary winding, partial discharge, expected life time, protection scheme. Providing Security of Vital Data for Conventional MicrocontrollerApplications Bayram AKEMİR and Hasan ÜZÜLMEZ Selcuk University, Turkey Abstract—Microcontrollers are widely used in industrial world, and almost all kind of devices were based on microcontroller to achieve high flexibility and abilities. All microcontrollers have nonvolatile and volatile memories to execute the software. During the running, microcontroller calculates many variables and records them to any non-volatile memory to use later. After re-energizing, microcontroller takes the data calculated before the power off and executes the program. In case of any electrical writing error or any power loss during the writing procedure, un-written memory blocks or any un-written data leads to malfunctions. Proposed method uses a gray code based signed two memory blocks to secure the memory reserved for data. Microcontroller uses these memory blocks in alternately. Even if microcontroller has no any real-time ability, gray code provides a guarantee which block is written in last. For every re-starting microcontroller dos not lose the data. In case of any reading problem during the starting, microcontroller has two chances to decide the action. One is to start with default values and the other is to start with the previous data. This study is offered in elevator application not to lose position and vital values. SE31 Index Terms—Data security, Microcontroller, Memory, Non-volatile, Gray code. Neural Network Predictive Control of the System Unified Power Flow Controller (UPFC) Larouci Benyekhlef and Boufaden Kada University of Science and Technology of Oran USTO.MB, Algeria Abstract—In our present article, we studied the control of a unified power flow controller (UPFC) by the Neural Network Predictive controller to improve the stability of 18 Conference Schedule the electrical power network, hence providing security under increased power flow conditions and it is able to control simultaneously and independently the real power and the reactive power of the line.. We proposed the application of a regulator based on neural network predictive control for a robust drive of system UPFC. In order to test the parametric robustness of the various control developed in this work, the performance of the neural network predictive controller is simulated on a two bus test system. The simulation results show the power and the accuracy of the neural network predictive controller and the effective in improving the transient power system stability and very robust against variable transmission line parameters. SE37 Index Terms—UPFC, FACTS, Neural Network Predictive regulator, PI-D. Instrument for Measurement of Transfer Ratio Voltage Transformers Pavel F. Baranov, Valeriy N. Borikov, Edvard I. Tsimbalist National Research Tomsk Polytechnic University, Russia Abstract—The paper presents the instrument for measurement of transfer ratio voltage transformers in the frequency range. The instrument distinctive feature is measuring of small differential signal of the voltages with sensitivity 2 nV against the background of large common-mode signal. The instrument features, its technical and metrological parameters are also considered. SE65 Index Terms—voltage transformer, lock-in amplifier with a differential input, common-mode rejection ratio, inductive voltage divider, transfer ratio An Approach to Optimum Route and Site Selection of a Steam Gathering System for Geothermal Power Plants using Multiple Weight Distance Transform Magnus Thor Jonsson University of Iceland, Iceland Abstract—This article proposes a new approach to select the location for separators and routes for two phase flow pipelines in a geothermal steam gathering system. Multiple weight distance transform is presented and used to find the optimum location of site for a steam separator based on the flow capacity of geothermal wells. The routes are monotonic and the incline is slight in order to minimize the pressure drop and the slug flow conditions in the pipeline. A map with weighted distance for five wells shows the accessible area and the route from each well is calculated. The optimum site location reduces the total pipe length from all wells by 9%. SE204 Index Terms—Geothermal, Two Phase Flow, Distance Transform, Route and Site Selection. The Air Solar Collectors: Introduction of Chicanes to Favour the Heat Transfer and Temperature in the Air Stream Dynamics Omar Mahfoud, Abdelhafid Moummi and Noureddine Moummi Centre de Developpement des Energies Renouvelables, Algeria Abstract—The thermal performance of a single pass solar air heater with chicanes attached was investigated numerically using a 2D model of solar air stream dynamics collectors where the turbulence standard (𝐤−𝛆) model has been implemented. The chicane is formed with two parts: the first is perpendicular to the air flow and the second 19 Conference Schedule part is titled (α), they are mounted in successive rows, oriented perpendicular to the air flow and soldered to the back plate. The predicted results are validated by comparing with the literatures semi-empirical and experimental data and shown a reasonable agreement. Effects of relevant parameters as the (Reynolds number, chicanes upper parts tilts angles and air mass flow rates) on the heat transfer coefficient and temperature development are discussed. It is apparent that the turbulence created by the chicanes resulting in greater increase in heat transfer inside the air stream dynamics. SE205 Index Terms—Solar air collector, chicanes, heat transfer, temperature, performance. Cost Effective Maintenance of Wind Turbines Using Finite State Markov Model Lahcene Boukelkoul Electrical Engineering Dpt University of 20th Aug 1955 Skikda Algeria Abstract—Nowadays the cost effectiveness concept becomes a decision-making and technology evaluation metric. The cost of energy metric accounts for the effect of reliability through levelized replacement cost and unscheduled maintenance cost parameters. One key of the proposed approach is the idea of maintaining the WTs which can be captured via use of a finite state Markov chain. Such a model can be embedded within a probabilistic operation and maintenance simulation reflecting the action to be done. In this paper a finite state Markov model is used for decision problems with number of determined periods (life cycle) to predict the cost according to the option of the maintenance adopted. The minimum cost is taken as the optimal solution. SE206 Index Terms—Maintenance, cost, Markov decision process, finite state. Significant of Isothermal Flow Studies for High Swirling Flow in Unconfined Burner Norwazan A.R. and Mohd. Jaafar M.N. Universiti Pertahanan Nasional Malaysia, Malaysia Abstract—This paper is presents numerical simulation of isothermal swirling turbulent flows in a combustion chamber of an unconfined burner. Isothermal flows of with three different swirl numbers, SN of axial swirler are considered to demonstrate the effect of flow axial velocity and tangential velocity to define the center recirculation zone. The swirler is used in the burner that significantly influences the flow pattern inside the combustion chamber. The inlet velocity, U0 is 30 m/s entering into the burner through the axial swirler that represents a high Reynolds number, Re to evaluate the differences of SN. The significance of center recirculation zone investigation affected by differences Re also has been carried out in order to define a good mixing of air and fuel. A numerical study of non-reacting flow into the burner region is performed using ANSYS Fluent. The Reynolds–Averaged Navier–Stokes (RANS) realizable k-ε turbulence approach method was applied with the eddy dissipation model. An attention is focused in the flow field behind the axial swirler downstream that determined by transverse flow field at different radial distance. The results of axial and tangential velocity were normalized with the U0. There are also studied the effect of difference inlet velocity from 30 m/s to 60 m/s to the axial velocity flow. The velocity profiles’ behaviour are obviously changes after existing the swirler up to x/D = 0.3 plane. However, their flow patterns are similar for all SN after x/D = 0.3 plane towards the outlet of a burner. Index Terms—Burner, swirling flow, axial velocity, tangential velocity, realizable k-ε 20 Conference Schedule SE306 Design of a Gorlov Turbine from Marine Current Energy Extraction Niranjwan Chettiar, Sumesh Narayan, Jai Nendran Goundar, and Ashneel Deo The University of the South Pacific, Fiji Abstract—As fossil fuels near depletion and their detrimental side effects become prominent on ecosystems, the world searches renewable sources of energy. Marine current energy is an emerging and promising renewable energy resource. Marine current energy can be alternative energy source for electricity production. Many marine current converters are designed to tap marine current energy; however, Gorlov turbine proves to have minimum manufacturing and maintenance cost, hence giving desired power output. A 0.3m diameter and 0.6m long 3 bladed Gorlov turbine was designed, fabricated and test to analyse its performance. The turbine produces average power 15 W and proves to be quite efficient for marine current energy extraction. SE307 Index Terms—Renewable Energy, Marine current Energy, Gorlov Turbine, Design, Experimentation. Design and Performance Analysis of Micro Wind Turbine for Fiji Ashneel Deo, Jai Nendran Goundar, Sumesh Narayan and Niranjwan Chettiar The University of the South Pacific, Fiji Abstract—Today’s major research area is based on finding alternatives to fossil fuels. Wind energy can contribute significantly towards renewable energy production. A functional wind turbine built locally proposes a huge impact for Fiji and the Pacific Islands renewable energy industry. The design has to take into consideration the wind speed of the pacific which is quite different from other countries. A low Reynolds number airfoil was selected and modified for horizontal axis wind turbine (HAWT) and its aerodynamic characteristic was studied. The analysis were done using XFoil software, the numerical results were validated with experimental results before analysis were done. The Q-blade Software is used to design the blade for the wind turbine. The cut in velocity of wind turbine is 3 ms-1, which is a big achievement when it comes for the power generation. The rated power is 50 watts at rated velocity of 6.5 ms-1 and the cut of velocity is at 20 ms-1. The numerical results were validated with experimental results. The peak power after measurement was 23.73 watts at wind speed of 8 ms-1. SE308 Index Terms—Renewable energy, Horizontal axis micro wind turbine, Airfoils, Blade design. Design of a Ducted Cross Flow Turbine for Fiji Jai Nendran Goundar, Niranjwan Chettiar, Sumesh Narayan, Ashneel Deo, and Deepak Prasad The University of the South Pacific, Fiji Abstract—Marine current energy is clean and reliable energy source. It can be alternative energy source to produce electricity if tapped with a suitable marine current energy converter. Pacific Island countries (PIC) like Fiji can reduce the amount of Fossil fuel used. However for most energy converters designed perform well at marine current velocities above 2m/s and it needs to be installed at depths of 20 – 40m also installation and the maintenance cost of such devise will be quite high if it needs to be installed in Fiji. Therefore a ducted cross flow turbine was designed, which can give desired output 21 Conference Schedule at minimum installation and maintenance cost. A dusted cross flow turbine has been design taking into account for its operating condition. The turbine was modelled and analyzed in commercial; Computational Fluid dynamic (CFD) code ANSYS-CFX. The code was first validated and with experiment results and finally performance analysis of full scale turbine was carried out. The designed turbine can have maximum efficiency of 56% producing rated power of 21kW; it produces 0.77kW at cut in speed of 0.65m/s. SE314 Index Terms—Renewable energy, Ducted cross flow turbine, Design, Experimental validation, Performance analysis. Efficiency Estimation of Thermoelectric Generators Application in the Liquefied Natural Gas Gasifiers Artem Novikov, Dmitriy Uglanov, and Alexander Dovgyallo Samara State Aerospace University, Russia Abstract—The object of the research is a thermoelectric generator installed in a liquefied natural gasgasifier. In this article the numerical estimation of parameters of thermoelectric generators (TEG) atcryogenic temperatures are presented and the experimental study of the thermoelectric properties ofTEG at low temperatures as well as the outlook for using thermoelectric generators as a part ofindustrial liquefied natural gas gasifier has been carried out. In the process used heat transfer theoryof cylindrical thin wall with a one-sided fins and the estimation of thermoelectric performance ofTEG. As a result the experimental work has been investigated by TEG parameters at cryogenictemperatures; the evaluation of TEG number to produce electrical energy has been considered. Index Terms—Thermoelectric generator, alternative energy sources, utilization of cold energy,liquefied natural gas, gasification Afternoon Session Authors’ Oral Presentation 13:00pm-16:00pm Session 4(SALON TERRAZA B) ICNB2014- Composites materials Session Chair:Prof. Junhua Yu, Seoul National University, South Korea NB002 Method of heat balances for calculating heat transfer in flat multilayer nanostructures Vladimir I. Khvesyuk and Denis A. Vorobyov Bauman Moscow State Technical University, Russia Abstract—We suggest method of calculation of one-dimensional temperature field in 22 Conference Schedule multilayer nanostructures. Our method allows obtaining non-stationary temperature distribution in the periodical and non-periodical spatial structures with a different degree of periodicity. Comparison temperature distributions in the multilayer nanostructures and equivalent continuous samples are performed in this study. In addition we suggest experimental application of our method for estimation an average value of thermal Kapitza resistance. NB005 Index Terms—Multilayer nanostructures, Kapitza resistance, heat transfer, ballistic thermal conductivity Determination of the Gel-Fluid Phase Transition Temperature of Single Supported Phospholipid Bilayers using QCM-D: Fundamentals and Applications Andreas Wargenau and Nathalie Tufenkji McGill University, Canada Abstract—Supported phospholid bilayers (SPBs) have been demonstrated as valuable experimental models for fundamental studies of biomembranes and their interactions with various solutes, biomolecules and nanoparticles. Herein, we report a novel method to detect the temperature-induced gel-fluid phase transitions of single SPBs using a quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation monitoring (QCM-D). The proposed approach, which utilizes viscosity changes of the ambient medium to determine the temperature in the immediate environment of the SPB, enables the determination of the gel-fluid phase transition temperature with a precision of ± 0.1 °C. As transition temperatures obtained in this manner do not depend on the temperature scan rate, the method also facilitates systematic evaluation of the transition kinetics. The precise determination of both the transition temperature and the transition time not only allows for fundamental studies on the transition behavior of these particular bilayers, but also opens up new possibilities in the development of biosensing tools. Possible applications including the detection of bilayer interactions with nanoparticles and membrane soluble compounds are discussed based on various examples. NB006 Index Terms—Gel-Fluid Phase Transition, Supported Phospholipid Bilayer, Quartz Crystal Mechanical and Morphological Properties of Buckminster Fullerene (C60) Added Glass Fiber Reinforced Polyamide 66 Multiscale Composites ReyhanKeskin, IkilemGocek and GuralpOzkoc Pamukkale University, Turkiye Abstract—In the present study, Buckminster Fullerene and glass fiber reinforced Polyamide 66 multiscale composites were produced using laboratory type twin screw extruder and injection molding machines, respectively. The glass fiber reinforcement was set as 30 wt % and samples A, B and C were produced with 0.1, 0.5 and 2.0 wt % Buckminster Fullerene addition besides the glass fiber reinforcement. Tensile tests were conducted and their results were compared with samples having only 30 wt % glass fiber reinforcement to investigate the effect of Buckminster Fullerene addition. The morphological structure of the multiscale composites were investigated using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis Index Terms—Multiscale composites, tensile strength, morphology, fiber-matrix 23 Conference Schedule NB009 adhesion, glass fiber, Buckminster Fullerene, SEM analysis Synthesis and Characterization of Carbon Nanotubes-Quicklime Nanocomposites using Co Catalysts Supported on CaODerived from Carbonate Stones Ruzanna Ibrahim, MohdZobir Hussein, Nor AzahYusof and Fatimah Abu Bakar Universiti Putra Malaysia Abstract—This work involves the synthesis of carbon nanotube-quicklime nanocomposites(CQNs) via the CVD technique of n-hexane using Co metal catalysts supported on CaO obtained from local carbonate stones. The CVD process was conducted at temperatures between 600°C and 900°C. XRD results show that at temperatures higher than 700°C, peaks attributable to CNTs are present. As the composition of the catalysts is changed, it was shown that the catalyst composition of 10, 15 and 20wt% Co exhibit peaks that are attributable to CNTs the sample obtained using when Co/CaO (20wt%) catalyst giving the highest XRD peak intensity. Transmission electron microscopy of the CQNs confirmed the existence of nanotube morphology in the samples. Raman spectroscopy of the CQNs samples show that CQNs synthesized using 20wt% Co gave the highest IG/ID ratio (2.169) indicating a highest degree of graphitization. Incorporation of the CaO from carbonate stones in this type of CNT nanocomposites may be useful in application as advanced building materials. NB016 Index Terms—Carbon nanotubes, nanocomposite, calcium oxide, chemical vapour deposition Optical Properties of CztseNanocrystalline Thin Films for Photovoltaic Devices Anderson DussanCuenca, Heiddy P. Quiroz, Jorge A. Calderón and Sandra M. López Universidad Nacional de Colombia, Colombia Abstract—Presents a study of optical properties from transmittance measurements as a function of wavelength to CZTSe thin films (Cu2ZnSnSe4) using Bhattacharyya model and basic elements from the Swanepoel theory. The optical constants such as the absorption coefficient (α), the refractive index (n), the extinction coefficient (k) and physical properties such as gap (Eg), the real and imaginary part of the dielectric function (1 and 2) and the film thickness (d), were determined. Gap values between 1.2 and 1.7 eV were obtained for compound when the mass (MX) of ZnSe was varied during the deposition stage. Inhomogeneity and high surface roughness were observed by SEM measurements for all samples. Size grain varying between 458.16 and 630.28 nm were obtained while the ZnSe binary mass varied from 0.171 to 0.153 g. Refractive index and extinction coefficient of Cu2ZnSnSe4 films were obtained for λ = 800 nm. A decrease of ε1 and ε2 was observed as the wavelength increases; it is associated with the presence of binary phases in the XRD patterns. NB019 Index Terms—CZTSe compound, thin films, optical properties, Dielectric function, semiconductors Graphene-CNTs into Neuron-Synapse Like Configuration a New Class of Hybrid NanoComposites Antonio F. Avila, Aline M. de Oliveira, Viviane C. Munhoz and Glaucio C. Pereira Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais, Brazil Abstract—This paper describes the experimental procedures for developing and testing 24 Conference Schedule of a new class of hybrid nanocomposites, the neuron-synapse configuration ones. Two carbon based nanostructures, multiwall carbon nanotubes and multi-layered graphene, were incorporated to carbon epoxy laminated. The processing technique employed which includes a combination of sonication and high shear mixing allows the formation of a neuron-synapse nanostructure.X-ray diffractometry indicates that multi-layer graphene (MLG) has an average diameter close to 22 nm. TEM observations and ramanspectroscopy revealed a thickness of 10 graphene layers, and a hybrid nanostructure where MWNT interpenetrated the MLG nanostructure. The hybrid nanostructure seems to be linked by Van der Walls bonds. This could be the reason for large crack density generated during short-beam bending tests. No significant stiffness changes were observed in both, tensile and bending, tests, while tensile strength were improved by 19% with 1 wt.% addition ofgraphene the interlaminar shear strength, was increased by 22% with the addition of MWNTs and 2.5% with the graphene (1 wt.%) and MWNT (0.3 wt.%) together. NB033 Index Terms—Graphene, Carbon Nanotubes, Composite Materials, Mechanical Properties, Nanostructure Morphology Nanoclay as Anti-Blistering Agent in Polyester Based Coating: Effect of Sea Water and Distilled Water Exposure SitiNorasmahSurip, Abd Malik AbdRahman and Wan NurRaihan Wan Jaafar UniversitiTeknologi MARA, Malaysia Abstract—This study was conducted to investigate the effect of nanoclay on hardness, pull off and blistering effect of polyester based coating. Polyester coat, nanoclay and hardener (MEKP) were mixed and mechanically stirred for one hour at ambient temperature at a shear rate of 1000 rpm. Prepared coating was then applied on the surface of plywood for the characterization of the hardness and pull off strength and for the observation of blistering effect towards sea and distilled water. As a result, 6% nanoclay loading gives better hardness strength which is 65% increment from unmodified polyester. However, the pull off strength shows that 2% of nanoclay loading gives higher strength among others with 114% increment compared to unmodified polyester coating. Blister was mostly observed at samples without nanoclay loading for both sea water and distilled water. While the less blistering effect was present at 2% nanoclay loading for sea water and 4% nanoclay loading for distilled water. The presence of nanoclay within the coating improves its bonding ability and the decreasing the micro space within the polymer. Blistering effect for highest and lowest frequency was observed by electron scanning microscope (SEM). NB035 Index Terms—Modifiedpolyestercoating,nanoclay, anti-blister Preparation and Characterisation of Surface Adsorbed Reduced Graphene Oxide/PolyanilineNanocomposite on Polymer Membrane for Trimethylamine Sensing Rey Alfred G. Rañola, Isabella Concina, ElisabettaComini, Fortunato B. Sevilla and Giorgio Sberveglieri University of Santo Tomas, Philippines/Sensor Lab, University of Brescia, Italy Abstract—A graphene/polyaniline (rGO/PANi) nanocomposite was synthesized by solution blending method and deposited on to a nylon-6 membrane via vacuum assisted self-assembly (VASA) method to fabricate a flexible material applied as a chemoresistive 25 Conference Schedule gas sensor for trimethylamine (TMA). The morphological and structural characterization of surfaced adsorbed polymer nanocomposite was carried out by FT-IR, SEM, UV-Vis and surface profilometry. While, electrical property was carried out by four-point probe measurement. Prepared rGO/PANinanocomposite has a percolation threshold around 0.40% vol. fraction, with a conductivity of 8.28 S/m (rsd = 3.0%, n=3) and thickness around 38.58 μm (rsd = 7.63%, n=3. The composite sensor exhibited linear range from 45 to 230 mg/L (r2= 0.9962) and the calculated limit of detection was 25.30 mg/L. It exhibited a repeatable response to TMA gas. NB203 Index Terms—Graphenenanocomposite, chemiresistor, trimethylamine, surface adsorbed nanocomposite Improved Dna Immobilization and Binding Efficiency on Novel Carboxylic Acid Surfaces Milena Rowinska Dublin City University, Ireland Abstract—A new methodfor the fabrication of carboxylic acidgroups on solid supports is reported. The carboxylic acid functional layer is obtained by spin-coating dissolved polymethmethacrylate (PMMA)onto an underlying solid substrate (e.g. plastic, glass, gold) and oxidizing it with either UV light-ozone (UV/O3) or oxygen plasma. The thickness of the spin-coated layer can be as low as 5nm, and can be controlled by manipulation of PMMA concentration, spin time and spin speed.This surface can be applied in fabricationof surface arrays of ssDNA (single-stranded DNA)and point-of-care devices, which are at the center of some of the most active areas in biological research. A well-known approach applied by many researchers for producing microarrays is to modify the DNA oligomers with a functional group that allows covalent attachment to a reactive group on the surface. 1-Ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide (EDC) was used as linker and amino-modified ssDNA probe. EDC reacts with the carboxylic acid surface to form an o-acrylisourea intermediate, which subsequently reacts with an amine-terminated ssDNA oligomer to form amide bonds. However, during immobilization experiments, it was observed that the ssDNA probe binds not only via its modified terminus but also by its nucleobases. We show that DNA has the ability to anchor itself via the amine groups present in the backbone (BB) nucleobases (Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine) and that this bindingnegativelyaffects hybridization efficiency during subsequent hybridization assays. In order to improve hybridization efficacy, click chemistry (CC), was demonstrated as a bio-orthogonal and highly specific alternative, which does not promote binding of probe to the surface via multiple anchoring points on the backbone. Both immobilization techniques were compared and direct hybridization experiments with short ssDNAoligomerswere performed. It was found that hybridization efficiency is 40% higher for CCthan for EDC linking at room temperature. To conclude, PMMA is a versatile substrate suitable for DNA microarrays. CC immobilization is more suited and specific, can be performed at room temperature and results in higher hybridization efficacy when compared to EDC linking chemistry. NB204 Index Terms—Surface science, click chemistry, DNA immobilization, DNA hybridisation Hollow TiO2 Spherical Structures Prepared by Microwave-assisted Hydrothermal Treatment without Template 26 Conference Schedule Carine Ribeiro, Carine S. S., Zenatti, Alessandra and Ribeiro, Anderson O. Federal University of ABC, Brazil Abstract—Three-dimensional hollow spherical structures has good performances that attract significant attention nowadays, due to their higher specific surface area, lower density, better cell permeation and greater light-harvesting capacity. Hence, the hollow TiO2 spherical structures has been used in many areas and applications, including photocatalysts, electrochromic devices, gas sensor, dye sensitized solar cells, biomedical implants and field emitters, delivery carriers and adsorbents. In this work, hollow TiO2 spherical structures were prepared by microwave-assisted hydrothermal treatment without template. A solution containing 0.2 grams of TiO2 amorphous spheres synthetized previously by sol-gel method was mixed with NaF, ethanol and water and transferred to a 100 mL Teflon-lined autoclave, which was sealed and kept at 180ºC for 1 h. After, the material was washed seven times with ethanol and centrifuged. Results of X-ray diffraction (XRD) showed crystal planes of TiO2 anatase. Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (FESEM) showed the different morphology of the material before and after microwave-assisted hydrothermal treatment (Figure 1). Other characterization will be realized, such as, superficial area, pore volume and compositional analyzes FTIR and Raman spectroscopy. NB207 Index Terms— Fabrication and Characterization of Nanosilver Intercalated Graphene Embedded High Density Polyethylene composite thin films Mahmoud BorhaniZarandi, NooshinMoshtzan and Mohammad Reza Nateghi Islamic Azad University, Yazd Branch, Iran Yazd university, Iran Abstract—Graphenenanoflakes were prepared from expanded graphite by direct ultrasonication. Silver nanoparticles were prepared in dimethyl formamide at the presence of polyvinyl pyrrolidone as stabilizer by direct reduction method. The colloidal solution of synthesized Ag nanoparticles was added to the ultrasonicatedgraphene suspension so that the silver to graphene weight ratio of 1:1 is achieved in final solution. HDPE/graphene/Ag composites were fabricated using melt mixing method. The composite thin films were characterized by SEM, TEM, XRD, DSC, and four point probe techniques. For comparison, HDPE/graphene composites were also prepared by similar method. Electrical resistance measurements reveal that the HDPE/graphene/Ag composite layers in comparison with HDPE/graphene show lower percolation threshold (1.8 vol.% vs. 2.2 vol.% of conducting phase) and very higher maximum electrical conductivity (1.0×10−3 S/cm vs. 1.0×10−7 S/cm) at 7.8 vol.% of the conducting phase loading. Changes in crystallinity percent and melting temperature of the composite samples were studied by DSC technique. It was recognized that the crystallinity and melting temperature of composite samples containing graphene/Ag is more dependent in conductive phase content than HDPE/graphene composite films. 10 C increase of melting temperature in HDPE/graphene/Ag samples by 10 wt% loading of conducting phase is indicating the increase of crystallinity and then density of the samples. XRD results indicated that the size of crystallites and distance between crystal plates are constant. 