“Camp for Company” How to structure a business idea August 2013
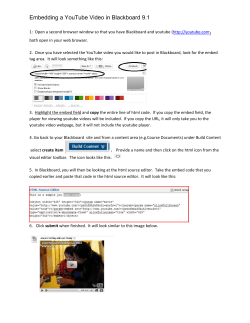
“Camp for Company” How to structure a business idea Business Model Generation August 2013 Some diagrams and concepts taken from Business Model Foundry Gmbh 12/08/2013 1 Business Model Generation Crazy Business Ideas: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WBe9lyv6U_g You can have the best idea, but without identifying who your customer is, what value you deliver and how much it costs, you probably are going to loose time and money. 8/12/2013 2 What is a business model • A business model allows you to explain how you plan to make money out of your idea • Defining a business model involves heavy thinking and it is fun • Following the following 9 steps (elements of a business model) will make designing your business model easier and more fun What is a business model: http://www.slideshare.net/Alex.Osterwalder/what-is-a-business-model 12/08/2013 3 The 9 building blocks of a Business Model 12/08/2013 4 The customer: the source of your revenues 12/08/2013 5 Identify who your customer is • The customer is the king! He is the one who will buy your product or services and the one who is going to pay • For understanding your customer readiness to buy, you have to analyze who your customer is • In order to understand who your customer is, just start imagining who could be interested in your product/service • Categorizing your customers into segments is a great help; Segments could be: •Geographic: where does the customer live •Demographic: age, gender •Income: how much does the customer earn •Family status: married, single, with kids etc. •Job: what is the customer’s occupation •Hobbies: what hobbies does the customer have 12/08/2013 6 Excercise: Please identify a potential customer for a new type of energy-drink. Hint: you could consider: • • • • • • • • • • • • Geographic: where does the customer live Demographic: age, gender Income: how much does the customer earn Family status: married, single etc. Job: what is the customer’s occupation Hobbies: what hobbies does the customer have Needs: what needs does the customer have ……………………………… ……………………………… ……………………………… ……………………………… ……………………………… 12/08/2013 7 The value proposition 12/08/2013 8 ...but was does the customer need/want? The Value Proposition explains what needs/desires the customer has and how the product/service offered by you is going to serve/meet the need. If the product/service is going to meet a client’s need, then he will have a benefit and should be ready to pay for it. Lets see this short introduction: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rIGBzCVaXV0 12/08/2013 9 Value offered to customers 1 Which elements may contribute to creation of Value for a customer? Newness. Satisfy an entirely new set of needs that customers previously didn’t perceive (e.g.: technology); Performance. Improve product or service performance (e.g.: faster PCs); Customization. Products and services are tailored to the specific needs of individual customers or Customers Segments; “Getting the job done”. Help a customer get certain jobs done. The client can focus on core aspects of his company (e.g.: Hilti); Convenience/Usability. Make things more convenient or easier to use (e.g.: iPod e iTunes); 12/08/2013 10 Value offered to customers 2 Design. A product may stand out because of superior design. (e.g.: fashion and consumer electronics); Brand/Status. Use or display a specific brand (e.g.: Rolex); Price. Offer similar value at a lower price, but low-price Value Propositions have implications for the rest of a business model (e.g.: EasyJet, Ryanair, free news paper); Cost reduction. Help customers reduce costs (e.g.: CMR software application); Risk reduction. Reduce the risk that customers incur when purchasing products or services (e.g.: used car with a (only) oneyear service guarantee); Accessibility. Make products and services available to customers who previously lacked access to them (e.g.: financial products for corporations (private jets)). 12/08/2013 11 Excercise: Please identify what need the energy-drink is going to meet: Hint: you could consider: • • • • • • • • • • • • Performance: Staying awake, e.g. before an exam Status: it is cool to drink it, I feel like a star Taste: it tastes soooo good Income: how much does the customer earn ……………………………… ……………………………… ……………………………… ……………………………… ……………………………… ……………………………… ……………………………… ……………………………… 12/08/2013 12 Reaching the customer: Delivery & Promotion 12/08/2013 13 Delivery channels ….I found a customer need, a product/service that serves it, but how can I deliver/offer the product/service to my customers. Through which channels do our Customer Segments want to be reached? How are we reaching them now? Finding the right way to deliver and promote the product/service is strategic for making a purchase easy. Making it difficult to buy a product, reduces the chances that the client is going to buy. Marketing 4 Ps: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JIirzTdaey4 Pizza delivery: http://dsc.discovery.com/tv-shows/othershows/videos/prototype-this-automated-pizza-delivery.htm 12/08/2013 14 Delivery channels Own Partner Channel Types Sales force Direct Web sales Own stores Partner stores Indirect Wholesaler Channel Phases 1. Awareness 2. Evaluation 3.Purchase 4.Delivery 5.After sales How do we raise awareness about our company’s products and services? How do we help customers evaluate our organization’s Value Proposition? How do we allow customers to purchase specific products and services? How do we deliver a Value Proposition to customers? How do we provide postpurchase customer support? 