VCGDB: A Virtual and Dynamic Genome Database of the Chinese
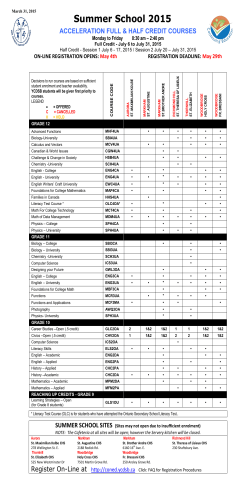
VCGDB: A Virtual and Dynamic Genome Database of the Chinese Population Jiayan Wu Associate Professor Director of Science and Technology Department Director of Core Facility Beijing Institute of Genomics, Chinese Academy of Sciences 2015-04-25 Outline Background Data source Analyze workflow Result interpretation Database construction Genome visualization tool Summary Perspective Background (Big data) 4’V’ definition of Big data: Volume,Variety,Veracity,Velocity. Meyer M A, Laney D. Gartner, 2012,1. Knowledge Information Information Size Data Data Knowledge Computer Science/Domain Science Domain Science/Computer Science Year Background (references) Current reference genome: linear, static sequence from limited samples. UCSC Human Genome Feb. 2009 (hg19) Mar. 2006 (hg18) May. 2004 (hg17) NCBI Human Genome Jul. 2003 (hg16) Apr. 2003 (hg15) Reference Year Platform Method Caucasian individual(CEU) 2007 ABI 3730XL De novo assembly Yoruba individual(YRI) 2008 Illumina GA1s MAQ mapping Chinese individual(YH) 2008 Illumina GA SOAP mapping+assembly Korean individual(AK1) 2009 Illumina GA GMAP mapping Irish individual 2010 Illumina GAII SNP calling Background (projects) Human Genome Draft 2001 The human genome holds an extraordinary trove of information about human development, physiology, medicine and evolution. International Human Genome Mapping Consortium. Nature, 2001, 409(6822):934-941 1000 Genomes Project 2008 The first project to sequence the genomes of a large number of people, to provide a comprehensive resource on human genetic variation. 1000 Genomes Project Consortium. Nature, 2010, 467(7319):1061-1073. Data source Code Population Record Sample Read Count Base Count CHB Chinese Han in Beijing 2690 147 36,855,116,194 2.08E+12 CHS 762 100 21,619,855,963 1.61E+12 3452 247 58,474,972,157 3.69E+12 Chinese Han South Total CHN: Chinese population CHB: North Chinese sub-population CHS: South Chinese sub-population Dynamic genome: Data Capacity (After Compression) CHS RAW 1.3 TB CHB RAW 2.0 TB CHS BAM 2.0 TB CHB BAM 2.8 TB complex, dynamic, widely related personal human genomes contain genome variations, insertions/deletions, structure variations, etc. Concentrate on big differentiation. data: Quantity, Handling, Usage to reveal potential population Data analyze workflow Data preprocessing Data size reduction Sample level analysis Population level analysis Genomic annotation Result interpretation Data size reduction 194 pileup files, 70+GB/file, 15TB in total Chrom Position Ref Sample 1 Sample 3 Sample 4 Sample 5 Sample 6 Chr10 10001 A AAAA AAAAA AAAAAA Chr10 10002 A AAAA AAAAT AA Chr10 10003 G GGGG GGGGGG GGGGG Chr10 10004 C CCCC Chr11 10002 A AAAT AAAAAG TTTAAA TTTTTA Chr11 10010 G GG GGGG GGGGGT GGG Chr12 10003 G CCC CCC CCCCCC C Chr12 10004 G GGG TTT GGGGT G ChrX 10005 A AAAAAA AAAAAA AAAAAA AAAAAA GGGGG GGGGGG CC AAAAAA AAAAAA Candidate dynamic information Candidate dynamic information of 55,549,120 CDPs. Data volume reduced by 98% without losing any detail information. 10 4 CDP Average(max-min) Coverage Status 10 3 10 2 10 1 0 CHS_RANGE CHB_RANGE CHS_AVG CHB_AVG Data analyze workflow Data preprocessing Data size reduction Sample level analysis Population level analysis Genomic annotation Result interpretation Genetic variation analysis Single high-coverage sample: AAAAAAATTAAAAAAAAGAACAAAATTTTTAAAAAAAAAATTTTCAA Multiple low-coverage samples: AAAAT AAAT AAT TTT AAAAG AAAAC AAAC AAAAG AAAAC AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAATTTTTTGGCCC AAAAT AAAT AAT TTT AAAAG AAAAC AAAC AAAAG Sample level: Population level: A A A T A AAAAAAT A A A Dynamic position types Major allele against GRCh37 reference genome. MAIR High probability (≥50%) indel position. Minor allele (>5%) against GRCh37 reference genome. Rare variation (≤5%) against GRCh37 reference genome. Dynamic information statistics Genomic annotation(Annovar) Enrichment analysis of MAIR in GWAS trait locations in the Chinese and GRCh37 genomes Top Matches CHN CHS CHB 1 Height (110/324) Height (108/324) Height (110/324) 2 Multiple sclerosis (41/187) Multiple sclerosis (41/187) Multiple sclerosis (41/187) 3 Crohn's disease (36/181) Crohn's disease (40/181) Crohn's disease (38/181) 4 Body mass index (34/109) Body mass index (34/109) Coronary heart disease (37/151) 5 Coronary heart disease (34/151) Coronary heart disease (33/151) Body mass index (36/109) 6 Type 2 diabetes (33/164) Type 2 diabetes (32/164) Bipolar disorder (32/109) 7 Rheumatoid arthritis (31/170) LDL cholesterol (32/114) Type 2 diabetes (31/164) 8 LDL cholesterol (31/114) HDL cholesterol (31/118) Rheumatoid arthritis (30/170) 9 Bipolar disorder (30/109) Type 1 diabetes (29/107) Bone mineral density (30/87) 10 Bone mineral density (30/87) Bone mineral density (29/87) LDL cholesterol (30/114) Chinese population comparison Consensus Chinese genomes Use anti-conflict algorithm to generate the