27 Conference Schedule NB212 Index Terms— Numerical Investigation of a High Performance Subwavelength Grating based PlasmonicBiosensor MahinTahmasebpour University of Tabriz, Iran Abstract—A Localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) biosensor based on a subwavelength grating structure is studied numerically for detection of bulk refractive change of aqueous environments such as biological buffer solutions. A high grating thickness of 40 nm and a short grating period of 50 nm are selected to evaluate numerically the effect of the other grating structural parameter i.e. fill factor (f.f) on the sensor performance including dispersion curve, sensitivity, FWHM, MRR and resonance angle. Evaluation shows that corresponding wavelength to the effective resonance of surface plasmons which locating in near infrared (NIR) wavelength range is displaced with f.f value. Also, as shown for some f.f values sensitivity is enhanced slightly whereas FWHM, MRR and resonance angle is increased. Thus with adjusting both of operating wavelength and f.f value, it is possible to get a better performance for the plasmonic sensor. NB213 Index Terms—Subwavelength grating, Localized surface plasmon, Biosensor, Near infrared wavelengths Indium Tin Oxide for Super-resolution Light Microscopy Study Xun Lu, ThibaultTabarinc, Philip R. Nicovich, S. R. C. Vivekchanda, Katharina Gaus and J. Justin Gooding University of New South Wales, Australia Abstract—Super-resolution light microscopy techniques such asphotoactivated localization microscopy (PALM) and stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy (STORM) can break the diffraction limit and achieve a resolution of tens of nanometres.1, 2 Fundamentally, both techniques rely on the temporal separation of fluorescence emission of those individual fluorophores in the specimen so that the size of the point spread function (PSF) can be reduced, leading to a nanometre-sized localization precision.As originally introduced, PALM uses photoconvertable and photoactivatable fluorescent proteins while STORM, utilizes reversible photoswitching of specially paired organic fluorophores.As biomolecules such as peptides and proteins are usually up to several nanometres, it is, in principle, possible to localize single molecules by this technique. Indium tin oxide coated glass substrates (ITO) werechosen in this research because well-designed chemical modification can be achievedon the ITO surface. It was previously reported that a variety of sophisticated and wellcontrolled chemical modifications can be applied on ITO surface, such as self-assembling of organophosphonic acid, alkane-thiols or carboxylic acids.3, 4, 5Also ITO is both optically transparent and electronically conductive, which additionallyenables optical and electrochemical study simultaneously. The purpose of this study was to explore the applicability of ITO instead of glass as a substrate for super-resolution lightmicroscopy (PALM/dSTORM6) use and demonstrate super-resolution light microscopy imaging of biological structures and single molecules on ITO substrate. Herein, a quantitative study was processed through calculating and 28 Conference Schedule localizing fluorescently(Alexa Fluor 647) labelled BSA molecules on glass substrates.Furthermore, fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy (FLIM) was carried out to measure the lifetime of Alexa Fluor 647 on both glass and ITO surfaces to see if there was any change in its photophysical property. Then, both ITO and glass were utilized as substrates for dual-colour imaging of NIH-3T3 cell under both PALM and dSTORM. Finally, ITO substrates were functionalized with RGD peptides of different densities by varying the ratio of hydroxyl and methoxy terminated monolayers during surface modification (Figure 1). Then tdEos-Paxillinlabelledfocal adhesions (FAs) ofthe NIH-3T3 cells were imaged under PALM; meanwhilethe Alexa Fluor 647 labelled RGD molecules were detected on the same area under dSTORM. NB302 Index Terms— Studying Properties of RNA Nanotubes via Molecular Dynamics Roderick Melnik and Shyam Badu Wilfrid Laurier University, Canada Abstract—RNA molecules are very flexible in nature. This feature allows us to build various motifs which are essential in bio-nanotechnological applications. Based on the previous studies on RNA nanorings, in this contribution we analyze the structure and properties of RNA nanotubes, where we focus on nanotubes consisting of up to five nanorings of around 20nm in diameter. We have developed a molecular dynamics (MD) method and implemented it by using the NAMD and VMD packages to study the structural and thermal properties of the nanotube in physiological solutions. In particular, we have analyzed such characteristics as the Root Mean Square Deviation (RMSD), the radius of gyration, the number of hydrogen bonds per base pairs, and the radial distribution function for the different nanoclusters in nanotubes of various sizes. The variations of energy and temperature with simulation time have been studied for all sets of simulations. Variations in RMSD, radius of gyration and the radial distribution function with temperature have been analyzed in detail. Furthermore, the number of 23Na+ions around the nanotubes within the distance of 5A at two different temperatures has also been studied. It has been found that the number of ions accumulated around the nanotubes within the specified distance is growing with increase in temperature from 310K to 510K. The final configurations of the systems simulated at 510K have been considered as the starting point for further MD simulations at 310K. We confirmed the process of ion evaporation with temperature decrease. This is due to the phenomenon of self-stabilization. Index Terms— 29 Conference Schedule Afternoon Session Authors’ Oral Presentation 13:00pm-16:00pm Session 5(SALON TERRAZA C) ICMPM2014- Electrical materials and alloys materials Session Chair:Dr. Sabuj Mallik, University of Greenwich, United Kingdom PM009 Effect of Fiber Content on Failure Modes of Glass Fiber Reinforced Injection Molded Polyamide 66 Composites Ikilem Gocek, Reyhan Keskin and Guralp Ozkoc Istanbul Technical University, Turkey Abstract—In the present study, glass fiber reinforced Polyamide 66 composites were produced using laboratory type twin screw extrusion and injection molding processes. The glass fiber reinforcement was applied at 1, 10, 15, 20, 25 and 30 wt% loadings. The morphological structure of the samples and failure modes of glass fiber reinforced Polyamide 66 composites were investigated using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis on fractured surfaces of tensile tested samples in this study PM012 Index Terms—Fiber reinforced composites, failure mechanisms, fiber-matrix adhesion, glass fiber, polyamide66, SEM analysis The Effects of Either Height of Bellows Ends on the Stress Distributionaccording to Rotation Angles Jinbong KIM Hanseo University, KOREA Abstract—As analysis research, the effect of either height of bellows ends on the stress distribution has been proposed in the study. Rotation angle only is considered as a boundary condition. FEM solution for a u-shaped flexible tube under the action of angle of rotation is obtained. The design factor, convolution height of bellows ends, is considered for the simulation. The analysis is performed using the finite element analysis program. The maximum von-Mises stress and its reduction rate according to the height of bellows ends is compared respectively. PM013 Index Terms—Flexible tube, von-Mises stress, Lateral deflection, Stress Reduction Rate. Tuning the Microwave Dielectric Properties ofNd0.96Yb0.04(Mg0.5Sn0.5)O3 by Introducing Ca0.8Sr0.2TiO3 Yih-Chien Chen,Chih-Hung Li, Hua-Xian Liu, and Jing-Yu Fu Lunghwa University of Science and Technology, Taiwan 30 Conference Schedule Abstract—The influence of sintering temperature on the microwave dielectric properties and microstructure of the (1-y)Nd0.96Yb0.04(Mg0.5Sn0.5)O3-yCa0.8Sr0.2TiO3 ceramic system were investigated with a view to their application in microwave devices. The (1-y)Nd0.96Yb0.04(Mg0.5Sn0.5)O3-yCa0.8Sr0.2TiO3 ceramic systems were prepared using the conventional solid-state method. The X-ray diffraction patterns of the (1-y)Nd0.96Yb0.04(Mg0.5Sn0.5)O3-yCa0.8Sr0.2TiO3 ceramic system shifted to higher angle as y increased. A dielectric constant of 38.2, a quality factor (Q×f) of 53,500 GHz, and a temperature coefficient of resonant frequency of -3 ppm/℃were obtained when the 0.4 Nd0.96Yb0.04(Mg0.5Sn0.5)O3–0.6Ca0.8Sr0.2TiO3 ceramic system was sintered at 1600 ℃ for 4h. PM016 Index Terms—(1-y)Nd0.96Yb0.04(Mg0.5Sn0.5)O3-yCa0.8Sr0.2TiO3, constant, Quality factor, Temperature coefficient of resonant frequency. Stress-strain behaviour of dielectric elastomer for actuators Raj Kumar Sahu, K. Patra, S. Bhaumik, A. K. Pandey and D. K. Setua National Institute of Technology, Raipur, India Dielectric Abstract—Dielectric elastomer (DE) is gaining importance for potential strategic and commercial application as actuators. This paper reports the experimental investigation on different mechanical phenomena at large deformation of a commercially available acrylic dielectric elastomer material, VHB 4910 (3M) which is widely used for dielectric elastomer actuator (DEA) research. Attempts are made for accurate and precise experimental determination of nonlinear stress-strain, strain rate dependent hysteresis behaviour and cyclic softening of this material. It is observed that with the increase in strain rate maximum stress at a particular strain increases whereas hysteresis loss decreases. In the cyclic loading case after a particular number of cycles almost the hysteresis loss and maximum stress becomes constant. These experimental results are likely to be interesting for the designers for proper designing and characterization of the actuators fabricated with this material. PM018 IndexTerms—Dielectric elastomer actuators, acrylic rubber, large deformation, hysteresis, stress softening Flow Behavior of Wood Treated with Melamine Formaldehyde Resin under Non-equilibrium Thermal-compression Tsunehisa Miki, Rumiko Nakaya, Masako Seki, Soichi Tanaka, Nobuo Sobue, Ichinori Shigematsu, Kozo Kanayama National institute of advanced industrial science and technology (AIST), Japan Abstract—A uni-axial compression test of solid wood containing a melamine formaldehyde resin and moisture at a heating condition was carried out to investigate fluidity of solid wood aiming at application of wood-flow-forming with an acceptable pressure level. Results show that there is a preferable moisture condition for initiation of flow phenomenon of the resin-treated wood. Since the decrease in the flow stress of wood generating pronounced size change in the drying process was distinguished, there might be a positiveeffect of the non-equilibrium state in moisture on the ease in generation of flow deformation. Index Terms—Wood, Flow, Non-equilibrium Thermal-compression, Deformation, 31 Conference Schedule PM020 Plastic Forming Artificial Neural Network Modeling of Titanium Alloy Tribological Behaviour in Beta Solution Treated Condition Srinivasu Gangi Setti and R. N. Rao National Institute of Technology Raipur (NITRR), India Abstract—In the present investigation artificial neural network (ANN) approach was used for the prediction of wear and friction properties of low cost near beta titanium alloy β solution treated condition. The input parameters are load, track diameter and β solution treated temperature and output parameters are %weight loss, coefficient of friction and temperature generated between the pin and disc. In order to get the best model, different parameters like number of layers, number of hidden neurons, and transfer functions are changed. The data obtained in sliding wear tests were divided into two sets training data and testing data. A neural network was trained using a training data set and was validated using test data. The best network for prediction of tribological properties of these β solution treated specimens was 3-[11]1-[9]2-3 layer recurrent with purelin transfer function and trainlm is training function. The percentage error for %weight loss, coefficient of friction and temperature are 2.8, 1.7 and 5.3 respectively. PM026 Index Terms—Artificial neural networks, Beta titanium alloys, Tribology Investigation into effect of Cutting Conditions on surface roughness while dry machining Al-11%Si and Al-11%Si- 1% Bi Die Casting alloy Mohsen Marani Barzani, Ahmed A. D.Sarhan, Saeed Farahani,Ramesh Singh University of Malaya, Kuala Lumpur, 50603, Malaysia Abstract—These days turning process is required to more accurate and efficientin machining process. It has effect on surface of workpiece and decrease manufacturing coast. Therefore, understanding the key factors in machining parameters is important to develop effective machining strategies. In this study, an experimental investigation was conducted to determine the effects of cutting speeds and feed rates on surface roughness in turning of the Al %11Siand Al-11%Si- 1% Bidie cast alloys. Experimental trials carried out using coated carbide inserts (PVD). Three different cutting speeds, 70, 130 and 250 m/min and three feed rates 0.05, 0.1 and 0.15 mm/rev were used with a 0.15 mm constant depth of cut for all experiments. Additionally scanning electron microscope (SEM) was employed to clarify the different types of silicon morphology. Results revealed that surface roughness increased with increasing feed rate from 0.05 to 0.15 mm/rev and decreased with increasing cutting speed from 70 to 250 m/min. The result showed that workpiece containing Bi had the best surace roughnes with lamillar silicon shape in comoareson with aluminium-silicon with flake-silicon shape. PM027 Index Terms—Turning,Surface roughness, Microstructure, Bismuth, Silicon morphology. Optimizing detection parameters of magnetic Barkhausen noise using heat affect zone in welded ship steel plate Mohamed Sawalem, Mohamed Blaow and Ibrahim Adarrat University of Misurata, Libya Abstract—Magnetic Barkhausen noise measurements on a welded marine steel plate 32 Conference Schedule were performed in a line that passes through the weld bead and extends to the base metal from both sides of the weld. The heat affected zone was characterized by a pattern in the peak height as a function of distance from the weld bead. Barkhausen noise profile analysis by extracting relevant parameters like peak position, profile area and profile half width was also performed. The result showed a clear variation in MBN profile parameters in a way similar to that of the profile peak height. It could be concluded that MBN profile parameters superimposed as a function of measurement distance from the weld bead may provide an accurate determination of the affected material near the weld bead. The variation in MBN profile parameters was enhanced by microstructural and mechanical changes along the measurement line. This experiment demonstrates that the Barkhausen noise profile parameters could be used to track various manufacturing and maintenance processes of steel instead of using a single parameter like the root mean square (rms) to eliminate the variability of results and narrow the tolerance of acceptance criterion. PM031 Index Terms—Magnetic Barkhausen emission (MBN), Residual stress, welding, Structurally affected zone (SAZ), Mechanically affected zone (MAZ), Heat affected zone (HAZ) The Mechanical Response for Metallic Closed-Cell Foam at High-Strain Rates Charles E. Lord, Zhen Huang University of Sheffield, UK Abstract—As the trend for lighter more efficient structures continues, the requirement for alternative materials follows. One material that has gained attention more recently is