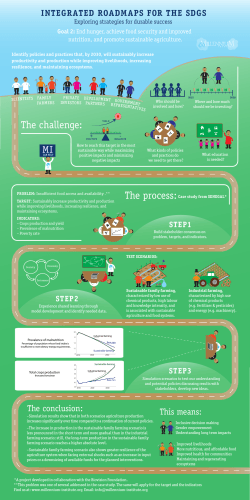
3.5 Food Resources
3.5 Food Resources Food Issues MEDC / LEDC Food Production and Distribution Imbalance in food distribution Over 1 billion people are living in poverty and starving in LEDC countries MEDC Average Caloric Intake = 3314 LEDC Average Caloric Intake = 2666 Causes: Unequal distribution Lack of access to clean water Poor harvesting / farming practices (overgrazing/ overfishing) Undernourishment worldwide Food Waste Terrestrial vs. Aquatic Food Production Systems VS Aquatic Food Production Aquatic Food Food Production: is harvested from high tropic levels due to human preference (ex. salmon). Photosynthesis is less efficient by producers due to light reflection of water Terrestrial Food Production Terrestrial Most Food Production: food harvested from low tropic levels (producers / herbivores) Energy conversions less efficient on land Food Production affects the Environment Biodiversity Soil Water Air Human Health Increasing food production output GMO- Genetically Modified Organisms Change genetic make up of living things to make them look, feel, and taste different Pesticides- chemicals used to kill pest organisms Herbicides- chemicals used to kill weeds Fertilizers- chemicals used to grow larger crops Irrigation- canals used to bring in more water Antibiotics/ Growth Hormones- used to grow healthier and larger animals Biodiversity Loss Loss of grasslands forests and wetland for cultivation Loss of genetic diversity (wild crops replaced with monocrops) Soil Erosion Loss of fertility Salinization Desertification Increase soil pH Water Waste water produced Aquifer depletion from increased irrigation Air Large fossil fuel use in farming equipment causes release of greenhouse gases (CO2, N2O, and CH4) Pesticide sprays Human Health Nitrates Blue in Drinking water baby Pesticides Bacterial (E. coli) contamination of meat North American Cereal Farming vs. Asian Subsistence Farming Comparison Pair #1 North American Cereal Farming Inputs: Fertilizers, pesticides, fossil fuels, labor, sunlight, water equipment Characteristics: Heavy use of fossil fuels, lots of farming technology, monocrops (only one crop) Socio- Cultural: Fast production, large amounts, lots of waste Environmental impact: loss biodiversity Outputs: Air pollution , water pollution, wheat/corn, lots of income ($$) Asian Subsistence Farming Inputs: lots of human labor, water, sunlight Characteristics: grow only enough to eat to feed family & community, low tech Socio- Cultural: mostly LEDC, poor Environmental impact: maintains biodiversity, reduces pollution Outputs: Usually mixed crops; corn, beans and squash (all in same field) Intensive Beef Production vs. Maasia Tribal Livestock Comparison Pair # 2 MEDC- Intensive Beef Production Inputs: Hormones, antibiotics, labor, cattle feed (corn), breeding stock of cattle Characteristics: Many cattle in crowded area Socio- Cultural: Fast production, large quantities, lots of waste/ death Environmental impact: disease, waste Outputs: Air pollution, water pollution, beef, lots of income ($$) LEDC- Maasai Tribal Livestock Inputs: Labor, Cattle feed/ grazing grass Characteristics: large herds of cattle, used as only food source “Nomadic Herding” Socio- Cultural: Cattle are THE source of life (even used as currency) Environmental impact: overgrazing, nomadic behavior Outputs: meat, milk, blood Salmon Farming in Norway vs. RiceFish Farming in Thailand Comparison Pair # 3 Salmon Farming in Norway Inputs: antibiotics, fish food, cages, labor Characteristics: fish raised in large quantity Socio- Cultural: MEDC, employs large number of workers Environmental impact: growth of algae, water pollution Outputs: salmon, water pollution Rice-Fish Farming Thailand Inputs: labor, seed Characteristics: fish and rice grown together in same, self sustaining ecosystem (fed by natural food chain) Socio- Cultural: LEDC countries, Environmental impact: reduces waste maintains biodiversity Outputs: rice, fish, income Slash and Burn/ Shifting Cultivation Slash and Burn / Shifting Cultivation Input: Labor, plow, oxen, seed Characteristics: Tropical forest set on fire to clear the land & ash fertilizes soil. After land is used farmers repeat this process Socio-cultural: Typically harvested food is sold in community, low population density Environment: Loss of biodiversity, fertility, ecosystem production decreases Output: Monocrop, air pollution, income kg grain required to produce 1 kg of meat GMO Become more sustainable
© Copyright 2026