consensus reference genome. Population-specific against ref positions Major indels CHS reference HG19 reference Analyze conflicts CHB reference CHN reference Mapping of 15 Asian genomes onto the VCG, YH and GRCh37 reference genomes. Database Construction Database: MySQL Engine: MyISAM Tables: 128 Data size: 50GB Index size: 4.9GB Records: 183,919,098 Database Optimizing Data level optimizing Separate data by chromosome “BTree” indexes support “<>=” query Reasonable split sequences ---- “ref table” MySQL level optimizing Database Capacity Dynamic Pos CHN Dynamic Pos CHS Dynamic Pos CHB Autosome 33,780,152 19,591,609 24,109,529 Heterosome 1,747,140 937,088 1,222,844 1,006 673 654 35,528,298 20,529,370 25,333,027 Indel CHN Indel CHS Indel CHB Autosome 392,074 454,215 345,647 Heterosome 14,360 17,323 12,346 25 20 59 406,459 471,558 358,052 Chondriosome Total Chondriosome Total Rare Variant CHN Rare Variant CHS Rare Variant CHB Autosome 27,258,690 12,505,097 17,688,051 Heterosome 1,477,821 632,253 939,627 907 569 536 28,737,418 13,137,919 18,628,214 Chondriosome Total VCGDB contains 35 millions of single nucleotide variations, 0.5 millions of indels and 29 millions of rare variations, associate with position based genomic annotation information and consensus reference genomes of defined populations in China, instead of the former static linear sequence. http://vcg.cbi.ac.cn Search Page Browser Page Web search page features 1. Fuzzy search Web searching is implemented with HGNC that realize fuzzy searching of genes. 2. Dynamic level sorting All columns containing dynamic level of the positions can be sorted by clicking the title. 3. VCGBrowser linkage Help users to locate the region they want to browse easily. VCGBrowser development Features: Searching optimization Cross platform Large region browse Genome comparison Seemless zooming Drag zooming Real-time searching Cross platform Usage Users have three ways to use VCGBrowser. It is both a web-based applet and a client-based cross platform application, which can be used either in an internet browser or downloaded as a local software. Also users can use our java web start jnlp to run a local application online. Web Applet Local Application Java Web Start JNLP Feature: seamless zooming VCGBrowser has a zoom bar on the left that support a smooth real-time seamless zooming to any resolution from the genomic level that shows the dynamic distribution of interested region, to the nucleotide level that all residues and detail information can be recognized clearly. Feature: drag zooming Drag Zooming: Drag the mouse on any region you are interested in, and the browser would instantly zoom to the region you select. Large region browse and comparison VCGBrowser: Up to chromosome level browsing. Down to nucleoside level comparison. Feature: real-time querying Reference area GRCh37 ref refGene duplication gwas CHN dynamic bar CHN area CHN ref CHN indel CHN rare variant CHS dynamic bar CHS area CHS ref CHS indel CHS rare variant CHB dynamic bar CHB area CHB ref CHB indel CHB rare variant Summary VCGDB is a “virtual” database VCGDB is “virtual” because the reference genome provided in the database is the statistical result of terabases of sequencing data from hundreds of Chinese individuals that describe the genetic variation features specific to the Chinese population. chr pos nuc support 1 14635 A *180 1 14636 T *180 6 34632 G *107 6 44632 +AA *187 21 54322 -G *190 X 34221 T *93 Summary VCGDB is a “dynamic” database VCGDB is “dynamic” because we use methods as comentropy to analyze and evaluate the dynamic variation rate and probability of all genetic variation information in several levels like sample or population and integrate them with individual characters and genomic annotation information. T C A ACG T TACG Gene: PALB2 GWAS: Biopolar disorder Summary VCGDB is a big data solution VCGDB offers a feasible strategy for processing big data to keep pace with the growing volume of biological data and provides a robust resource based on the massive amounts of genomics data for genomics studies and investigations into genetic diseases. VCGBrowser is a flexible genome visualization tool VCGDB also provides a highly interactive user-friendly virtual Chinese genome browser (VCGBrowser) with functions like fuzzy searching, seamless zooming and real-time searching. Users can use mature databases and analysis tools process their researches. Perspectives Bigger data and higher coverage Sequencing projects such as Precision Medicine Initiative, UK10K, The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA), and deCODE Genetics in Iceland are and/or will generate ultra-large volumes of human genome data with higher coverage. How about Chinese population? More accurate algorithm and cloud based platform Genome alignment software support dynamic genome Data analyze platform based on cloud or supercomputing Acknowledgement Thanks for Dr. Yunchao Ling & Dr. Jingfa Xiao Thank you!
© Copyright 2026