porous metallic foam. One drawback to these materials is that there is limited pedigree and understanding of their performance. As with all materials, the use of metallic foam for structures requires knowledge of its mechanical properties; including at high-strain rates. The focus of this paper is to determine the compressive mechanical properties and the influencing parameters for AISI 4340 steel closed-cell foam under high-strain rates (776s-1 to 3007s-1). ANSYS commercial finite element code is used to simulate a closed-cell sample under a split Hopkinson pressure bar test. In this paper the pores are considered to be spherical in shape for simplification while various parameters such as the pore size, the number of pores, the distribution of pores, and the strain rate are varied. Each of these parameters gives this material a unique response which is presented in this paper. PM032 Index Terms—porous metal foam, closed-cell foam, high-strain rate, split Hopkinson pressure bar The Effect of Rise Angle of V-Hull Non Ballast Ship on Seakeeping performance Hesham Elkady, Duanfeng Han and Lianggao Gao Harbin Engineering University, China Abstract—In this paper a new concept in ship design was used to be alternative of ballast water system, to emerge that remedy the introduction of invasive marine species and the disadvantages of ballast water treatment systems.Thus, the hydrodynamic influences due to hull line variation of this kind of ships were studied, using the invariant cross-section area curve under the design draft to change the rise angle at bottom. Then numerical calculation was used to get the seakeeping at each angle. Two 3D models were 33 Conference Schedule constructed for 59000 DWT oil tankers and 35000 DWT bulk carriers, where the result of the bulk carrier was exposed. PM202 Index Terms—Hull line, Non-Ballast ship, Rise angle, Seakeeping, RMS for Rolling, RMS for Vertical acceleration, Bottom Slamming probability, Dick wetness probability. Experimental researches of Co-Cr Alloys powders manufactured by sintering process DMLS and Ni-Cr Alloys used in dentistry BĂILĂ Diana-Irinel University POLITEHNICA of Buchares, Romania Abstract—The purpose of this study was to evaluate the chemical and metallurgical aspects, mechanical properties and hardness of the Co-Cr alloy powders manufactured by sintering process DMLS and compared with Ni-Cr alloys used for personalized dental crowns. In dentistry are develop new methods to obtain personalized dental crowns quickly, the cost is not expensive and is identically with the dental scan realized by dentist. DMLS sintering manufacturing is a new method who permits to realize in the same day the dental crowns with the first control. Powders of Co-Cr alloys presents good sintered properties, good mechanical properties and the sintered probes don’t present tensile strength in the material after DMLS process. PM303 Index Terms—Ni-Cr alloys, Co-Cr alloys powders, Sintering Process DMLS, granulometry powder, electronic microscopy SEM, dental crown sintered. Experimental analysis of the structural and functional fatigue in shape memory alloy Nitinol wires when subjected to cyclic thermo-mechanical loading Anchal G, K. R. Frei, C. S. Upadhyay, D. J. Hartl Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur, India Abstract—The concept of deployable panels for solar energy and for moisture absorption is fascinating and is emerging as a new field of research. It requires sun or wind tracing using a solar or humidity sensor. Mechanism to move system uses stepper motors and is bulky. If new mechanism can be derived using SMA wires, it can be significant reduction in weight and complexity of the device. Ideally it can also serve to improve solar harvesting devices in space structures. Towards this, preliminary study is done on such devices using origami methods and test set-up is made. Index Terms—Shape memory alloys, cyclic thermo-mechanical loading, induced fatigue, hardening effect. Coffee Break 16:00pm-16:10pm 34 Conference Schedule Afternoon Session Authors’ Oral Presentation 16:10pm-19:00pm Session 6(SALON TERRAZAA) ICPSE2014-Power Systems and Control Engineering Session Chair:Prof. Magnus Thor Jonsson, University of Iceland, Iceland SE02 Optimal Coordination of Power System Stabilizer in Multi-machine Power System by using Hybrid Big Bang-big Crunch Algorithm Mojtaba Mohamadi, Hasan Shokouhandeh,Mojtaba Eslami Endargoli, Manouchehr Jafari Kaliji, and Hadi Jafari Kaliji MazandaranElectricalDistribution co, Iran Abstract—The main goal of this study is to enhance the stability of multi-machine power system by coordination of power system stabilizers. The objective considered is to design the proposed controller as a defined optimization matter. Hybrid Big Bang-Big Crunch (HBB-BC) algorithm was used to minimize cost function. The proposed algorithm was applied to a four-machine system and the influence of proposed algorithm in setting the stabilizers parameters was studied under different conditions. The results of simulations denote high efficiency of the algorithm in designing stabilizers compared with other optimization algorithms such as particles swarm algorithm (PSO). SE07 Index Terms—Power System Stabilizer, Hybrid Big Bang Big Crunch Algorithm, Multi-machine Power System, Low Frequency Oscillation. An Application of Economic Dispatch Problem using Game Theory Nezihe YILDIRANand Emin TACER Bahcesehir University, Turkey Abstract—This paper presents a game theory application for economic dispatch problem. In this application, economic dispatch problem has been applied to 6 thermal stations in 14-bus, 380kV power system in Turkey, by taking the generator limits and total demand into account, but transmission losses have been neglected. To find the optimum dispatch strategy Nash equilibrium has been used with MATLAB. Instead of following any particular strategy, the entire system has been analyzed. At the end of this paper, it was shown; calculated system total cost is smaller than the total cost of genetic algorithm and Lagrange function applications. SE08 Index Terms—Economic dispatch, optimization, game theory, Nash equilibrium. Energy Management and Control of a Solar Electric Vehicle Bendjedia Bachir,A.Hadjadj, F.bouchafaa, A.Benhouia,M.Temmir, and N. Rizoug 35 Conference Schedule Amar Telidji University, Algeria Abstract—This paper deals a detailed study, control and energy management of a solar vehicle Multisource Power Supply. A PVG is used as the principal energy source and the batteries are used as secondary/storage source. The use of this last source can reduce strongly the power stress imposed on the primary source. Two DC / DC converters to establish the power transmission to the traction part connect the power sources (PVGbattery) to the DC bus. The main source (PVG) is connected to a Boost converter which controlled by an MPPT strategy. Finally, an energy management strategy based on satisfying the load power requirement is used, for this reason, a DC-DC buck-boost converter to control batteries bank is used. SE12 Index Terms—Energy Management, PVG, DC-DC Converter, MPPT, Batteries. DC bus control of Back-to-Back connected Two-Level PWM Rectifier-Five-Level NPC Voltage Source Inverter to Torque Ripple Reduction in Induction Motor Thameur Abdelkrim, Karima Benamrane, Badreddine Bezza Applied Research Unit on Renewable Energies, Algeria Abstract—This paper proposes a regulation method of back-to-back connected two-level PWMrectifier-five-level Voltage Source Inverter (VSI) in order to reduce the torque ripple in inductionmotor. First part is dedicated to the presentation of the feedback control of two-level PWM rectifier.In the second part, five-level Neutral Point Clamped (NPC) voltage source inverter balancing DCbus algorithm is presented. A theoretical analysis with a complete simulation of the system ispresented to prove the excellent performance of the proposed technique. SE21 Index Terms—Back-to-back connection, two-level rectifier, Five-level NPC VSI, Feedback control,Redundant vectors, Torque ripple. Analysis and initialization of GE wind turbine control model ELVISA BECIROVIC, JAKUB OSMIC, DANIEL TOAL, MIRZA KUSLJUGIC, NEDJELJKO PERIC EPC Elektroprivreda BiH d.d. Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina Abstract—In this paper the analysis of a General Electric Wind Turbine Control Model (GEWTCM) and comparison with a Generic Wind Turbine Control Model (GWTCM) is presented. The analysis is performed for the GEWTCM stationary state. Based on the analysis, a systematic method for the GEWTCM initializations as well as a methodology for calculation of the GEWTCM operating point in steady state are presented. It has been shown that, due to lack of limiting of the pitch controller and pitch compensation, uniqueness of solution for initial and steady state values of all GEWTCM state variables are ensured except for the state variables of the pitch controller and pitch compensation. Conclusions from the analysis can help in the implementation of the wind turbine control model in power system dynamic simulation software packages in applications with variable wind speed. SE24 Index Terms—Generic wind turbine control model, GE wind turbine control model, analysis, initialization, anti-windup. Study of Distributed Generation Units Impact on Pricing On The Wholesale Power 36 Conference Schedule Energy Market Ilya D. Polyakov, Stepan A. Dmitriev and Pavel V. Chusovitin Ural Federal University named after the first President of Russia B.N. Yeltsin, Russia Abstract—This paper is devoted to the study of distributed generation units impact on pricing on the wholesale power energy market. The paper deals with results the analysis of the wholesale electricity market and power. This analysis is necessary for proper impact assessment of distributed generation units on a total optimization. Optimization calculations performed for the real power system, when distributed generation units operating the basic and peak modes, as well as the cost-effectiveness of this modes. SE33 Index Terms—Distributed generation units, optimization, wholesale electricity market and power, factors, electric energy. A New Financial Model and Economic Feasibility of Grid-Connected PV Power Plants for the Future of Renewable Energy in Turkey Nurettin Çetinkaya Selçuk University, Turkey Abstract—In this study, the economic feasibility of grid-connected photovoltaic (PV) power plants is investigated. In addition, a new financial model for renewable power system is proposed. The proposed structure of the financial model, operation and economics has been examined. Other objects of this study are to win more for both operator and the investor, and to set out the latest legal regulation for investment in Turkey’s emerging solar power market and to provide some guidelines to potential investors who appreciated country’s huge solar energy potential. Different options customer owned systems, operation systems, and other models are evaluated in detail. Feasibility is made for PV power plant. The proposed financial model is applied to PV power plant. Conclusions are discussed to find the best financial model for solar PV power plant systems. SE36 Index Terms—Economic feasibility, photovoltaic power plant, renewable energy support policies. Method for Determining Line Drop Compensator Control Parameters of Low-Voltage Regulator Using Random Forest Hiroshi Kikusato, Naoyuki Takahashi, Jun Yoshinaga, Yu Fujimoto, Yasuhiro Hayashi, Shinichi Kusagawa and Noriyuki Motegi Waseda University, Japan Abstract—Compensation of a voltage within the appropriate range becomes difficult when a large number of photovoltaic (PV) systems are installed. As a solution to this problem, the installation of a low-voltage regulator (LVR) has been studied. In this paper, we propose a method for instantly and accurately determining the line drop compensator (LDC) method parameters as a part of a voltage management scheme, which consists of prediction, operation, and control. In the proposed method, the solution candidates of the proper LDC parameters are narrowed by using a random forest that learns the relationship between the power-series data and the properness of the LDC parameters, thereby reducing the computational cost. We performed numerical simulations to verify the validity of the proposed method. From the results, the LDC 37 Conference Schedule parameters can be rapidly and accurately determined. Additionally, the desirable voltage control performance is verified. SE40 Index Terms—Distribution system, voltage control, low-voltage regulator (LVR), line drop compensator (LDC) method, random forest. Possibility of Four-Phase Grids Application in Russian Power System Alexandra Khalyasmaa, Dmitry Bliznyuk, and Andrey Plyasunov Ural Federal University named after the first President of Russia B.N. Yeltsin, Russia Abstract—This paper is devoted to four-phase electrical grids of high and extra-high voltage, principles of its formation and its possible operation and maintenance in united power system of Russia. Development of new simulation model of four-phase power grid for further realization in software is under consideration. Special attention is given to compliance with present both technical and economical requirements of this model in Russian Federation. Economic analysis of four-phase power system applying is done by means of comparison of different kinds of transmission Ural – Siberia. SE42 Index Terms—four-phase electrical grids, four-phase power line, three-to-four phase transformer, long distance power transmission. Maximum PV Penetration Capacity Evaluation of a Novel Method for Determining LDC Control Parameters of Step Voltage Regulators Shunsuke Kawano, Shinya Yoshizawa, Yu Fujimoto and Yasuhiro Hayashi Waseda University, Japan Abstract—This paper presents a new method for determining the load drop compensator (LDC) parameters of a load ratio transformer (LRT) and step voltage regulator (SVR) used in an electrical power distribution system. Because the voltage control effect produced by an LRT and SVR depends on the combination of their respective LDC parameters, these should be determined properly in order to control voltage within a proper range. Introduction of photovoltaic generation systems into a distribution system makes voltage control difficult and causes the optimal parameters to vary between dayand nighttime. In the proposed method, the parameters are reset every hour based on a database of all feasible parameters during every hour in the past. Simulation results in which the maximum PV penetration capacity of the proposed method is compared with that of a centralized control method are used to evaluate the performance of the proposed method. SE51 Index Terms—Electrical power distribution, voltage control, photovoltaic system, step voltage regulator, LDC method Voltage Reduction Field Test On a Distribution Substation Eduardo Vega-Fuentes, J.M. Cerezo-Sánchez, S. León-del Rosario and A. Vega-Martínez University of Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Spain Abstract—This paper highlights the relationship between power demand and voltage level on the distribution network. It shows how a small change in voltage with existing assets