12/08/2013 15 Excercise: Please identify how you can deliver your energy drink to the customer and how you will promote it. Hint: you could consider: A)Delivery: • • • • • • Through a supermarket? E-Commerce? Gas stations? ……………………………… ……………………………… ……………………………… B) Promotion: • Newspapers? Which ones? • TV channels? • Sponsoring? Formula 1? • ……………………………… • ……………………………… 12/08/2013 16 Make sure that the customer loves you 12/08/2013 17 Customer relationships Customer relationships may be driven by the following motivations: Customer acquisition; Customer retention; Boosting sales (upselling). (e.g.: mobile network operator. Free cell-phones, special offers focused on customer retention, increased average revenue per customer). Social media are a very powerful tool to build and strengthen customer relations. CRM: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=g-OP8xZmAJM CRM Cowboy: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=l59lIKG4Gs0 12/08/2013 18 Customer relationships What type of relationship does each of our Customer Segments expect us to Establish and maintain? Which ones have we established? How costly are they? How are they integrated with the rest of our business model? There are several categories of Customer Relationship: Personal assistance (human interaction); Dedicated personal assistance (one to one contact client /worker e.g.: private banking); Self-service. No direct relationship with customers. It provides all the necessary means for customers to help themselves (e.g. phone help-desk); Automated services. Self-service with automated processes (e.g.: online profiles, recognize individual customers - Amazon); Communities. Facilitate connections between community members in order to allow users to exchange knowledge and solve each other’s problems. Co-creation. Create value with customers participation (e.g.: YouTube, solicit customers to create content for public consumption). 12/08/2013 19 What will bring me money? 12/08/2013 20 Revenue Streams The Revenue Streams Building Block represents the cash a company generates from each Customer Segment. For what value are our customers really willing to pay? A business model can involve two different types of Revenue Streams: Transaction revenues resulting from one-time customer payments (pay for a car); Recurring revenues resulting from ongoing payments to either deliver a Value Proposition to customers or provide post-purchase customer support (pay a leasing/rent fee) 12/08/2013 21 Revenue Streams There are several ways to generate Revenue Streams: Asset sales. Derives from selling ownership rights to a physical product (e.g.: car); Usage fee. Generated by the use of a particular service. The more a service is used, the more the customer pays (e.g.: hotel); Subscription fees. Generated by selling continuous access to a service (e.g.: online games, monthly subscription fee); Lending/Renting/Leasing. Created by temporarily granting someone the exclusive right to use a particular asset for a fixed period of time. 12/08/2013 22 Revenue Streams Licensing. Generated by giving customers permission to use protected intellectual property in exchange for licensing fees (e.g.: media industry, content owners retain copyright while selling usage licenses to third parties); Brokerage fees. Derives from intermediation services performed on behalf of two or more parties (e.g.: credit card providers earn revenues by taking a percentage of the value of each sales transaction executed between merchants and customers); Advertising. Results from fees for advertising a particular product, service or brand (e.g.: sponsored event). 12/08/2013 23 Revenue Streams Each Revenue Stream might have different pricing mechanisms. There are two main types of pricing mechanism: fixed and dynamic pricing. PRICING MECHANISMS Fixed Menu Pricing Predefined prices are based on static variables Fixed prices for individual List price products, services or other Value Propositions Dynamic Pricing Prices change based on market conditions Price negotiated between two or more Negotiation partners depending on negotiation (bargaining) power and negotiation skills Product feature dependent Price depends on the number or quality of Value Proposition features Yield management Price depends on inventory and time of purchase (normally used for perishable resources such as airline seats) Customer segment dependent Price depends on the type and characteristic of a Customer Segment Real-timemarket Price is established dynamically based on supply and demand Auctions Price determined by outcome of competitive bidding Volume dependent Price as a function of the quantity purchased Pricing for an entrepreneur: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=I_ihmqU-hvM 12/08/2013 24 Excercise: How many energy-drink cans do you plan to sell? At what price? Do you plan also to sell merchandising (e.g. Red Bull). At what price? Number cans sold ..… X average price ..… = Revenues …… Gadgets sold ..… X average price ..… = Revenues …… TOTAL REVENUES 12/08/2013 ……… 25 What do I need to manufacture/offer the product? 