delivers a very meaningful response in power demand and in energy consumption. A 24 hour field trial at a utility without any experience with Conservation Voltage 38 Conference Schedule Reduction (CVR) is described. CVR effects are assessed by acombined comparison-regression method resulting in at least 9.42 MWh energy saved during the test, equivalent to the consumption of 848 households in the region. The energy savings achievable within the network under this study have been characterized and the attainable yearly savings on the Canary Islands distribution networks, are on the whole estimated. SE61 Index Terms—Conservation voltage reduction (CVR), demand reduction, distribution efficiency, energy saving, field trial. Classification of Selected Zingiberaceae Famili of Essential Oil Using E-Nose and Discriminant Factorial Analysis (DFA) Techniques: An Initial Study Sahrim Lias, Nor Azah Mohamad Ali, Mailina Jamil, Azrina Aziz and Siti Humeirah Ab Ghani Forest Research Institute Malaysia (FRIM), Malaysia Abstract—Essential oils are very valuable natural resources and considered as secondary metabolites. They are produced from several parts of aromatic plant by using different type of extraction techniques. Each technique produced slightly different output oil yield and smell however they produced the same major chemicals compound markers when they are analysed using chemical analysis and profiling technique. Pure essential oils are known to have very strong odor and there are several techniques used to differentiate the volatile odor generated. In this study, Electronic Nose (E-Nose) technology is used to distinguish the smell among 8 samples selected within the same Zingiberaceae Famili. Their pattern recognition profiles were examined by statistical analysis using Discriminant Factorial Analysis (DFA). The result shows that the E-Nose technology combined with DFA were succesfully discriminating all 8 samples within the same Famili with significant p-values < 0.05 across all samples and 100% recognition value. SE303 Index Terms—Essential oils, aromatic plant, Electronic Nose, discriminant factorial analysis Sea Bed Logging Applications: Predicting Hydrocarbon Depth using Mathematical Equations Hanita Daud, RADZUAN RAZALI and VIJANTH ASIRVADAM Universiti Teknologi PETRONAS, Malaysia Abstract—The aim of this research is to develop 1-D mathematical equation that relates Normalized mean Square Error (NMSE) to depth of hydrocarbon (HC) for data processed using cubic spline interpolation in sea bed logging (SBL) application. Simulations were conducted using CST software that replicated real SBL environment to generate synthetic data. Frequency of 0.25Hz was used and sediment thicknesses were varied from 1000m to 3000m and incremented at every 250m. Data collected were interpolated using cubic spline and NMSE were calculated between original and interpolated data. Mathematical equation that relates NMSE (y) and depth of hydrocarbon (x) was constructed in terms of linear, exponential, logarithm and polynomial degree 2, 3, 4 and R2 were calculated for each equation. Mathematical equation using exponential function was adopted because it has reasonably high R2 and can be inversed easily. Average percentage error was calculated between calculated and measured data to achieve 5 % or lower values. If achievable, this model was accepted as forward mathematical model for SBL. Otherwise, the coefficients were adjusted and the 39 Conference Schedule processes repeated until minimum average error was achieved. Index Terms—Sea Bed Logging, Cubic Spline Interpolation, Normalized Mean Square Error. Afternoon Session Authors’ Oral Presentation 16:10pm-19:00pm Session 7(SALON TERRAZA B) ICNB2014- Nanosensors and biochemical materials Session Chair: NB001 NB007 Sensitive Determination Papain Conjugated Cdse Quantum Dots by Dynamic Light Scattering Analysis Arup Ratan Mandal, ArturIshteev, Sergey Volchematiev and Denis Kuznetsov National University of Science and Technology "MISiS", Russia Abstract—A strong, simple and rapid method for determination enzyme (papain) conjugated quantum dots (QDs) by dynamic light scattering (DLS) is proposed in this report. Yellow CdSe QDs are synthesized with changing the precursor ratio and confirmed by absorption and emission spectra. Shape and size of synthesized QDs are checked by transmission electron microscope (TEM). Both absorption and emission spectra reveal very strong quantum confinement effect as expected; yellow excitonic emission is observed at room temperature for photoluminescence spectra (PL). The peak maxima are appreciably red-shifted when QDs are conjugated with positively charged papain enzyme. The details possible mechanism is described here, which is very interesting and scarcely addressed before. Index Terms—Yellow-quantum dots, dynamic light scattering, absorption, photoluminescence Characterization of ZnO Films based Sensors Prepared by Different Techniques Sonik Bhatia, NehaVerma, Aman Mahajan and R.K Bedi KanyaMahaVidyalaya, India Abstract—In the present research, zinc oxide (ZnO) films have been prepared by simple solution method and spray pyrolysis on different substrates (glass and sapphire) for different molar concentrations (0.2M & 0.25M). The films were subjected to different substrate temperatures (400°C and 450°C respectively. These were characterized for SEM and XRD and the average size of the crystallites were in range of 300 and 200nm for the films on Saphire and glass at higher substrate temperature. FTIR analysis has been carried out and optimization conditions were used in order to confirm the significant peaks and phase transformation. The films were subjected to ethanol gas for these substrates and corresponding electrical properties were carried out by two probe method 40 Conference Schedule and was found that the films for sapphire substrate prepared by spray pyrolysis method showed more conductance at higher temperatures than glass. Optical properties were also studied for these films and was found that films prepared by spray on sapphire shows less transmittance at higher substrate temperatures in comparison to the films on glass. NB010 Index Terms—Nanoparticles, spray pyrolysis, solution synthesis, sensors Response Surface Methodology to Optimize the Preparation of Chitosan/Alginate Nanoparticles Containing Curcumin Diethyl Disuccinate SettaponBhunchu, PornchaiRojsitthisak, and PraneeRojsitthisak Chulalongkorn University, Thailand Abstract—Curcumin diethyl disuccinate (CDD)is a succinate prodrug of curcumin that hasbetter anti-colon cancer and antinociceptive activities than curcumin and improved stability in phosphate buffer at pH 7.4. However, formulation of CDD for pharmaceutical use is limited. Therefore, this study focused on preparation of chitosan/alginate nanoparticles containing CDD and optimization of the formulation using response surface methodology. Chitosan/alginate nanoparticles were prepared by o/w emulsification and ionotropicgelification. The optimized formulation of nanoparticles containing CDD had achitosan/alginate mass ratio of 0.05:1, a CDD concentration of 3 mg/ml, and a Tween 80®content of 4.05% (w/v). Response surface methodology was found to bean effective techniqueforoptimization of the preparation of chitosan/alginatenanoparticles using a limited number of experiments. NB013 Index Terms—Response surface methodology, Curcumin diethyl disuccinate, Chitosan, Alginate, Nanoparticles, Box-Behnken statistical design Nanocrystalline Cu2ZnSnSe4Thin Films for Solar Cells Application: Microdiffraction and Structural Characterization Heiddy Paola Quiroz Gaitán and Anderson Dussan Universidad Nacional de Colombia, Colombia Abstract—This work presents a study the structural characterization of Cu2ZnSnSe4 (CZTSe) thin films by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and microdiffraction (XRMD) measurements. Samples were deposited varying both mass (MX) and substrate temperature (TS) at which the Cu and ZnSe composites were evaporated. CZTSe samples were deposited by co-evaporation method in three stages. From X-ray diffraction (XRD) measurements, it was possible to establish, with increased Ts, the presence of binary phases associated to the quaternary composite during the material’s growth process. A stannite-type structure in Cu2ZnSnSe4 thin films and sizes of the crystallites varying between 30 and 40 nm, were obtained. X-ray microdiffraction was used to investigate interface orientations and strain distributions when were varied deposition parameters. It was found that around the main peak, 2ϴ = 27.1°, the Cu1.8Se and ZnSe binary phases predominate, which are formed during the subsequent material selenization stage. A Raman spectroscopy study revealed Raman shifts associated to the binary composites observed via XRD. NB014 Index Terms—CZTSe compound, thin films, Structural properties, MicroXRD Optical and Morphological Properties of Tio2 Nanotubes for Sensor Applications Heiddy P. Quiroz and Anderson Dussan Cuenca 41 Conference Schedule Universidad Nacional de Colombia, Colombia Abstract—Highly-ordered TiO2 nanotube arrays were fabricated by electrochemical anodizing, using titanium foils as the anode and cathode and changing the amount of fluoride (NH4F) in the solution. The effect of synthesis parameters, such as, ethylene glycol solutions containing different amounts of water, NH4F, anodizing voltage, and current density were studied on the optical and morphological properties. It was observed from XRD espectra, that Anatase and Rutile phases were influenced by annealing, between 300 and 723 K, for all the samples, while morphological changes were not observed. Nanotubes diameters varying beteween 20 and 50 nm with diferent length sizes were observed from SEM micrographics. A high absorption for the UV region and a gap band round of 3.1 eV were obtained from spectrophotometry measurements. The correlation between the synthesis parameters and the optical properties presented are an excellent indicator for the TiO2 nanotubes application as optical sensors. NB015 Index Terms—TiO2, nanotubes, morphological properties, optical sensors Molecular tune of Vanadylphthalocynine Layers for Plastic Electronic Applications Beynor Antonio Paez-Sierra, Fredy Mesa and Anderson Dussan Cuenca Universidad Nacional de Colombia, Colombia Abstract—Engineering, stability and orientation of semiconducting molecules are necessary to achieve the high efficiency of multifunctional organic-based devices. Several conjugated molecules facilitate the use of external magnetic fields to tailor both their molecular orientation and electronic properties while being processed for bio or opto-electronic applications. In this work, molecular thin films of vanadylphthalocynine (VOPc) layers forming conducting channels in organic field-effect transistors were investigated. Three systems based on 100 nm thick VOPc thin film were grown, one in absence of magnetic field, while the other two with parallel and perpendicular to the substrate plane, respectively. Devices were ex-situ investigated by electrical characterization and confocal scanning Raman spectroscopy (SRS). All molecular layers growth on Au electrodes presented enhancement of the Raman signal. NB017 Index Terms—Raman spectroscopy, nanophotonics, SERS, organic semiconductors, VOpc plastic electronics, VanadylPhthalocynine, spectroscopy, organic electronics Electroneuromyograph Turushev N. V., Avdeeva D. K., Grigoriev M. G. National Research Tomsk Polytechnic University, Russia Abstract—The present article describes the methods of muscle electroneuromyographic study. The analysis of the existing electroneuromyographic diagnostic unit configurations commercially available at Russian and foreign markets is executed. The unit developed in the laboratory No. 63 of the Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) Institute of the National Research Tomsk Polytechnic University, its functional layout and main characteristics are considered. The present article focuses on the use of more sensitive equipment for better human body study. The results of measurements executed by means of unit developed are provided. Index Terms—Electroneuromyograph, 42 electroneuromyography, electromyography, Conference Schedule NB018 biopotential, medical devices, use of silver chloride nanoelectrodes Heart Condition Imaging with The Help of Hardware and Software Complex Based on The Cardiographic Equipment on Nanosensors M. G. Grigoriev, N. V. Turushev, D. K. Avdeeva National Research Tomsk Polytechnic University, Russia Abstract—Precision methods and devices for diagnostics of cardiovascular diseases are one of the main directions for development of modern technology in the field of medical instrument engineering. However, there are no small devices that allow for the diagnostics of cardiac muscle with precision accuracy and without operative intervention at this stage. This study presents the problems associated with cardiovascular diseases (CVD) and the analysis of various organizations engaged in development of efficient means for CVD diagnostics. Two-component FitzHugh - Nagumo model and heart condition imaging algorithm are considered. Aspects of work aimed at designing and developing of the hardware and software complex based on the information obtained with the help of an electrocardiograph on nanosensors. The obtained results are presented. NB022 Index Terms—Functional diagnostic, electrocardiographic, cardiovascular system, transmembrane potential Investigating a Functionalized Terthiophene Surface for the Detection of Progesterone using Surface Plasmon Resonance Marsilea Adela Booth, Ashton Partridge and Yinqiu Wu The New Zealand Institute for Plant & Food Research Limited, New Zealand Abstract—Herein we report a rapid and sensitive surface Plasmon resonance (SPR) biosensor to detect progesterone (P4), a model analyte of small molecules. A terthiophene scaffold with an oligoethylene glycol (OEG) linker is used as an anchor for the P4-ovalbumin (OVA) immobilization on gold to form a stable, regenerable SPR surface. Subsequently, inhibition SPR immunoassays based on this terthiophene/OVA-P4 surface have demonstrated that P4 limit of detection (LOD) in buffer solution was 0.13 ng ml-1. Due to the rapidity of each measurement (less than 5 min per measurement), and the high sensitivity of the assay, we believe the sensing platform may hold great potential for P4 detections NB026 Index Terms—Terthiophene, Progesterone, Surface Plasmon Resonance, Biosensor A Study on Slip Controller for Safety Improvement of Running Flat Road for Motorized Wheelchair Bo-Min Kim, Won-Yung Lee and Eung-Hyuk Lee Korean Polytechnic University, South Korea Abstract—A slip controller that can move against the off-track and control excursion caused by slips while driving a motorized wheelchair is proposed. Detecting slips in a motorized wheelchair is to detect states of the motorized wheelchair and its motors in a traveling condition. For carrying it, slip ratios are calculated using a slip detection algorithm based on the information obtained from the six-axis IMU sensor and the encoders, which are connected to both left and right motors. The calculated slip ratios are used as control variables for improving the safety in a motorized wheelchair. 43 Conference Schedule In the experiment of the slip controller proposed in this study, slips are verified in a proposed track. Also, it is verified that the maximum slip ratio section is determined while turning left or right. NB030 Index Terms—Motorized Wheelchair, Slip, Slip Controller, Torque Chemiresistor Gas Sensor Array Based on Conducting Polymers for The Discrimination of Virgin Coconut Oil Rey Alfred G. Rañola, Karen S. Santiago and Fortunato B. Sevilla University of Santo Tomas, Philippines Abstract—An array of chemiresistors based on conducting polymers was assembled for the differentiation of VCO.Thechemiresistor sensors were fabricated through the potentiostaticelectrodeposition of polyaniline, polypyrrole and poly(3-methylthiophene) on the gap separating two planar gold electrodes set on a Teflon substrate.The electrical resistance of the sensors were measured and observed to change when exposed to the headspace of oil samples.The sensor response was rapid and exhibited good reversibility and reproducibility.Different signals were obtained for each coconut oil sample and pattern recognition techniques were employed for the analysis of the data.The developed E-nose system was able to discriminate VCO from refined, bleached and deodorized coconut oil (RBDCO) and rancid VCO. NB038 Index Terms—Gas sensor array; conducting polymers; virgin coconut oil; electronic nose; chemiresistor Temperature Induced Plasmon Shift of Quantum Particles Mufei Xiao CNYN-UNAM, Mexico Abstract—It is of recent interest to study plasmonics of metallic particles that are so small that carriers in the conduction band are separated at discrete subbands due to quantum confinement. These small metallic particles are referred as quantum particles in the present work. The modifications of the plasmons of the quantum particles are studied with an every-electron-count computational scheme. The quantum size effects are incorporated into classic descriptions of small particle plasmons with the emphasis on intra-subband fluctuations caused by the quantum confinement. The carrier redistribution at the subbands is related to the operational temperature via Fermi-Dirac expression. Numerical results have shown that both the frequency and the strength of the plasmons are modified as a function of the particle size and the operational temperature. The discovery suggests that potential applications to tune the plasmonics of quantum particles externally would be possible. The environment temperature can be conveniently controlled by light, electricity, or other means. NB301 Index Terms—Plasmonics; quantuam particles; temperature dependence Gold Nanoparticles as Drug Delivery Vehicle for Chondroitin Sulphate (Cs) to Treat Osteoarthritis PriyankaDwivedi, Meenalkowshik, Ashok kumar , VijayashreeNayak Birla Institute of Technology and Science-Pilani, K. K. Birla Goa Campus, India Abstract—Osteoarthritis (OA) is a disease which is characterized by joint pain, swelling 44 Conference Schedule and stiffness due to wear and tear of articular cartilage and has limited self repair capacity due to its avascular and aneural nature. Nanotherapeutics use nanomaterials for various biomedical applications such as drug delivery, diagnostics and biosensors. This work focuses on the use of gold nanoparticles for enhancing the delivery of chondroitin sulphate (CS)-a drug used in the treatment of Osteoarthritis (OA). CS has already shown many benefits in treating osteoarthritis. Gold nanoparticles were synthesized and combined with CS. Gold nanoparticles were characterized by Transmission electron microscopy (TEM), XRD analysis. Further invitro analyses of this combination of Gold nanoparticles with CS (AuNp-CS)on primary goat chondrocytes were done by various assays like MTT, Hoescht staining, Glycosaminoglycan and collagen studies. Cell viability studies by MTT revealed that Gold nanoparticles –CS (AuNp-CS) stimulated cell proliferation. There was increase in cell viability observed by Gold nanoparticles-CS than Native CS at same concentration. Similar Results were also observed with GAG and Collagen assay. There was 2.18 and 2.05 fold increase observed in GAG and collagen production when gold nanoparticles–CS(AuNp-CS) was added in combination than native CS. So this study shows that this combination of gold nanoparticles-CS stimulates chondrocyte proliferation and enhances Extracellular matrix production (ECM). Thus giving us the insight for the applicability of gold nanoparticles as a carrier for osteoarthritic drug CS which can hold potential for treatment of disease. NB311 Index Terms— Silver Nanoparticles and Luminescent Silver Nanodots under Oxidative Stress Junhua Yu Seoul National University, South Korea Abstract—Silver nanodots consisting of a few silver atoms are becoming excellent fluorophores thanks to their small size, high brightness and excellent photostability. Initially, such clusters were prepared in noble gas matrices due to their vulnerability to oxidization. New protection groups has improved their stability in aqueous solution, leading to the synthesis of a series of spectrally-pure silver nanodots with emissions ranging from the blue to the near-IR. The exact structures of various silver nanodots remain unclear. We examined the photo-responses of various silver nanodots in oxidizing environments. Oxidants bleaches most of nanodot emitters, but only the red and near-IR emitters correlates with the formation of an oxidant-resistant blue emitter. The HPLC-MS indicates that the blue is an oxidized species. Based on such a unique phenomenon, we have demonstrated the advantage of the blue emitter as an imaging agent in oxidizing environments and designed ratiometric luminescence probes for the ultralow concentration detection. We also investigated the generation of silver nanodots by etching silver nanoparticles. The addition of chelating agents, such as polyamines or ssDNA molecules, accelerates the degradation of large silver nanoparticles to a stable stage of silver nanoparticles, which might be critical to the generation of emissive silver nanodots. The etching process is strongly pH dependent, and the binding between silver and the etching groups is crucial for efficient etching. The active centres are especially important for the formation of silver nanodots. We have shown that etching of silver nanoparticles can be an alternative to generate new silver nanodot emitters. Index Terms—Silver, nanoparticles, nanodots, clusters, oxidizing, luminescence, mechanism 45 Conference Schedule Afternoon Session Authors’ Oral Presentation 16:10pm-19:00pm Session 8(SALON TERRAZA C) ICPSE2014-Electrical and electronic materials Prof. Hamid Bentarzi, UMBB University, Boumerdes, Algeria Session Chair: A Supervisory Power Flow Controller for aHybrid Power System AbderrahmaneOuadi and Hamid Bentarzi UMBB University, Boumerdes, Algeria Opening Speech SE15 Abstract—Hybrid power system presented in this work focuses on the combination of wind, solar,and energy storing systems for sustainable power generation. The output power of wind turbine isonly available under a specific speed or higher. The solar energy varies hourly, daily and seasonallywhich depends on variation of solarirradiation. A generator-set with a battery bank can beintegrated with the wind and PV-system to ensure the continuity of power supply for all conditions.The paper aims to model and simulate the transient and steady state behavior of a Solar-Windhybrid power generation system together with energy storage bank. Besides, a supervisory powerflow controller has been developed which determines a power source that is selected to operate inorder to satisfy the load demand taking into account the sun irradiance and the wind speed. Theenergy storage bank may be used to store an excess of power from the renewable energy system(RES) that will be used when there is insufficient supplied power. If either the available power fromthe wind turbine or from the solar panels or both of them cannot satisfy the load demand thegenerator set system will be used to satisfy the load demand. The functionality of the presentedHybrid Power System has been successfully designed and simulated using Matlab/Simulink tool. Index Terms—Hybrid power system, wind turbine, solar system, Energy storing system. Transparent and Hydrophilic TiO2 Anatase as Top-Protective Layer for CSP Reflectors Houda Ennaceri, Asmae Khaldoun, Abdelilah Benyoussef, Tristan Köhler, Rodrigo Sáez-Araoz and Ahmed Ennaoui Al Akhawayn University, Morocco Abstract—Titanium Dioxide is an important material that is used in many industrial applications such as photo-catalysis, glass-defogging, self-cleaning, waste water purification and anti-bacterial sterilization. The strong photo-catalysis of TiO2, and therefore its ability to decompose dirt and organic contaminants makes it an excellent top-protective layer candidate for CSP reflectors. The aim of this study consists of the 46 Conference Schedule deposition of a transparent and hydrophilic TiO2 layer on top of the Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) mirrors without altering their specular reflectance. The strong photo-catalysis and hydrophilicity of TiO2 will decompose the dirt and organic matter on the surface of the mirrors, which would be cleaned away from the reflectors’ surface by rain, therefore minimizing the use of water for cleaning the CSP mirrors. In this study, polycrystalline anatase TiO2 layers were deposited on glass substrates with different thicknesses. The contact angle measurements show that the hydrophilicity of TiO2 increases with increasing surface roughness, with Water Contact Angle (WCA) of 52°and 30°for 48 nm and 100 nm, respectively. Super-hydrophilicity (WCA < 5°) was achieved for thicker TiO2 layers, with WCA of 8°and 1°for 177 nm and 220 nm, respectively. The deposition of a 48 nm-thick TiO2 layer on glass showed a high transmittance in the visible and Near Infrared (NIR) range (75%), whereas the transmission decreased with increasing thicknesses of TiO2. Therefore, a TiO2 layer of 48 nm thickness is suggested in this study as a hydrophilic top-protective layer since it preserved the specular reflectance of the mirrors (97.5%) in the NIR range, compared to 98.6% without the TiO2 layer. SE43 Index Terms—TiO2 anatase, Hydrophilicity, Specular Reflectance, Self-Cleaning, CSP. Equipment State Assessment System Based on ANFIS Alexandra Khalyasmaa, Artem Aminev, Andrey Sergeev, Stepan Dmitriev and Dmitry Bliznyuk Ural Federal University named after the first President of Russia B.N. Yeltsin, Russia Abstract—The paper analyzes the modern expert systems to assess the technical condition of power stations and substations high-voltage equipment. The main problems of modern expert systems and their possible solutions are determined. As the structure and their basic construction principles are considered. Also this paper proposes an algorithm for the expert system model using fuzzy inference on the basis of technical diagnostics and tests. As a case study of assessment of power transformers state based on dissolved gas analysis in the oil is presented. SE47 Index Terms—technical state assessment, expert systems, hybrid neural network, ANFIS, chromatographic gas analysis. SINS/CNS Integration Algorithm and Simulations for Extended Time Flights using Linearized Kalman Filter Khan Badshah, Qin Yongyuan, and Jinliang Zhang Northwestern Polytechnical University (NPU), China Abstract—A robust integration algorithm of Strapdown Inertial Navigation System/Celestial Navigation System (SINS/CNS) is designed and investigated in this paper. The main objective of the developed integration scheme is the estimation and correction of unacceptable SINS’ errors in long time navigation missions. A Charged Couple Device (CCD) star sensor is utilized as a CNS suite in this work for integration with SINS. A mathematical model is developed to transform the CCD measurements to Psi-angle vector and transformations of different frames were exercised. A Linearized Kalman Filter (LKF) with a modified measurement model is used to optimally fuse the data of SINS and CNS. Finally, simulation results for extended time flight are produced 47 Conference Schedule to show the integrity and validity of the designed integration algorithm. SE54 Index Terms—Celestial navigation system, Strapdown inertial navigation system, integrated navigation, Kalman filtering, charged coupled device and star sensor. Numerical Simulation of Thermal Plasma Gasification Process Sooseok Choi Jeju National University, Republic of Korea Abstract—Numerical analysis of plasma gasification process was carried out base on the combination of magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) and computational fluid dynamics (CFD). A two stage gasification system which consists of a heater and a plasma rector was used to enhance syngas production in the present work. Nitrogen thermal plasma jet generated by a low power plasma torch was analyzed by a self-developed MHD code, and complex thermal flow field in the plasma reactor was simulated with a commercial CFD code. The accuracy of numerical simulation was confirmed from the comparison between numerical results and experimentally measured data of arc voltage and reactor temperature. From the numerical analysis, a high temperature for the thermal cracking of methane was expected in the upper region of the plasma reactor. SE56 Index Terms—Thermal plasma, Gasification, Numerical Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD), Computational fluid dynamics (CFD). Advanced Combined 3D Scanner based on Ultrasonic and Infrared Waves Evgeny A. Rybakov, Dmitrii P. Starikov and Denis Y. Berchuk National Research Tomsk Polytechnic University, Russian Federation analysis, Abstract—This article contains information about creating special unit for scanning 3D objects andpractical applicability of computational electromagnetics. The main part of the unit is ultrasonictransducer and infrared sensor, which are send waves to the object and receives back waves forcalculating distance. After that, microcontroller send to PC data, and computer program create modelfor printing from the plastic, gypsum, brass etc. SE58 Index Terms—Plastic, ultrasonic, infrared, shaft, clutch, stage, and microcontroller. Low Cost Treatment for Remediation Coal Mining Water using Shrimp Shell in Natura, aiming to Obtain Water that Enable the Reuse for Secondary Non-potable Purposes Dámaris Núñez Gómez, María Ángeles Lobo-Récio and Flávio Rubens Lapolli UNIVERSIDADE FEDERAL DE SANTA CATARINA – UFSC, BRAZIL Abstract—The acid mine drainage (AMD) is one of the most serious problems of mining on an international level, with high negative impacts on hydric courses and water life. The main characteristics of AMD are low pH and high sulfate and different metals ions (Cd, Cu, Ni, Pb, Zn, Fe, Al, Cr, Mn, Mg, etc.) concentration, many of which demonstrate to be toxics for the ecosystems, and, in last case, to the health and quality of human life. The objective of this research was study the potential of the shrimp shell in natura for removal of metals and acids present in mine impacted waters (MIW), aiming to obtain, after