12/08/2013 26 Key Resources The key Resources Building block describes the most important assets required to make a business model work Key Resources can be categorized as follows: Physical. Includes physical assets such as manufacturing facilities, buildings, vehicles, machines, systems, point-of-sales and distribution networks Intellectual. These are resources such as brands, proprietary knowledge, patents and copyrights, partnerships and customer database. Human. People are particularly prominent in certain business models such as knowledge-intensive and creative industries Financial. These are resources and/or financial guarantees, such as cash, lines of credit and stock option. Energy Drink manufacturing: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Wq_LW77xRak Ice cream manufacturing: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rE6mrqpZA-g 12/08/2013 27 Excercise: What resources/machines etc. do you need for producing the energy drink? •……………………………… • ……………………………… • ……………………………… •……………………………… • ……………………………… • ……………………………… •……………………………… • ……………………………… • ……………………………… 12/08/2013 28 What activities do I have to do to offer the product? 12/08/2013 29 Key activities The key Resources Building block describes the most important assets things a company must do to make its business model Work. Key Activities can be categorized as follows: Production. These activities relate to designing, making and delivering a product in substantial quantities and/or of superior quality (e.g.: manufacturing firms); Problem solving. Relate to coming up with new solutions to individual customer problems. Consultancies and services organizations Platform/Network. Networks, matchmaking platforms, software, brands (e.g.: eBay, Visa). http://education-portal.com/academy/lesson/four-functions-of-managementplanning-organizing-leading-controlling.html 12/08/2013 30 Do I need partners ? Who is the right partner? 12/08/2013 31 Key partnerships The key Resources Building block describes the network of suppliers and partners that make the business model Work. There are four different types of partnership: Strategic alliances between non-competitors; Competition. Strategic partnership between competitors; Joint venture. To develop new business; Buyer-supplier relationship. To assure reliable supplies; Strategic partnerships: http://www.inc.com/video/201111/ask-gerber-building-strategic-partnerships.html 12/08/2013 32 Key partnerships It can be useful to distinguish between three motivations for creating partnerships: Optimization and economy of scale. It is illogical for a company to own all resources or perform every activity by itself. They are usually formed to reduce costs, and often involve outsourcing or sharing infrastructure; Reduction of risk and uncertainty. It is applied in a competitive environment with competitors in others specific area. (strategic alliances) (e.g.: Blu-ray and group of consumer electronics); Acquisition of particular resources and activities. They extend their own capabilities by relying on other firms to furnish particular resources or perform certain activities. Such partnership can be motivated by needs to acquire knowledge, licenses or access to customers. 12/08/2013 33 .....but, how much is it going to cost? 12/08/2013 34 Cost structure The Cost Structure describes all costs incurred to operate a Business model. There are two classes of business model Cost Structure Cost-driven. They focus on minimizing costs wherever possible. This approach aims at creating and maintaining the leanest possible Cost Structure. Maximum automation and extensive outsourcing (e.g.: low-cost airlines); Value-driven. When a company is less concerned with the cost implications of a particular business model design and instead focus on value creation. (e.g.: Luxury hotels, personalized service). 12/08/2013 35 Cost structure Cost Structures can have the following characteristics: Fixed costs. Costs that remain the same despite the volume of goods or services produced (e.g.: salaries, rents and physical manufacturing facilities); Variable costs. Costs that vary proportionally with the volume of goods or services produced (e.g.: music festivals); Economies of scale. Cost advantages that a business enjoys as its output expands (e.g.: lower bulk purchase rates); Economies of scope. Cost advantages that a business enjoys due to a larger scope of operations (e.g.: same distribution channels for different products); 12/08/2013 36 Excercise: What costs will occur for producing the energy drink? •Ingredients: • Cans: • Wages: • Rents: • Promotion/marketing: • ……………………………… •……………………………… • ……………………………… € ….……… € ….……… € ….……… € ….……… € ….……… € ….……… € ….……… € ….……… TOTAL € …………. 12/08/2013 37 Business Model Generation 12/08/2013 38 ...and make sure that all blocks fit 12/08/2013 39 A system supported by hypotheses All elements of a business model, must be conceived as a part of a puzzle. The complete puzzle will create value for the customer and for the company. Tom Hulme: http://vimeo.com/13888824 12/08/2013 40 Business Model Generation 12/08/2013 41 Business Model Generation 12/08/2013 42 Business Model Generation 12/08/2013 43 Business Model Generation 12/08/2013 44 Business Model Generation 12/08/2013 45 Thank you for your kind attention Massimo Andriolo Stefano Martincigh 12/08/2013 46
© Copyright 2026