treatment, water within legal standards that enable its reuse for secondary non-potable purposes. The waters studied came from the coalfield of state of Santa Catarina (Brazil), with pH around 3, and high levels of Al, Fe, Mn and 48 Conference Schedule SO42-. Shrimp shell is rich in chitin, able to remove metal ions via adsorption mechanisms, and in calcium carbonate, able to neutralize the acidity of the impacted water. Preliminary trials were performed in batches to analyze the influence of the pH in relation to the quantity of substratum/ water volume, the time of contact and the agitation velocity in the remediation of MIW. The results show that the elevation of the pH of the samples was higher with the shrimp shells rather than with the commercial chitin. A factorial approach was made by design compost central rotational (DCCR). In terms of efficiency in the removal of pollutant specimens, it was possible to determine that the best experimental conditions are 188 rpm and 8,975g L-1 of shrimp shells. The kinetic studies revealed that the model of pseudo second order provided the best adjustments of experimental data, confirming that the control of the velocity is by a chemical adsorption mechanism. The results of the treatment confirmed its suitability to remove efficiently acidity and metals. So, the sustainable character of the proposed treatment can be pointed out, with which it has been possible to transform an extremely toxic water in an effluent capable of being used as reuse water for secondary non-potable purposes by a cheap technology, giving an added value to a residue initially without value, the shrimp shell. SE59 Index Terms—Mine impacted water (MIW), chitin, biosorption, removal of metals, removal of acidity. Numerical Simulation of Turbulent Thermal Fluid in Tee Water Duct Cooled Nuclear Reactor Mohammed Aounallah, Mustapha Belkadi, Lahouari Adjlout and Omar Imine University of Sciences and Technology Mohamed Boudiaf of Oran USTO-MB, Algeria Abstract—The turbulent and thermal mixing in a vertically oriented T-junction is investigated numerically using ANSYS FLUENT software. By taking account the buoyancy forces, a steady state three-dimensional turbulent flow is considered with a Reynolds number of 0.4×105 at the cold inlet and 3.3×105 at the hot entrance. The k-ε standard model with standard wall function is chosen to provide closure for the Reynolds stress tensor. The numerical results presented in the form of velocity vectors field and contours of temperature distribution gave a good prediction of the dynamic and the thermal fields namely in the mixing region where a reversed flow is captured. SE63 Index Terms—Thermal mixing, turbulent fluid, Tee junction, nuclear reactor Dielectric Proprieties and Relaxation Behavior of High Density Polyethylene (HDPE) F.BenabedandTaharSeghier Laboratoire d’Etudes et Développement des Matériaux Semi-conducteurs et Diélectriques, Laghouat,Algeria Abstract—The method of dielectric spectroscopy is an instrument of choice for the diagnosis of insulation used in high voltage and also to assess the quality of the insulation of HV equipment such as transformers, cables, capacitors, etc… This method allows to estimating the state and the quality of the insulation using the dielectric response of the frequency range. In this article, we have presented results of dielectric studies in high-density polyethylene (HDPE) by means of dielectric relaxation spectroscopy (DRS) in frequency range 10-2 - 106 Hz and temperature between -60 and 60 °C, we will invest this method to measure the dielectric properties 49 Conference Schedule and evaluate the performance of this insulator witch has always been chosen as a model polymer material because it is the simplest polymer with respect to its chemical structure and is used in a wide range of applications in daily life. SE67 Index Terms—High density polyethylene, Dielectric proprieties, Spectroscopy, Temperature Tool Wear of Aluminum/Chromium/Tungsten-based-coated Cemented Carbide in Cutting Hardened Sintered Steel Tadahiro Wada and Hiroyuki Hanyu Nara National College of Technology, Japan Abstract—In order to improve both the scratch strength and the micro-hardness of (Al,Cr)N coating film, the cathode material of an aluminum/chromium/tungsten target was used in adding the tungsten (W) to the cathode material of the aluminum/chromium target. In this study, hardened sintered steel was turned with (Al60,Cr25,W15)N, (Al60,Cr25,W15)(C,N), (Al64,Cr28,W8)(C,N), (Al,Cr)N and (Ti,Al)N coated cemented carbide tools. The tool wear of the coated cemented carbide tool was experimentally investigated. The following results were obtained: (1) In cutting hardened sintered steel at the cutting speed of 0.42 m/s using the (Al60,Cr25,W15)N, the (Al60,Cr25,W15)(C,N), the (Al64,Cr28,W8)(C,N), the (Ti,Al)N and (Al,Cr)N coated tools, the wear progress of the (Al64,Cr28,W8)(C,N) coated tool became slowest among that of the five coated tools. (2) The wear progress of the (Al60,Cr25,W15)(C,N) coated tool was almost equivalent to that of the (Al64,Cr28,W8)(C,N) coated tool. However, at a high cutting speed of 1.67 m/s, the wear progress of the (Al60,Cr25,W16)(C,N) coated tool was faster than that of the (Al64,Cr28,W8)(C,N) coated tool. SE301 Index Terms—Cutting, physical vapor deposition coating method, (Al,Cr,W)N coating film, (Al,Cr,W)(C,N) coating film, hardened sintered steel. Lattice Boltzmann Modeling of the Effective Thermal Conductivity for Complex Structured Multiphase Building Materials Mazhar Hussain and Wen-Quan Tao Xi’an Jiaotong University, China Abstract—The effective thermal conductivity is an important parameter used to predict the thermal performance analysis of complex structured porous building materials. The observation of porous structure of building materials on REV (representative elementary volume) scale showed that pores can be classified into meso and macro pores. In contrast to the traditional models usually used for the (macro-meso) pore connection , a new numerical random generation macro-meso pores (RGMMP) method, based on geometrical and morphological information acquired from measurements or experimental calculations, is proposed here. Along with proposed structure generating tool RGMMP a high efficiency LBM, characterized with the energy conservation and appropriate boundary conditions at numerous interfaces in the complex system, for the solution of the governing equation is described which yields a powerful numerical tool to obtain accurate solutions. Then present model is validated with some theoretical and experimental values of effective thermal conductivity of typical building materials. The comparison of present model and experimental results shows that the proposed model 50 Conference Schedule agrees much better with the experimental data than the traditional theoretical models. Therefore, the present model is not limited to the described building materials but can also be used for predicting the effective thermal conductivity of any type of complex structured building materials. SE302 Index Terms—Lattice Boltzmann method, RGMMP, Effective thermal conductivity, Building materials. Effect of Glass Superposition on the Efficiency of the ET 200 Flat Plate Solar Collector Nabila Ihaddadene,RazikaIhaddadene, and Abdelwahhabbetka Department of Mechanical Engineering, M’Sila University, Algeria Abstract—This research document presents an experimental study on the effect of the superposition of glass panes on the functioning of a solar thermal collector. Experiments were carried out on an active solar energy demonstration system (ET 200). Three (03) commercial glass panes of 3mm, 5mm and 8mm thick were used.In the first experiment the collector glass was replaced by the superposition of the two panes of 3 and 5mm thick. In the second experiment the collector glass was replaced by the thickest glass (8mm). The glass of 8mm thick leaves more energy, generated from the halogen lamp, to penetrate inside the collector than the composed glass (3mm+5mm), which leaves less energy reaching the absorber. The glass pane of 8mm thick has an efficiency of about 44% against 40% for the composed glass (3mm+5mm). The glass composed from the superposition of the panes of 3mm and 5mm thick exerts a distinct effect, on the solar collector, than the simple glass of 8mm thick. SE312 Index Terms—Solar energy, Flat plate collector efficiency, Glass superposition, commercial glass. Time Varying Meshing Stiffness of Cracked Sun and Ring Gears of Planetary Gear Train MUHAMMAD ARIF ABDULLAH and LIU GUANG LEI Northwestern Polytechnical University, China Abstract—The time varying meshing stiffness of normal and cracked spur gears of planetary gear train is studied by applying the unit normal forces at mesh point on the face width along the line of action of the single gear tooth in FE based software Ansys Workbench 14.5. The tooth deflections due to the applied forces at one mesh point are noted and a deflection matrix is established which is solved using Matlab to get net deflection and finally the meshing stiffness of gear tooth at particular mesh point. The process is repeated for other mesh points of gear tooth by rotating it to get meshing stiffness for whole gear tooth. Index Terms—Meshing stiffness, unit normal force, planetary gear train. 51 Conference Schedule Poster Presentation: SE03 Optimization of Distribution Functions for the Hysteresis Preisach Model by Genetic Algorithms Mounir BOUDJERDA, Mounir Amir, Mourad ZERGOUG, Siham AZZI and Mouhamed Sahnoun Welding and NDT Research Centre (CSC), Algeria Abstract—The description of hysteresis is one of the classical problems in magnetic materials. Theprogress in its solution determines the reliability of modeling and the quality of design of a widerange of contemporary devices, as well as devices that will be created in the future. The intensiveinvestigations in hysteresis modeling were induced by the fact that accuracy models of magnetichysteresis must be studied yet. In this paper, several identification procedures of the distributionfunctions of the Preisach model will be investigated by means of a genetic algorithm. The proposed approach has been applied to model the behavior of many samples and distributionfunctions are optimized which will give accurate results of the hysteresis loop. The results show therobustness and efficiency of genetic algorithm to model the phenomenon of hysteresis loop. Thiswork can give solutions about the ferromagnetic material evaluations and shows the optimization ofdistribution functions according to the material behaviors. SE35 Index Terms—Preisach Model, distribution functions, genetic algorithms GA, Optimization. Development of a Plasma-Dump Combustor for VOC Destruction Young Nam Chun, Eun Hyuk Kim, Mun Sup Lim and Woo Il Cheon Chosun University, Korea Abstract—Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are gases with low calorific values produced from the painting or drying process whose stable combustion cannot be ensured by direct combustion. In this study, a novel plasma-dump combustor was proposed to remove the VOCs. The combustor is combined the concept of a plasma burner, a dump combustor and a 3D matrix burner. Therefore, it can achieve high destruction with low input energy and stable flame at low temperature. The toluene was used as a representative VOC. The toluene reduction characteristic was examined according to the total gas feed, toluene concentration, dump injector position, and 3D matrix heat accumulator. The toluene decomposition efficiency was 99.5%, and the energy efficiency was 447.2 g/kWh was at the optimum operating conditions. SE313 Index Terms—volatile organic compounds (VOCs), toluene decomposition, plasma combustor, dump combustor, matrix burner. A Grating Monopole Antenna on Metamaterial Using MSRR for DVB-T Application C. Zebiri, M. Lashab, F. Benabdelaziz, R. A. Hameed and F. Elmegri UNIVERSITY CONSTANTINE 1, Algeria Abstract—This work presents a novel broadband monopole antenna for digital video 52 Conference Schedule broadcasting-terrestrial (DVB-T) application. The proposed antenna consists of a grating patch and a concave rectangular ground plane with defected ground plane, and the Multiple Split-Ring Resonator (MSRR). The added part in the ground plane and the meta-material are used to enable the antenna height reduction for fixed ranges of operating frequency. The proposed antenna can operate from 468 MHz to 894 MHz frequency range corresponding to 62.5% of impedance bandwidth for |S11| better than -7.5 dB. This covers the working frequency band (470–862 MHz) of DVB-T system. The radiation pattern of the proposed antenna is omnidirectional across the desired operating frequency band. Details of the proposed antenna designs and experimental results of the constructed prototypes are presented and discussed. PM025 Index Terms—antenna, DVB-T, radiation pattern, defected ground plane, MSRR, meta-material. The microstructure evolution and hardness behavior of AZ91 containing Sn magnesium alloy Sugun Lim Gyeongsang National University,Korea Abstract—In this study, the microstructure evolution and Hardness of AZ91-containing Sn magnesium alloy during the solid solution and the aging heat treatment processes were investigated using the optical microscopy, scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, and Rockwell hardness techniques. The XRD results showed that the main phases in the as-casted alloy were α-Mg, Mg17Al12,and Mg2Sn. The SEM images obtained from the solution treatment of the AZ91-containing Sn magnesium alloy showed that the Mg17Al12 phases in the alloy were dissolved in the matrix due to the increased holding time during the solution treatment, but the Mg2Sn phases were clearly observed. The highest degree of hardness of the AZ91-containing Sn magnesium alloy appeared to have been 82HRE at the aging temperature of 200ºC. Index Terms—AZ91 alloy, aging behavior, solution treatment, Sn addition, Mg2Sn. Day 3, Saturday, December 20, 2014-Tour ConferenceVenue 53 Conference Schedule Hotel Avenida Palace http://www.icpse.org/venue.html Add: Gran Vía de les Corts Catalanes, 605 08007 Barcelona, Spain Directo: +34 637 413 785 Hotel: +34 93 301 96 00 Fax. +34 93 304 37 89 Welcome to American Society for (www.asr.org) Upcoming Conferences: DATE NAME ICSST 2015 PAPER WILL BE PUBLISHED BY 2015 the 4th International Conference on Security Science and Technology http://www.icsst.org/ Jan15-16, 2015 Portsmouth, UK ICNCS 2015 2015 the 4th International Conference on Network and ComputerScience http://www.icncs.org/ ICK 2015 Research 2015 International Conference on Knowledge http://www.ick.org/ 54 All accepted papers will be published in the volume of International Journal of Engineering and Technology (IJET) (ISSN; 1793-8244 (Online Version); 1793-8236 (Print Version)) All accepted papers will be published in the volume ofInternational Journal of Future Computer and Communication (IJFCC) (ISSN: 2010-3751) Abstracting/ Indexing: Google Scholar, Engineering & Technology Digital Library, and Crossref, DOAJ, Electronic Journals Library, EI (INSPEC, IET). All accepted papers will be published in the volume of International Journal of Knowledge Engineering (IJKE) Conference Schedule All accepted papers of ICMM 2015 will be published by Applied Mechanics and Materials Journal (ISSN: 1660-9336). Feb 12-13, 2015 Busan, South Korea Mar19-20, 2015 Florence, Italy ICMM 2015 2015 6th International Conference on Mechatronics and Manufacturing http://www.icmm.org/ ICAEE 2015 2015 the 2nd International Conference on Advances in Electronics Engineering http://www.icaee.org/ ICAPM 2015 2015 5th International Conference on Applied Physics and Mathematics http://www.icapm.org/ ICMLC 2015 2015 7th International Conference on Machine Learning and Computing http://www.icmlc.org/ ICEIT 2015 2015 4th International Conference on Educational and Information Technology http://www.iceit.org/ ICICN 2015 2015 3rd International Conference on Information and Computer Networks http://www.icicn.org/ 55 Indexed by Elsevier: SCOPUS www.scopus.com and Ei Compendex (CPX) www.ei.org. Cambridge Scientific Abstracts (CSA)www.csa.com, Chemical Abstracts (CA) www.cas.org, Google and Google Scholar google.com, ISI (ISTP, CPCI, Web of Science) www.isinet.com, Institution of Electrical Engineers (IEE) www.iee.org, etc. All accepted papers of ICAEE 2015 will be published by International Journal of Information and Electronics Engineering (IJIEE) (ISSN: 2010-3719) Indexed by Google Scholar, Electronic Journals Library,Engineering & Technology Digital Library,Crossref and ProQuest, DOAJ, Ei (INSPEC, IET). All accepted papers of ICAPM 2015 will be published by International Journal of Applied Physics and Mathematics (IJAPM) (ISSN: 2010-362X) Indexed by EI (INSPEC, IET),Chemical Abstracts Services (CAS), DOAJ,Electronic Journals Library, Engineering & Technology Digital Library, Nanowerk Database, Crossref, Google Scholar and ProQuest. All accepted papers of ICMLC 2015 will be published by International Journal of Machine Learning and Computing (IJMLC) (ISSN: 2010-3700) Indexed byEngineering & Technology Digital Library, Google Scholar, Crossref, ProQuest, Electronic Journals Library, DOAJ and EI (INSPEC, IET). All accepted papers of ICEIT 2015 will be published by Journal of Information and Education Technology (IJIET). (ISSN: 2010-3689) Indexed byEI (INSPEC, IET),Cabell's Directories, DOAJ, Electronic Journals Library, Engineering & Technology Digital Library, EBSCO, Google Scholar, Crossref and ProQuest. All accepted papers of ICICN 2015 will be published by Journal of Advances in Computer Networks (ISSN: 1793-8244) Indexed byEngineering & Technology Digital Library, EBSCO, DOAJ, Electronic Journals Library, Ulrich's Periodicals Directory, International Computer Science Digital Library (ICSDL), ProQuest, and Google Scholar. Conference Schedule All accepted papers of ICFD 2015 will be published by Applied Mechanics and Materials Journal (ISSN: 1660-9336) April 6-7, 2015 Orlando, USA April 28-29, 2015 Ankara, Turkey ICFD 2015 2015 International Conference on Fluid Dynamics http://www.icfd.org/ ICCEB 2015 2015 4th International Conference on Computer Engineering and Bioinformatics http://www.icceb.org/ ICTLE 2015 2015 4th International Conference on Traffic and Logistic Engineering http://www.ictle.org/ ICCIT 2015 2015 International Conference on Computer and Information Technology http://www.iccit.org/ Indexed byElsevier: SCOPUS www.scopus.com and Ei Compendex (CPX) www.ei.org. Cambridge Scientific Abstracts (CSA)www.csa.com, Chemical Abstracts (CA) www.cas.org, Google and Google Scholar google.com, ISI (ISTP, CPCI, Web of Science) www.isinet.com, Institution of Electrical Engineers (IEE) www.iee.org, etc. All accepted papers of ICCEB 2015 will be published by International Journal of Engineering and Technology (IJET) (ISSN: 1793-8236). Indexed byChemical Abstracts Services (CAS), DOAJ, Engineering & Technology Digital Library, Google Scholar, Ulrich Periodicals Directory, Crossref, ProQuest, Electronic Journals Library, Index Copernicus, EI (INSPEC, IET). All accepted papers of ICTLE 2015 will be published by Journal of Traffic and Logistics Engineering (JTLE) (ISSN: 2301-3680) Indexed byUlrich's Periodicals Directory, Google Scholar, EBSCO, Engineering & Technology Digital Library and Electronic Journals Digital Library. All accepted papers of ICCIT 2015 will be publishedin the one of the following Journal with ISSN. Journal of Software (JSW, ISSN 1796-217X) International Journal of Computer Theory and Engineering (IJCTE) (ISSN: 1793-8201) Indexed byIndex Copernicus, Electronic Journals Library, EBSCO, Engineering & Technology Digital Library, Google Scholar, Ulrich's Periodicals Directory, Crossref, ProQuest, WorldCat, and EI (INSPEC, IET), Cabell's Directories. International Journal of Computer and Electrical Engineering (IJCEE) (ISSN: 1793-8163) Indexed byUlrich's Periodicals Directory, Google Scholar, EBSCO, Engineering & Technology Digital Library, Crossref, ProQuest, EI (INSPEC, IET), and Electronic Journals Library Lecture Notes on Information Theory (ISSN: 2301-3788) Indexed by EI(INSPEC, IET), Ulrich's Periodicals Directory, Google Scholar, EBSCO, Engineering & Technology Digital Library and etc. 56 Conference Schedule All accepted papers of ICEEE 2015 will be publishedin the one of the following Journal with ISSN. Applied Mechanics and Materials Journal (ISSN: 1660-9336) Indexed by Elsevier: SCOPUS www.scopus.com and Ei Compendex (CPX) www.ei.org. Cambridge Scientific Abstracts (CSA)www.csa.com, Chemical Abstracts (CA) www.cas.org, Google and Google Scholar google.com, ISI (ISTP, CPCI, Web of Science) www.isinet.com, Institution of Electrical Engineers (IEE) www.iee.org, etc. ICEEE 2015 2015 2nd International Conference on Electrical and Electronics Engineering http://www.iceee.org/ International Journal of Electronics and Electrical Engineering (ISSN: 2301-380X) Indexed byUlrich's Periodicals Directory, Google Scholar, EBSCO, Engineering & Technology Digital Library, etc. Journal of Automation and Control Engineering (ISSN: 2301-3702) Indexed byEI (INSPEC, IET), Ulrich's Periodicals Directory, Google Scholar, EBSCO, Engineering & Technology Digital Library and etc. International Journal of Electrical Energy (ISSN: 2301-3656) Indexed byEI(INSPEC, IET), Ulrich's Periodicals Directory, Google Scholar, EBSCO, Engineering & Technology Digital Library and etc. All accepted papers of IOAC 2015 will be published by Applied Mechanics and Materials Journal (ISSN: 1660-9336) May 9-10, 2015 Bali, Indonesia ICOAC 2015 2015 International Conference on Automatic Control http://www.icoac.org/ Indexed byElsevier: SCOPUS www.scopus.com and Ei Compendex (CPX) www.ei.org. Cambridge Scientific Abstracts (CSA)www.csa.com, Chemical Abstracts (CA) www.cas.org, Google and Google Scholar google.com, ISI (ISTP, CPCI, Web of Science) www.isinet.com, Institution of Electrical Engineers (IEE) www.iee.org, etc. All accepted papers of ICMML 2015 will be published by Advanced Materials Research (ISSN: 1022-6680). ICMMT 2015 2015 6th International Conference on Material and Manufacturing Technology http://www.icmml.org/ Indexed byElsevier: SCOPUSwww.scopus.com and Ei Compendex (CPX) www.ei.org/. Cambridge Scientific Abstracts (CSA) www.csa.com, Chemical Abstracts (CA) www.cas.org, Google and Google Scholar google.com, ISI (ISTP, CPCI, Web of Science) www.isinet.com , Institution of Electrical Engineers (IEE)www.iee.org , etc 57 Conference Schedule All accepted papers of ICRE 2015 will be publishedin the one of the following Journal with ISSN. Advanced Materials Research (ISSN: 1022-6680). ICRE 2015 2015 International Conference on Reliability Engineering http://www.icre.org/ Indexed byElsevier: SCOPUSwww.scopus.com and Ei Compendex (CPX) www.ei.org/. Cambridge Scientific Abstracts (CSA) www.csa.com, Chemical Abstracts (CA) www.cas.org, Google and Google Scholar google.com, ISI (ISTP, CPCI, Web of Science) www.isinet.com , Institution of Electrical Engineers (IEE)www.iee.org , etc Journal of Engineering and Technology (IJET) (ISSN: 1793-8236). Indexed byChemical Abstracts Services (CAS), DOAJ, Engineering & Technology Digital Library, Google Scholar, Ulrich Periodicals Directory, Crossref, ProQuest, Electronic Journals Library, Index Copernicus, EI (INSPEC, IET). All accepted papers of ICLB 2015 will be published by Advanced Materials Research (ISSN: 1022-6680). June 6-7, 2015 Chengdu, China ICLB 2015 2015 International Conference on Lithium Batteries http://www.iclb.org/ ICCSN 2015 2015 the 7th International Conference on Communication Software and Networks http://www.iccsn.org/ Indexed byElsevier: SCOPUSwww.scopus.com and Ei Compendex (CPX) www.ei.org/. Cambridge Scientific Abstracts (CSA) www.csa.com, Chemical Abstracts (CA) www.cas.org, Google and Google Scholar google.com, ISI (ISTP, CPCI, Web of Science) www.isinet.com , Institution of Electrical Engineers (IEE)www.iee.org , etc All accepted papers of ICCSN 2015 will be publishedin the one of the following Journal with ISSN. WIT Transactions on Information and Communication Technologies (ISSN: 1743-3517) Indexed byEI Compendex, Scopus and ISI. Journal of Communications (JCM) (ISSN: 1796-2021; DOI: 10.12720/jcm) Indexed byEI Compendex; SCOPUS; ULRICH's Periodicals Directory; Google Scholar; INSPEC; etc. 58 Conference Schedule All accepted papers of ICIIP 2015 will be publishedin the one of the following Journal with ISSN. WIT Transactions on Information and Communication Technologies (ISSN: 1743-3517) ICIIP 2015 2015 the 4th International Conference on Intelligent Information Processing http://www.iciip.org/ Indexed byEI Compendex, Scopus and ISI. Journal of Industrial and Intelligent Information (ISSN: 2301-3745; DOI: 10.12720/jiii) Indexed by EI(INSPEC, IET), Google Scholar, EBSCO, Engineering & Technology Digital Library and etc. All accepted papers of ICWOC 2015 will be publishedin the one of the following Journal with ISSN. WIT Transactions on Information and Communication Technologies (ISSN: 1743-3517) ICWOC 2015 ICDDM 2015 July 2-3, 2015 Chicago, USA 2015 the 4th International Conference on Wireless and Optical Communications http://www.icwoc.org/ The 2015 4th International Conference on Database and Data Mining http://www.icddm.org/ ICKD 2015 The 2015 4th International Conference onKnowledge Discovery http://www.ickd.org/ ICOIP 2015 The 2015 4th International Conference onOptoelectronics and Image Processing http://www.icoip.org/ 59 Indexed byEI Compendex, Scopus and ISI. International Journal of Future Computer and Communication (ISSN: 2010-3751; DOI: 10.7763/IJFCC) Indexed byGoogle Scholar, Engineering & Technology Digital Library, and Crossref,DOAJ, Electronic Journals Library, EI (INSPEC, IET). All accepted papers of ICDDM 2015 will be published by WIT Transactions on Information and Communication Technologies (ISSN: 1743-3517) Indexed byEI Compendex, Scopus and ISI. All accepted papers of ICKD 2015 will be published by International Journal of Computer Theory and Engineering (IJCTE)(ISSN: 1793-8201) Indexed by Electronic Journals Library, EBSCO, Engineering & Technology Digital Library, Google Scholar, INSPEC, Ulrich's Periodicals Directory, Crossref, ProQuest, WorldCat, and EI(INSPEC, IET). All accepted papers of ICDDM 2015 will be published by WIT Transactions on Information and Communication Technologies (ISSN: 1743-3517) Indexed byEI Compendex, Scopus and ISI. Conference Schedule All accepted papers of ICROM 2015 will be published by Applied Mechanics and Materials (ISSN: 1660-9336) ICROM 2015 2015 2nd International Conference on Robotics and Mechatronics http://www.icrom.org/ ICAME 2015 2015 the 4th International Conference on Advances in Mechanics Engineering http://www.icame.org/ July 20-21, 2015, Madrid, Spain Indexed by Elsevier: SCOPUSwww.scopus.com and Ei Compendex (CPX) www.ei.org/. Cambridge Scientific Abstracts (CSA) www.csa.com, Chemical Abstracts (CA) www.cas.org, Google and Google Scholar google.com, ISI (ISTP, CPCI, Web of Science) www.isinet.com , Institution of Electrical Engineers (IEE)www.iee.org , etc All accepted papers of ICROM 2015 will be published by Applied Mechanics and Materials (ISSN: 1660-9336) Indexed by Elsevier: SCOPUSwww.scopus.com and Ei Compendex (CPX) www.ei.org/. Cambridge Scientific Abstracts (CSA) www.csa.com, Chemical Abstracts (CA) www.cas.org, Google and Google Scholar google.com, ISI (ISTP, CPCI, Web of Science) www.isinet.com , Institution of Electrical Engineers (IEE)www.iee.org , etc Submitted conference papers will be reviewed by technical committees of the Conference. All accepted papers will be published in one of the following Journals. International Journal of Electronics and Electrical Engineering(IJEEE) (ISSN: 2301-380X) ICCSS 2015 2015 5th International Conference on Circuits, System and Simulation http://www.iccss.org/ included in Ulrich's Periodicals Directory, Google Scholar, EBSCO, Engineering & Technology Digital Library and Electronic Journals Digital Library. International Journal of Information and Electronics Engineering(IJIEE) (ISSN: 2010-3719) included in Google Scholar, Electronic Journals Library, Engineering & Technology Digital Library, Crossref and ProQuest, DOAJ, Ei (INSPEC, IET). All accepted papers will be published in one of the indexed Journals after being selected. Aug 22-23, 2015 New Taipei, Taiwan ICOSP 2015 2015 International Conference on Signal Processing http://www.icosp.org/ WIT Transactions on Information and Communication Technologies (ISSN: 1743-3517) Indexed by EI Compendex, Scopus and ISI. International Journal of Signal Processing Systems (IJSPS) (ISSN: 2315-4535) Indexing: Ulrich's Periodicals Directory, Google Scholar, EBSCO, Engineering & Technology Digital Library, etc. 60 Conference Schedule All accepted papers will be published in one of the indexed Journals after being selected. International Journal of Computer Theory and Engineering (IJCTE) (ISSN: 1793-8201) DOI: 10.7763/IJCTE Editor-in-Chief: Prof. Wael Badawy ICCCD 2015 2015 the 5th International Conference on Computer and Communication Devices http://www.icccd.org/ Abstracting/Indexing: Index Copernicus, Electronic Journals Library, EBSCO, Engineering & Technology Digital Library, Google Scholar, Ulrich's Periodicals Directory, Crossref, ProQuest, WorldCat, and EI (INSPEC, IET), Cabell's Directories. International Journal of Computer and Communication Engineering (IJCCE)(ISSN: 2010-3743) DOI: 10.7763/IJCCE Editor-in-Chief: Dr. Maode Ma ICRAS 2015 2015 5th International Conference on Robotics and Automation Sciences Abstracting/ Indexing: EI (INSPEC, IET), Google Scholar, Engineering & Technology Digital Library, ProQuest, and Crossref, Electronic Journals Library The ICRAS 2015 proceedings will be published by IEEE and all the papers will be archived in the IEEE Xplore and indexed by Ei Compendex and ISI. http://www.icras.org/ Sep 19-20, 2015 Hong Kong ICSTE 2015 2015 7th International Conference on Software Technology and Engineering http://www.icste.org/ Note 61 All accepted papers will be published in the volume of Lecture Notes on Software Engineering (LNSE) (ISSN: 2301-3559), and will be included in the EI (INSPEC, IET),DOAJ, Electronic Journals Library, Engineering & Technology Digital Library, Ulrich's Periodicals Directory, International Computer Science Digital Library (ICSDL), ProQuest and Google Scholar. Conference Schedule 62 Conference Schedule 63
© Copyright 2026